Submitted:
24 July 2024
Posted:
26 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
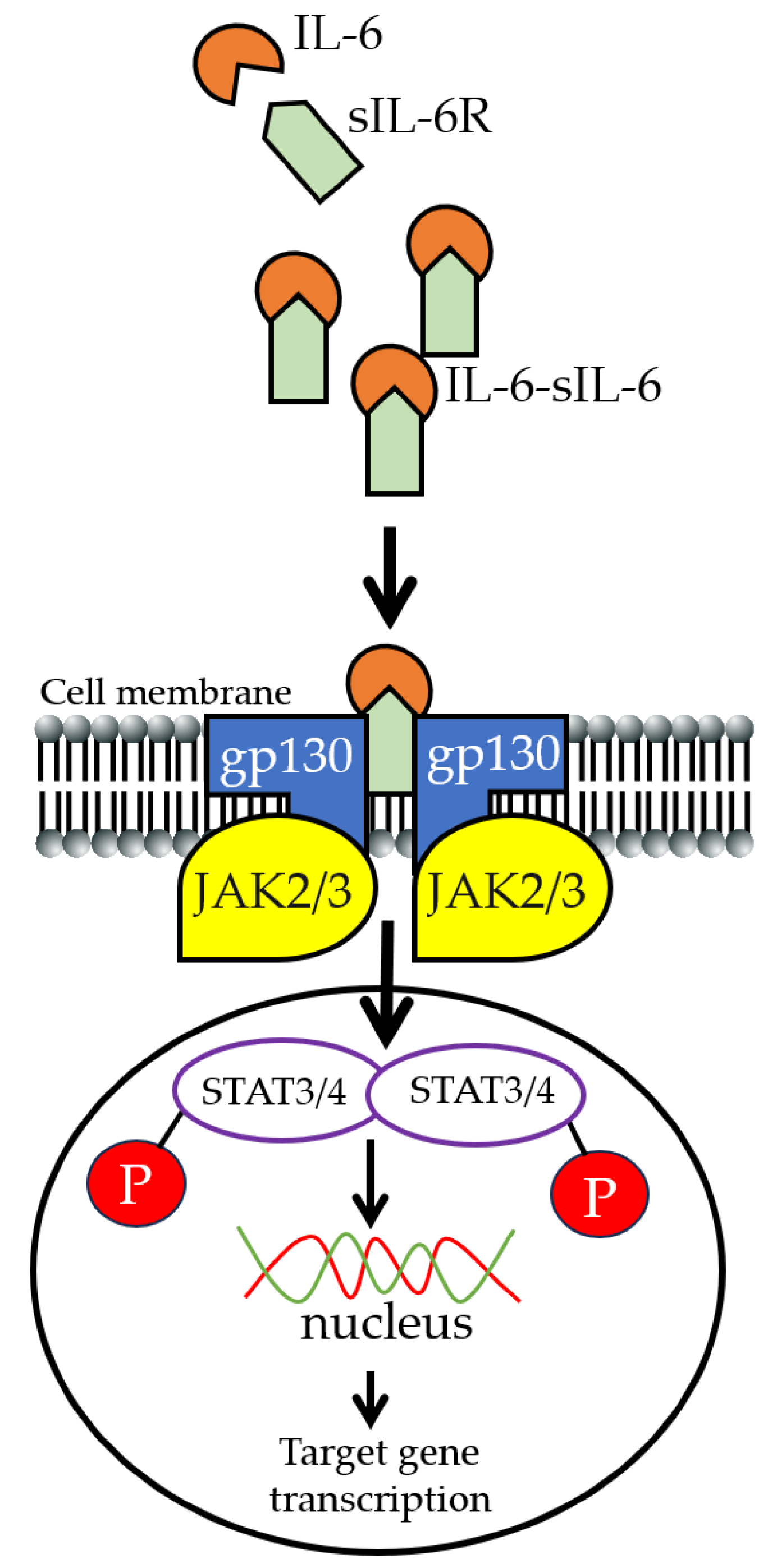
2. IL-6 Signaling
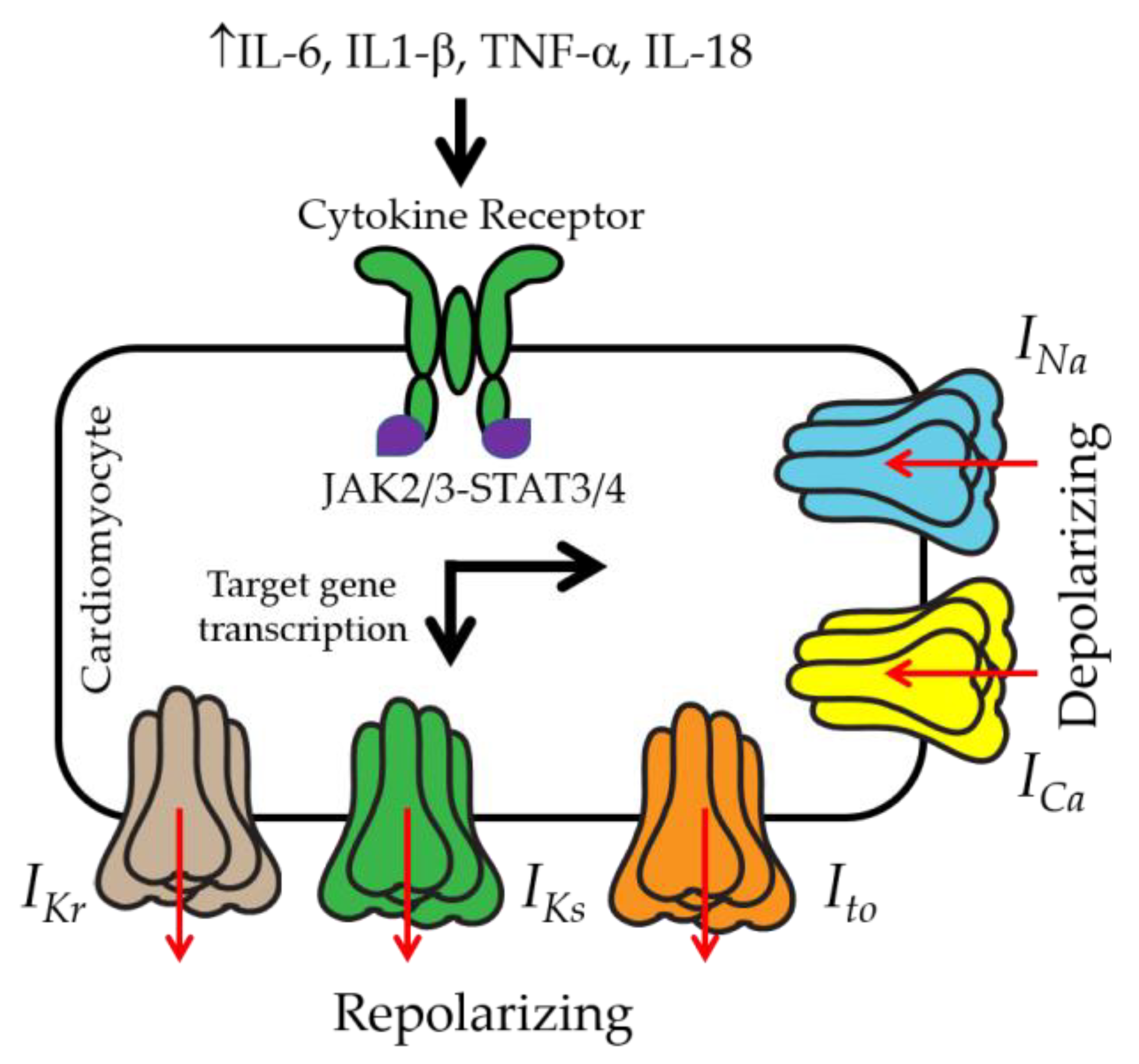
3. IL-6 and Ventricular Electrical Activity
4. Anti-IL-6 Inhibitors
5. Importance of Preclinical Models for Studying IL-6 Trans-Signaling
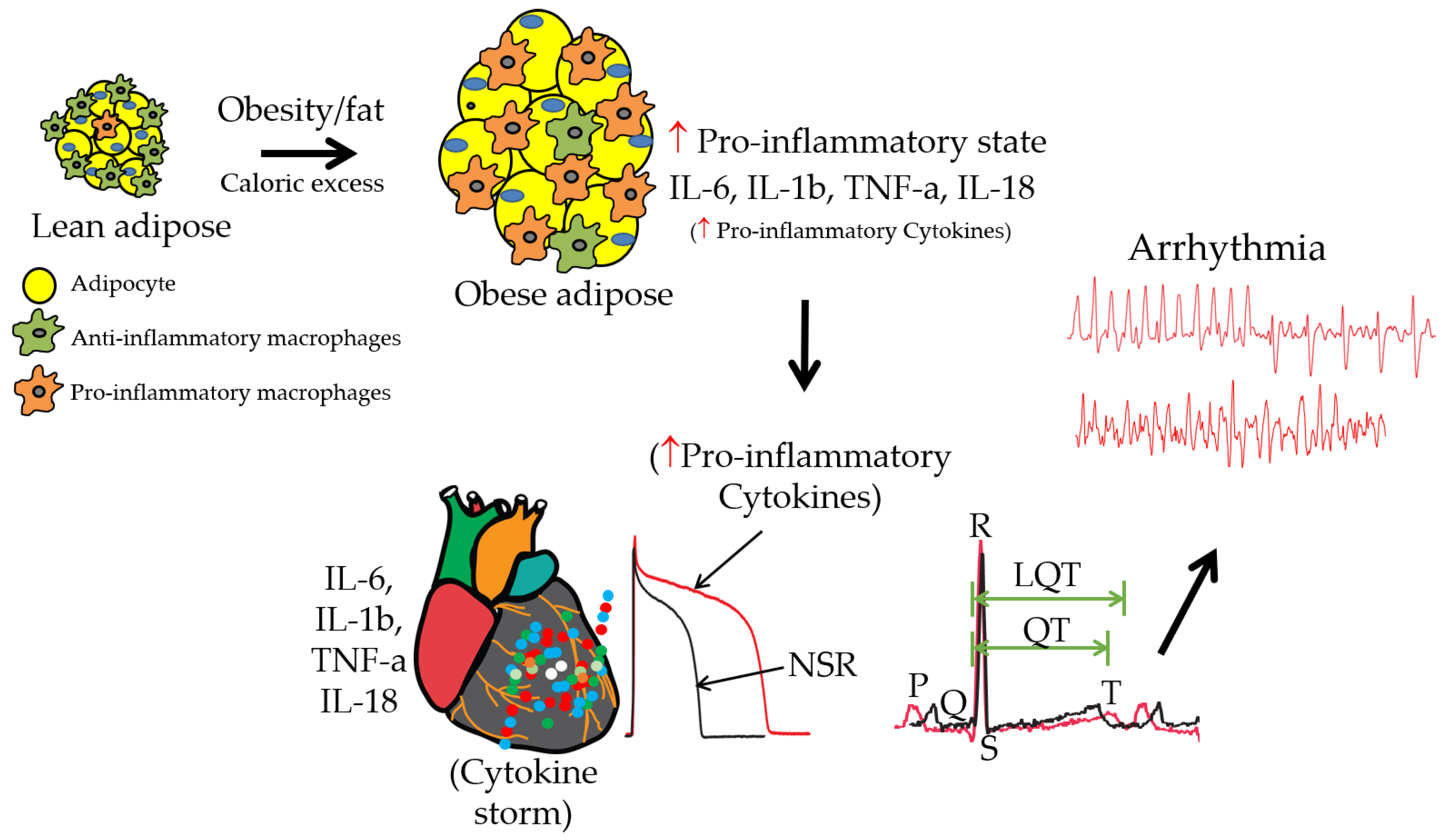
6. Insights into Significant Knowledge Gaps and Future Directions in Obesity, Inflammation, and Ventricular Arrhythmias
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nonstandard Abbreviations and Acronyms | |
| TCZ | Tocilizumab |
| IKr | Rapidly activating delayed rectifier K current |
| IKs | Slowly activating delayed rectifier K current |
| INa | Sodium current |
| ICa,L | L-type Ca current |
| IK1 | Inwardly rectifying K current |
| LQT | Long QT |
| QTc | QT interval corrected for heart rate |
| FFAs | Free fatty acids |
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| hERG | Human ether-á-go-go-related gene |
| HEK | Human embryonic kidney |
| ERG | Ether-á-go-go-related gene |
| APD | Action potential duration |
| EAT | Epicardial adipose tissue |
| SCD | Sudden cardiac death |
| VF | Ventricular fibrillation |
| VT | Ventricular tachycardia |
| PC | Purkinje cells |
References
- Srinivasan, N. T.; Schilling, R. J., Sudden Cardiac Death and Arrhythmias. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev 2018, 7, (2), 111-117. [CrossRef]
- Chugh, S. S.; Reinier, K.; Teodorescu, C.; Evanado, A.; Kehr, E.; Al Samara, M.; Mariani, R.; Gunson, K.; Jui, J. , Epidemiology of Sudden Cardiac Death: Clinical and Research Implications. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases 2008, 51(3), 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huikuri, H. V.; Castellanos, A.; Myerburg, R. J. , Sudden death due to cardiac arrhythmias. N Engl J Med 2001, 345(20), 1473–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podrid, P. J.; Myerburg, R. J., Epidemiology and stratification of risk for sudden cardiac death. Clin Cardiol 2005, 28, (11 Suppl 1), I3-11. [CrossRef]
- Kallergis, E. M.; Goudis, C. A.; Simantirakis, E. N.; Kochiadakis, G. E.; Vardas, P. E., Mechanisms, Risk Factors, and Management of Acquired Long QT Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. The Scientific World Journal 2012, 2012, 212178. [CrossRef]
- Drew, B. J.; Ackerman, M. J.; Funk, M.; Gibler, W. B.; Kligfield, P.; Menon, V.; Philippides, G. J.; Roden, D. M.; Zareba, W.; American Heart Association Acute Cardiac Care Committee of the Council on Clinical, C.; Council on Cardiovascular, N.; American College of Cardiology, F., Prevention of torsade de pointes in hospital settings: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology Foundation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010, 55, (9), 934-47.
- Lazzerini, P. E.; Capecchi, P. L.; Laghi-Pasini, F.; Boutjdir, M., Autoimmune channelopathies as a novel mechanism in cardiac arrhythmias. Nat Rev Cardiol 2017. [CrossRef]
- Pietrasik, G.; Goldenberg, I.; McNitt, S.; Moss, A. J.; Zareba, W., Obesity as a risk factor for sustained ventricular tachyarrhythmias in MADIT II patients. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2007, 18, (2), 181-4. [CrossRef]
- Sabbag, A.; Goldenberg, I.; Moss, A. J.; McNitt, S.; Glikson, M.; Biton, Y.; Jackson, L.; Polonsky, B.; Zareba, W.; Kutyifa, V., Predictors and Risk of Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias or Death in Black and White Cardiac Patients: A MADIT-CRT Trial Substudy. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 2016, 2, (4), 448-455.
- Sabbag, A.; Sidi, Y.; Kivity, S.; Beinart, R.; Glikson, M.; Segev, S.; Goldenberg, I.; Maor, E., Obesity and exercise-induced ectopic ventricular arrhythmias in apparently healthy middle aged adults. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2016, 23, (5), 511-7. [CrossRef]
- Remme, C. A., Sudden Cardiac Death in Diabetes and Obesity: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Can J Cardiol 2022, 38, (4), 418-426. [CrossRef]
- Mukerji, R.; Terry, B. E.; Fresen, J. L.; Petruc, M.; Govindarajan, G.; Alpert, M. A., Relation of left ventricular mass to QTc in normotensive severely obese patients. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012, 20, (9), 1950-4. [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T. M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L. E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C. J.; Lear, S. A.; Ndumele, C. E.; Neeland, I. J.; Sanders, P.; St-Onge, M.-P., Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, (21), e984-e1010. [CrossRef]
- Hookana, E.; Junttila, M. J.; Puurunen, V. P.; Tikkanen, J. T.; Kaikkonen, K. S.; Kortelainen, M. L.; Myerburg, R. J.; Huikuri, H. V., Causes of nonischemic sudden cardiac death in the current era. Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, (10), 1570-5. [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A. A.; Gottdiener, J. S.; Bartz, T. M.; Sotoodehnia, N.; DeFilippi, C.; See, V.; Deo, R.; Siscovick, D.; Stein, P. K.; Lloyd-Jones, D. , Inflammation and sudden cardiac death in a community-based population of older adults: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Heart Rhythm 2013, 10(10), 1425-32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hales, C. M.; Carroll, M. D.; Fryar, C. D.; Ogden, C. L., Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017-2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020, (360), 1-8.
- Hubert, H. B.; Feinleib, M.; McNamara, P. M.; Castelli, W. P. , Obesity as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a 26-year follow-up of participants in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1983, 67, (5), 968–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F. B. , The Epidemiology of Obesity: A Big Picture. Pharmacoeconomics 2015, 33, (7), 673–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P. W.; D’Agostino, R. B.; Sullivan, L.; Parise, H.; Kannel, W. B. , Overweight and obesity as determinants of cardiovascular risk: the Framingham experience. Arch Intern Med 2002, 162, (16), 1867–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ades, P. A.; Savage, P. D. , Obesity in coronary heart disease: An unaddressed behavioral risk factor. Prev Med 2017, 104, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, S. M.; Lee, G.; Jeong, S.-M.; Park, S. Y.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Son, J. S.; Yun, J.-M.; Park, S. M. , Association of Obesity or Weight Change With Coronary Heart Disease Among Young Adults in South Korea. JAMA Internal Medicine 2018, 178, (8), 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebong, I. A.; Goff, D. C.; Rodriguez, C. J.; Chen, H.; Bertoni, A. G. , Mechanisms of heart failure in obesity. Obes Res Clin Pract 2014, 8(6), e540–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semsarian, C.; Ingles, J. , Molecular autopsy in victims of inherited arrhythmias. J Arrhythm 2016, 32(5), 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khatib, S. M.; Stevenson, W. G.; Ackerman, M. J.; Bryant, W. J.; Callans, D. J.; Curtis, A. B.; Deal, B. J.; Dickfeld, T.; Field, M. E.; Fonarow, G. C.; et al. , 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for Management of Patients With Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation 2018, 138(13), e272–e391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kien, C. L.; Bunn, J. Y.; Ugrasbul, F. , Increasing dietary palmitic acid decreases fat oxidation and daily energy expenditure. Am J Clin Nutr 2005, 82(2), 320–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T. S.; Goldberg, I. J. , Sphingolipids, lipotoxic cardiomyopathy, and cardiac failure. Heart Fail Clin 2012, 8, (4), 633–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haim, T. E.; Wang, W.; Flagg, T. P.; Tones, M. A.; Bahinski, A.; Numann, R. E.; Nichols, C. G.; Nerbonne, J. M. , Palmitate attenuates myocardial contractility through augmentation of repolarizing Kv currents. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2010, 48(2), 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Redfors, B.; Stahlman, M.; Tang, M. S.; Miljanovic, A.; Mollmann, H.; Troidl, C.; Szardien, S.; Hamm, C.; Nef, H.; Boren, J.; Omerovic, E. , A mouse model reveals an important role for catecholamine-induced lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of stress-induced cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail 2013, 15(1), 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, R. P.; Musa, H.; Gomez, M. S.; Avula, U. M.; Herron, T. J.; Kalifa, J.; Anumonwo, J. M. , Free Fatty Acid Effects on the Atrial Myocardium: Membrane Ionic Currents Are Remodeled by the Disruption of T-Tubular Architecture. PLoS One 2015, 10(8), e0133052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromolaran, A. S.; Colecraft, H. M.; Boutjdir, M. , High-fat diet-dependent modulation of the delayed rectifier K(+) current in adult guinea pig atrial myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 474(3), 554–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anumonwo, J. M. B.; Herron, T. , Fatty Infiltration of the Myocardium and Arrhythmogenesis: Potential Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Ye, D.; Wang, Z.; Pan, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Xu, S.; Pan, W.; Yin, Z.; Ye, J.; Wan, J. , The Role of Interleukin-6 Family Members in Cardiovascular Diseases. Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine 2022, 9, 818890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromolaran, A. S.; Srivastava, U.; Ali, A.; Chahine, M.; Lazaro, D.; El-Sherif, N.; Capecchi, P. L.; Laghi-Pasini, F.; Lazzerini, P. E.; Boutjdir, M. , Interleukin-6 inhibition of hERG underlies risk for acquired long QT in cardiac and systemic inflammation. PLoS One 2018, 13(12), e0208321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M. K. H.; Martinez-Mateu, L.; Do, J.; Aromolaran, K. A.; Saiz, J.; Aromolaran, A. S. , Macrophage-Dependent Interleukin-6-Production and Inhibition of I(K) Contributes to Acquired QT Prolongation in Lipotoxic Guinea Pig Heart. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22(20). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, K. T.; Chang, C. Y.; Chang, L. F.; Nesaretnam, K. , Modulation of obesity-induced inflammation by dietary fats: mechanisms and clinical evidence. Nutr J 2014, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P. M.; Libby, P.; MacFadyen, J. G.; Thuren, T.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Koenig, W.; Shimokawa, H.; Everett, B. M.; Glynn, R. J. , Modulation of the interleukin-6 signalling pathway and incidence rates of atherosclerotic events and all-cause mortality: analyses from the Canakinumab Anti-Inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS). Eur Heart J 2018, 39(38), 3499–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. , The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011, 1813(5), 878–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancey, C.; Corbi, P.; Froger, J.; Delwail, A.; Wijdenes, J.; Gascan, H.; Potreau, D.; Lecron, J. C. , Secretion of IL-6, IL-11 and LIF by human cardiomyocytes in primary culture. Cytokine 2002, 18(4), 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zheng, R.; Hu, S.; Ma, Y.; Choudhry, M. A.; Messina, J. L.; Rue, L. W., 3rd; Bland, K. I.; Chaudry, I. H. , Mechanism of cardiac depression after trauma-hemorrhage: increased cardiomyocyte IL-6 and effect of sex steroids on IL-6 regulation and cardiac function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2004, 287(5), H2183–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lust, J. A.; Donovan, K. A.; Kline, M. P.; Greipp, P. R.; Kyle, R. A.; Maihle, N. J. , Isolation of an mRNA encoding a soluble form of the human interleukin-6 receptor. Cytokine 1992, 4(2), 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. , IL-6 trans-signaling via the soluble IL-6 receptor: importance for the pro-inflammatory activities of IL-6. International journal of biological sciences 2012, 8(9), 1237–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S.; Jenkins, B. J.; Garbers, C.; Moll, J. M.; Scheller, J. , Targeting IL-6 trans-signalling: past, present and future prospects. Nat Rev Immunol 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. , Gp130 and the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annual review of immunology 1997, 15, 797–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, J. A.; Rose, N. R.; Cihakova, D. , The varying faces of IL-6: From cardiac protection to cardiac failure. Cytokine 2015, 74(1), 62–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaboration, I. R. G. C. E. R. F.; Sarwar, N.; Butterworth, A. S.; Freitag, D. F.; Gregson, J.; Willeit, P.; Gorman, D. N.; Gao, P.; Saleheen, D.; Rendon, A.; et al. , Interleukin-6 receptor pathways in coronary heart disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 82 studies. Lancet 2012, 379(9822), 1205–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Isshiki, H.; Sugita, T.; Tanabe, O.; Kinoshita, S.; Nishio, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T. , A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. Embo j 1990, 9(6), 1897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Nishio, Y.; Inoue, M.; Wang, X. J.; Wei, S.; Matsusaka, T.; Yoshida, K.; Sudo, T.; Naruto, M.; Kishimoto, T. , Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell 1994, 77(1), 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Hirata, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Minamoto, S.; Aono, A.; Nishimoto, N.; Kajita, T.; Taga, T.; Yoshizaki, K.; Akira, S.; Kishimoto, T. , Structure and function of a new STAT-induced STAT inhibitor. Nature 1997, 387(6636), 924–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner-Klein, M.; Grujovic, A.; Irlbeck, C.; Obradović, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Koerkel-Qu, H.; Lu, X.; Treitschke, S.; Köstler, C.; Botteron, C.; et al. , Interleukin-6 trans-signaling is a candidate mechanism to drive progression of human DCCs during clinical latency. Nature Communications 2020, 11(1), 4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. , The Soluble Interleukin 6 Receptor: Advanced Therapeutic Options in Inflammation. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2017, 102(4), 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Wen, Z.; Darnell, J. E. , Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science 1994, 264(5155), 95–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J. E., Jr., STATs and gene regulation. Science 1997, 277, (5332), 1630-5. [CrossRef]
- Horvath, C. M.; Darnell, J. E. , The state of the STATs: recent developments in the study of signal transduction to the nucleus. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1997, 9(2), 233–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imada, K.; Leonard, W. J. , The Jak-STAT pathway. Mol Immunol 2000, 37(1-2), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, O. P.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. , Interleukin-6 and diabetes: the good, the bad, or the indifferent? Diabetes 2005, 54 Suppl 2, S114–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, C. M.; Hövelmeyer, N.; Wunderlich, F. T. , Mechanisms of chronic JAK-STAT3-SOCS3 signaling in obesity. JAK-STAT 2013, 2(2), e23878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galic, S.; Sachithanandan, N.; Kay, T. W.; Steinberg, G. R. , Suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS) proteins as guardians of inflammatory responses critical for regulating insulin sensitivity. Biochem J 2014, 461(2), 177–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadsworth, P. A.; Singh, A. K.; Nguyen, N.; Dvorak, N. M.; Tapia, C. M.; Russell, W. K.; Stephan, C.; Laezza, F. , JAK2 regulates Nav1.6 channel function via FGF14(Y158) phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2020, 1867(10), 118786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yu, H. , Identification of WP1066, an inhibitor of JAK2 and STAT3, as a K(V) 1.3 potassium channel blocker. Br J Pharmacol 2021, 178(13), 2617–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, Z.; Almilaji, A.; Honisch, S.; Pakladok, T.; Liu, G.; Bhavsar, S. K.; Ruth, P.; Shumilina, E.; Lang, F. , Upregulation of the large conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channels by Janus kinase 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2014, 306(11), C1041–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, Z.; Bhavsar, S. K.; Lang, F. , Downregulation of ClC-2 by JAK2. Cell Physiol Biochem 2012, 29(5-6), 737–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, Z.; Luo, D.; Sopjani, M.; Bhavsar, S. K.; Lang, F. , Down-regulation of the epithelial Na(+) channel ENaC by Janus kinase 2. J Membr Biol 2014, 247(4), 331–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Hosseinzadeh, Z.; Zhang, B.; Froeschl, M.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Stournaras, C.; Lang, F. , Decrease of Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry and Increase of Na+/Ca2+ Exchange by Pharmacological JAK2 Inhibition. Cell Physiol Biochem 2016, 38(2), 683–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.; Zhang, W.; Karle, C. A.; Kathofer, S.; Schols, W.; Kubler, W.; Kiehn, J. , Deletion of protein kinase A phosphorylation sites in the HERG potassium channel inhibits activation shift by protein kinase A. J Biol Chem 1999, 274(39), 27457–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Melman, Y.; Palma, E.; Fishman, G. I.; McDonald, T. V. , Cyclic AMP regulates the HERG K(+) channel by dual pathways. Curr Biol 2000, 10(11), 671–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockerill, S. L.; Tobin, A. B.; Torrecilla, I.; Willars, G. B.; Standen, N. B.; Mitcheson, J. S. , Modulation of hERG potassium currents in HEK-293 cells by protein kinase C. Evidence for direct phosphorylation of pore forming subunits. J Physiol 2007, 581 Pt 2, 479–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, L.; Xu, Y. , Different protein kinase C isoenzymes mediate inhibition of cardiac rapidly activating delayed rectifier K(+) current by different G-protein coupled receptors. Br J Pharmacol 2017, 174(23), 4464–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WU, L.-M.; UEDA, K.; HIRANO, Y.; FURUKAWA, T.; HIRAOKA, M. , HERG POTASSIUM CHANNEL IS REGULATED BY PROTEIN TYROSINE KINASE (PTK) IN HUMAN EMBRYONIC KIDNEY CELLS. In Advances in Electrocardiology 2004, pp 54-56.
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, H.; Zhang, D.; Fan, X.; Du, X.; Gamper, N.; Zhang, H. , Transcriptional Regulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels Contributes to GM-CSF-Induced Pain. J Neurosci 2019, 39(26), 5222–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Gao, Y.; Shi, J. , Regulation of TRPM7 Function by IL-6 through the JAK2-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, (3), e0152120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koglin, J.; Glysing-Jensen, T.; Gadiraju, S.; Russell, M. E. , Attenuated Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy in Mice With Targeted Deletion of the Transcription Factor STAT4. Circulation 2000, 101(9), 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenungsson, E.; Gustafsson, J.; Leonard, D.; Sandling, J.; Gunnarsson, I.; Nordmark, G.; Jönsen, A.; Bengtsson, A. A.; Sturfelt, G.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Elvin, K.; Sundin, U.; Garnier, S.; Simard, J. F.; Sigurdsson, S.; Padyukov, L.; Syvänen, A.-C.; Rönnblom, L. , A STAT4 risk allele is associated with ischaemic cerebrovascular events and anti-phospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Annals of the rheumatic diseases 2010, 69(5), 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinert, C.; Gembardt, F.; Böhme, I.; Tetzner, A.; Wieland, T.; Greenberg, B.; Walther, T. , Identification of intracellular proteins and signaling pathways in human endothelial cells regulated by angiotensin-(1–7). Journal of Proteomics 2016, 130, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, M. J.; Shakespear, M. R.; Kamal, N. A.; Fairlie, D. P. , HDAC inhibitors: modulating leukocyte differentiation, survival, proliferation and inflammation. Immunol Cell Biol 2012, 90(1), 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakespear, M. R.; Halili, M. A.; Irvine, K. M.; Fairlie, D. P.; Sweet, M. J. , Histone deacetylases as regulators of inflammation and immunity. Trends Immunol 2011, 32(7), 335–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z. Z.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y.; Yin, H. M.; Zhang, C. Y.; Su, D.; Yan, L. F.; Gu, A. H.; Zhou, Y. , The pro-inflammatory signalling regulator Stat4 promotes vasculogenesis of great vessels derived from endothelial precursors. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 14640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R. L.; Potthoff, M. J.; Haberland, M.; Qi, X.; Matsuzaki, S.; Humphries, K. M.; Richardson, J. A.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E. N. , Maintenance of cardiac energy metabolism by histone deacetylase 3 in mice. J Clin Invest 2008, 118(11), 3588–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Singh, N.; Mullican, S. E.; Everett, L. J.; Li, L.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X.; Epstein, J. A.; Lazar, M. A. , Diet-induced lethality due to deletion of the Hdac3 gene in heart and skeletal muscle. The Journal of biological chemistry 2011, 286, (38), 33301–33309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraviglia, V.; Alcalde, M.; Campuzano, O.; Bellin, M. , Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: Secondary Event or Active Driver? Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine 2021, 8, 784715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerbonne, J. M.; Kass, R. S. , Molecular physiology of cardiac repolarization. Physiol Rev 2005, 85(4), 1205–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bers, D. M.; Despa, S. , Na+ transport in cardiac myocytes; Implications for excitation-contraction coupling. IUBMB life 2009, 61(3), 215–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varro, A.; Nanasi, P. P.; Lathrop, D. A. , Potassium currents in isolated human atrial and ventricular cardiocytes. Acta Physiol Scand 1993, 149(2), 133–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aromolaran, A. S.; Subramanyam, P.; Chang, D. D.; Kobertz, W. R.; Colecraft, H. M. , LQT1 mutations in KCNQ1 C-terminus assembly domain suppress IKs using different mechanisms. Cardiovasc Res 2014, 104(3), 501–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puckerin, A.; Aromolaran, K. A.; Chang, D. D.; Zukin, R. S.; Colecraft, H. M.; Boutjdir, M.; Aromolaran, A. S. , hERG 1a LQT2 C-terminus truncation mutants display hERG 1b-dependent dominant negative mechanisms. Heart Rhythm 2016, 13(5), 1121–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, E. P.; Yuan, C.; Navedo, M. F.; Dixon, R. E.; Nieves-Cintron, M.; Scott, J. D.; Santana, L. F. , Restoration of normal L-type Ca2+ channel function during Timothy syndrome by ablation of an anchoring protein. Circ Res 2011, 109(3), 255–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wit, A. L. , Afterdepolarizations and triggered activity as a mechanism for clinical arrhythmias. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2018. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R. D.; Kumar, S.; Kalman, J. M.; Sanders, P.; Sacher, F.; Hocini, M.; Jais, P.; Haisaguerre, M.; Lee, G. , Sudden Cardiac Death and Ventricular Arrhythmias: State of the Art in 2018-2019: Chapter 13: Catheter Ablation of Ventricular Fibrillation. Heart Lung Circ 2018.
- Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Xiao, P. , Associations between common ion channel single nucleotide polymorphisms and sudden cardiac death in adults: A MOOSE-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97(38), e12428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubeddu, L. X. , Drug-induced Inhibition and Trafficking Disruption of ion Channels: Pathogenesis of QT Abnormalities and Drug-induced Fatal Arrhythmias. Curr Cardiol Rev 2016, 12(2), 141–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medenwald, D.; Kors, J. A.; Loppnow, H.; Thiery, J.; Kluttig, A.; Nuding, S.; Tiller, D.; Greiser, K. H.; Werdan, K.; Haerting, J. , Inflammation and prolonged QT time: results from the Cardiovascular Disease, Living and Ageing in Halle (CARLA) study. PLoS One 2014, 9(4), e95994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzerini, P. E.; Acampa, M.; Capecchi, P. L.; Fineschi, I.; Selvi, E.; Moscadelli, V.; Zimbone, S.; Gentile, D.; Galeazzi, M.; Laghi-Pasini, F. , Antiarrhythmic potential of anticytokine therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: tocilizumab reduces corrected QT interval by controlling systemic inflammation. Arthritis care & research 2015, 67(3), 332–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlan, A. M.; Panoulas, V. F.; Smith, J. P.; Fisher, J. P.; Kitas, G. D. , Association between corrected QT interval and inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2015, 42(3), 421–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzerini, P. E.; Laghi-Pasini, F.; Bertolozzi, I.; Morozzi, G.; Lorenzini, S.; Simpatico, A.; Selvi, E.; Bacarelli, M. R.; Finizola, F.; Vanni, F.; Lazaro, D.; Aromolaran, A.; El Sherif, N.; Boutjdir, M.; Capecchi, P. L. , Systemic inflammation as a novel QT-prolonging risk factor in patients with torsades de pointes. Heart 2017. [CrossRef]
- Carella, M. J.; Mantz, S. L.; Rovner, D. R.; Willis, P. W., 3rd; Gossain, V. V.; Bouknight, R. R.; Ferenchick, G. S. , Obesity, adiposity, and lengthening of the QT interval: improvement after weight loss. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996, 20(10), 938–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milovančev, A.; Stokic, E. In Corrected QT Interval and Corrected QT Dispersion in Obesity, 2019; 2019.
- Hagiwara, Y.; Miyoshi, S.; Fukuda, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Ikegami, Y.; Tanimoto, K.; Murata, M.; Takahashi, E.; Shimoda, K.; Hirano, T.; Mitamura, H.; Ogawa, S. , SHP2-mediated signaling cascade through gp130 is essential for LIF-dependent I CaL, [Ca2+]i transient, and APD increase in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2007, 43(6), 710–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landstrom, A. P.; Dobrev, D.; Wehrens, X. H. T. , Calcium Signaling and Cardiac Arrhythmias. Circ Res 2017, 120(12), 1969–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Gao, L.; Zhang, W.; Xin, X.; Chen, K.; Srivastava, U.; Ginjupalli, V. K. M.; Cupelli, M.; Lazzerini, P. E.; Capecchi, P. L.; Chen, L.; Boutjdir, M. , Arrhythmogenic mechanisms of interleukin-6 combination with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in inflammatory diseases. Sci Rep 2022, 12(1), 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. H.; Rozanski, G. J. , Effects of human recombinant interleukin-1 on electrical properties of guinea pig ventricular cells. Cardiovasc Res 1993, 27(3), 525–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bänsch, D.; Oyang, F.; Antz, M.; Arentz, T.; Weber, R.; Val-Mejias, J. E.; Ernst, S.; Kuck, K.-H. , Successful Catheter Ablation of Electrical Storm After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2003, 108(24), 3011–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IDEKER, R. E.; KONG, W.; POGWIZD, S. , Purkinje Fibers and Arrhythmias. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology 2009, 32(3), 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SINHA, A.-M.; SCHMIDT, M.; MARSCHANG, H.; GUTLEBEN, K.; RITSCHER, G.; BRACHMANN, J.; MARROUCHE, N. F. , Role of Left Ventricular Scar and Purkinje-Like Potentials During Mapping and Ablation of Ventricular Fibrillation in Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology 2009, 32(3), 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gintant, G. , An evaluation of hERG current assay performance: Translating preclinical safety studies to clinical QT prolongation. Pharmacol Ther 2011, 129(2), 109–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A. J. J. M. D.; Roden, D. M. M. D. , DRUG THERAPY: Drug-Induced Prolongation of the QT Interval. The New England Journal of Medicine 2004, 350(10), 1013–22. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo, B.; Sweidan, R.; Rajagopalan, C. V.; Lazzara, R. , Role of Na+:Ca2+ exchange current in Cs(+)-induced early afterdepolarizations in Purkinje fibers. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 1994, 5(11), 933–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surawicz, B. , Role of potassium channels in cycle length dependent regulation of action potential duration in mammalian cardiac Purkinje and ventricular muscle fibres. Cardiovasc Res 1992, 26, (11), 1021–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, W.; Boyden, P. A. , The Purkinje cell; 2008 style. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2008, 45(5), 617–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- András, V.; Tomek, J.; Nagy, N.; Virág, L.; Passini, E.; Rodriguez, B.; Baczkó, I. , Cardiac transmembrane ion channels and action potentials: cellular physiology and arrhythmogenic behavior. Physiological Reviews 2021, 101(3), 1083–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, B. P.; Rosen, M. R. , Effects of pacing on triggered activity induced by early afterdepolarizations. Circulation 1984, 69(5), 1013–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monserrat, M.; Saiz, J.; Ferrero, J. M.; Torres, V.; Ferrero, J. M.; Thakor, N. V. In Influence of Purkinje-muscle coupling on EAD development: a simulation study, Computers in Cardiology 1997, 7-10 Sept. 1997, 1997; 1997; pp 513-516.
- Boyden, P. A.; Hirose, M.; Dun, W. , Cardiac Purkinje cells. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7(1), 127–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, V.; Sampson, K. J.; Kass, R. S. , Modeling tissue- and mutation- specific electrophysiological effects in the long QT syndrome: role of the Purkinje fiber. PLoS One 2014, 9(6), e97720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyden, P. A. , Purkinje physiology and pathophysiology. Journal of interventional cardiac electrophysiology : an international journal of arrhythmias and pacing 2018, 52(3), 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Nattel, S.; Wang, Z. , Impairment of HERG K(+) channel function by tumor necrosis factor-alpha: role of reactive oxygen species as a mediator. J Biol Chem 2004, 279(14), 13289–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnerat, G.; Alarcon, M. L.; Vasconcellos, L. R.; Hochman-Mendez, C.; Brasil, G.; Bassani, R. A.; Casis, O.; Malan, D.; Travassos, L. H.; Sepulveda, M.; Burgos, J. I.; Vila-Petroff, M.; Dutra, F. F.; Bozza, M. T.; Paiva, C. N.; Carvalho, A. B.; Bonomo, A.; Fleischmann, B. K.; de Carvalho, A. C.; Medei, E. , Macrophage-dependent IL-1beta production induces cardiac arrhythmias in diabetic mice. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Fei, Y. D.; Kim, T. Y.; Xie, A.; Batai, K.; Greener, I.; Tang, H.; Ciftci-Yilmaz, S.; Juneman, E.; Indik, J. H.; et al. , IL-18 mediates sickle cell cardiomyopathy and ventricular arrhythmias. Blood 2021, 137(9), 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. , The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, (13). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, Z.; Heymes, C.; Corbaz, A.; Logeart, D.; Alouani, S.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Seidler, T.; Hasenfuss, G.; Chvatchko, Y.; Shah, A. M.; Tedgui, A. , Evidence for altered interleukin 18 (IL)-18 pathway in human heart failure. Faseb j 2004, 18(14), 1752–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, L. C.; Mezzaroma, E.; Van Tassell, B. W.; Marchetti, C.; Carbone, S.; Abbate, A.; Toldo, S. , Interleukin-18 as a therapeutic target in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure. Mol Med 2014, 20(1), 221–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldo, S.; Mezzaroma, E.; O’Brien, L.; Marchetti, C.; Seropian, I. M.; Voelkel, N. F.; Van Tassell, B. W.; Dinarello, C. A.; Abbate, A. , Interleukin-18 mediates interleukin-1-induced cardiac dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2014, 306(7), H1025–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vm, M.; Al, S.; Aa, A.; As, Z.; Av, K.; Rs, O.; Im, M.; Ga, K. , Circulating interleukin-18: Association with IL-8, IL-10 and VEGF serum levels in patients with and without heart rhythm disorders. Int J Cardiol 2016, 215, 105–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbers, C.; Heink, S.; Korn, T.; Rose-John, S. , Interleukin-6: designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2018, 17(6), 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. , Current status and prospects of IL-6–targeting therapy. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology 2022, 15(5), 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, R. M.; Frigault, M. J.; Fradley, M. G.; Jain, M. D.; Mahmood, S. S.; Awadalla, M.; Lee, D. H.; Zlotoff, D. A.; Zhang, L.; Drobni, Z. D.; et al. , Cardiovascular Events Among Adults Treated With Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells (CAR-T). J Am Coll Cardiol 2019, 74(25), 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P. M.; Rane, M. , Interleukin-6 Signaling and Anti-Interleukin-6 Therapeutics in Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation Research 2021, 128(11), 1728–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A. F.; Ettich, J.; Weitz, H. T.; Krusche, M.; Floss, D. M.; Scheller, J.; Moll, J. M. , Exclusive inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling by soluble gp130(FlyR)Fc. Cytokine: X 2021, 3(4), 100058. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- George, M. J.; Jasmin, N. H.; Cummings, V. T.; Richard-Loendt, A.; Launchbury, F.; Woollard, K.; Turner-Stokes, T.; Diaz, A. I. G.; Lythgoe, M.; Stuckey, D. J.; Hingorani, A. D.; Gilroy, D. W. , Selective Interleukin-6 Trans-Signaling Blockade Is More Effective Than Panantagonism in Reperfused Myocardial Infarction. JACC: Basic to Translational Science 2021, 6(5), 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceicao, M.; Forcina, L.; Wiklander, O. P. B.; Gupta, D.; Nordin, J. Z.; Vrellaku, B.; McClorey, G.; Mager, I.; Grgens, A.; Lundin, P.; Musaro, A.; Wood, M. J. A.; Andaloussi, S. E.; Roberts, T. C. , Engineered extracellular vesicle decoy receptor-mediated modulation of the IL6 trans-signalling pathway in muscle. Biomaterials 2021, 266, 120435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H. J.; Zhang, Z.; Jung, D. Y.; Jun, J. Y.; Ma, Z.; Jones, K. E.; Chan, S. Y.; Kim, J. K. , Nutrient stress activates inflammation and reduces glucose metabolism by suppressing AMP-activated protein kinase in the heart. Diabetes 2009, 58(11), 2536–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Lu, Y.; Lu, K.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, N.; Dong, Q.; Chen, L.; Du, Y. , Interleukin-6-Mediated-Ca(2+) Handling Abnormalities Contributes to Atrial Fibrillation in Sterile Pericarditis Rats. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 758157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, R. C. , Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet 2021, 397(10285), 1637–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Kotake, S.; Sato, K.; Kim, K. J.; Takahashi, N.; Udagawa, N.; Nakamura, I.; Yamaguchi, A.; Kishimoto, T.; Suda, T.; Kashiwazaki, S. , Interleukin-6 and soluble interleukin-6 receptors in the synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis patients are responsible for osteoclast-like cell formation. J Bone Miner Res 1996, 11(1), 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, L.; Chen, C.; Bhagat, S. S.; Parker, R. A.; Ostor, A. J. , Risk of adverse events including serious infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tocilizumab: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 2011, 50(3), 552–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J. S.; Beaulieu, A.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; Ramos-Remus, C.; Rovensky, J.; Alecock, E.; Woodworth, T.; Alten, R.; Investigators, O. , Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 2008, 371(9617), 987–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Jones, G. , Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody treatment in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Rev Recent Clin Trials 2006, 1(3), 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashiri, S. Y.; Kawakami, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Imazato, T.; Iwamoto, N.; Fujikawa, K.; Aramaki, T.; Tamai, M.; Nakamura, H.; Ida, H.; Origuchi, T.; Ueki, Y.; Eguchi, K. , Effects of the anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, on serum lipid levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 2011, 31(4), 451–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zhong, J.; Xie, M.; Ran, Z.; Tang, T.; Yang, M.; Guo, T.; Xu, B.; Cai, Z.; Ma, L.; Schreiber, S.; Chen, M. , 775b Olamkicept, an IL-6 Trans-Signaling Inhibitor, is Effective for Induction of Response and Remission in A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial in Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2021, 161(2), e28–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Cao, Q.; Zhong, J.; Xie, M.; Ran, Z.; Tang, T.; Yang, M.; Guo, T.; Xu, B.; Cai, Z.; Schreiber, S.; Chen, M. , DOP01 Efficacy and safety of the IL-6 trans-signalling inhibitor olamkicept: a phase 2 randomized, placebo-controlled trial in moderately to severely active Ulcerative Colitis. Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis 2021, 15 Supplement_1, S041–S042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, S.; Aden, K.; Bernardes, J. P.; Conrad, C.; Tran, F.; Hoper, H.; Volk, V.; Mishra, N.; Blase, J. I.; Nikolaus, S.; Bethge, J.; Kuhbacher, T.; Rocken, C.; Chen, M.; Cottingham, I.; Petri, N.; Rasmussen, B. B.; Lokau, J.; Lenk, L.; Garbers, C.; Feuerhake, F.; Rose-John, S.; Waetzig, G. H.; Rosenstiel, P. , Therapeutic Interleukin-6 Trans-signaling Inhibition by Olamkicept (sgp130Fc) in Patients With Active Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160(7), 2354–2366 e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, D. M.; Waetzig, G. H.; Schuett, H.; Marx, M.; Schulte, B.; Garbers, C.; Lokau, J.; Vlacil, A.-K.; Schulz, J.; Seoudy, A. K.; Schieffer, B.; Rosenstiel, P.; Seeger, M.; Laudes, M.; Rose-John, S.; Lützen, U.; Grote, K.; Schreiber, S. , Case Report: Arterial Wall Inflammation in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease is Reduced by Olamkicept (sgp130Fc). Frontiers in Pharmacology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Peng, S.; Chen, S.; Zhou, G.; Wei, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhou, C.; Ye, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, J. , Selective blockade of interleukin 6 trans-signaling depresses atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20(12), 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakonczay, Z., Jr.; Hegyi, P.; Takacs, T.; McCarroll, J.; Saluja, A. K. , The role of NF-kappaB activation in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Gut 2008, 57, (2), 259–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M. J.; Jasmin, N. H.; Cummings, V. T.; Richard-Loendt, A.; Launchbury, F.; Woollard, K.; Turner-Stokes, T.; Garcia Diaz, A. I.; Lythgoe, M.; Stuckey, D. J.; Hingorani, A. D.; Gilroy, D. W. , Selective Interleukin-6 Trans-Signaling Blockade Is More Effective Than Panantagonism in Reperfused Myocardial Infarction. JACC Basic Transl Sci 2021, 6, (5), 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakos, N. A.; Taleb, I.; Kyriakopoulos, C. P.; Shah, K. S.; Javan, H.; Richins, T. J.; Yin, M. Y.; Yen, C. G.; Dranow, E.; Bonios, M. J.; Alharethi, R.; Koliopoulou, A. G.; Taleb, M.; Fang, J. C.; Selzman, C. H.; Stellos, K.; Drakos, S. G. , Circulating and Myocardial Cytokines Predict Cardiac Structural and Functional Improvement in Patients With Heart Failure Undergoing Mechanical Circulatory Support. J Am Heart Assoc 2021, 10(20), e020238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbin, A.; Aromolaran, K. A.; Aromolaran, A. S. , STAT4 Mediates IL-6 Trans-Signaling Arrhythmias in High Fat Diet Guinea Pig Heart. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, (14), 7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, M.; Yin, L.; Ingelsson, E. , Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular risk in a nation-wide cohort study after the withdrawal of rofecoxib. Eur Heart J 2012, 33(15), 1928–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Christiansen, C. F.; Mehnert, F.; Rothman, K. J.; Sorensen, H. T. , Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and risk of atrial fibrillation or flutter: population based case-control study. BMJ 2011, 343, d3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Hooft, C. S.; Heeringa, J.; Brusselle, G. G.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J. C.; Kingma, J. H.; Sturkenboom, M. C.; Stricker, B. H. , Corticosteroids and the risk of atrial fibrillation. Arch Intern Med 2006, 166, (9), 1016–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caterina, R.; Ruigomez, A.; Rodriguez, L. A. , Long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of atrial fibrillation. Arch Intern Med 2010, 170, (16), 1450–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frustaci, A.; Chimenti, C.; Bellocci, F.; Morgante, E.; Russo, M. A.; Maseri, A. , Histological substrate of atrial biopsies in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Circulation 1997, 96(4), 1180–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granier, M.; Massin, F.; Pasquie, J. L. , Pro- and anti-arrhythmic effects of anti-inflammatory drugs. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem 2013, 12(1), 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M.; Van Wagoner, D. R.; Nattel, S. , Role of inflammation in atrial fibrillation pathophysiology and management. Circ J 2015, 79, (3), 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, I.; Matsumoto, M.; Tsuji, S.; Nomura, M.; Toyoshima, K.; Seya, T. , Molecular cloning and functional characterization of guinea pig IL-12. International Immunology 2001, 13(9), 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, R.; Tomsits, P.; Loy, S.; Zhang, Z.; Pauly, V.; Schuttler, D.; Clauss, S. , Cardiac Macrophages and Their Effects on Arrhythmogenesis. Front Physiol 2022, 13, 900094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aprikian, O.; Reynaud, D.; Pace-Asciak, C.; Leone, P.; Blancher, F.; Monnard, I.; Darimont, C.; Mace, K. , Neonatal dietary supplementation of arachidonic acid increases prostaglandin levels in adipose tissue but does not promote fat mass development in guinea pigs. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2007, 293, (5), R2006–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Freake, H. C.; Fernandez, M. L. , Gender and hormonal status affect the regulation of hepatic cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase activity and mRNA abundance by dietary soluble fiber in the guinea pig. Atherosclerosis 2002, 163, (1), 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Gonzalez, M.; Volek, J. S.; Sharman, M.; Contois, J. H.; Fernandez, M. L. , Dietary carbohydrate and cholesterol influence the number of particles and distributions of lipoprotein subfractions in guinea pigs. J Nutr Biochem 2006, 17(11), 773–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M. L.; Volek, J. S. , Guinea pigs: A suitable animal model to study lipoprotein metabolism, atherosclerosis and inflammation. Nutrition & Metabolism 2006, 3(1), 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Johnson, D. G. , cDNA cloning and expression of guinea pig neutrophil attractant protein-1 (NAP-1). NAP-1 is highly conserved in guinea pig. J Immunol 1993, 151(11), 6225–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M. L.; Volek, J. S. , Guinea pigs: a suitable animal model to study lipoprotein metabolism, atherosclerosis and inflammation. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2006, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Shryock, J. C.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Antzelevitch, C.; Belardinelli, L. , Antiarrhythmic effects of ranolazine in a guinea pig in vitro model of long-QT syndrome. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004, 310(2), 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, T.; Rudy, Y. , Quantitative comparison of cardiac ventricular myocyte electrophysiology and response to drugs in human and nonhuman species. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2012, 302(5), H1023–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Takimoto, E.; Dimaano, V. L.; DeMazumder, D.; Kettlewell, S.; Smith, G.; Sidor, A.; Abraham, T. P.; O’Rourke, B. , Inhibiting mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchange prevents sudden death in a Guinea pig model of heart failure. Circ Res 2014, 115(1), 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; DeMazumder, D.; Sidor, A.; Foster, D. B.; O’Rourke, B. , Mitochondrial ROS Drive Sudden Cardiac Death and Chronic Proteome Remodeling in Heart Failure. Circ Res 2018, 123, (3), 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuttler, D.; Bapat, A.; Kaab, S.; Lee, K.; Tomsits, P.; Clauss, S.; Hucker, W. J. , Animal Models of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ Res 2020, 127(1), 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joukar, S. , A comparative review on heart ion channels, action potentials and electrocardiogram in rodents and human: extrapolation of experimental insights to clinic. Lab Anim Res 2021, 37, (1), 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souidi, M.; Combettes-Souverain, M.; Milliat, F.; Eckhardt, E. R.; Audas, O.; Dubrac, S.; Parquet, M.; Férézou, J.; Lutton, C. , Hamsters predisposed to sucrose-induced cholesterol gallstones (LPN strain) are more resistant to excess dietary cholesterol than hamsters that are not sensitive to cholelithiasis induction. J Nutr 2001, 131(6), 1803–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorfman, S. E.; Smith, D. E.; Osgood, D. P.; Lichtenstein, A. H. , Study of diet-induced changes in lipoprotein metabolism in two strains of Golden-Syrian hamsters. J Nutr 2003, 133(12), 4183–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nistor, A.; Bulla, A.; Filip, D. A.; Radu, A. , The hyperlipidemic hamster as a model of experimental atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 1987, 68(1-2), 159–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, N. J.; Normandin, D. E. , Alterations in Ito1, IKr and Ik1 density in the BIO TO-2 strain of syrian myopathic hamsters. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1997, 29(12), 3211–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Miao, J.; Tabaran, A. F.; O’Sullivan, M. G.; Anderson, K. J.; Scott, P. M.; Wang, Z.; Cormier, R. T. , A novel cancer syndrome caused by KCNQ1-deficiency in the golden Syrian hamster. Journal of carcinogenesis 2018, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S. H.; Chen, Y. C.; Higa, S.; Lin, C. I. , Oscillatory transient inward currents in ventricular myocytes of healthy versus myopathic Syrian hamster. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2004, 31, (10), 668–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, V.; Blythe, H.; Wood, E. G.; Sandhar, B.; Sarker, S. J.; Balmforth, D.; Ambekar, S. G.; Yap, J.; Edmondson, S. J.; Di Salvo, C.; Wong, K.; Roberts, N.; Uppal, R.; Adams, B.; Shipolini, A.; Oo, A. Y.; Lawrence, D.; Kolvekar, S.; Lall, K. S.; Finlay, M. C.; Longhi, M. P. , Obesity and diabetes are major risk factors for epicardial adipose tissue inflammation. JCI Insight 2021, 6(16). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, M.; Petraglia, L.; Poggio, P.; Valerio, V.; Cabaro, S.; Campana, P.; Comentale, G.; Attena, E.; Russo, V.; Pilato, E.; Formisano, P.; Leosco, D.; Parisi, V. , Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases in the Elderly: The Role of Epicardial Adipose Tissue. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 844266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, T.; Zhang, L.; Zalewski, A.; Mannion, J. D.; Diehl, J. T.; Arafat, H.; Sarov-Blat, L.; O’Brien, S.; Keiper, E. A.; Johnson, A. G.; Martin, J.; Goldstein, B. J.; Shi, Y. , Human epicardial adipose tissue is a source of inflammatory mediators. Circulation 2003, 108(20), 2460–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konwerski, M.; Gąsecka, A.; Opolski, G.; Grabowski, M.; Mazurek, T. , Role of Epicardial Adipose Tissue in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Review. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11, (3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernault, A. C.; Verkerk, A. O.; Bayer, J. D.; Aras, K.; Montanes-Agudo, P.; Mohan, R. A.; Veldkamp, M.; Rivaud, M. R.; de Winter, R.; Kawasaki, M.; van Amersfoorth, S. C. M.; Meulendijks, E. R.; Driessen, A. H. G.; Efimov, I. R.; de Groot, J. R.; Coronel, R. , Secretome of atrial epicardial adipose tissue facilitates reentrant arrhythmias by myocardial remodeling. Heart Rhythm 2022, 19(9), 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Muniz, M. G.; Palfreeman, M.; Setzu, N.; Sanchez, M. A.; Saenz Portillo, P.; Garza, K. M.; Gosselink, K. L.; Spencer, C. T. , Obesity Exacerbates the Cytokine Storm Elicited by Francisella tularensis Infection of Females and Is Associated with Increased Mortality. Biomed Res Int 2018, 2018, 3412732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, J.; Nakagawa, M.; Watanabe, N.; Nakamura, M. , Ubiquitin-like protein MNSFbeta covalently binds to Bcl-G and enhances lipopolysaccharide/interferon gamma-induced apoptosis in macrophages. FEBS J 2013, 280(5), 1281–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.; Garg, V.; Shrestha, R.; Sanguinetti, M. C.; Kamp, T. J.; Wu, J. C. , Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes as Models for Cardiac Channelopathies: A Primer for Non-Electrophysiologists. Circ Res 2018, 123(2), 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourrier, M.; Fedida, D. , The Emergence of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) as a Platform to Model Arrhythmogenic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




