Submitted:
07 August 2024
Posted:
11 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
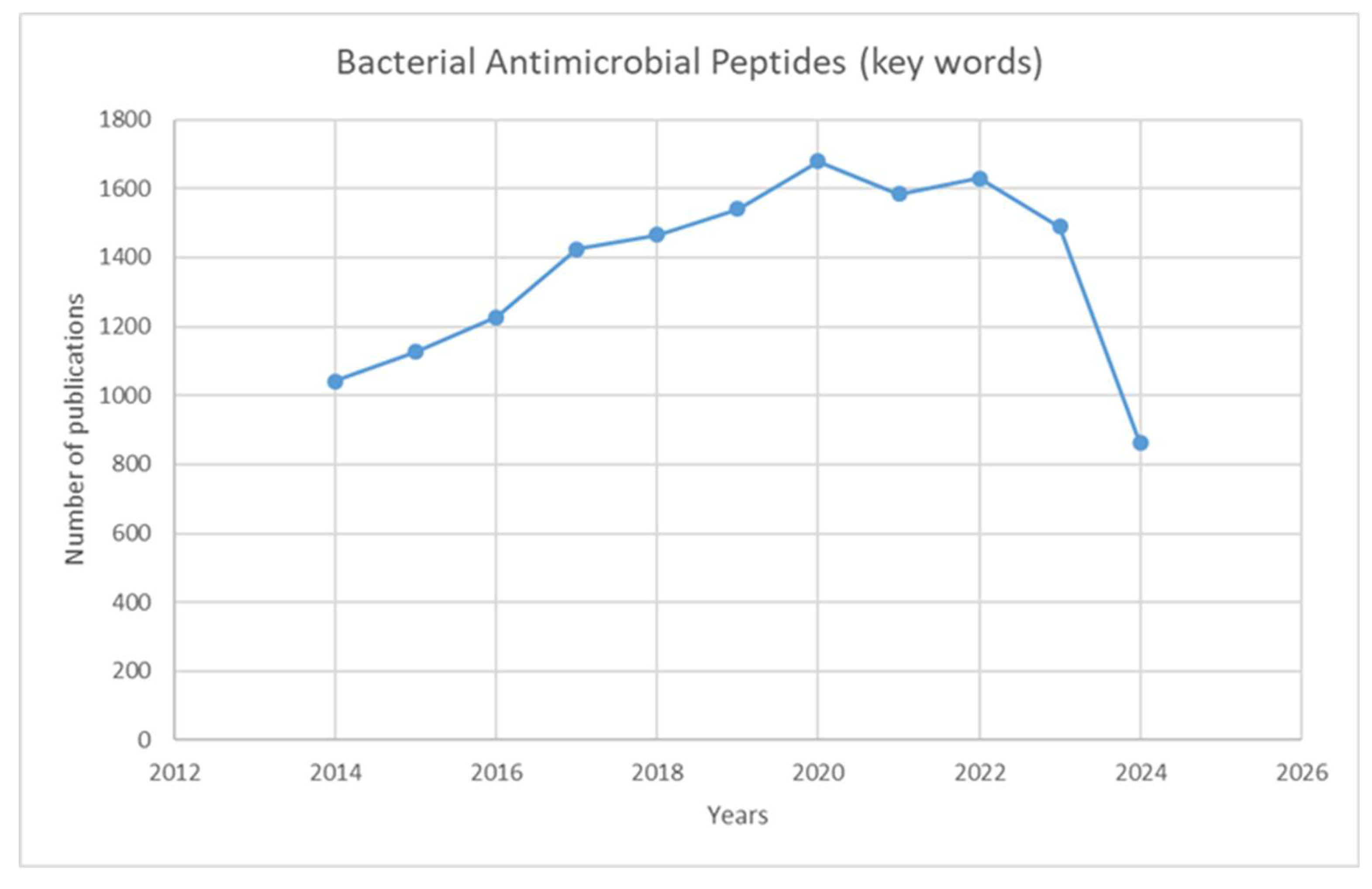
1. Introduction
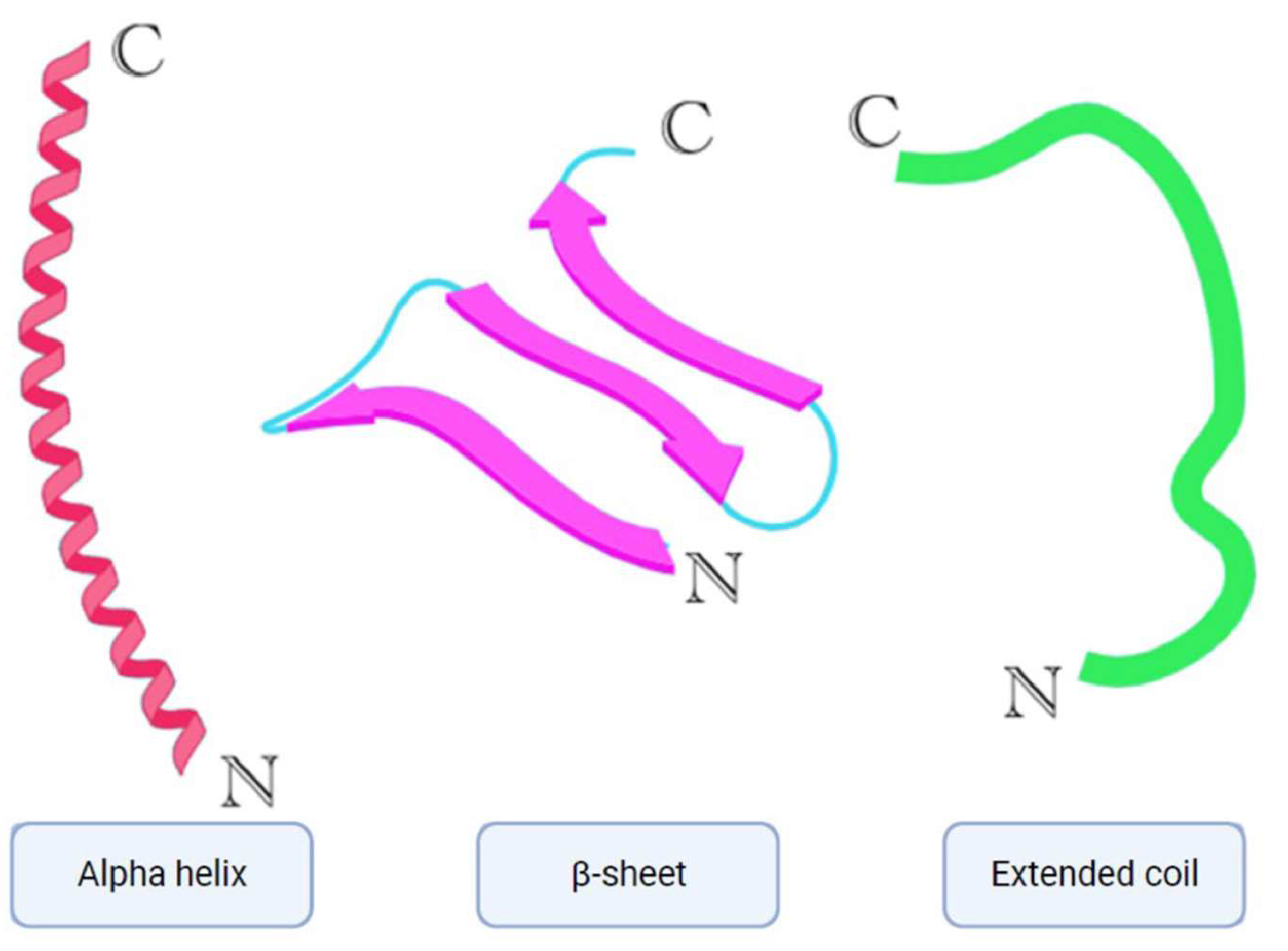
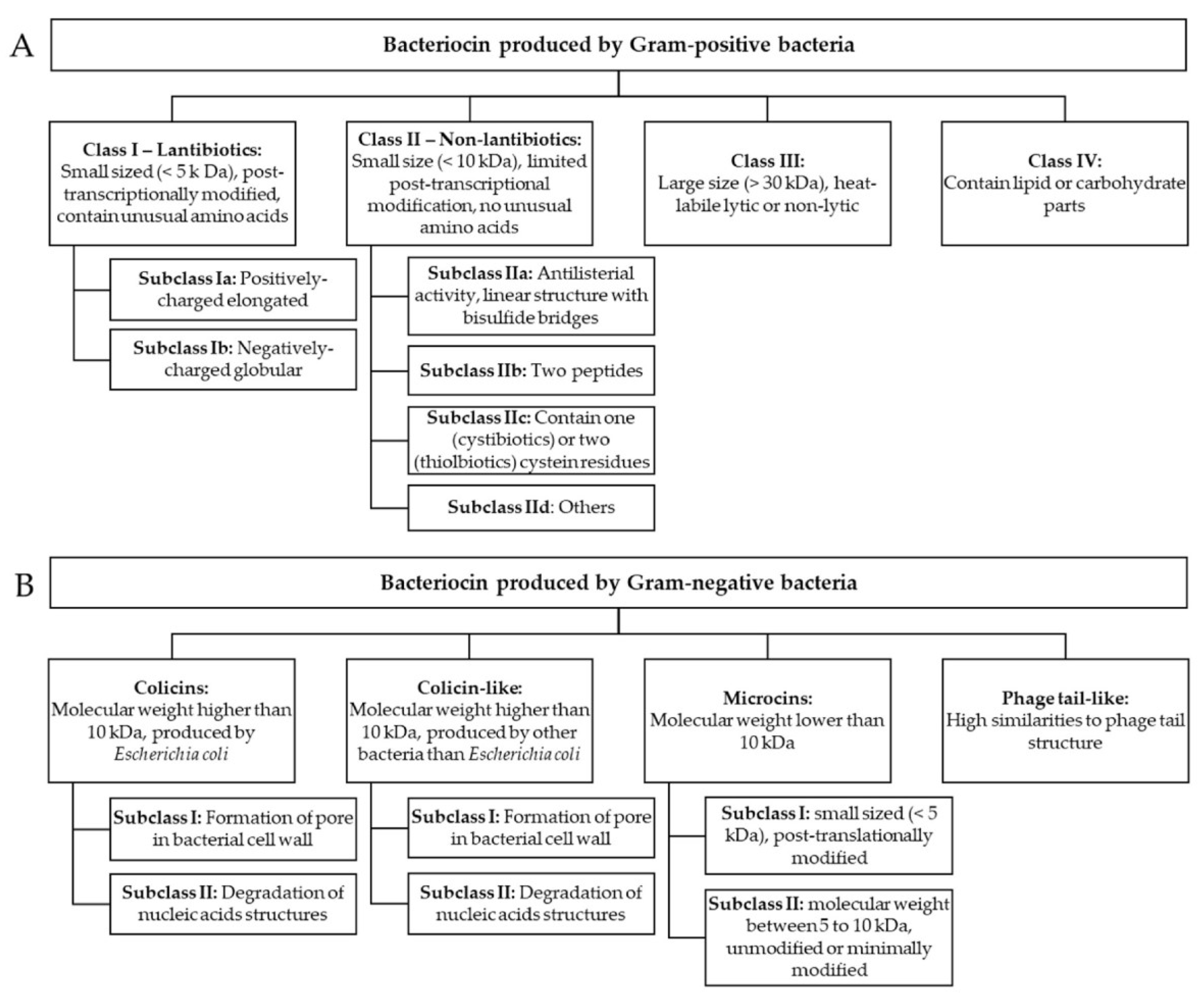
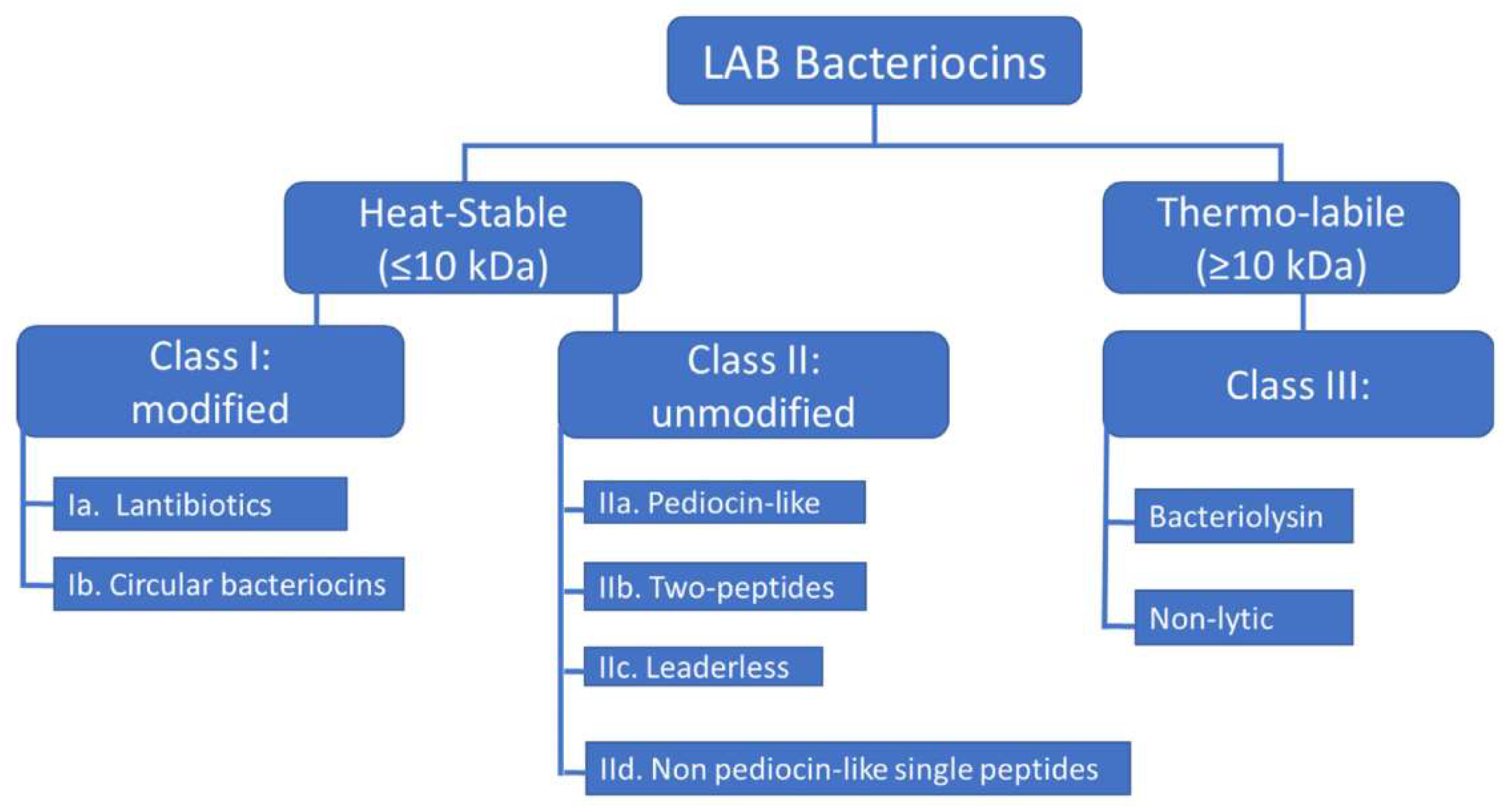
2. Classification
2.1. Bacterial AMPs Produced by Gram-Negative Bacteria
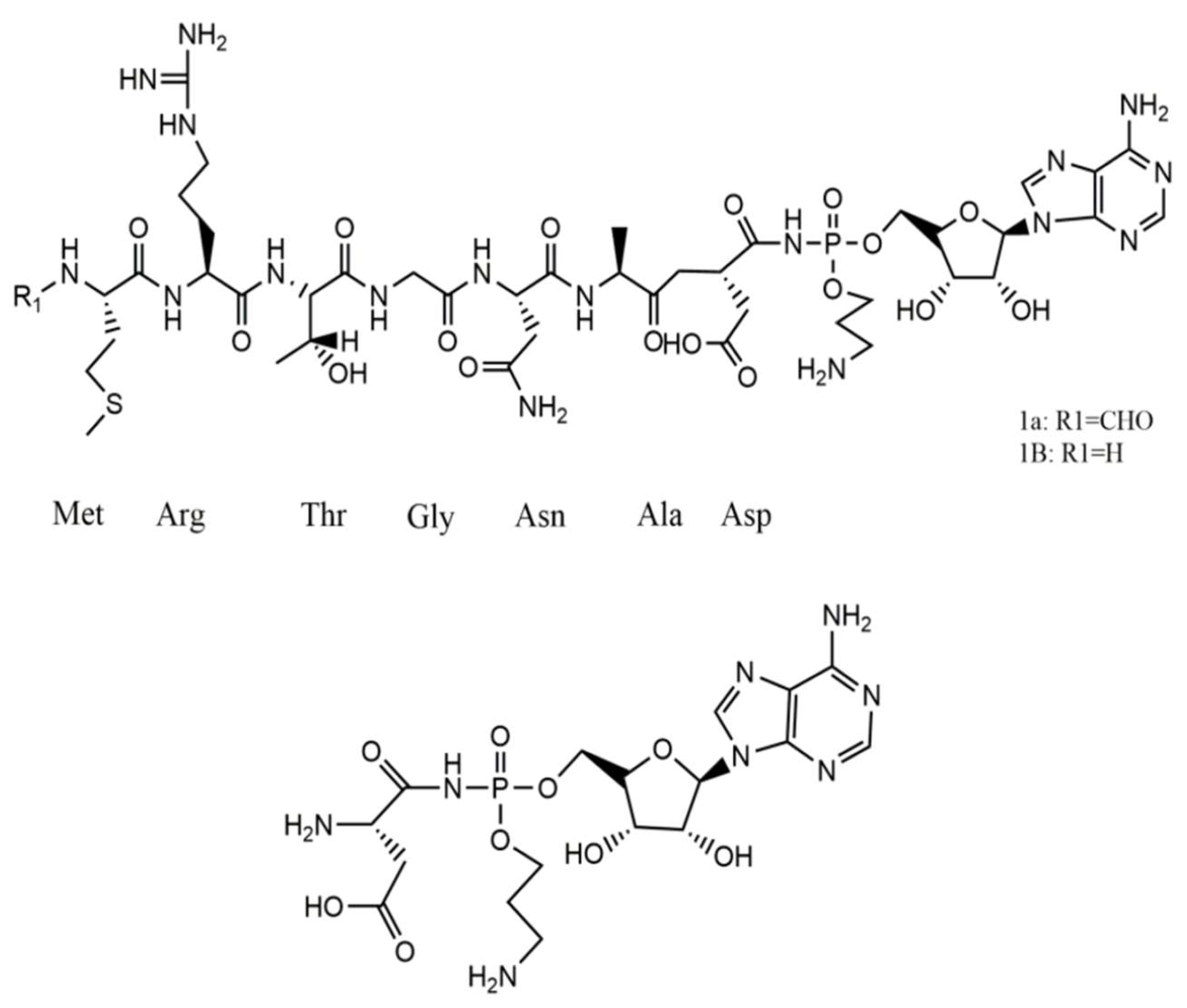
2.1.1. Colicins
2.1.2. Phage Tail-Like
2.2. Bacterial AMPs Produced by Gram-Positive Bacteria
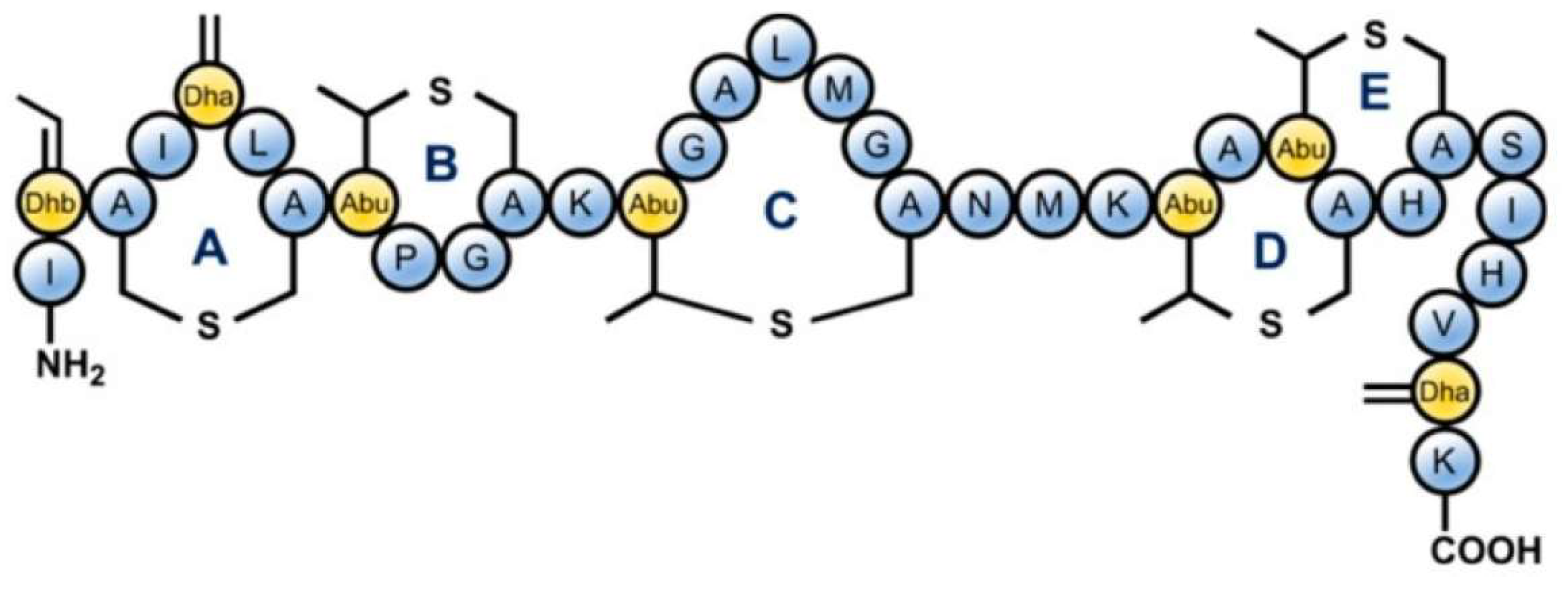
2.2.1. Lantibiotics
2.2.2. Thiopeptides
2.2.3. Modified Thiazole/Oxazole-Microcins-Boromycins
2.2.4. Sactibiotics
3. Sources
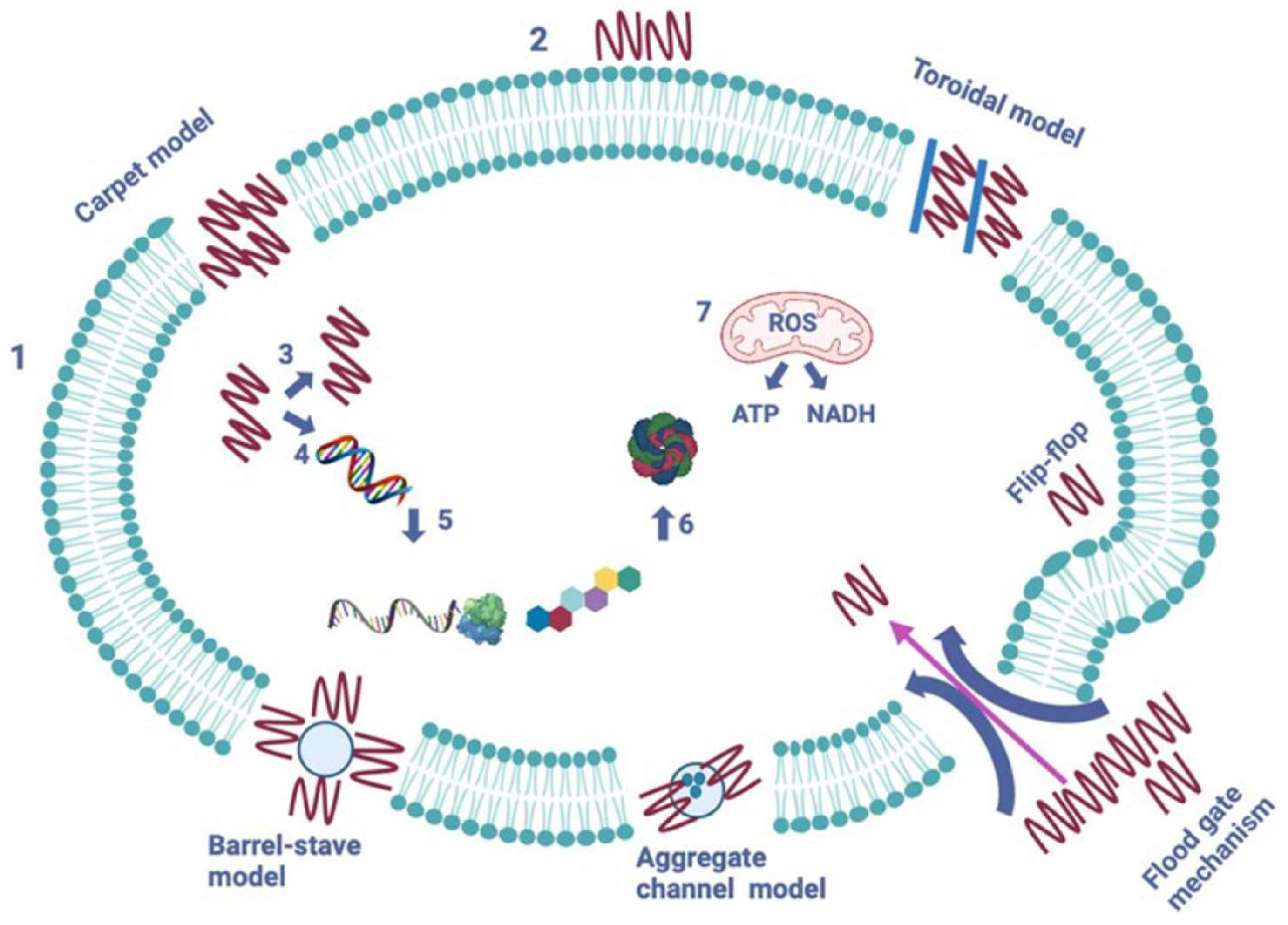
4. Mechanisms of Action
5. Effect on Human Health
6. Limitations and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mabrouk, D. M. Antimicrobial Peptides: Features, Applications and the Potential Use against Covid-19. Molecular Biology Reports 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassaa, I. A.; Rafei, R.; Moukhtar, M.; Zaylaa, M.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Asehraou, A.; Omari, K. E.; Shahin, A.; Hamze, M.; Chihib, N.-E. LABiocin Database: A New Database Designed Specifically for Lactic Acid Bacteria Bacteriocins. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2019, 54, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanzolini, T.; Bruschi, M.; Rinaldi, A.C.; Magnani, M.; Fraternale, A. Multitalented Synthetic Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antiviral Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziato, G.; Costantino, G. Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): A Patent Review (2015–2020). Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents 2020, 30, 931–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, M. Antimicrobial Peptides Demonstrate Activity against Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2023, 15, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satchanska, G.; Davidova, S.; Gergova, A. Diversity and Mechanisms of Action of Plant, Animal, and Human Antimicrobial Peptides. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria Rosa, Loffredo; Nencioni, L.; Maria Luisa, Mangoni; Casciaro, B. Antimicrobial Peptides for Novel Antiviral Strategies in the Current Post-COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of peptide science 2023, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Peptide Database. Unmc.edu. https://aps.unmc.edu/. Accessed on 27.07.2024.
- Freitas, E. D.; Bataglioli, R. A.; Oshodi, J.; Beppu, M. M. Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Potential Application in Antiviral Coating Agents. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2022, 217, 112693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajbakhsh, M.; Karimi, A.; Fallah, F.; Akhavan, M. M. Overview of Ribosomal and Non-Ribosomal Antimicrobial Peptides Produced by Gram Positive Bacteria. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2017, 63, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, B. H.; Gaynord, J.; Rowe, S. M.; Deingruber, T.; Spring, D. R. The Multifaceted Nature of Antimicrobial Peptides: Current Synthetic Chemistry Approaches and Future Directions. Chemical Society Reviews 2021, 50, 7820–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, A.; Alhanout, K.; Duval, R.E. Bacteriocins, Antimicrobial Peptides from Bacterial Origin: Overview of Their Biology and Their Impact against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrushali, Somase; Desai, S. A.; Patel, V. P.; Patil, V.; Kunal Bhosale. Antimicrobial Peptides: Potential Alternative to Antibiotics and Overcoming Limitations for Future Therapeutic Applications. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics 2024, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageitos, J. M.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Calo-Mata, P.; Villa, T. G. Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): Ancient Compounds That Represent Novel Weapons in the Fight against Bacteria. Biochemical pharmacology 2017, 133, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Kjos, M.; Nes, I. F.; Diep, D. B.; Lotfipour, F. Natural Antimicrobial Peptides from Bacteria: Characteristics and Potential Applications to Fight against Antibiotic Resistance. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2012, 113, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madi-Moussa, D.; Belguesmia, Y.; Charlet, A.; Drider, D.; Coucheney, F. Lacticaseicin 30 and Colistin as a Promising Antibiotic Formulation against Gram-Negative β-Lactamase-Producing Strains and Colistin-Resistant Strains. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimina, M.; Babich, O.; Prosekov, A.; Sukhikh, S.; Ivanova, S.; Shevchenko, M.; Noskova, S. Overview of Global Trends in Classification, Methods of Preparation and Application of Bacteriocins. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascales, E.; Buchanan, S. K.; Duche, D.; Kleanthous, C.; Lloubes, R.; Postle, K.; Riley, M.; Slatin, S.; Cavard, D. Colicin Biology. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2007, 71, 158–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patz, S.; Becker, Y.; Richert-Pöggeler, K. R.; Berger, B.; Ruppel, S.; Huson, D. H.; Becker, M. Phage Tail-like Particles Are Versatile Bacterial Nanomachines – a Mini-Review. Journal of Advanced Research 2019, 19, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravej, H.; Moravej, Z.; Yazdanparast, M.; Heiat, M.; Mirhosseini, A.; Moosazadeh Moghaddam, M.; Mirnejad, R. Antimicrobial Peptides: Features, Action, and Their Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria. Microbial Drug Resistance (Larchmont, N.Y.) 2018, 24, 747–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigui Gallardo-Becerra; Cervantes-Echeverría, M. ; Cornejo-Granados, F.; Vazquez-Morado, L. E.; Ochoa-Leyva, A. Perspectives in Searching Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) Produced by the Microbiota. Microbial Ecology 2023, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yang, F.; Huang, J.; Yu, H.; Qiao, S. Microcin C7 as a Potential Antibacterial-Immunomodulatory Agent in the Postantibiotic Era: Overview of Its Bioactivity Aspects and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7213 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, B.; Rodríguez, A.; Suárez, E. Antimicrobial Peptides Produced by Bacteria: The Bacteriocins. New Weapons to Control Bacterial Growth 2016, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.; Zhang, Z.; Glassey, E.; Piro Siuti; Clardy, J. ; Voigt, C. A. Systematic Mining of the Human Microbiome Identifies Antimicrobial Peptides with Diverse Activity Spectra. Nature Microbiology 2023, 8, 2420–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baindara, P.; Chaudhry, V.; Mittal, G.; Liao, L. M.; Matos, C. O.; Khatri, N.; Franco, O. L.; Patil, P. B.; Korpole, S. Characterization of the Antimicrobial Peptide Penisin, a Class Ia Novel Lantibiotic from Paenibacillus Sp. Strain A3. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2016, 60, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newstead, L.L.; Varjonen, K.; Nuttall, T.; Paterson, G.K. Staphylococcal-Produced Bacteriocins and Antimicrobial Peptides: Their Potential as Alternative Treatments for Staphylococcus aureus Infections. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basi-Chipalu, S.; Sthapit, P.; Dhital, S. A Review on Characterization, Applications and Structure-Activity Relationships of Bacillus Species-Produced Bacteriocins. Drug Discoveries & Therapeutics 2022, 16, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anumudu, C.; Hart, A.; Miri, T.; Onyeaka, H. Recent Advances in the Application of the Antimicrobial Peptide Nisin in the Inactivation of Spore-Forming Bacteria in Foods. Molecules 2021, 26, 5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Mukai, K.; Kaweewan, I.; Nakagawa, H.; Hosaka, T.; Kodani, S. Heterologous Production and Structure Determination of a New Lanthipeptide Sinosporapeptin Using a Cryptic Gene Cluster in an Actinobacterium Sinosporangium Siamense. Journal of Microbiology (Seoul, Korea) 2023, 61, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, A. A.; Suga, H. Introduction to Thiopeptides: Biological Activity, Biosynthesis, and Strategies for Functional Reprogramming. Cell Chemical Biology 2020, 27, 1032–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, L.; Kazmaier, U.; Truman, A. W.; Koehnke, J. Bottromycins - Biosynthesis, Synthesis and Activity. Natural Product Reports 2021, 38, 1659–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, H.; Rea, M.; Cotter, P.; Hill, C.; Ross, R. The Sactibiotic Subclass of Bacteriocins: An Update. Current Protein & Peptide Science 2015, 16, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, Karsten A. S.; Kincannon, W. M.; Bandarian, V. Leveraging Substrate Promiscuity of a Radical S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine RiPP Maturase toward Intramolecular Peptide Cross-Linking Applications. ACS Central Science 2022, 8, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balandin, S. V.; Sheremeteva, E. V.; Ovchinnikova, T. V. Pediocin-like Antimicrobial Peptides of Bacteria. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2019, 84, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divyashree, M.; Mani, M. K.; Reddy, D.; Kumavath, R.; Ghosh, P.; Azevedo, V.; Barh, D. Clinical Applications of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): Where Do We Stand Now? Protein & Peptide Letters 2020, 27, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yousef, A. E. Antimicrobial Peptides Produced by Brevibacillus Spp.: Structure, Classification and Bioactivity: A Mini Review. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2018, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Yan, Z.-B.; Meng, Y.-M.; Hong, X.-Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.-J.; Cheng, X.-R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.-Y. Antimicrobial Peptides: Mechanism of Action, Activity and Clinical Potential. Military Medical Research 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafuente, I.; Sevillano, E.; Nuria Peña; Cuartero, A. ; Hernández, P. E.; Cintas, L. M.; Estefanía Muñoz-Atienza; Borrero, J. Production of Pumilarin and a Novel Circular Bacteriocin, Altitudin A, by Bacillus Altitudinis ECC22, a Soil-Derived Bacteriocin Producer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 2020–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikova, T.V. Structure, Function, and Therapeutic Potential of Marine Bioactive Peptides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Deber, C. M. Interaction of Designed Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides with the Outer Membrane of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Scientific Reports 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, W. A.; Sharma, O.; Zakharov, S. D. On Mechanisms of Colicin Import: The Outer Membrane Quandary. Biochemical Journal 2018, 475, 3903–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beis, K.; Rebuffat, S. Multifaceted ABC Transporters Associated to Microcin and Bacteriocin Export. Research in Microbiology 2019, 170, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Straus, S.K. Antimicrobial Peptides: Diversity, Mechanism of Action and Strategies to Improve the Activity and Biocompatibility In Vivo. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götz, F.; Perconti, S.; Popella, P.; Werner, R.; Schlag, M. Epidermin and Gallidermin: Staphylococcal Lantibiotics. International Journal of Medical Microbiology 2014, 304, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbandi, A.; Asadi, A.; Mahdizade Ari, M.; Ohadi, E.; Talebi, M.; Halaj Zadeh, M.; Darb Emamie, A.; Ghanavati, R.; Kakanj, M. Bacteriocins: Properties and Potential Use as Antimicrobials. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis 2021, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.R. The Century-Long Journey of Peptide-Based Drugs. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ramos, A.; Madi-Moussa, D.; Coucheney, F.; Drider, D. Current Knowledge of the Mode of Action and Immunity Mechanisms of LAB-Bacteriocins. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talapko, J.; Meštrović, T.; Juzbašić, M.; Tomas, M.; Erić, S.; Horvat Aleksijević, L.; Bekić, S.; Schwarz, D.; Matić, S.; Neuberg, M.; Škrlec, I. Antimicrobial Peptides—Mechanisms of Action, Antimicrobial Effects and Clinical Applications. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewies, A.; Du Plessis, L. H.; Wentzel, J. F. Antimicrobial Peptides: The Achilles’ Heel of Antibiotic Resistance? Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins 2018, 11, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheau Ling Puan; Pirasannah Erriah; Al-adil, M. ; Normi, Y. M.; Nur, W.; Ali; Siti Aqlima Ahmad; Siti Nurbaya Oslan; Lim, S.; Sabri, S. Antimicrobial Peptides from Bacillus Spp. And Strategies to Enhance Their Yield. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2023, 107, 5569–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xia, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Tang, N.; Tong, X.; Wang, M.; Ye, X.; Feng, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Human Gut Microbiome Using Deep Learning. Nature Biotechnology 2022, 40, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Shao, C.; Li, G.; Shan, A.; Chou, S.; Wang, J.; Ma, Q.; Dong, N. Conversion of Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptides into Species-Specific Antimicrobials Capable of Precisely Targeting Pathogenic Bacteria. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Walia, D.; Batra, N. Chapter 6 - Fresh-Cut Fruits: Microbial Degradation and Preservation. ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128115152000068.
- Kravchenko, S. V.; Domnin, P. A.; Grishin, S. Y.; Panfilov, A. V.; Azev, V. N.; Mustaeva, L. G.; Gorbunova, E. Y.; Kobyakova, M. I.; Surin, A. K.; Glyakina, A. V.; Fadeev, R. S.; Ermolaeva, S. A.; Galzitskaya, O. V. Multiple Antimicrobial Effects of Hybrid Peptides Synthesized Based on the Sequence of Ribosomal S1 Protein from Staphylococcus Aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 524–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, M.; Park, J.; Yeom, J.-H.; Joo, M.; Lee, K. Rediscovery of Antimicrobial Peptides as Therapeutic Agents. Journal of Microbiology 2021, 59, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H.; Yi, H. Antimicrobial Peptides: Classification, Design, Application and Research Progress in Multiple Fields. Frontiers in Microbiology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C. H.; Lu, T. K. Development and Challenges of Antimicrobial Peptides for Therapeutic Applications. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, M. Antimicrobial Peptides Demonstrate Activity against Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2023, 15, 454–469 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonk, M.; Růžek, D.; Vilcinskas, A. Compelling Evidence for the Activity of Antiviral Peptides against SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2021, 13, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtada, R.; Herce, H. D.; Yin, D. J.; Moroco, J. A.; Wales, T. E.; Engen, J. R.; Walensky, L. D. Design of Stapled Antimicrobial Peptides That Are Stable, Nontoxic and Kill Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Mice. Nature Biotechnology 2019, 37, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Song, Y. Mechanism of Antimicrobial Peptides: Antimicrobial, Anti-Inflammatory and Antibiofilm Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cresti, L.; Cappello, G.; Pini, A. Antimicrobial Peptides towards Clinical Application—A Long History to Be Concluded. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4870 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço, A.L.P.; Rios, T.B.; da Silva, Á.P.; Franco, O.L.; Ramada, M.H.S. Peptide Stapling Applied to Antimicrobial Peptides. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-T.; Yang, L.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-T.; Lai, C.-W.; Ko, C.-F.; Shih, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-H. Intelligent De Novo Design of Novel Antimicrobial Peptides against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaaytah, A.; Mohammed, G.; Abualhaijaa, A.; Al-Balas, Q. Development of Novel Ultrashort Antimicrobial Peptide Nanoparticles with Potent Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Drug Design, Development and Therapy 2017, 11, 3159–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic Peptides: Current Applications and Future Directions. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S. J.; O’Brien-Simpson, N. M.; Pantarat, N.; Sulistio, A.; Wong, E. H. H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lenzo, J. C.; Holden, J. A.; Blencowe, A.; Reynolds, E. C.; Qiao, G. G. Combating Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria with Structurally Nanoengineered Antimicrobial Peptide Polymers. Nature Microbiology 2016, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, T.; Chetia, M.; Chatterjee, S. Antimicrobial Peptides and Proteins: From Nature’s Reservoir to the Laboratory and Beyond. Frontiers in Chemistry 2021, 9, 691532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Z.; Yang, P.; Lei, J.; Zhao, J. Biological Function of Antimicrobial Peptides on Suppressing Pathogens and Improving Host Immunity. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, T.J.; Munshi, T.; Lopez-Perez, P.M.; Tran, A.C.; Cosgrove, C.; Bartolf, A.; Menichini, M.; Rindi, L.; Parigger, L.; Malanovic, N.; et al. Specific Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides Enhance the Recovery of Low-Load Quiescent Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Routine Diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjell, C. D.; Hiss, J. A.; Hancock, R. E. W.; Schneider, G. Designing Antimicrobial Peptides: Form Follows Function. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2011, 11, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
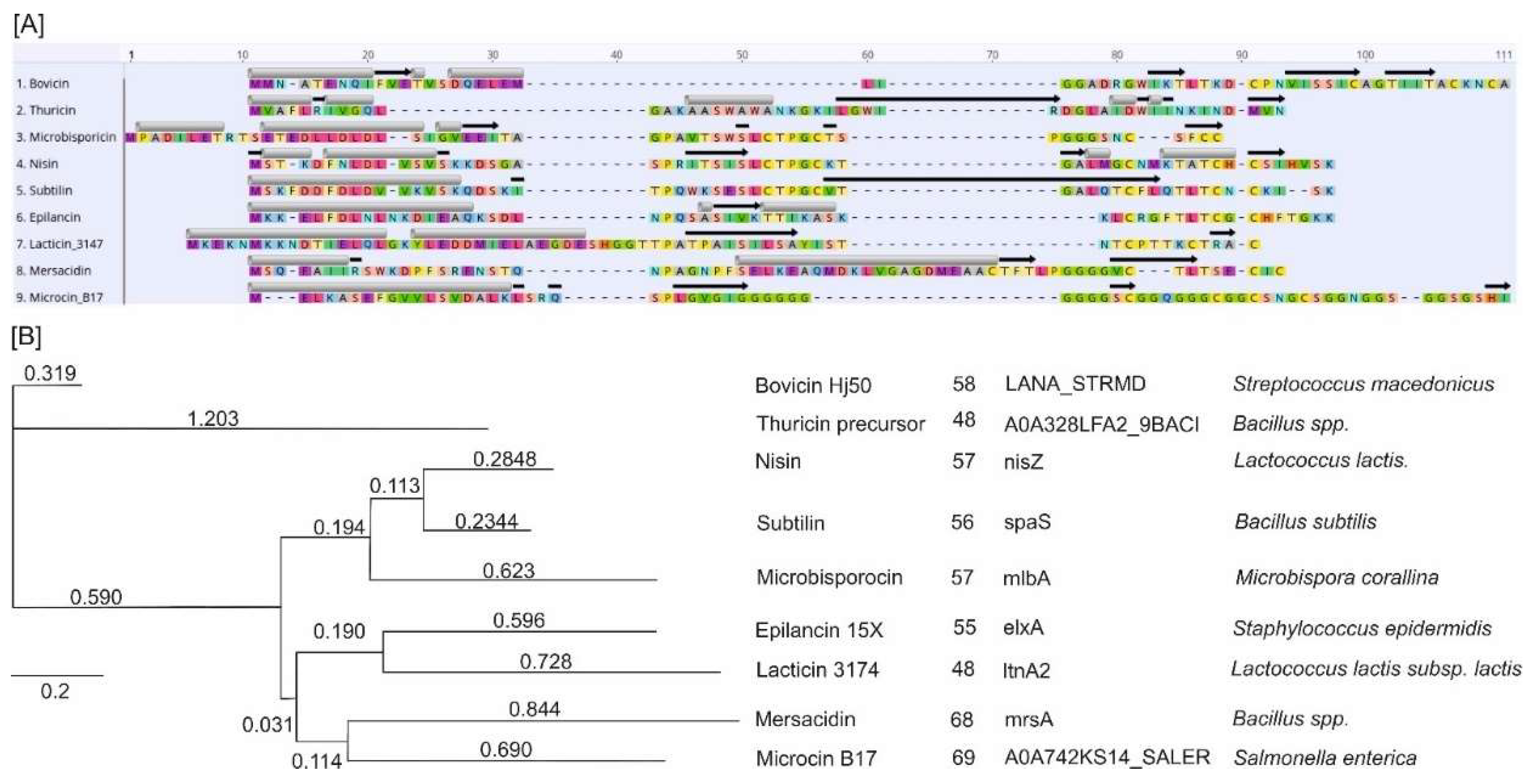
| Bacteriocin | UniProt ID | Amino acid sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Nisin | P29559 | MSTKDFNLDLVSVSKKDSGASPRITSISLCTPGCKTGALMGCNMKTATCHCSIHVSK |
| Colicin M | A0A761KWA3 | METLTVHAPSPSTNLPSYGNGAFSLSAPHVPGAGPLLVQVVYSFFQSPNMCLQALTQLEDYIKKHGASNPLTLQIISTNIGYFCNAERNLVLHPGISVYDAYHFAKPAPSQYDYRSMNMKQMSGNVTTPIVALAHYLWGNGAERSVNIANIGLKISPMKINQIKDIIKSGVVGTFPVSTKFTHATGDYNVITGAYLGNITLKTEGTLTISANGSWTYNGVVRSYDDKYDFNASTHRGVIGESLTRLGAMFSGKEYQILLPGEIHIKESGKR |
| Microcin B17 | A0A742KS14 | MELKASEFGVVLSVDALKLSRQSPLGVGIGGGGGGGGGGSCGGQGGGCGGCSNGCSGGNGGSGGSGSHI |
| Subtilin | P10946 | MSKFDDFDLDVVKVSKQDSKITPQWKSESLCTPGCVTGALQTCFLQTLTCNCKISK |
| Lacticin 3147 | O87237 | MKEKNMKKNDTIELQLGKYLEDDMIELAEGDESHGGTTPATPAISILSAYISTNTCPTTKCTRAC |
| Thuricin precursor | A0A328LFA2 | MVAFLRIVGQLGAKAASWAWANKGKILGWIRDGLAIDWIINKINDMVN |
| Epilancin 15X | P86047 | MKKELFDLNLNKDIEAQKSDLNPQSASIVKTTIKASKKLCRGFTLTCGCHFTGKK |
| Microbisporicin | W2EQT3 | MPADILETRTSETEDLLDLDLSIGVEEITAGPAVTSWSLCTPGCTSPGGGSNCSFCC |
| Mersacidin | A0A2H4RAU1 | MSQEAIIRSWKDPFSRENSTQNPAGNPFSELKEAQMDKLVGAGDMEAACTFTLPGGGGVCTLTSECIC |
| Bovicin HJ50 | H2A7G5 | MMNATENQIFVETVSDQELEMLIGGADRGWIKTLTKDCPNVISSICAGTIITACKNCA |
| Bacterial AMP | Source | Active against |
|---|---|---|
| Colicin | E. coli | Enterobacter, Escherichia, Klebsiella, Morganella, Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia |
| Gramicidin | B. brevis | Gram-positive; Gram-negative |
| Microvionin | Microbacterium arborescens | MRSA and Streptococcus pneumonia |
| Plantazolicin | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens | Closely related strains of the genus Bacillus |
| Goadsporin | Streptomyces spp | Closely related strains of the genus Streptomyces |
| Sonorensin | B. sonorensis | B. subtilis, E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Vibrio vulnificus |
| Nisin | Lactococcus, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus spp. | Staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, bacilli, and listeria |
| Epidermin | S. epidermidis | S. haemolyticus, S. capitis, S. simulans, S. saprophyticus, S. hominis, S. epidermidis, S. aureus |
| Microcin C7 | E. coli | Enterobacter, Escherichia, Klebsiella, Morganella, Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia |
| Microcin L | E. coli | Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica, Shigella spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Abp118 | Lactobacillus salivarius | Listeria monocytogenes |
| Pediocin | Pediococcus spp | Listeria spp. |
| Bovicin HC5 | Streptococcus bovis | Listeria monocytogenes |
| Bottromycin A2 | Streptomyces bottropensis | MRSA, VRE |
| Enterocin A | Enterococcus faecium | Listeria monocytogenes |
| Bacteriocin | Producer strain | Active against | MIC (mg/L) |
Inhibition Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nisin A | Lactococcus lactis | MRSA Vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus (VISA) VRE |
0.5–4.1 2–>8.3 2–>8.3 |
|
| Epidermin | Staphylococcus epidermidis |
Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus agalactiae |
>14 >14 |
|
| Bovicin HC5 | Streptococcus bovis | Listeria monocytogenes | >16 | |
| Bottromycin A2 | Streptomyces bottropensis | MRSA VRE |
1 0.5 |
|
| Pediocin PA-1 | Pediococcus acidilactici | Listeria monocytogenes | 0.0013–0.0062 | |
| Enterocin A | Enterococcus faecium | Listeria monocytogenes | 0.0002–0.0011 | |
| Microcin L | Escherichia coli |
Escherichia coli Salmonella enterica Shigella spp. Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
12–18 12–18 12–18 8–12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




