Submitted:
30 August 2024
Posted:
30 August 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Method
Forward Modelling
- 1)
- the unknowns are placed at the cell center and discretized on the cell surface using a simple method similar to FDM.
- 2)
- Unstructured meshes can be applied as FEM, allowing calculations with topography and local subdivision.
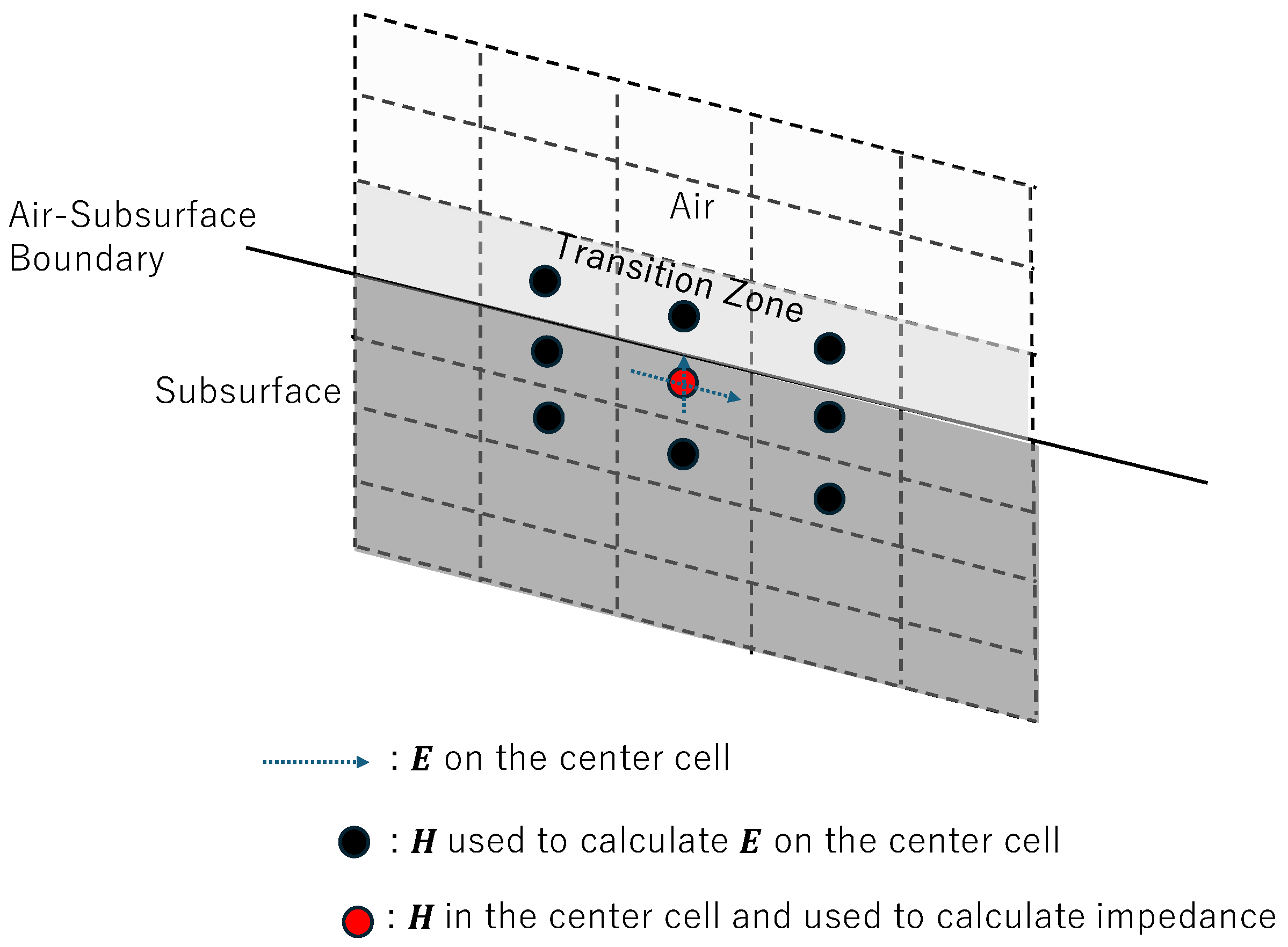
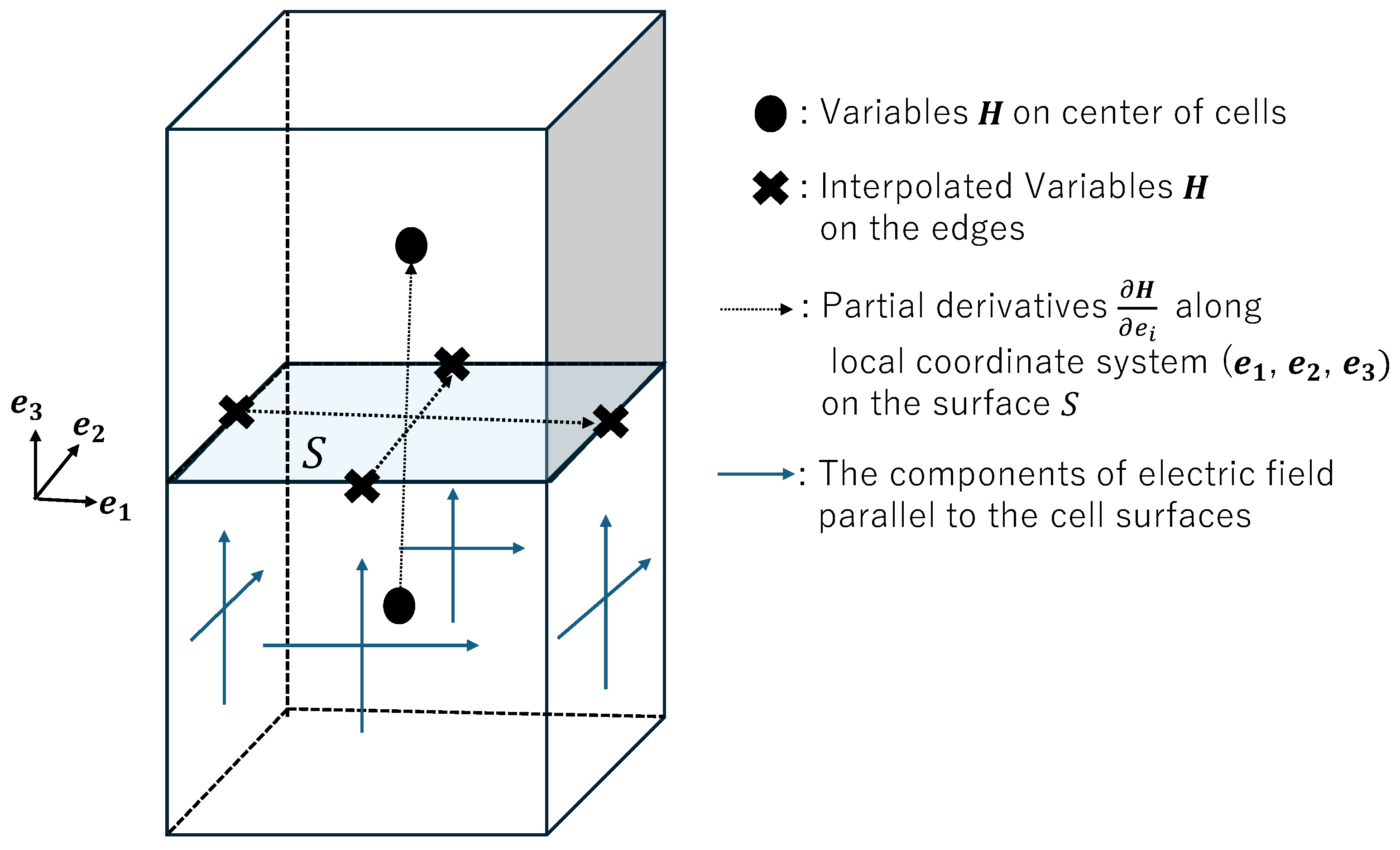
Inversion
Numerical Examples
Forward Modelling Considering Topography.
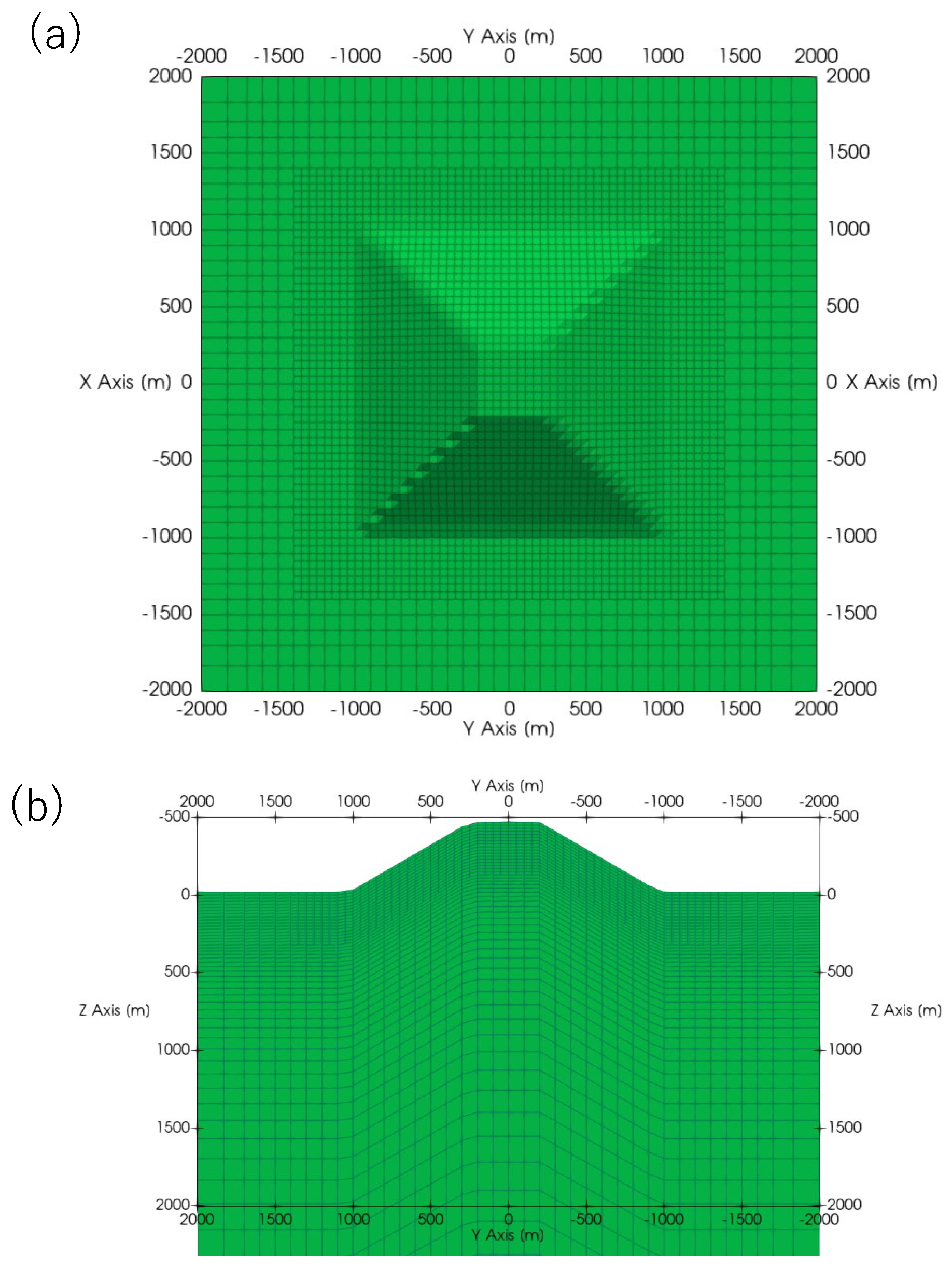
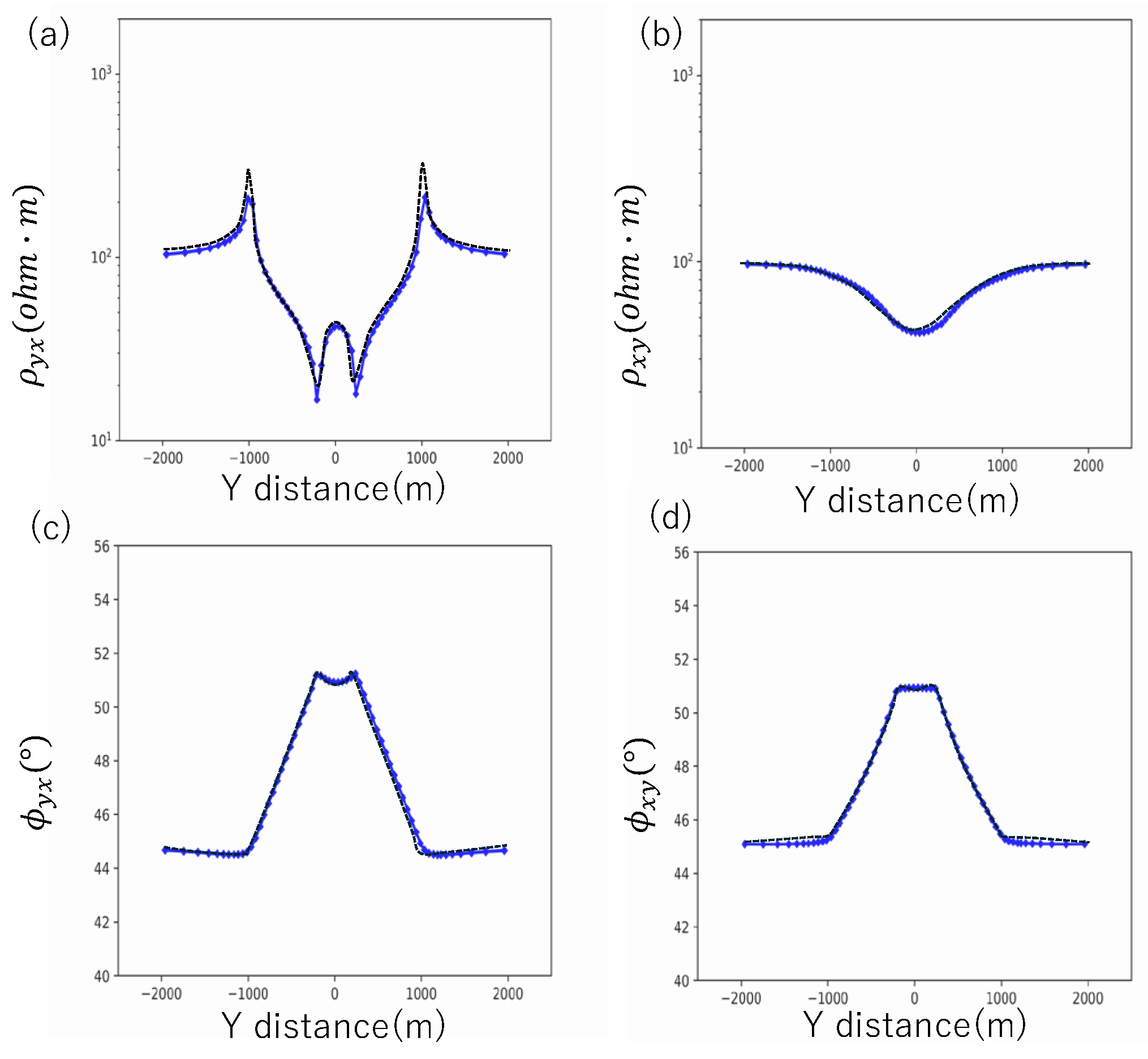
Forward Modelling Considering Resistivity Heterogeneity

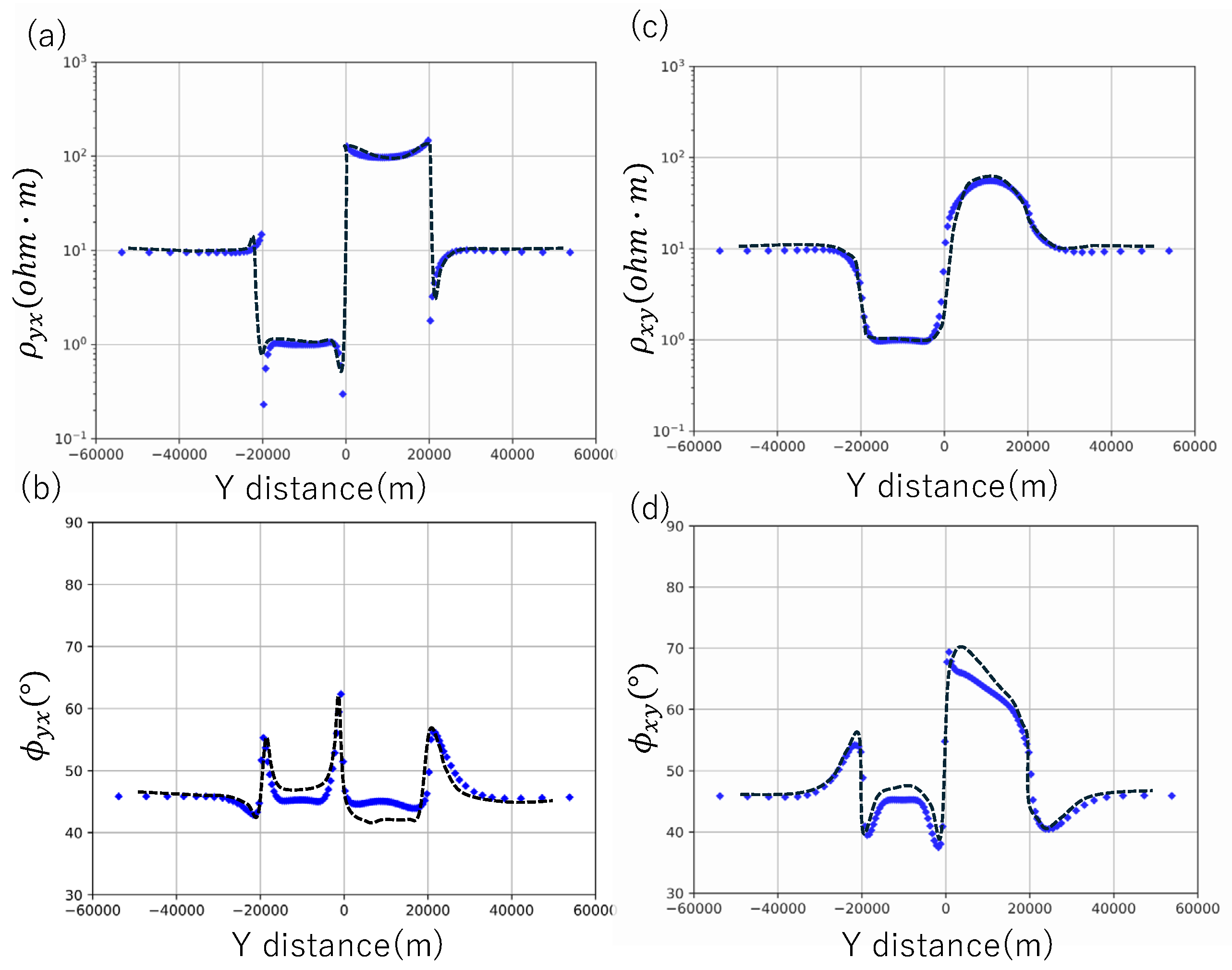
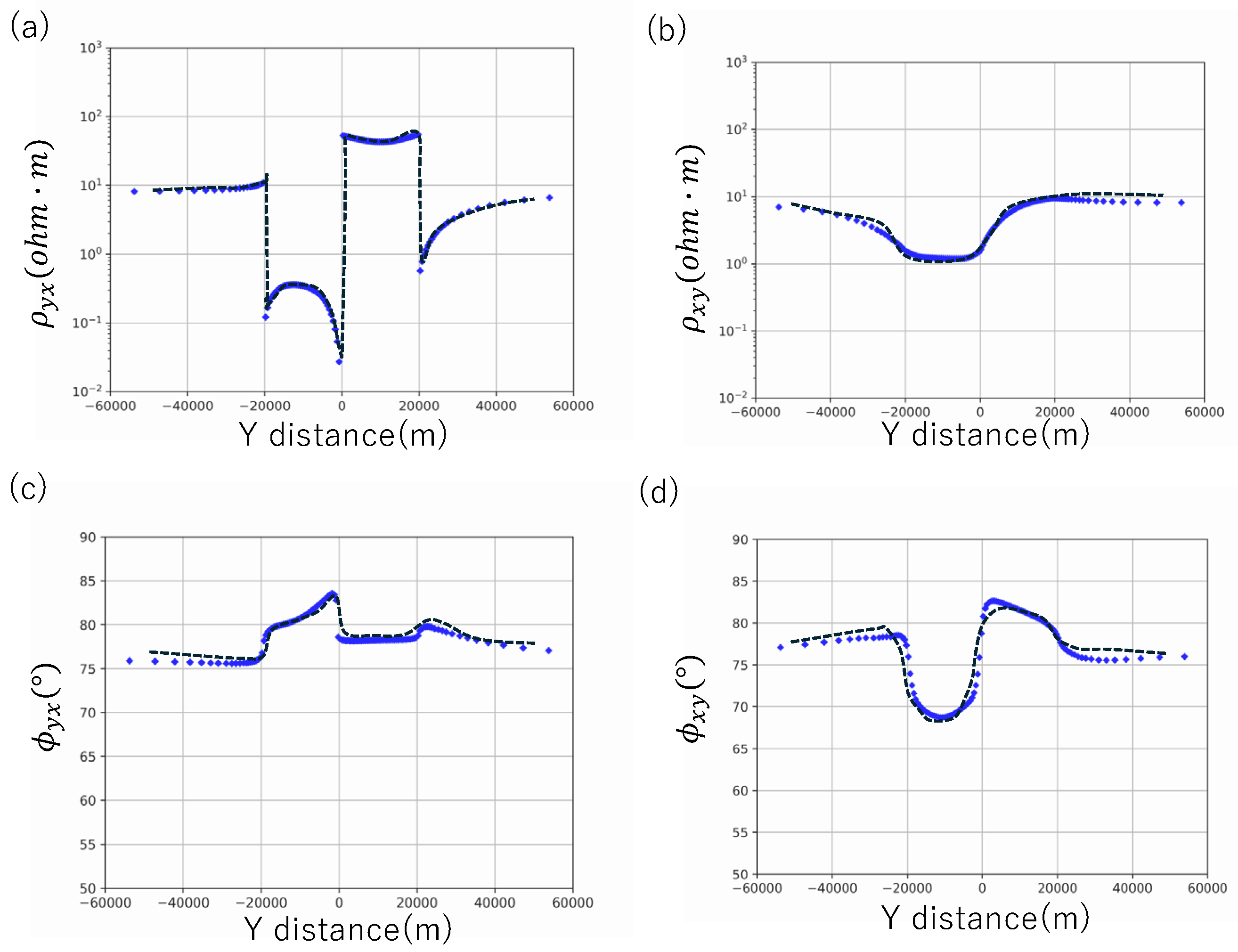
Inversion for Dublin Secret Model 2
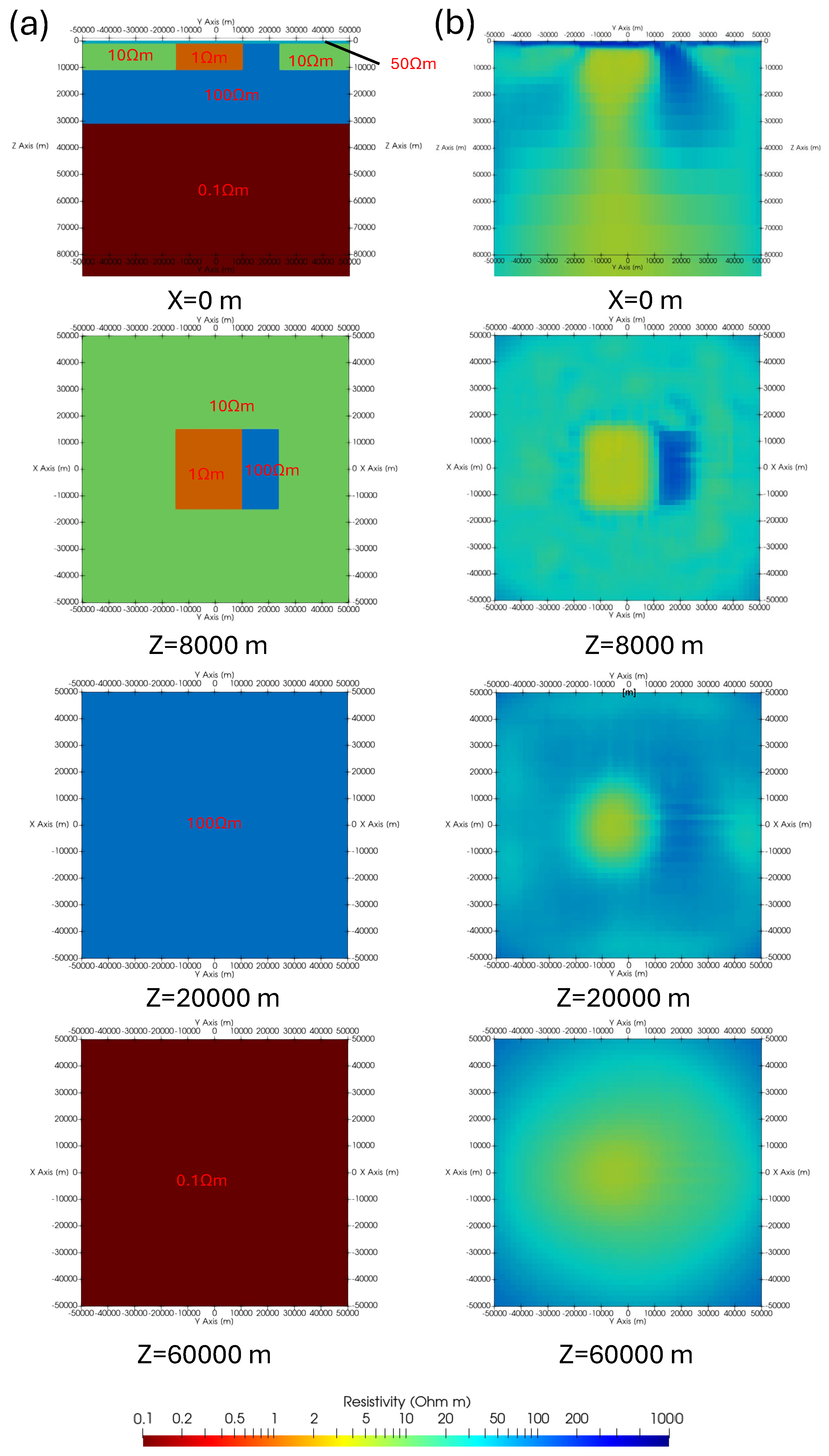
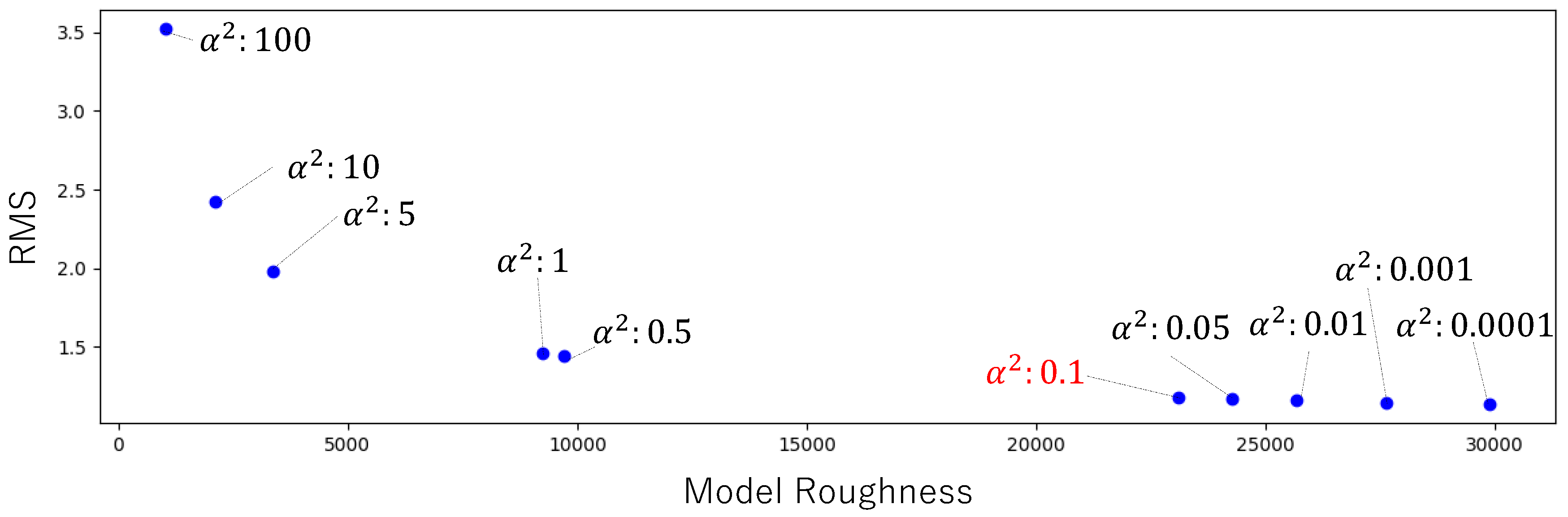
Conclusion
Acknowledgement
References
- Dong, Hao, and Gary D. Egbert. 2019. “Divergence-Free Solutions to Electromagnetic Forward and Adjoint Problems: A Regularization Approach.” Geophysical Journal International 216 (2): 906–18. [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Maki, Masahiro Yoshida, and Seiji Fujino. 2006. “BiCGSafe Method with Crout Version of ILU Decomposition Giving Triple Safe Keys for Convergence.” IPSJ Transactions on Advanced Computing Systems 47 (7): 52–60.
- Groom, Ross W, and Richard C Bailey. 1989. “Decomposition of Magnetotelluric Impedance Tensors in the Presence of Local Three-Dimensional Galvanic Distortion.” JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH 94 (B2): 1913–25.
- Jacobi, Benoît, Gaël Guennebaud, and other contributor. 2024. “Eigen.”, https://eigen.tuxfamily.org/.
- Jahandari, H., and C. G. Farquharson. 2015. “Finite-Volume Modelling of Geophysical Electromagnetic Data on Unstructured Grids Using Potentials.” Geophysical Journal International 202 (3): 1859–76. [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, Masahide. 2024. “Kv - a C++ Library for Verified Numerical Computation.”, http://verifiedby.me/kv/.
- Kelbert, Anna, Naser Meqbel, Gary D. Egbert, and Kush Tandon. 2014. “ModEM: A Modular System for Inversion of Electromagnetic Geophysical Data.” Computers and Geosciences 66 (May):40–53. [CrossRef]
- Key, Kerry W., Steven C. Constable, and Chester J. Weiss. 2006. “Mapping 3D Salt Using the 2D Marine Magnetotelluric Method: Case Study from Gemini Prospect, Gulf of Mexico.” Geophysics 71 (1). [CrossRef]
- Kingma, Diederik P., and Jimmy Ba. 2014. “Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization,” December. http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980.
- Mackie, Randall L, Theodore R Madden, and Wannamaker Philip E. 1993. “Three-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Modeling Using Difference Equations - Theory and Comparisons to Integral Equation Solutions.” GEOPHYSICS. Vol. 58. http://segdl.org/.
- Miensopust, Marion P., Pilar Queralt, Alan G. Jones, Dmitry Avdeev, Anna Avdeeva, Ralph Uwe Börner, David Bosch, et al. 2013. “Magnetotelluric 3-D Inversion-a Review of Two Successful Workshops on Forward and Inversion Code Testing and Comparison.” Geophysical Journal International 193 (3): 1216–38. [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhata, Yuji, and Toshihiro Uchida. 2004. “3D Magnetotelluric Modeling Using the T-Ω Finite-Element Method.” Geophysics 69 (1): 108–19. [CrossRef]
- Nam, Myung Jin, Hee Joon Kim, Yoonho Song, Tae Jong Lee, Jeong-Sul Son, and Jung Hee Suh. 2007. “3D Magnetotelluric Modelling Including Surface Topography.” Geophysical Prospect 55 (2): 277–87. [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Yasuo. 2002. “ON TWO-DIMENSIONAL MODELING OF MAGNETOTELLURIC FIELD DATA.” Surveys in Geophysics 23:251–73.
- O’Hara, Keith. 2024. “OptimLib.”, https://www.kthohr.com/optimlib.html.
- Plessix, Rene Edouard. 2006. “A Review of the Adjoint-State Method for Computing the Gradient of a Functional with Geophysical Applications.” Geophysical Journal International. [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Yutaka. 2004. “Three-Dimensional Inversion of Static-Shifted Magnetotelluric Data.” Earth Planets Space. Vol. 56.
- Siripunvaraporn, Weerachai, Gary Egbert, and Yongwimon Lenbury. 2002. “Numerical Accuracy of Magnetotelluric Modeling: A Comparison of Finite Difference Approximations.” LETTER Earth Planets Space. Vol. 54.
- Siripunvaraporn, Weerachai, Gary Egbert, Yongwimon Lenbury, and Makoto Uyeshima. 2005. “Three-Dimensional Magnetotelluric Inversion: Data-Space Method.” Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 150 (1-3 SPEC. ISS.): 3–14. [CrossRef]
- Takakura, Shinichi. 2014. “Estimation of a Regional Geothermal System by the Electromagnetic Exploration.” BUTSURI-TANSA 67 (3): 195–203.
- Toh, Hiroaki, Adam SCHULTZ, and Makoto Uyeshima. 2000. “Electromagnetic Induction in Fully Heterogeneous Spheres Using the Staggered Grid Finite Difference Method.”.
- Uchida, Toshihiro. 2022. “Consideration on Three-Dimensional Inversion of Magnetotelluric Data by Finite-Difference Modeling Including Topography: Data Interpretation at Northern Hakkoda Area.” Journal of the Geothermal Research Society of Japan 44 (1): 7–21.
- Uchida Toshihiro, and Yusuke Yamaya. 2023. “Three-Dimensional Finite-Element and Finite Difference Inversions of Magnetotelluric Data: Application at Northern Hakkoda Geothermal Area.” Journal of the Geothermal Research Society of Japan 45 (3): 175–94. [CrossRef]
- Usui, Yoshiya. 2015. “3-D Inversion of Magnetotelluric Data Using Unstructured Tetrahedral Elements: Applicability to Data Affected by Topography.” Geophysical Journal International 202 (2): 828–49. [CrossRef]
- Usui, Yoshiya, Makoto Uyeshima, Hideaki Hase, Hiroshi Ichihara, Koki Aizawa, Takao Koyama, Shin’ya Sakanaka, et al. 2024. “Three-Dimensional Electrical Resistivity Structure Beneath a Strain Concentration Area in the Back-Arc Side of the Northeastern Japan Arc.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 129 (5). [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Xiaoxiong, Jie Liu, Yian Cui, and Chunye Gong. 2022. “A Scalable Parallel Algorithm for 3-D Magnetotelluric Finite Element Modeling in Anisotropic Media.” IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 60. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




