Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
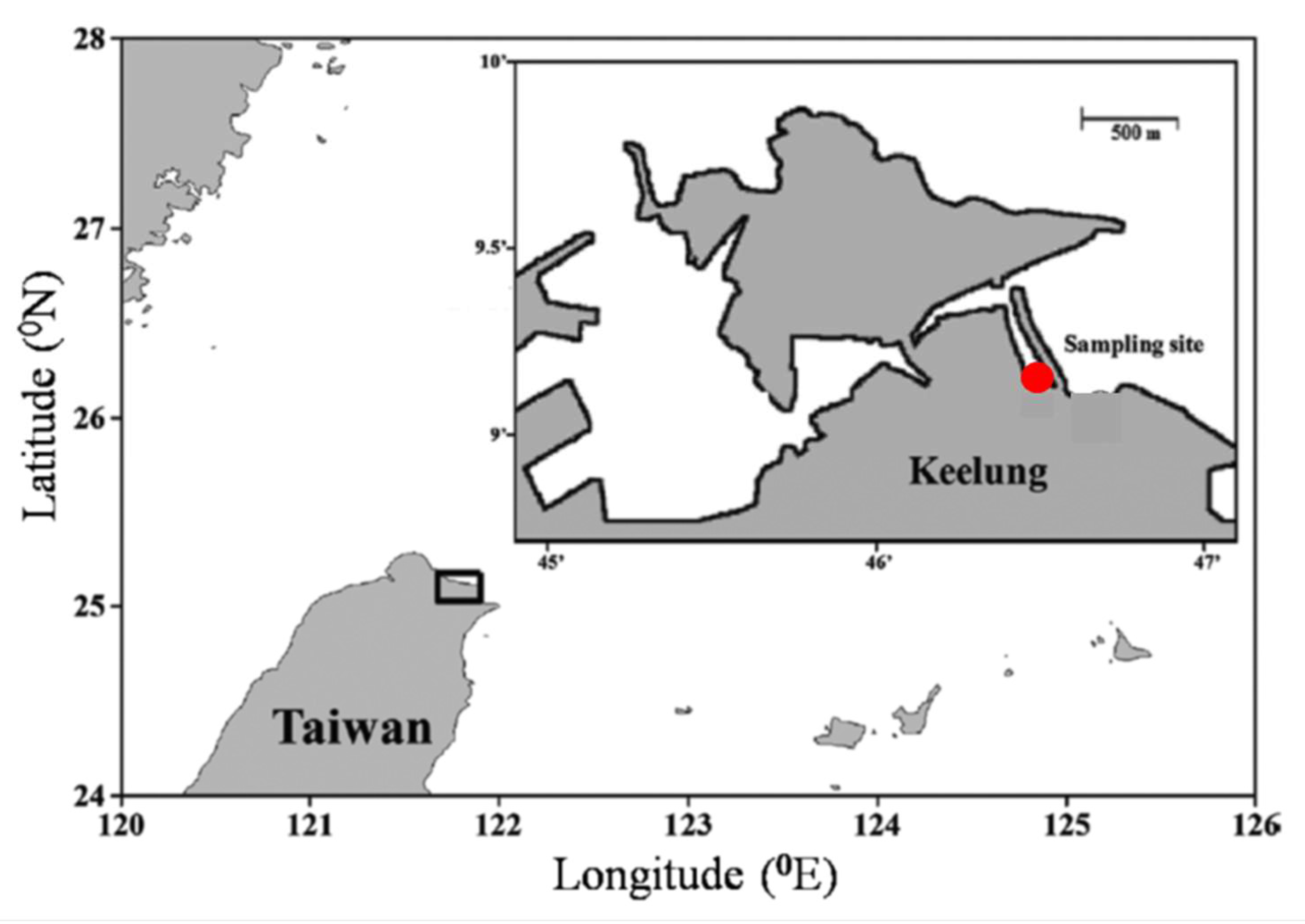
2.1. Study Site and Samplings
2.2. Net Increased Abundance of Bacteria and Picophytoplankton
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analyses
3. Results
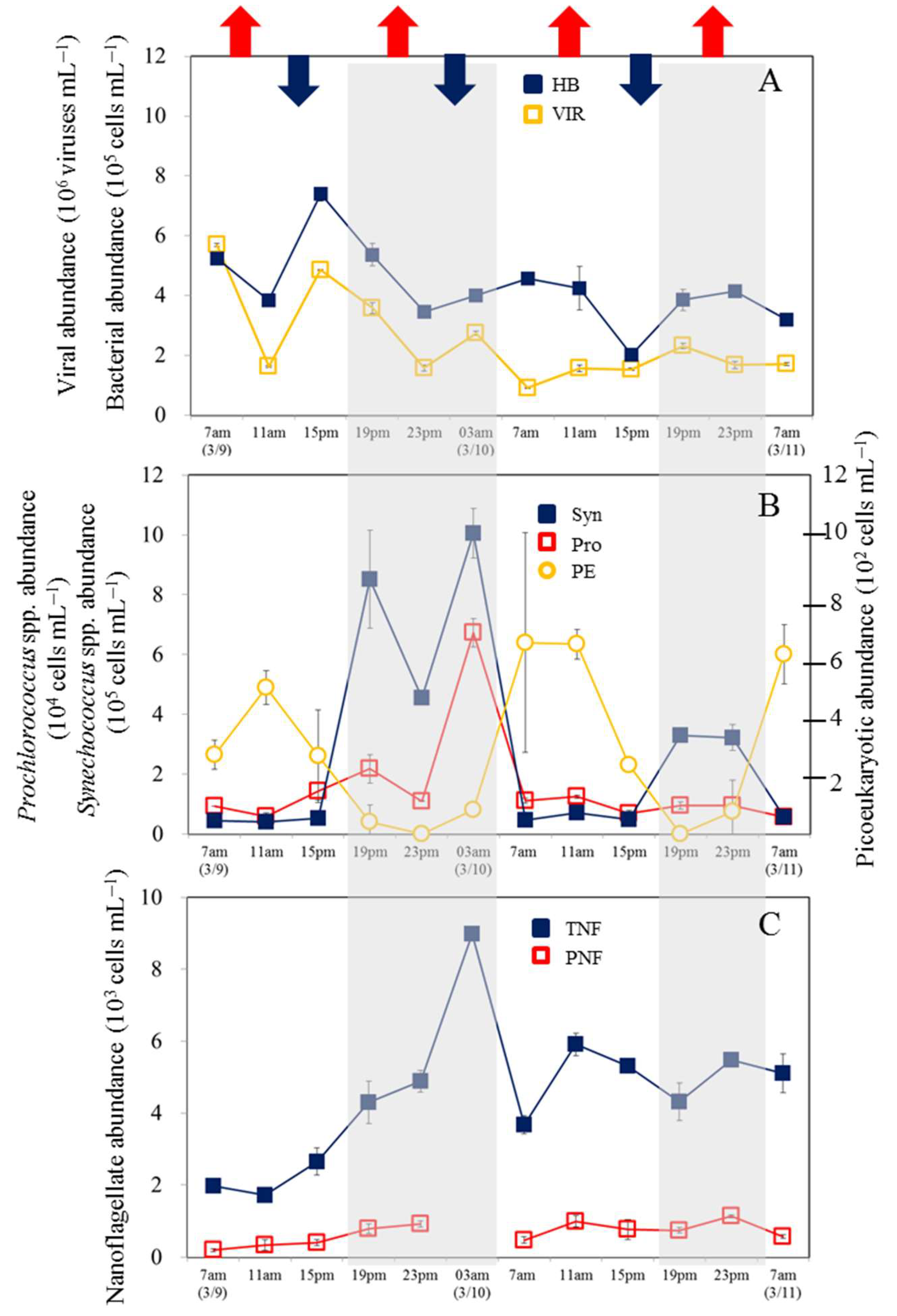
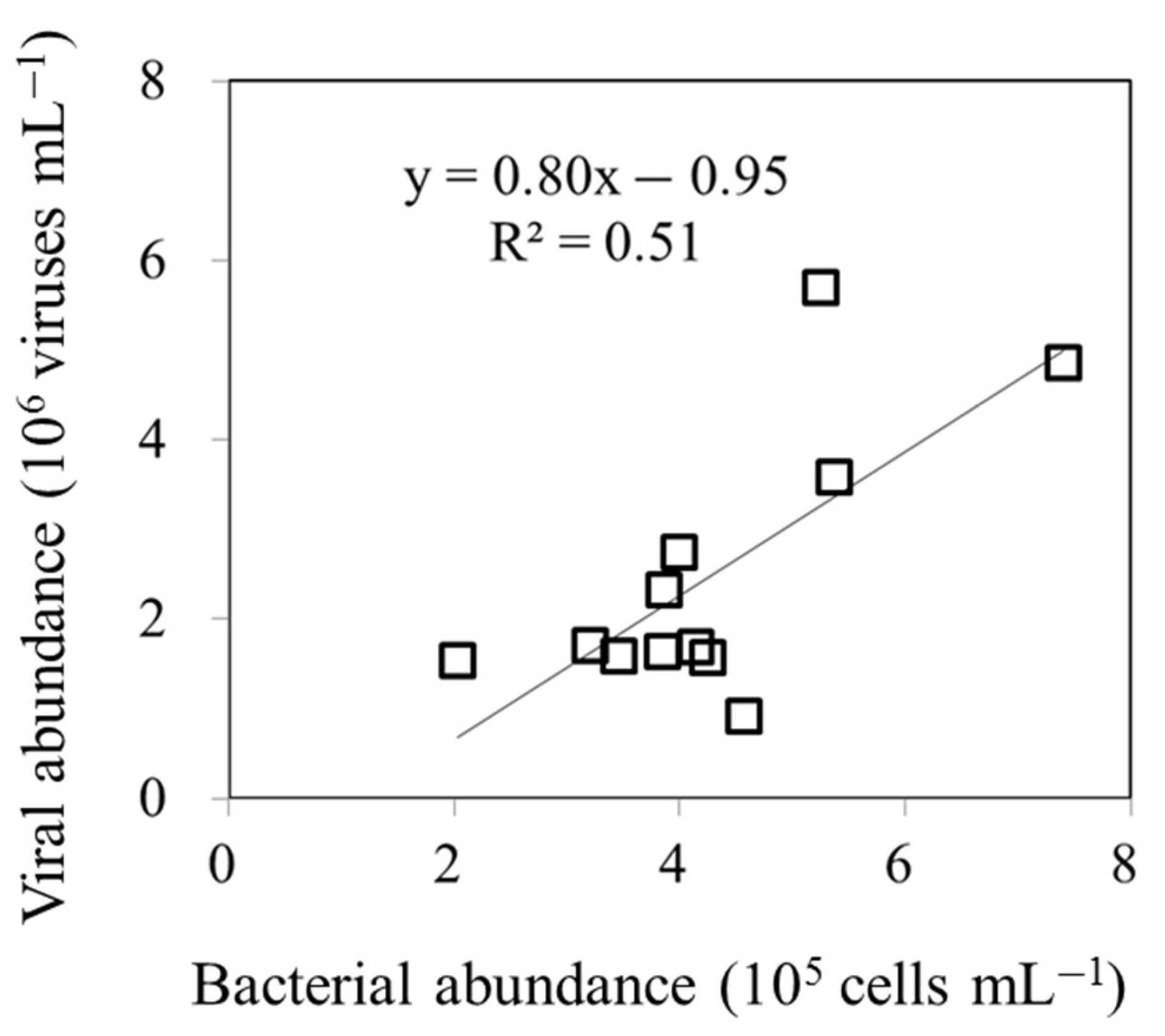
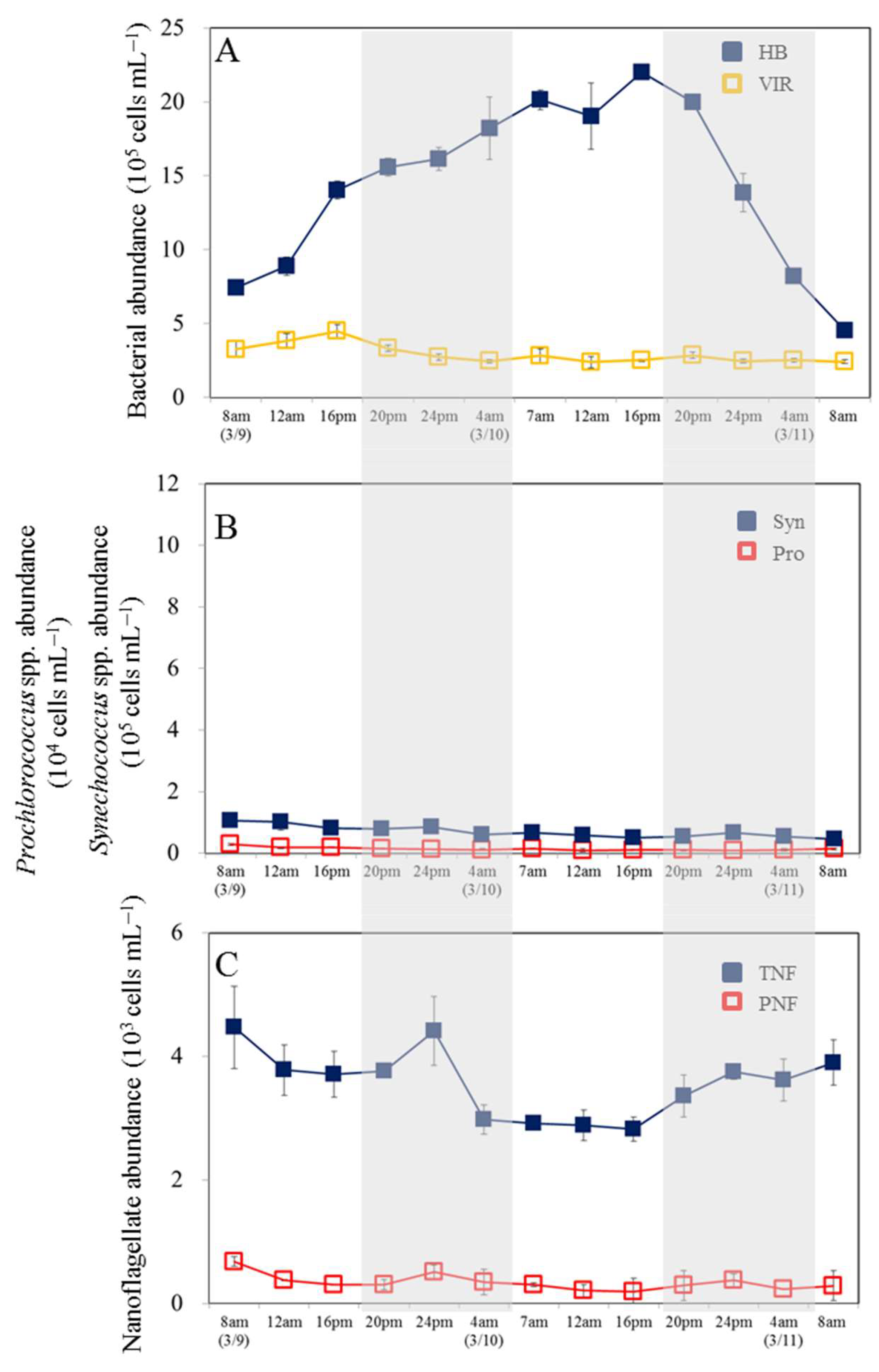
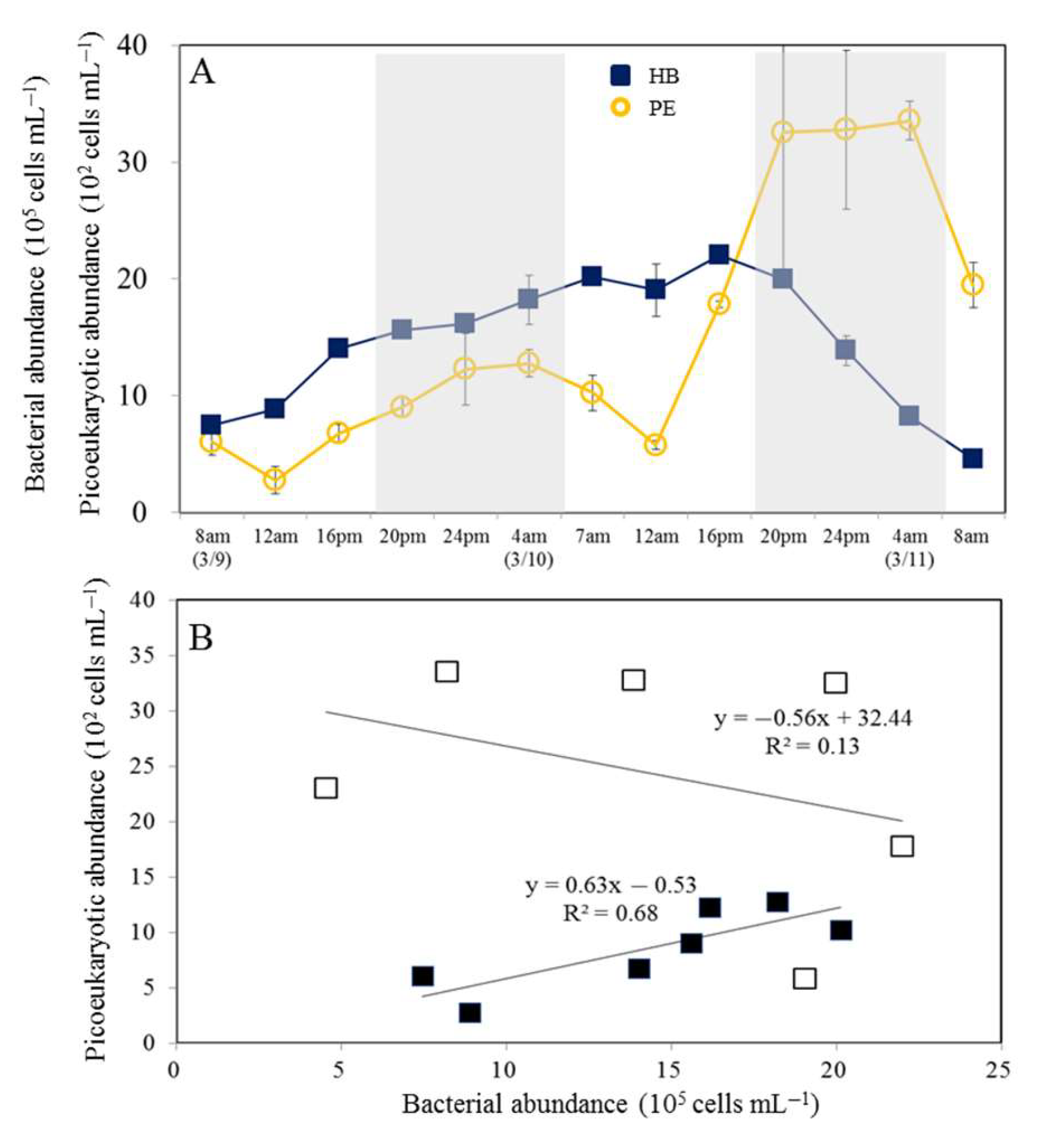
3.1. Temporal Variability in Bacterial and Viral Abundance
3.2. Temporal Variability in Picophytoplankton and Nanoflagellate Abundance
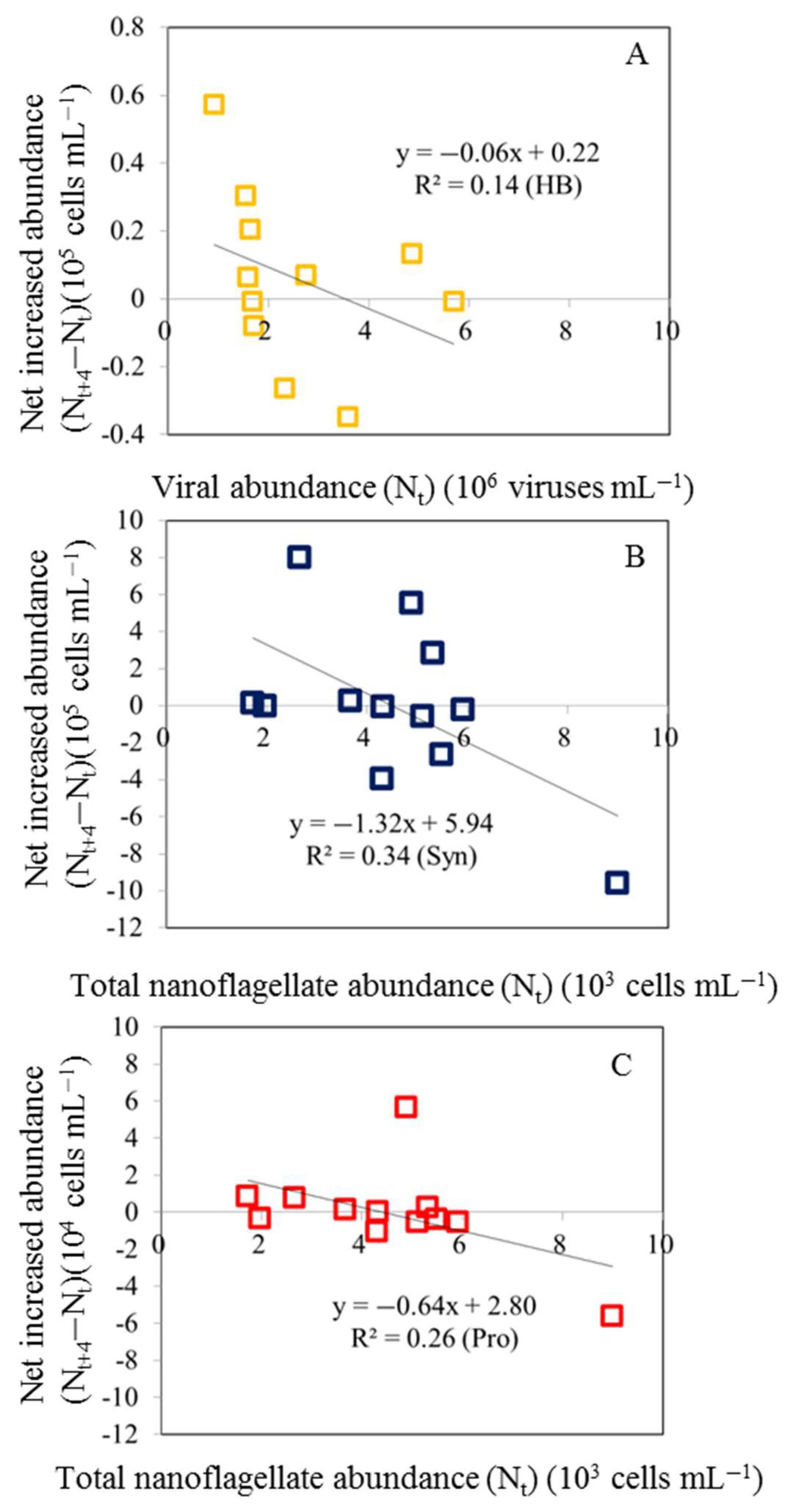
3.3. Net Increased Abundance of Bacteria and Picophytoplankton
3.4. Temporal Variability in Microbial Communities in the Experimental Incubations
4. Discussion
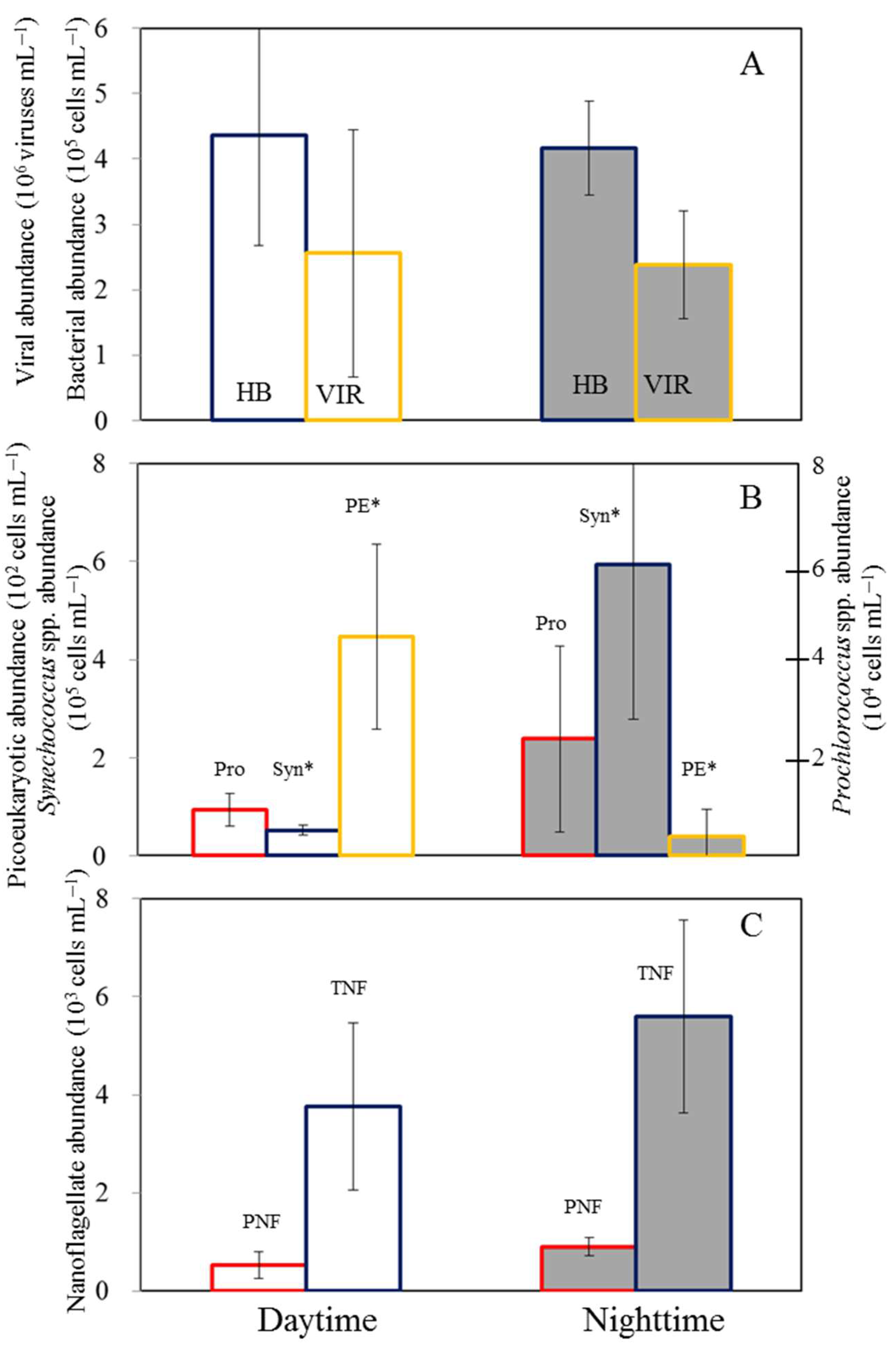
4.1. Diel Patterns in Bacterial and Viral Abundance
4.2. Diel Patterns in Picophytoplankton Abundance
4.3. Diel Variations in HB and Picophytoplankton in Incubation Experiment
4.4. Potential Role of Picoeukaryotes
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moran, X.A.G.; Lopez-Urrutia, A.; Calvo-Diaz, A.; et al. Increasing importance of small phytoplankton in a warmer ocean. Global Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1137–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flombaum, P.; Wang, W.-L.; Primeau, F. W.; et al. Global picophytoplankton niche partitioning predicts overall positive response to ocean warming. Nat Geosci. 2020, 13, 116–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, S.; Lennon, J.-F.; Marie, D.; Vaulot, D. Picoplankton population dynamics in coastal waters of the N. W. Mediterranean Sea. Limnol Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1916–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaulot, D.; Marie, D. Diel variability of photosynthetic picoplankton in the equatorial Pacific. J Geophys Res. 1999, 104, 3297–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaulot, D.; Lebot, N.; Marie, D.; Fukai, E. Effect of phosphorus on the Synechococcus cell cycle in surface in Mediterranean waters during summer. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996, 132, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A. Y.; Chiang, K. P.; Chang, J.; Gong, G. C. Seasonal diel variations of picoplankton and nanoplankton in a subtropical western Pacific coastal ecosystem. Limnol Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, T.; Gasol, J. M. Short-time scale coupling of picoplankton community structure and single-cell heterotrophic activity in winter in coastal NW Mediterranean Sea waters. J Plank Res. 2014, 36, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C. H.; Golden, S. S; Ishiura, M.; Kondo, T. Circadian clocks in prokaryotes. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 21, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, S.; Partensky, F.; Lennon, J. F.; et al. Diel patterns of growth and division in marine picoplankton in cultures. J Phycol. 2001, 37, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommaruga, R.; Hofer, J.S.; Alonso-Sáez, L.; et al. Differential sunlight sensitivity of picophytoplankton from surface Mediterranean coastal waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2154–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, S.; Partensky, F.; Marie, D.; et al. Cell cycle regulation by light in Prochlorococcus strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001, 67, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.R.; leB. WILLIAMS, P. J.; Azam, F.; Hobbie, J. E. The microbial loop. Oceanogr. 2007, 20, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.; Herndl, G.J.; Weinbauer, M.G. Diel cycles in viral infection of bacterioplankton in the North Sea, Aquat Microb Ecol. 2004, 35, 207-216.
- Tsai, A.Y.; Gong, G.C.; Sanders, R.W.; Chiang, K.P.; Huang, J.K.; Chan, Y.F. Viral lysis and nanoflagellate grazing as factors controlling diel variations of Synechococcus spp. summer abundance in coastal waters of Taiwan. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2012, 66, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, P. E.; Ribalet, F.; Armbrust, E.V.; White, A.; Caron, D.A. Diel oscillations in the feeding activity of heterotrophic and mixotrophic nanoplankton in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2020, 85, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, A.Y.; Chiang, K.P.; Chan, Y. F.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, J. Pigmented nanoflagellates in the coastal western subtropical Pacific are important grazers on Synechococcus populations. J Plank Res. 2007, 29, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecker, D.K.; Hansen, P.J.; Caron, D.A.; Mitra, A. Mixotrophy in the marine plankton. Annu Rev Mar Sci.
- Tsai, A.Y.; Chin, W.M.; Chiang, K.P. Diel patterns of grazing by pigmented nanoflagellates on Synechococcus spp. in the coastal ecosystem of subtropical western Pacific. Hydrobiol. 2009, 636, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, A.Y.; Gong, G.C.; Sanders, R.W.; Chen, W.H.; Chao, C.F.; Chiang, K.P. Importance of bacterivory by pigmented and heterotrophic nanoflagellates during the warm season in a subtropical western Pacific coastal ecosystem. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2011, 63, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.W.; Gast, R.J. Bacterivory by phototrophic picoplankton and nanoplankton in Arctic waters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2012, 80, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKie-Krisberg, Z.M.; Sanders, R.W. Phagotrophy by the picoeukaryotic green alga Micromonas: implications for Arctic Oceans. The ISME J. 2014, 8, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.-F.; Tsai, A.-Y.; Ishikawa, A.; Chiang, K.P. Seasonal dynamics of ciliate cysts and the impact of short-term change of salinity in a eutrophic coastal marine ecosystem. Terr Atmo Ocean Sci. 2013, 24, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussaard, C.P.D. Optimization of procedures for counting viruses by flow cytometry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammes, F.; Egli, T. Cytometric methods for measuring bacteria in water: advantages, pitfalls and applications. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010, 397, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Díaz, A.; Morán, X. A. G. Seasonal dynamics of picoplankton in shelf waters of the southern Bay of Biscay. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2006, 42, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.M.; Caron, D.A.; Sieracki, M.E.; Poulton, N. Counting heterotrophic nanoplanktonic protists in cultures and aquatic communities by flow cytometry. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2004, 34, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglione, J.F.; Mevel, G.; Pujo-Pay, M.; Mousseau, L.; Lebaron, P.; Goutx, M. Diel and seasonal variations in abundance, activity and community structure of particle-attached and free-living bacteria in NW Mediterranean Sea, Microb Ecol. 2007, 54, 217–231.
- Ruiz-González, C.; Lefort, T.; Massana, R.; Simó, R.; Gasol, J. M. Diel changes in bulk and single-cell bacterial heterotrophic activity in winter surface waters of the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Limnol Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiah, F.K. Diel cycles of heterotrophic bacterioplankton abundance and production in the ocean surface waters. Aquat Microb Ecol. 1999, 17, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Sáez, L.; Gasol, J. M. Seasonal variations in the contributions of different bacterial groups to the uptake of low-molecular-weight compounds in northwestern Mediterranean coastal waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3528–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šimek, K.; Pernthaler, J.; Weinbauer, M. G.; Hornák, K.; Dolan, J. R.; Nedoma, J.; et al. Changes in bacterial community composition and dynamics and viral mortality rates associated with enhanced flagellate grazing in a mesoeutrophic reservoir. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2723–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.C.; Gong, G.C.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, P.W.Y.; Tsai, A.Y. Diel variation of viral production in a coastal subtropical marine system. Diver. 2021, 13, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winget, D.M.; Wommack, K.E. Diel and daily fluctuations in virioplankton production in coastal ecosystems. Environ Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2904–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylward, F.O.; Boeuf, D.; Mende, D.R.; Wood-Charlson, E.M.; Vislova, A.; Eppley, J.M.; Romano, A.E.; DeLong, E.F. Diel cycling and long-term persistence of viruses in the ocean’s euphotic zone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017, 114, 11446–11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Watai, H.; Haruki, N.; Morimoto, D.; Kaneko, H.; Honda, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Hingamp, P.; Sako, Y.; et al. Locality and diel cycling of viral production revealed by a 24 h time course cross-omics analysis in a coastal region of Japan. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, S.; Heldal, M.; Iglesias-Rodriguez, D.; Larsen, A.; Wilson, W.; Bratbak, G. Flow cytometric analysis of an Emiliana huxleyi bloom terminated by viral infection. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2002, 27, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttle, C.A.; Chen, F. Mechanisms and rates of decay of marine viruses in seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3721–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, R.T.; Fuhrman, J.A. Virus decay and its cause in coastal waters. Appl Environ Microblol. 1997, 63, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylward, F.O.; Boeuf, D.; Mende, D.R.; Wood-Charlson, E.M.; Vislova, A.; Eppley, J.M.; Romano, A.E.; DeLong, E.F. Diel cycling and long-term persistence of viruses in the ocean’s euphotic zone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11446–11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, V.I.; Suzina, N.E.; Polivtseva, V.N.; Boronin, A.M. Ultramicrobacteria: formation of the concept and contribution of ultramicrobacteria to biology. Microbiol. 2012, 81, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, C.; Casotti, R.; Vantrepotte, V.; Conversano, F. Vertical variability and diel dynamics of picophytoplankton in the Strait of Sicily, Mediterranean Sea, in summer. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 2007, 346, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B. J.; DuRand, M.D. Diel cycles in surface waters of the equatorial Pacific. Deep Sea Res II: Top Stud Oceanogr. 2601. [Google Scholar]
- Christaki, U.; Giannakourou, A.; Van Wambeke, F.; Grégori, G. Nanoflagellate predation on auto-and heterotrophic picoplankton in the oligotrophic Mediterranean Sea. J Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 1297–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.B.; Waterbury, J.B.; Chisholm, S.W. Cyanophages infecting the oceanic cyanobacterium Prochlorococcus. Nature 2003, 424, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.; Fang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Tidal effects on diel variations of picoplankton and viruses in the Changjiang estuary. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limn. 2010, 28, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.R.; Goericke, R.; Chisholm, S.W. Comparative physiology of Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus: influence oflight and temperature on growth pigments fluorescence and absorptive properties. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 1995, 16, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grébert, T.; Doré, H.; Partensky, F.; Farrant, G.K.; Boss, E.S.; Picheral, M.; Acinas, S.G. Light color acclimation is a key process in the global ocean distribution of Synechococcus cyanobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, K. Picophytoplankton size and biomass around equatorial eastern Indian Ocean. Microbiol Open. 2019, 8, e00629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, E.; Marañón, E.; Serret, P.; Morán X. A., G. Potential causes for the unequal contribution of picophytoplankton to total biomass and productivity in oligotrophic waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003. 254, 101–109. [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Díaz, A.; Díaz-Pérez, L.; Suárez, L.Á.; Morán, X.A.G.; Teira, E.; Marañón, E. Decrease in the autotrophic-to-heterotrophic biomass ratio of picoplankton in oligotrophic marine waters due to bottle enclosure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5739–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieskes W. W., C.; Kraay G., W.; Baars M., A. Current 14C methods for measuring primary production: gross underestimates in oceanic waters. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1979, 13, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, L.R.; Sheldon, J.E.; Sheldon, W.M.Jr. Changes in bacterial numbers and leucine assimilation during estimations of microbial respiratory rates in seawater by the precision Winkler method. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, E.B.; Sherr, B.F. Sigmon C.T. Activity of marine bacteria under incubated and in situ conditions. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 20, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.L.; Buckley, E.N.; Palumbo, A.V. Response of marine bacterioplankton to differential filtration and confinement. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 47, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flöder, S.; Hansen, T.; Ptacnik, R. Energy–dependent bacterivory in Ochromonas minima–A strategy promoting the use of substitutable resources and survival at insufficient light supply. Protist. 2006, 157, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, M. Photosynthetic picoplankton dynamics in Lake Tahoe: temporal and spatial niche partitioning among prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. J. Plank. Res. 2009, 31, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardillier, L.; Zubkov, M.V.; Pearman, J.; Scanlan, D.J. Significant CO2 fixation by small prymnesiophytes in the subtropical and tropical northeast Atlantic Ocean. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothhaupt, K.O. Laboratorary experiments with a mixotrophic chrysophyte and obligately phagotrophic and photographic competitors. Ecol. 1996, 77, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




