Submitted:
24 July 2024
Posted:
26 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
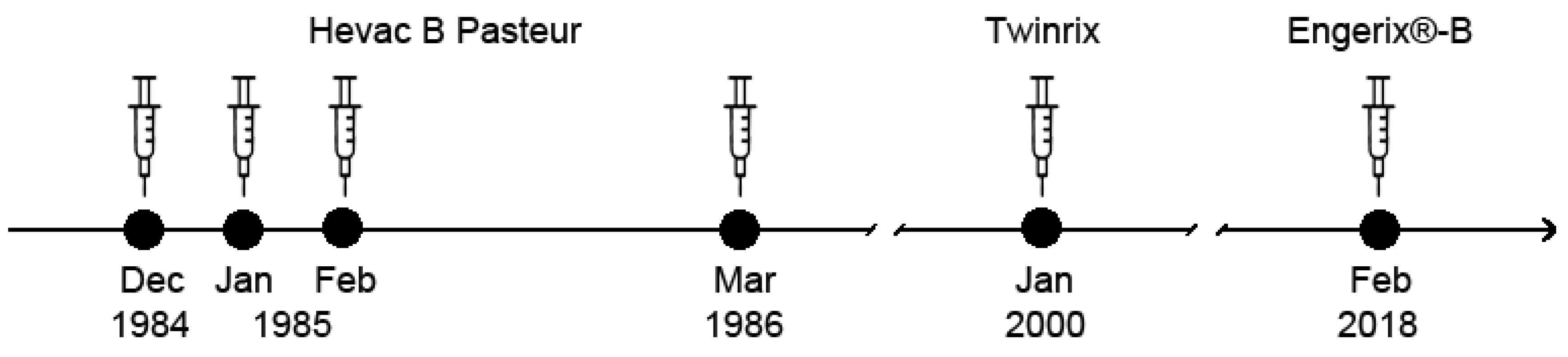
2.1. Vaccines and Immunization Schedule
2.2. Serological Assays
| preS-derived peptides | Accession№. | Sequence |
| Peptides mapping the N-terminal epitopes of preS | ||
| Peptide A (aa 1-29) Peptide B (aa 30-61) Peptide C (aa 17-51) |
AAT28735 | CMGGWSSKPRKGMGTNLSVPNPLGFFPDHQ |
| CLDPAFGANSNNPDWDFNPIKDHWPAANQVGVG | ||
| CSVPNPLGFFPDHQLDPAFGANSNNPDWDFNPIKDH | ||
| Overlapping peptides spanning the whole preS sequence | ||
| P1 (aa 2-31) P2 (aa 22-51) P3 (aa 42-71) P4 (aa 62-91) P5 (aa 82-111) P6 (aa 102-131) P7 (aa 122-151) P8 (aa 142-174) |
AAT28735 | GGWSSKPRKGMGTNLSVPNPLGFFPDHQLD |
| LGFFPDHQLDPAFGANSNNPDWDFNPIKDH DWDFNPIKDHWPAANQVGVGAFGPGLTPPH AFGPGLTPPHGGILGWSPQAQGILTTVSTI QGILTTVSTIPPPASTNRQSGRQPTPISPP GRQPTPISPPLRDSHPQAMQWNSTAFHQAL WNSTAFHQALQDPRVRGLYFPAGGSSSGTV PAGGSSSGTVNPAPNIASHISSISARTGDPVTN | ||
| Peptides covering the NTCP attachment site of genotypes A-H | ||
| Genotype A Genotype B Genotype C Genotype D Genotype E Genotype F Genotype G Genotype H |
APD28359 | GTNLSVPNPLGFFPDHQLDPAFGANSNNPDWDFNPIKDH |
| BAA88276 | GTNLSVPNPLGFFPDHQLDPAFKANSENPDWDLNPHKDN | |
| BAA32833 | GTNLSVPNPLGFFPDHQLDPAFGANSNNPDWDFNPNKDH | |
| BAD02320 BAC65105 AAG49720 BAB64320 BAB69786 |
GQNLSTSNPLGFFPDHQLDPAFRANTANPDWDFNPNKDT GKNHSTTNPLGFFPDHQLDPAFRANTRNPDWDHNPNKDH GQNLSVPNPLGFFPDHQLDPLFRANSSSPDWDFNKNKDN GKNLSTSNPLGFLPDHQLDPAFRANTNNPDWDFNPKKDP GQNLSVPNPLGFFPDHQLDPLFRANSSSPDWDFNTNKDN |
|
2.3. preS Micro-Array Production and Sample Analysis
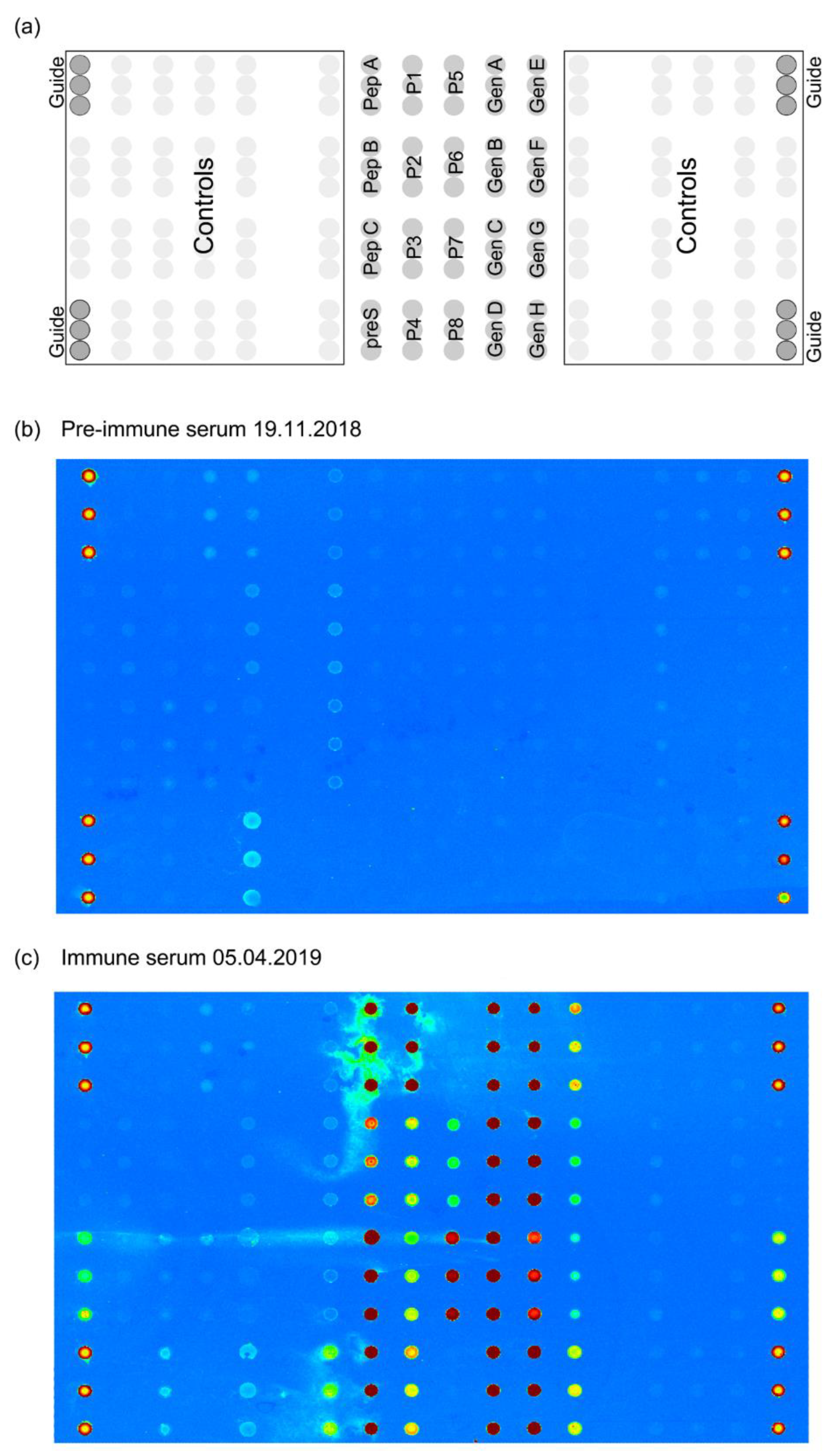
2.4. Determination of Antibody Reactivity to HBV Sub-Viral Particles
2.5. Virus Neutralization Assay
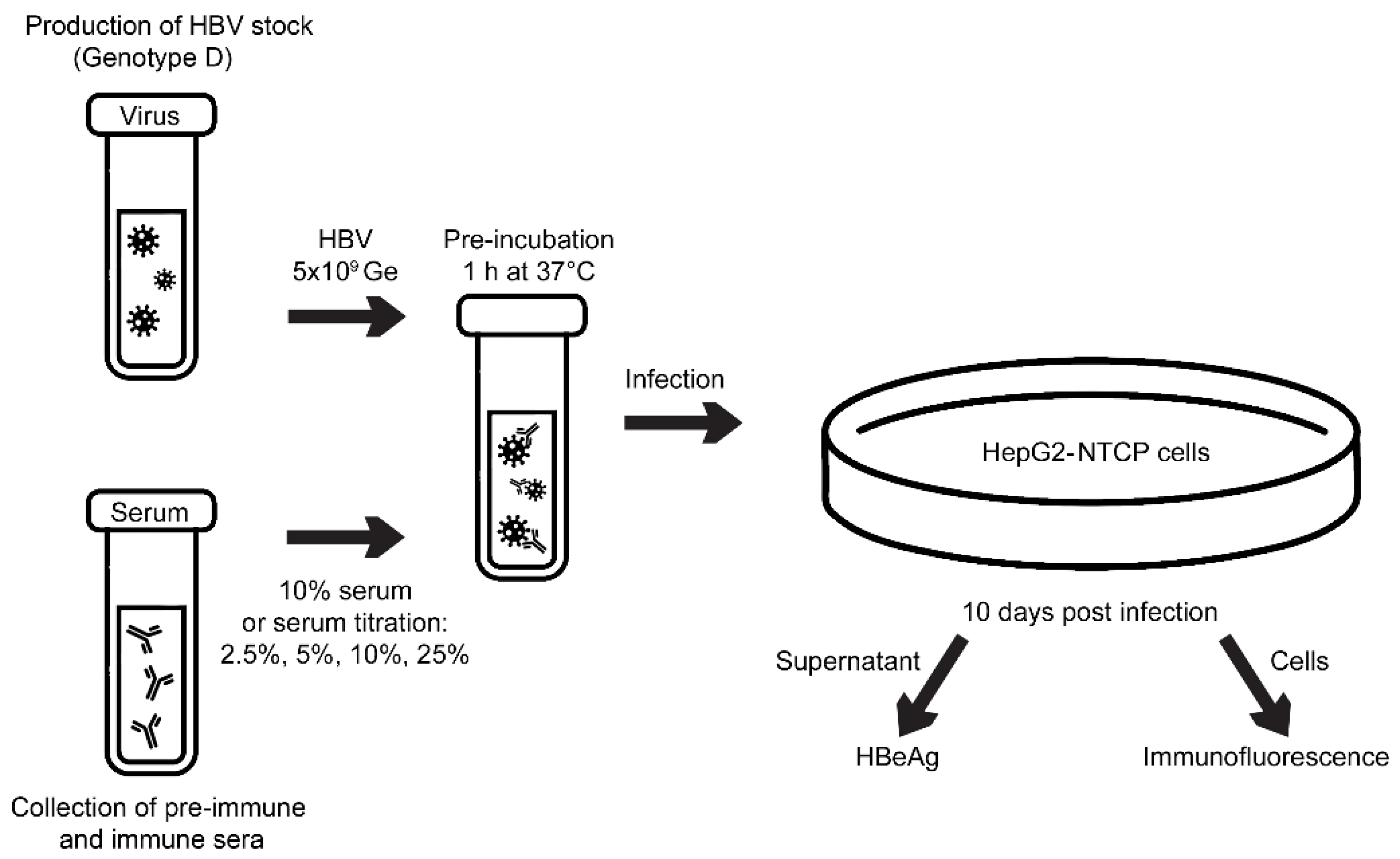
2.6. CD4+/CD8+ T Cell Proliferation Assay and Cytokine Responses
3. Results
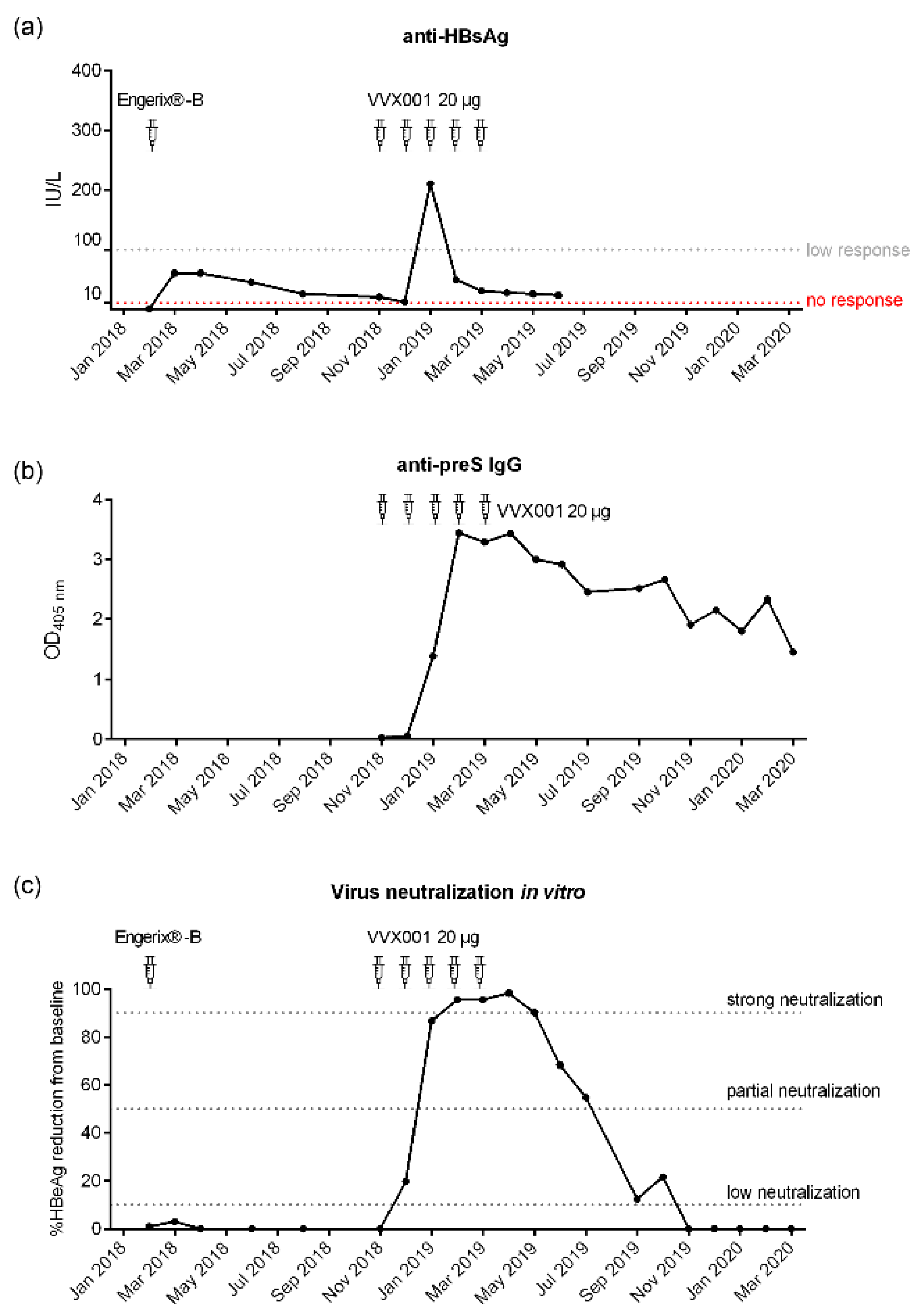
3.1. Repeated Vaccination with HBsAg-Based Vaccines Induced Only Low Anti-HBs Responses in the Study Subject
3.2. VVX001 Induces Robust HBV-Specific Antibody Responses Directed Mainly to the N-Terminus of the preS-Containing NTCP Binding Site
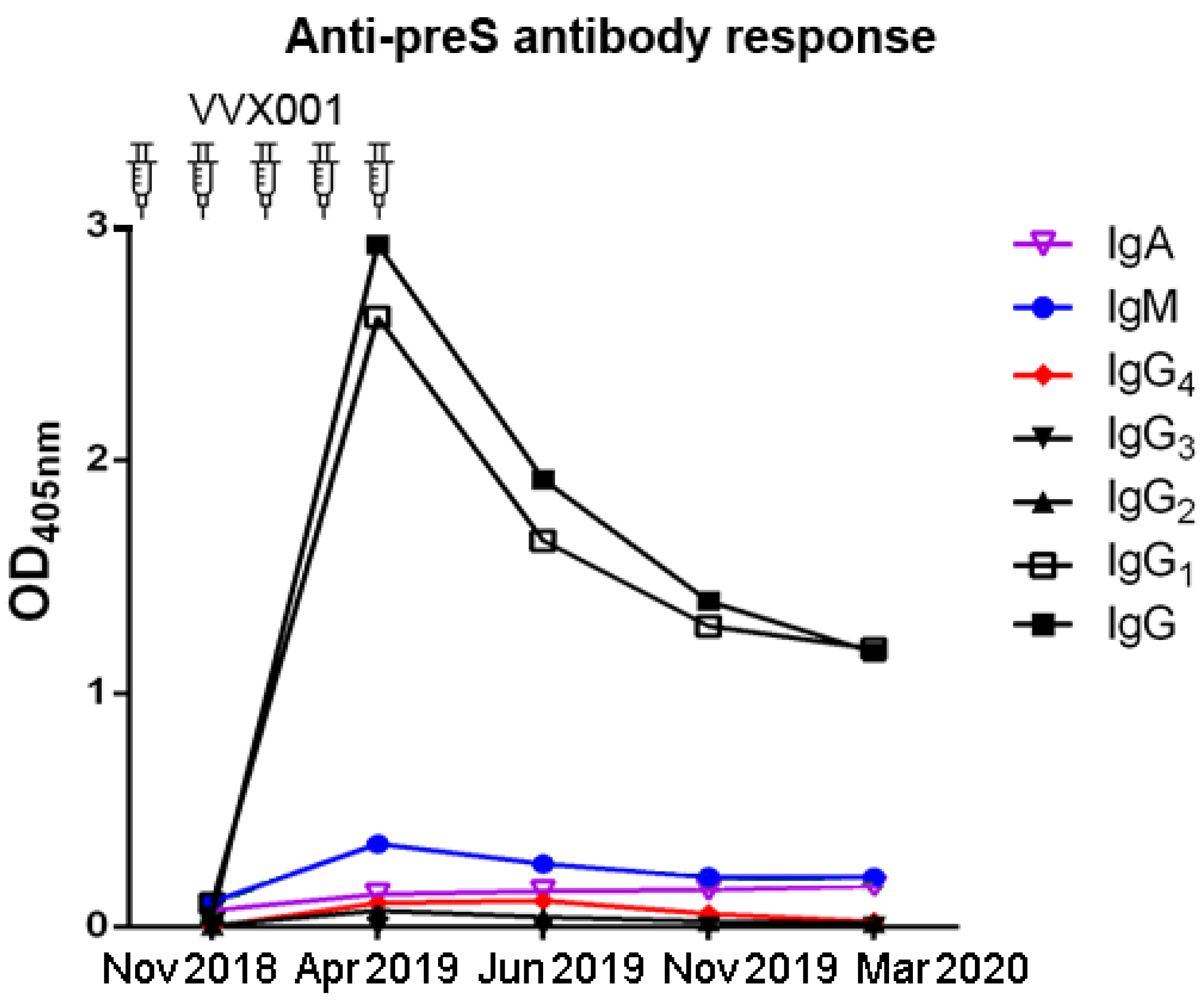
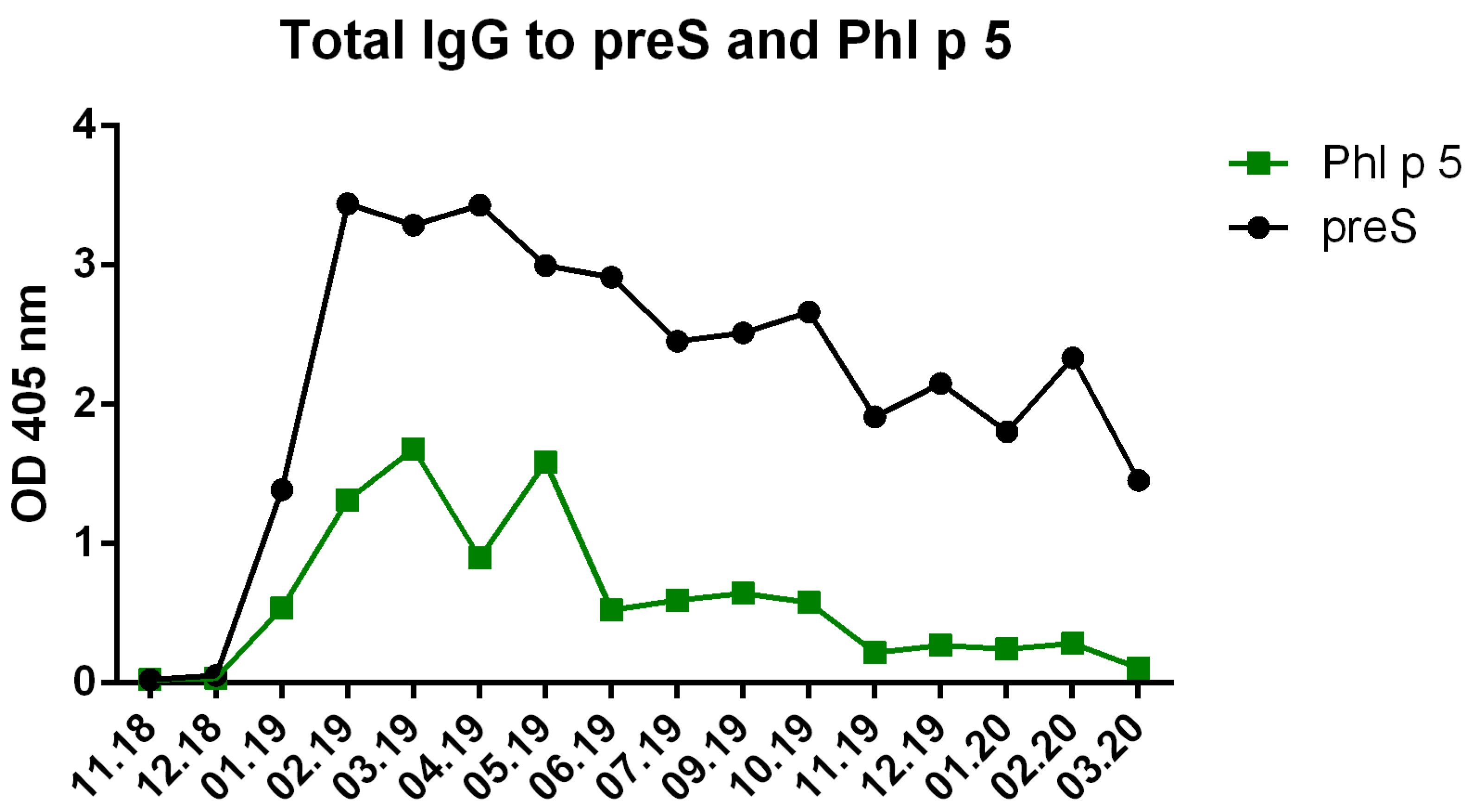
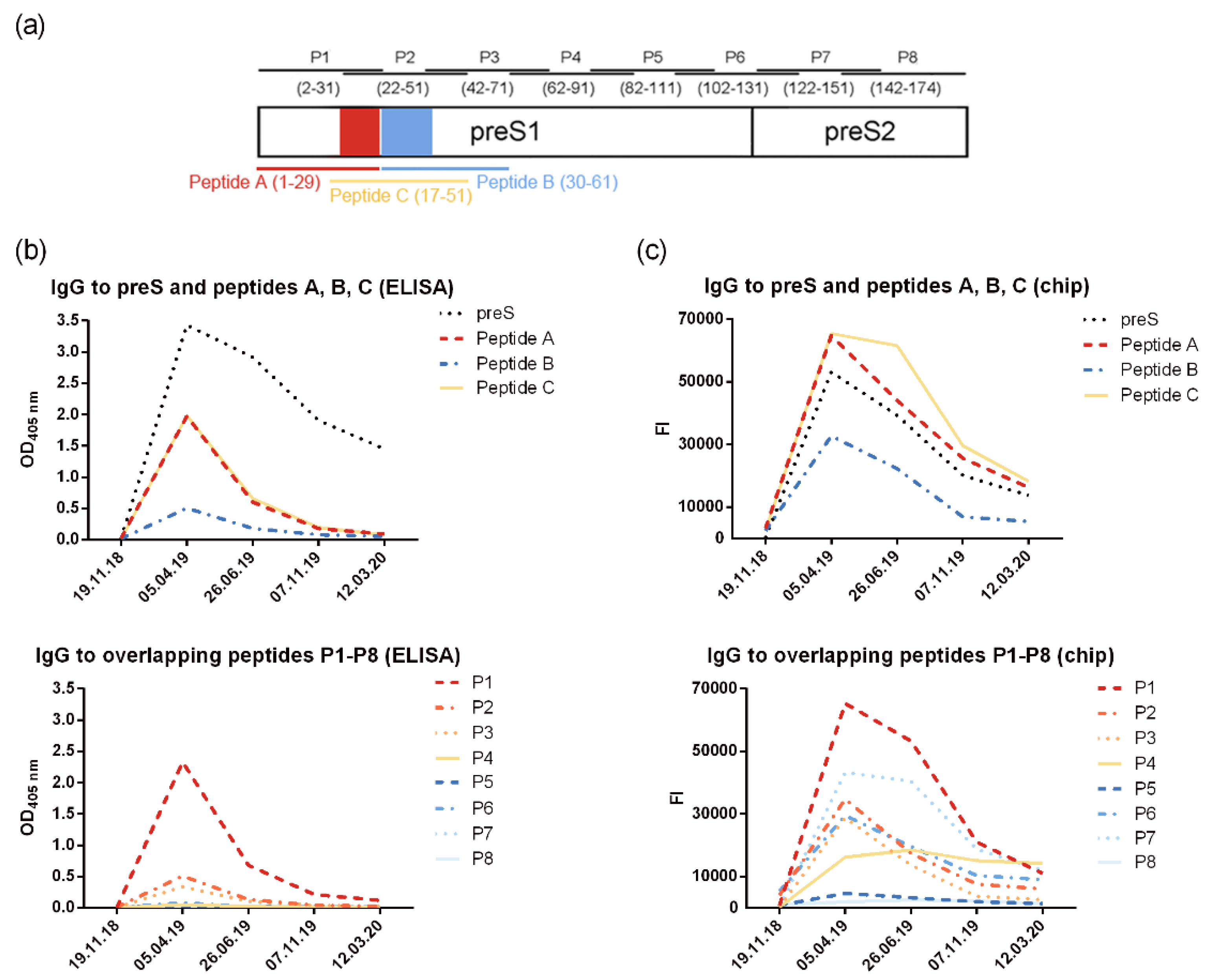
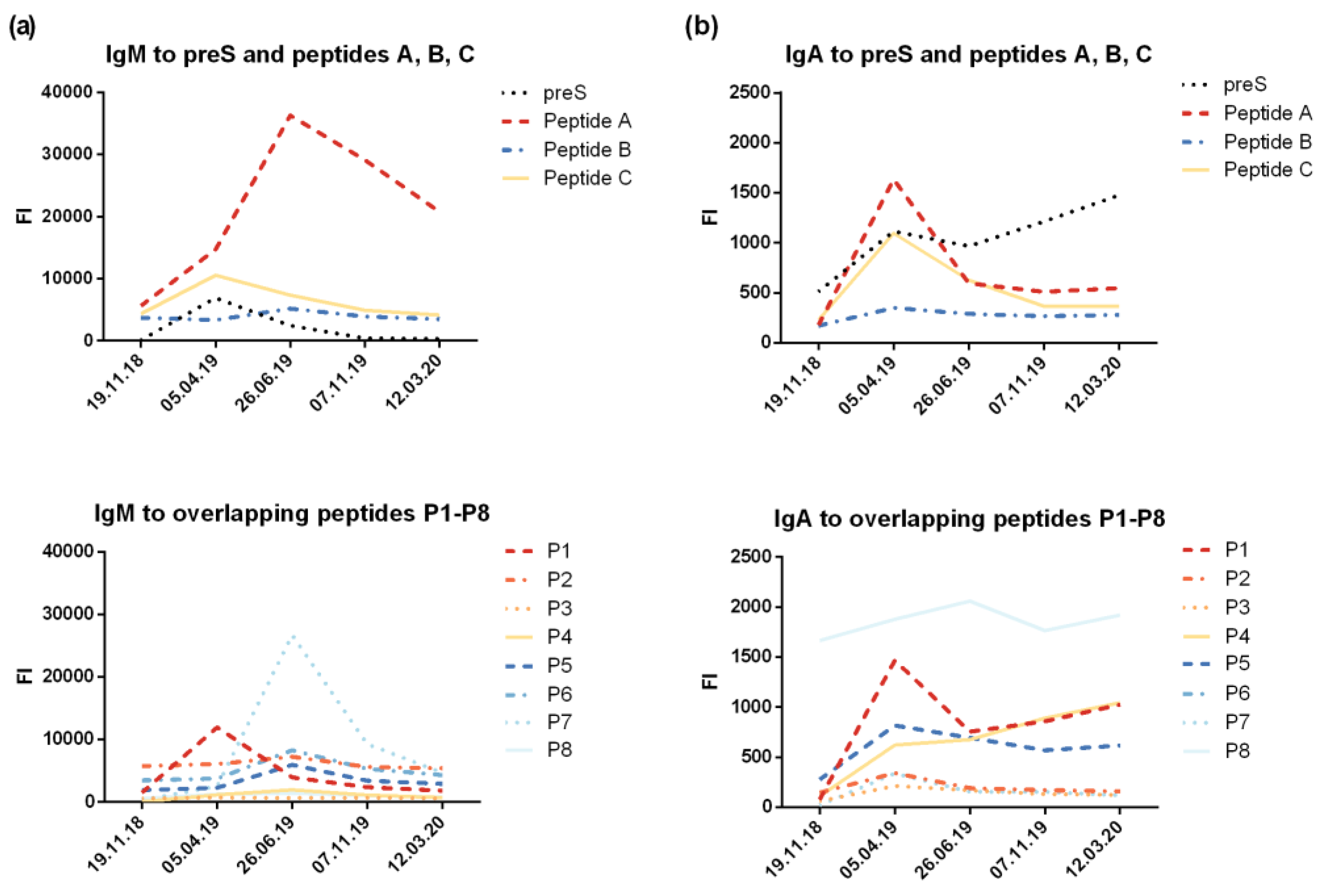
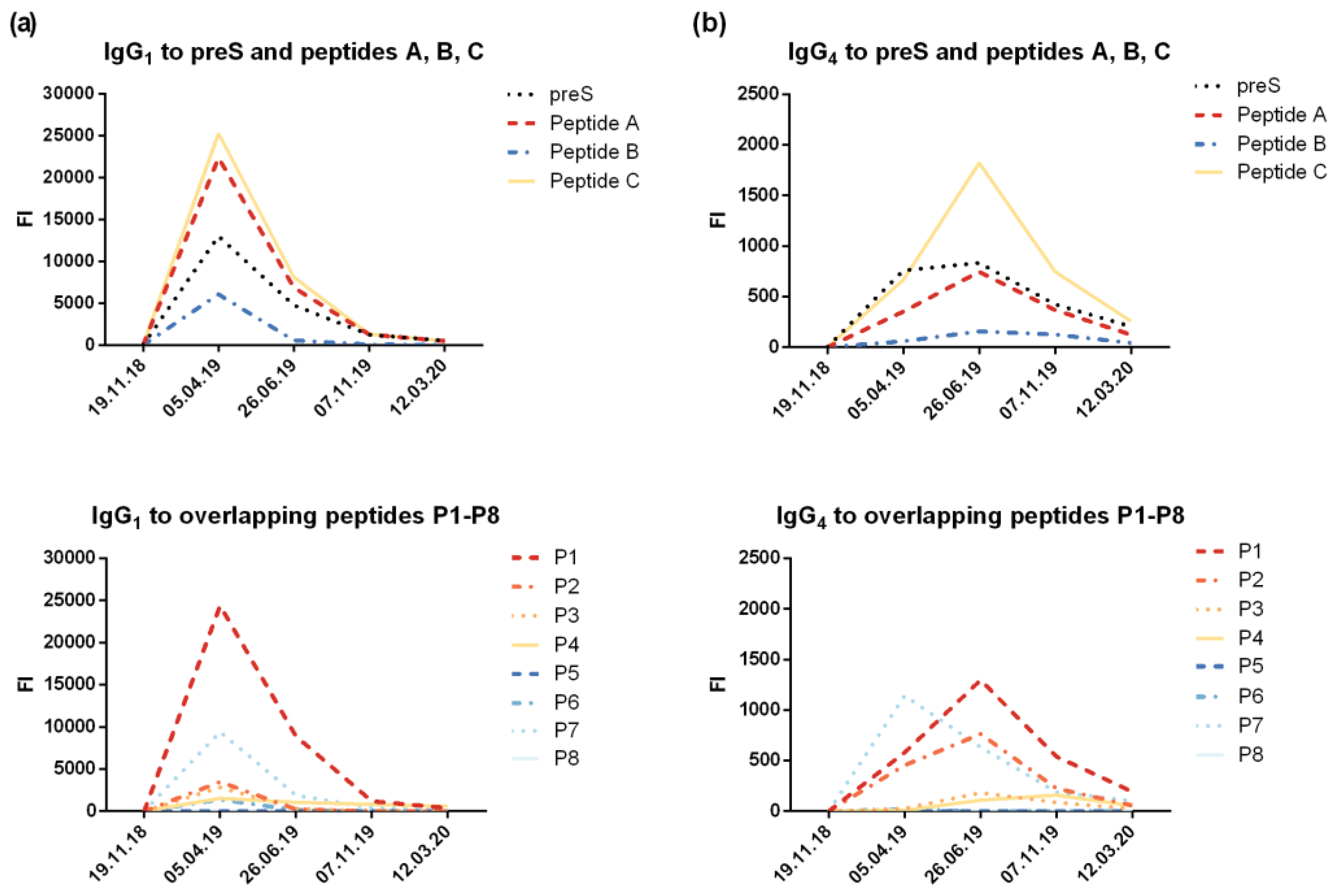
3.3. VVX001-Induced Antibodies Cross-React with HBV Genotypes A-H
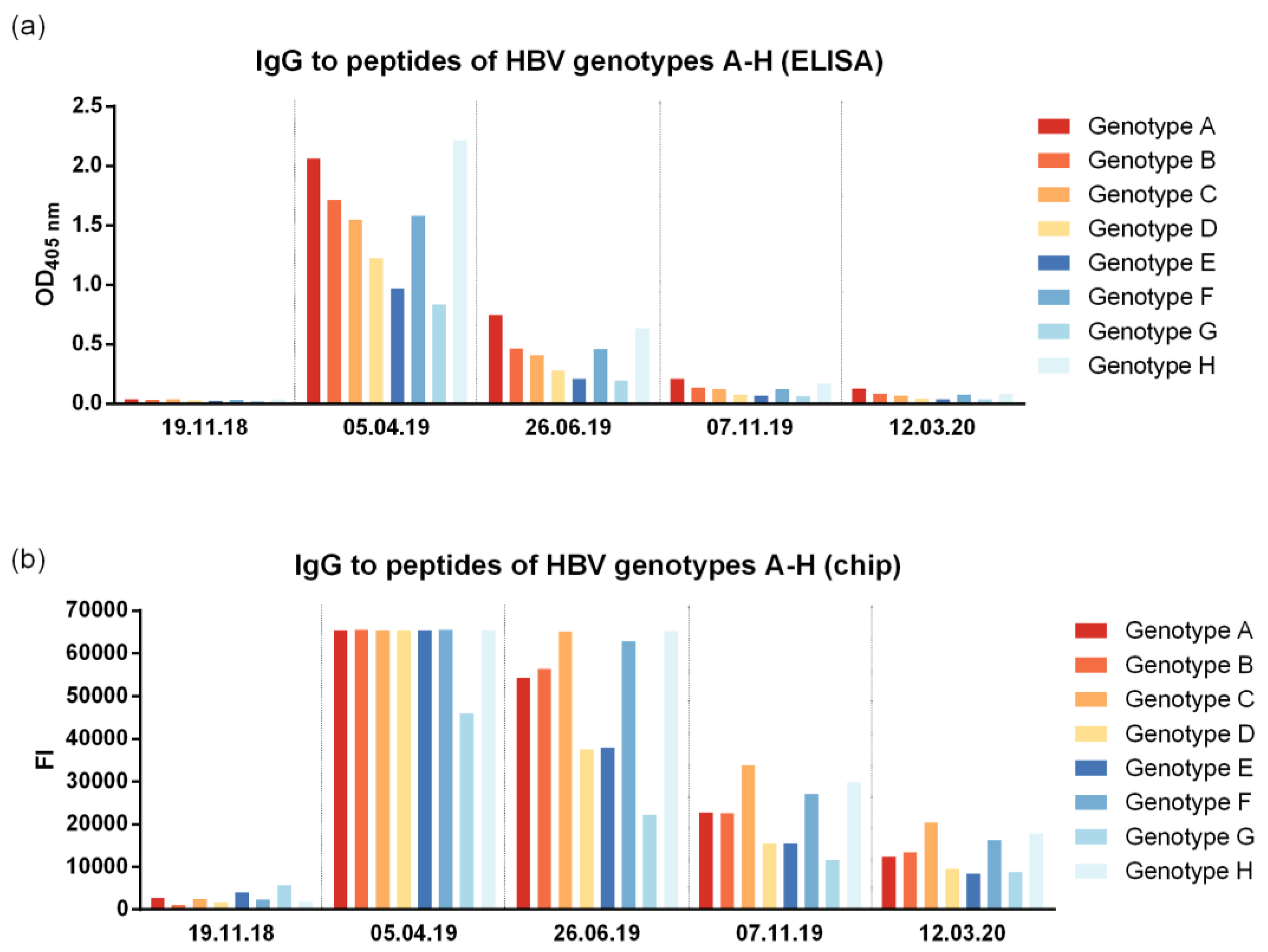
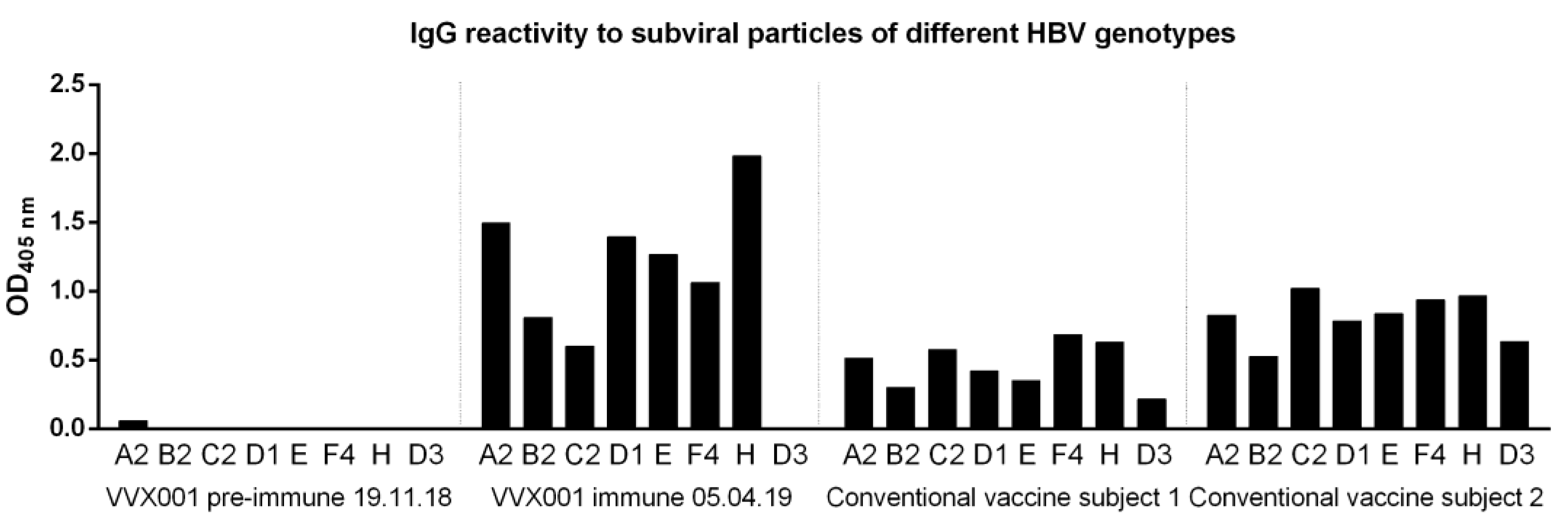
3.4. VVX001-Induced Antibodies Strongly Neutralize HBV Infection In Vitro
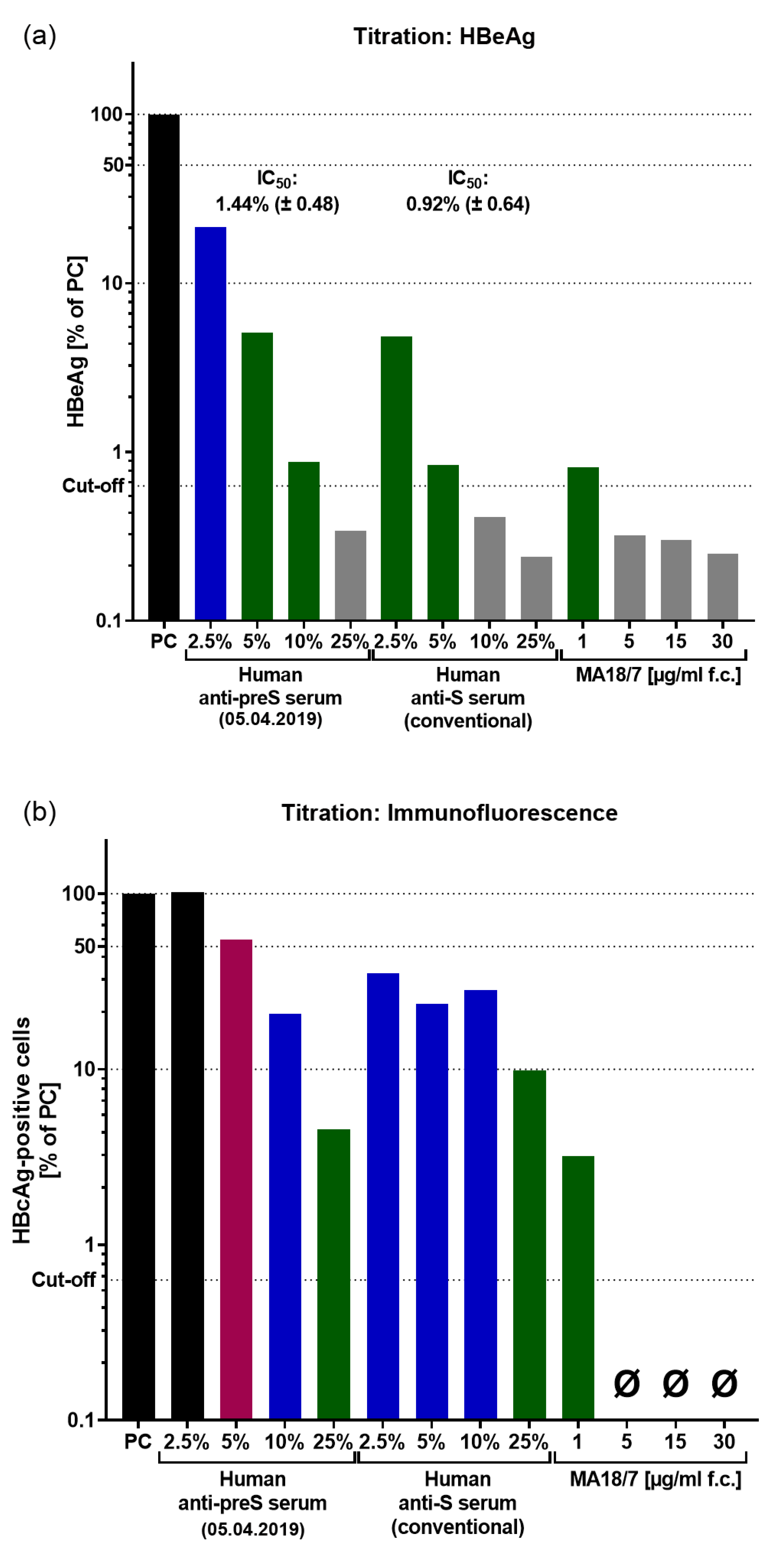
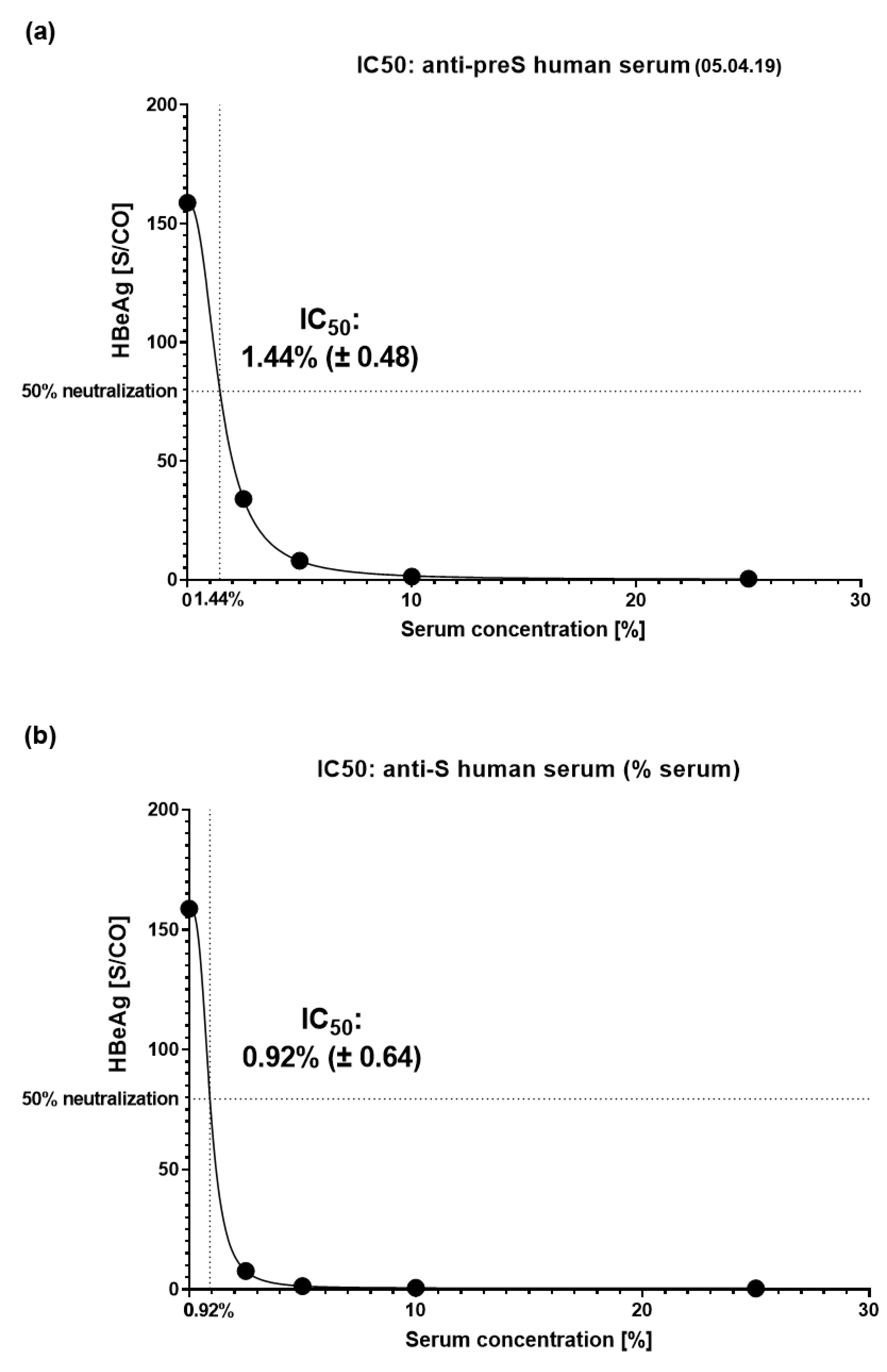
3.5. VVX001 Induces a Sustained preS-Specific CD3+CD4+ Cellular Response Which Is Accompanied by a Mixed Th2/Th1 Cytokine Response
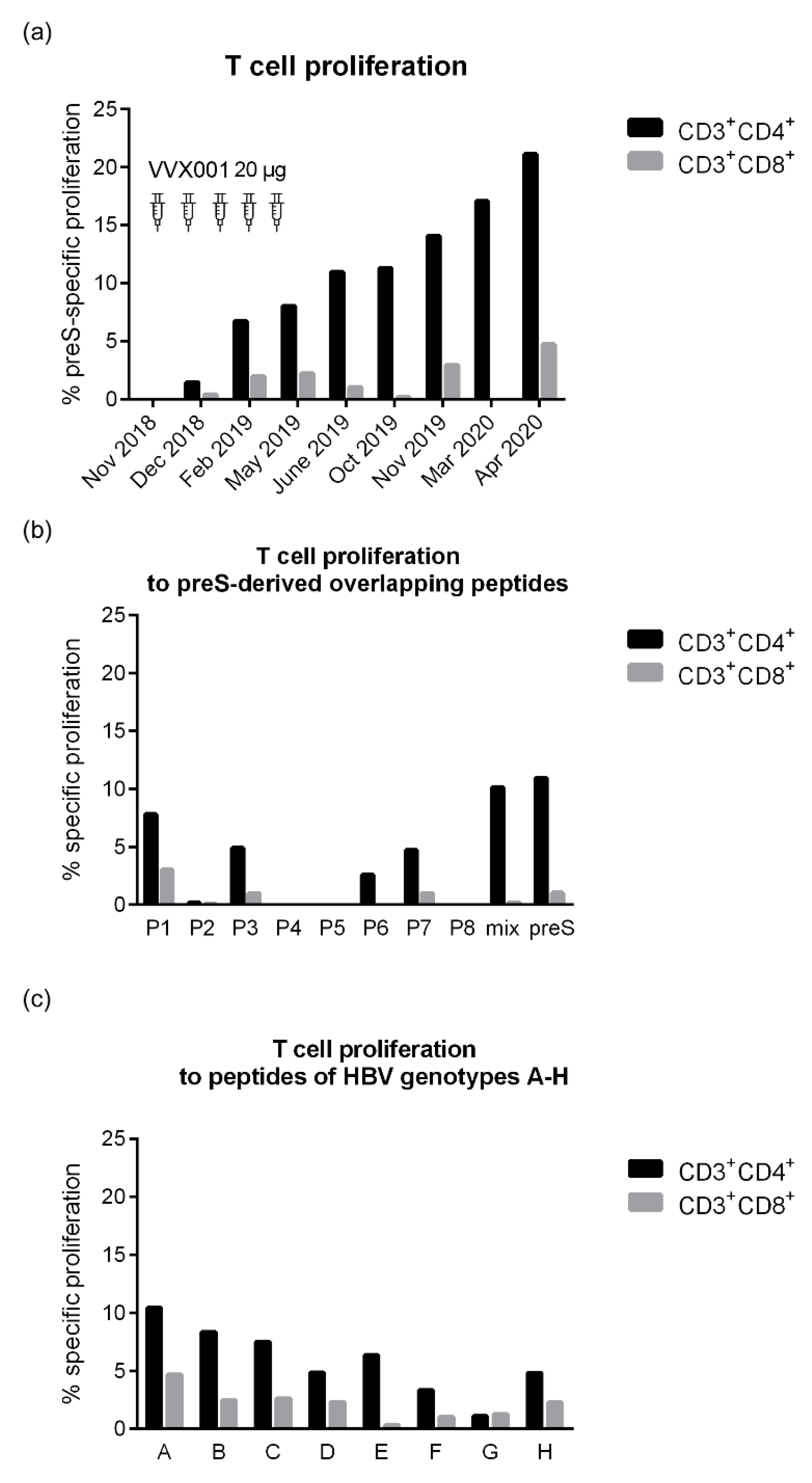
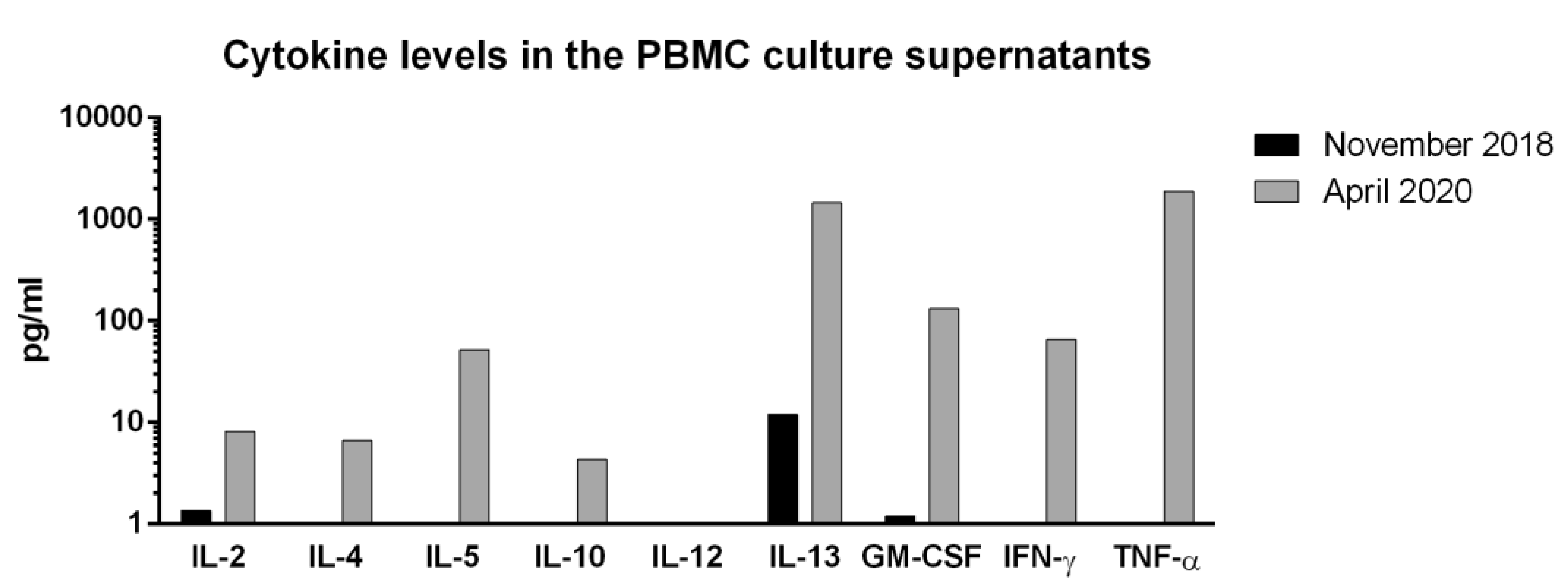
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization Global Hepatitis Report: Action for Access in Low-and Middle-Income Countries, 2024. Global Hepatitis Programme; 2024; ISBN 9789240091672.
- Gerlich, W.H. Prophylactic Vaccination against Hepatitis B: Achievements, Challenges and Perspectives. Med Microbiol Immunol 2015, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H.; Glebe, D. Hepatitis B-Impfung: Altbewährt, Doch Nicht Perfekt. Hepatitis & More 2010, 2, https://www.hepatitisandmore.de/archiv/2010–2/fobi_gerlichshtml. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zakrzewicz, D.; Nosol, K.; Irobalieva, R.N.; Mukherjee, S.; Bang-Sørensen, R.; Goldmann, N.; Kunz, S.; Rossi, L.; Kossiakoff, A.A.; et al. Structure of Antiviral Drug Bulevirtide Bound to Hepatitis B and D Virus Receptor Protein NTCP. Nat Commun 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieglmayer, P.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Schmutz, R.; Lemell, P.; Zieglmayer, R.; Weber, M.; Kiss, R.; Blatt, K.; Valent, P.; Stolz, F.; et al. Mechanisms, Safety and Efficacy of a B Cell Epitope-Based Vaccine for Immunotherapy of Grass Pollen Allergy. EBioMedicine 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, C.; Schöneweis, K.; Georgi, F.; Weber, M.; Niederberger, V.; Zieglmayer, P.; Niespodziana, K.; Trauner, M.; Hofer, H.; Urban, S.; et al. Immunotherapy With the PreS-Based Grass Pollen Allergy Vaccine BM32 Induces Antibody Responses Protecting Against Hepatitis B Infection. EBioMedicine 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulaeva, I.; Cornelius, C.; Zieglmayer, P.; Zieglmayer, R.; Schmutz, R.; Lemell, P.; Weber, M.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Karaulov, A.; Henning, R.; et al. Quantification, Epitope Mapping and Genotype Cross-Reactivity of Hepatitis B PreS-Specific Antibodies in Subjects Vaccinated with Different Dosage Regimens of BM32. EBioMedicine 2020, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salm, K. Herstellung von Hevac B Pasteur, Dtsch Arztebl. Dtsch Arztebl 1983, 80, A-75. [Google Scholar]
- Gattinger, P.; Niespodziana, K.; Stiasny, K.; Sahanic, S.; Tulaeva, I.; Borochova, K.; Dorofeeva, Y.; Schlederer, T.; Sonnweber, T.; Hofer, G.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Requires Antibodies against Conformational Receptor-Binding Domain Epitopes. Allergy: European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2022, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupinek, C.; Wollmann, E.; Baar, A.; Banerjee, S.; Breiteneder, H.; Broecker, B.M.; Bublin, M.; Curin, M.; Flicker, S.; Garmatiuk, T.; et al. Advances in Allergen-Microarray Technology for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Allergy: The MeDALL Allergen-Chip. Methods 2014, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudy, M.; Hanschmann, K.M.; Kress, J.; Nick, S.; Campos, R.; Wend, U.; Gerlich, W.; Nübling, C.M. First WHO International Reference Panel Containing Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes A-G For Assays Of The Viral DNA. J Clin Virol. 2012, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudy, M; Hanschmann, KM; Scheiblauer, H; Wend, U; Schüttler, C; et al. Collaborative study to establish a World Health Organization international Hepatitis B virus genotype panel for HBsAG Assays. World Health Organization. 2011. Available at: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/70785.
- Kucinskaite-Kodze, I.; Pleckaityte, M.; Bremer, C.M.; Seiz, P.L.; Zilnyte, M.; Bulavaite, A.; Mickiene, G.; Zvirblis, G.; Sasnauskas, K.; Glebe, D.; et al. New Broadly Reactive Neutralizing Antibodies against Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen. Virus Res 2016, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosten, C.; Weber, M.; Seifried, E.; Roth, W.K. Evaluation of a New PCR Assay with Competitive Internal Control Sequence for Blood Donor Screening. Transfusion (Paris) 2000, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, A; Döring, B; Mohr, C; Geipel, A; Geyer, J; Glebe, D. Kinetics of the bile acid transporter and hepatitis B virus receptor Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) in hepatocytes. J Hepatol. 2014, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Dominguez Souza, B.F.; König, A.; Rasche, A.; de Oliveira Carneiro, I.; Stephan, N.; Corman, V.M.; Roppert, P.L.; Goldmann, N.; Kepper, R.; Müller, S.F.; et al. A Novel Hepatitis B Virus Species Discovered in Capuchin Monkeys Sheds New Light on the Evolution of Primate Hepadnaviruses. J Hepatol 2018, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glebe, D.; Aliakbari, M.; Krass, P.; Knoop, E. V.; Valerius, K.P.; Gerlich, W.H. Pre-S1 Antigen-Dependent Infection of Tupaia Hepatocyte Cultures with Human Hepatitis B Virus. J Virol 2003, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quah, B.J.C.; Warren, H.S.; Parish, C.R. Monitoring Lymphocyte Proliferation in Vitro and in Vivo with the Intracellular Fluorescent Dye Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate Succinimidyl Ester. Nat Protoc 2007, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinger, P.; Kratzer, B.; Tulaeva, I.; Niespodziana, K.; Ohradanova-Repic, A.; Gebetsberger, L.; Borochova, K.; Garner-Spitzer, E.; Trapin, D.; Hofer, G.; et al. Vaccine Based on Folded Receptor Binding Domain-PreS Fusion Protein with Potential to Induce Sterilizing Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Allergy: European Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2022, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenta, R.; Campana, R.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Niederberger, V. Vaccine Development for Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy Based on Recombinant Allergens and Synthetic Allergen Peptides: Lessons from the Past and Novel Mechanisms of Action for the Future. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2016, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Campana, R.; Niederberger, V. Recombinant Allergy Vaccines Based on Allergen-Derived B Cell Epitopes. Immunol Lett 2017, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederberger, V.; Neubauer, A.; Gevaert, P.; Zidarn, M.; Worm, M.; Aberer, W.; Malling, H.J.; Pfaar, O.; Klimek, L.; Pfützner, W.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Immunotherapy with the Recombinant B-Cell Epitope–Based Grass Pollen Vaccine BM32. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2018, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H. Hepatitis-B-Impfstoffe – Geschichte, Erfolge, Herausforderungen Und Perspektiven. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2022, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, J.N.; Zuckerman, A.J. Recombinant Hepatitis B Triple Antigen Vaccine: Hepacarer®. Expert Rev Vaccines 2002, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggendorf, H.; Shouval, D.; Roggendorf, M.; Gerken, G. Longterm Outcome of Therapeutic Vaccination with a Third Generation Pre-S/S HBV Vaccine (PreHevbrioR) of Chronically HBV Infected Patients. J Pers Med 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert Koch-Institut Empfehlung Der Ständigen Impfkommission (STIKO) Beim Robert Koch-Institut - 2017/2019. Epidemiologischen Bulletin 2018.
- Gerlich, W.H. “Dual Use”: The Anti-Allergy Vaccine BM32 and Its HBV Carrier Protein. EBioMedicine 2020, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Distribution of Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes and Subgenotypes. Medicine (United States) 2021, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focke-Tejkl, M.; Weber, M.; Niespodziana, K.; Neubauer, A.; Huber, H.; Henning, R.; Stegfellner, G.; Maderegger, B.; Hauer, M.; Stolz, F.; et al. Development and Characterization of a Recombinant, Hypoallergenic, Peptide-Based Vaccine for Grass Pollen Allergy. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2015, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, C.M; Sominskaya, I.; Skrastina, D.; Pumpens, P.; El Wahed, A.A.; Beutling, U.; Frank, R.; Fritz, H.J.; Hunsmann, G.; Gerlich, W.H.; Glebe, D. N-Terminal Myristoylation-Dependent Masking Of Neutralizing Epitopes In The Pres1 Attachment Site Of Hepatitis B Virus. J Hepatol. 2011, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time point | Date | IgG1, µg/mL | IgG4, µg/mL |
| preS-specific | |||
| Baseline (before VVX001 vaccination) 1 month after the last injection 4 months after the last injection 8 months after the last injection 12 months after the last injection |
19.11.2018 | 6.19 | 0 |
| 05.04.2019 | 1940.72 | 15 | |
| 26.06.2019 07.11.2019 12.03.2020 |
1347.55 868.05 679.51 |
16.4 4.4 0 |
|
| Peptide A-specific | |||
| Baseline (before VVX001 vaccination) 1 month after the last injection 4 months after the last injection 8 months after the last injection 12 months after the last injection |
19.11.2018 | 0 | 0 |
| 05.04.2019 26.06.2019 07.11.2019 12.03.2020 |
72.24 24.8 9.91 5.85 |
1.55 2.7 0 0 |
|
| Peptide B-specific | |||
| Baseline (before VVX001 vaccination) 1 month after the last injection 4 months after the last injection 8 months after the last injection 12 months after the last injection |
19.11.2018 | 0 | 0 |
| 05.04.2019 | 23.42 | 0 | |
| 26.06.2019 | 9 | 0 | |
| 07.11.2019 12.03.2020 |
4.45 2.85 |
0 0 |
|
| Peptide C-specific | |||
| Baseline (before VVX001 vaccination) 1 month after the last injection 4 months after the last injection 8 months after the last injection 12 months after the last injection |
19.11.2018 | 1.23 | 0 |
| 05.04.2019 26.06.2019 07.11.2019 12.03.2020 |
90.09 29.48 11.4 7.41 |
3.3 5 0 0 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





