Submitted:
18 July 2024
Posted:
22 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
References
- Sood, A.; Jeong, W.; Palma-Zamora, I.; Abdollah, F.; Butaney, M.; Corsi, N.; et al. Description of Surgical Technique and Oncologic and Functional Outcomes of the Precision Prostatectomy Procedure (IDEAL Stage 1-2b Study). Eur Urol. 2022, 81, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Long, Q.; Guan, B.; Mu, L.; Tian, J.; Jiang, Y.; Bai, X.; Wu, D. Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy Is More Beneficial for Prostate Cancer Patients: A System Review and Meta-Analysis. Med SciMonit. 2018, 24, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amano, K.; Suzuki, K.; Ito, Y. Changes in quality of life and lower urinary tract symptoms over time in cancer patients after a total prostatectomy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Support Care Cancer. 2022, 30, 2959–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkhasov, R.M.; Lee, T.; Huang, R.; Berkley, B.; Pinkhasov, A.M.; Dodge, N.; et al. Prediction of Incontinence after Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: Development and Validation of a 24-Month Incontinence Nomogram. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDiarmid, S.A. Incontinence after radical prostatectomy: Pathophysiology and management. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2001, 2, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagens, M.J.; Veerman, H.; de Ligt, K.M.; Tillier, C.N.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; van Moorselaar, R.J.A.; et al. Functional outcomes rather than complications predict poor health-related quality of life at 6 months after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Robot Surg. 2022, 16, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikita, K.; Honda, M.; Shimizu, R.; Teraoka, S.; Kawamoto, B.; Yumioka, T.; et al. Longitudinal, 5-year long-term outcomes for urinary continence and quality of life after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy in Japanese patients. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2022, 14, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondoputro, W.; Thompson, J.; Evans, M.; Bolton, D.; Frydenberg, M.; Murphy, D.G.; et al. How Does Age Affect Urinary Continence following Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy? A Prospective Multi-Institutional Study Using Independently Collected, Validated Questionnaires. J Urol. 2022, 207, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.J.; Truesdale, M.D.; Hruby, G.W.; Landman, J.; Badani, K.K. Impacting factors for recovery of erectile function within 1 year following robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J Sex Med. 2011, 8, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, N.; Miyazaki, T.; Tsubouchi, K.; Okabe, Y.; Shibayama, K.; Emoto, D.; Matsuoka, W.; Maruta, H.; Aoyagi, C.; Matsuzaki, H.; Irie, S.; Nakamura, N.; Matsuoka, H. Comprehensive approach for preserving cavernous nerves and erectile function after radical prostatectomy in the era of robotic surgery. Int J Urol. 2021, 28, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, F.; Preece, P.; Kapoor, J.; Everaerts, W.; Murphy, D.G.; Corcoran, N.M.; Costello, A.J. Preservation of the neurovascular bundles is associated with improved time to continence after radical prostatectomy but not long-term continence rates: Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2015, 68, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haglind, E.; Carlsson, S.; Stranne, J.; Wallerstedt, A.; Wilderäng, U.; Thorsteinsdottir, T.; Lagerkvist, M.; Damber, J.E.; Bjartell, A.; Hugosson, J.; Wiklund, P.; Steineck, G.; LAPPRO steering committee. Urinary Incontinence and Erectile Dysfunction After Robotic Versus Open Radical Prostatectomy: A Prospective, Controlled, Nonrandomised Trial. Eur Urol. 2015, 68, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, H.; Weng, X.; Liu, X. Intrafascial nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy improves patients' postoperative continence recovery and erectile function: A pooled analysis based on available literatures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018, 97, e11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grøn Jensen, L.C.; Boie, S.; Axelsen, S. International consultation on incontinence questionnaire - Urinary incontinence short form ICIQ-UI SF: Validation of its use in a Danish speaking population of municipal employees. PLoS ONE. 2022, 17, e0266479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sanchez-Salas, R.; Tourinho-Barbosa, R.; Sivaraman, A.; Borges, R.C.; Candela, L.; Cathala, N.; Mombet, A.; Marra, G.; Sanchez, L.R.; Boumezrag, C.B.; Lanz, C.; Macek, P.; Korkes, F.; Cathelineau, X. Assessing the efficacy of pelvic floor muscle training and duloxetine on urinary continence recovery following radical prostatectomy: A randomized clinical trial. Prostate. 2024, 84, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacci, M.; Ierardi, A.; Rose, A.D.; Tazzioli, S.; Scapaticci, E.; Filippi, S.; Maggi, M.; Nicita, G.; Carini, M.; Montorsi, F. Vardenafil can Improve Continence Recovery after Bilateral Nerve Sparing Prostatectomy: Results of a Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacci, M.; De Nunzio, C.; Sakalis, V.; Rieken, M.; Cornu, J.N.; Gravas, S. Latest Evidence on Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence. J Clin Med. 2023, 12, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kadono, Y.; Ueno, S.; Yaegashi, H.; Ofude, M.; Izumi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Mizokami, A.; Miwa, S.; Miyagi, T.; Namiki, M. Urodynamic evaluation before and immediately after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2014, 84, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadono, Y.; Ueno, S.; Iwamoto, D.; Takezawa, Y.; Nohara, T.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A.; Namiki, M. ChronologicalUrodynamic Evaluation of ChangingBladder and UrethralFunctionsAfter Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy. Urology. 2015, 85, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadono, Y.; Ueno, S.; Kadomoto, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Takezawa, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Nohara, T.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A.; Gabata, T.; et al. Use of pre-operativefactorsincludingurodynamicevaluations and nerve-sparingstatus for predictingurinary continence recoveryafter robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: Nerve-sparing technique contributes to the reduction of postprostatectomy incontinence. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2016, 35, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadono, Y.; Nohara, T.; Kawaguchi, S.; Naito, R.; Urata, S.; Nakashima, K.; Iijima, M.; Shigehara, K.; Izumi, K.; Gabata, T.; et al. Investigating the mechanismunderlyingurinary continence recoveryafter radical prostatectomy:Effectiveness of a longer urethralstump to preventurinary incontinence. BJU Int. 2018, 122, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefermehl, L.; Bossert, K.; Ramakrishnan, V.M.; Seifert, B.; Lehmann, K. A Prospective Analysis of the Effects of Nerve-Sparing Radical Prostatectomy on Urinary Continence Based on Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite and International Index of Erectile FunctionScoringSystems. Int Neurourol J. 2018, 22, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Secin, F.P.; Serio, A.; Bianco FJJr Karanikolas, N.T.; Kuroiwa, K.; Vickers, A.; Touijer, K.; Guillonneau, B. Preoperative and intraoperativeriskfactors for side-specific positive surgicalmargins in laparoscopic radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. EurUrol. 2007, 51, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.R.; Sivaraman, A.; Coelho, R.F.; Chauhan, S.; Palmer, K.J.; Orvieto, M.A.; Camacho, I.; Coughlin, G.; Rocco, B. Pentafecta:a new concept for reportingoutcomes of robot-assistedlaparoscopic radical prostatectomy. EurUrol. 2011, 59, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, D.R.; Hyndman, M.E.; Segal, R.L.; Mettee, L.Z.; Trock, B.J.; Feng, Z.; Su, L.M.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Pavlovich, C.P. Urinaryoutcomes are significantlyaffected by nerve sparingqualityduring radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2013, 82, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Wu, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhai, G.; Wu, J. Cavernous Nerve InjuryResulted Erectile Dysfunction and Regeneration. J ImmunolRes. 2021, 2021, 5353785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Walsh, P.C.; Donker, P.J. Impotence following radical prostatectomy: Insight intoetiology and prevention. J Urol. 1982, 128, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficarra, V.; Novara, G.; Rosen, R.C.; Artibani, W.; Carroll, P.R.; Costello, A.; Menon, M.; Montorsi, F.; Patel, V.R.; Stolzenburg, J.U.; Van der Poel, H.; Wilson, T.G.; Zattoni, F.; Mottrie, A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2012, 62, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanda, M.G.; Dunn, R.L.; Michalski, J.; Sandler, H.M.; Northouse, L.; Hembroff, L.; Lin, X.; Greenfield, T.K.; Litwin, M.S.; Saigal, C.S.; Mahadevan, A.; Klein, E.; Kibel, A.; Pisters, L.L.; Kuban, D.; Kaplan, I.; Wod, D.; Ciezki, J.; Shah, N.; Wei, J.T. Quality of life and satisfaction withoutcomeamong prostate-cancer survivors. N Engl J Med. 2008, 358, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, M.S.; Lubeck, D.P.; Henning, J.M.; Carroll, P.R. Differences in urologist and patient assessments of healthrelatedquality of life in men with prostate cancer:results of the CaPSUREdatabase. J Urol. 1998, 159, 1988–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ICIQ category (11 months post surgery (IQR 9,12) | Number of patients (percentage) | Early full continence -number of patients (6 weeks post surgery) (percentage from the group) | Erectile preservation (number of patient with pre-op erectile function) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slight (1-5) | 9 (31%) | 4 (44%) | 2 (4) |
| Moderate (6-12) | 9 (31%) | 2 (22%) | 1 (4) |
| Severe and very severe (13-21) | 11 (38%) | 1 (9%) | 0 (4) |
| ICIQ<=12 (n=18) | ICIQ > 12 (n=11) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average ICIQ(IQR) | 6.5(2.25-10.75) | 16.4(14.5-18) | |
| Age (IQR) | 67.3(63.9-73.3) | 69.4(67-72.7) | 0.44 |
| Pre op PSA(ng/ml) (IQR) | 9.1(6.6-9.9) | 16(9-22.2) | 0.02 |
| Number of patients withpre op LUTS (IPSS>7) | 8 (45%) | 5 (45%) | 0.96 |
|
ISUP score 1 2 3 4 5 |
1 (5.5%) 8 (44.4%) 5 (27.7%) 2 (11.1%) 2 (11.1%) |
0 (0%) 3 (27.2%) 4 (36.3%) 2 (18.1%) 0 (0%) *ISUPx – after hormonal treatment – 2 (18.1%) |
0.302 |
| Prostate size (gram) | 68(55-73) | 63.2(49.5-65.3) | 0.6 |
|
pT stage (2009) T2 T3a T3b |
8 (44.4%) 9 (50%) 1 (5.5%) |
1 (9%) 9 (82%) 1 (9%) |
0.136 |
| Full 6W continence day | 8 (45%) | 3 (27%) | 0.37 |
| Full 6W continence night | 8 (45%) | 2 (18%) | 0.14 |
| Overall (n=29) |
ICIQ score ≤ 12 (n=18) |
ICIQ score >12 (n=11) |
P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
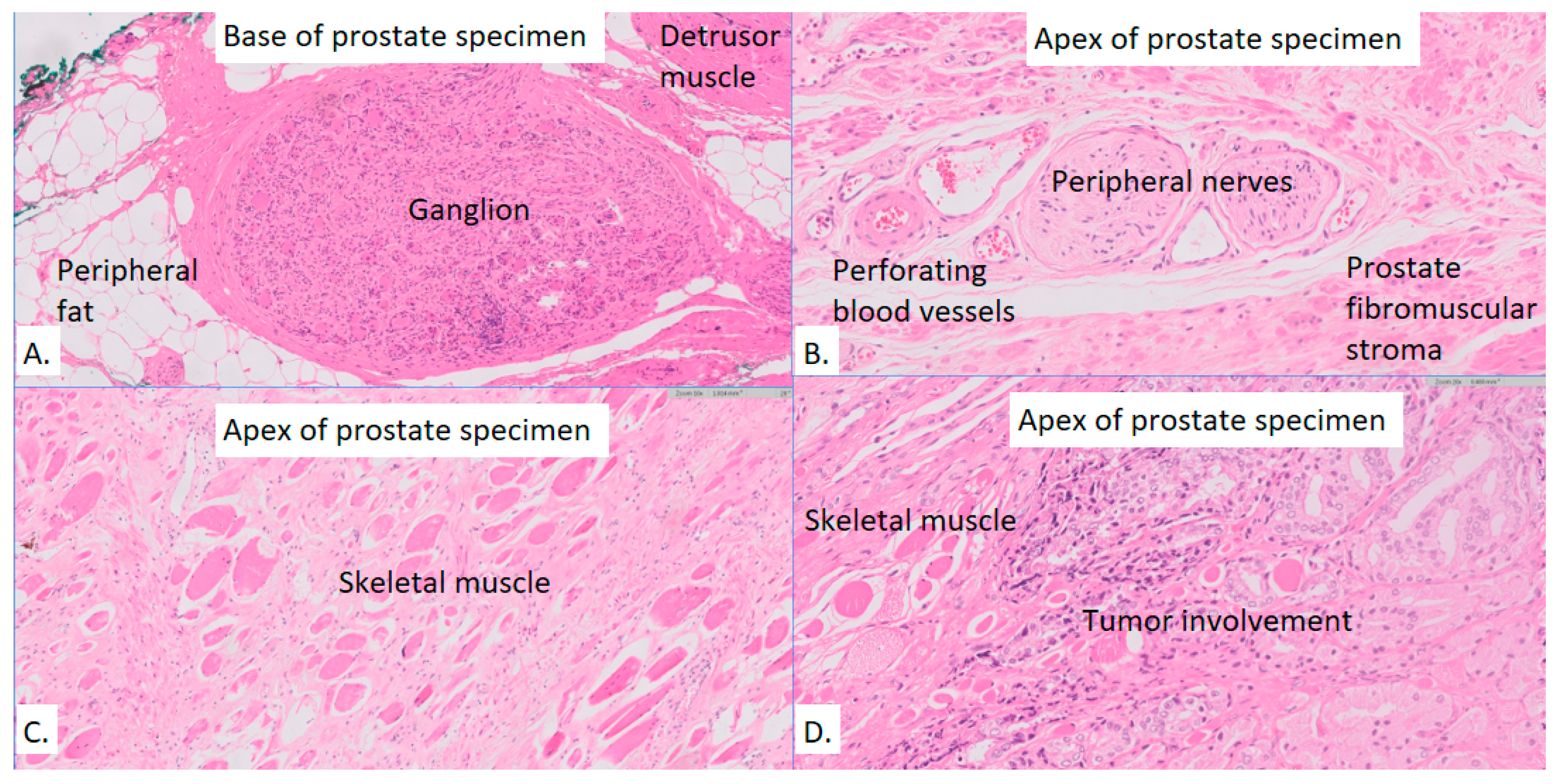
| Presence of ganglion in the base, n (%) | 19 (65%) | 11 (61%) | 8 (72%) | 0.22 |
| Presence of ganglion in the apex, n (%) | 12 (41%) | 8 (44%) | 4 (36%) | 0.11 |
| Proportional area of detrusor muscle in the base, median (IQR) | 0.54 (0.31-1.00) | 0.45 (0.29-0.92) | 0.60 (0.40-1.00) | 0.57 |
| Proportional area of striated muscle at the apex, median (IQR) | 0.13 (0.07-0.24) | 0.13 (0.06-0.24) | 0.13 (0.08-0.24) | 1.00 |
| # of nerves at the base, median (IQR) | 52 (13-139) | 69 (11-152) | 36 (14-108) | 0.65 |
| # of nerves at the apex, median (IQR) | 59 (28-129) | 61 (28-142) | 51 (33-116) | 0.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





