Submitted:
26 July 2024
Posted:
30 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects, Task and Experimental Design
2.2 EEG Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Spectral Current Density Analyses
2.2.2 Phase-Amplitude Coupling (PAC)
2.3 Statistical Analyses
2.3.1 Clinical Measures
2.3.2 Task Performance Accuracy
2.3.3 Spectral Current Density Analyses
2.3.4 PAC
3. Results
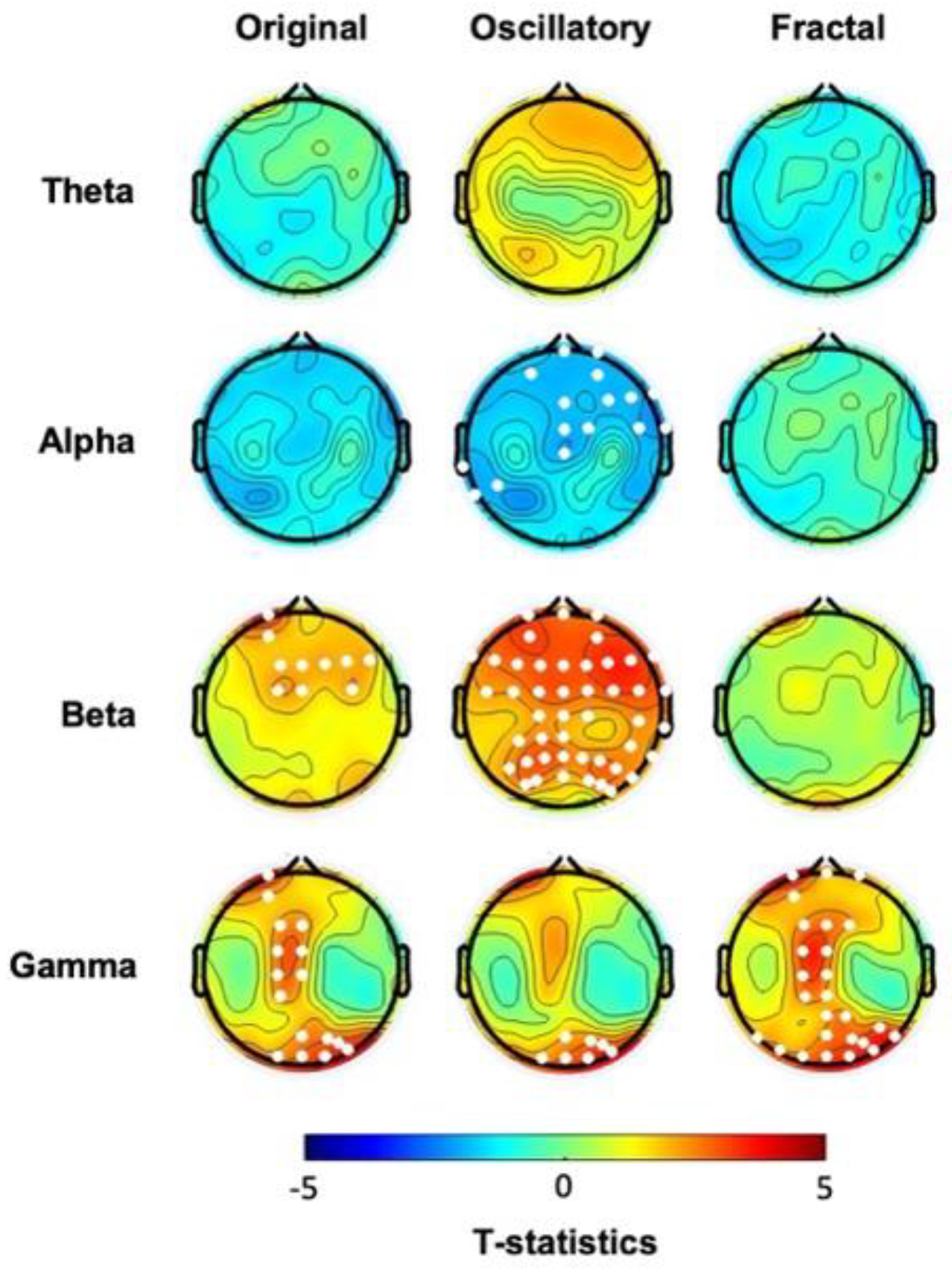
3.1. At Baseline, hBDI Displays Greater Beta and Gamma Oscillatory Activity Than CTL
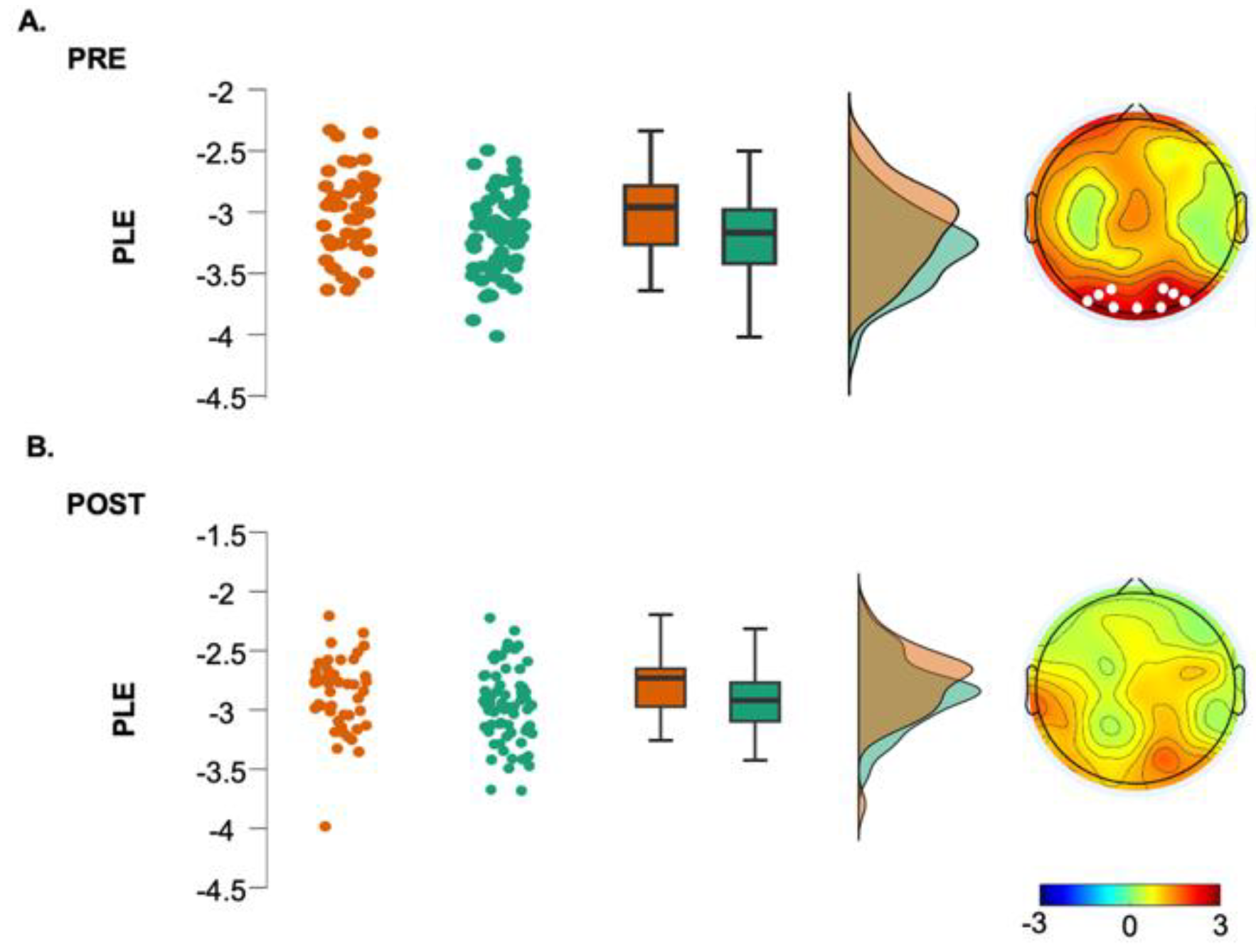
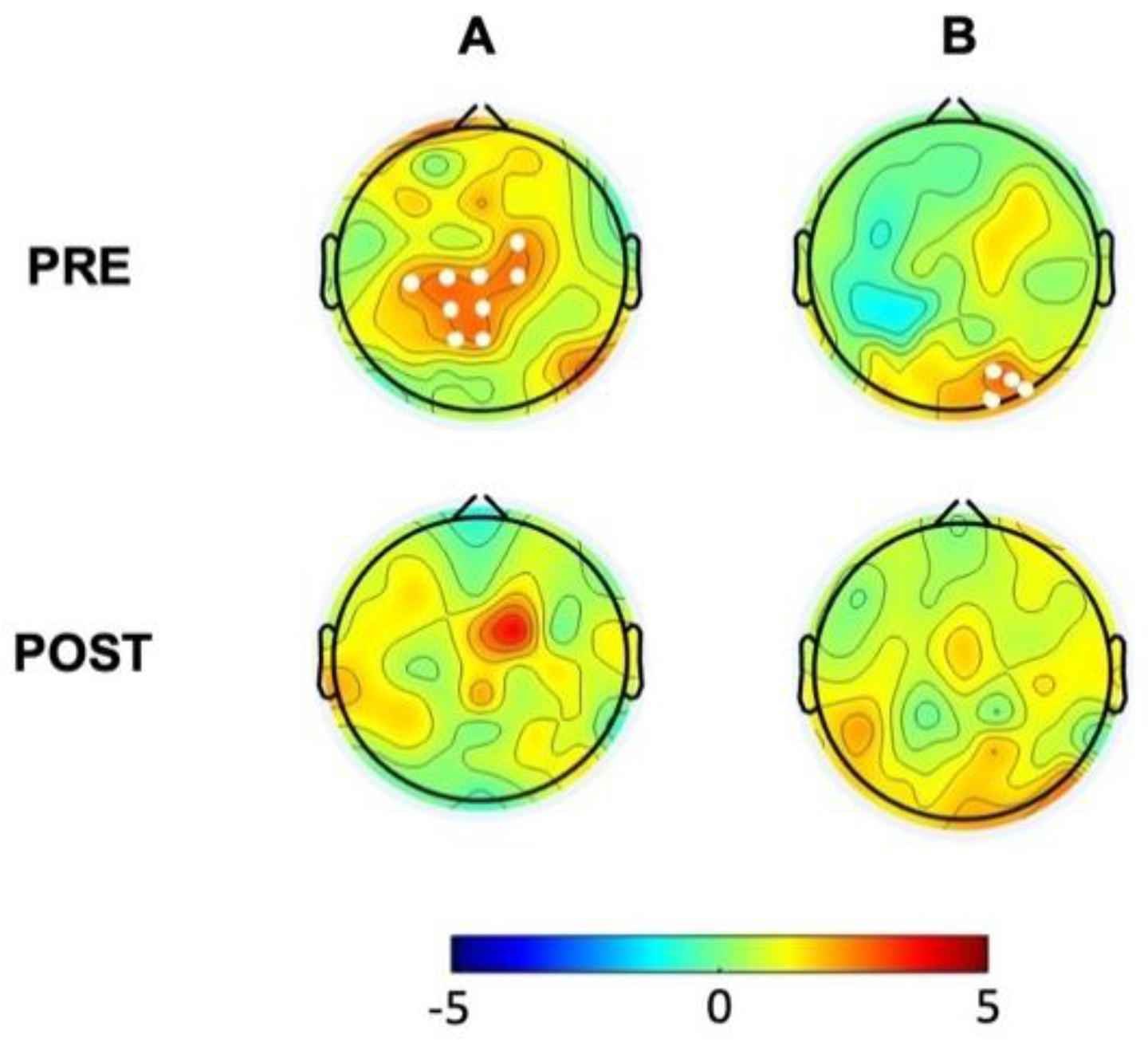
3.2 The hBDI Group Displayed Greater Theta-Beta and Theta-Gamma PAC
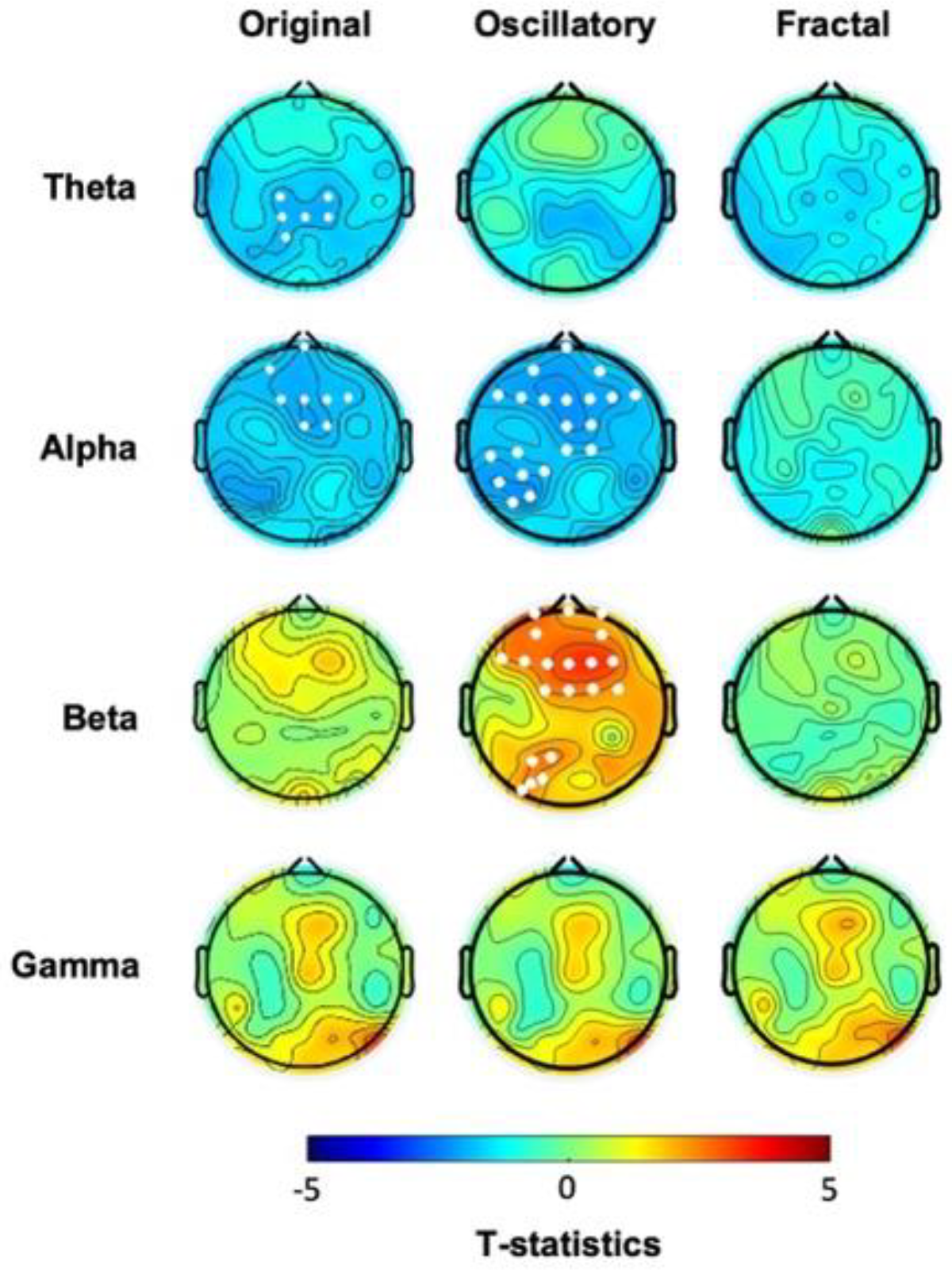
3.3 EEG activity at Rest Changes After One-Hour Task Practice
3.4 Phase-Amplitude Coupling Is Greater in hBDI Only at Baseline
4. Discussion
4.1 Over-Sensitive Behavioral Inhibition System Is Linked To Depression And Anxiety
4.2 Depression Is Characterized By Greater Beta Power During Resting State EEG Before the Task
4.3 Gamma Power at Rest Is Greater In Depression
4.4 Phase-Amplitude Coupling is Greater in hBDI Only before the Task
4.5 Oscillatory Activity Increases After Task Practice in CTL but Not in hBDI
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grineski, S.E.; Morales, D.X.; Collins, T.W.; Nadybal, S.; Trego, S. Anxiety and Depression among US College Students Engaging in Undergraduate Research during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of American College Health 2024, 72, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyapong-Opoku, G.; Agyapong, B.; Obuobi-Donkor, G.; Eboreime, E. Depression and Anxiety among Undergraduate Health Science Students: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Behav Sci (Basel) 2023, 13, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibodeau, R.; Jorgensen, R.S.; Kim, S. Depression, Anxiety, and Resting Frontal EEG Asymmetry: A Meta-Analytic Review. J Abnorm Psychol 2006, 115, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ruan, M.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y. Major Depressive Disorder: Advances in Neuroscience Research and Translational Applications. Neurosci Bull 2021, 37, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Ke, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, T.; Xia, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M. Energy Metabolism in Major Depressive Disorder: Recent Advances from Omics Technologies and Imaging. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 141, 111869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Mahaluf, J.P.; Roxin, A.; Mayberg, H.S.; Compte, A. A Computational Model of Major Depression: The Role of Glutamate Dysfunction on Cingulo-Frontal Network Dynamics. Cerebral Cortex 2017, 27, 660–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-T.; Tan, Z.-L.; Hirjak, D.; Northoff, G. Brain-Wide Changes in Excitation-Inhibition Balance of Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review of Topographic Patterns of GABA- and Glutamatergic Alterations. Mol Psychiatry 2023, 28, 3257–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarawagi, A.; Soni, N.D.; Patel, A.B. Glutamate and GABA Homeostasis and Neurometabolism in Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 637863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, G.A.; Hill, K.R.; Wengler, K.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Parsey, R.V.; DeLorenzo, C. Does the Change in Glutamate to GABA Ratio Correlate with Change in Depression Severity? A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Mol Psychiatry 2022, 27, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.; Czéh, B.; Kole, M.H.P.; Michaelis, T.; Lucassen, P.J. Alterations of Neuroplasticity in Depression: The Hippocampus and Beyond. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 14, S481–S490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ge, T.; Leng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Fan, J.; Yang, W.; Cui, R. The Role of Neural Plasticity in Depression: From Hippocampus to Prefrontal Cortex. Neural Plasticity 2017, 2017, 6871089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L. From Serotonin to Neuroplasticity: Evolvement of Theories for Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drevets, W. Functional Anatomical Correlates of Antidepressant Drug Treatment Assessed Using PET Measures of Regional Glucose Metabolism. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 12, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzagalli, D.A. Frontocingulate Dysfunction in Depression: Toward Biomarkers of Treatment Response. Neuropsychopharmacol 2011, 36, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobe, E. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Major Depressive Disorder. NDT 2013, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaglia, F. The Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Psychiatric Disease. Dev Disabil Res Revs 2010, 16, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stork, C.; Renshaw, P.F. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Bipolar Disorder: Evidence from Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Research. Mol Psychiatry 2005, 10, 900–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; John, A.; Howarth, F.C. Increased Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Zucker Diabetic Rat Liver and Brain. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015, 35, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, K.A.L.; Mao, X.; Case, J.A.C.; Kang, G.; Shungu, D.C.; Gabbay, V. Increased Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid Lactate in Depressed Adolescents. Eur. psychiatr. 2016, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shungu, D.C.; Weiduschat, N.; Murrough, J.W.; Mao, X.; Pillemer, S.; Dyke, J.P.; Medow, M.S.; Natelson, B.H.; Stewart, J.M.; Mathew, S.J. Increased Ventricular Lactate in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. III. Relationships to Cortical Glutathione and Clinical Symptoms Implicate Oxidative Stress in Disorder Pathophysiology. NMR in Biomedicine 2012, 25, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, J.; Hock, A.; Henning, A.; Seifritz, E.; Boeker, H.; Grimm, S. Increased Pregenual Anterior Cingulate Glucose and Lactate Concentrations in Major Depressive Disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2017, 22, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grønli, J.; Rempe, M.J.; Clegern, W.C.; Schmidt, M.; Wisor, J.P. Beta EEG Reflects Sensory Processing in Active Wakefulness and Homeostatic Sleep Drive in Quiet Wakefulness. J Sleep Res 2016, 25, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardi, M.F.; Tatti, E.; Quartarone, A. Beta Power and Movement-Related Beta Modulation as Hallmarks of Energy for Plasticity Induction: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2021, 88, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.B.; Ricci, S.; Tatti, E.; Panday, P.; Girau, E.; Lin, J.; Thomson, B.O.; Chen, H.; Marshall, W.; Tononi, G.; et al. Neural Fatigue Due to Intensive Learning Is Reversed by a Nap but Not by Quiet Waking. Sleep 2021, 44, zsaa143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatti, E.; Ricci, S.; Nelson, A.B.; Mathew, D.; Chen, H.; Quartarone, A.; Cirelli, C.; Tononi, G.; Ghilardi, M.F. Prior Practice Affects Movement-Related Beta Modulation and Quiet Wake Restores It to Baseline. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.B.; Moisello, C.; Lin, J.; Panday, P.; Ricci, S.; Canessa, A.; Di Rocco, A.; Quartarone, A.; Frazzitta, G.; Isaias, I.U.; et al. Beta Oscillatory Changes and Retention of Motor Skills during Practice in Healthy Subjects and in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Front Hum Neurosci 2017, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, L.; Lim, K.-L. Chapter 13 - Energy Regulation and Parkinson’s Disease. In Genetics, Neurology, Behavior, and Diet in Parkinson’s Disease; Martin, C.R., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press, 2020; pp. 205–220 ISBN 978-0-12-815950-7.
- Chahine, L.M.; Zhu, X.; Ehrenkranz, R.; Chen, H.; Glynn, N.W.; Rosano, C. Changes in Self-Reported Energy Levels in Prodromal Parkinson’s Disease. Mov Disord 2021, 36, 1276–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempster, P.A.; Perju-Dumbrava, L. The Thermodynamic Consequences of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, J.F.; Bismark, A.W.; Frank, M.J.; Allen, J.J.B. Multiple Dissociations Between Comorbid Depression and Anxiety on Reward and Punishment Processing: Evidence From Computationally Informed EEG. Comput Psychiatr 2019, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, J.F.; Bismark, A.; Frank, M.J.; Allen, J.J. Larger Error Signals in Major Depression Are Associated with Better Avoidance Learning. Front. Psychol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.H.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. An Inventory for Measuring Depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielberger, C.D. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory for Adults. 1983.
- Carver, C.S.; White, T.L. Behavioral Inhibition, Behavioral Activation, and Affective Responses to Impending Reward and Punishment: The BIS/BAS Scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1994, 67, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.J.; Seeberger, L.C.; O’reilly, R.C. By Carrot or by Stick: Cognitive Reinforcement Learning in Parkinsonism. Science 2004, 306, 1940–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An Open Source Toolbox for Analysis of Single-Trial EEG Dynamics Including Independent Component Analysis. J Neurosci Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pion-Tonachini, L.; Kreutz-Delgado, K.; Makeig, S. ICLabel: An Automated Electroencephalographic Independent Component Classifier, Dataset, and Website. Neuroimage 2019, 198, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.-M. FieldTrip: Open Source Software for Advanced Analysis of MEG, EEG, and Invasive Electrophysiological Data. Comput Intell Neurosci 2011, 2011, 156869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Liu, Z. Separating Fractal and Oscillatory Components in the Power Spectrum of Neurophysiological Signal. Brain Topogr 2016, 29, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tort, A.B.L.; Komorowski, R.; Eichenbaum, H.; Kopell, N. Measuring Phase-Amplitude Coupling between Neuronal Oscillations of Different Frequencies. J Neurophysiol 2010, 104, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, E.; Oostenveld, R. Nonparametric Statistical Testing of EEG- and MEG-Data. J Neurosci Methods 2007, 164, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yang, M.; Xi, X.; Guo, Y.; Fang, M.; Cheng, L.; Du, Y. Comorbid Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Its Association with Quality of Life in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 40511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Sampson, N.A.; Berglund, P.; Gruber, M.J.; Al-Hamzawi, A.; Andrade, L.; Bunting, B.; Demyttenaere, K.; Florescu, S.; de Girolamo, G.; et al. Anxious and Non-Anxious Major Depressive Disorder in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci 2015, 24, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopwood, M. Anxiety Symptoms in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: Commentary on Prevalence and Clinical Implications. Neurol Ther 2023, 12, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.W.; Kim, Y.-K.; Jeon, H.J. Comorbid Anxiety and Depression: Clinical and Conceptual Consideration and Transdiagnostic Treatment. In Anxiety Disorders: Rethinking and Understanding Recent Discoveries; Kim, Y.-K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 219–235. ISBN 978-981-329-705-0. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Yamagata, S.; Ritchie, S.J.; Barker, E.D.; Ando, J. Etiological Pathways of Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms Linked to Personality Traits: A Genetically-Informative Longitudinal Study. Journal of Affective Disorders 2021, 291, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuyama, A.; Kubo, T.; Shinkawa, H.; Sugawara, D. The Roles of Trait and Process Resilience in Relation of BIS/BAS and Depressive Symptoms among Adolescents. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoshima, K.; Masuya, J.; Ono, M.; Honyashiki, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Kusumi, I.; Inoue, T. Effects of the Interaction between Affective Temperaments and BIS/BAS on Depressive Symptoms in Individuals with Major Depressive Disorder. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 15841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Luo, Y.; Chang, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, R.; Jiang, Y.; Xi, H. The Mediating Role of Cognitive Emotion Regulation in BIS/BAS Sensitivities, Depression, and Anxiety Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults in China. Psychology Research and Behavior Management 2020, 13, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasch, K.L.; Rottenberg, J.; Arnow, B.A.; Gotlib, I.H. Behavioral Activation and Inhibition Systems and the Severity and Course of Depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 2002, 111, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilty, L.C.; Mackew, L.; Bagby, R.M. Distinct Profiles of Behavioral Inhibition and Activation System Sensitivity in Unipolar vs. Bipolar Mood Disorders. Psychiatry Research 2014, 219, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingelkurts, A.A.; Fingelkurts, A.A. Altered Structure of Dynamic Electroencephalogram Oscillatory Pattern in Major Depression. Biological Psychiatry 2015, 77, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kang, C.; Wei, Z.; Qu, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y. Beta Oscillations in Major Depression – Signalling a New Cortical Circuit for Central Executive Function. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 18021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanaugh, B.C.; Fukuda, A.M.; Gemelli, Z.T.; Thorpe, R.; Tirrell, E.; Vigne, M.; Jones, S.R.; Carpenter, L.L. Pre-Treatment Frontal Beta Events Are Associated with Executive Dysfunction Improvement after Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression: A Preliminary Report. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2023, 168, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-García, I.; Silva, J.; Villena-González, M.; Campos-Arteaga, G.; Artigas-Vergara, C.; Luarte, N.; Rodríguez, E.; Bosman, C.A. Increase in Beta Power Reflects Attentional Top-Down Modulation After Psychosocial Stress Induction. Front Hum Neurosci 2021, 15, 630813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, B.; Haegens, S. Beyond the Status Quo: A Role for Beta Oscillations in Endogenous Content (Re)Activation. eNeuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, N.M.; Fietz, J.; Kopf-Beck, J.; Kappelmann, N.; Brem, A.-K. Separating EEG Correlates of Stress: Cognitive Effort, Time Pressure, and Social-Evaluative Threat. European Journal of Neuroscience 2022, 55, 2464–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporn, S.; Hein, T.; Herrojo Ruiz, M. Alterations in the Amplitude and Burst Rate of Beta Oscillations Impair Reward-Dependent Motor Learning in Anxiety. eLife 9 e50654. [CrossRef]
- Roh, S.-C.; Park, E.-J.; Shim, M.; Lee, S.-H. EEG Beta and Low Gamma Power Correlates with Inattention in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. J Affect Disord 2016, 204, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohier, B.; Ferracci, L.; Surguladze, S.A.; Lawrence, E.; El Hage, W.; Kefi, M.Z.; Allain, P.; Garre, J.-B.; Le Gall, D. Cognitive Inhibition and Working Memory in Unipolar Depression. J Affect Disord 2009, 116, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, H.R. Major Depressive Disorder Is Associated with Broad Impairments on Neuropsychological Measures of Executive Function: A Meta-Analysis and Review. Psychological Bulletin 2013, 139, 81–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stordal, K.I.; Lundervold, A.J.; Egeland, J.; Mykletun, A.; Asbjørnsen, A.; Landrø, N.I.; Roness, A.; Rund, B.R.; Sundet, K.; Oedegaard, K.J.; et al. Impairment across Executive Functions in Recurrent Major Depression. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 2004, 58, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrena, C.; Branco, L.D.; Shansis, F.M.; Fonseca, R.P. Executive Function Impairments in Depression and Bipolar Disorder: Association with Functional Impairment and Quality of Life. Journal of Affective Disorders 2016, 190, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.L.; Brown, E.C.; Ramasubbu, R.; Kiss, Z.H.T. Intrinsic Local Beta Oscillations in the Subgenual Cingulate Relate to Depressive Symptoms in Treatment-Resistant Depression. Biol Psychiatry 2016, 80, e93–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillas-Romero, A.; Tortella-Feliu, M.; Bornas, X.; Putman, P. Spontaneous EEG Theta/Beta Ratio and Delta–Beta Coupling in Relation to Attentional Network Functioning and Self-Reported Attentional Control. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2015, 15, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, P.-O.; Fossati, P.; Pochon, J.-B.; Levy, R.; Lebastard, G.; Lehéricy, S.; Allilaire, J.-F.; Dubois, B. Cognitive Control and Brain Resources in Major Depression: An fMRI Study Using the n-Back Task. Neuroimage 2005, 26, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, E.J.; Simonotto, E.; Ebmeier, K.P. Limbic Over-Activity in Depression during Preserved Performance on the n-Back Task. Neuroimage 2006, 29, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, T.P.; Herrojo Ruiz, M. State Anxiety Alters the Neural Oscillatory Correlates of Predictions and Prediction Errors during Reward-Based Learning. NeuroImage 2022, 249, 118895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, R.J.; Pizzagalli, D.; Nitschke, J.B.; Putnam, K. Depression: Perspectives from Affective Neuroscience. Annu Rev Psychol 2002, 53, 545–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffer, C.E.; Davidson, R.J.; Saron, C. Frontal and Parietal Electroencephalogram Asymmetry in Depressed and Nondepressed Subjects. Biol Psychiatry 1983, 18, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van der Vinne, N.; Vollebregt, M.A.; van Putten, M.J.A.M.; Arns, M. Stability of Frontal Alpha Asymmetry in Depressed Patients during Antidepressant Treatment. NeuroImage: Clinical 2019, 24, 102056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.J.B.; Cohen, M.X. Deconstructing the “Resting” State: Exploring the Temporal Dynamics of Frontal Alpha Asymmetry as an Endophenotype for Depression. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J. Anterior Cerebral Asymmetry and the Nature of Emotion. Brain and Cognition 1992, 20, 125–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, S.J.; Allen, J.J.B. Frontal Asymmetry as a Mediator and Moderator of Emotion: An Updated Review. Psychophysiology 2018, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, R.J.; Ekman, P.; Saron, C.D.; Senulis, J.A.; Friesen, W.V. Approach-Withdrawal and Cerebral Asymmetry: Emotional Expression and Brain Physiology: I. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1990, 58, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, G. Fractals in the Nervous System: Conceptual Implications for Theoretical Neuroscience. Front Physiol 2010, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stam, C.J. Nonlinear Dynamical Analysis of EEG and MEG: Review of an Emerging Field. Clinical Neurophysiology 2005, 116, 2266–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, P.J.; Watson, B.O. Gamma Oscillations as a Biomarker for Major Depression: An Emerging Topic. Transl Psychiatry 2018, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cape, E.G.; Jones, B.E. Differential Modulation of High-Frequency Gamma-Electroencephalogram Activity and Sleep-Wake State by Noradrenaline and Serotonin Microinjections into the Region of Cholinergic Basalis Neurons. J Neurosci 1998, 18, 2653–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajós, M.; Hoffmann, W.E.; Robinson, D.D.; Yu, J.H.; Hajós-Korcsok, É. Norepinephrine but Not Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Enhance Theta and Gamma Activity of the Septo-Hippocampal System. Neuropsychopharmacol 2003, 28, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwagar, Z.; Wylezinska, M.; Jezzard, P.; Evans, J.; Ashworth, F.; Sule, A.; Matthews, P.M.; Cowen, P.J. Reduction in Occipital Cortex Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Concentrations in Medication-Free Recovered Unipolar Depressed and Bipolar Subjects. Biol Psychiatry 2007, 61, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanacora, G.; Gueorguieva, R.; Epperson, C.N.; Wu, Y.-T.; Appel, M.; Rothman, D.L.; Krystal, J.H.; Mason, G.F. Subtype-Specific Alterations of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Glutamate in Patients with Major Depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004, 61, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanacora, G.; Treccani, G.; Popoli, M. Towards a Glutamate Hypothesis of Depression. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Sawa, A.; Iyo, M. Increased Levels of Glutamate in Brains from Patients with Mood Disorders. Biol Psychiatry 2007, 62, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lally, N.; Mullins, P.G.; Roberts, M.V.; Price, D.; Gruber, T.; Haenschel, C. Glutamatergic Correlates of Gamma-Band Oscillatory Activity during Cognition: A Concurrent ER-MRS and EEG Study. NeuroImage 2014, 85, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolkunov, D.; Rubin, D.; Mujica-Parodi, L. Power Spectrum Scale Invariance Quantifies Limbic Dysregulation in Trait Anxious Adults Using fMRI: Adapting Methods Optimized for Characterizing Autonomic Dysregulation to Neural Dynamic Time Series. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuciu, P.; Varoquaux, G.; Abry, P.; Sadaghiani, S.; Kleinschmidt, A. Scale-Free and Multifractal Time Dynamics of fMRI Signals during Rest and Task. Front Physiol 2012, 3, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.J. Scale-Free Properties of the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Signal during Rest and Task. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 13786–13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, F.M.; Porcaro, C.; Cottone, C.; Cancelli, A.; Rossini, P.M.; Tecchio, F. Electroencephalographic Fractal Dimension in Healthy Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0149587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.J. Scale-Free Brain Activity: Past, Present, and Future. Trends Cogn Sci 2014, 18, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.J.; Chan, A.H.W.; Jette, N.; Bender, H.A.; Saad, A.E.; Saez, I.; Panov, F.; Ghatan, S.; Yoo, J.Y.; Singh, A.; et al. Elevated Phase Amplitude Coupling as a Depression Biomarker in Epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior 2024, 152, 109659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Su, F.; Kang, X.; Ke, Y.; Ming, D. Altered Fronto-Central Theta-Gamma Coupling in Major Depressive Disorder during Auditory Steady-State Responses. Clinical Neurophysiology 2023, 146, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Su, F.; Chen, S.; Ke, Y.; Ming, D. Altered Gamma Oscillations and Beta–Gamma Coupling in Drug-Naive First-Episode Major Depressive Disorder: Association with Sleep and Cognitive Disturbance. Journal of Affective Disorders 2022, 316, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, Y.; Zomorrodi, R.; Saeki, T.; Rajji, T.K.; Blumberger, D.M.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Nakamura, M. Resting-State EEG Gamma Power and Theta–Gamma Coupling Enhancement Following High-Frequency Left Dorsolateral Prefrontal rTMS in Patients with Depression. Clinical Neurophysiology 2017, 128, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Meij, R.; Kahana, M.; Maris, E. Phase–Amplitude Coupling in Human Electrocorticography Is Spatially Distributed and Phase Diverse. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, T. Synaptic Plasticity-Related Neural Oscillations on Hippocampus–Prefrontal Cortex Pathway in Depression. Neuroscience 2015, 292, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, P.T.; Lisman, J.E. Bidirectional Synaptic Plasticity Induced by a Single Burst during Cholinergic Theta Oscillation in CA1 in Vitro. Neuron 1995, 15, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Large, E.W.; Kolen, J.F. Resonance and the Perception of Musical Meter. Connection Science 1994, 6, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakatos, P.; Shah, A.S.; Knuth, K.H.; Ulbert, I.; Karmos, G.; Schroeder, C.E. An Oscillatory Hierarchy Controlling Neuronal Excitability and Stimulus Processing in the Auditory Cortex. Journal of Neurophysiology 2005, 94, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakatos, P.; Karmos, G.; Mehta, A.D.; Ulbert, I.; Schroeder, C.E. Entrainment of Neuronal Oscillations as a Mechanism of Attentional Selection. Science 2008, 320, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, P.; Nikolić, D.; Singer, W. The Gamma Cycle. Trends in Neurosciences 2007, 30, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głombik, K.; Detka, J.; Kurek, A.; Budziszewska, B. Impaired Brain Energy Metabolism: Involvement in Depression and Hypothyroidism. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Østergaard, L.; Jørgensen, M.B.; Knudsen, G.M. Low on Energy? An Energy Supply-Demand Perspective on Stress and Depression. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2018, 94, 248–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, C.; Westlin, C.; Quigley, K.S.; Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Barrett, L.F. Allostasis, Action, and Affect in Depression: Insights from the Theory of Constructed Emotion. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 2022, 18, 553–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, S.; Tatti, E.; Nelson, A.B.; Panday, P.; Chen, H.; Tononi, G.; Cirelli, C.; Ghilardi, M.F. Extended Visual Sequence Learning Leaves a Local Trace in the Spontaneous EEG. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Guo, H.; Han, T.; Wang, H. Lactate: A Prospective Target for Therapeutic Intervention in Psychiatric Disease. Neural Regeneration Research 2024, 19, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas-Orth, C.; Schneider, J.; Lewen, A.; McQueen, J.; Hasenpusch-Theil, K.; Theil, T.; Hardingham, G.E.; Bading, H.; Kann, O. The Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter Is Crucial for the Generation of Fast Cortical Network Rhythms. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2020, 40, 2225–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CTL mean (SD) |
hBDI mean (SD) |
U |
p-value |
|
| Age (yrs) | 18.97 (1.22) | 18.74 (1.14) | 1.30 | 0.25 |
| BDI | 1.73 (1.65) | 22.22 (4.9) | 85.90 | < 0.001 |
| TAI | 31.05 (5.49) | 55.76 (7.08) | 83.49 | < 0.001 |
| BIS | 19.44 (3.05) | 22.72 (3.07) | 26.38 | < 0.001 |
| BAStot | 40.45 (4.94) | 39.17 (5.68) | 1.07 | 0.30 |
| BASrew | 17.67 (1.71) | 17.13 (2.15) | 1.52 | 0.22 |
| BASfun | 11.88 (2.17) | 11.52 (2.93) | 0.07 | 0.79 |
| BASdrv | 10.89 (2.15) | 10.52 (2.79) | 0.03 | 0.86 |
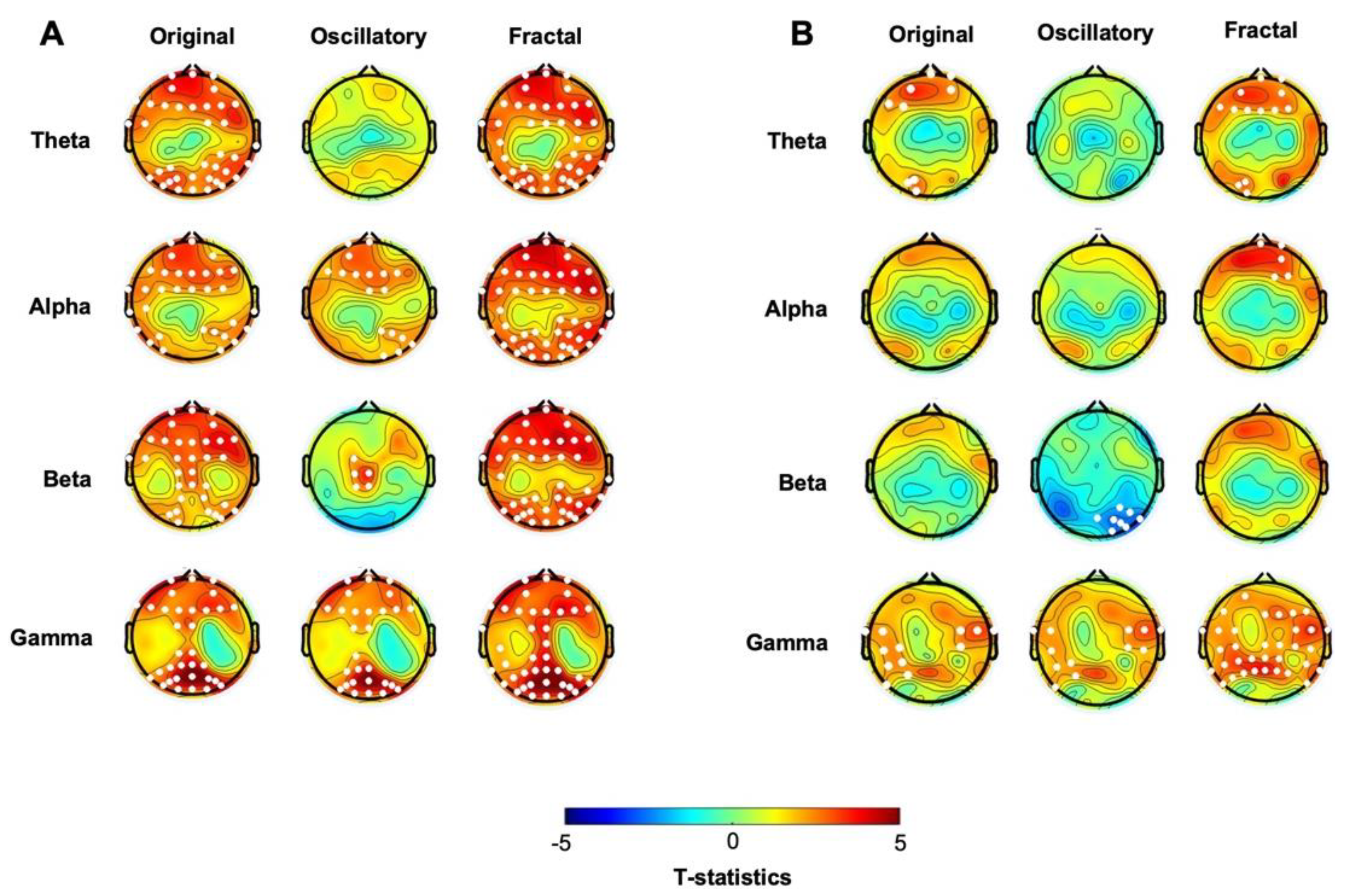
| Pre-task: hBDI>CTL | Post-task: hBDI>CTL | |
| Theta | ORIG: none OSCIL: none FRACT: none |
ORIG: centro-parietal OSCIL: none FRACT: none |
| Alpha | ORIG: none OSCIL: R frontal & L temporal FRACT: none |
ORIG: frontal OSCIL: from frontal to L parietal FRACT: none |
| Beta |
ORIG: frontal OSCIL: fronto-parietal FRACT: none |
ORIG: frontal OSCIL: fronto-parietal FRACT: none |
| Gamma |
ORIG: central midline & occipital OSCIL: R parieto-occipital FRACT: midline & parieto-occipital |
ORIG: central midline & occipital OSCIL: R parieto-occipital FRACT: none |
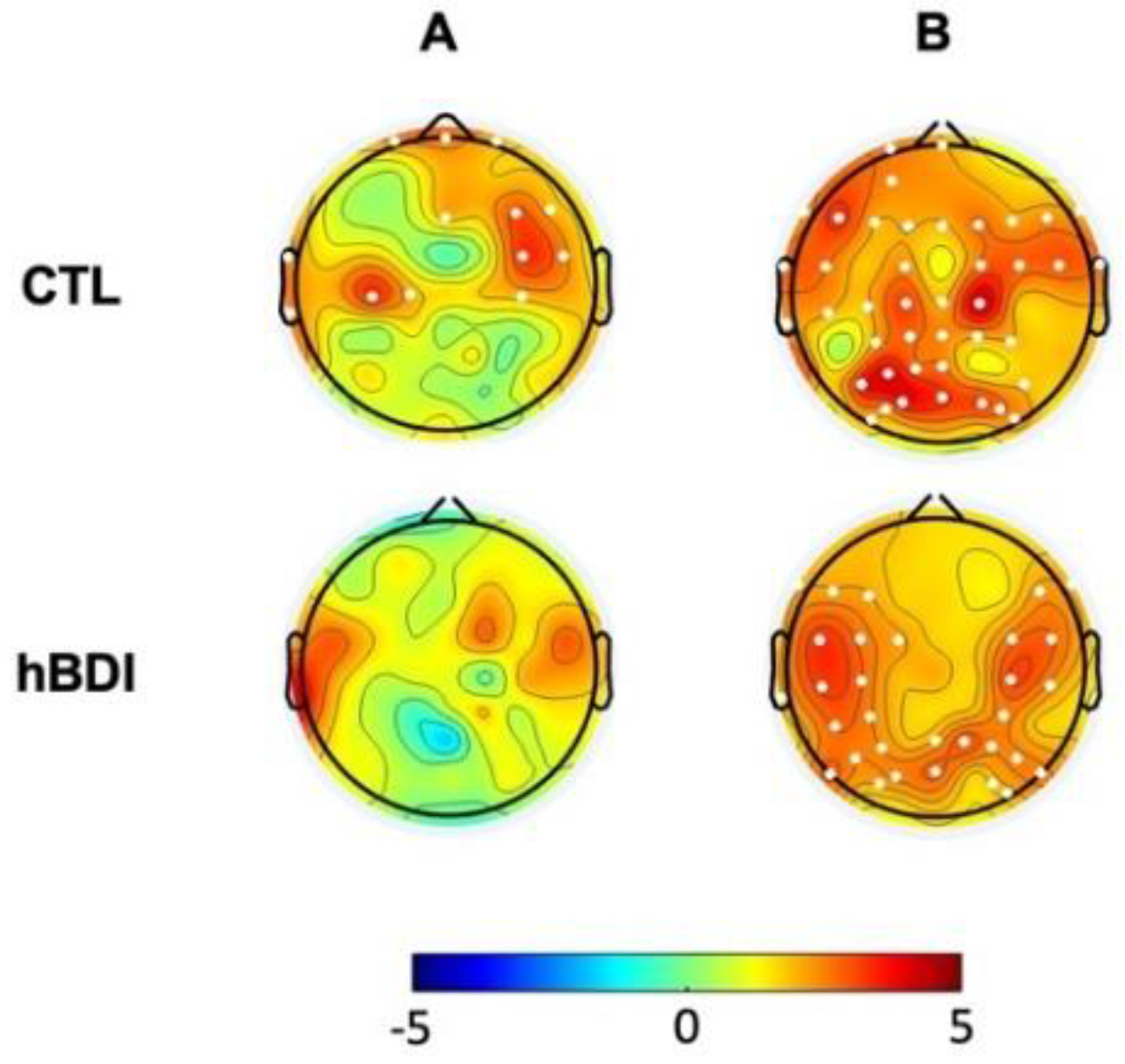
| CTL: post-task>pre-task | hBDI: post-task>pre-task | |
| Theta |
ORIG: frontal & occipital OSCIL: none FRACT: most all electrodes |
ORIG: frontal & occipital OSCIL: none FRACT: frontal & occipital |
| Alpha |
ORIG: frontal & R parietal OSCIL: frontal & R occipital FRACT: most all electrodes |
ORIG: none OSCIL: none FRACT: frontal |
| Beta |
ORIG: from frontal to occipital OSCIL: central FRACT: frontal & occipital |
ORIG: none OSCIL: R parieto-occipital FRACT: none |
| Gamma |
ORIG: frontal & occipital OSCIL: frontal & occipital FRACT: most all electrodes |
ORIG: L & R centro-parietal OSCIL: fronto-centro-parietal FRACT: L centro-parietal & R fronto-central |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





