Submitted:
24 July 2024
Posted:
25 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
Participants
Protocols
Equipment
Data Processing
- The absolute value of the angular velocity () of the wheelchair around the vertical axis [ in °/s], determined from the frame IMU.
- The wheelchair linear velocity () [in m/s] (more especially, the velocity of the midpoint between both rear wheels centres), determined from IMU on both rear wheels (obtained under the assumption that both rear wheels are rolling without slipping on ground).
- The absolute value of wheelchair linear velocity () [in m/s]
- The wheelchair curvature radius (), expressed in the MWC coordinate system and align with the line passing through both rear wheels centres under the condition of rolling without slipping of both rear wheel), [in m] from the following equation (Eq. 1) based on linear and angular velocities. R is the distance between the center of the wheelchair frame and the point around which the wheelchair rotates.
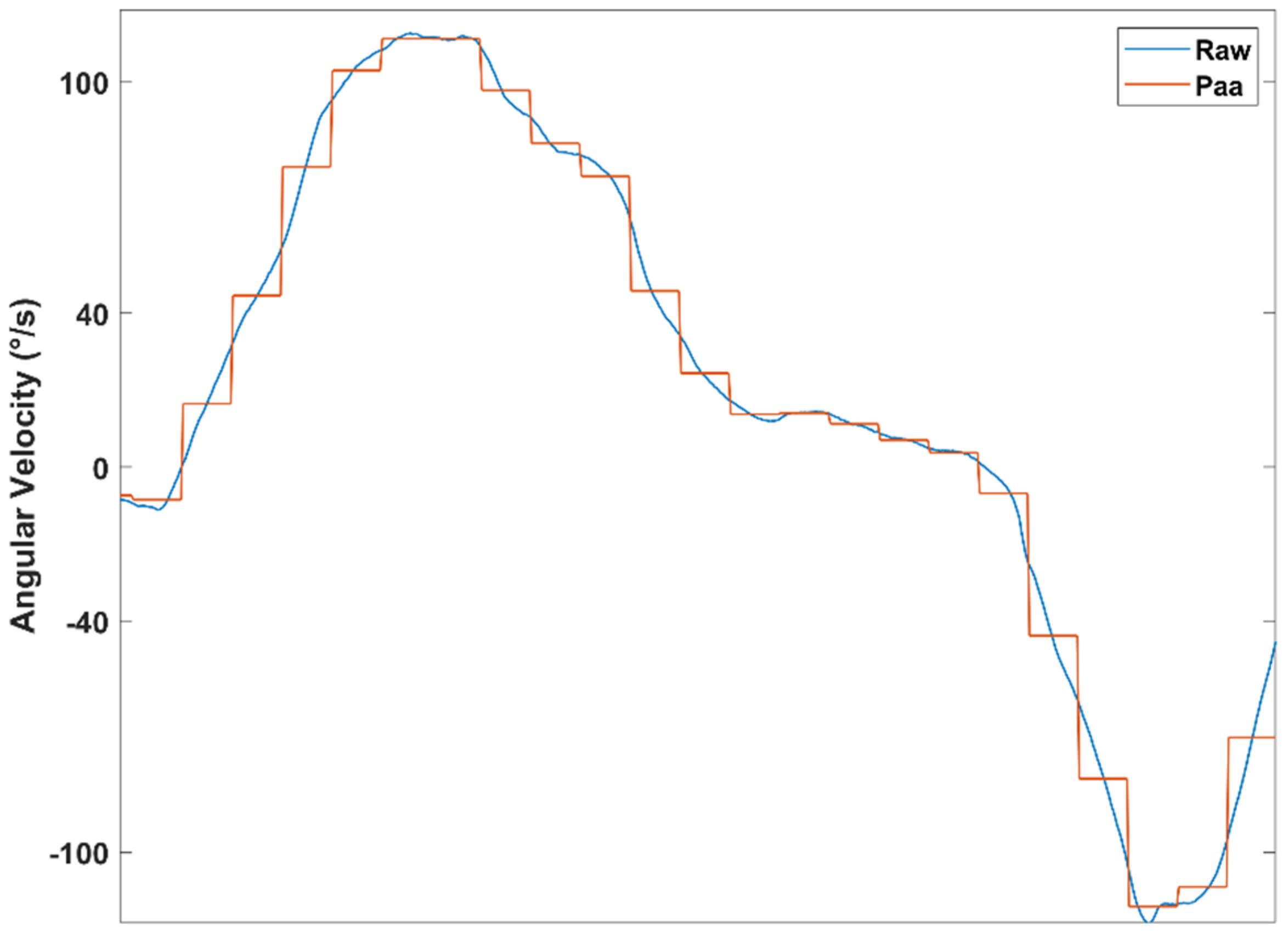
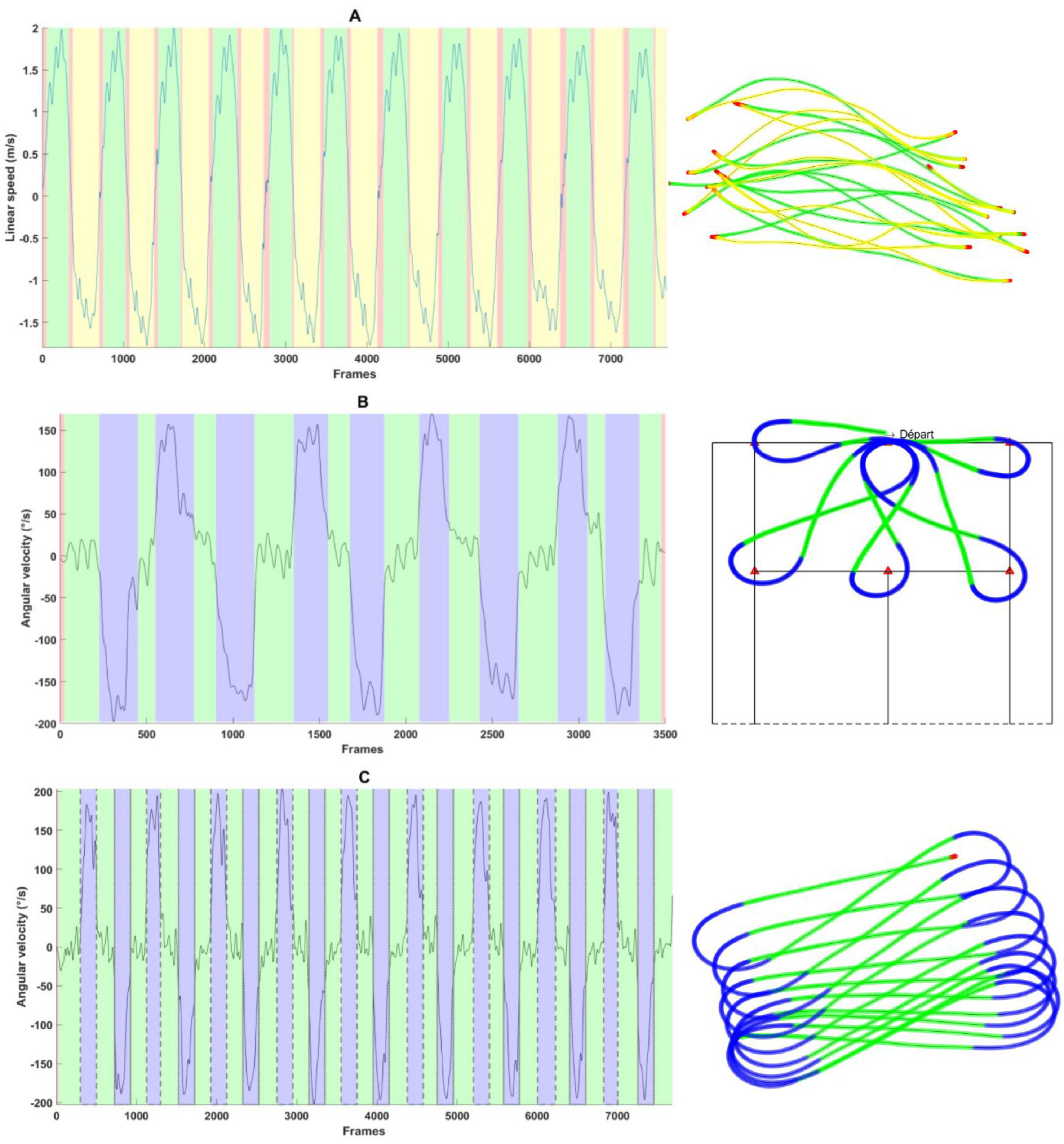
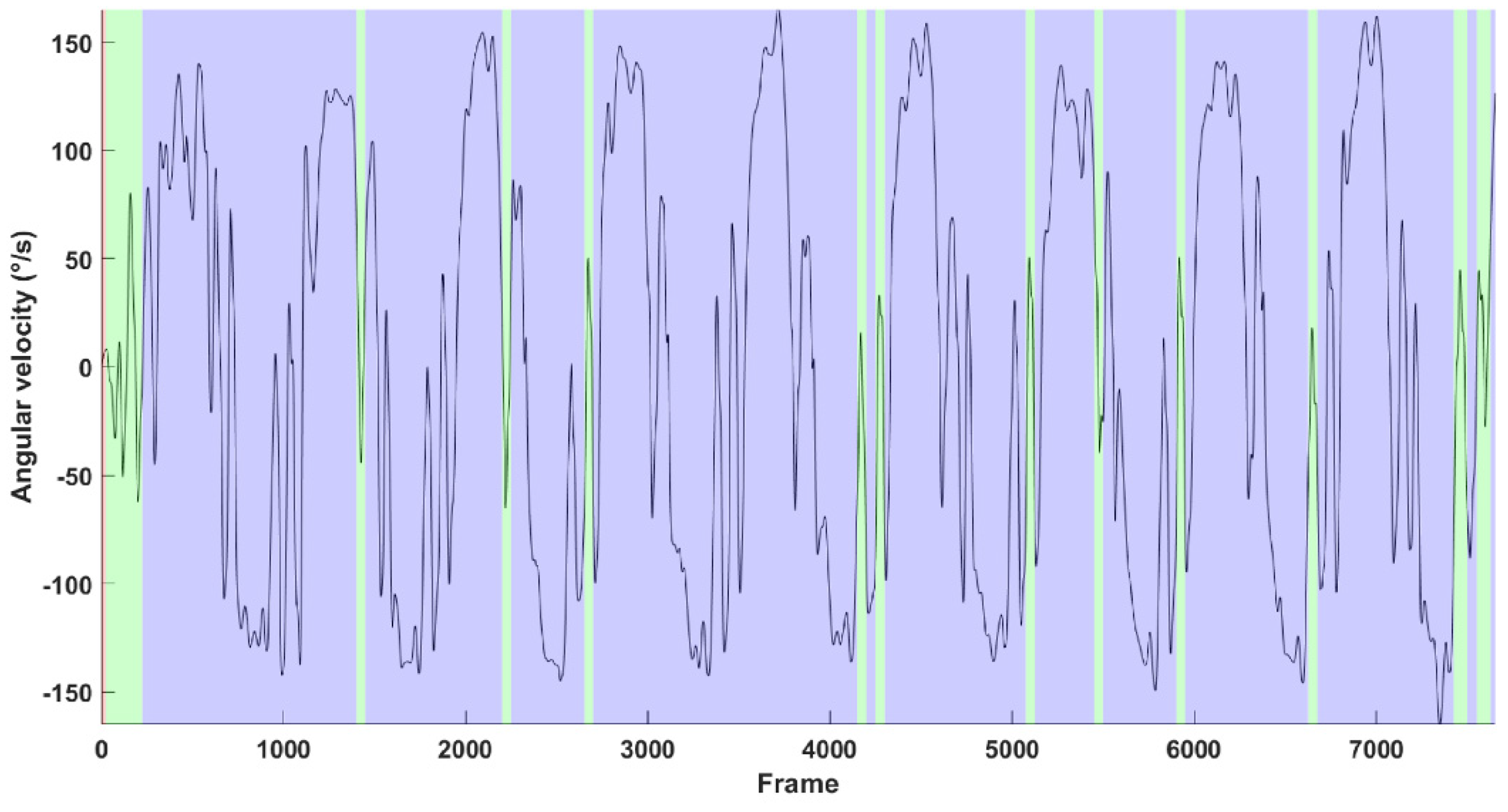
Symbolic Time Series Analysis
- -
- A (static): red
- -
- B (forward propulsion): green
- -
- C (backward propulsion): yellow
- -
- D (pivot rotation): pink
- -
- E (tight rotation): cyan
- -
- F (wide rotation): blue
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tolerico, M.L.; Ding, D.; Cooper, R.A.; Spaeth, D.M.; Fitzgerald, S.G.; Cooper, R.; Kelleher, A.; Boninger, M.L. Assessing Mobility Characteristics and Activity Levels of Manual Wheelchair Users. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2007, 44, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonenblum, S.E.; Sprigle, S.; Caspall, J.; Lopez, R. Validation of an Accelerometer-Based Method to Measure the Use of Manual Wheelchairs. Med. Eng. Phys. 2012, 34, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Liu, T.; Jones, M.; Qian, G.; Jan, Y.K. Characterization of Wheelchair Maneuvers Based on Noisy Inertial Sensor Data: A Preliminary Study. Ann Int Conf IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 2014, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, P.C.; Cardinale, M.; Murray, A.; Gastin, P.; Kellmann, M.; Varley, M.C.; Gabbett, T.J.; Coutts, A.J.; Burgess, D.J.; Gregson, W.; et al. Monitoring Athlete Training Loads: Consensus Statement. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindall, P.; Lenton, J.; Cooper, R.; Tolfrey, K.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V. Data Logger Device Applicability for Wheelchair Tennis Court Movement. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Pay, A.; Sanz-Rivas, D. Physical and Technical Demand in Professional Wheelchair Tennis on Hard, Clay and Grass Surfaces: Implication for Training. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2021, 21, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.; Menear, K.; Schmid, M.; Hunter, G.; Malone, L. Physiological Responses of Skilled Players during a Competitive Wheelchair Tennis Match. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, J.; Mason, B.; Perrat, B.; Smith, M.; Goosey-tolfrey, V. The Validity and Reliability of a Novel Indoor Player Tracking System for Use within Wheelchair Court Sports. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, B.S.; van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Hutchinson, M.J.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Division, Result and Score Margin Alter the Physical and Technical Performance of Elite Wheelchair Tennis Players. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, J.M.; Mason, B.S.; Malone, L.A.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Effect of Team Rank and Player Classification on Activity Profiles of Elite Wheelchair Rugby Players. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloxham, L.A.; Bell, G.J.; Bhambhani, Y.; Steadward, R.D. Time Motion Analysis and Physiological Profile of Canadian World Cup Wheelchair Basketball Players. Sport. Med. Train. Rehabil. 2001, 10, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindall, P.; Lenton, J.P.; Tolfrey, K.; Cooper, R.A.; Oyster, M.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Wheelchair Tennis Match-Play Demands: Effect of Player Rank and Result. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2013, 8, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, T.; Vegter, R.J.K.; van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Hoekstra, A.E.; van der Woude, L.H.V.; de Groot, S. Six Inertial Measurement Unit-Based Components Describe Wheelchair Mobility Performance during Wheelchair Tennis Matches. Sport. Eng. 2023, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Berger, M.A.M.; Bregman, D.J.J.; Veeger, D.H.E.J. Wearable Wheelchair Mobility Performance Measurement in Basketball, Rugby, and Tennis: Lessons for Classification and Training. Sensors (Switzerland) 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberca, I.; Watier, B.; Chénier, F.; Brassart, F.; Faupin, A. Wheelchair Badminton: A Narrative Review of Its Specificities. Biomechanics 2024, 4, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindall, P.; Lenton, J.P.; Whytock, K.; Tolfrey, K.; Oyster, M.L.; Cooper, R.A.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Criterion Validity and Accuracy of Global Positioning Satellite and Data Logging Devices for Wheelchair Tennis Court Movement. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2013, 36, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, C.; Orr, R.; O’Connor, H.; West, C. Global Positioning Systems (GPS) and Microtechnology Sensors in Team Sports: A Systematic Review. Sport. Med. 2013, 43, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Pay, A.; Torres-Luque, G.; Sanz-Rivas, D. Activity Patterns in Male and Female Wheelchair Tennis Matches. Kinesiology 2017, 49, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, B.S.; van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Hutchinson, M.J.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Division, Result and Score Margin Alter the Physical and Technical Performance of Elite Wheelchair Tennis Players. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Berger, M.A.M.; Bregman, D.J.J.; Lagerberg, A.H.; Veeger, H.E.J. Opportunities for Measuring Wheelchair Kinematics in Match Settings; Reliability of a Three Inertial Sensor Configuration. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 3398–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietveld, T.; Vegter, R.J.K.; van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Hoekstra, A.E.; van der Woude, L.H.V.; De Groot, S. Wheelchair Mobility Performance of Elite Wheelchair Tennis Players during Four Field Tests: Inter-Trial Reliability and Construct Validity. PLoS One 2019, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakatchina, S.; Weissland, T.; Astier, M.; Pradon, D.; Faupin, A. Performance, Asymmetry and Biomechanical Parameters in Wheelchair Rugby Players. Sport. Biomech. 2021, 00, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydon, D.S.; Pinder, R.A.; Grimshaw, P.N.; Robertson, W.S.P. Using a Robust Design Approach to Optimize Chair Set-up in Wheelchair Sport 2018, 482. [CrossRef]
- Van Der Slikke, R.M.A.; De Witte, A.M.H.; Berger, M.A.M.; Bregman, D.J.J.; Veeger, D.J.H.E.J. Wheelchair Mobility Performance Enhancement by Changing Wheelchair Properties: What Is the Effect of Grip, Seat Height, and Mass? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietveld, T.; Vegter, R.J.K.; van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Hoekstra, A.E.; van der Woude, L.H.V.; de Groot, S. Six Inertial Measurement Unit-Based Components Describe Wheelchair Mobility Performance during Wheelchair Tennis Matches. Sport. Eng. 2023, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.; Burnett, A.; Farrow, D.; Gabbett, T.; Newton, R. Sports-Science Roundtable: Does Sports-Science Research Influence Practice? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2006, 1, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop D An Applied Research Model for the Sport Sciences. Sport. Med. 2008, 38, 253–263. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.C. A Review on Time Series Data Mining. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2011, 24, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Keogh, E.; Wei, L.; Lonardi, S. Experiencing SAX: A Novel Symbolic Representation of Time Series. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2007, 15, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junejo, I.N.; Aghbari, Z. Al Using SAX Representation for Human Action Recognition. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2012, 23, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITF Wheelchair Tennis Classification Rules. 2023.
- BWF Para Badminton Classification. 2020.
- Poulet, Y.; Brassart, F.; Simonetti, E.; Pillet, H.; Faupin, A.; Sauret, C. Analyzing Intra-Cycle Velocity Profile and Trunk Inclination during Wheelchair Racing Propulsion. Sensors 2023, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansiot, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lo, B.; Yang, G.Z. WISDOM: Wheelchair Inertial Sensors for Displacement and Orientation Monitoring. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, F.K. Speed Measurements in Wheelchair Sports – Theory and Application. Sport. Technol. 2012, 5, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, E.; Chakrabarti, K.; Pazzani, M.; Mehrotra, S. Dimensionality Reduction and Similarity Search in Large Time Series Databases. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2001, 3, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.M.; Mason, B.S.; Perrat, B. Activity Profiles of Elite Wheelchair Rugby Players during Competition. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Wheelchair tennis | Wheelchair badminton | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics |
Total (n = 36) |
Open (m = 8 / f = 5) |
Quad (m = 4 / f = 1) |
WH1 (m = 7 / f = 4) |
WH2 (m = 4 / f = 3) |
| Age (years) | 40 (9.5) | 36.2 (11.1) | 44 (5.8) | 43.9 (6.1) | 40 (10.9) |
| Mass (kg) | 66.7 (13) | 66.7 (16.9) | 69.4 (11.5) | 69 (10) | 61 (9.9) |
| Years of training | 9.2 (6.5) | 12.3 (8) | Unknown | 7 (2.7) | 7.1 (5.3) |
| a | b | c | d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m/s) | ≤ 0.05 | 0.05 < v < 0.5 | ≥ 0.5 | |
| (m/s) | ≤ -0.05 | -0.05 < v < 0.05 | ≥ 0.05 | |
| (°/s) | < 40 | > 40 | ||
| (m) | ≤ 0.2 | 0.2 < < 0.5 | ≥ 0.5 |
| Static | Forward propulsion | Backward propulsion | Pivot rotation | Tight rotation | Wide rotation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b b b | d d d | d d d | ||||
| b b b | b b b | b b b | c c c | c c c | c c c | |
| c c c | a a a | |||||
| b b b | c c c | d d d | ||||
| A A A | B B B | C C C | D D D | E E E | F F F |
| Tests | Figure-of-eight test | Star test | FP-BP test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP | Rotations | FP | Rotations | FP | BP | |
| Observations | 20 (1.3) | 19 (1.6) | 10 | 9 | 12 (1.8) | 11 (1.9) |
| SAX method | 19 (2.7) | 19 (3.0) | 10 (0.6) | 9 (0.3) | 12 (1.8) | 11 (1.9) |
| CV (%) | 3.6 | 3.4 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





