Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Carbon Footprints (CFPs)
1.2. Role of Data Automation and Decision Support Systems (DSS) in Decarbonization
2. Data Automation in Environmental Management
2.1. Solid Waste Management (SWM)
2.2. Wastewater Treatment (WWT)
2.3. Contaminated Soil Remediation (CSR)
- the vast amount of data collected by IoT devices raises concerns about security and privacy. Robust data governance frameworks are needed to ensure data protection and prevent misuse;
- implementing these technologies requires significant investment in sensor networks, AI software, and blockchain infrastructure. Public-private partnerships and innovative financing models are crucial for wider adoption;
- integrating these complex technologies necessitates a skilled workforce capable of managing, analyzing, and maintaining the systems. Training programs and capacity building are essential;
- ensuring compatibility between different IoT devices, AI platforms, and blockchain systems is vital for seamless data exchange and system integration; and
- AI algorithms need to be designed with fairness and transparency in mind to avoid bias in waste management decisions.
3. Decision Support Systems
3.1. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
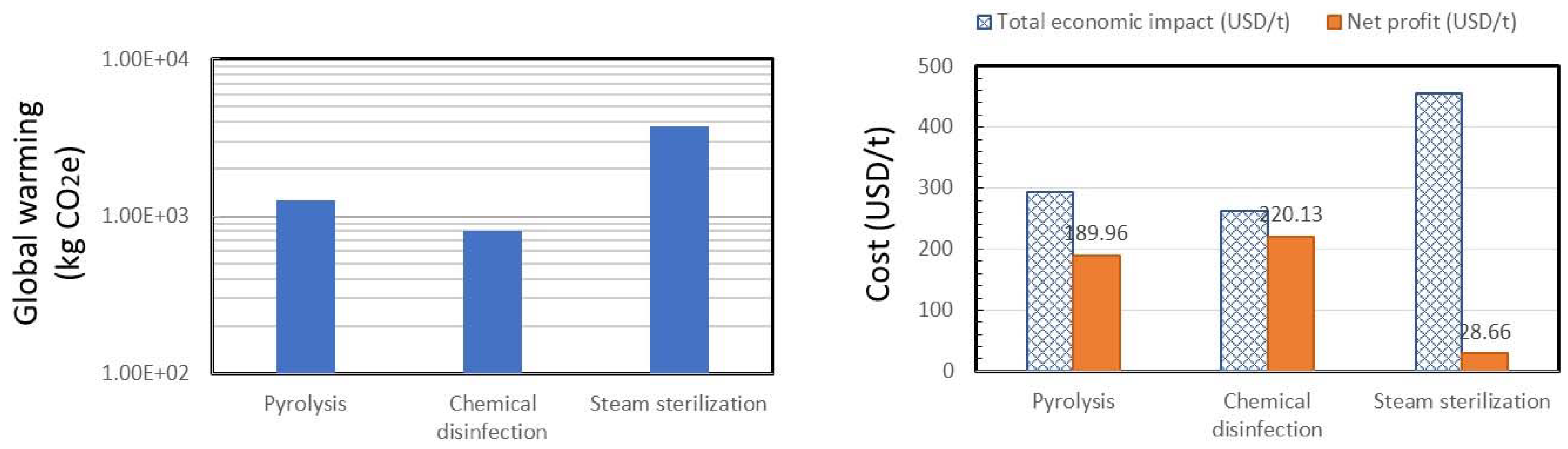
3.1.1. Solid Waste Management (SWM)
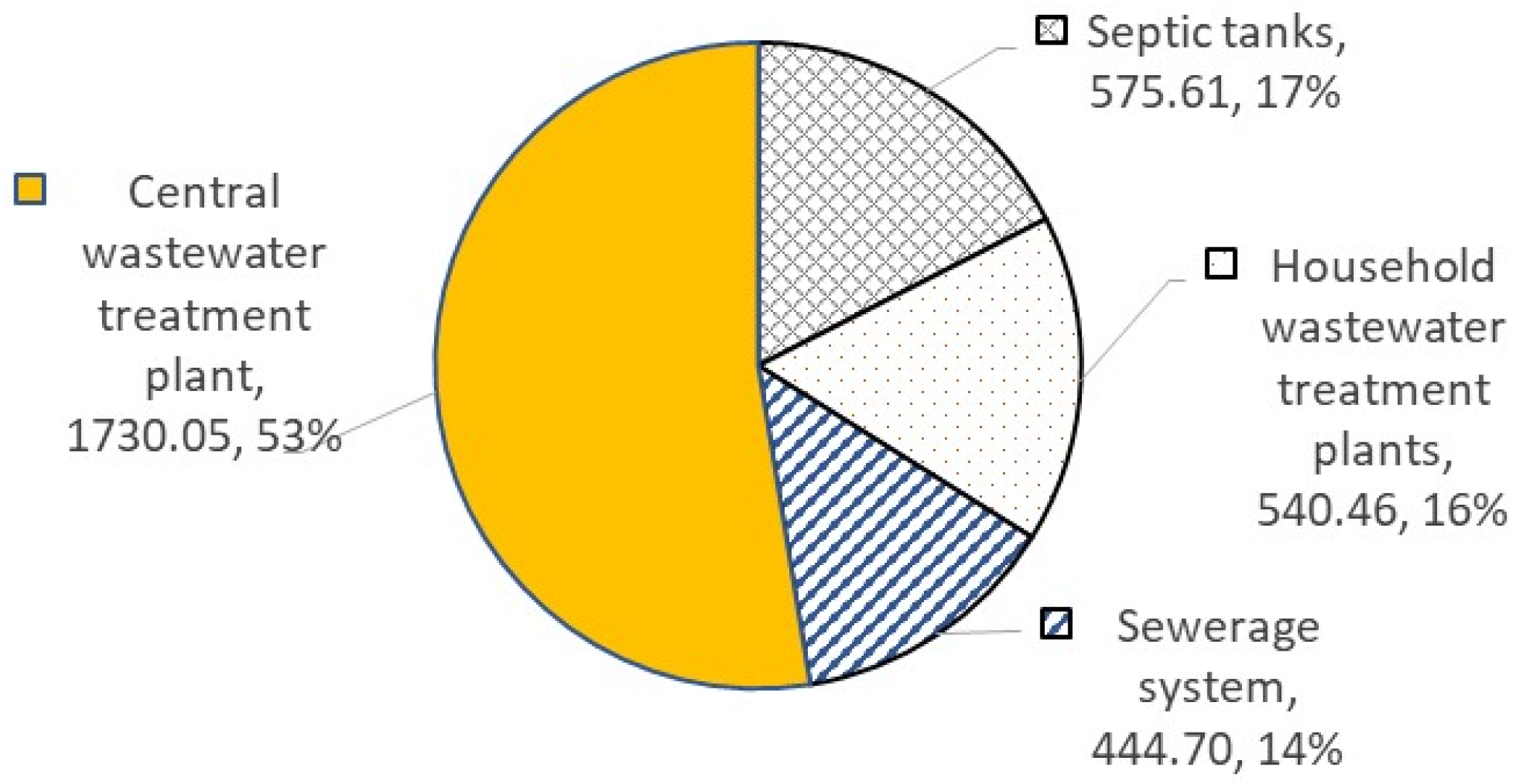
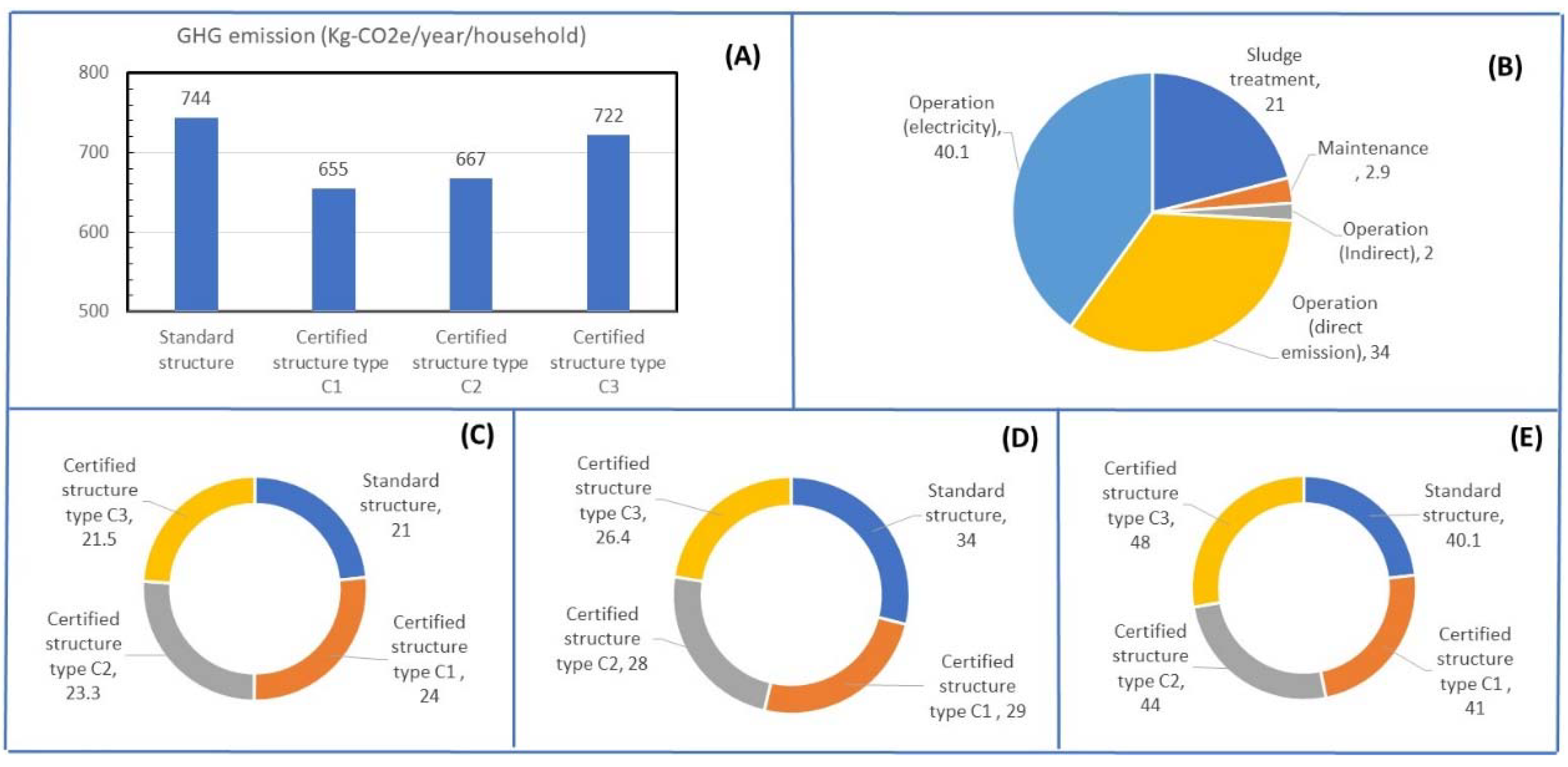
3.1.2. Wastewater Treatment (WWT)
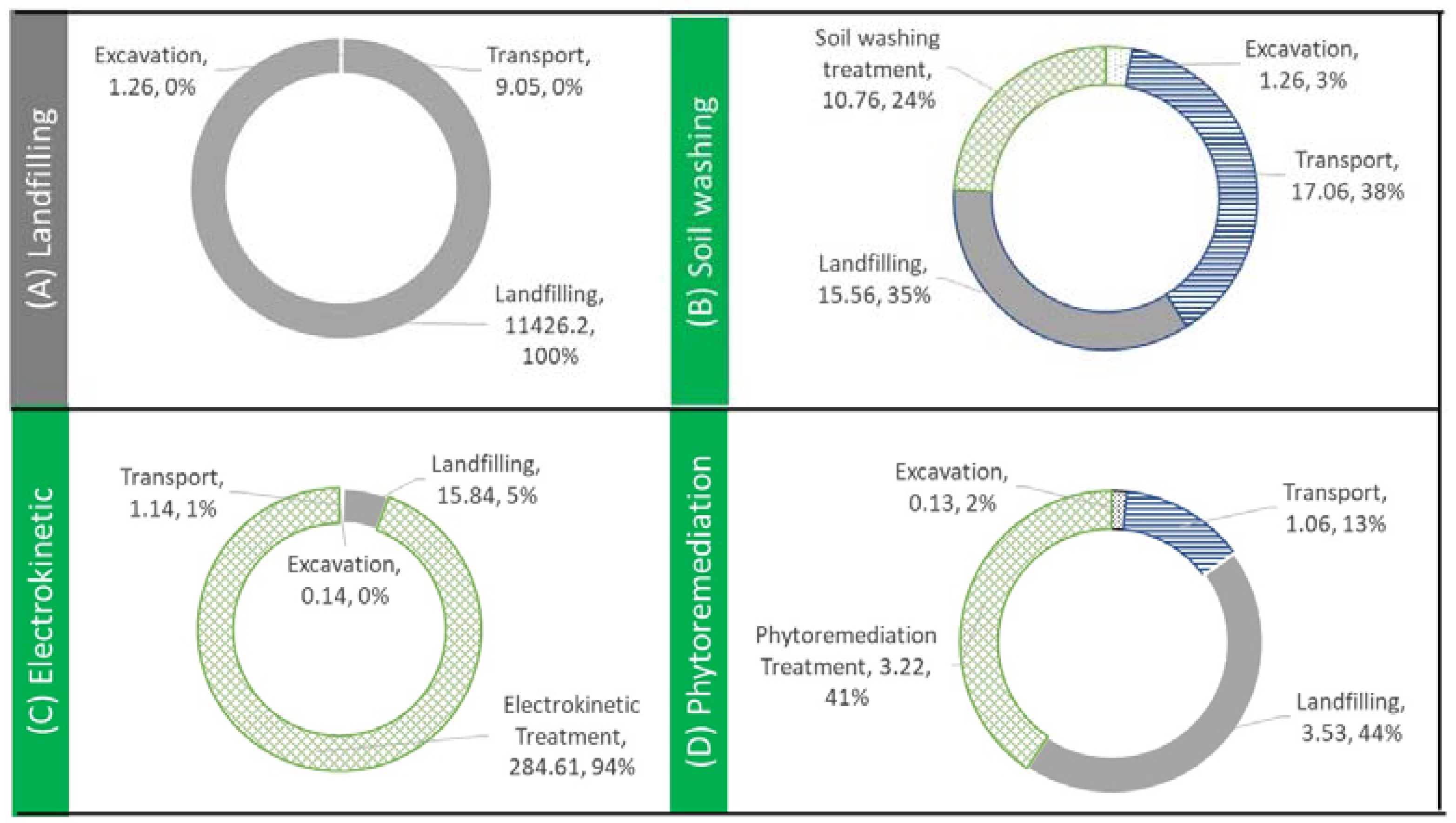
3.1.3. Contaminated Soil Remediation (CSR)
3.2. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis
3.2.1. Solid Waste Management (SWM)
3.2.2. Contaminated Soil Remediation (CSR)
3.2.3. Optimal Contractual Delivery Method
4. Conclusion
References
- Metcalf and Eddy. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, C.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wong, M.S. Carbon footprint analyses of mainstream wastewater treatment technologies under different sludge treatment scenarios in China. Water, 2015, 7, 918–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas, L.; Alsina, X.F.; Snip, L.; Vanrolleghem, P. Comparison of different modeling approaches to better evaluate greenhouse gas emissions from whole wastewater treatment plants. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2854–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweetapple, C.; Fu, G.; Butler, D. Identifying sensitive sources and key control handles for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from wastewater treatment, Water Res. , 2014, 62, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetapple, C.; Fu, G.; Butler, D. Identifying key sources of uncertainty in the modelling of greenhouse gas emissions from wastewater treatment, Water Res., 2013, 47(13) 4652-4665. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, Y.; Li, B.; Pang, H.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, X. Wastewater treatment technology selection under various influent conditions and effluent standards based on life cycle assessment, Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 2020, 154. [CrossRef]
- McCarty, P.L.; Bae, J.; Kim, J. Domestic wastewater treatment as a net energy producer–can this be achieved? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45(17), 7100–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Liu, R.; Huang, X. Evaluation of the potential for operating carbon neutral WWTPs in China, Water Res. 2015, 87, 424-431. [CrossRef]
- Zawartka, P.; Burchart-Korol, D.; Blaut, A. Model of Carbon Footprint Assessment for the Life Cycle of the System of Wastewater Collection, Transport and Treatment. Scientific Reports (2020) 10:5799. [CrossRef]
- Vocciante, M.; D'Auris, A. de F.; Franchi, E.; Petruzzelli, G.; Ferro, S., CO2 footprint analysis of consolidated and innovative technologies in remediation activities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Al Mamuna, M.D.A.; Hussain, A.; Basri, H.; Begum, R.A. A review on technologies and their usage in solid waste monitoring and management systems: Issues and challenges. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoa, T.A.; Phuc, C.H.; Lam, P.D.; Nhu, L.M.B.; Trong, N.M.; Phuong, N.T.H.; Dung, N.V.; Tan-Y, N.; Nguyen, H.N.; Duc, D.N.M. Waste management system using iot-based machine learning in university. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 6138637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassou, M.; Bourekkadi, S.; Khoulji, S.; Slimani, K.; Chikri, H.; Kerkeb, M.L. Blockchain-based medical and water waste management conception. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 234, 00070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Van Fan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, M.; Liu, X.; Klemeš, J.J. Data-driven analytical framework for waste-dumping behavior analysis to facilitate policy regulations. Waste Manag. 2020, 103, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, R.; Venkatakrishnan, P.; Balaji, N. Intelligent based novel embedded system based iot enabled air pollution monitoring system. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2020, 77, 103172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, T.J.; Islam, M.S.; Misran, N.; Baharuddin, M.H.; Arshad, H.; Islam, M.D.R.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Rmili, H.; Islam, M.T. An internet of things based smart waste management system using lora and tensorflow deep learning model. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 148793–148811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.D.; Kang, H.; Ilankoon, I.M.S.K.; Chong, C.Y. Electronic waste collection systems using internet of things (IoT): Household electronic waste management in Malaysia. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, S. IoT based sustainable smart waste management system evaluation using MCDM model under interval-valued q-rung ortho-pair fuzzy environment. Technol. Soc., 2022, 71, 102100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, X.; Alhaskawi, A.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Q.; et al. A deep learning approach for medical waste classification. Sci. Rep., 2022, 12(1), 2159. [CrossRef]
- Gopikumar, S.; Raja, S.; Robinson, Y.H.; Shanmuganathan, V.; Rho, S. A method of landfill leachate management using internet of things for sustainable smart city development. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 66, 102521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouki, J.; Azrour, M.; Fattah, G.; Dhiba, D.; El Hajjaji, S. Intelligent monitoring system for biogas detection based on the Internet of Things: mohammedia, Morocco city landfill case. Big Data Min. Anal. 2021, 4(1), 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, J.; Wang, H.; Boczkaj, G.; Mahlknecht, J.; Singh, S.V.; Wang, C. Bibliometric analysis of artificial intelligence in wastewater treatment: Current status, research progress, and future prospects. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12, 113152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, J.A.; et al. Assessment of site contaminated soil remediation based on an input output life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yang, C.; Lan, L.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Zhou, C. A novel total nitrogen prediction method based on recurrent neural networks utilizing cross-coupling attention and selective attention, Neurocomputing, 2023, 527, 48–59.
- Yaqub, M.; Asif, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, W. Modeling of a full-scale sewage treatment plant to predict the nutrient removal efficiency using a long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network, J. Water Process Eng., 2020, 37, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Pooi, C.K.; Tan, K.M.; Huang, S.; Shi, X.; Ng, H.Y. A novel long short-term memory artificial neural network (LSTM)-based soft-sensor to monitor and forecast wastewater treatment performance, J. Water Process Eng., 2023. 54, 104041. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Duan, H.; Yan, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Deep learning-based data driven model for detecting time-delay water quality indicators of wastewater treatment plant influent, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 467, 143483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, A.; Ayesa, E.; Linaza, M.T.; Rivas, A.; Salterain, A. Application of mathematical tools to improve the design and operation of activated sludge plants. Case study: the new WWTP of Galindo-Bilbao Part II: operational strategies and automatic controllers. In: Water Science and Technology, 2001, 167-174.
- Ayesa, E.; De la Sota, A.; Grau, P.; Sagarna, J.M.; Salterain, A.; Suescun, J. Supervisory control strategies for the new WWTP of Galindo-Bilbao: the long run from the conceptual design to the full-scale experimental validation. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiza, M.; Bengoechea, A.; Grau, P.; De Keyser, W.; Nopens, I.; Brockmann, D.; Steyer, J.P.; Claeys, F.; Urchegui, G.; Fernandez, O.; Ayesa, E. Add control: plant virtualization for control solutions in WWTP. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.; Marques, R.; Raposo, R.; Martins, M.; Alves, R.; Povoa, P.; Irizar, I.; Beltran, S.; Craamer, P.; Urchegui, G.; Oehmen, A. The impact of the art-ICA control technology on the performance, energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions of full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 213, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, A.; Nuca, I. Automation of wastewater treatment plant. Conference: 2019 International Conference on Electromechanical and Energy Systems (SIELMEN). [CrossRef]
- Oduah, U.I.; Ogunye, E.B. A smart solution for preventing environmental pollution caused by overflowing onsite sewage septic tank. Heliyon., 2023, 9(4), e14925. [CrossRef]
- Porro, J. Using AI to reduce process emissions from water utilities. https://iwa-network.org/using-ai-to-reduce-process-emissions-from-water-utilities/.
- Khan, A.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, S.K. Multi-hazard disaster studies: monitoring, detection, recovery, and management, based on emerging technologies and optimal techniques. Int. J. disaster risk Reduct. 2020, 47, 101642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, R.; Shoushtari, N.A.; Mirza, B.; Salahi, A. Experimental investigation, modeling and optimization of membrane separation using artificial neural network and multi-objective optimization using genetic algorithm, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2013, 91(5), 883-903. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, K.; Gao, X.; Cheng, X.; Shen, Y.; Wen, Z.; Piran, M.J. Energy and materials-saving management via deep learning for wastewater treatment plants, IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 191694-191705.
- Adibimanesh, B.; Polesek-Karczewska, S.; Bagherzadeh, F.; Szczuko, P.; Shafighfard, T. Energy consumption optimization in wastewater treatment plants: machine learning for monitoring incineration of sewage sludge, Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 56, 103040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, H.C.; Song, Y.P.; Zhou, S.Q.; Li, Q.N.; Liang, B.; Wang, A.J. Machine learning framework for intelligent aeration control in wastewater treatment plants: Automatic feature engineering based on variation sliding layer, Water Res. 2023, 246, 120676.
- Popescu, S.M.; Mansoor, S.; Wani, O.A.; Kumar, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, A.; Arya, V.M.; Kirkham, M.B.; Hou, D.; Bolan, N.; Chung, Y.S. Artificial intelligence and IoT driven technologies for environmental pollution monitoring and management. Front. Environ. Sci., 2024, 12, 1336088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.B.; Rayner, J.L.; Donn, M.J. Advancing Autonomous sensing and prediction of the subsurface environment: a review and exploration of the challenges for soil and groundwater contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30(8):19520-19535. [CrossRef]
- Sookhak Lari, K.; Davis, G.B.; Rayner, J.L. Towards a digital twin for characterizing natural source zone depletion: a feasibility study based on the Bemidji site. Water Res., 2022, 208, 117853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S. K.; Baskaran, B. An improved real-time water quality monitoring embedded system with IoT on unmanned surface vehicle. Ecol. Inf., 2021, 65, 101421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.O. Principles and applications of time domain electrometry in geo-environmental engineering. Taylor & Francis Publishers, UK, ISBN 041541 1297, 603, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Said, R.A.; Al Shawawreh, N.K. A TDR system for subsurface pollutants detection (II): Application & analysis,” Symposium TDR2001: Innovative Applications of TDR Technology, Infrastructure Technology Institute, Northwestern, Evanston, Illinois, September 5-7, 2001.
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Said, R.; AlShawawreh, N.K. Development of a methodology for evaluating subsurface concentrations of pollutants using electrical polarization technique. Geotechnical Testing Journal, GTJODJ, 2002, 25(2), 157-167. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Said, R.A.; AlShawawreh, N.K.; El-Bassouni, M.Y. Evaluation of water content and ionic concentrations of soils via frequency domain analysis of TDR waveforms. International Journal of Subsurface Sensing Technologies and Applications, 2003, 4(2), 159-186. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Said, R.A.; El-Bassiouni, M.Y. Eigen-decomposition of TDR waveforms: A novel method to determine water content and pore fluid concentration of sandy soils. Environmental Geology, 2003b, 45(1), 132-143.
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Said, R.A. TDR detection of nonaqueous phase liquids in sandy soils using the eigen-decomposition method. Environmental Geology J., 2004, 47, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Said, R.A. Detection of organic pollutants in sandy soils via TDR and eigen-decomposition. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2005, 76, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Hawas, Y. Neuro-fuzzy logic model for evaluating water content of sandy soils. International Journal of Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2004, 19, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivavec, T.M.; Mackenzie, P.D.; Baghel, S.S.; Salvo, J.J. Method and system to remotely monitor groundwater treatment. US Patent; US6491828B1(2002).
- Van Thanh, N. Optimal waste-to-energy strategy assisted by fuzzy mcdm model for sustainable solid waste management. Sustainability, 2022, 14, 6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisar, M.; Garg, S.K. Selection of sewage treatment technology using analytic hierarchy process. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 56, 3433–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewalkar, S.V.; Shastri, S.S. Integrated life cycle assessment and life cycle cost assessment based fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making approach for selection of appropriate wastewater treatment system. J. Water Process Eng., 2022, 45, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, G. Using multi-criteria decision-making to optimize solid waste management. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem., 2022, 37, 100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, B.G.; Yetilmezsoy, K. A Hybrid Fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS Approach for Implementation of Smart Sustainable Waste Management Strategies. Sustainability, 2023, 15, 6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabirifar, K.; Ashour, M.; Yazdani, M.; Mahdiyar, A.; Malekjafarian, M. Cybernetic-parsimonious MCDM modeling with application to the adoption of Circular Economy in waste management. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 139, 110186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Cote, K. Decision analysis of polluted sites - A fuzzy set approach. An International Journal of Waste Management, 1999, 19, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcomini, A.; Suter II, G.W.; Critto, A. Decision support systems for risk-based management of contaminated sites. Springer Sciences Business Media, New York, 2009. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Onwubuya, K.; Cundy, A.B.; Puschenreiter, M.; Kumpiene, J.; Bone, B.; Greaves, J.; Teasdale, P.; Mench, M.; Tlusto, P.; Mikhalovsky, S.; Waite, S.; Friesl-Hanl, W.; Marschner, B.; Müller, I. Developing decision support tools for the selection of “gentle” remediation approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407(24), 6132–6142. [CrossRef]
- Rosen, L.; Back, P.E.; Soderqvis, T.; Norrman, J.; Brinkhoff, P.; Norberg, T.; Volchko, Y.; Norin, M.; Bergknut, M.; Doberl, D. SCORE: A novel multi-criteria decision analysis approach to assessing the sustainability of contaminated land remediation. Sci. Total Environ., 2015, 511, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huysegoms, L.; Cappuyns, V. Critical review of decision support tools for sustainability assessment of site remediation options. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Paleologos, E.; Howari, F. , Pollution assessment for sustainable practices in applied sciences and engineering. Elsevier, 1138p., ISBN: 978-0-12-809582-9.
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Paleologos, E.K. Sustainable pollution assessment practices. Chapter 1, In Mohamed, A.M.O., Paleologos, E., and Howari, F. (2021b) “Pollution Assessment for Sustainable Practices in Applied Sciences and Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Paleologos, E.K.; Mohamed, A.M. O, Risk Analysis and Management. Chapter 2, In Mohamed, A.M.O., Paleologos, E., and Howari, F. (2021). Pollution Assessment for Sustainable Practices in Applied Sciences and Engineering. Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Feng, F; Ghorbani, H.; Radwan, A.E. Predicting groundwater level using traditional and deep machine learning algorithms. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12. [CrossRef]
- Kiker, G.A.; Bridges, T.S.; Varghese, A.; Seager, P.T.P.; Linkov, I. Application of multicriteria decision analysis in environmental decision making. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2005, 1(2), 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundy, A.B.; Bardos, R.P.; Church, A.; Puschenreiter, M.; Friesl-Hanl, W.; Müller, I.; Neu, S.; Mench, M.; Witters, N.; Vangronsveld, J. Developing principles of sustainability and stakeholder engagement for “gentle” remediation approaches: the European context. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 129, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri-Rad, M.; Berndtsson, R.; Aminifar, A.; McKnight, U.S.; O’Connor, D.; Persson, K. M. , DynSus: dynamic sustainability assessment in groundwater remediation practice. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stezar, I.C.; Ozunu, A.; Barry, D.L. The role of stakeholder attitudes in managing contaminated sites: survey of Romanian stakeholder awareness. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2014, 21, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.B.; Trentin, A.W.S.; Visentin, C.; Thome, A. Sustainable remediation through the risk management perspective and stakeholder involvement: a systematic and bibliometric view of the literature. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255 (Part 1), 113221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, J.; Rai, T. Engaging with residents' perceived risks and benefits about technologies as a way of resolving remediation dilemmas. Sci. Total Environ., 2017, 601- 602, 1649–1669. [CrossRef]
- Ibanez-Fores, V.; Bovea, M.D.; Perez-Belis, V. A holistic review of applied methodologies for assessing and selecting the optimal technological alternative from a sustainability perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 70, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuyns, V. Inclusion of social indicators in decision support tools for the selection of sustainable site remediation options. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 184 (Part 1), 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huysegoms, L.; Rousseau, S.; Cappuyns, V. Friends or foes? Monetized life cycle assessment and cost-benefit analysis of the site remediation of a former gas plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619(4), 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, G.L.; Binning, P.J.; Bondgaard, M.; Bjerg, P.L. Multi-criteria assessment tool for sustainability appraisal of remediation alternatives for a contaminated site. J. Soils Sediments, 2018, 18 (11), 3334-3348. [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.B.; Visentin, C.; da Silva Trentin, A.W.; Thome, A. List of relevant sustainability indicators in remediation processes and their validation by stakeholders. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, C.; da Silva Trentin, A.W.; Braun, A.B.; Thome, A. Application of life cycle assessment as a tool for evaluating the sustainability of contaminated sites remediation: a systematic and bibliographic analysis. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 672, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.H.; Laitinen, V.; Havukainen, J.; Horttanainen, M. Carbon footprint of different recovery options for the re-pulping reject from liquid packaging board waste treatment process. Waste Management, 2021, 136, 93–103; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Antia, H. Geo-environmental Engineering, Elsevier, Amsterdam, ISBN: 0-444-89847-6, 707p, (1998).
- Song, Y.; Hou, D.; Zhang, J.; O’Connor, D.; Li, G.; Gu, G.; Li, S.; Liu, P. Environmental and socio-economic sustainability appraisal of contaminated land remediation strategies: a case study at a mega-site in China. Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 610–611, 391–401. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. ; Chen, A; Xu, L. ; Xie, H.; Qiao, H.; Lin, Q.; Cai, K. A deep learning CNN architecture applied in smart near-infrared analysis of water pollution for agricultural irrigation resources, Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, V.; Carreno, M.; Gil-Nagel, A.; Serrano-Castro, P.J.; Serratosa, J.M.; Toledo, M.; Alvarez-Baron, E.; Gil, A.; Subías-Labazuy, S. Identifying key unmet needs and value drivers in the treatment of focal-onset seizures (FOS) in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) in Spain through multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA). Epilepsy Behav., 2021, 22, 108222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murcia, N.N.S.; Ferreira, F.A.F.; Ferreira, J.J.M. , Enhancing strategic management using a “quantified VRIO”: adding value with the MCDA approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change, 2022, 174, 121251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemming, G.; Hauschild, M.Z.; Bjerg, P.L. Life cycle assessment of soil and groundwater remediation technologies: literature review. Int. J. LCA, 2012, 15(1), 115-127. [CrossRef]
- Favara, P.; Skance, O. Overview of LCAs as applied to remediation projects. Encyclop. Sustain. Technol., 2017, 1, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucek, L.; Klemes, J.J.; Kravanja, Z. A review of footprint analysis tools for monitoring impacts on sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 34, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Zhan, S.; Yu, Z.; Hong, J.; Congcong, Q. Life-cycle environmental and economic assessment of medical waste treatment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, S0959652617325155–. [CrossRef]
- Bulle, C.; Margni, M.; Patouillard, L.; Boulay, A. M.; Bourgault, G.; de Bruille, V.; Cao, V.; Hauschild, M.; Henderson, A.; Humbert, S.; KashefHaghighi, S.; Kounina, A.; Laurent, A.; Levasseur, A.; Liard, G.; Rosenbaum, R.K.; Roy, P. O.; Shaked, S.; Fantke, P.; Jolliet, O. IMPACT world þ: A globally regionalized life cycle impact assessment method. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2019, 24, 1653–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Steinmann, Z.J.N.; Elshout, P.M.F.; Stam, G.; Verones, F.; Vieira, M.; Zijp, M.; Hollander, A.; van Zelm, R. Recipe2016: A harmonised life cycle impact assessment method at midpoint and endpoint level. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2017, 22, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itsubo, N.; Sakagami, M.; Kuriyama, K.; Inaba, A. Statistical analysis for the development of national average weighting factors – visualization of the variability between each individual’s environmental thoughts. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2012, 17, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas, L.; Foley, J.; Guest, J.S.; Hospido, A.; Larsen, H.F.; Morera, S.; Shaw, A. Life cycle assessment applied to wastewater treatment: State of the art. Water Research, 2013, 47 (15), 5480–5492. [CrossRef]
- Sabeen, A. H.; Noor, Z.Z.; Ngadi, N.; Almuraisy, S.; Raheem, A.B. Quantification of environmental impacts of domestic wastewater treatment using life cycle assessment: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 190, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Schmid, A.; Tarpani, R.R.Z. Life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment in developing countries: A review. Water Research, 2019, 153, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Toja, Y.; et al. Benchmarking wastewater treatment plants under an eco-efficiency perspective. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 567, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Toja, Y.; et al. Dynamic environmental efficiency assessment for wastewater treatment plants. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2018, 23, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meile, C.; Porubsky, W.P.; Walker, R.L.; Payne, K. Natural attenuation of nitrogen loading from septic efuents: Spatial and environmental controls. Water Research, 2010, 44, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, J.D.; Gotkowitz, M.B.; Bradbury, K.R. Using groundwater model to evaluate strategies for drinking-water protection in rural subdivisions. Journal of the American Planning Association, 2010, 76(3), 295-304. [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Paterson, E.; Withers, P.J.A.; Stutter, M. Septic tanks discharges as multi-pollutant hotspot in catchments. Science of Total Environment, 2016, 542, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaider, L.A.; Ackerman, J.M.; Rudel, R.A. Septic systems as sources of organic wastewater compounds in domestic drinking water wells in a shallow sand and gravel aquifer. Science of Total Environment, 2016, 547, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opher, T.; Friedler, E. , Comparative LCA of decentralized wastewater treatment alternatives for non-potable urban reuse. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 182, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tjandraatmadja, G.; Grant, A.L.; Grant, T.; Pamminger, F. Sustainable sewerage servicing options for peri-urban areas with failing septic systems. Water Science & Technology, 2010, 62, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, V.J.; Mihelcic, J.R.; Gierke, J.S. Life cycle assessment of vertical and horizontal fow constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment considering nitrogen and carbon greenhouse gas emissions. Water Research, 2011, 45, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfi, M.; Flores, L.; Ferrer, I. Life Cycle Assessment of wastewater treatment systems for small communities: Activated sludge, constructed wetlands and high rate algal ponds. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2017, 161, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morera, S.; Corominas, L.; Rigola, M.; Poch, M.; Comas, J. Using a detailed inventory of a large wastewater treatment plant to estimate the relative importance of construction to the overall environmental impacts. Water Research, 2017, 122, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limphitakphong, N.; Pharino, C.; Kanchanapiya, P. Environmental impact assessment of centralized municipal wastewater management in Thailand. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 2016, 21, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, I.; Yoshikawa, N.; Asakawa, S.; Noguchi, Y.; Amano, K. Life-cycle analysis of environmental loads from household septic systems in Japan focusing on effluent water discharge. Water Sci Technol., 2023, 88(11), 2719-2732. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Kirkwood, N.; Maksimovic, C.; Zheng, X.; O’Connor, D.; Jin, Y.; Hou, D. Nature based solutions for contaminated land remediation and brownfield redevelopment in cities: a review, Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 663, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Maiti, S.K. Biochar assisted phytoremediation and biomass disposal in heavy metal contaminated mine soils: a review, Int. J. Phytoremediation, 2020, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, K.; Gao, Z.; Harbottle, M.; Sapsford, D.; Cleall, P. Life cycle assessment and cost-benefit analysis of nature-based solutions for contaminated land remediation: A mini-review. Heliyon. 2023, 10, 20632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, K.; Harbottle, M.; Sapsford, D.; Beames, A.; Cleall, P. Integration of ecosystem services and life cycle assessment allows improved accounting of sustainability benefits of nature-based solutions for brownfield redevelopment, J. Clean. Prod. 2023b, 137352. [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Al-Tabbaa, A.; O’Connor, D.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Wang, L.,Kirkwood, N.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Bolan, N.S.; Rinklebe, J. Sustainable remediation and redevelopment of brownfield sites, Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4(4) 271–286. [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.K.; Baker, L.A.; Boyer, T.H.; Drechsel, P.; Gifford, M.; Hanjra, M.A.; Parameswaran, P.; Stoltzfus, J.; Westerhoff, P.; Rittmann, B.E. Total Value of Phosphorus Recovery. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 50, 6606–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneses, M.; Concepción, H.; Vrecko, D.; Vilanova, R. Life Cycle Assessment as an environmental evaluation tool for control strategies in wastewater treatment plants. J. Clean. Prod., 2015, 107, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, M.; Maalcke-Luesken, F.A.; Jetten, M.S.; Huijbregts, M.A. Removing nitrogen from wastewater with side stream anammox: What are the trade-offs between environmental impacts? Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 2016, 107, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuyns, V. LCA based evaluation of site remediation: Opportunities and limitations. Chemistry Today, 2013, 31(2), 18-21.
- AF Center for Engineering and the Environment Sustainable remediation tool. Version 2.2 User Guide September 2011 https://www.enviro.wiki/images/5/5a/AFCEE-2011.SRTUserGuide.pdf.
- ESTCP. Quantifying life-cycle environmental footprints of soil and groundwater remedies estcp Project # ER-201127 July 2013. Prepared by Naval facilities engineering and expeditionary warfare center and tetra tech. https://sepub-prod-0001-124733793621-us-gov-west-1.s3.us-gov-west-1.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/project_documents/ER-201127-FR.pdf?VersionId=_g06YLpwX0p_HRZ2TjfvWAPTG8mwvXkR.
- Mohan, D. Screening with LNAPL-weathering code RT3D-OW and CO2 Tauw Rekentool. Master of Science Final Thesis, Tauw.
- Praamstra, T. Carbon footprint of soil remediation. Proceedings of the green remediation conference; 2009 9–10 Nov; Copenhagen, Denmark; 2009. [http://www.eugris.info/ newsdownloads/GreenRemediation/proc_decision_support.htm].
- Amponsah, N.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L. A review of life cycle greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of commonly used ex-situ soil treatment technologies. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2018, 186, 514–525, ISSN 0959-6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkanani, Z.; Mohtar, R.; Al-Enezi, S.; Smith, P.K.; Calabrese, S.; Ma, X.; Abdullah, M. AI-assisted systematic review on remediation of contaminated soils with PAHs and heavy metals, Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2024, 468, 133813, ISSN 0304-3894. [CrossRef]
- Achillas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Karagiannidis, A.; Banias, G.; Perkoulidis, G. The use of multi-criteria decision analysis to tackle waste management problems: A literature review. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhao, H.R. Optimal site selection of electric vehicle charging station by using fuzzy TOPSIS based on sustainability perspective. Appl. Energy, 2015, 158, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.Z. Design and Implementation of Web GIS-Based Decision-Making Assistance System for Remediation of Contaminated Sites. Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yantai, (2018).
- Zheng, Z.J.; Lin, M.Y.; Chiueh, P.T.; Lo, S.L. Framework for determining optimal strategy for sustainable remediation of contaminated sediment: a case study in northern Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 654, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.H.; Hong, L.; Jiang, C.Y.; Li, Y. Assessment system of POPs contaminated site remediation technology based on PROMETHEE II. Environ. Eng. 2014, 32(09), 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.H.; Teng, Y.G.; Chen, H.Y.; et al. A coupled optimization of groundwater remediation alternatives screening under health risk assessment: an application to a petroleum-contaminated site in a typical cold industrial region in northeastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.C.P.; Terencio, D.P.S.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Fernandes, L.F.S. A combined GIS-MCDA approach to prioritize stream water quality interventions, based on the contamination risk and intervention complexity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.L.; Huang, G.H.; Qin, X.S.; Fan, Y.R. Evaluation of remedial options for a benzene-contaminated site through a simulation-based fuzzy-MCDA approach. J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 213-214, 421–433. [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Wei, J.; Gao, S.; Ma, B. Promoting corporate sustainability through sustainable resource management: a hybrid decision-making approach incorporating social media data. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev., 2020, 85, 106459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balenzentis, T.; Streimikiene, D.; Siksnelyte-Butkiene, I. Energy storage selection for sustainable energy development: the multi-criteria utility analysis based on the ideal solutions and integer geometric programming for coordination degree. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 91, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshangi, N.; Gharakhanlou, N.M.; Razin, S.R.G. Evaluation of potential sites in Iran to localize solar farms using a GIS-based Fermatean fuzzy TOPSIS. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yi, S.; Chen, W.; Cundy, A.B. Application of a novel multi-criteria decision analysis approach for evaluating the sustainability of contaminated site management: An example from China. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 2024, 104, 107327; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM, ASTM E2893 – 16-1 Standard Guide for Greener Cleanups, 2016.
- Sánchez, M. A. Integrating sustainability issues into project management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 96, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvius, A.J.G.; Marnewick, C. Interlinking sustainability in organizational strategy, project portfolio management and project management: A conceptual framework. Procedia Computer Science, 2022, 196, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajani, M.; Ruge, G.; Jugdev, K. An integrative review of project portfolio management literature: thematic findings on sustainability mindset, assessment, and integration. Project Management Journal, 2023, 54(6) 629–650; [CrossRef]
- Schipper, R.P.J.; Silvius, A.J.G. Towards a conceptual framework for sustainable project portfolio management. International Journal of Project Organisation and Management, 2018, 10(3), 191–221. [CrossRef]
- Martinsuo, M.; Geraldi, J. Management of project portfolios: Relationships of project portfolios with their contexts. International Journal of Project Management, 2020, 38(7), 441-453. [CrossRef]
- Sabini, L.; Muzio, D.; Alderman, N. 25 years of ‘sustainable projects:’ What we know and what the literature says. International Journal of Project Management, 2019, 37(6), 820–838. [CrossRef]
- Al Nahyan, M.T.; Hawas, Y.E.; Sherif, M.; Basheerudeen, B. A fuzzy-based decision-support system for the analysis of suitability of megaproject delivery methods. Journal modern pm.Com. 2019, 7(1) pp. 121-137.
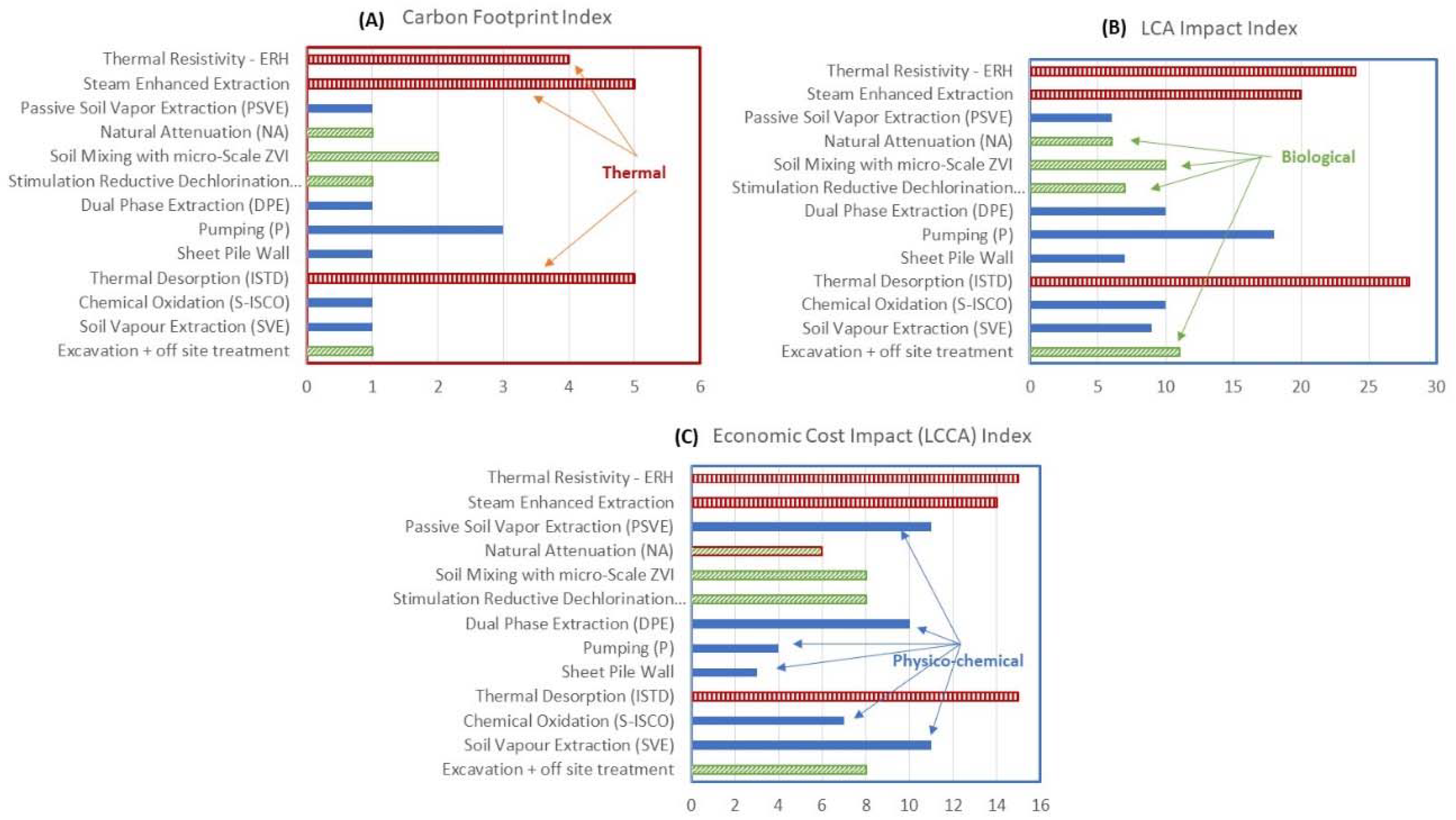
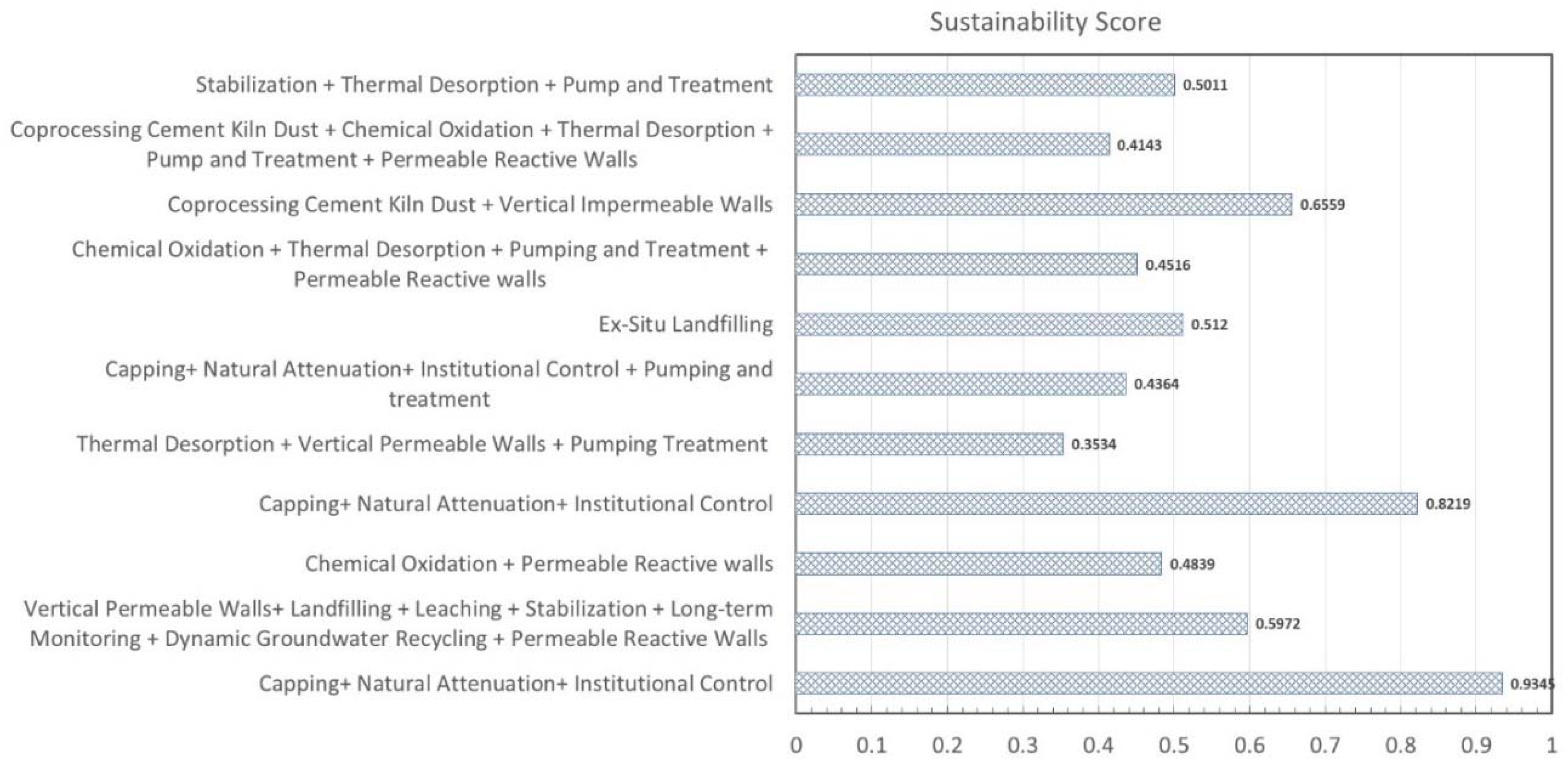
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





