Submitted:
10 August 2024
Posted:
12 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Software
2.3. Analysis Methods
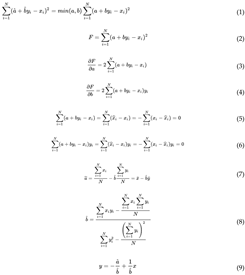
2.4. Confidence Bounds Methods
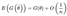
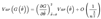
2.5. Ranking Methods
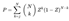
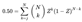
2.6. Procedure
- Data Acquisition and Conversion: Obtain failure rate data for centrifugal compressors with electrical motor drivers from Oreda 6 Taxonomy 1.1.1.1, which is provided in terms of failures per 106 hours [14]. Convert this failure rate into Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) by normalizing it to hours per year.
- Weibull Parameters Calculation:
- Beta (β): Calculate the shape parameter β using the Rank Regression on X, which characterizes the failure rate's variability. Beta (β) equation © 2004 Nelson, as follows [15].
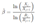
- 2.
- Eta (η): Determine the scale parameter η in hours, representing the characteristic life of the equipment. Eta (η) equation © 2006 Abernethy, R. B. as follows [16].
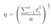
- 3.
- LK Value: Compute the log-likelihood (LK) value for model fit assessment. LK Value equation © 2003 Lawless, J. F. as follows [17].
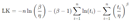
- 4.
- Rho (ρ): Calculate the reliability at time t = 8760 hours to determine R(t=8760 hr), the probability of survival. Rho (ρ) equation © 2003 Meeker as follows [18].
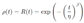
- Reliability and Probability Calculations:
- Reliability (R): Compute reliability at t = 8760 hours using the the Weibull reliability function. Reliability (R) equation © 1981 Barlow as follows [20].
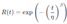
- 2.
- Probability of Failure (Q): Compute the probability of failure at t = 8760 hours using the Weibull cumulative distribution function. Probability of Failure (Q) equation © 2004 Nelson as follows [16].
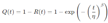
- 3.
- Reliable Life: Determine the reliable life for a reliability level R = 0.99, which indicates the time at which 99% of the units are expected to still be operational. Reliable Life equation © 2014 Meeker as follows [19].
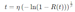
- 4.
- Mean Life (MTTF): Calculate the Mean Time To Failure (MTTF) using the Weibull distribution parameters. Mean Life (MTTF) equation © 2003 Lawless, J. F. as follows [17].
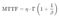
- 5.
- Mean Remaining Life (MRL): Estimate the Mean Remaining Life, which is the average time remaining before failure, given a unit is still operational. Mean Remaining Life (MRL) equation © 2014 Meeker as follows [19].
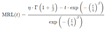
- 6.
- Failure Rate: Calculate the failure rate at any given time, which can be derived from the Weibull distribution’s probability density function. Failure rate equation © 1981 Barlow as follows [20].
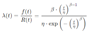
- Repeat Calculations: Ensure all calculations are performed iteratively to validate and refine the parameters, ensuring accurate results for the Weibull analysis.
- This procedure outlines the steps to perform Weibull analysis from acquisition data, providing a comprehensive approach to assessing and optimizing maintenance strategies.
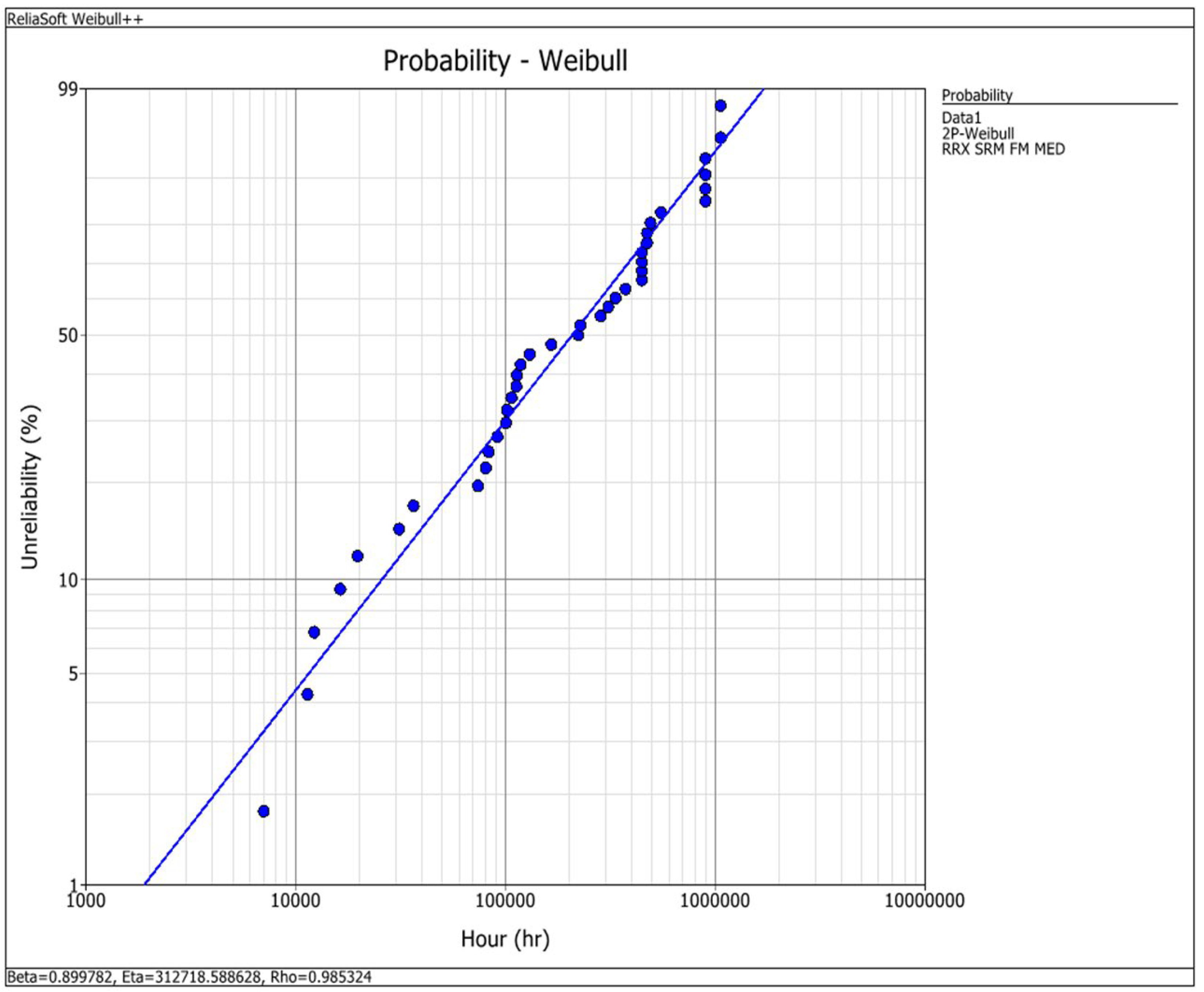
3. Results
3.1. Probability Weibull Graph
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
References
- Spüntrup, F. , Londono, J., Skourup, C., Thornhill, N., & Imsland, L. (2018). Reliability improvement of compressors based on asset fleet reliability data. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 51, 217-224. [CrossRef]
- Silver, E., & Fiechter, C. (1995). Preventive maintenance with limited historical data. European Journal of Operational Research, 82, 125-144. [CrossRef]
- Genschel, U. , & Meeker, W. (2010). A Comparison of Maximum Likelihood and Median-Rank Regression for Weibull Estimation. Quality Engineering, 22, 236 - 255. [CrossRef]
- Langseth, H. , & Lindqvist, B. (2006). Competing risks for repairable systems : A data study. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 136, 1687-1700. [CrossRef]
- Amari, S. (2006). Bounds on MTBF of Systems Subjected to Periodic Maintenance. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 55, 469-474. [CrossRef]
- Dhanisetty, V. , Verhagen, W., & Curran, R. (2015). Optimising maintenance intervals for multiple maintenance policies: a cross-industrial study. International Journal of Agile Systems and Management, 8, 219-242. [CrossRef]
- Hottinger Bruel & Kjaer Inc. (2024). Introduction to Life Data Analysis. https://bit.ly/3YGKoqk.
- Hottinger Bruel & Kjaer Inc. (2024). Appendix A: Least Squares/Rank Regression Equations on x. bit.ly/4fCs7QR.
- Hottinger Bruel & Kjaer Inc. (2024). Fisher Matrix Confidence Bounds. https://bit.ly/46IXjtu.
- Hottinger Bruel & Kjaer Inc. (2024). Parameter Estimation Median Ranks. https://bit.ly/3YXIYIb.
- Chen, T. , Kowalski, J., Chen, R., Wu, P., Zhang, H., Feng, C., & Tu, X. (2016). Rank-preserving regression: a more robust rank regression model against outliers. Statistics in Medicine, 35, 3333 - 3346. [CrossRef]
- Jongerius, S. (2022). Coverage of lifetime confidence bounds for highly censored and few Weibull distributed data.
- Taneja, V. S. (1992). An overview of reliability growth models and their potential use for NASA applications.
- DNV GL, SINTEF, & NTNU. (2015). OREDA Offshore and Onshore Reliability Data Handbook. Vol-1 Topside Equipment 6th Edition.
- Jiang, R. , & Murthy, D. (2011). A study of Weibull shape parameter: Properties and significance. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf., 96, 1619-1626. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W. B. (2004). Accelerated testing: statistical models, test plans, and data analysis. John Wiley & Sons.
- Abernethy, R. B. (2006). Reliability Engineering and Risk Analysis: A Practical Guide. CRC Press.
- Lawless, J. F. (2003). Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data. John Wiley & Sons.
- Meeker, W. Q. , & Escobar, L. A. (2014). Statistical Methods for Reliability Data. John Wiley & Sons.
- Barlow, R. E. , & Proschan, F. (1981). Mathematical Theory of Reliability. John Wiley & Sons.
- Bianchini, A., Pellegrini, M., & Rossi, J. (2019). Maintenance scheduling optimization for industrial centrifugal pumps. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 10, 848-860. [CrossRef]
| Failure Mode | Mean FR/(106hours) | MTBF (hours) |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | 81,31 | 12298,61 |
| Critical Abnormal Instrument Reading | 32,02 | 31230,48 |
| Critical Breakdown | 0,94 | 1063829,79 |
| Critical Erratic Output | 3,23 | 309597,52 |
| Critical External Leakage Process medium | 1,81 | 552486,19 |
| Critical External Leakage Utility medium | 4,38 | 228310,50 |
| Critical Fail to start on demand | 9,33 | 107181,14 |
| Critical internal leakage | 3,51 | 284900,28 |
| Critical Plugged/choked | 2,03 | 492610,84 |
| Critical spurious stop | 12,38 | 80775,44 |
| Critical vibration | 8,79 | 113765,64 |
| Critical Other | 9,82 | 101832,99 |
| Critical Unknown | 1,11 | 900900,90 |
| Degraded | 87,7 | 11402,51 |
| Degraded Abnormal Instrument Reading | 27,39 | 36509,68 |
| Degraded Erratic Output | 8,86 | 112866,82 |
| DegradedExternal Leakage Process medium | 12 | 83333,33 |
| Degraded External Leakage Utility medium | 13,49 | 74128,98 |
| Degraded internal leakage | 8,44 | 118483,41 |
| Degraded Low Output | 0,94 | 1063829,79 |
| Degraded Parameter deviation | 4,49 | 222717,15 |
| Degraded plugged/choked | 2,98 | 335570,47 |
| Degraded spurious stop | 2,11 | 473933,65 |
| Degraded structural deficiency | 1,11 | 900900,90 |
| Degraded vibration | 10,89 | 91827,36 |
| Degraded other | 2,23 | 448430,49 |
| Degraded unknown | 2,23 | 448430,49 |
| incipient | 141,7 | 7057,16 |
| incipient Abnormal Instrument Reading | 50,6 | 19762,85 |
| incipient External Leakage Process medium | 9,93 | 100704,93 |
| incipient External Leakage Utility medium | 7,64 | 130890,05 |
| incipient High Output | 1,11 | 900900,90 |
| incipient internal leakage | 2,23 | 448430,49 |
| incipient Minor in-service problems | 61,1 | 16366,61 |
| incipient other | 6,03 | 165837,48 |
| incipient unknown | 2,23 | 448430,49 |
| unknown | 2,67 | 374531,84 |
| unknown Abnormal Instrument Reading | 2,11 | 473933,65 |
| Weibull Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Beta (β) | 0.899782 |
| Eta (η) | 312718.5886 hours |
| LK Value | -533.917585 |
| Rho (ρ) | 0.985324 |
| Reliability & Probability | Value |
|---|---|
| Reliability R(t=8760 hours) | 0.960710 |
| Probability of Failure Q(t=8760 hours) | 0.039290 |
| Reliable Life (R=99%) | 1882.852877 hours |
| Mean Life (MTTF) | 329080.800992 hours |
| Mean Remaining Life (MRL) | 333610.832804 hours |
| Failure Rate | 0.000004/hour |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




