Submitted:
09 August 2024
Posted:
12 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To the best of our knowledge, this is the latest comprehensive survey of WiFi sensing area, covering most recently great progresses made over the past 5 years.
- We categorize existing studies from two distinct perspectives, i.e., application-based and methodology-based, and present in-depth analysis of recent works.
- We highlight the key challenges encountered in existing studies and present a thorough discussion about three promising research directions of WiFi sensing.
2. Preliminary
2.1. Channel State Information
2.2. Signal Sensing Models
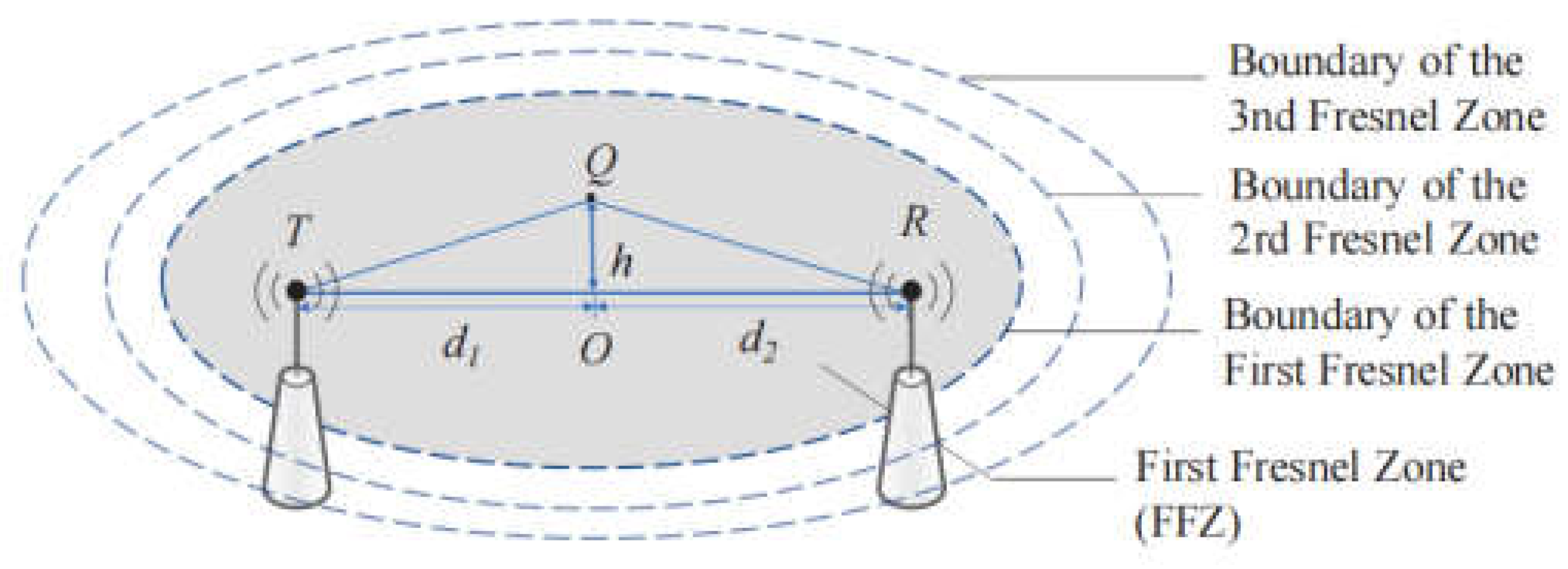
2.2.1. Fresnel zone-based reflection model
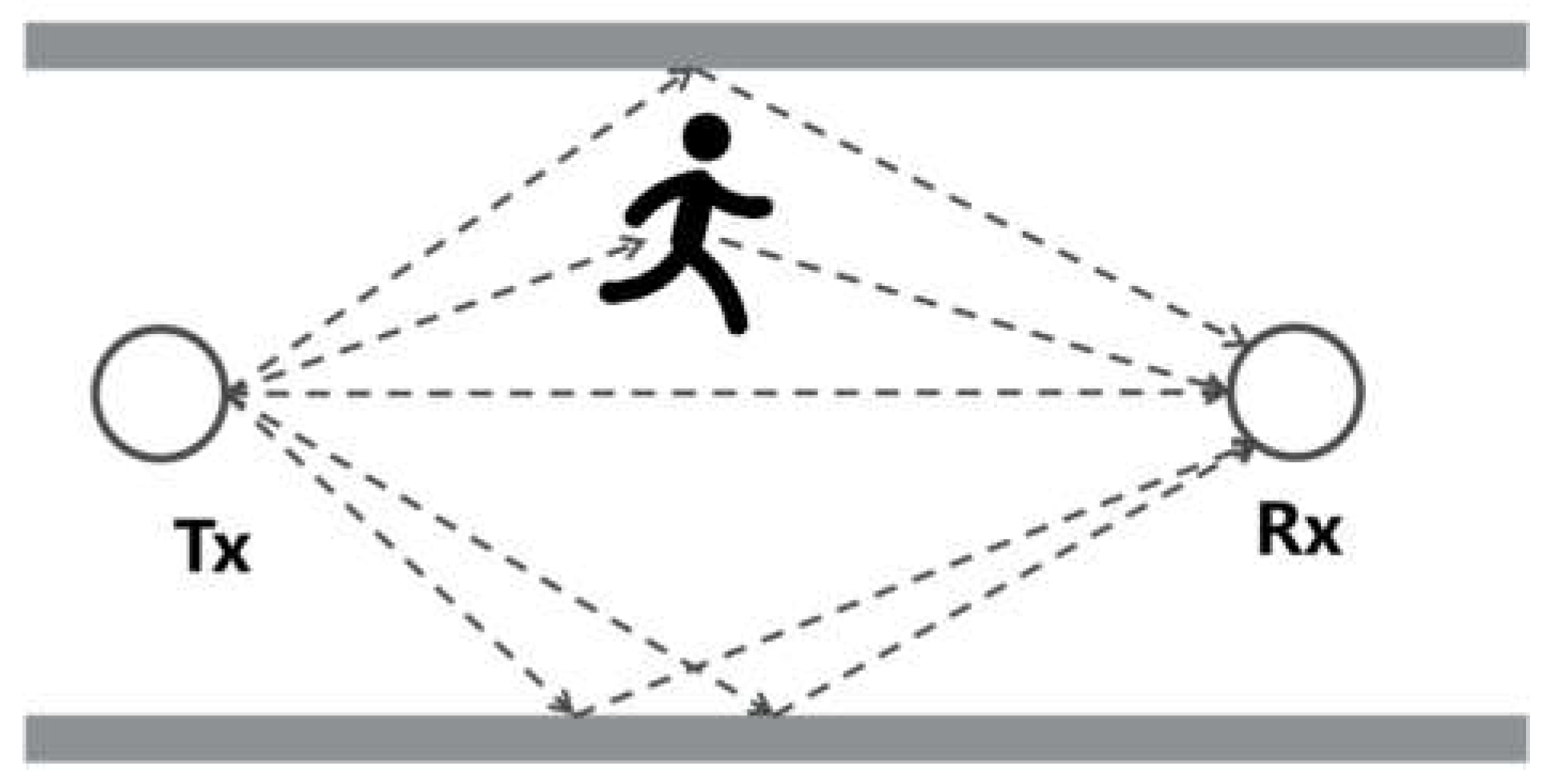
2.2.2. Fresnel zone-based diffraction model
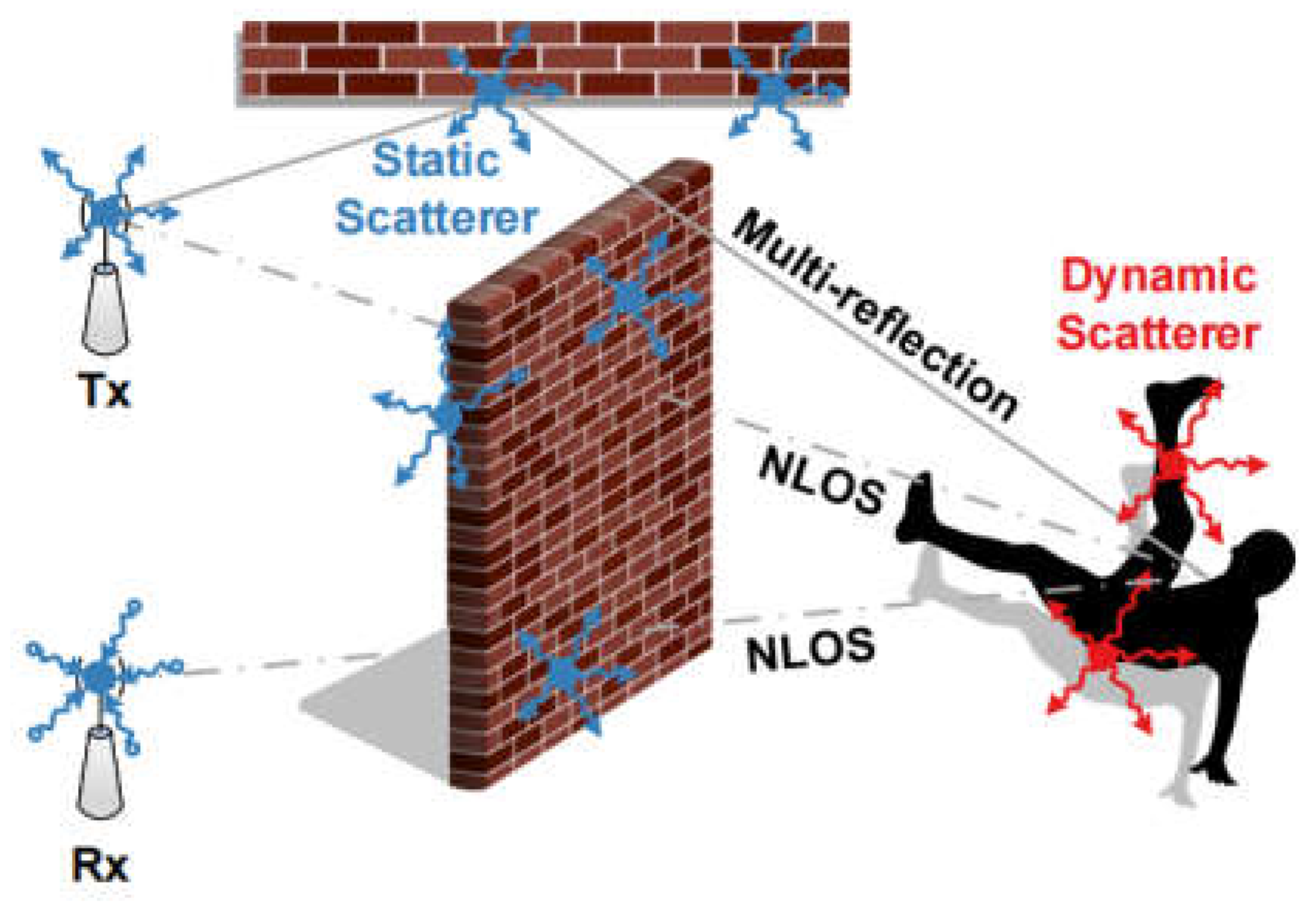
2.2.3. Scattering sensing Model
3. WiFi Sensing
3.1. WiFi sensing applications
3.2. WiFi sensing methodologies
4. Challenges
5. Future research trend discussion
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, A.; et al., "A Survey on Fundamental Limits of Integrated Sensing and Communication," in IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 994-1034, Secondquarter 2022.
- Liu F. et al., "Integrated Sensing and Communications: Toward Dual-Functional Wireless Networks for 6G and Beyond," in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 1728-1767, June 2022.
- Meneghello F.; Chen C.; Cordeiro C.; Restuccia F.; "Toward Integrated Sensing and Communications in IEEE 802.11bf Wi-Fi Networks," in IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 128-133, July 2023.
- Wu C.; Wang B.; Au O.; Liu K.; "Wi-Fi Can Do More: Toward Ubiquitous Wireless Sensing," in IEEE Communications Standards Magazine, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 42-49, June 2022.
- Li X.; Cui Y.; Zhang J.; Liu F.; Zhang D.; Hanzo L.; "Integrated Human Activity Sensing and Communications," in IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 90-96, May 2023.
- Yang Z.; Zhou Z. and Liu Y.; 2013. From RSSI to CSI: Indoor localization via channel response. ACM Comput. Surv. 46, 2, Article 25 (November 2013), 32 pages.
- Zhang F.; Wu C.; Wang B.; Lai H.; Han Y. and Ray Liu K.; 2019. WiDetect: Robust Motion Detection with a Statistical Electromagnetic Model. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 3, 3, Article 122 (September 2019), 24 pages.
- Zhang F.; Niu K.; Xiong J.; Jin B.; Gu T.; Jiang Y.; Zhang D.; 2019. Towards a Diffraction-based Sensing Approach on Human Activity Recognition. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 3, 1, Article 33 (March 2019), 25 pages.
- Gong W.; Liu J.; 2018. SiFi: Pushing the Limit of Time-Based WiFi Localization Using a Single Commodity Access Point. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2, 1, Article 10 (March 2018), 21 pages.
- Zhang D.; Wang H.; Wu D.; "Toward Centimeter-Scale Human Activity Sensing with Wi-Fi Signals," in Computer, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 48-57, Jan. 2017.
- Wang, Z.; et al., "A Survey on Human Behavior Recognition Using Channel State Information," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 155986-156024, 2019.
- Ma Y.; Zhou G.; Wang S.; 2019. WiFi Sensing with Channel State Information: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 52, 3, Article 46 (May 2020), 36 pages.
- Tan S.; Ren Y.; Yang J.; Chen Y.; "Commodity WiFi Sensing in Ten Years: Status, Challenges, and Opportunities," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 18, pp. 17832-17843, 15 Sept.15, 2022.
- Xiao J.; Li H.; Wu M.; Jin H.; Jamal Deen M.; Cao J.; 2022. A Survey on Wireless Device-free Human Sensing: Application Scenarios, Current Solutions, and Open Issues. ACM Comput. Surv. 55, 5, Article 88 (May 2023), 35 pages.
- Chen C.; Zhou G.; Lin Y.; 2023. Cross-Domain WiFi Sensing with Channel State Information: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 55, 11, Article 231 (November 2023), 37 pages.
- Halperin D.; Hu W.; Sheth A.; Wetherall D.; 2010. Predictable 802.11 packet delivery from wireless channel measurements. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 40, 4 (October 2010), 159–170.
- Halperin D.; Hu W.; Sheth A.; Wetherall D.; 2011. Tool release: gathering 802.11n traces with channel state information. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 41, 1 (January 2011), 53.
- Wang H.; Zhang D.; Ma J.; Wang Y.; Wang Y.; Wu D.; Gu T.; Xie B.; 2016. Human respiration detection with commodity wifi devices: do user location and body orientation matter? In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp '16). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 25–36.
- Wu D.; Zhang D.; Xu C.; Wang H.; Li X.; "Device-Free WiFi Human Sensing: From Pattern-Based to Model-Based Approaches," in IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 55, no. 10, pp. 91-97, Oct. 2017.
- Zhang F.; Zhang D.; Xiong J.; Wang H.; Niu K.; Jin B.; Wang Y.; 2018. From Fresnel Diffraction Model to Fine-grained Human Respiration Sensing with Commodity Wi-Fi Devices. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2, 1, Article 53 (March 2018), 23 pages.
- Yang Z.; Zhang Y.; Chi G.; Zhang G.; 2022. "Hands-on wireless sensing with Wi-Fi: A tutorial," 2022. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2206.09532.
- Zhang F.; Chen C.; Wang B.; Liu K. J. R.; "WiSpeed: A Statistical Electromagnetic Approach for Device-Free Indoor Speed Estimation," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 2163-2177, June 2018.
- Zeng X.; Wang B.; Wu C.; Regani S. D.; Liu K. J. R.; "WiCPD: Wireless Child Presence Detection System for Smart Cars," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 24, pp. 24866-24881, 15 Dec.15, 2022.
- Hu Y.; Ozturk M. Z.; Wang B.; Wu C.; Zhang F.; Liu K. J. R.; "Robust Passive Proximity Detection Using Wi-Fi," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 7, pp. 6221-6234, 1 April1, 2023.
- Zhu G.; Wang B.; Gao W.; Hu Y.; Wu C.; Liu K. J. R.; "WiFi-Based Robust Human and Non-human Motion Recognition With Deep Learning," 2024 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops and other Affiliated Events (PerCom Workshops), Biarritz, pp. 769-774, France, 2024.
- Zhu G.; Hu Y.; Wang B.; Wu C.; Zeng X.; Liu K. J. R.; "Wi-MoID: Human and Nonhuman Motion Discrimination Using WiFi With Edge Computing," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 13900-13912, 15 April15, 2024.
- Zhang Y.; Zheng Y.; Zhang G.; Qian K.; Qian C.; Yang Z.; 2021. GaitSense: Towards Ubiquitous Gait-Based Human Identification with Wi-Fi. ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 18, 1, Article 1 (February 2022), 24 pages.
- Wu C.; Zhang F.; Hu Y.; Liu K. J. R.; 2021. GaitWay: Monitoring and Recognizing Gait Speed Through the Walls. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 20, 6 (June 2021), 2186–2199.
- Wang D.; Yang J.; Cui W.; Xie L.; Sun S.; "CAUTION: A Robust WiFi-Based Human Authentication System via Few-Shot Open-Set Recognition," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 18, pp. 17323-17333, 15 Sept.15, 202.
- Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D. Wi-PIGR: Path Independent Gait Recognition With Commodity Wi-Fi. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2021, 21, 3414–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang J.; Chen X.; Zou H.; Wang D.; Xie L.; "AutoFi: Toward Automatic Wi-Fi Human Sensing via Geometric Self-Supervised Learning," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 8, pp. 7416-7425, 15 April15, 2023.
- Deng L.; Yang J.; Yuan S.; Zou H.; Lu C. X.; Xie L.; "GaitFi: Robust Device-Free Human Identification via WiFi and Vision Multimodal Learning," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 625-636, 1 Jan.1, 2023.
- Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Fan, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D. Wi-Diag: Robust Multisubject Abnormal Gait Diagnosis With Commodity Wi-Fi. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 11, 4362–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q. Context-Aware Wireless-Based Cross-Domain Gesture Recognition. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13503–13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao R.; Zhang M.; Zhang J.; Li Y.; Yi E.; Wu D.; Wang L.; Zhang D.; 2021. Towards Position-Independent Sensing for Gesture Recognition with Wi-Fi. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 5, 2, Article 61 (June 2021), 28 pages.
- Zhang J.; Li Y.; Xiong H.; Dou D.; Miao C.; Zhang D.; "HandGest: Hierarchical Sensing for Robust-in-the-Air Handwriting Recognition With Commodity WiFi Devices," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 19, pp. 19529-19544, 1 Oct.1, 2022.
- Gao R.; Li W.; Xie Y.; Yi E.; Wang L.; Wu D.; Zhang D.; 2022. Towards Robust Gesture Recognition by Characterizing the Sensing Quality of WiFi Signals. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 6, 1, Article 11 (March 2022), 26 pages.
- Niu K.; Zhang F.; Wang X.; Lv Q.; Luo H.; Zhang D.; "Understanding WiFi Signal Frequency Features for Position-Independent Gesture Sensing," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 21, no. 11, pp. 4156-4171, 1 Nov. 2022.
- Zhang, Y.; et al., "Widar3.0: Zero-Effort Cross-Domain Gesture Recognition With Wi-Fi," in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 44, no. 11, pp. 8671-8688, 1 Nov. 2022.
- Xing T.; Yang Q.; Jiang Z.; Fu X.; Wang J.; Wu C. Q.; Chen X.; 2022. WiFine: Real-Time Gesture Recognition Using Wi-Fi with Edge Intelligence. ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 19, 1, Article 11 (February 2023), 24 pages.
- Liu Y.; Yu A.; Wang L.; Guo B.; Li Y.; Yi E.; Zhang D.; 2024. UniFi: A Unified Framework for Generalizable Gesture Recognition with Wi-Fi Signals Using Consistency-guided Multi-View Networks. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 7, 4, Article 168 (December 2023), 29 pages.
- Yang, M.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, R.; Wu, F.; Yin, L.; Yang, Y.; 2023. WiTransformer: A Novel Robust Gesture Recognition Sensing Model with WiFi. Sensors. 2023; 23(5):2612.
- Wang, D.; Yang, J.; Cui, W.; Xie, L.; Sun, S.; "AirFi: Empowering WiFi-Based Passive Human Gesture Recognition to Unseen Environment via Domain Generalization," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 1156-1168, Feb. 2024.
- Gao, R.; et al., "WiCGesture: Meta-Motion-Based Continuous Gesture Recognition With Wi-Fi," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 11, no. 9, pp. 15087-15099, 1 May1, 2024.
- Wang, F.; Zhang, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, B.; Liu K. J., R.; "Respiration Tracking for People Counting and Recognition," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 5233-5245, June 2020.
- Ma, Y.; Arshad, S.; Muniraju, S.; Torkildson, E.; Rantala, E.; Doppler, K.; Zhou, G. Location- and Person-Independent Activity Recognition with WiFi, Deep Neural Networks, and Reinforcement Learning. ACM Trans. Internet Things 2021, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, J.; Cui, W.; Xie, L.; Sun, S.; "Multimodal CSI-Based Human Activity Recognition Using GANs," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 8, no. 24, pp. 17345-17355, 15 Dec.15, 2021.
- Niu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, D.; Shah R., C.; Tanriover, C.; Lu, H.; Zhang, D.; WiMonitor: Continuous Long-Term Human Vitality Monitoring Using Commodity Wi-Fi Devices. Sensors. 2021; 21(3):751.
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, B.; Liu K. J., R.; "DeFall: Environment-Independent Passive Fall Detection Using WiFi," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 11, pp. 8515-8530, 1 June1, 2022.
- Ding, X.; Hu, C.; Xie, W.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, J.; Jiang, T.; 2022. Device-Free Multi-Location Human Activity Recognition Using Deep Complex Network. Sensors. 2022; 22(16):6178.
- Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Zou, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, Q.; Xie, L.; "EfficientFi: Toward Large-Scale Lightweight WiFi Sensing via CSI Compression," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 15, pp. 13086-13095, 1 Aug.1, 2022.
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, F.; Yu, J.; Ren, J.; Wang, Z.; Gong, W.; 2022. "Target-oriented Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation for WiFi-based HAR," IEEE INFOCOM 2022 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, London, United Kingdom, 2022, pp. 420-429.
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; "Rethinking Fall Detection With Wi-Fi," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 6126-6143, 1 Oct. 2023.
- Meneghello, F.; Garlisi, D.; Di Fabbro, N.; Tinnirello, I.; Rossi, M.; "SHARP: Environment and Person Independent Activity Recognition With Commodity IEEE 802.11 Access Points," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 6160-6175, 1 Oct. 2023.
- Liu J.; Li W.; Gu T.; Gao R.; Chen B.; Zhang F.; Wu D.; Zhang D.; 2023. Towards a Dynamic Fresnel Zone Model to WiFi-based Human Activity Recognition. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 7, 2, Article 65 (June 2023), 24 pages.
- Shi W.; Wang X.; Niu K.; Wang L.; Zhang D.; 2023. WiCross: I Can Know When You Cross Using COTS WiFi Devices. In Adjunct Proceedings of the 2023 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing & the 2023 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computing (UbiComp/ISWC '23 Adjunct). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 133–136.
- Zhou Z.; Wang F.; Gong W.; 2024. I-Sample: Augment Domain Adversarial Adaptation Models for WiFi-based HAR. ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 20, 2, Article 38 (March 2024), 20 pages.
- Yang, J.; Tang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, L.; 2024. MaskFi: Unsupervised Learning of WiFi and Vision Representations for Multimodal Human Activity Recognition. arXiv:2402.19258.
- Sheng B.; Han R.; Xiao F.; Guo Z.; Gui L.; 2024. MetaFormer: Domain-Adaptive WiFi Sensing with Only One Labelled Target Sample. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 8, 1, Article 39 (March 2024), 27 pages.
- Pan Y.; Zhou Z.; Gong W.; Fang Y.; 2024. "SAT: A Selective Adversarial Training Approach for WiFi-based Human Activity Recognition," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing. [CrossRef]
- Yang J.; Zou H.; Xie L.; "SecureSense: Defending Adversarial Attack for Secure Device-Free Human Activity Recognition," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 823-834, Jan. 2024.
- Luo F.; Khan S.; Jiang B.; Wu K.; 2024. "Vision Transformers for Human Activity Recognition using WiFi Channel State Information," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y.; Wang G.; Liu H.; Gong W.; Gao F.; 2024. "WiFi-Based Indoor Human Activity Sensing: A Selective Sensing Strategy and a Multi-Level Feature Fusion Approach," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal. [CrossRef]
- Niu K.; Wang X.; Zhang F.; Zheng R.; Yao Z.; Zhang D.; "Rethinking Doppler Effect for Accurate Velocity Estimation With Commodity WiFi Devices," in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 40, no. 7, pp. 2164-2178, July 2022.
- Wu D. et al., "WiTraj: Robust Indoor Motion Tracking With WiFi Signals," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 3062-3078, 1 May 2023.
- Li W.; Gao R.; Xiong J.; Zhou J.; Wang L.; Mao X.; Yi E.; Zhang D.; 2024. WiFi-CSI Difference Paradigm: Achieving Efficient Doppler Speed Estimation for Passive Tracking. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 8, 2, Article 63 (May 2024), 29 pages.
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, D.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, F.; Chen, Y.; "Multi-Person Passive WiFi Indoor Localization With Intelligent Reflecting Surface," in IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 6534-6546, Oct. 2023.
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, D.; Deng, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, F.; Chen, Y.; 2024. “Practical Passive Indoor Localization With Intelligent Reflecting Surface,” in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing ( Early Access ).
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, B.; Liu K. J., R.; "RF-Based Indoor Moving Direction Estimation Using a Single Access Point," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 462-473, 1 Jan.1, 2022.
- Chi G.; Yang Z.; Xu J.; Wu C.; Zhang J.; Liang J.; Liu Y.; 2022. Wi-drone: wi-fi-based 6-DoF tracking for indoor drone flight control. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications and Services (MobiSys '22). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 56–68.
- Zeng Y.; Wu D.; Xiong J.; Liu J.; Zhang D.; 2020. MultiSense: Enabling Multi-person Respiration Sensing with Commodity WiFi. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 4, 3, Article 102 (September 2020), 29 pages.
- Zhang, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, B.; Wu, M.; Bugos, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.J.R. SMARS: Sleep Monitoring via Ambient Radio Signals. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 20, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; et al., "WiFi-Sleep: Sleep Stage Monitoring Using Commodity Wi-Fi Devices," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 8, no. 18, pp. 13900-13913, 15 Sept.15, 2021.
- Liu J.; Zeng Y.; Gu T.; Wang L.; Zhang D.; 2021. WiPhone: Smartphone-based Respiration Monitoring Using Ambient Reflected WiFi Signals. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 5, 1, Article 23 (March 2021), 19 pages.
- Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Ong, J.-B.; Wang, D.; Xie, L.; 2022. "ResFi: WiFi-Enabled Device-Free Respiration Detection Based on Deep Learning," 2022 IEEE 17th International Conference on Control & Automation (ICCA), Naples, Italy, 2022, pp. 510-515.
- Xie, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.; "Robust WiFi Respiration Sensing in the Presence of Interfering Individual," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 23, no. 8, pp. 8447-8462, Aug. 2024.
- Jiang W.; Xue H.; Miao C.; Wang S.; Lin S.; Tian C.; Murali S.; Hu H.; Sun Z.; Su L.; 2020. Towards 3D human pose construction using wifi. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MobiCom '20). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 23, 1–14.
- Li C.; Liu Z.; Yao Y.; Cao Z.; Zhang M.; Liu Y.; 2020. Wi-fi see it all: generative adversarial network-augmented versatile wi-fi imaging. In Proceedings of the 18th Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (SenSys '20). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 436–44.
- Ren Y.; Wang Z.; Wang Y.; Tan S.; Chen Y.; Yang J.; 2022. GoPose: 3D Human Pose Estimation Using WiFi. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 6, 2, Article 69 (July 2022), 25 pages.
- Pallaprolu A.; Korany B.; Mostofi Y.; 2022. Wiffract: a new foundation for RF imaging via edge tracing. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing And Networking (MobiCom '22). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 255–267.
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, H.; Yuan, S.; Zou, H.; Xie, L.; Yang, J.; "MetaFi++: WiFi-Enabled Transformer-Based Human Pose Estimation for Metaverse Avatar Simulation," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 16, pp. 14128-14136, 15 Aug.15, 2023.
- Wang, X.; Niu, K.; Yu, A.; Xiong, J.; Yao, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; 2023. WiMeasure: Millimeter-level Object Size Measurement with Commodity WiFi Devices. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 7, 2, Article 79 (June 2023), 26 pages.
- Yin, C.; et al., "PowerSkel: A Device-Free Framework Using CSI Signal for Human Skeleton Estimation in Power Station," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 11, no. 11, pp. 20165-20177, 1 June1, 2024.
- Yao Z.; Wang X.; Niu K.; Zheng R.; Wang J.; Zhang D.; 2024. WiProfile: Unlocking Diffraction Effects for Sub-Centimeter Target Profiling Using Commodity WiFi Devices. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom '24). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 185–199.
- Wu, D.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al.; 2022. WiFi CSI-based device-free sensing: from Fresnel zone model to CSI-ratio model. CCF Trans. Pervasive Comp. Interact. 4, 88–102.
- Niu K.; Wang X.; Yao Z.; Zhang F.; Cheng S.; Jiang Y.; Zhang D.; 2023. How Target’s Location and Orientation Affect Velocity Extraction Accuracy in WiFi Sensing Systems. In Proceedings of the ACM Turing Award Celebration Conference - China 2023 (ACM TURC '23). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 35–36.
- Zhang F.; Jin B.; Zhang D.; 2023. Ubiquitous Wireless Sensing - Theory, Technique and Application. In Proceedings of the ACM Turing Award Celebration Conference - China 2023 (ACM TURC '23). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 33–34.
- Zhang, J.A.; Wu, K.; Huang, X.; Guo, Y.J.; Zhang, D.; Heath, R.W. Integration of Radar Sensing into Communications with Asynchronous Transceivers. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2022, 60, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng Y.; Wu D.; Xiong J.; Zhang D.; "Boosting WiFi Sensing Performance via CSI Ratio," in IEEE Pervasive Computing, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 62-70, 1 Jan.-March 2021.
- Zeng Y.; Wu D.; Xiong J.; Yi E.; Gao R.; Zhang D.; 2019. FarSense: Pushing the Range Limit of WiFi-based Respiration Sensing with CSI Ratio of Two Antennas. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 3, 3, Article 121 (September 2019), 26 pages.
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiong, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhang, D.; 2022. Exploring Multiple Antennas for Long-range WiFi Sensing. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 5, 4, Article 190 (Dec 2021), 30 pages.
- Li Y.; Wu D.; Zhang J.; Xu X.; Xie Y.; Gu T.; Zhang D.; 2022. DiverSense: Maximizing Wi-Fi Sensing Range Leveraging Signal Diversity. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 6, 2, Article 94 (July 2022), 28 pages.
- Wang X.; Niu K.; Xiong J.; Qian B.; Yao Z.; Lou T.; Zhang D.; 2022. Placement Matters: Understanding the Effects of Device Placement for WiFi Sensing. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 6, 1, Article 32 (March 2022), 25 pages.
- Xie Y.; Li Z.; Li M.; 2015. Precise Power Delay Profiling with Commodity WiFi. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MobiCom '15). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 53–64.
- Gringoli F.; Schulz M.; Link J.; Hollick M.; 2019. Free Your CSI: A Channel State Information Extraction Platform For Modern Wi-Fi Chipsets. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Wireless Network Testbeds, Experimental Evaluation & Characterization (WiNTECH '19). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 21–28.
- Hernandez S. M.; Bulut E.; 2020. "Lightweight and Standalone IoT Based WiFi Sensing for Active Repositioning and Mobility," 2020 IEEE 21st International Symposium on "A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks" (WoWMoM), Cork, Ireland, 2020, pp. 277-286.
- Hernandez, S.M.; Bulut, E. WiFi Sensing on the Edge: Signal Processing Techniques and Challenges for Real-World Systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2022, 25, 46–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gringoli F.; Cominelli M.; Blanco A.; Widmer J.; 2021. AX-CSI: Enabling CSI Extraction on Commercial 802.11ax Wi-Fi Platforms. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM Workshop on Wireless Network Testbeds, Experimental evaluation & CHaracterization (WiNTECH '21). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 46–53.
- Jiang, Z.; Luan, T.H.; Ren, X.; Lv, D.; Hao, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Xi, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, R. Eliminating the Barriers: Demystifying Wi-Fi Baseband Design and Introducing the PicoScenes Wi-Fi Sensing Platform. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 4476–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Narui, H.; Dayal, S.; Ermon, S.; Valaee, S. A Survey on Behavior Recognition Using WiFi Channel State Information. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma Y.; Zhou G.; Wang S.; Zhao H.; Jung W.; 2018. SignFi: Sign Language Recognition Using WiFi. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2, 1, Article 23 (March 2018), 21 pages.
- Palipana S.; Rojas D.; Agrawal P.; Pesch D.; 2018. FallDeFi: Ubiquitous Fall Detection using Commodity Wi-Fi Devices. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 1, 4, Article 155 (December 2017), 25 pages.
- Guo, L.; et al., "Wiar: A Public Dataset for Wifi-Based Activity Recognition," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 154935-154945, 2019.
- Zheng Y.; Zhang Y.; Qian K.; Zhang G.; Liu Y.; Wu C.; Yang Z.; 2019. Zero-Effort Cross-Domain Gesture Recognition with Wi-Fi. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services (MobiSys '19). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 313–325.
- Xiao R.; Liu J.; Han J.; Ren K.; 2021. OneFi: One-Shot Recognition for Unseen Gesture via COTS WiFi. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (SenSys '21). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 206–219.
- Yang J.; Chen X.; Zou H.; Lu X.; Wang D.; Yang S. J.; Huang H.; Zhou Y.; Chen X.; Xu Y.; Yuan S.; Zou H.; Lu X.; and Xie L.; 2023. MM-Fi: Multi-Modal Non-Intrusive 4D Human Dataset for Versatile Wireless Sensing. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, A. Oh, T. Naumann, A. Globerson, K. Saenko, M. Hardt, and S. Levine (Eds.), Vol. 36. Curran Associates, Inc., 18756–18768.
- Xie, S.; Xie, L.; 2023. SenseFi: A library and benchmark on deep-learning-empowered WiFi human sensing. Patterns 4, 3 (2023), 100703.
- Cominelli, M.; Gringoli, F.; Restuccia, F.; 2023. "Exposing the CSI: A Systematic Investigation of CSI-based Wi-Fi Sensing Capabilities and Limitations," 2023 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023, pp. 81–90.
- Yi E.; Zhang F.; Xiong J.; Niu K.; Yao Z.; Zhang D.; 2024. Enabling WiFi Sensing on New-generation WiFi Cards. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 7, 4, Article 205 (December 2023), 26 pages.
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, K.; Wu, C.; 2023. SLNet: A Spectrogram Learning Neural Network for Deep Wireless Sensing. In 20th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 23). USENIX Association, Boston, MA, 1221–1236.
- Chi G.; Yang Z.; Wu C.; Xu J.; Gao Y.; Liu Y.; Han T. X.; 2024. RF-Diffusion: Radio Signal Generation via Time-Frequency Diffusion. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom '24). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 77–92.
- Hou W.; Wu C.; 2024. RFBoost: Understanding and Boosting Deep WiFi Sensing via Physical Data Augmentation. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 8, 2, Article 58 (May 2024), 26 pages.
- He Y.; Liu J.; Li M.; Yu G.; Han J.; 2024. "Forward-Compatible Integrated Sensing and Communication for WiFi," in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications. [CrossRef]
- Wu C.; Huang X.; Huang J.; Xing G.; 2023. Enabling Ubiquitous WiFi Sensing with Beamforming Reports. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2023 Conference (ACM SIGCOMM '23). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 20–32.
- Yi, E.; Wu, D.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, F.; Niu, K.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; 2024. BFMSense: WiFi Sensing Using Beamforming Feedback Matrix. In 21st USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI24). USENIX Association, Santa Clara, CA, 1697–1712.
- Korany, B.; Karanam C., R.; Cai, H.; Mostofi, Y.; 2019. XModal-ID: Using WiFi for Through-Wall Person Identification from Candidate Video Footage. In The 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MobiCom '19). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 36, 1–15.

| Year | Reference | Application | Performance | User number | Device type | NLOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | WiCPD [23] | In-car child presence detection | 96.56%-100% real-time detection rate | 1 | NXP Wi-Fi chipset | Y |
| 2023 | Hu et al. [24] | Proximity detection |
95% and 99% true positive rate for distance-based and room-based detection | 1 | NXP Wi-Fi chipset | Y |
| 2024 | Zhu et al. [25] |
Human and non-human differentiation |
95.57% average accuracy | 1 human or pet | COTS device | Y |
| 2024 | WI-MOID [26] | Edge device-based human and non-human differentiation | 97.34% accuracy and 1.75% false alarm rate | 1 human or non-human subject | WiFi edge device | Y |
| Year | Reference | Application | Performance | User number | Device type | NLOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | GaitSense [27] | Gait-based human identification | 93.2% for 5 users and 76.2% for 11 users | 11 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2021 | GaitWay [28] | Gait speed estimation | 0.12 m median error | 1 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2022 | CAUTION [29] | Gait-based human authentication | 93.06 average accuracy | 15 | TP-Link N750 router | N |
| 2022 | Wi-PIGR [30] | Gait recognition | 93.5% for single user and 77.15% for 50 users | 1-50 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2023 | Auto-Fi [31] | Gesture and gait recognition | 86.83% for gesture; 79.61% for gait | 1 | Atheros chipset | N |
| 2023 | GaitFi [32] | Gait recognition | 94.2% accuracy | 12 | TP-Link N750 router | N |
| 2024 | Wi-Diag [33] | Multi-subject abnormal gait diagnosis | 87.77% average accuracy | 4 | Intel 5300 | N |
| Year | Reference | Application | Performance | User number | Device type | NLOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | Kang et al. [34] | Gesture recognition | 3%-12.7% improvement | 1 | Widar Dataset | N |
| 2021 | WiGesture [35] | Gesture recognition | 92.8%-94.5% accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2022 | HandGest [36] | Handwriting recognition | 95% accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2022 | DPSense-WiGesture [37] | Gesture recognition | 94% average accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2022 | Niu et al. [38] | Gesture recognition | 96% accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2022 | Widar 3.0 [39] | Cross-domain gesture recognition | 92.7% in-domain and 82.6%-92.4% cross-domain accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2022 | WiFine [40] | Gesture recognition | 96.03% accuracy in 0.19 seconds | 1 | Raspberry Pi 4B | N |
| 2023 | UniFi [41] | Gesture recognition | 99% and 90%-98% accuracy for in-domain and cross-domain recognition | 1 | Widar dataset | N |
| 2023 | WiTransformer [42] | Gesture recognition | 86.16% accuracy | 1 | Widar dataset | N |
| 2024 | AirFi [43] | Gesture recognition | 90% accuracy | 1 | TP-Link N750 router | N |
| 2024 | WiCGesture [44] | Continuous gesture recognition | 89.6% for digits and 88.3% for Greek letters | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| Year | Reference | Application | Performance | User number | Device type | NLOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Wang et al. [45] | People counting and recognition | 86% average accuracy | 4 | COTS devices | N |
| 2021 | Ma et al. [46] | Activity recognition | 97% average accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2021 | MCBAR [47] | Activity recognition | 90% average accuracy | 1 | Atheros chipset | N |
| 2021 | WiMonitor [48] | Location and activity monitoring | N/A | 1 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2022 | DeFall [49] | Fall detection | 95% detection rate and 1.5% false alarm rate | 1 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2022 | Ding et al. [50] | Activity recognition | 96.85% average accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2022 | EfficientFi [51] | Activity recognition | 98% accuracy | 1 | TP-Link N750 router | N |
| 2022 | TOSS [52] | Activity recognition | 82.69% average accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2023 | FallDar [53] | Fall detection | 5.7% false alarm reate and 3.4% missed alarm rate | 1 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2023 | SHARP [54] | Activity recognition | 95% average accuracy | 1 | ASUS RT-AC86U router | N |
| 2023 | Liu et al. [55] | Moving receiver-based activity recognition | 10 °, 1 cm and 98% accuracy for direction, displacement and activity estimation | 1 | COTS WiFi 6 device | N |
| 2023 | WiCross [56] | Target passing detection | 95% accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2024 | i-Sample [57] | Activity recognition | 10% accuracy gain | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2024 | MaskFi [58] | Activity recognition | 97.61% average accuracy | 1 | TP-Link N750 router | N |
| 2024 | MetaFormer [59] | Activity recognition | Improved accuracy in various cross-domain scenarios | 1 | SiFi, Widar, Wiar datasets | N |
| 2024 | SAT [60] | Activity recognition | Improved accuracy and robustness | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2024 | SecureSense [61] | Activity recognition under adversarial attack | Robust performance under various attacks | 1 | TP-Link N750 router | N |
| 2024 | Luo et al. [62] | Activity recognition | 98.78% accuracy | 1 | UT-HAR dataset | N |
| 2024 | WiSMLF [63] | Activity recognition | 92% average accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| Year | Reference | Application | Performance | User number | Device type | NLOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | Niu et al. [64] | Velocity estimation-based tracing | 9.38 cm/s, 13.42° and 31.08cm median error in speed, heading and location estimation | 1 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2023 | WiTraj [65] | Human walking tracking | 2.5% median tracking error | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2024 | FewSense [66] | Tracking | 34 cm median error | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| Year | Reference | Application | Performance | User number | Device type | NLOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | MultiSense [71] | Multi-person respiration sensing | 0.73 bpm mean error | 4 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2021 | SMARS [72] | Breath estimation and sleep stage recognition | 0.47 bpm median error and 88% accuracy | 1 | Atheros chipset | Y |
| 2021 | WiFi-Sleep [73] | Sleep stage monitoring | 81.8% accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2021 | WiPhone [74] | Respiration monitoring | 0.31 bpm average error | 1 | ASUS RT-AC86U router and Google Nexus 5 smartphone | Y |
| 2022 | ResFi [75] | Respiration detection | 96.05% accuracy | 1 | ASUS RT-AC86U router | N |
| 2024 | Xie et al. [76] | Respiration sensing with interfering individual | 32% mean absolute error reduction | 1 | VNA or Intel 5300 | N |
| Year | Reference | Application | Performance | User number | Device type | NLOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | WiPose [77] | Pose construction | 2.83 cm average error | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2020 | WiSIA [78] | Target imaging | N/A | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2022 | GoPose [79] | 3D human pose estimation | 4.7 cm accuracy | 1 or 2 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2022 | Wiffract [80] | Still object imaging | 86.7% letter reading accuracy | 1 | Intel 5300 | Y |
| 2023 | MetaFi++ [81] | Pose estimation | 97.3% for PCK@50 | 1 | TP-Link N750 router | N |
| 2023 | WiMeasure [82] | Object size measurement | 2.6 mm median error | 1 | Intel 5300 | N |
| 2024 | PowerSkel [83] | Pose estimation | 96.27% for PCK@50 | 1 | ESP 32 IoT SoC | N |
| 2024 | WiProfile [84] | 2D target Profiling | 1 cm median absolute error | 1 target with proper size range | Intel 5300 | N |
| Year | Reference | Methodology | Performance | Base signal | Sensing range | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | GaitWay [28] | Scattering model | 0.12 m median error | ACF of CSI | 20 m×23 m | 1500 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2021 | SMARS [72] | Scattering model | 0.47 bpm median error and 88% accuracy | ACF of CSI | 10 m | 30 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | DeFall [49] | Scattering model | 95% detection rate and 1.5% false alarm rate | ACF of CSI | Multi-room | 1500 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | Wiffract [80] | Keller's Geometrical Theory of Diffraction | 86.7% letter reading accuracy | Power of CSI | 1.5 m | two pairs of Tx-Rx; two dimension RX grid synthesis |
| 2023 | Liu et al. [55] | Dynamic Fresnel zone model | 10 °, 1 cm and 98% accuracy for direction, displacement and activity estimation | CSI | Single room | 100 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | WiCross [56] | Diffraction model-based phase pattern extraction | 95% accuracy | CSI ratio | 1 m | 1000 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | WiMeasure [82] | Diffraction model | 2.6 mm median error | CSI ratio | Near the LOS path | 500 Hz; three pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | WiProfile [84] | Diffraction effect-based profiling + inverse Fresnel transform | 1 cm median absolute error | CSI | 1.5 m×1 m | 500 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx; One reference receiving antenna connected to Rx via feeder line |
| Year | Reference | Methodology | Performance | Base signal | Sensing range | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | MultiSense [71] | ICA-based BSS | 0.73 bpm mean error | Constructed reference-CSI-based signal ratio | 4 m×7.5 m | 200 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2020 | Wang et al. [45] | Statistical pattern analysis | 86% accuracy | PSD of CSI | 3.5 m | 10 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2021 | WiGesture [35] | MNP feature extraction | 92.8%-94.5% accuracy | CSI ratio | 4 m×7 m | 400 Hz; two pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2021 | WiMonitor [48] | Doppler frequency and activity intensity pattern extraction | N/A | CSI ratio | Multi-room | 200 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2021 | WiPhone [74] | Ambient reflection-based pattern extraction | 0.31 bpm average error | CSI amplitude | Multi-room apartment | 50 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx with LOS blocked |
| 2022 | HandGest [36] | Hand-centric feature extraction, i.e., DPV and MRV | 4.7 cm accuracy | CSI ratio | 1 m | 500 Hz; two pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | Niu et al. [64] | DFS-based velocity estimation + receiver selection | 96.05% accuracy | CSI ratio | 7 m×9.8 m | 1000 Hz; six pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | DPSense-WiGesture [37] | Signal segmentation + sensing quality-based signal processing | 94% average accuracy | CSI | 1.2 m | 400 Hz; two pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | Niu et al. [38] | Position-independent feature extraction, i.e., movement fragment and relative motion direction change | 96% accuracy | CSI ratio | 2 m×2 m | 1000 Hz; 2 pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | WiCPD [23] | feature-based motion, stationary and transition target detector | 96.56%-100% real-time detection rate | ACF of CSI | Car | 30 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | Hu et al. [24] | Sub-carrier correlation and covariance feature extraction | 95% and 99% true positive rate for distance-based and room-based detection | Power of CSI | Multi-room | 30 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | WiTraj [65] | DFS extraction + multi-view trajectory estimation + motion detection | 2.5% median tracking error | CSI ratio | 7 m×6 m | 400 Hz; three pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | Xie et al. [76] | Respiratory energy-based interference detection and convex optimization-based beam control | 32% mean absolute error reduction | CSI | 9 m×6 m | Single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | WiCGesture [44] | Meta motion-based signal segmentation and back-tracking searching-based identification | 89.6% for digits and 88.3% for Greek letters | CSI ratio | 1 m | 400 Hz; Two pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | FewSense [66] | TD-CSI-based doppler speed estimation | 34 cm median error | Time domain CSI difference | 7 m×7 m | 1000 Hz; Two pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | WI-MOID [26] | Physical and statistical pattern extraction + SVM + state machine | 97.34% accuracy and 1.75% false alarm rate | ACF of CSI | Multi-room | 1500 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| Year | Reference | Methodology | Performance | Base signal | Sensing range | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | WiPose [77] | CNN + LSTM | 2.83 cm average error | 3D velocity profile of CSI | Single room | 1000 Hz; three pairs of Tx-Rx; distributed deployed receiving antennas |
| 2020 | WiSIA [78] | cGAN | N/A | Power of CSI | 2.1 m | 1000 Hz; two pairs od Tx-Rx; receiving antennas orthogonal to each other |
| 2021 | Kang et al. [34] | Adversarial learning and attention scheme | 3%-12.7% improvement | DFS of CSI | 2 m×2m | two pairs of Tx-Rx from Widar dataset |
| 2022 | GaitSense [27] | CNN + LSTM + transfer learning + data augmentation | 98% accuracy | Gait-BVP of CSI | 4.6 m×4.4 m | 1000 Hz; six pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2021 | Ma et al. [46] | CNN + reinforcement learning | 97% average accuracy | CSI amplitude | 6.8 m×4 m | 100 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2021 | MCBAR [47] | GAN and semi-supervised learning | 90% average accuracy | CSI amplitude | 6.5 m×6.3 m | single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2021 | WiFi-Sleep [73] | Respiration and movement pattern extraction + CNN-BiLSTM | 81.8% accuracy | CSI ratio | Close to the bed | 200 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | CAUTION [29] | Few-shot learning | 93.06 average accuracy | CSI amplitude | 5.2 m×7.2 m | Single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | Ding et al. [50] | DCN + transfer learning | 96.85% average accuracy | CSI | 6 m×8 m | 200 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | EfficientFi [51] | DNN | 98% accuracy | CSI amplitude | 6.5 m×5 n | 500 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | GoPose [79] | 2D AOA spectrum + CNN + LSTM | 93.2% for 5 users and 76.2% for 11 users | CSI phase | 4 m×4 m | 1000 Hz; four pairs of Tx-Rx; L-shaped receiving antennas |
| 2022 | ResFi [75] | CNN-based classification | 95% accuracy | CSI amplitude | 1 m | 10 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | TOSS [52] | Meta learning + pseudo label strategy | 82.69% average accuracy | CSI | Single room | Single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | Widar 3.0 [39] | BVP feature + CNN-RNN | 92.7% in-domain and 82.6%-92.4% cross-domain accuracy | BVP of CSI | 2 m×2 m | 1000 Hz; six pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | WiFine [40] | data enhancement-based feature extraction + lightweight neural network | 96.03% accuracy in 0.19 seconds | CSI | Single room | Single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2022 | Wi-PIGR [30] | Spectrogram optimization + CNN + LSTM | 93.5% for single user and 77.15% for 50 users | CSI amplitude | 5m×5 m | 1000 Hz; two pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | Auto-Fi [31] | Geometric self-supervised learning + few-shot calibration | 86.83% for gesture; 79.61% for gait | CSI amplitude | Single room | 100 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | GaitFi [32] | RCN + LSTM + feature fusion | 94.2% accuracy | CSI + video | 2.1 m | 800 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | MetaFi++ [81] | CNN + Transformer | 97.3% for PCK@50 | CSI + video | Single room | 1000 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | FallDar [53] | Scattering model + VAE generative model + DNN adversarial learning model | 5.7% false alarm rate and 3.4% missed alarm rate | ACF of CSI | 3.6 m×8.4 m | 1000 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | SHARP [54] | Phase correction-based DFS extraction + Nerual network | 95% average accuracy | CSI | 5 m×6 m | 173 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2023 | UniFi [41] | DFS extraction + consistency-guided multi-view deep network + mutual information-based regularization | 99% and 90%-98% accuracy for in-domain and cross-domain recognition | CSI ratio | 2 m×2 m | Widar dataset |
| 2023 | WiTransformer [42] | Transformer | 86.16% accuracy | BVP of CSI | 2 m×2 m | Widar dataset |
| 2024 | AirFi [43] | Data augmentation + adversarial learning +domain generalization | 90% accuracy | CSI amplitude | 4 m×4 m | Single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | i-Sample [57] | Intermediate sample generation + domain adversarial adaptation | 10% accuracy gain | CSI | Single room | Single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | MaskFi [58] | Transformer-based encoder + Gate Recurrent Unit network | 97.61% average accuracy | CSI + video | Single room | 1000 Hz; Single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | MetaFormer [59] | Transformer-based spatial-temporal feature extraction + match-based meta-learning approach | Improved accuracy in various cross-domain scenarios | CSI | Single room | SiFi, Widar, Wiar datasets |
| 2024 | PowerSkel [83] | Knowledge distillation network based on collaborative learning and self-attention | 96.27% for PCK@50 | CSI + Kinect video | Single room | Three pairs of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | SAT [60] | Calibrated confidence-based adversarial sample selection + adversarial learning | Improved accuracy and robustness | CSI | Single room | Single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | SecureSense [61] | Consistency-guided adversarial learning | Robust performance under various attacks | CSI amplitude | 5 m×6.5 m | 1000 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | Luo et al. [62] | Transformer | 98.78% accuracy | CSI | Single room | UT-HAR dataset |
| 2024 | Wi-Diag [33] | Independent component analysis-based blind source separation + CycleGAN | 87.77% average accuracy | CSI | 7 m×8 m | 1000 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | WiSMLF [63] | High frequency energy-based sensing scheme selection + VGG/LSTM-based multi-level feature fusion | 92% average accuracy | CSI | Single room | 100 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| 2024 | Zhu et al. [25] | ResNet18 | 95.57% average accuracy | Amplified ACF of CSI | 6 m×6.5 m | 1500 Hz; single pair of Tx-Rx |
| Cross-domain scheme | Related work |
|---|---|
| Generative adversarial network | [33,47,53,61] |
| Transfer learning | [27,31,34,43,50,57,60] |
| Few-shot learning | [29,31,43,52] |
| Domain-independent feature extraction | [23,24,25,26,27,28,30,34,35,36,37,38,39,41,42,44,49,53,54,64,65,66,72] |
| Data augmentation | [27,43,57] |
| CNN +LSTM/GRU/Transformer | [25,30,32,39,41,42,46,58,59,62,81] |
| Year | CSI extraction tool | IEEE standard | Related work |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 802.11n CSI Tool [17] | 802.11 n | [27,28,30,33,35,36,37,38,39,44,46,48,49,50,52,53,56,57,60,63,64,65,66,71,73,77,78,79,80,82,84] |
| 2015 | Atheros CSI Tool [94] | 802.11n | [29,31,32,47,51,58,61,72,81,94] |
| 2019 | Nexmon CSI [95] | 802.11 ac | [40,54,74,75,95] |
| 2020 | ESP32 CSI Tool [96,97] | any computer, smartphone or even standalone | [83,96,97] |
| 2021 | AX-CSI [98] | 802.11 ax | [98] |
| 2022 | PicoScenes [99] | 802.11 a/g/n/ac/ax | [70,99] |
| Year | Dataset | Description | Tool | Related work |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | UT-HAR [100] | Activity data | 802.11n CSI Tool | [31,46,62] |
| 2018 | SignFi [101] | Sign data | 802.11n CSI Tool | [40,59] |
| 2018 | FallDeFi [102] | Fall data | 802.11n CSI Tool | [46,53] |
| 2019 | WiAR [103] | Activity and Gesture data | 802.11n CSI Tool | [59] |
| 2019 | Widar [104] | Gesture data | 802.11n CSI Tool | [31,34,39,41,42,43,59] |
| 2021 | OneFi [105] | Gesture data | 802.11n CSI Tool | [105] |
| 2023 | MM-Fi [106] | Multi-modal dataset | Atheros CSI Tool | [58] |
| 2023 | NTU-Fi [107] | Activity and Gait data | Atheros CSI Tool | [62] |
| 2023 | SHARP [54] | Activity data | Nexmon CSI | [54] |
| 2023 | Cominelli [108] | Activity data | AX-CSI | [108] |
| 2023 | WiTraj [65] | Trajectory data | 802.11n CSI Tool | [65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





