Submitted:
27 June 2024
Posted:
27 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Soil Sampling
2.2. Experimental Design and Weather Conditions
2.3. Irrigation System and Schedule
2.4. Chemical and Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
| Year | Germination | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DH‡ | PER | CAT | NR | UR | |
| 2015 | 6.930 | 4.340 | 5.120 | 0.311 | 4.780 |
| 2016 | 25.30 | 4.490 | 2.420 | 3.452 | 6.890 |
| 2017 | 18.40 | 8.970 | 2.021 | 7.890 | 6.590 |
| Mean | 16.88 | 5.930 | 3.187 | 3.884 | 6.087 |
| Treatment | Ripening | Maturity | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DH‡ | PER | CAT | NR | UR | DH | PER | CAT | NR | UR | ||
| Irrigation | N0 | 13.55 | 7.717 | 3.192 | 4.800 | 5.032 | 18.21 | 4.819 | 2.887 | 6.260 | 8.144 |
| N1 | 33.38 | 9.394 | 3.641 | 4.884 | 4.030 | 18.03 | 4.606 | 2.825 | 5.248 | 6.370 | |
| N2 | 29.51 | 8.205 | 3.783 | 3.174 | 3.646 | 24.35 | 5.643 | 3.103 | 4.077 | 4.551 | |
| N3 | 23.60 | 8.266 | 4.799 | 5.471 | 4.980 | 57.86 | 3.843 | 4.261 | 6.067 | 7.758 | |
| Mean | 25.01 | 8.395 | 3.853 | 4.582 | 4.422 | 29.61 | 4.728 | 3.269 | 5.413 | 6.706 | |
| No irrigation | N0 | 27.25 | 7.198 | 3.574 | 7.134 | 4.364 | 16.92 | 6.710 | 2.284 | 2.486 | 6.623 |
| N1 | 27.58 | 9.242 | 3.368 | 2.970 | 5.959 | 37.26 | 4.209 | 1.897 | 5.211 | 7.808 | |
| N2 | 27.33 | 8.601 | 4.310 | 7.901 | 3.195 | 55.62 | 8.235 | 3.069 | 3.888 | 8.040 | |
| N3 | 53.08 | 7.473 | 3.843 | 7.927 | 3.242 | 45.51 | 5.185 | 2.595 | 4.568 | 9.758 | |
| Mean | 33.79 | 8.128 | 3.774 | 6.483 | 4.190 | 38.83 | 6.085 | 2.462 | 4.038 | 8.057 | |
| LSD for | |||||||||||
| Development phases | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 1.013 | ns | |
| Irrigation | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | 1.813 | 0.970 | 0.132 | ns | |
| N fertilization | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Development phases x Irrigation | ns | ns | ns | 1.559 | ns | ns | ns | ns | 1.724 | ns | |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hofman, G.; Van Cleemput, O. Soil and plant nitrogen. international fertilizer industry. Association 2004, Paris, 1-49. http://www.betuco.be/compost/Soil%20and%20plant%20nitrogen.pdf.
- Cowden, C.C.; Shefferson, R.P.; Mohan, J.E. Mycorrhizal mediation of plant and ecosystem responses to soil warming. In Ecosystem Consequences of Soil Warming; Mohan, J.E., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: location, 2019; pp. 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girkin, N.T.; Cooper, H.V. Nitrogen and ammonia in soils. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment, Second ed.; Goss, M.J., Oliver, M., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: location, 2023; pp. 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafreen, M.; Vishwakarma, K.; Shrivastava, N.; Kumar, N. Physiology and Distribution of Nitrogen in Soils; Eds, Cruz; et al. Physiology and Distribution of Nitrogen in Soils; Eds Cruz et al. In: Soil Nitrogen Ecology, Soil Biology, Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2021, 2, pp.8-13. [CrossRef]
- Moeskops, B.; Buchan, D.; Sleutel, S.; Herawaty, L.; Husen, E.; Saraswati, R.; Setyorini, D.; De Neve, S. Soil microbial communities and activities under intensive organic and conventional vegetable farming in West Java, Indonesia. Appl Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, M.; Morales, E.; Cummings, J.; Nicholas Rios, N.; Giatpaiboon, S.; Mogul, R. Simple kinetics, assay, and trends for soil microbial catalases. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 610, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L. Phenol oxidase, peroxidase and organic matter dynamics of soil. Soil Biol. Bioch. 2010, 42, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Varma, A. Role of enzymes in maintaining soil health. Soil enzymology. 2010, Springer. [CrossRef]
- Abdelmagid, H.M.; Tabatabai, M.A. Nitrate reductase activity in soils. Soil Biol. Bioch. 1987, 19, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Kandeler, E.; Ruggiero, P. Enzyme Activities and Microbiological and Biochemical Processes in Soil. In Activity, Ecology, and Applications; Burns, R.G., Dick, R.P., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 2002; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martínez, V.; Cano, A.; Johnson, J. Simultaneous determination of multiple soil enzyme activities for soil healthbiogeochemical indices. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 121–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balota, E.L.; Colozzi-Filho, A.; Andrade, D.S.; Dick, R.P. Long-term tillage and crop rotation effects on microbial biomass and C and N mineralization in a Brazilian Oxisol. Soil Till. Res. 2004, 77, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicardi, M.; Garcia-Prechac, F.; Frioni, L. Soil microbial indicators sensitive to land use conversion from pastures. to commercial Eucalyptus grandis (Hill ex Maiden) plantations in Uruguay. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 27, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfreda, L.; Ruggiero, P. Enzyme activities in soil. In Soil Biology; Nannipieri, P., Smalla, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 257–311. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, D.R.; Babu, Y.J.; Adhyaa, T. Long-term application of compost influences microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a tropical Aeric Endoaquept planted to rice under flooded condition. Soil Boil Biochem. 2007, 39, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B. Defining and assessing soil quality. In Defining soil quality for a sustainable environment; Soil Science Society of America. Special Publication No. 15; Doran, J.W., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, 1994; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, A.D.; Bungau, S.; Tit, D.M.; Melinte, C.E.; Purza, L.; Badea, G.E. Effects of long term application of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil enzymes. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwin, K.H.; Wardle, D.A. New indices for quantifying the resistance and resilience of soil biota to exogenous disturbances. Soil Biol Biochem. 2004, 36, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Staff Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 11th ed.; USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, 2010; pp. 1–346.
- Żarski, J.; Treder, W.; Dudek, S.; Kuśmierek-Tomaszewska, R. Establish irrigation deadlines on the basis of simple meteorological measurements. Infra Ecol Rural Area 2011, 6, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Bashour, I.I.; Sayegh, A.H. Methods of analysis for soils of arid and semi-arid regions. 2007, Rome, Italy.
- Kandeler, E.; Gerber, H. Short-term assay of soil urease activity using colorimetric determination of ammonium. Biol Fertil Soil. 1988, 6, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandeler, E. Enzymes involved in nitrogen metabolism. In Methods in Soil Biology; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 163–184. [Google Scholar]
- Thalmann A Zur Methodik derestimmung der Dehydrodgenaseaktivität in Boden mittels Triphenytetrazoliumchlorid (TTC). Landwirtsch Forsch. 1968, 21, 249–258.
- Johnson, J.L.; Temple, K.L. Some variables affecting the measurement of “catalase activity” in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J. 1964, 28, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, J.N. Origin and range of enzymes in soil. In Soil Enzymes; Academic R.G. Burns, Press: London, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Dugo, V.; Durand, J.L.; Gasta, L.F. Water deficit and nitrogen nutrition of crops. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otori, K.; Tanabe, N.; Maruyama, T.; Sato, S.; Yanagisawa, S.; Tamoi, M.; Shigeoka, S. Enhanced photosynthetic capacity increases nitrogen metabolism through the coordinated regulation of carbon and nitrogen assimilation in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res. 2017, 130, 909–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Z.; Wanga, Y.; Jianga, L.; Wanga, G.; Yang, C.H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z. Drought enhances nitrogen uptake and assimilation in maize roots. Agron J 2016, 109, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.W. Carbon and nitrogen assimilation in relation to yield: Mechanisms are the key to understanding production systems. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cui, Y.; Luo, Y. Irrigation efficiency and water-saving potential considering reuse of return flow. Agri. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; An, J.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, N. Effects of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse soil organic nitrogen fractions and soil-soluble nitrogen pools. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 216, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Lv, J.Z.; Yang, L.; Ahmad, S.; Farooq, S.; Zeeshan, M.; Zho, X.B. Low irrigation water minimizes the nitrate nitrogen losses without compromising the soil fertility, enzymatic activities and maize growth. BMC Plant Biol 2022, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Martín, L.; Meijide, A.; Garcia-Torres, L.; Vallejo, A. Combination of drip irrigation and organic fertilizer for mitigating emissions of nitrogen oxides in semiarid climate. Agric Ecosys Environ. 2010, 137, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shao, L.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Gu, L.; Dong, S.; Bing, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Effect of different nitrogen and irrigation treatments on yield and nitrate leaching of summer maize (Zea mays L.) under lysimeter conditions. Agric Water Manag. 2014, 137, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinweg, J.M.; Dukes, J.S.; Wallenstein, M.D. Modeling the effects of temperature and moisture on soil enzyme activity: linking laboratory assays to continuous field data. Soil Biol. Bioch. 2012, 55, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, A.; Cetin, S.C.; Turgay, O.C.; Kizilkaya, R. Soil enzymes as indication of soil quality. Soil enzymology. Springer, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Deng, L.; Guo, X.; Han, F.; Ju, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X. Patterns of soil microbial nutrient limitations and their roles in the variation of soil organic carbon across a precipitation gradient in an arid and semi-arid region. Sci. Total Environm. 2019, 658, 1440–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, K.; Luo, Y.; Du, L.; Tian, R.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Shao, W. Responses of Soil Enzyme Activity to Long-Term Nitrogen Enrichment and Water Addition in a Typical Steppe. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.J.; Zhao, F.Z.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Differential responses of soil microbial biomass and carbon-degrading enzyme activities to altered precipitation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, L. Costimulation of soil glycosidase activity and soil respiration by nitrogen addition. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 23, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Zhu, B.A. A meta-analysis of soil extracellular enzyme activities in response to global change. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Xing, F.; Sun, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, X.; Chen, C.; Li, Z. Responses of soil extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community properties to interaction between nitrogen addition and increased precipitation in a semi-arid grassland ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeler, B.L.; Hobbie, S.E.; Kellogg, L.E. Effects of Long-Term Nitrogen Addition on Microbial Enzyme Activity in Eight Forested and Grassland Sites: Implications for Litter and Soil Organic Matter Decomposition. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Zhang, T.; Guo, R.; Cao, H.; Shi, L.; Guo, J.; Sun, W. Response of soil enzyme activity to warming and nitrogen addition in a meadow steppe. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, I.; Snell, H.; Bardgett, R.D. High throughput method for measuring urease activity in soil. Soil Biol. Bioch. 2019, 427, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, W.; Zhu, L.; Yan, X. Different forms and proportions of exogenous nitrogen promote the growth of alfalfa by increasing soil enzyme activity. Plan. Theory 2022, 11, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, B.; Xie, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Yan, C. Research on the nitrogen cycle in rhizosphere of Kandelia obovata under ammonium 425 and nitrate addition. Mar. Pollut. 2013, 76, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovieno, P.; Morra, L.; Leone, A.; Pagano, L.; Alfani, A. Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil respiration and enzyme activities 434 of two Mediterranean horticultural soils. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2009, 45, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajawa, H.A.; Dell, C.J.; Rice, C.W. Changes in enzyme activities and microbial biomass of tallgrass prairie soil as related to burning and 437 nitrogen fertilization. Soil Biol. Bioch. 1999, 31, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Ye, C. Soil N2O and NOx emissions are directly linked with N-cycling enzymatic activities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraich, E.A.; Ahmad, R.; Ashraf, M.Y. Role of mineral nutrition in alleviation of drought stress in plants. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 764–777. [Google Scholar]
- Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J. The role of plants in the effects of global change on nutrient availability and stoichiometry in the plant-soil system. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1741–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimel, J.; Balser, T.C.; Wallenstein, M. Microbial stress-response physiology and its implications for cosystem function. Ecology 2007, 88, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolińska, A.; Stępniewska, Z. Dehydrogenase activity in the soil environment. In Dehydrogenases; Canuta R.A., Ed., IntechOpen: Lodnon, UK, 2012; pp. 1–183. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, P.; Kong, C. Urease, invertase, dehydrogenase and polyphenoloxidase activities in paddy soils influenced by allelopathic rice variety. Europ. J Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtak, K.; Gałązka, A.; Niedźwiecki, J. Changes in soil enzymatic activity caused by hydric stress. Pol. J Environl Stud 2020, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, S.A. Effect of irrigation on the biology of soil. Natural Resour. Sustain. Developm. 2013, 3, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Zong, R.; Lin, H.; Dhital, Y.D.; Ayantobo, O.O.; Chen, P.; Li, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, Z. Responses of soil nutrient and enzyme activities to long-term mulched drip irrigation (MDI) after the conversion of wasteland to cropland. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 190, 104976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Gao, R.; Xi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Long-term effects of irrigation using water from the river receiving treated industrial wastewater on soil organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 135, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, A.; Ball, R.; Schipansk, M. Plant and soil microbial responses to irrigation retirement in semiarid cropping systems. Environ. Res. Commun. 2022, 4, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alster, C.J.; German, D.P.; Lu, Y.; Allison, S.D. Microbial enzymatic responses to drought and to nitrogen addition in a southern California grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 64, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P. Life in dry soils: effects of drought on soil microbial communities and processes. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 49, 409–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Becerra, C.A.; Blankinship, J. Estimating decay dynamics for enzyme activities in soils from different ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Xue, S. Dynamics of soil specific enzyme activities and temperature sensitivities during grassland succession after farmland abandonment. Catena 2021, 199, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.Q.; Wang, W. Stoichiometry of soil extracellular enzyme activity along a climatic transect in temperate grasslands of northern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemanowicz, J. Activity of selected enzymes as markers of ecotoxicity in technogenic salinization soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019, 26, 13014–13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


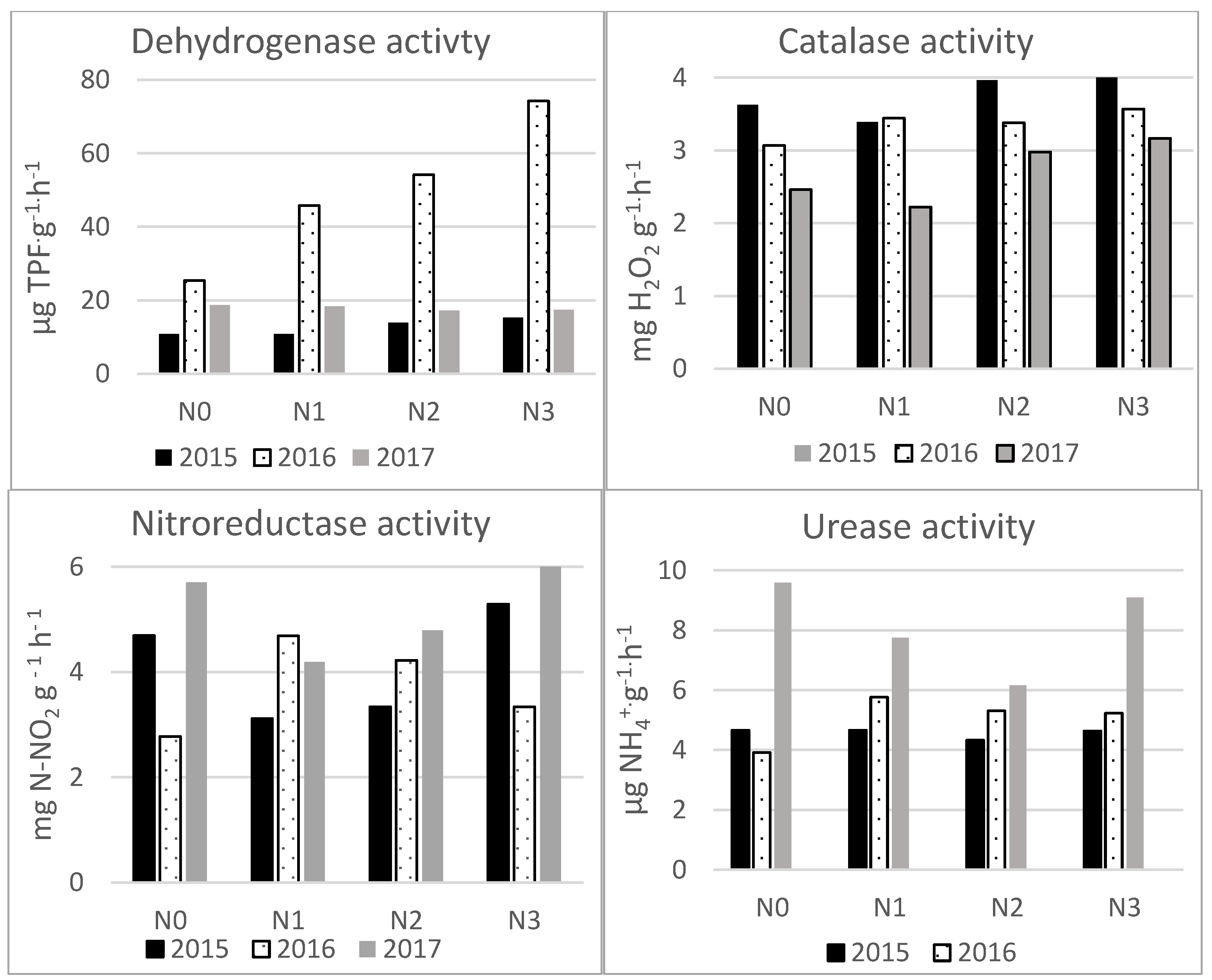
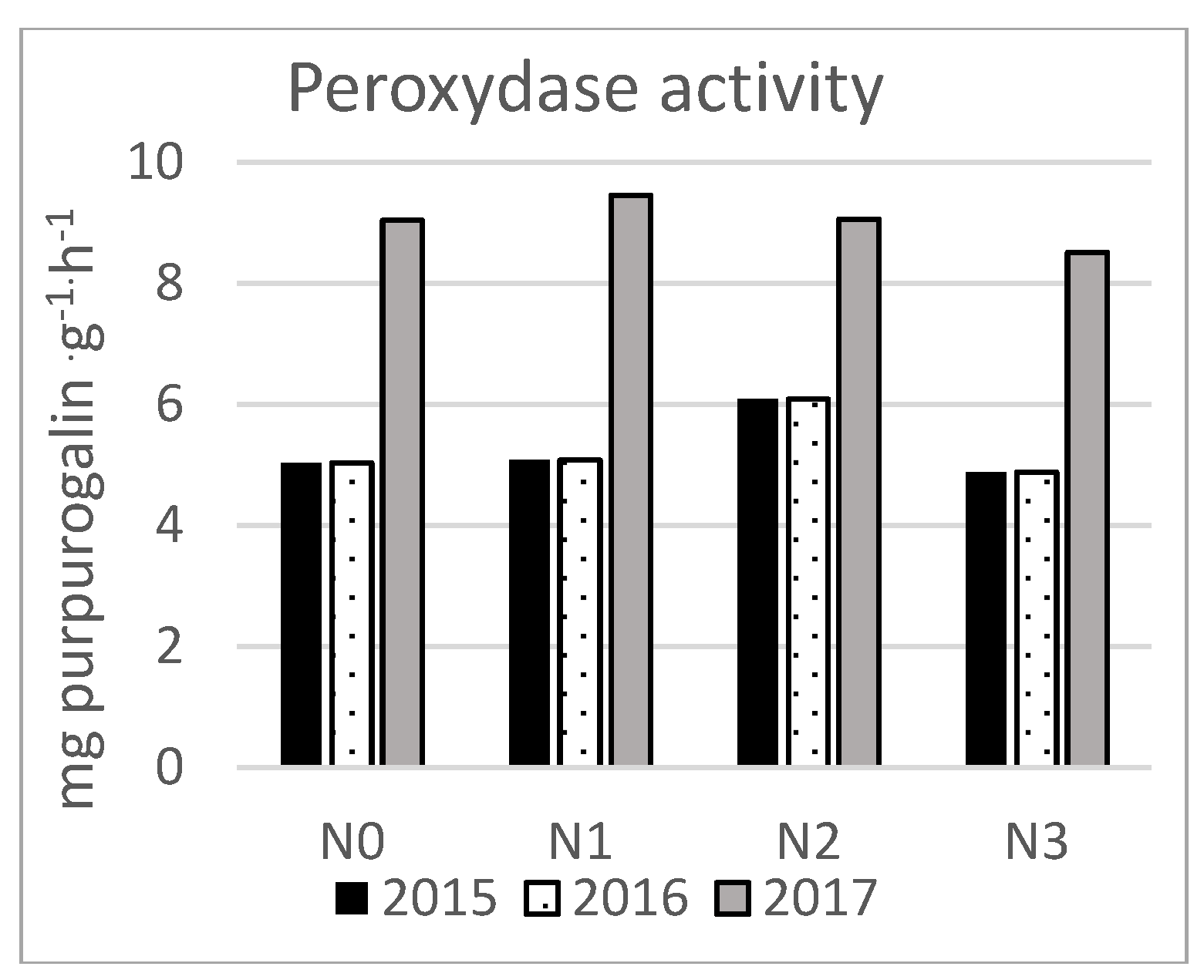
| Soil properties | Content |
|---|---|
| TOC | 7.60-7.70 g.kg-1 |
| TN | 0.70-0.76 g.kg-1 |
| pH KCL | 5.8-6.2 |
| P available | 64.0 mg.kg-1 |
| K available | 125.0 mg.kg-1 |
| SO42- | 12 mg.kg-1 |
| Irrigation factor | Fertigation factor | Nitrogen fertigation level |
|---|---|---|
| W0—no irrigation W1—optimal irrigation | N0 | control |
| N1 | pre-sowing 30 kg⋅ha-1 | |
| N2 | pre-sowing 60 kg⋅ha-1 | |
| N3 | 90 kg⋅ha-1 (pre-sowing 60 kg⋅ha-1 and top dressing 30 kg⋅ha-1 in shooting) |
| Growing season | t (°C) | P (mm) | Date | Irrigation dose (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 13.8 | 193.3 | 26 May | 30 |
| 3 June | 30 | |||
| 10 June | 25 | |||
| 1 July | 30 | |||
| 6 July | 20 | |||
| in total | 135 | |||
| 2016 | 14.3 | 386.7 | 24 May | 35 |
| 8 June | 32 | |||
| in total | 77 | |||
| 2017 | 13.1 | 474.8 | 29 May | 20 |
| 9 June | 20 | |||
| 28 June | 15 | |||
| in total | 55 | |||
| Average 1991–2020 | 14.8 | 324.5 | – | – |
| NH4 | NO3 | Nmin | |||||||||||
| Term | N dose | IRR | NIRR | mean | IRR | NIRR | mean | IRR | NIRR | mean | |||
| Germination | N0 | 6.107 | 6.107 | 6.107 | 2.657 | 2.657 | 2.657 | 39.437 | 39.437 | 39.437 | |||
| Ripening | N0 | 4.310 | 3.957 | 4.133 | 10.023 | 6.497 | 8.260 | 64.502 | 47.040 | 55.771 | |||
| N1 | 4.513 | 4.383 | 4.448 | 7.703 | 13.147 | 10.425 | 54.977 | 78.885 | 66.931 | ||||
| N2 | 5.217 | 8.040 | 6.628 | 21.930 | 29.850 | 25.890 | 122.16 | 125.51 | 123.83 | ||||
| N3 | 6.060 | 6.357 | 6.208 | 23.777 | 19.637 | 21.707 | 134.27 | 116.97 | 125.62 | ||||
| Average | 5.025 | 5.684 | 5.355 | 15.858 | 17.283 | 16.570 | 93.976 | 92.100 | 93.038 | ||||
| Maturity | N0 | 4.413 | 3.777 | 4.095 | 6.553 | 6.937 | 6.745 | 32.683 | 31.545 | 32.114 | |||
| N1 | 4.667 | 2.960 | 3.813 | 3.150 | 20.260 | 11.705 | 35.175 | 104.49 | 69.833 | ||||
| N2 | 3.030 | 4.397 | 3.713 | 10.763 | 20.953 | 15.525 | 67.235 | 106.10 | 86.670 | ||||
| N3 | 5.603 | 3.573 | 4.588 | 25.330 | 19.753 | 22.542 | 101.87 | 118.31 | 110.09 | ||||
| Average | 4.428 | 3.677 | 4.053 | 11.449 | 16.976 | 14.213 | 59.240 | 90.111 | 74.676 | ||||
| LSD for Development phases Irrigation N fertilization |
n.s. n.s. n.s. |
n.s. n.s. 10.754 |
n.s. n.s. 39.517 |
||||||||||
| Interaction: Development phases x Irrigation | 1.506 |
n.s. |
n.s. |
||||||||||
| Types of soil enzymes | RAW | N-fertilization |
|---|---|---|
| Catalase | -0.0712 | 0.2001 |
| Dehydrogenase | 0.0735 | 0.2576 |
| Peroxidase | -0.1652 | -0.0087 |
| Urease activity | 0.0532 | 0.0000 |
| Nitroreductase | 0.0676 | 0.0711 |
| Variables dependent (y) | Variables independent (x) | Equation | Correlation coefficient (r) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalase activity Dehydrogenase activity Peroxidase activity Urease activity Nitroreductase activity Peroxidase activity Urease activity |
NH4+ NO3- NH4+ NH4+ Urease activity NO3- Peroxidase |
y=2.8422+0.64010x y=3.8906+0.28549x y=3.6836+0.54160x y=7.6386-0,3937x y=6.2506-0.2875x y=3.6337+1.2621x y=6.9388-0.1986x |
0.299 0.523 0.331 -0.297 -0.340 0.336 -0.245 |
| N doses | The resistance index RS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | UR | CT | PX | DH | |
| N0 | -0.206 | 0.627 | 0.934 | 0.560 | 0.859 |
| N1 | 0.986 | -0.597 | 0.991 | 0.828 | 0.319 |
| N2 | 0.907 | 0.395 | 0.580 | 0.521 | 0.425 |
| N3 | 0.506 | 0.660 | 0.444 | 0.589 | 0.573 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





