Submitted:
24 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. GDNF Alleviates Colitis Symptoms and Attenuates Serum Inflammatory Markers in DSS-induced UC Mice
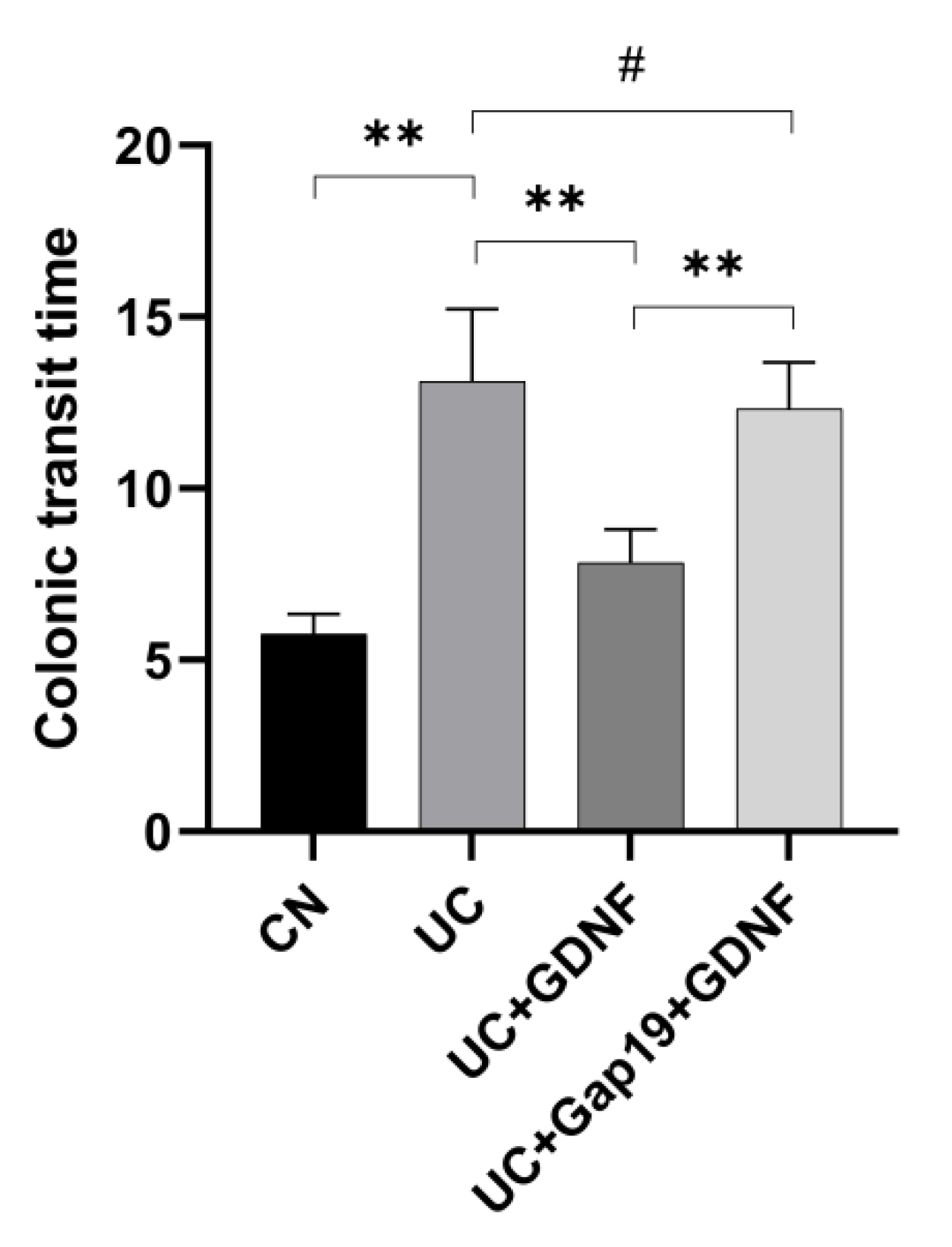
3.2. GDNF Improves Colonic Transit Time in DSS-Induced UC Mice through Cx43
2.3. GDNF Improves Colonic Histopathological Changes in DSS-Induced UC Mice through Cx43
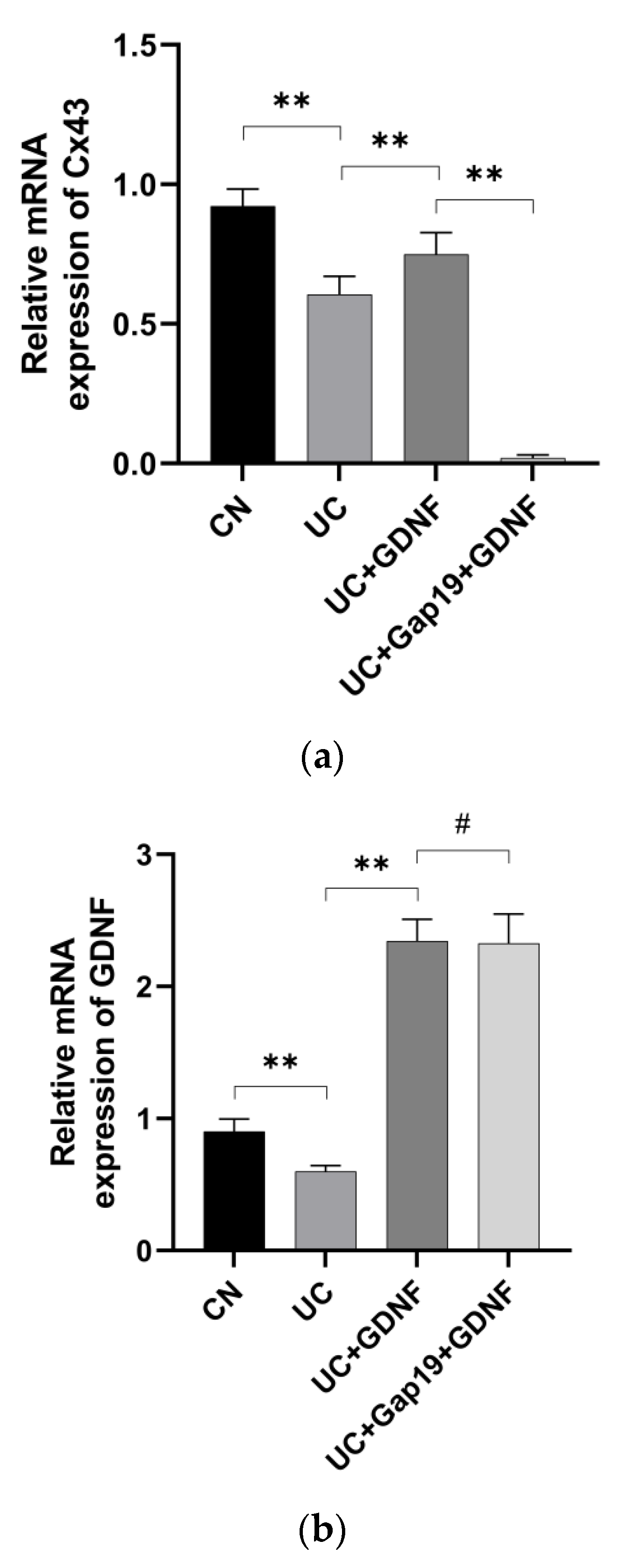
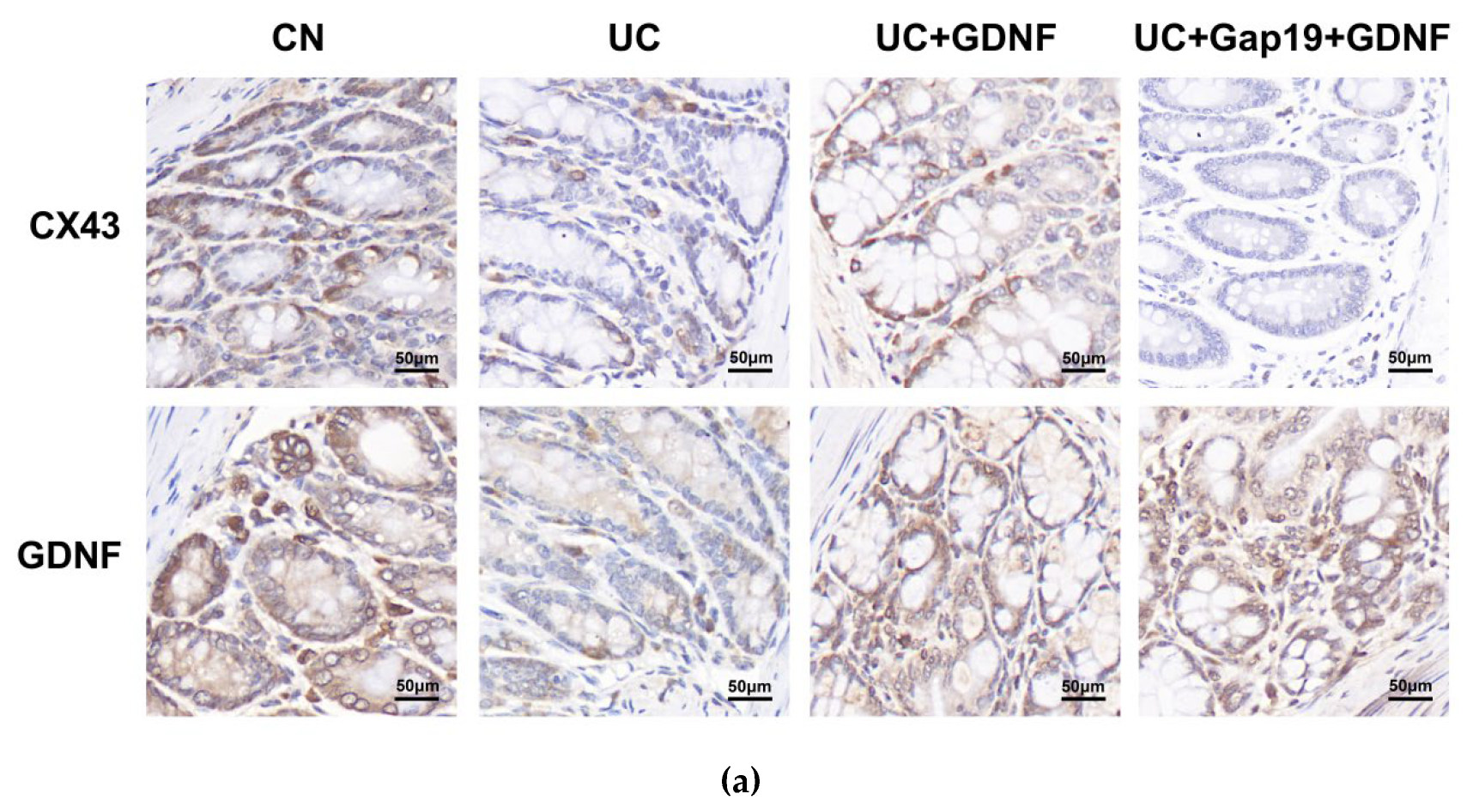
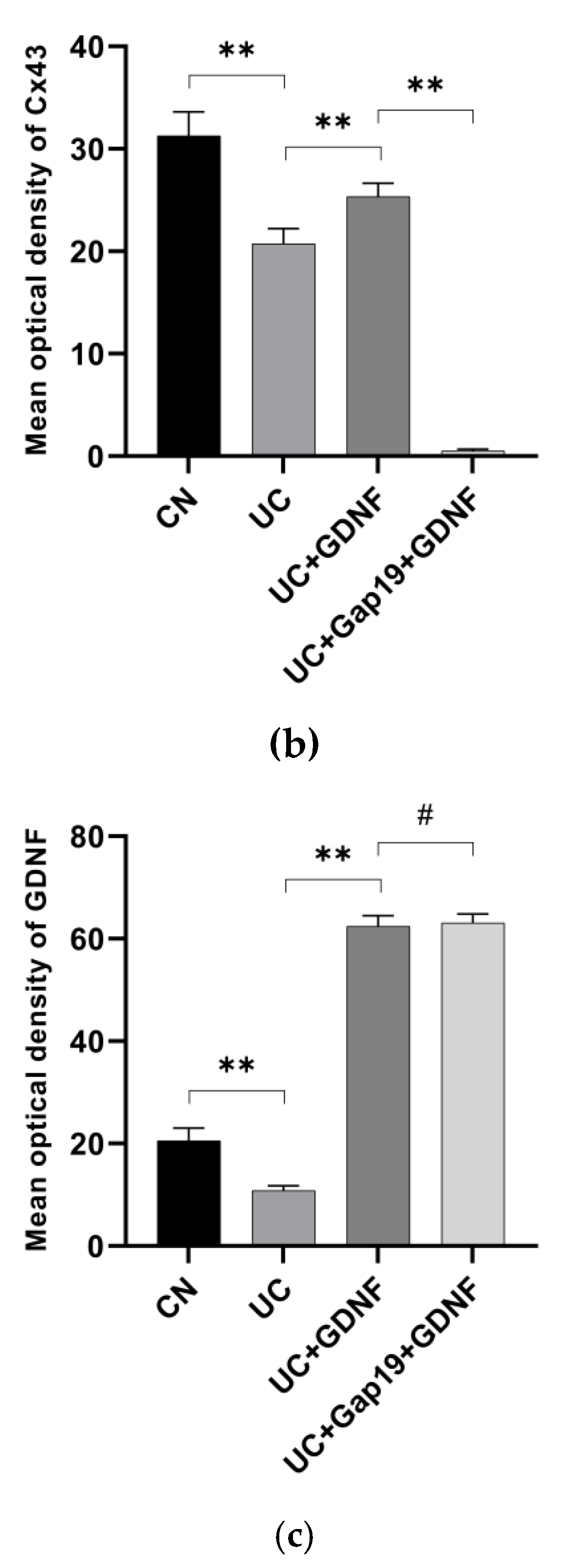
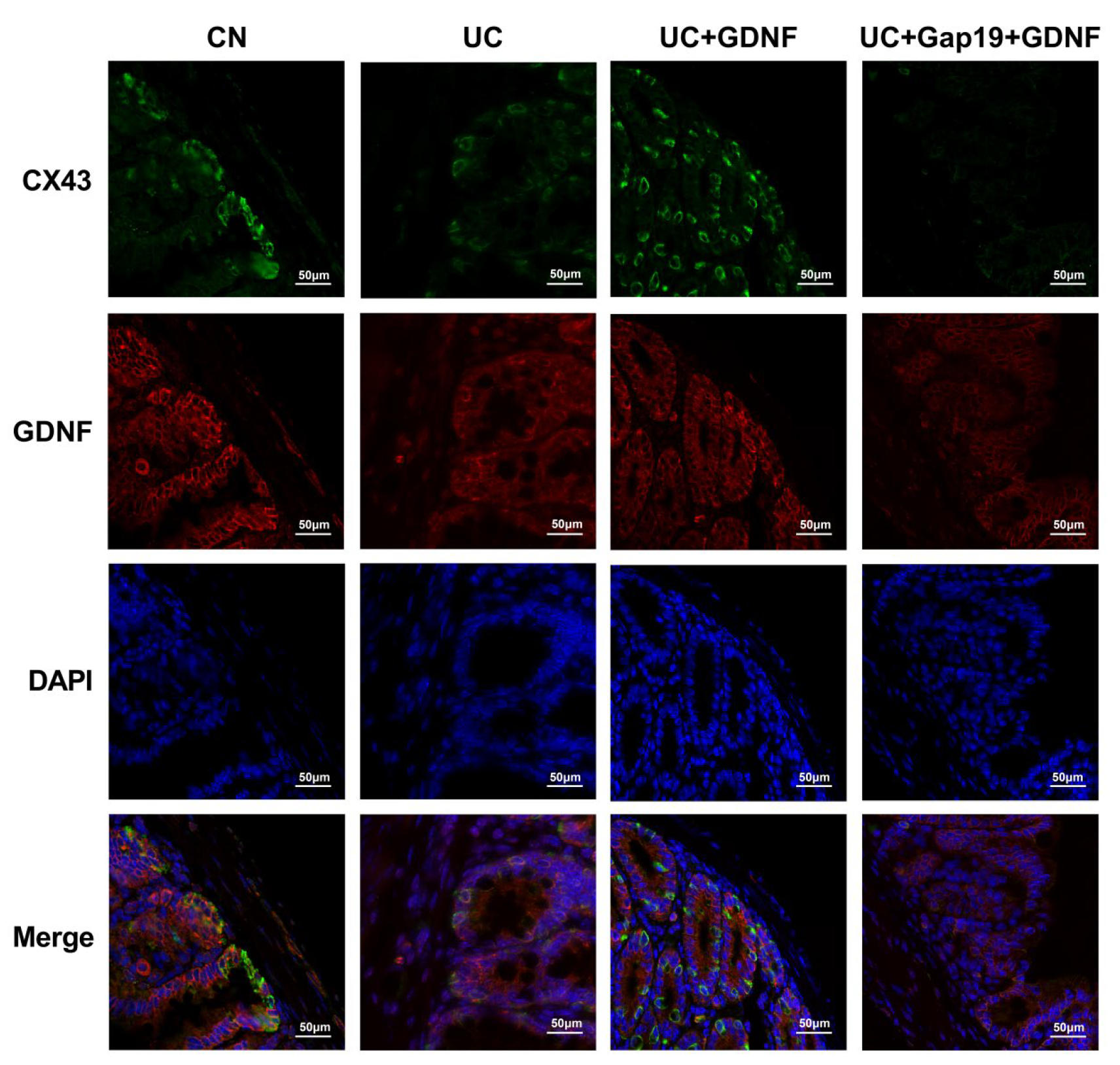
3.4. GDNF and Cx43 Expression in the Colon Are Decreased in Mice with DSS-Induced UC
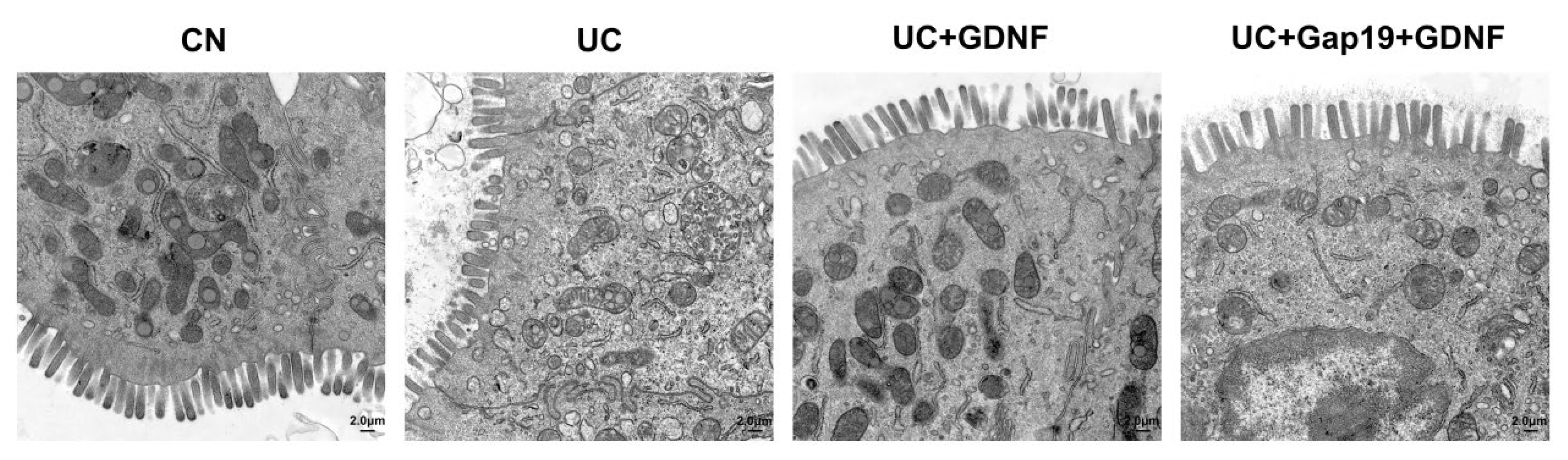
2.5. Ultrastructure of Colon Tissue in DSS-Induced UC Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Induction of Ulcerative Colitis
4.3. Surgical Procedure
4.4. Analysis of Colonic Transit Time
4.5. Histopathological Examinations
4.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.7. Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.8. Immunofluorescent studies of Cx43 and GDNF
4.9. Relative quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gros,B.; Kaplan,G.G. Ulcerative Colitis in Adults: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(10):951-965.
- Cui,G.; Li,J.; Liu,H.; Laugsand, J.B.; Liu,Z. Differences in inflammatory bowel diseases between East and West: a Chinese perspective. J Public Health (Berl.).2021; 29:19–26. [CrossRef]
- Ng, S. C.; Shi, H. Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F. E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E. I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J. C. Y.; Chan, F. K. L.; Sung, J. J. Y.; Kaplan, G. G. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies [published correction appears in Lancet. 2020 Oct 3;396(10256):e56]. Lancet.2017;390(10114):2769-2778.
- Walsh, A.J; Bryant, R.V; Travis, S.P. Current best practice for disease activity assessment in IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(10):567-579. [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Sebastian, S. A.; Parmar, M. P.; Ghadge, N.; Padda, I.; Keshta, A. S.; Minhaz, N.; Patel, A. Factors influencing the quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease: A comprehensive review. Dis Mon. 2024;70(1S):101672. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.G.; Ng,S.C. Understanding and Preventing the Global Increase of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:313-321 e2. [CrossRef]
- Salem, M. B.; El-Lakkany, N. M.; Seif El-Din, S. H.; Hammam, O. A.; Samir, S. Diosmin alleviates ulcerative colitis in mice by increasing Akkermansiamuciniphila abundance, improving intestinal barrier function, and modulating the NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways. Heliyon. 2024;10(6):e27527.
- Kishi,K.; Kaji,N.; Tsuru,Y.; Hori,M. A Novel Noninvasive Method for Quantitative Detection of Colonic Dysmotility Using Real-Time Ultrasonography. Digestion. 2021;102(5):731-741.
- da Silva Watanabe, P.; Cavichioli, A. M.; D'Arc de Lima Mendes, J.; Aktar, R.; Peiris, M.; Blackshaw, L. A.; de Almeida Araújo, E. J. Colonic motility adjustments in acute and chronic DSS-induced colitis. Life Sci. 2023;321:121642.
- KERN, F.; Jr, ALMY, T. P.; ABBOT, F. K.; BOGDONOFF, M. D. The motility of the distal colon in nonspecific ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1951;19:492–503. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S. N.; Bazzocchi, G.; Chan, S.; Akashi, K.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.; Yanni, G.; Mena, I.; Snape, W. J. JrColonic motilityand transit in health and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1991; 101: 1289–97.
- Gershon, M.D.; Margolis, K.G. The gut, its microbiome, and the brain: connections and communications. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(18):e143768. [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.L.; Taheri, N.; Zhang,Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Hayashi Y. The critical role of muscularis macrophages in modulating the enteric nervous system function and gastrointestinal motility. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2024;60:1-9.
- Li, H.; Fan, C.; Lu, H.; Feng, C.; He, P.; Yang, X.; Xiang, C.; Zuo, J.; Tang, W.Protective role of berberine on ulcerative colitis through modulating enteric glial cells-intestinal epithelial cells-immune cells interactions. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020;10(3):447-461. [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, P.; Vollmer-Conna, U.; Hadzi-Pavlovic, D.; Grimm, M.C. A Review of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Model of Microbial, Immune and Neuropsychological Integration. Public Health Rev. 2021;42:1603990.
- Le Berre, C.; Naveilhan, P.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M. Enteric glia at center stage of inflammatory bowel disease. Neurosci Lett. 2023;809:137315. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, S.; He, X.; Xiong, Q.; Gao, J.; Hou, S.; Huang, S.; He, L.; Liang, J. Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides ameliorated ulcerative colitis via inhibiting inflammation and enhancing intestinal epithelial barrier function. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;180:633-642. [CrossRef]
- Spalinger, M. R.; Sayoc-Becerra, A.; Ordookhanian, C.; Canale, V.; Santos, A. N.; King, S. J.; Krishnan, M.; Nair, M. G.; Scharl, M.; McCole, D. F. The JAK Inhibitor Tofacitinib Rescues Intestinal Barrier Defects Caused by Disrupted Epithelial-macrophage Interactions. J Crohns Colitis. 2021;15(3):471-484. [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, N.; Boerner, K.; Waschke, J. Targeting desmosomal adhesion and signalling for intestinal barrier stabilization in inflammatory bowel diseases-Lessons from experimental models and patients. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021;231(1):e13492.
- Peracchia, C. Gap Junction Channelopathies and Calmodulinopathies. Do Disease-Causing Calmodulin Mutants Affect Direct Cell-Cell Communication?. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9169.
- Zuo, T.; Liu, Y.; Duan, M.; Pu, X.; Huang, M.; Zhang, D.; Xie, J. Platelet-derived growth factor PDGF-AA upregulates connexin 43 expression and promotes gap junction formations in osteoblast cells through p-Akt signaling. BiochemBiophys Rep. 2023;34:10146.
- Totland, M.Z.; Rasmussen, N.L.; Knudsen, L.M.; Leithe E. Regulation of gap junction intercellular communication by connexin ubiquitination: physiological and pathophysiological implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(4):573-591.
- Schumacher, S.; Tahiri, H.; Ezan, P.; Rouach, N.; Witschas, K.; Leybaert L. Inhibiting astrocyte connexin-43 hemichannels blocks radiation-induced vesicular VEGF-A release and blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Glia. 2024;72(1):34-50.
- Katturajan, R.; Evan Prince, S. A role of connexin 43 on the drug-induced liver, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract toxicity with associated signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2021;280:119629.
- Meşe, G.; Richard, G.; White, T.W. Gap junctions: basic structure and function. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127(11):2516-2524.
- Jindal, S.; Chockalingam, S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Packirisamy, G. Connexin and gap junctions: perspectives from biology to nanotechnology based therapeutics. Transl Res. 2021;235:144-167.
- Goodenough, D.A.; Paul, D.L.Gapjunctions.Cold Spring HarbPerspect Biol. 2009;1(1):2576.
- Wong, J.; Chopra, J.; Chiang, L. L. W.; Liu, T.; Ho, J.; Wu, W. K. K.; Tse, G.; Wong, S. H. The Role of Connexins in GastrointestinalDiseases. J Mol Biol. 2019; 431: 643-652.
- Coyle. D.; Doyle, B.; Murphy, J.M.; O'Donnell, A.M.; Gillick J, Puri.P. Expression of connexin 26 and connexin 43 is reduced in Hirschsprung's disease. J Surg Res. 2016;206(1):242-251.
- DiCello, J. J.; Carbone, S. E.; Saito, A.; Pham, V.; Szymaszkiewicz, A.; Gondin, A. B.; Alvi, S.; Marique, K.; Shenoy, P.; Veldhuis, N. A.; Fichna, J.; Canals, M.; Christopoulos, A.; Valant, C.; & Poole, D. P. Positive allosteric modulation of endogenous delta opioid receptor signaling in the enteric nervous system is a potential treatment for gastrointestinal motility disorders. Am J PhysiolGastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022;322(1):G66-G78. [CrossRef]
- Broadhead, M. J.; Bayguinov, P. O.; Okamoto, T.; Heredia, D. J.; & Smith, T. K. Ca2+ transients in myenteric glial cells during the colonic migrating motor complex in the isolated murine large intestine. J Physiol. 2012 Jan 15;590(2): 335-350. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, N.; Shi, X.; Chen, J. Synchronized dual pulse gastric electrical stimulation induces activation of enteric glial cells in rats with diabetic gastroparesis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014;2014:964071. [CrossRef]
- Howlett, P.J.; Ward, A.S.; Duthie, H.L. Gastric emptying after vagotomy. Proc RSoc Med. 1974;67: 836-838.
- Maes, M.; Cogliati, B.; Crespo, Yanguas S.; Willebrords, J.; Vinken, M. Roles of connexins and pannexins in digestive homeostasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015;72:2809–21.
- Meir, M.; Burkard, N.; Ungewiß, H.; Diefenbacher, M.; Flemming, S.; Kannapin, F.; Germer, C. T.; Schweinlin, M.; Metzger, M.; Waschke, J.; Schlegel, N. Neurotrophic factor GDNF regulates intestinal barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(7):2824-2840. [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Du, Y.; Li, X.; Kambey, P. A.; Wang, L.; Xia, Y.; Tang, C.; Shi, M., Zai-Li, L.; Zai-E, X.; Xiao-Ling, Q.; Dian-Shuai, G. Lower GDNF Serum Level Is a Possible Risk Factor for Constipation in Patients With Parkinson Disease: A Case-Control Study. Front Neurol. 2022;12:777591. [CrossRef]
- Soret, R.; Schneider, S.; Bernas, G.; Christophers, B.; Souchkova, O.; Charrier, B.; Righini-Grunder, F.; Aspirot, A.; Landry, M.; Kembel, S. W.; Faure, C.; Heuckeroth, R. O.; Pilon, N. Glial Cell-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Induces Enteric Neurogenesis and Improves Colon Structure and Function in Mouse Models of Hirschsprung Disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(5):1824-1838.e17. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Clamon, L.C.; Manoim, J.E.; Ormerod, K.G.; Parnas, M.; Littleton, J.T. Glial ER and GAP junction mediated Ca2+ waves are crucial to maintain normal brain excitability. Glia. 2022;70(1):123-144. [CrossRef]
- Ponsaerts, R.; Wang, N.; Himpens, B.; Leybaert, L.; Bultynck, G. The contractile system as a negative regulator of the connexin 43 hemichannel. Biol Cell. 2012;104(7):367-377.
- Abudara, V.; Bechberger, J.; Freitas-Andrade, M.; De Bock, M.; Wang, N.; Bultynck, G.; Naus, C. C.; Leybaert, L.; Giaume, C. The connexin43 mimetic peptide Gap19 inhibits hemichannels without altering gap junctional communication in astrocytes. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:306. [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Aitken, J.D.; Malleshappa, M.; Vijay-Kumar M. Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. CurrProtoc Immunol. 2014;104:15.25.1-15.25.14. [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Q.Y. Hepatic and intestinal biotransformation gene expression and drug disposition in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mouse model. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020;10(1):123-135. [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.; Youssef, M. E.; Sharaf, H.; Amin, N. A.; El-Shedody, R.; Aboutouk, F. H.; El-Galeel, Y. A.; El-Hefnawy, A.; Shabaka, D.; Khalifa, A.; Saleh, R. A.; Osama, D.; El-Zoghby, G.; Gobba, N. A. BBG enhances OLT1177-induced NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation by targeting P2X7R/NLRP3 and MyD88/NF-κB signaling in DSS-induced colitis in rats. Life Sci. 2021;270:119123.
- Brown, I.A.; McClain, J.L.; Watson, R.E.; Patel, B.A.; Gulbransen, B.D. Enteric glia mediate neuron death in colitis through purinergic pathways that require connexin-43 and nitric oxide. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;2(1):77-91. [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Williams, M. P2 purinergic receptors: modulation of cell function and therapeutic potential. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;295(3):862-869.
- Idzko, M.; Ferrari, D.; Eltzschig, H.K. Nucleotide signalling during inflammation. Nature. 2014;509(7500):310-317. [CrossRef]
- Drewes, A.M.; Frøkjaer, J.B.; Larsen, E.; Reddy, H.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Gregersen, H. Pain and mechanical properties of the rectum in patients with active ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006;12(4):294-303. [CrossRef]
- Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Antonioli, L.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Gori, G.; Blandizzi, C.; Del Tacca, M. Effects of a bicarbonate-alkaline mineral water on digestive motility in experimental models of functional and inflammatory gastrointestinal disorders. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2008;30(4):261-269. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S. N.; Bazzocchi, G.; Chan, S.; Akashi, K.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.; Yanni, G.; Mena, I.; Snape, W. J. Colonic motility and transit in health and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1991;101(5):1289-1297. [CrossRef]
- Haase, A. M.; Gregersen, T.; Christensen, L. A.; Agnholt, J.; Dahlerup, J. F.; Schlageter, V.; Krogh, K. Regional gastrointestinal transit times in severe ulcerative colitis. NeurogastroenterolMotil. 2016;28(2):217-224. [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, S.; Tahiri, H.; Ezan, P.; Rouach, N.; Witschas, K.; Leybaert L. Inhibiting astrocyte connexin-43 hemichannels blocks radiation-induced vesicular VEGF-A release and blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Glia. 2024;72(1):34-50.
- Montalbán-Rodríguez, A.; Abalo, R.; López-Gómez, L. From the Gut to the Brain: The Role of Enteric Glial Cells and Their Involvement in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(2):1294.
- Bannerman, P.; Nichols, W.; Puhalla, S.; Oliver, T.; Berman, M.; Pleasure, D. Early migratory rat neural crest cells express functional gap junctions: Evidence that neural crest cell survival requires gap junction function. Journal of Neuroscience Research. 2000, 61(6):605-615.
- Seki, K.; KomuroT. Immunocytochemical demonstration of the gap junction proteins connexin 43 and connexin 45 in the musculature of the rat small intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 2001 Dec; 306(3):417-22.
- Coyle, D.; Doyle, B.; Murphy, J. M.; O'Donnell, A. M.; Gillick, J.; Puri, P.Expression of connexin 26 and connexin 43 is reduced in Hirschsprung's disease. J Surg Res. 2016 Nov; 206(1):242-251.
- Katturajan, R.; Evan Prince, S. A role of connexin 43 on the drug-induced liver, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract toxicity with associated signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2021;280:119629.
- Bar, K.J.; Facer, P.A.; Williams, N.S.; Tam, P.K.; Anand, P.R. Glial-derived neurotrophic factor in human adult and fetal intestine and in Hirschsprung's disease. Gastroenterology 4: 1381-1385, 1997.
- Sánchez, M.P.; Silos-Santiago, I.; Frisén, J.; He, B.; Lira SA.; Barbacid M. Renal agenesis and the absence of enteric neurons in mice lacking GDNF. Nature. 1996;382(6586):70-73. [CrossRef]
- Steinkamp, M.; Gundel, H.; Schulte, N.; Spaniol, U.; Pflueger, C.; Zizer, E.; von Boyen, G. B. GDNF protects enteric glia from apoptosis: evidence for an autocrine loop. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12:6. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.;Fan, C.; Lu, H.; Feng, C.; He, P.; Yang, X.; Xiang, C.; Zuo, J.; Tang, W.Protective role of berberine on ulcerative colitis through modulating enteric glial cells-intestinal epithelial cells-immune cells interactions. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020;10(3):447-461. [CrossRef]
- Delmar, M.; Makita, N. Cardiac connexins, mutations and arrhythmias. CurrOpinCardiol. 2012;27(3):236-241. [CrossRef]
- Abudara, V.; Bechberger, J.; Freitas-Andrade, M.; De Bock, M.; Wang, N.; Bultynck, G.; Naus, C. C.; Leybaert, L.; Giaume, C. The connexin43 mimetic peptide Gap19 inhibits hemichannels without altering gap junctional communication in astrocytes. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:306.
- Sun, T.; Li, D.; Hu, S.; Huang, L.; Sun, H.; Yang, S.; Wu, B.; Ji, F.; Zhou, D. Aging-dependent decrease in the numbers of enteric neurons, interstitial cells of Cajal and expression of connexin43 in various regions of gastrointestinal tract. Aging (Albany NY). 2018 Dec 11;10(12):3851-3865. [CrossRef]
- Seki, K.; Komuro, T. Immunocytochemical demonstration of the gap junction proteins connexin 43 and connexin 45 in the musculature of the rat small intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 2001;306(3):417-422.
- McClain, J.; Grubišić, V.; Fried, D.; Gomez-Suarez, R. A.; Leinninger, G. M.; Sévigny, J.; Parpura, V.; Gulbransen, B. D. Ca2+ Responses in Enteric Glia Are Mediated by Connexin-43 Hemichannels and Modulate Colonic Transit in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2014 Feb;146(2):497-507. [CrossRef]
- Akbarali, H.I.; Pothoulakis, C.; Castagliuolo, I. Altered ion channel activity in murine colonic smooth muscle myocytes in an experimental colitis model. BiochemBiophys Res Commun. 2000;275(2):637-642.
- Zhang, J.; Chandrasekaran, G.; Li, W.; Kim, D. Y.; Jeong, I. Y.; Lee, S. H.; Liang, T.; Bae, J. Y.; Choi, I.; Kang, H.; Maeng, J. S.; Kim, M. K.; Lee, T.; Park, S. W.; Kim, M. J.; Kim, H. S.; Ro, H.; Bae, Y. C.; Park, H. C.; Choi, E. Y., et al. Wnt-PLC-IP3-Connexin-Ca2+ axis maintains ependymal motile cilia in zebrafish spinal cord. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1860.
- Schneider, R.; Leven, P.; Glowka, T.; Kuzmanov, I.; Lysson, M.; Schneiker, B.; Miesen, A.; Baqi, Y.; Spanier, C.; Grants, I.; Mazzotta, E.; Villalobos-Hernandez, E.; Kalff, J. C.; Müller, C. E.; Christofi, F. L.; Wehner, S. A novel P2X2-dependent purinergic mechanism of enteric gliosis in intestinal inflammation. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13(1):e12724. [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Huang, W.L.; Xing, B.P.; Fang, X.; Feng, M.; Jiang, C.M. Genistein Improves the Major Depression through Suppressing the Expression of miR-221/222 by Targeting Connexin 43. Psychiatry Investig. 2018;15(10):919-925.
- Yao, H.; Yan, J.; Yin, L.; Chen, W. Picroside II alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by suppressing the production of NLRP3 inflammasomes through NF-κB signaling pathway. ImmunopharmacolImmunotoxicol. 2022;44(3):437-446.
- Jeon, Y.D.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, D.K. Puerarin inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;124:109847.
- Jin, B.; Ha, S. E.; Wei, L.; Singh, R.; Zogg, H.; Clemmensen, B.; Heredia, D. J.; Gould, T. W.; Sanders, K. M.; Ro, S. Colonic Motility Is Improved by the Activation of 5-HT2B Receptors on Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Diabetic Mice. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jan;162(1):352.
- Camilleri, M.; Linden, D.R. Measurement ofgastrointestinal and colonic motor functionsin humans and animals. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jul;2(4):412–28.
- Tizro, P.; Choi, C.; Khanlou, N. Sample preparation fortransmission electron microscopy. Methods Mol Biol.2019;1897:417–424.
- Cheung, G.; Chever, O.; Rollenhagen, A.; Quenech'du, N.; Ezan, P.; Lübke, J. H. R.; Rouach, N. Astroglial Connexin 43 Regulates Synaptic Vesicle Release at Hippocampal Synapses. Cells. 2023;12(8):1133.
- Orellana, J. A.; Froger, N.; Ezan, P.; Jiang, J. X.; Bennett, M. V.; Naus, C. C.; Giaume, C.; Sáez, J. C. ATP and glutamatereleased via astroglial connexin 43 hemichannelsmediate neuronal death through activation of pannexin 1hemichannels. J Neurochem. 2011;118:826–840.
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408.
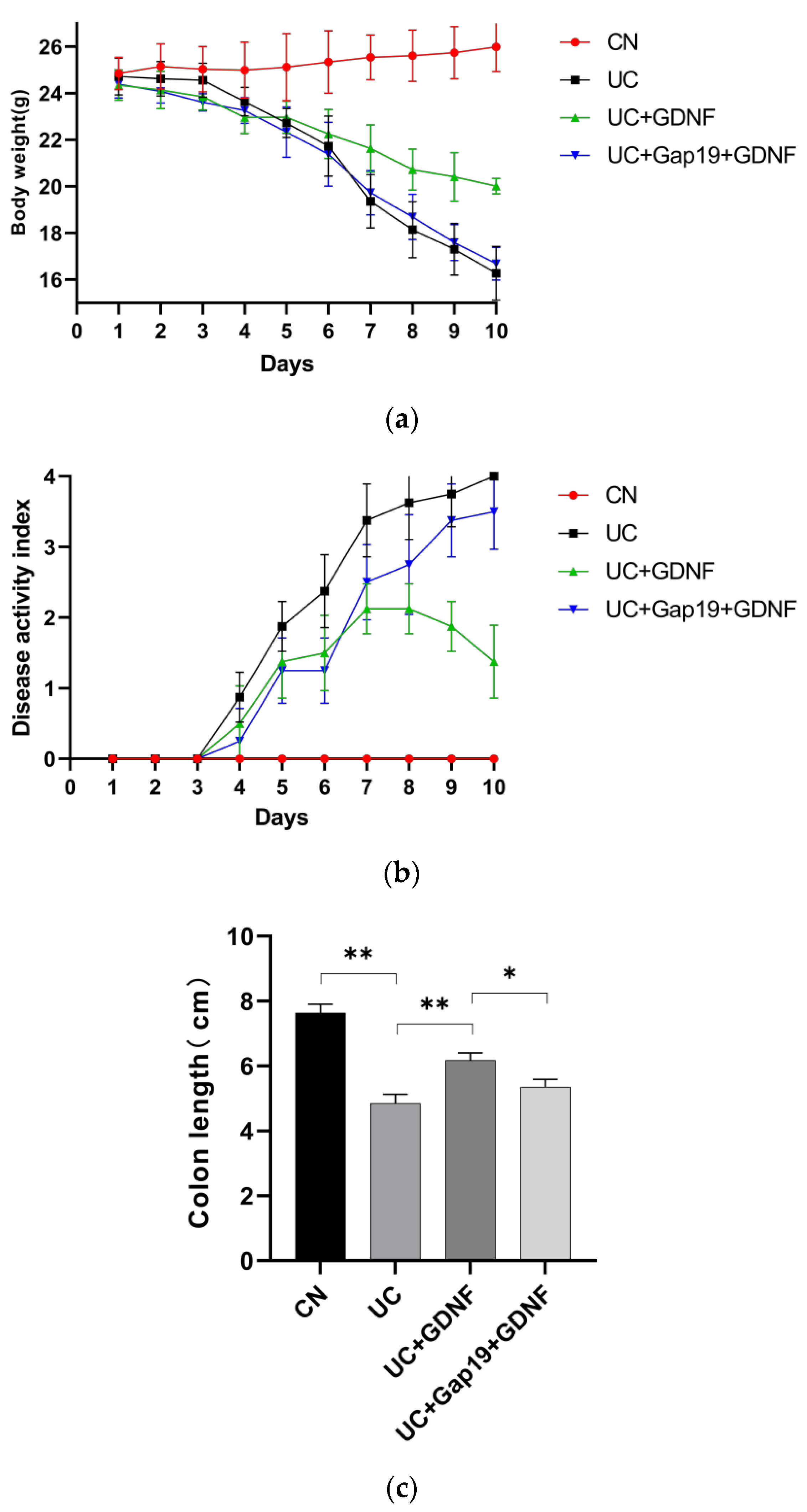
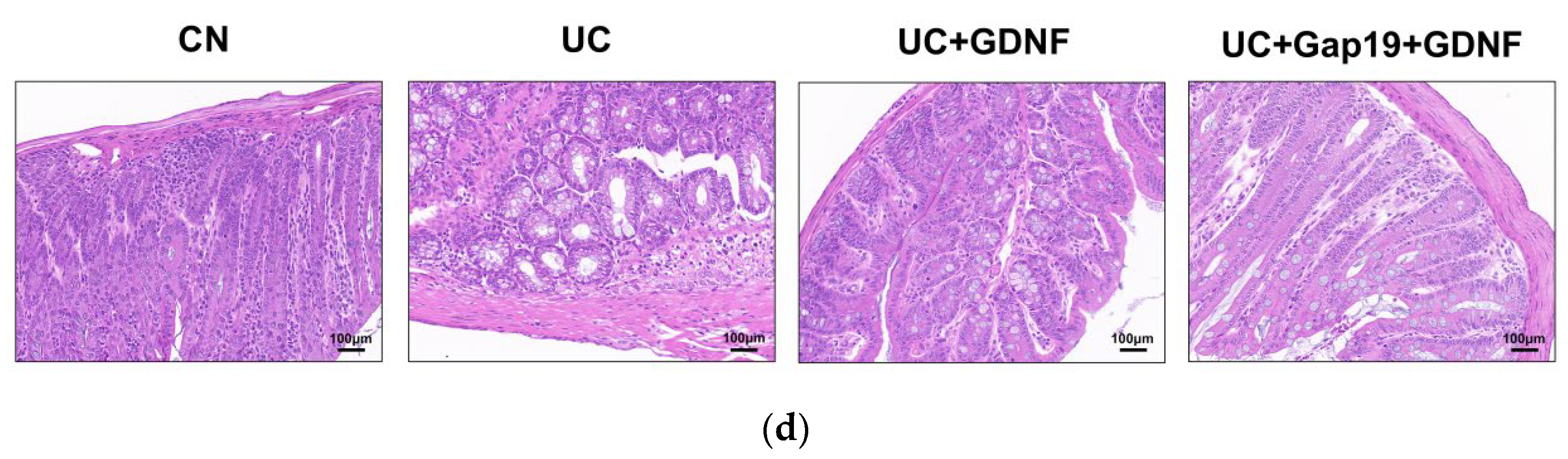
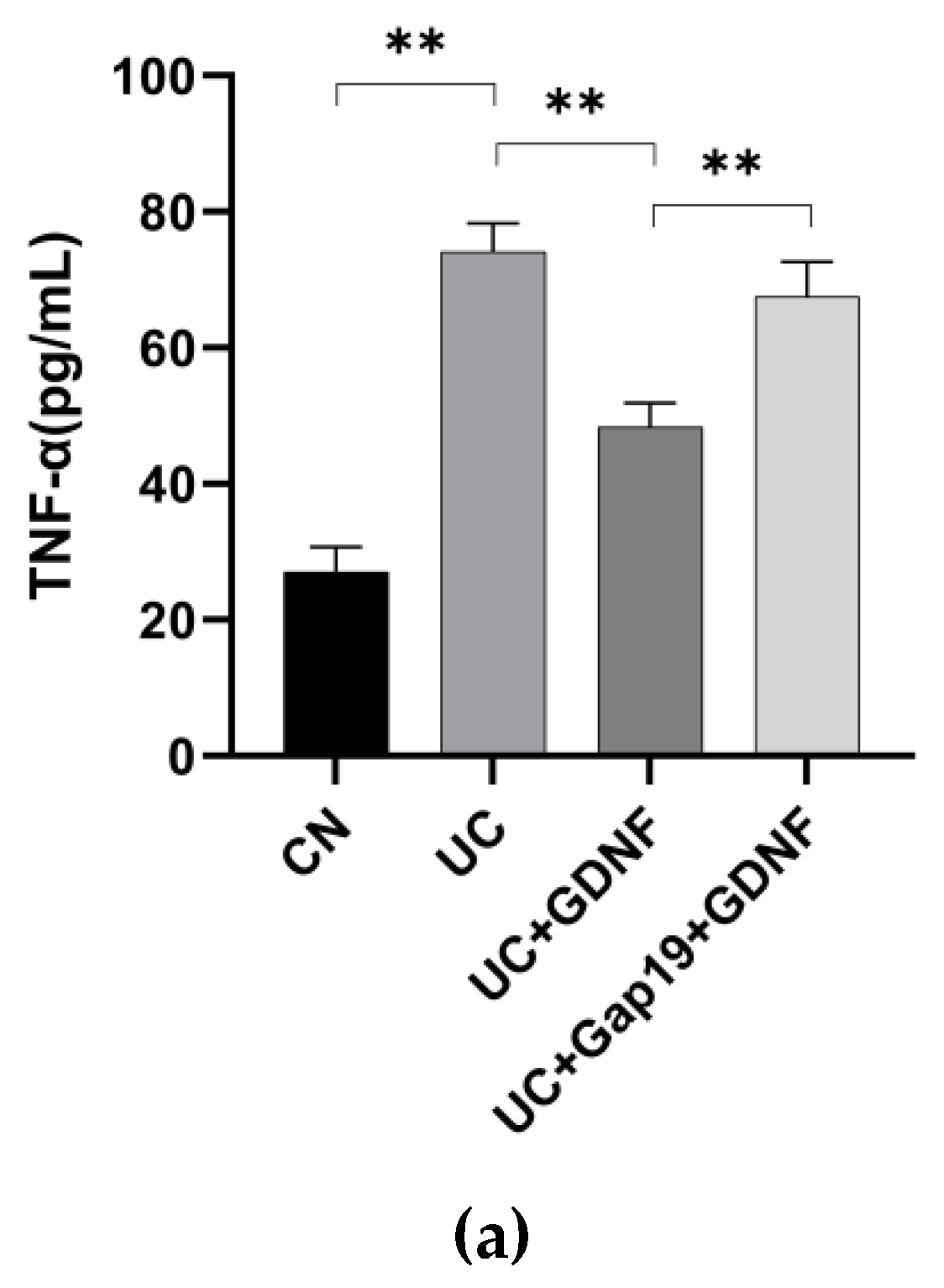
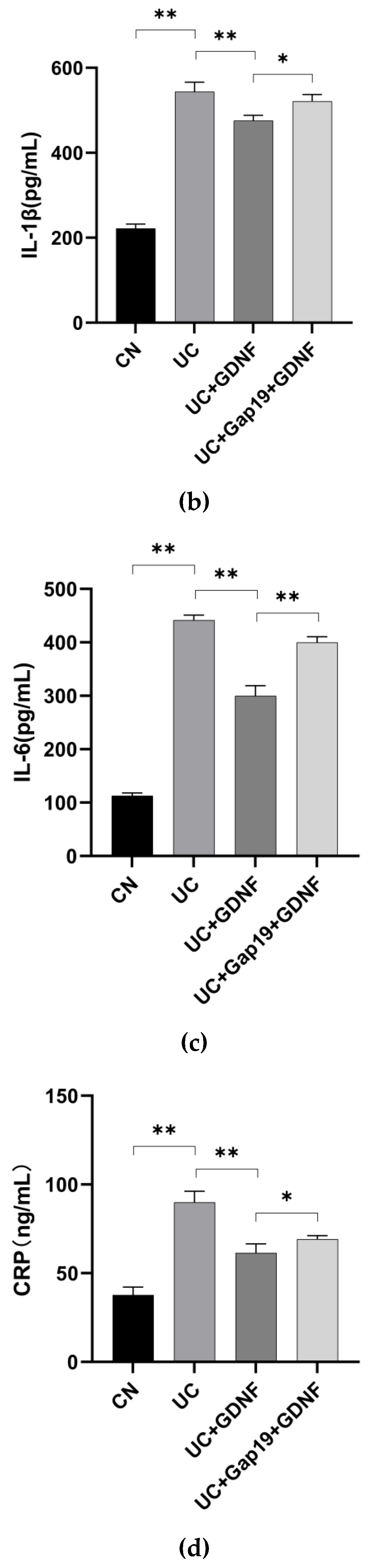
| DAI score | Weight loss(%) | Stool condition | Gross bleeding |
| 0 | None | Normal | None |
| 1 | 1-5 | ||
| 2 | 5-10 | Loose stools | Hemoccult positive |
| 3 | 10-20 | ||
| 4 | >20 | Diarrhea | Severe bleeding |
| GDNF | Forward | 5'-GTTAATGTCCAACTGGGGGTCTA-3' |
| GDNF | Reverse | 5'-ACAGCCACGACATCCCATAACT-3' |
| Cx43 | Forward | 5'-GGGTGATGAACAGTCTGCCTTT-3' |
| Cx43 | Reverse | 5'-AGCTTCTCTTCCTTTCTCATCACAT-3' |
| GAPDH | Forward | 5'-CCTCGTCCCGTAGACAAAATG-3' |
| GAPDH | Reverse | 5'-TGAGGTCAATGAAGGGGTCGT-3' |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




