Submitted:
16 July 2024
Posted:
17 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
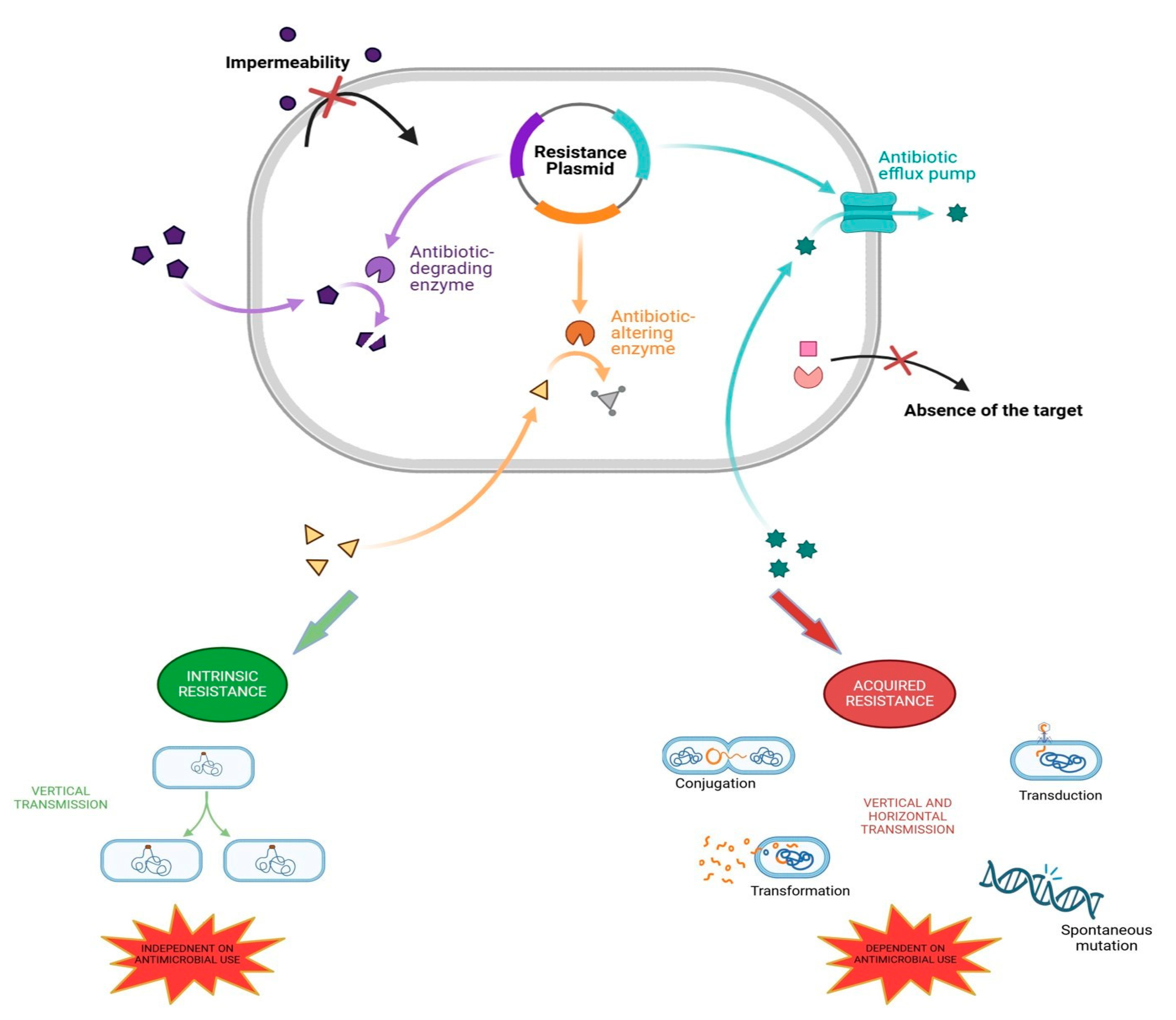
2. The Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria
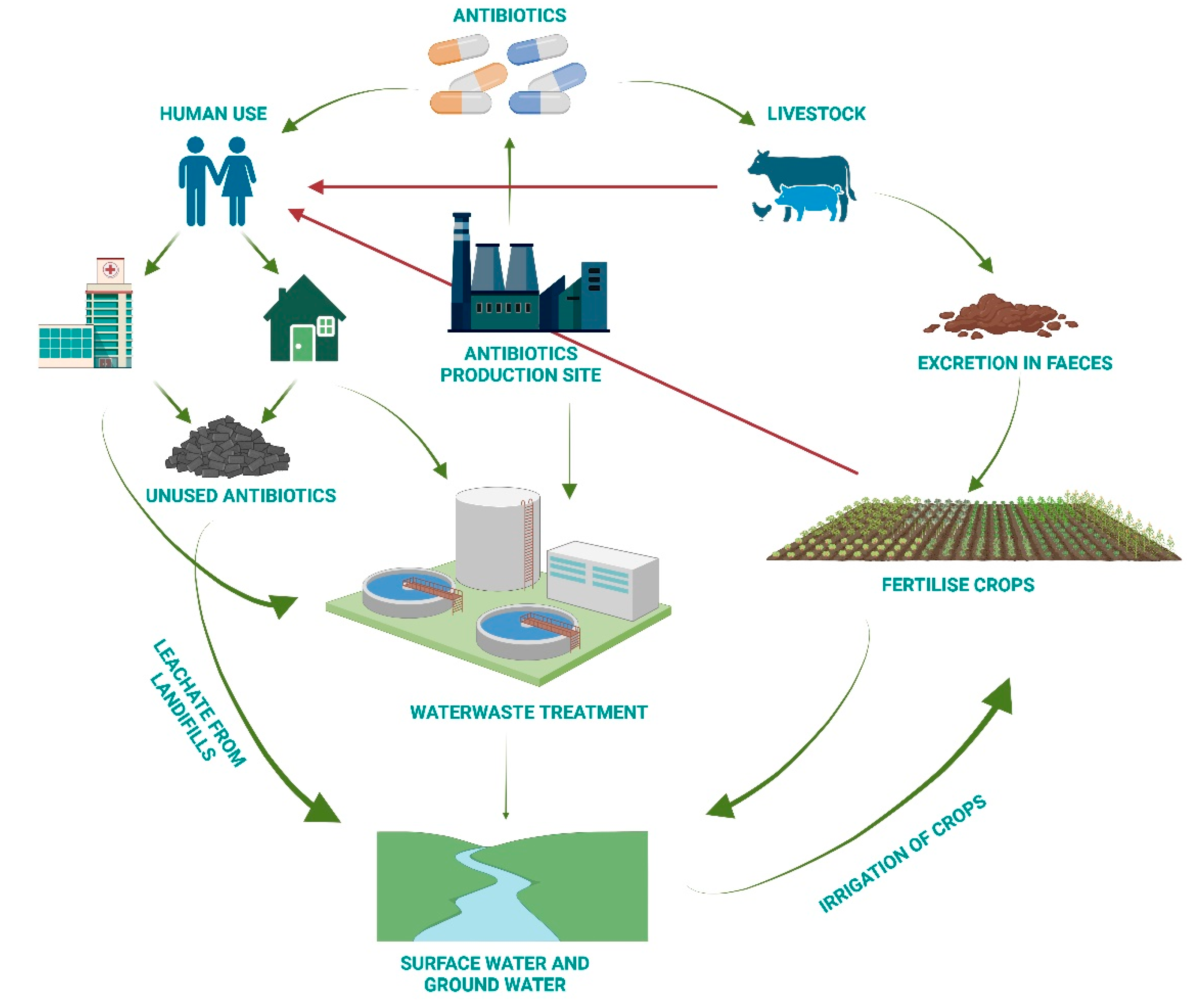
3. Reasons behind Antimicrobial Resistance
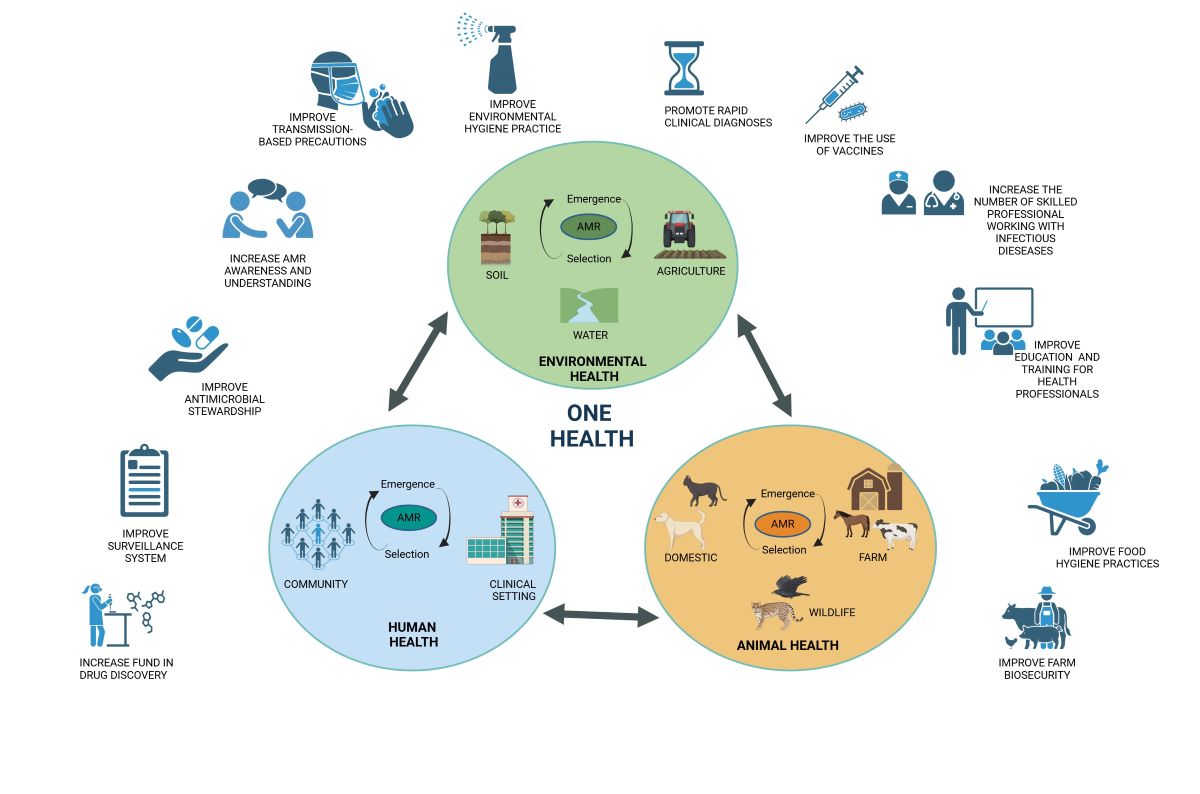
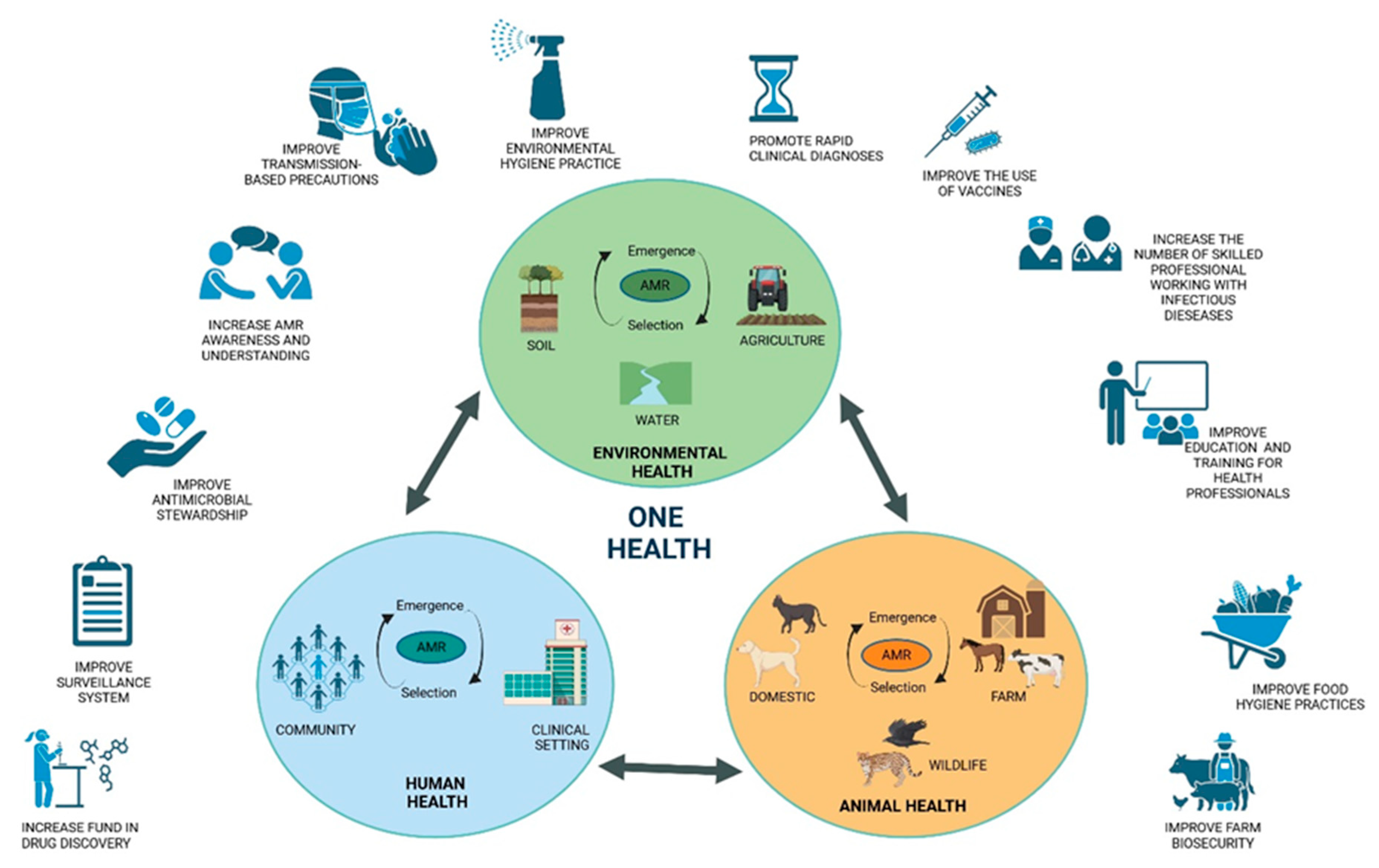
4. Tackling Antibiotic Resistance with a One Health Approach
5. Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals and Human Health
- The prohibition of the routine administration of antibiotics on farms in order to compensate for inadequate hygiene standards and to stimulate growth.
- It is recommended that there be a reduction in intensive farming and an increase in outdoor rearing in order to reduce overcrowding and stress, which are known to cause routine disease.
- A higher minimum weaning age for piglets is proposed as a means of reducing the incidence of weaning diarrhoea.
- It is recommended that animal health be monitored and that infected animals be isolated in order to prevent the spread of disease through the process of metaphylaxis.
- It is recommended that drugs be administered only after a careful clinical assessment and laboratory analysis have been conducted.
- It is of the utmost importance to maintain the highest standards of hygiene at breeding sites.
6. Antimicrobial Resistance from a One Health Perspective
- a.
- Increase awareness of the recycling of expired drugs in appropriate containers.
- b.
- Conduct research into new technologies for wastewater treatment.
- c.
- Take action on treatment facilities to minimise residual traces.
- d.
- Select the process that removes the greatest quantity of antibiotics.
- e.
- Set rigorous limits for antibiotic concentrations in water.
7. A Multi-Step Plan to Fight Antimicrobial Resistance
|
BOX 1: Focus on measures of infection control in hospitals. A bundle can be defined as a set of a few evidence-based practices that, when applied together and correctly, result in an improvement in the quality and outcome of processes that is greater than that achieved through the implementation of the practices separately. Bundles exist for different types of patients and different contexts (for example, bundles for the prevention of sepsis and for the management of catheters). It is also of paramount importance to implement infection control strategies, related to the local epidemiological context, in addition to adherence to standard hygiene precautions such as the use of personal protective equipment and hand washing. These strategies include specific measures to be used to treat infected patients and contain the spread of infection to other patients admitted to the same operating unit. Furthermore, it is of the utmost importance to implement infection control strategies that are aligned with the local epidemiological context. In addition, it is imperative to adhere to standard hygiene precautions, including the use of personal protective equipment and handwashing. Such strategies encompass the implementation of specific measures to be employed in the treatment of infected patients and the containment of the spread of infection to other patients admitted to the same operating unit. In particular, the following measures may be considered: 1. It is recommended that all individuals who may be at risk of multidrug resistance (MDR) bacteria (i.e. those who have previously been hospitalised, transferred from other departments, or have a history of previous infections) undergo screening upon admission to the hospital. 2. In the event of an infected patient, it is recommended that they be isolated, and any potential contacts should be placed in single rooms or, if necessary, in cohorts. 3. It is of the utmost importance that the environment in which the patient with an infectious disease is situated be thoroughly sanitised. 4. The distribution of healthcare personnel and equipment to the infected patient. The primary obstacle to the effective implementation of these regulations is frequently the dearth of sufficient financial resources to employ a sufficient number of adequately trained personnel and the lack of suitable premises for the isolation of patients. As a potential alternative proposal, one may consider the approach proposed by the French AP-HP outbreak control group in their prospective studies conducted in multi-hospital centres in France. In the work of Fournier et al., it is demonstrated how, in settings where it is not feasible to assign dedicated staff to each individual patient, hospitals have adopted the strategy of reorganising healthcare. This method involves initiating care on the ward from contact patients and concluding with infected patients, with the aim of minimising the potential for contamination. The implementation of this and other control measures has led to a statistically significant reduction in the incidence of outbreaks caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. |
8. What Can Each of Us Do to Contribute to the Solution?
| Box 2. The potential impact of each individual on the global threat of antimicrobial resistance. |
| If you are a citizen: |
| - Do not use antibiotics to treat colds or viral diseases; - Do not take antibiotics without a prescription; - Follow your doctor's instructions; Do not stop or extend treatment without approval; - Do not use antibiotics prescribed for other people or used for previous treatments; - Dispose of expired or unused medications in the appropriate containers; - Never visit at-risk subjects (infants, elderly, immunocompromised, hospitalized) if you are sick; - Learn more about antibiotic resistance and spread the news. |
| If you are a health worker: |
| - Administer antibiotics after careful clinical evaluation; - Choose the right antibiotic based on laboratory results; - Carefully evaluate the case before administering an antibiotic as prophylaxis; - Do effective antimicrobial stewardship; - Strictly observe hand hygiene practices and take all necessary precautions before visiting a patient; - Minimize contact between colonized and noncolonized patients. |
| If you are a member of health management: |
| - Monitor infections in the hospital; - Create guidelines for controlling alert microorganisms; - Ensure hygiene and infection control regulations are followed; - Ensure the environment is properly disinfected; - Correct errors promptly; - Ensure there are enough protective equipment and health staff; - Train health care workers. |
| If you are a breeder: |
| - Don't use antibiotics to make your animals grow; - Don't use antibiotics to prevent infections; - Don't use antibiotics without your vet's advice; - Follow your vet's instructions; - Look after your animals and keep an eye on their health; - Keep your production site clean. |
| If you are a policymaker: |
| - Raise awareness about antibiotic use and AMR; - Train the next generation; - Collect antibiotic use data to encourage research; - Invest in new technologies and drugs. |
9. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chala, B.; Hamde, F. Emerging and Re-emerging Vector-Borne Infectious Diseases and the Challenges for Control: A Review. Frontiers in public health 2021, 9, 715759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndtson, A.E. Increasing Globalization and the Movement of Antimicrobial Resistance between Countries. Surgical infections 2020, 21, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszewska, M.; Murray, G.G.R.; Ba, X.; Wood, R.; Holmes, M.A.; Weinert, L.A. Stable antibiotic resistance and rapid human adaptation in livestock-associated MRSA. eLife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muteeb, G.; Rehman, M.T.; Shahwan, M.; Aatif, M. Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidovic, N.; Vidovic, S. Antimicrobial Resistance and Food Animals: Influence of Livestock Environment on the Emergence and Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance. Antibiotics 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, M.K.H.; Gajdacs, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in microbes: History, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Journal of infection and public health 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Alam Tumpa, M.A.; Zehravi, M.; Sarker, M.T.; Yamin, M.; Islam, M.R.; Harun-Or-Rashid, M.; Ahmed, M.; Ramproshad, S.; Mondal, B.; et al. An Overview of Antimicrobial Stewardship Optimization: The Use of Antibiotics in Humans and Animals to Prevent Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, G.; De Gaetano, S.; Midiri, A.; Zummo, S.; Biondo, C. The Challenge of Overcoming Antibiotic Resistance in Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria: "Attack on Titan". Microorganisms 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmerzouga, I.; Al-Zammay, S.A.; Al-Shammari, M.M.; Alsaif, S.A.; Alhaidan, T.M.; Aljofan, M. Practices of patients consuming antibiotics and knowledge about antibiotic resistance in Hail region - Saudi Arabia. Future science OA 2019, 5, FSO420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lu, J.; Liu, D.; He, Y. Characteristics and risk factors of secondary bacterial infections in COVID-19 patients. Antimicrobial stewardship & healthcare epidemiology : ASHE 2023, 3, e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondo, C.; Ponzo, E.; Midiri, A.; Ostone, G.B.; Mancuso, G. The Dark Side of Nosocomial Infections in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Life 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, H.; Mathewos, M.; Abdeta, D. Potential Causes of Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance and Preventive Measures in One Health Perspective-A Review. Infection and drug resistance 2023, 16, 7515–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S. The challenges of implementing infection prevention and antimicrobial stewardship programs in resource-constrained settings. Antimicrobial stewardship & healthcare epidemiology : ASHE 2024, 4, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, S.; Shrestha, P.; Adhikari, B. Antimicrobial use in food animals and human health: time to implement 'One Health' approach. Antimicrobial resistance and infection control 2020, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, U.; Moodley, A.; Osbjer, K. Antimicrobial resistance at the livestock-human interface: implications for Veterinary Services. Revue scientifique et technique 2021, 40, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polianciuc, S.I.; Gurzau, A.E.; Kiss, B.; Stefan, M.G.; Loghin, F. Antibiotics in the environment: causes and consequences. Medicine and pharmacy reports 2020, 93, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Ma, L.; Yu, Q.; Yang, J.; Su, W.; Hilal, M.G.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, H. The source, fate and prospect of antibiotic resistance genes in soil: A review. Frontiers in microbiology 2022, 13, 976657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visca, A.; Di Gregorio, L.; Clagnan, E.; Bevivino, A. Sustainable strategies: Nature-based solutions to tackle antibiotic resistance gene proliferation and improve agricultural productivity and soil quality. Environmental research 2024, 248, 118395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dou, Q.; Smalla, K.; Wang, Y.; Johnson, T.A.; Brandt, K.K.; Mei, Z.; Liao, M.; Hashsham, S.A.; Schaffer, A.; et al. Gut microbiota research nexus: One Health relationship between human, animal, and environmental resistomes. mLife 2023, 2, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Khurshid, M.; Arshad, M.I.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.; Yasmeen, N.; Shah, T.; Chaudhry, T.H.; Rasool, M.H.; Shahid, A.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance: One Health One World Outlook. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2021, 11, 771510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Doo, H.; Keum, G.B.; Kim, E.S.; Kwak, J.; Ryu, S.; Choi, Y.; Kang, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.R.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in livestock, environment and humans: One Health perspective. Journal of animal science and technology 2024, 66, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Joji, R.M.; Shahid, M. Evolution and implementation of One Health to control the dissemination of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and resistance genes: A review. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2022, 12, 1065796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance: The Most Critical Pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, J.P. Behavioral responses in bacteria. Annual review of physiology 1992, 54, 683–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiology spectrum 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: a global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathogens and global health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, C.A.; Dominey-Howes, D.; Labbate, M. The antimicrobial resistance crisis: causes, consequences, and management. Frontiers in public health 2014, 2, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nature reviews. Microbiology 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, M.M.; Rambo, I.M.; Baker, B.J.; Reese, B.K. Diversity, Ecology, and Prevalence of Antimicrobials in Nature. Frontiers in microbiology 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, G.G.; Whyte, L.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Goordial, J.; Hanage, W.P.; Dantas, G.; Desai, M.M. Functional characterization of bacteria isolated from ancient arctic soil exposes diverse resistance mechanisms to modern antibiotics. PloS one 2015, 10, e0069533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, C.M.; Dutta, D.; Nguyen, A.N.T. Revisiting Antibiotic Resistance: Mechanistic Foundations to Evolutionary Outlook. Antibiotics 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS microbiology 2018, 4, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, C.; Hassan, K.A. The Gram-negative permeability barrier: tipping the balance of the in and the out. mBio 2023, 14, e0120523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghapour, Z.; Gholizadeh, P.; Ganbarov, K.; Bialvaei, A.Z.; Mahmood, S.S.; Tanomand, A.; Yousefi, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Yousefi, B.; Kafil, H.S. Molecular mechanisms related to colistin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Infection and drug resistance 2019, 12, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, C.; Grohmann, E. Horizontal Gene Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminov, R.I. Horizontal gene exchange in environmental microbiota. Frontiers in microbiology 2011, 2, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wintersdorff, C.J.; Penders, J.; van Niekerk, J.M.; Mills, N.D.; Majumder, S.; van Alphen, L.B.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Wolffs, P.F. Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance in Microbial Ecosystems through Horizontal Gene Transfer. Frontiers in microbiology 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; Eichenberger, E.M.; Shah, P.P.; Carugati, M.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an overview of basic and clinical research. Nature reviews. Microbiology 2019, 17, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lade, H.; Joo, H.S.; Kim, J.S. Molecular Basis of Non-beta-Lactam Antibiotics Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahari, N.I.N.; Engku Abd Rahman, E.N.S.; Irekeola, A.A.; Ahmed, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alotaibi, J.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Halawi, M.Y.; Alamri, I.A.; Almogbel, M.S.; et al. A Review of the Resistance Mechanisms for beta-Lactams, Macrolides and Fluoroquinolones among Streptococcus pneumoniae. Medicina 2023, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, R.; Obize, C.; Sibanda, T.; Abia, A.L.K.; Long, H. Evolution and Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance in Given Ecosystems: Possible Strategies for Addressing the Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Bu, J.H.; Cha, J.H.; Thawng, C.N.; Hwang, E.M.; Seong, H.J.; Sul, W.J.; et al. Mobile resistome of human gut and pathogen drives anthropogenic bloom of antibiotic resistance. Microbiome 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, H.; Berg, C. The concept of health in One Health and some practical implications for research and education: what is One Health? Infection ecology & epidemiology 2015, 5, 25300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzon, D.; Mavingui, P.; Boetsch, G.; Boissier, J.; Darriet, F.; Duboz, P.; Fritsch, C.; Giraudoux, P.; Le Roux, F.; Morand, S.; et al. The One Health Concept: 10 Years Old and a Long Road Ahead. Frontiers in veterinary science 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, V.; Sargeant, J.M. A quantitative approach to the prioritization of zoonotic diseases in North America: a health professionals' perspective. PloS one 2013, 8, e72172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angora, E.K.; Allienne, J.F.; Rey, O.; Menan, H.; Toure, A.O.; Coulibaly, J.T.; Raso, G.; Yavo, W.; N'Goran, E.K.; Utzinger, J.; et al. High prevalence of Schistosoma haematobium x Schistosoma bovis hybrids in schoolchildren in Cote d'Ivoire. Parasitology 2020, 147, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Viet, H.; Lam, S.; Nguyen-Mai, H.; Trang, D.T.; Phuong, V.T.; Tuan, N.D.A.; Tan, D.Q.; Thuy, N.T.; Thuy Linh, D.; Pham-Duc, P. Decades of emerging infectious disease, food safety, and antimicrobial resistance response in Vietnam: The role of One Health. One health 2022, 14, 100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, A.; Tremonte, P.; Lombardi, S.J.; Caturano, C.; Correra, A.; Sorrentino, E. From the Intersection of Food-Borne Zoonoses and EU Green Policies to an In-Embryo One Health Financial Model. Foods 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettenleiter, T.C.; Markotter, W.; Charron, D.F.; Adisasmito, W.B.; Almuhairi, S.; Behravesh, C.B.; Bilivogui, P.; Bukachi, S.A.; Casas, N.; Becerra, N.C.; et al. The One Health High-Level Expert Panel (OHHLEP). One health outlook 2023, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Garbisu, C. Expanding the focus of the One Health concept: links between the Earth-system processes of the planetary boundaries framework and antibiotic resistance. Reviews on environmental health 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, E.; Tilocca, B.; Roncada, P. Antimicrobial Resistance in Veterinary Medicine: An Overview. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caneschi, A.; Bardhi, A.; Barbarossa, A.; Zaghini, A. The Use of Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance in Veterinary Medicine, a Complex Phenomenon: A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei Sekyere, J. Antibiotic Types and Handling Practices in Disease Management among Pig Farms in Ashanti Region, Ghana. Journal of veterinary medicine 2014, 2014, 531952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Credille, B.; Berghaus, R.D.; Jane Miller, E.; Credille, A.; Schrag, N.F.D.; Naikare, H. Antimicrobial Metaphylaxis and its Impact on Health, Performance, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Contextual Antimicrobial Use in High-Risk Beef Stocker Calves. Journal of animal science 2024, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economou, V.; Gousia, P. Agriculture and food animals as a source of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. Infection and drug resistance 2015, 8, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: a One Health Perspective. Microbiology spectrum 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, R.; Semedo-Lemsaddek, T.; Cunha, E.; Tavares, L.; Oliveira, M. Antimicrobial Drug Resistance in Poultry Production: Current Status and Innovative Strategies for Bacterial Control. Microorganisms 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, P.J.; McEwen, S.A. One Health-Its Importance in Helping to Better Control Antimicrobial Resistance. Tropical medicine and infectious disease 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.J.; Wellington, M.; Shah, R.M.; Ferreira, M.J. Antibiotic Stewardship in Food-producing Animals: Challenges, Progress, and Opportunities. Clinical therapeutics 2020, 42, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, P.; Ceccarelli, D.; Odent, E.; Sarrazin, S.; Graveland, H.; Van Gompel, L.; Battisti, A.; Caprioli, A.; Franco, A.; Wagenaar, J.A.; et al. Antimicrobial Usage and Resistance in Companion Animals: A Cross-Sectional Study in Three European Countries. Antibiotics 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayobami, O.; Willrich, N.; Reuss, A.; Eckmanns, T.; Markwart, R. The ongoing challenge of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis in Europe: an epidemiological analysis of bloodstream infections. Emerging microbes & infections 2020, 9, 1180–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Asano, R.; Davies, J. Antimicrobial resistance gene delivery in animal feeds. Emerging infectious diseases 2004, 10, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.R.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Barrett, J.B.; Ladely, S.R. Effects of tylosin use on erythromycin resistance in enterococci isolated from swine. Applied and environmental microbiology 2004, 70, 4205–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, N.; Wang, M.; Gu, B.; Li, J.; Jin, H.; Xiao, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; et al. Prevalence of 16S rRNA Methylation Enzyme Gene armA in Salmonella From Outpatients and Food. Frontiers in microbiology 2021, 12, 663210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazards, E.P.o.B.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordonez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; et al. Role played by the environment in the emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) through the food chain. EFSA journal. European Food Safety Authority 2021, 19, e06651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietgen, M.; Sedlaczek, L.; Higgins, P.G.; Kaspar, H.; Ewers, C.; Gottig, S. Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Human and Veterinary Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Antibiotics 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Qiu, L.; Wang, G.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Li, R. Emergence and Transmission of Plasmid-Mediated Mobile Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-10 in Humans and Companion Animals. Microbiology spectrum 2022, 10, e0209722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutuku, C.; Gazdag, Z.; Melegh, S. Occurrence of antibiotics and bacterial resistance genes in wastewater: resistance mechanisms and antimicrobial resistance control approaches. World journal of microbiology & biotechnology 2022, 38, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Varela Della Giustina, S.; Llorca, M.; Barcelo, D.; Schubert, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Michael-Kordatou, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Martinez, J.L.; et al. Antibiotic residues in final effluents of European wastewater treatment plants and their impact on the aquatic environment. Environment international 2020, 140, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.W.K.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). British journal of biomedical science 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, M.A.A.; Rahman, S.; Cohall, D.; Bharatha, A.; Singh, K.; Haque, M.; Gittens-St Hilaire, M. Antimicrobial Stewardship: Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance and Protecting Global Public Health. Infection and drug resistance 2020, 13, 4713–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Mulchandani, R.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in food animals using priority drugs maps. Nature communications 2024, 15, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, P.C.; Assefa, Y.A.; Batikawai, S.M.; Reid, S.A. Strengthening antimicrobial resistance surveillance systems: a scoping review. BMC infectious diseases 2023, 23, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiru-Oredope, D.; Garraghan, F.; Olaoye, O.; Krockow, E.M.; Matuluko, A.; Nambatya, W.; Babigumira, P.A.; Tuck, C.; Amofah, G.; Ankrah, D.; et al. Development and Implementation of an Antimicrobial Stewardship Checklist in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Co-Creation Consensus Approach. Healthcare 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashwan, A.J.; Barakat, M.; Niaz, F.; Tariq, S.; Ahmed, S.K. Antimicrobial Resistance: Stewardship and One Health in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Cureus 2024, 16, e58478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mode of action | Drug class | Targets | Resistance | Specific drugs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
inhibition of cell wall synthesis |
Beta-Lactams |
Penicillin-binding protein |
blaZ mecA ampC bla |
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems Monobactams |
| Glycopeptides |
Peptidoglycan subunits | van | Vancomicin | |
| Polypeptides | Peptidoglycan subunits |
bceAB bceRS bacA |
Bacitracin | |
|
inhibition of protein synthesis |
Aminoglycosides | 30 s subunit |
aadA1 erm |
Gentamicin, Tobramycin Amikacin, Streptomicin |
| Tetracyclines | 30 s subunit |
tetM tetX |
Metacycline, Doxycycline, Minocycline | |
| Amphenicoli | 50 s subunit | cat | Chloramphenicol | |
| Macrolides | 50 s subunit | erm | Azithromycin Clarithromycin Erythromycin Fidaxomicin |
|
| Lincosamides | 50 s subunit | erm | Clindamycin | |
|
disruption of cell membrane integrity |
Polymyxins | Lipopolysaccharides |
mcr1 arnBCADTEF |
Colistin |
| Lipopeptides | Depolarizing the cell membrane | mprF | Daptomycin | |
|
inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis |
Quinolones | DNA |
gyrA grlA |
Ciprofloxacin Levofloxacin |
| Rifamycin | RNA |
drrABC, rpoB |
Rifampicin | |
| Antimetabolite activity | Pyrimidines + Sulfonamides | Folic acid synthesis enzymes | sul dfr | Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





