Submitted:
12 August 2024
Posted:
13 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. ACS Preparation
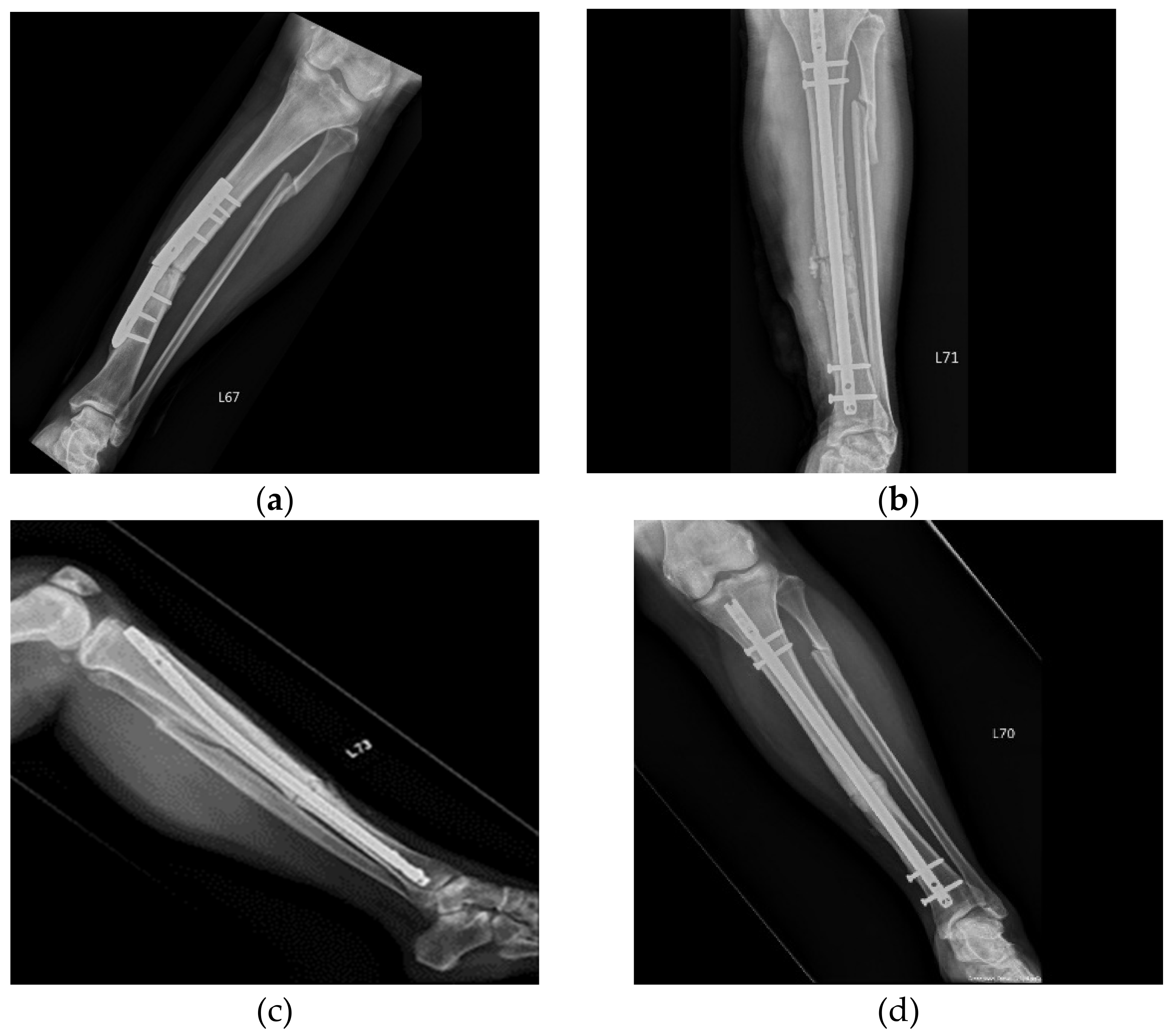
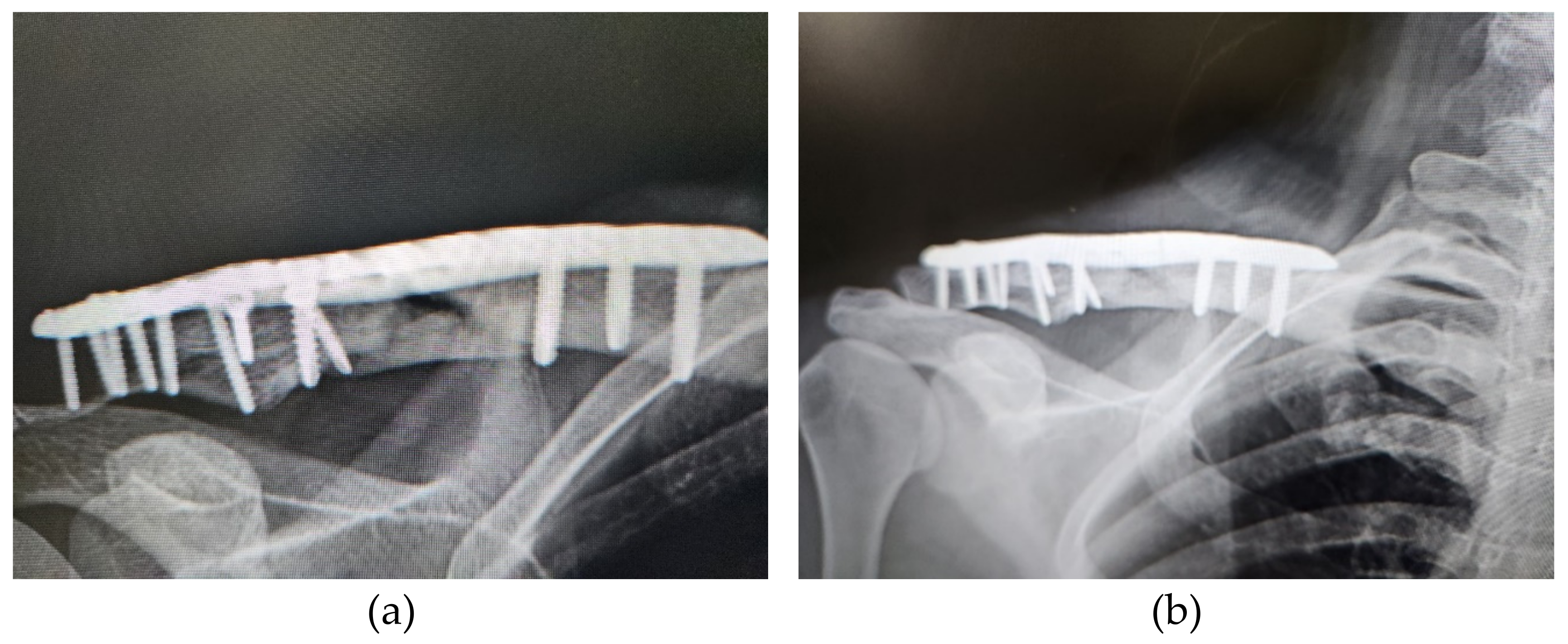
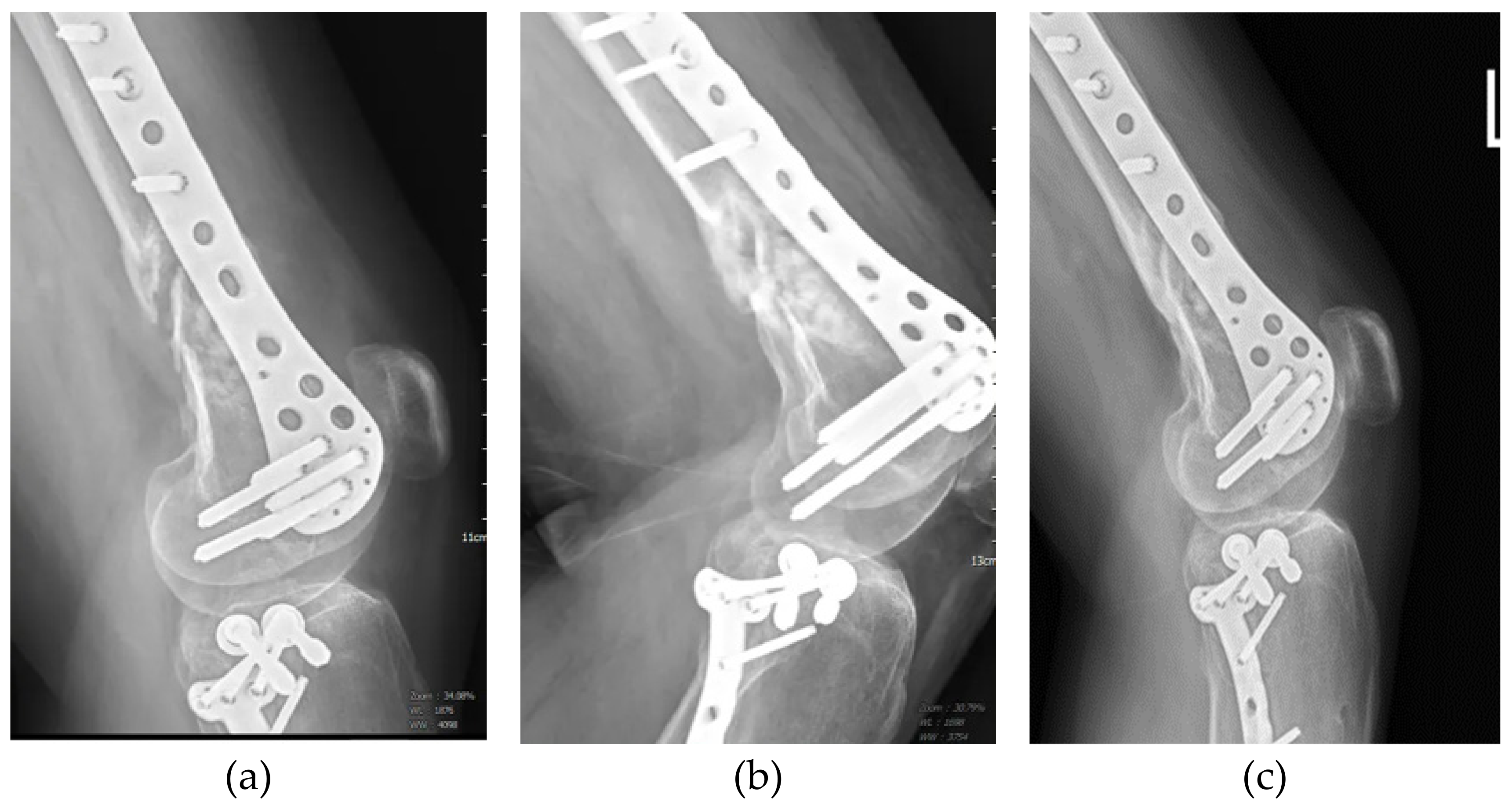
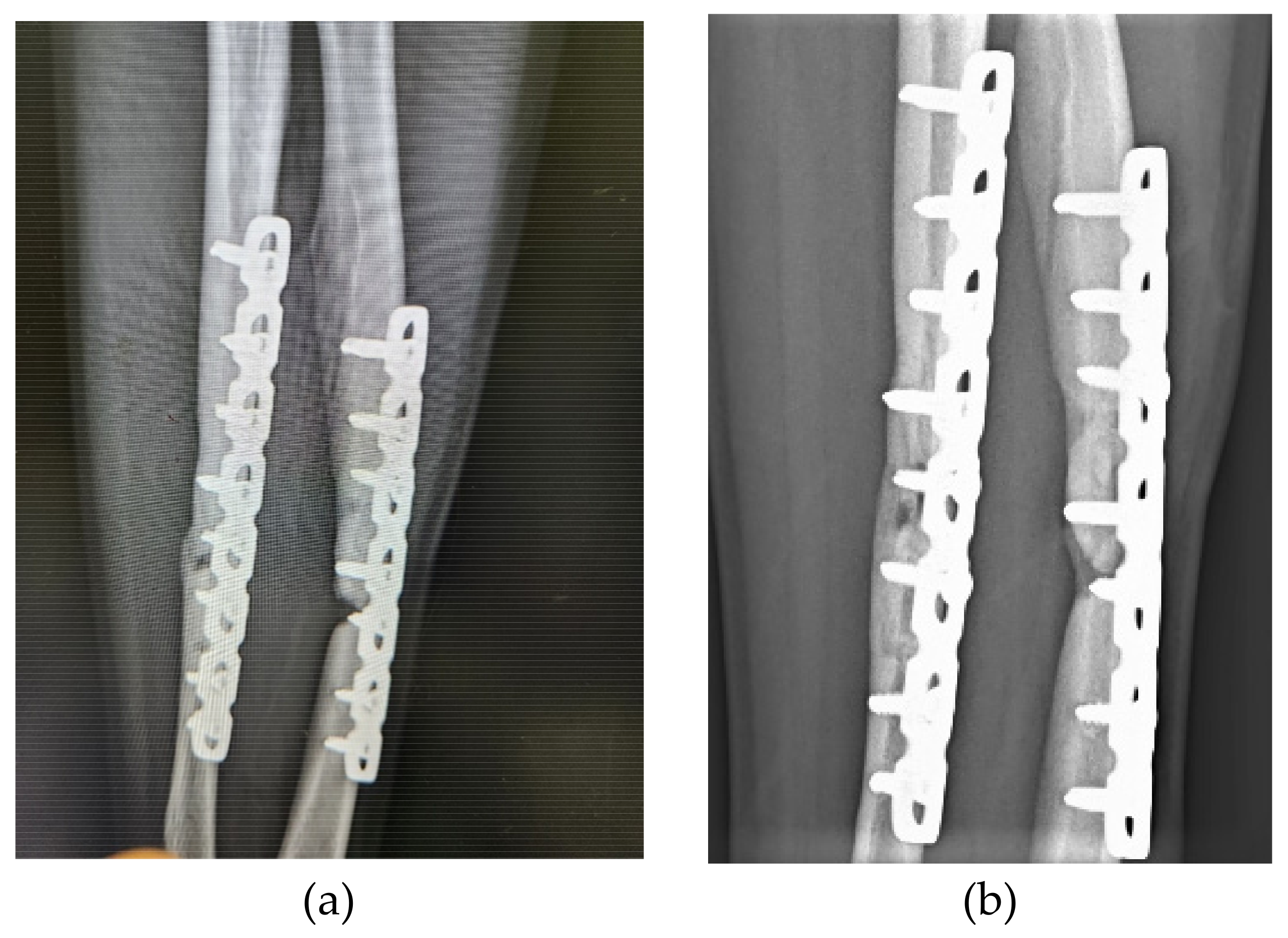
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Outcomes of ACS Injection
| Case | Age (years) | Sex | Diagnosis | Previous treatment outcomes | Non-union duration before ACS (months) | ACS Injection times | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | Female | Tibial fracture | Plate implant failure, followed by intramedullary nail at 9 months but still non-union | 9 | 3 | Union |
| 2 | 47 | Male | Right femoral shaft fracture | Non-union after ORIF | 9 | 3 | Union |
| 3 | 45 | Male | Right tibia and fibula fracture | Dynamization of distal screws on tibia; ACS injection was given on fibula. | 9 | 3 | Union |
| 4 | 39 | Female | Right clavicle fracture | Non-union after ORIF | 9 | 2 | Union |
| 5 | 66 | Male | Right upper femoral fracture | Plate implant failure, followed by gamma nail fixation at 9 months but still non-union | 9 | 3 | Non-union; due to unstable fixation |
| 6 | 34 | Male | Left distal femur fracture | Non-union after ORIF | 9 | 3 | Union |
| 7 | 53 | Male | Acetabulum bone defect | Non-union after total hip replacement | 25 | 1 | Union |
| 8 | 50 | Male | Left distal femur lateral condyle fracture | Non-union after ORIF | 36 | 2 | Union |
| 9 | 39 | Male | Right ulnar fracture | Non-union after ORIF | 14 | 2 | Union |
| 10 | 21 | Female | Right upper tibia fracture | Non-union after ORIF | 12 | 3 | Union |
| 11 | 27 | Male | Left radial & ulnar fracture | Non-union after ORIF | 9 | 3 | Union |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, C.H. Biomechanics of bone: determinants of skeletal fragility and bone quality. Osteoporos Int 2002, 13, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megas, P. Classification of non-union. Injury 2005, 36 Suppl 4, S30–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzioupis, C.; Giannoudis, P.V. Prevalence of long-bone non-unions. Injury 2007, 38 Suppl 2, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlundt, C.; Bucher, C.H.; Tsitsilonis, S.; Schell, H.; Duda, G.N.; Schmidt-Bleek, K. Clinical and Research Approaches to Treat Non-union Fracture. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2018, 16, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.; Wragg, N.M.; Shariatzadeh, M.; Wilson, S.A.-O. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) for the Management of Non-union Fractures.
- Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Guo, S.; Liu, S.; Jia, W.; Tuan, R.S.; Zhang, C. Comparative evaluation of MSCs from bone marrow and adipose tissue seeded in PRP-derived scaffold for cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7008–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsousou, J.; Thompson, M.; Hulley, P.; Noble, A.; Willett, K. The biology of platelet-rich plasma and its application in trauma and orthopaedic surgery. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery British Volume 2009, 91-B, 987-996. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Feng Y Fau—Zhang, C.Q.; Zhang Cq Fau—Chen, S.B.; Chen Sb Fau—Cheng, X.G.; Cheng, X.G. The regenerative effect of platelet-rich plasma on healing in large osteochondral defects.
- Galasso, O.; Mariconda, M.; Romano, G.; Capuano, N.; Romano, L.; Iannò, B.; Milano, C. Expandable intramedullary nailing and platelet rich plasma to treat long bone non-unions. J Orthop Traumatol 2008, 9, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanthan, S.R.; Kavitha, G.; Addi, S.; Choon, D.S.; Kamarul, T. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) enhances bone healing in non-united critical-sized defects: a preliminary study involving rabbit models. Injury 2011, 42, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calori, G.M.; Tagliabue, L.; Gala, L.; d’Imporzano, M.; Peretti, G.; Albisetti, W. Application of rhBMP-7 and platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of long bone non-unions: a prospective randomised clinical study on 120 patients. Injury 2008, 39, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldán, J.C.; Jepsen, S.; Miller, J.; Freitag, S.; Rueger, D.C.; Açil, Y.; Terheyden, H. Bone formation in the presence of platelet-rich plasma vs. bone morphogenetic protein-7. Bone 2004, 34, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, L.; Priddy, L.B.; Esancy, C.; Klosterhoff, B.S.; Stevens, H.Y.; Tran, L.; Guldberg, R.E. Delivery vehicle effects on bone regeneration and heterotopic ossification induced by high dose BMP-2. Acta Biomater 2017, 49, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, A.W.; LaChaud, G.; Shen, J.; Asatrian, G.; Nguyen, V.; Zhang, X.; Ting, K.; Soo, C. A Review of the Clinical Side Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 2016, 22, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltzer, A.W.; Moser, C.; Jansen, S.A.; Krauspe, R. Autologous conditioned serum (Orthokine) is an effective treatment for knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2009, 17, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, H.; Reinecke, J.; Becker, C.; Tholen, G.; Wehling, P. The production of anti-inflammatory cytokines in whole blood by physico-chemical induction. Inflamm Res 2003, 52, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizziero, A.; Giannotti, E.; Oliva, F.; Masiero, S.; Maffulli, N. Autologous conditioned serum for the treatment of osteoarthritis and other possible applications in musculoskeletal disorders. Br Med Bull 2013, 105, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darabos, N.; Haspl, M.; Moser, C.; Darabos, A.; Bartolek, D.; Groenemeyer, D. Intraarticular application of autologous conditioned serum (ACS) reduces bone tunnel widening after ACL reconstructive surgery in a randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2011, 19 Suppl 1, S36–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, M.B.; Berenbaum, F. Emerging targets in osteoarthritis therapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2015, 22, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, M.; Ometti, M.; Drossinos, A.; Pironti, P.; Santoleri, L.; Salini, V. Autologous conditioned serum: clinical and functional results using a novel disease modifying agent for the management of knee osteoarthritis. J Drug Assess 2020, 25, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.-G.; Yang, K.D.; Huang, L.-G.; Wang, C.-H.; Ko, W.-S. Comparisons of Cytokines, Growth Factors and Clinical Efficacy between Platelet-Rich Plasma and Autologous Conditioned Serum for Knee Osteoarthritis Management. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.A.; Palanca, A.A.; Bellino, M.J.; Lowenberg, D.W. Assessment of compromised fracture healing. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2012, 20, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, B.; Wragg, N.M.; Wilson, S.L. The use of PRP injections in the management of knee osteoarthritis. Cell Tissue Res 2019, 376, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsousou, J.; Thompson, M.; Hulley, P.; Noble, A.; Willett, K. The biology of platelet-rich plasma and its application in trauma and orthopaedic surgery: a review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2009, 91, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Bleek, K.; Schell, H.; Schulz, N.; Hoff, P.; Perka, C.; Buttgereit, F.; Volk, H.D.; Lienau, J.; Duda, G.N. Inflammatory phase of bone healing initiates the regenerative healing cascade. Cell Tissue Res 2012, 347, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganji, E.; Killian, M.L. Tendon healing in the context of complex fractures. Clin Rev Bone Miner Metab 2018, 16, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffarpasand, F.; Shahrezaei, M.; Dehghankhalili, M. Effects of Platelet Rich Plasma on Healing Rate of Long Bone Non-union Fractures: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial. Bull Emerg Trauma 2016, 4, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xing, F.; Luo, R.; Liu, M. Clinical Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Long-Bone Delayed Union and Nonunion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 771252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.; Wragg, N.M.; Shariatzadeh, M.; Wilson, S.L. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) for the Management of Non-union Fractures. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2021, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labibzadeh, N.; Emadedin, M.; Fazeli, R.; Mohseni, F.; Hosseini, S.E.; Moghadasali, R.; Mardpour, S.; Azimian, V.; Ghorbani Liastani, M.; Mirazimi Bafghi, A.; et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Implantation in Combination with Platelet Lysate Product Is Safe for Reconstruction of Human Long Bone Nonunion. Cell J 2016, 18, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, C.; Schultz, J.; Cheever, M.; Freeman, M.; Robinson, B.; Faulkner, S. A case series of percutaneous treatment of non-union fractures with autologous, culture expanded, bone marrow derived, mesenchymal stem cells and platelet lysate. J Bioengineer & Biomedical Sci S 2011, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Vauclair, F.; Goetti, P.; Nguyen, N.T.V.; Sanchez-Sotelo, J. Distal humerus nonunion: evaluation and management. EFORT Open Reviews 2020, 5, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfet, D.L.; Kloen, P.; Anand, N.; Rosen, H.S. Open reduction and internal fixation of delayed unions and nonunions of fractures of the distal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003, 85, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauclair, F.; Goetti, P.; Nguyen, N.T.V.; Sanchez-Sotelo, J. Distal humerus nonunion: evaluation and management. EFORT Open Rev 2020, 5, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidenberg, E.E.; Juarez Cesca, F.; Pastrana, M.J.; Zaidenberg, C.R. Pedicled Vascularized Bone Graft of the Distal Radius for Recalcitrant Nonunion of the Distal Humerus.
- Frölke, J.P.; Patka, P. Definition and classification of fracture non-unions. Injury 2007, 38 Suppl 2, S19–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmal, H.; Brix, M.; Bue, M.; Ekman, A.; Ferreira, N.; Gottlieb, H.; Kold, S.; Taylor, A.; Toft Tengberg, P.; Ban, I. Nonunion—consensus from the 4th annual meeting of the Danish Orthopaedic Trauma Society. EFORT Open Rev 2020, 5, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, K.H.; Baek, J.H.; Kim, M.S. Risk Factors for Non-Union after Open Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with Distal Humerus Fractures. J Clin Med 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froum, S.J.; Wallace, S.S.; Tarnow, D.P.; Cho, S.C. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on bone growth and osseointegration in human maxillary sinus grafts: three bilateral case reports. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2002, 22, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raghoebar, G.M.; Schortinghuis, J.; Liem, R.S.; Ruben, J.L.; van der Wal, J.E.; Vissink, A. Does platelet-rich plasma promote remodeling of autologous bone grafts used for augmentation of the maxillary sinus floor? Clin Oral Implants Res 2005, 16, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielecki, T.; Gazdzik, T.S.; Szczepanski, T. Benefit of percutaneous injection of autologous platelet-leukocyte-rich gel in patients with delayed union and nonunion. Eur Surg Res 2008, 40, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariconda, M.; Cozzolino, F.; Cozzolino, A.; D’Agostino, E.; Bove, A.; Milano, C. Platelet gel supplementation in long bone nonunions treated by external fixation. J Orthop Trauma 2008, 22, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanyam, K.; Alguvelly, R.; Mundargi, A.; Khanchandani, P. Single versus multi-dose intra-articular injection of platelet rich plasma in early stages of osteoarthritis of the knee: A single-blind, randomized, superiority trial. Arch Rheumatol 2021, 36, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Say, F.; Türkeli, E.; Bülbül, M. Is platelet-rich plasma injection an effective choice in cases of non-union? Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 2014, 81, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.J.; Tan, X.X.; Ju, H.Y.; Su, J.P.; Yan, W.; Song, X.G.; Qin, L.W.; Ju, C.J.; Wang, L.S.; Zou, D.B. Autologous platelet lysates local injections for treatment of tibia non-union with breakage of the nickelclad: a case report. Springerplus 2016, 5, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casati, L.; Celotti, F.; Negri-Cesi, P.; Sacchi, M.C.; Castano, P.; Colciago, A. Platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) contained in Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) stimulates migration of osteoblasts by reorganizing actin cytoskeleton. Cell Adhesion & Migration 2014, 8, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, H.; Duda, G.N.; Peters, A.; Tsitsilonis, S.; Johnson, K.A.; Schmidt-Bleek, K. The haematoma and its role in bone healing. J Exp Orthop 2017, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santolini, E.; West, R.; Giannoudis, P.V. Risk factors for long bone fracture non-union: a stratification approach based on the level of the existing scientific evidence. Injury 2015, 46 Suppl 8, S8–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, P.; Xie, X.; Fang, B. Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration. Mater Today Bio 2023, 18, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





