Submitted:
25 July 2024
Posted:
29 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Challenges in the Treatment of Unresectable HCC:
HCC Immune Microenvironment:
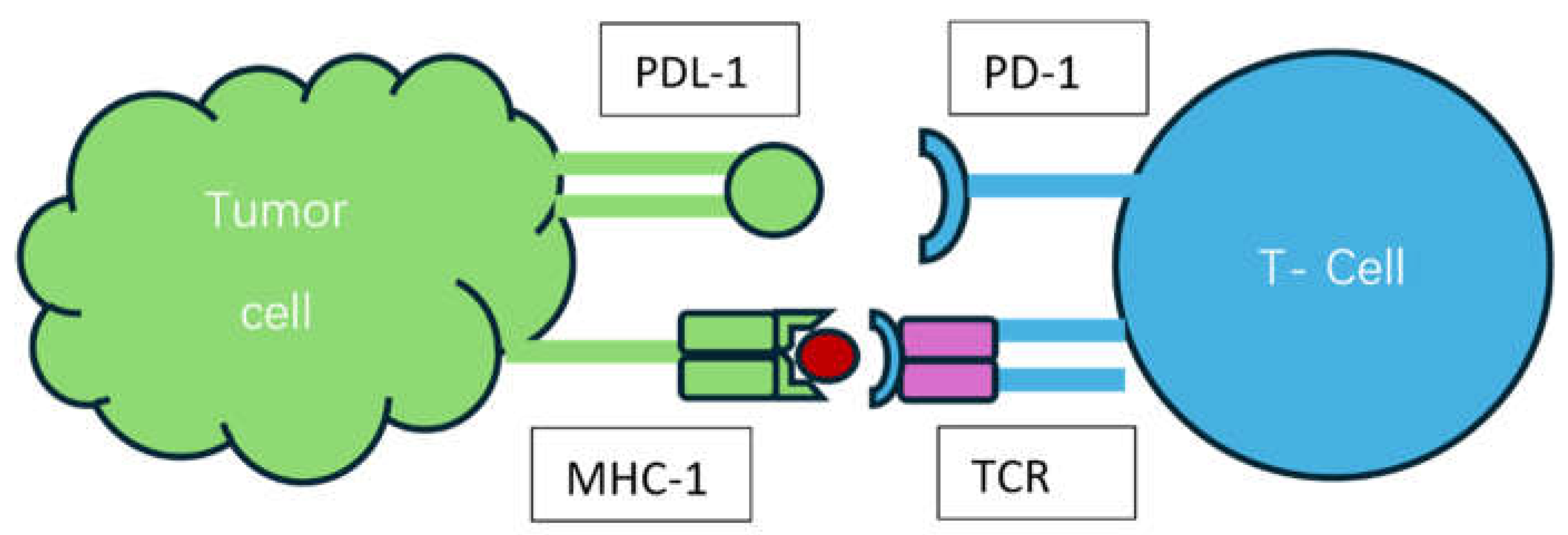
Mechanism of Action of ICIs and Biomarkers of Response: [Figure 2]
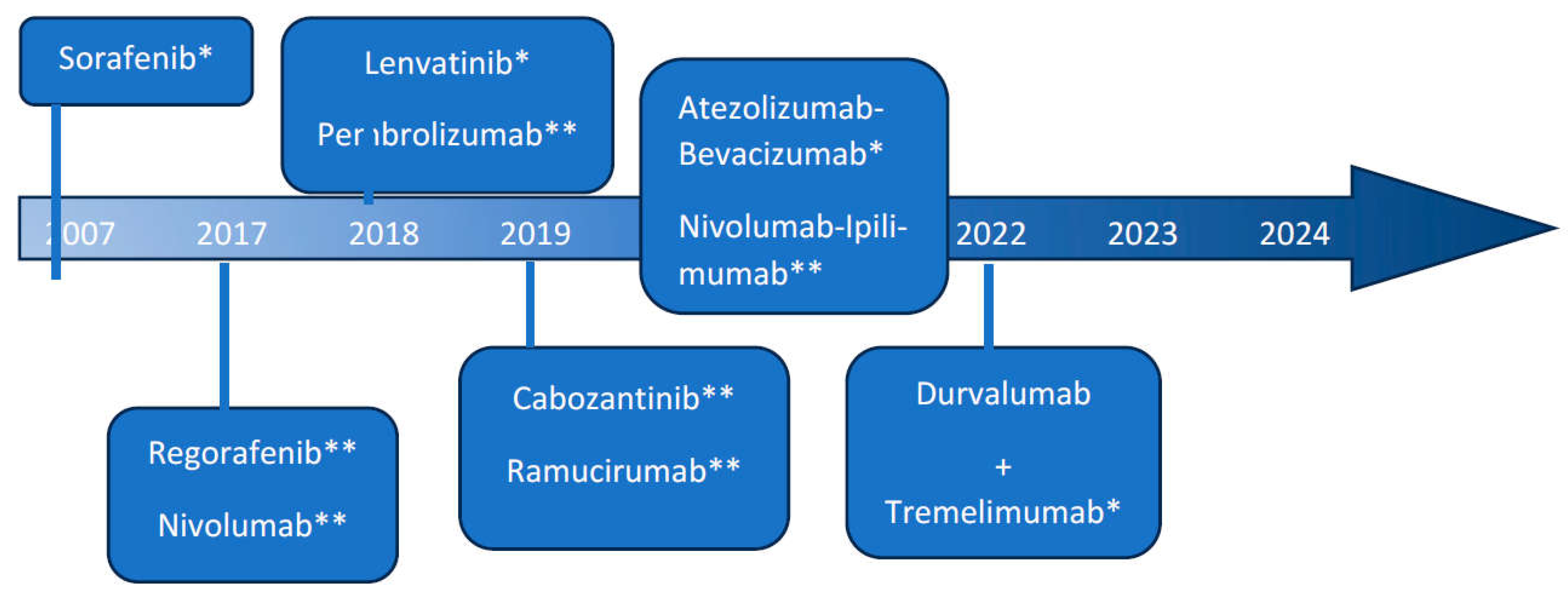
The Evolution of Immunotherapy in HCC-A Game Changer: [Figure]
SBRT in HCC-Does It Work?
The Rationale behind Combining SBRT and ICIs and the Evidence:
Current Guidelines and Future Direction:
Conclusion:
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ladd, A.D.; Duarte, S.; Sahin, I.; Zarrinpar, A. Mechanisms of drug resistance in HCC. Hepatology 2023, 79, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshuizen, J.; Peeper, D.S. Rational Cancer Treatment Combinations: An Urgent Clinical Need. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 1002–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, S.; D'Angio, G.; Evans, A.; Mitus, A. CLINICAL STUDIES OF ACTINOMYCIN D WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO WILMS' TUMOR IN CHILDREN*. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1960, 89, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, E.; Karon, M.; Levin, R.H.; Freireich, E.J.; Taylor, R.J.; Hananian, J.; Selawry, O.; Holland, J.F.; Hoogstraten, B.; Wolman, I.J.; et al. The Effectiveness of Combinations of Antileukemic Agents in Inducing and Maintaining Remission in Children with Acute Leukemia. Blood 1965, 26, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Lau, G.; Kudo, M.; Chan, S.L.; Kelley, R.K.; Furuse, J.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Kang, Y.-K.; Van Dao, T.; De Toni, E.N.; et al. Tremelimumab plus Durvalumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. NEJM Évid. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
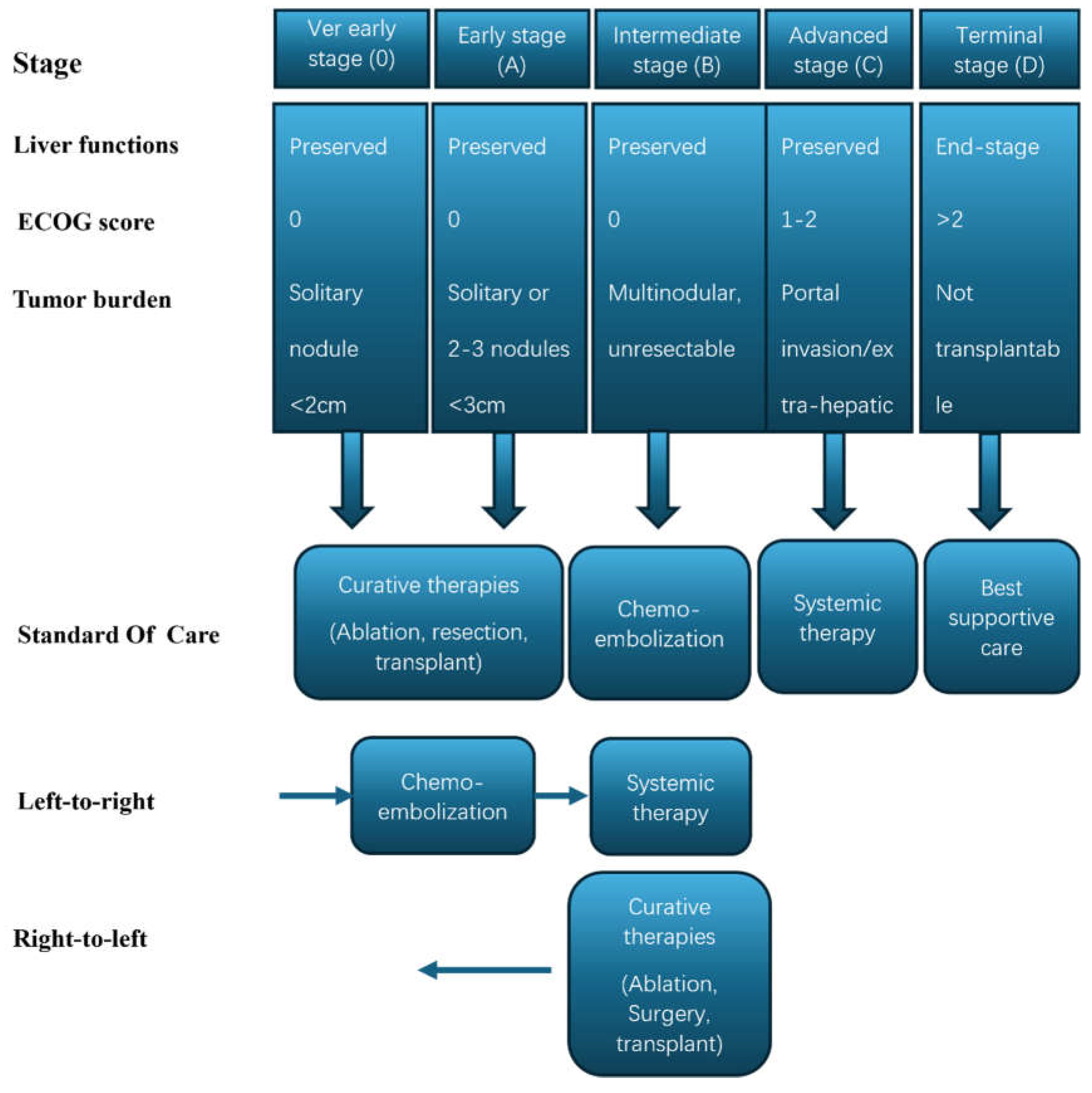
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisani, F.; Vitale, A.; Kudo, M.; Kulik, L.; Park, J.-W.; Pinato, D.J.; Cillo, U. Merits and boundaries of the BCLC staging and treatment algorithm: Learning from the past to improve the future with a novel proposal. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Kotwani, P.; Norman, J.; Shui, A.; Li, P.J.; Saxena, V.; Chan, W.; Yao, F.Y. AFP-L3 and DCP are superior to AFP in predicting waitlist dropout in HCC patients: Results of a prospective study. Liver Transplant. 2023, 29, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol, 2018. 69(1): p. 182-236.
- Hung, Y.-W.; Lee, I.-C.; Chi, C.-T.; Lee, R.-C.; Liu, C.-A.; Chiu, N.-C.; Hwang, H.-E.; Chao, Y.; Hou, M.-C.; Huang, Y.-H. Redefining Tumor Burden in Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Seven-Eleven Criteria. Liver Cancer 2021, 10, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, V.M.; Llovet, J.M.; Miceli, R.; Bhoori, S.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L.; Camerini, T.; Roayaie, S.; Schwartz, M.E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Predicting survival after liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: a retrospective, exploratory analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moris, D.; Shaw, B.I.; McElroy, L.; Barbas, A.S. Using Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumor Burden Score to Stratify Prognosis after Liver Transplantation. Cancers 2020, 12, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I Tsilimigras, D.; Moris, D.; Hyer, J.M.; Bagante, F.; Sahara, K.; Moro, A.; Paredes, A.Z.; Mehta, R.; Ratti, F.; Marques, H.P.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma tumour burden score to stratify prognosis after resection. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, A.; Lai, Q.; Farinati, F.; Bucci, L.; Giannini, E.G.; Napoli, L.; Ciccarese, F.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Di Marco, M.; Caturelli, E.; et al. Utility of Tumor Burden Score to Stratify Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Cancer: Results of 4759 Cases from ITA.LI.CA Study Group. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2018, 22, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K., D. Morioka, S. Conci, G.A. Margonis, Y. Sawada, A. Ruzzenente, et al., The Tumor Burden Score: A New "Metro-ticket" Prognostic Tool For Colorectal Liver Metastases Based on Tumor Size and Number of Tumors. Ann Surg, 2018. 267(1): p. 132-141.
- Jackson, R.; Psarelli, E.-E.; Berhane, S.; Khan, H.; Johnson, P. Impact of Viral Status on Survival in Patients Receiving Sorafenib for Advanced Hepatocellular Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Phase III Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, M.; Wu, H.; Deng, N.; Li, W.; Chen, J. Clinical study of lenvatinib in the treatment of hepatitis virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and antiviral therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 13, 1032881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.-L., S. Qin, M. Ikeda, P.R. Galle, M. Ducreux, T.-Y. Kim, et al., Updated efficacy and safety data from IMbrave150: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Hepatology, 2022. 76(4): p. 862-873.
- Pfister, D.; Núñez, N.G.; Pinyol, R.; Govaere, O.; Pinter, M.; Szydlowska, M.; Gupta, R.; Qiu, M.; Deczkowska, A.; Weiner, A.; et al. NASH limits anti-tumour surveillance in immunotherapy-treated HCC. Nature 2021, 592, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yao, Z.; Bai, H.; Duan, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Fei, K.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Treatment-related adverse events of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitor-based combination therapies in clinical trials: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, F.; Jiang, Y.; Ying, W.; Li, D.; Yang, D.; Xia, X.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; et al. A Cell-type-resolved Liver Proteome. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 3190–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.A.; Ganey, P.E.; Ju, C.; Kamendulis, L.M.; Rusyn, I.; Klaunig, J.E. Role of the Kupffer Cell in Mediating Hepatic Toxicity and Carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 96, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, C.S., K. Ban, H. Ithnin, H. Singh, R. Krishnan, S. Mokhtar, et al., Expression of interleukin-18, interferon-γ and interleukin-10 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunology Letters, 2002. 84(3): p. 163-172.
- Chen, J.; Zaidi, S.; Rao, S.; Chen, J.-S.; Phan, L.; Farci, P.; Su, X.; Shetty, K.; White, J.; Zamboni, F.; et al. Analysis of Genomes and Transcriptomes of Hepatocellular Carcinomas Identifies Mutations and Gene Expression Changes in the Transforming Growth Factor-β Pathway. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, F. and A. Mantovani, Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet, 2001. 357(9255): p. 539-45.
- Noy, R.; Pollard, J.W. Tumor-associated macrophages: From mechanisms to therapy. Immunity 2014, 41, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Shi, M.; Zhao, P.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; et al. Increased Regulatory T Cells Correlate With CD8 T-Cell Impairment and Poor Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2328–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-P.; Yan, J.; Xu, J.; Pang, X.-H.; Chen, M.-S.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Li, S.-P.; Zheng, L. Increased intratumoral IL-17-producing cells correlate with poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Gingold, J.A.; Su, X. Immunomodulatory TGF-β Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K.; Massagué, J. TGF-beta Inhibition and Immunotherapy: Checkmate. Immunity 2018, 48, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadzadeh, M.; Johnson, L.A.; Heemskerk, B.; Wunderlich, J.R.; Dudley, M.E.; White, D.E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Tumor antigen–specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood 2009, 114, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X. PD-1 and its ligands are important immune checkpoints in cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, L., J. Chen, H. Yan, Q. He, P. Luo, Z. Xu, et al., Research Status and Outlook of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2020. 14: p. 3625-3649.
- Buchbinder, E.; Hodi, F.S. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 and immune checkpoint blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3377–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A.D.; Skora, A.D.; Luber, B.S.; Azad, N.S.; Laheru, D.; et al. PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; van der Merwe, P.A.; Sivakumar, S. Biomarkers of response to PD-1 pathway blockade. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samstein, R.M.; Lee, C.-H.; Shoushtari, A.N.; Hellmann, M.D.; Shen, R.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Barron, D.A.; Zehir, A.; Jordan, E.J.; Omuro, A.; et al. Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M., S. Ricci, V. Mazzaferro, P. Hilgard, E. Gane, J.F. Blanc, et al., Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 2008. 359(4): p. 378-90.
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H., 3rd; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Edeline, J.; Cattan, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Palmer, D.; Verslype, C.; Zagonel, V.; Fartoux, L.; Vogel, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): A non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Merle, P.; Kudo, M.; Bouattour, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Breder, V.; Edeline, J.; Chao, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab As Second-Line Therapy in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, P.K.; Castet, F.; Torres-Martin, M.; Andreu-Oller, C.; Puigvehí, M.; Miho, M.; Radu, P.; Dufour, J.-F.; Verslype, C.; Zimpel, C.; et al. Molecular Markers of Response to Anti-PD1 Therapy in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Răileanu, M.; Straticiuc, M.; Iancu, D.-A.; Andrei, R.-F.; Radu, M.; Bacalum, M. Proton irradiation induced reactive oxygen species promote morphological and functional changes in HepG2 cells. J. Struct. Biol. 2022, 214, 107919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Krishnan, S.; Zhang, X.; Dong, L.; Briere, T.; Crane, C.H.; Martel, M.; Gillin, M.; Mohan, R.; Beddar, S. Proton Radiotherapy for Liver Tumors: Dosimetric Advantages Over Photon Plans. Med Dosim. 2007, 33, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, D.A.; Kayali, Z.; Grove, R.; Slater, J.D. The safety and efficacy of high-dose proton beam radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase 2 prospective trial. Cancer 2011, 117, 3053–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, B.; Park, J.-W. Proton beam radiotherapy vs. radiofrequency ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomized phase III trial. J. Hepatol. 2020, 74, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohri, N., W. A. Tomé, A. Méndez Romero, M. Miften, R.K. Ten Haken, L.A. Dawson, et al., Local Control After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Liver Tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2021. 110(1): p. 188-195.
- Kimura, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Kameoka, T.; Adachi, Y.; Kariya, S. The Current Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Cancers 2022, 14, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulik, L.; Heimbach, J.K.; Zaiem, F.; Almasri, J.; Prokop, L.J.; Wang, Z.; Murad, M.H.; Mohammed, K. Therapies for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma awaiting liver transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 67, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Kameoka, T.; Adachi, Y.; Kariya, S. The Current Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Cancers 2022, 14, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.H.-F., V. Vardhanabhuti, T.C.-L. Wong, K.-O. Lam, H.C.-W. Choi, K.W.-H. Chiu, et al., Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy and Liver Transplant for Liver Cancer: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Network Open, 2024. 7(6): p. e2415998-e2415998.
- Chen, Y.; Yang, P.; Du, S.; Zhou, J.; Huang, C.; Zhu, W.; Hu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zeng, Z. A phase II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) combined with sintilimab in patients with recurrent or oligometastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 4071–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, L.A.; Winter, K.A.; Knox, J.J.; Zhu, A.X.; Krishnan, S.; Guha, C.; Kachnic, L.A.; Gillin, M.; Hong, T.S.; Craig, T.; et al. NRG/RTOG 1112: Randomized phase III study of sorafenib vs. stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) followed by sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 489–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.S.; Sohn, D.H. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Inflammatory Diseases. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.; Baird, J.R.; Young, K.H.; Cottam, B.; Crittenden, M.R.; Friedman, S.; Gough, M.J.; Newell, P. Programmed cell death-1 blockade enhances response to stereotactic radiation in an orthotopic murine model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 47, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, H. , Abscopal effect of stereotactic radiotherapy combined with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy: Mechanisms, clinical efficacy, and issues. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2020. 40(12): p. 649-654.
- Garelli, E.; Rittmeyer, A.; Putora, P.M.; Glatzer, M.; Dressel, R.; Andreas, S. Abscopal Effect in Lung Cancer: Three Case Reports and a Concise Review. Immunotherapy 2019, 11, 1445–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juloori, A.; Katipally, R.R.; Lemons, J.M.; Singh, A.K.; Iyer, R.; Robbins, J.R.; George, B.; Hall, W.A.; Pitroda, S.P.; Arif, F.; et al. Phase 1 Randomized Trial of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Followed by Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone in Advanced/Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 115, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-L.; Chiu, K.W.-H.; Lee, F.A.-S.; Kong, F.-M.S.; Chan, A.C.-Y. Combined Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy Versus Transarterial Chemoembolization in Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 798832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-X.; Su, T.-S.; Gong, W.-F.; Zhong, J.-H.; Yan, L.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.-Q.; He, M.-L.; Zhang, R.-J.; Du, Y.-Q.; et al. Combining stereotactic body radiotherapy with camrelizumab for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm trial. Hepatol. Int. 2022, 16, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hong, H.; Fang, W.; Zhang, X.; Luo, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, J.; Fan, W.; Chi, X.; Peng, Y. Toripalimab in combination with Anlotinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma after SBRT: A prospective, single-arm, single-center clinical study. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1113389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F. and T.F. Greten, Gut microbiome in HCC - Mechanisms, diagnosis and therapy. J Hepatol, 2020. 72(2): p. 230-238.
- Ning, C., X. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Yang, X. Yang, J. Chao, et al., Radiation Therapy With Combination Therapy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Antiangiogenic Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 2024. 118(5): p. 1461-1471.
- Kwon, J.H.; Bae, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, B.O.; Jang, H.S.; Jang, J.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K.; Chung, K.W. Long-term effect of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma ineligible for local ablation therapy or surgical resection. Stereotactic radiotherapy for liver cancer. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 475–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.H.; Shim, J.H.; Ko, H.-K.; Chu, H.H.; Shin, J.H.; Yoon, H.-K.; Ko, G.-Y.; Gwon, D.I. Chemoembolization for Single Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Preserved Liver Function: Analysis of Factors Predicting Clinical Outcomes in a 302 Patient Cohort. Life 2021, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.-C.; Chang, W.-C.; Lo, C.-H.; Yang, J.-F.; Lee, M.-S.; Dai, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Fan, C.-Y.; Huang, W.-Y. Comparison of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Medium-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 105, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujold, A.; Massey, C.A.; Kim, J.J.; Brierley, J.; Cho, C.; Wong, R.K.; Dinniwell, R.E.; Kassam, Z.; Ringash, J.; Cummings, B.; et al. Sequential Phase I and II Trials of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerum, S.; Heinz, C.; Belka, C.; Walter, F.; Paprottka, P.; De Toni, E.N.; Roeder, F. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and oligometastatic liver disease. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, E.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Han, F.; Huang, H.; Liang, P.; Liu, J.; Wu, F.; et al. Efficacy of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Recurrent or Residual Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Yang, P.; Du, S.-S.; Zhuang, Y.; Huang, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, W.-C.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Liu, T.-S.; Zeng, Z.-C. Stereotactic body radiotherapy combined with sintilimab in patients with recurrent or oligometastatic hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase II clinical trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 3871–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Xu, B.; Hu, X.; Su, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yue, J.; Yu, J. Peripheral memory and naïve T cells in non-small cell lung cancer patients with lung metastases undergoing stereotactic body radiotherapy: predictors of early tumor response. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Combination therapy | Target | Indication | FDA approval date | ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | PD-1 + CTLA-4 | HCC who has been previously treated with sorafenib | March 10, 2020 | Cohort 4 of CHECKMATE-040 (NCT01658878) |
| Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab | PDL-1 + VEGF | unresectable or metastatic HCC who have not received prior systemic therapy | May 29, 2020 | IMbrave150 (NCT03434379) |
| Durvalumab + Tremelimumab | PDL-1 + CTLA4 | unresectable HCC | October 21, 2022 | HIMALAYA (NCT03298451) |
| ICI | SBRT dose | Regimen | Study Phase | 1ry endpoint | ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atezolizumab and bevacizumab | N/A | Atezolizumab on day 1 of two study cycles (21 days/cycle) and Bevacizumab 1x weekly for 2 study cycles | I | Proportion of patients with grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse events (TRAE) | NCT04857684 | Recruiting |
| Tislelizumab | 8 Gy × 3 fractions | SBRT (day 1,3,5) and Tislelizumab (day 1, 22, 50) | I | Delay to surgery, ORR, pathologic response rate, TRAE | NCT05185531 | Active, not recruiting |
| Sintilimab | 30-54 Gy in 3-6 fractions | SBRT (1-2 weeks) then Sintilimab (200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 1 year) 4-6 weeks after completion of SBRT | I | 24 week PFS rate | NCT04167293 | Unknown |
| Durvalumab and Tremelimumab |
N/A | Sequential administration of TACE and SBRT followed by Immunotherapy | II | Downstaging for hepatectomy | NCT04988945 | Recruiting |
| Tislelizumab and regorafenib | 8 Gy × 3-5 fractions | Tislelizumab 200mg every 21 days, and regorafenib 120mg for the first 21 days of a 28-day cycle, concurrently with SBRT to all visible lesions | II | PFS | NCT05917431 | Recruiting |
| Pembrolizumab and lenvatinib | Five-fraction SBRT (week 4-week 5) | Pembrolizumab 200mg every 3 weeks and lenvatinib 12/8 mg/day for 96 weeks, plus SBRT to the portal vein thrombus and adjacent HCC | Ib/II | Safety rate, ORR |
NCT05286320 | Not yet recruiting |
| Adebrelimab and Lenvatinib | 33-48 Gy in 6 fractions over 2 weeks | SBRT followed by lenvatinib (12 mg/day) orally once daily in combination with adebrelimab 1200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles. | II | PFS | NCT06261125 | Recruiting |
| Durvalumab and Tremelimumab | N/A | Arm I (hypofractionated RT, durvalumab) Arm II (hypofractionated RT, durvalumab, tremelimumab) |
II | ORR | NCT04430452 | Recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





