Submitted:
09 January 2025
Posted:
10 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Traditional educational systems often emphasize standardized testing over critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence, failing to address the diverse learning needs of students. This study, "Redesigning Education: A Transformative Approach," proposes comprehensive reforms aimed at transforming primary and secondary education to foster holistic student development. The goal is to ensure that all students thrive academically, emotionally, and socially. The study presents innovative approaches such as personalized education through AI, the creation of wellness schools, professional skill development programs, and the integration of social and emotional learning programs. The proposed curriculum overhaul emphasizes critical thinking, creativity, emotional intelligence, and practical life skills. Key reforms include continuous professional development for teachers, enhanced teacher training, comprehensive counseling services, robust student support systems, strengthened school-family collaboration, and the promotion of multiculturalism and inclusion through inclusive policies and cultural events. Additionally, upgrading school infrastructure to create safe and welcoming environments is highlighted as essential for student prosperity and happiness. The proposed reforms aim to create an inclusive, innovative, and supportive learning environment where all students can excel. By integrating these comprehensive changes, the study seeks to develop effective educational systems that promote the well-being and success of all students, equipping future generations for the challenges of a rapidly changing world. The findings suggest that such a holistic approach to education reform can bridge the gap between different socioeconomic groups, foster equity, and prepare students for lifelong success.
Keywords:
Introduction
The Need for Education Reform
Objectives of the Article
Methodology
Literature Review
Review of Contemporary Educational Books
Analysis of Peer-Reviewed Articles
Examination of Comprehensive Research Studies
Analysis of Specific Case Studies
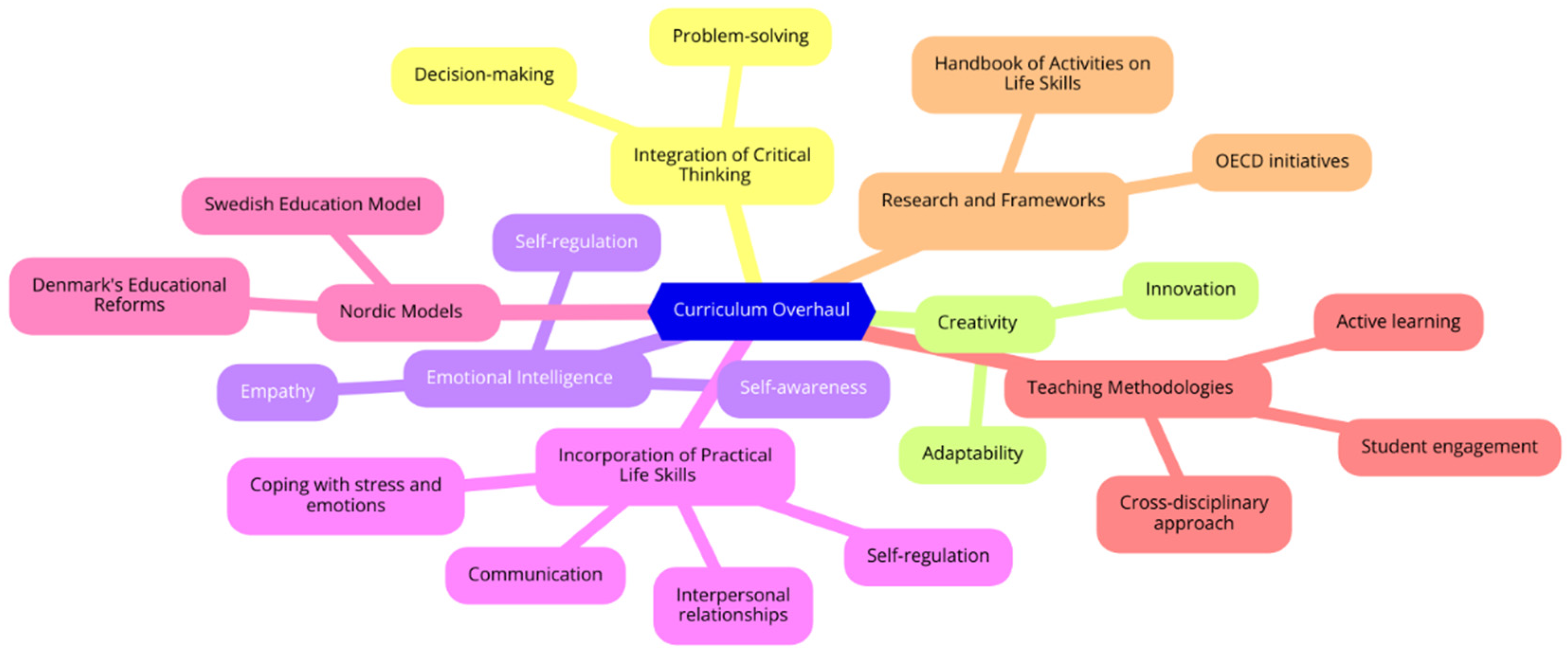
Curriculum Overhaul
Integration of Critical Thinking, Creativity, and Emotional Intelligence
Incorporation of Practical Life Skills
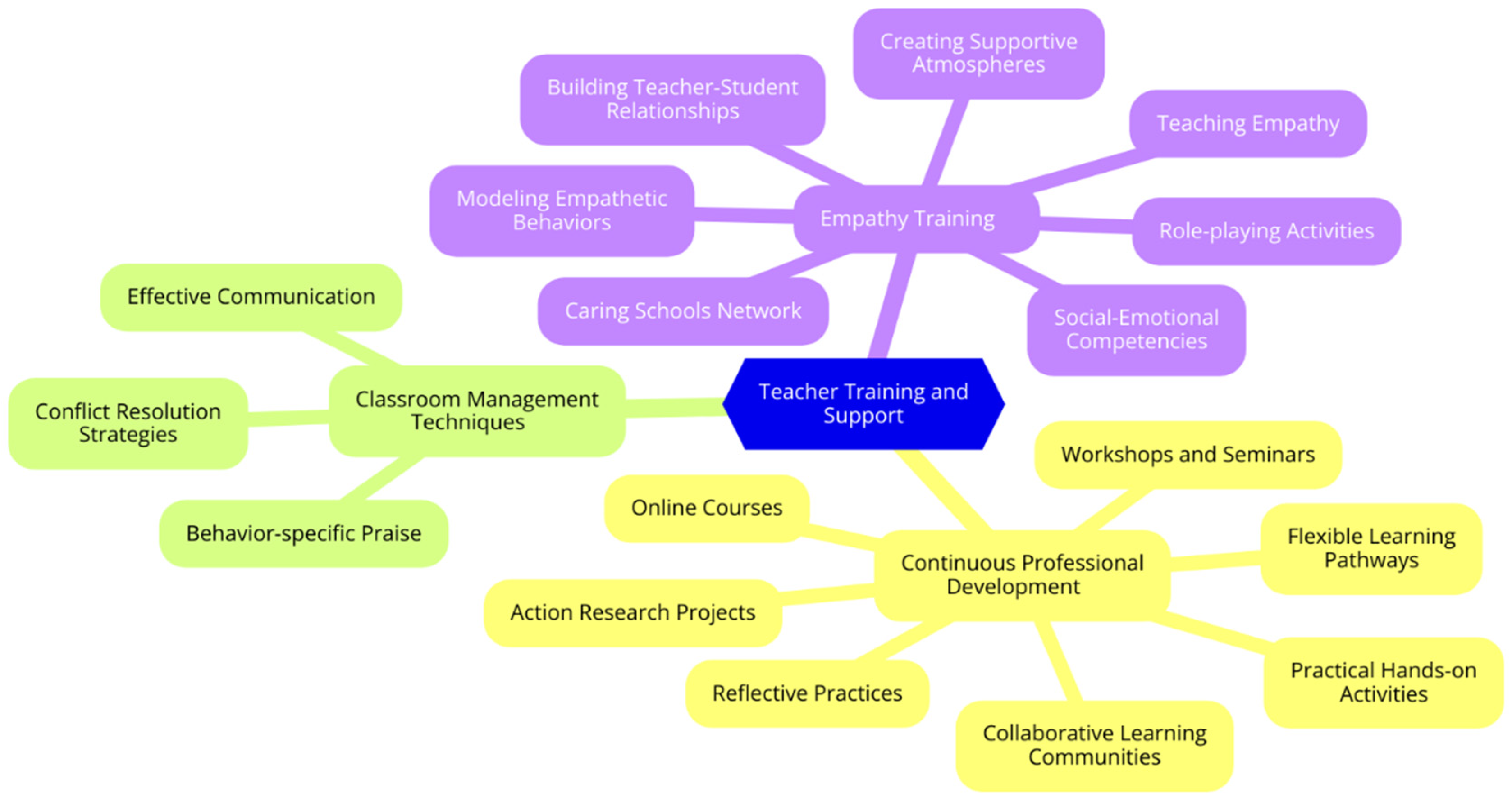
Teacher Training and Support
Continuous Professional Development
Classroom Management Techniques and Empathy Training
Introduction of Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) Programs
Benefits of SEL Programs
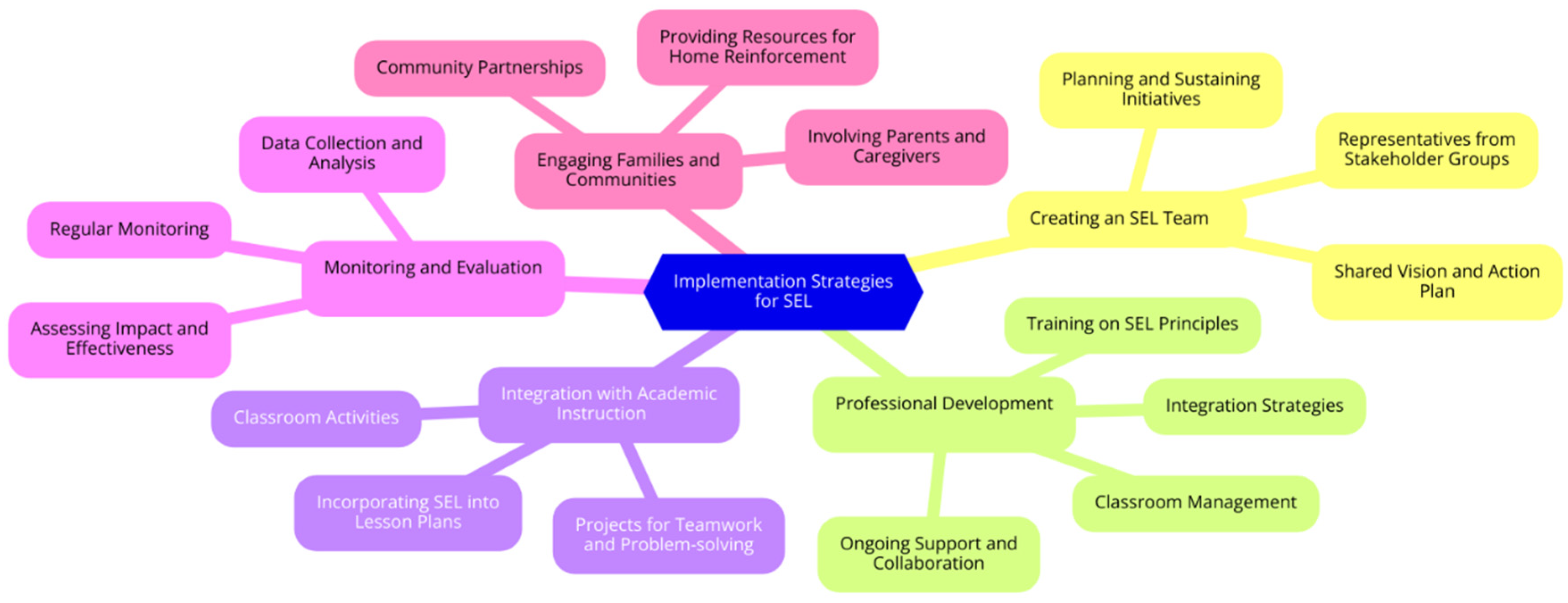
Implementation Strategies
- Creating an SEL Team: Establishing a dedicated SEL team is crucial for planning, implementing, and sustaining SEL initiatives. This team should include representatives from various stakeholder groups, such as administrators, teachers, students, parents, and community members. The team collaborates to develop a shared vision for SEL and to create an action plan that aligns with the school’s goals (Edutopia, 2023).
- Professional Development: Continuous professional development for educators is essential to equip them with the skills and knowledge needed to effectively implement SEL programs. This includes training on SEL principles, classroom management, and strategies for integrating SEL into academic lessons. Educators also benefit from ongoing support and collaboration opportunities to share best practices and address challenges (CASEL, 2023).
- Integration with Academic Instruction: SEL should be woven into the fabric of academic instruction. This can be achieved by incorporating SEL competencies into lesson plans and classroom activities. For example, teachers can design projects that require teamwork and problem-solving, helping students practice social-emotional skills in real-world contexts (Learning Policy Institute, 2023).
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Implementing SEL programs with fidelity involves regular monitoring and evaluation to assess their impact and effectiveness. Schools should collect and analyze data on student outcomes related to SEL competencies, academic performance, and overall school climate. This information can guide continuous improvement efforts and ensure that SEL initiatives are meeting their intended goals (Grant, Meyer, & Strambler, 2023).
- Engaging Families and Communities: Effective SEL implementation extends beyond the classroom to involve families and communities. Schools should engage parents and caregivers in SEL initiatives, providing them with resources and opportunities to reinforce SEL skills at home. Community partnerships can also support SEL by offering additional resources and programs that complement school-based efforts (CASEL, 2023).
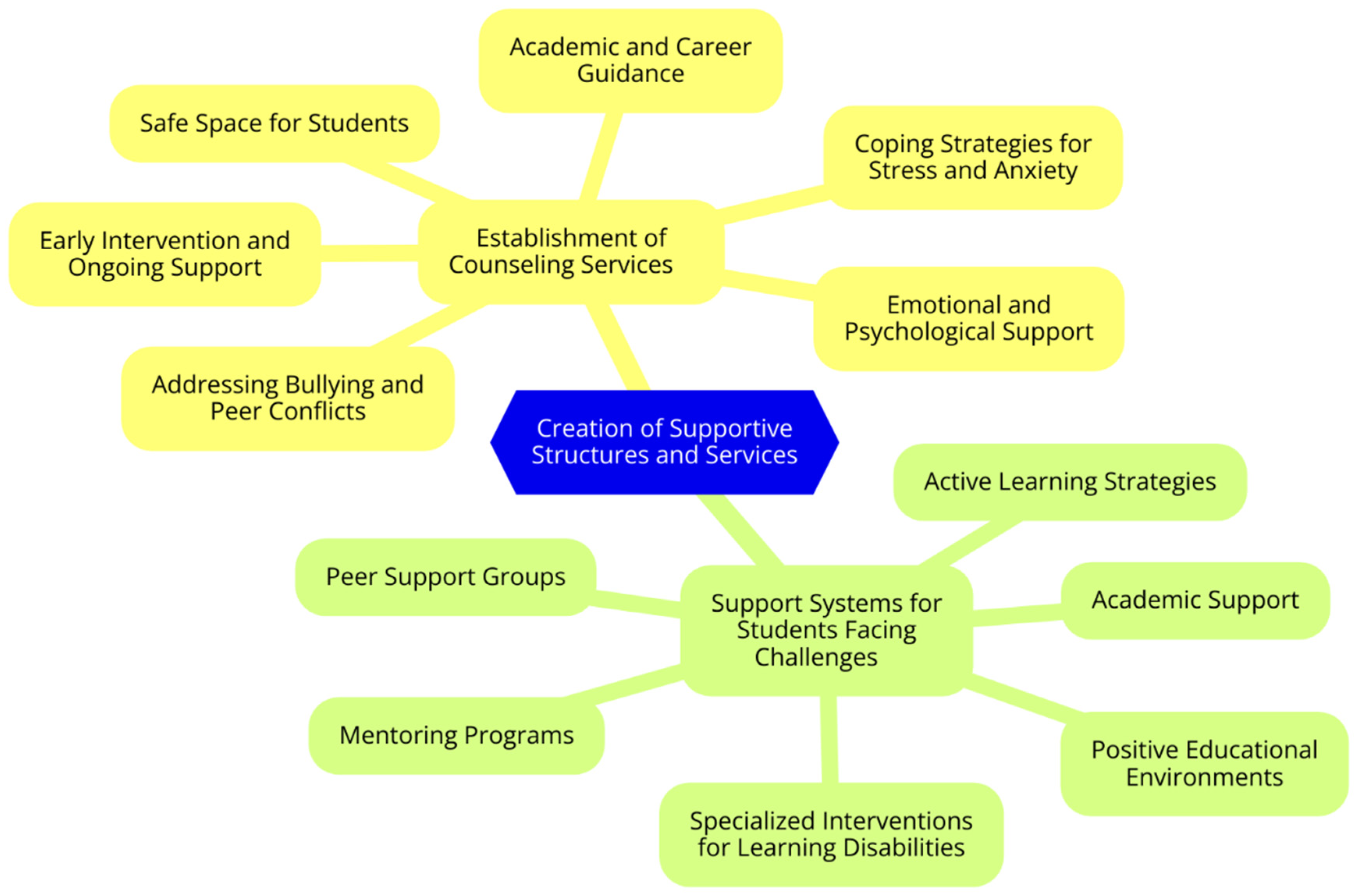
Creation of Supportive Structures and Services
Establishment of Counseling Services
Support Systems for Students Facing Challenges
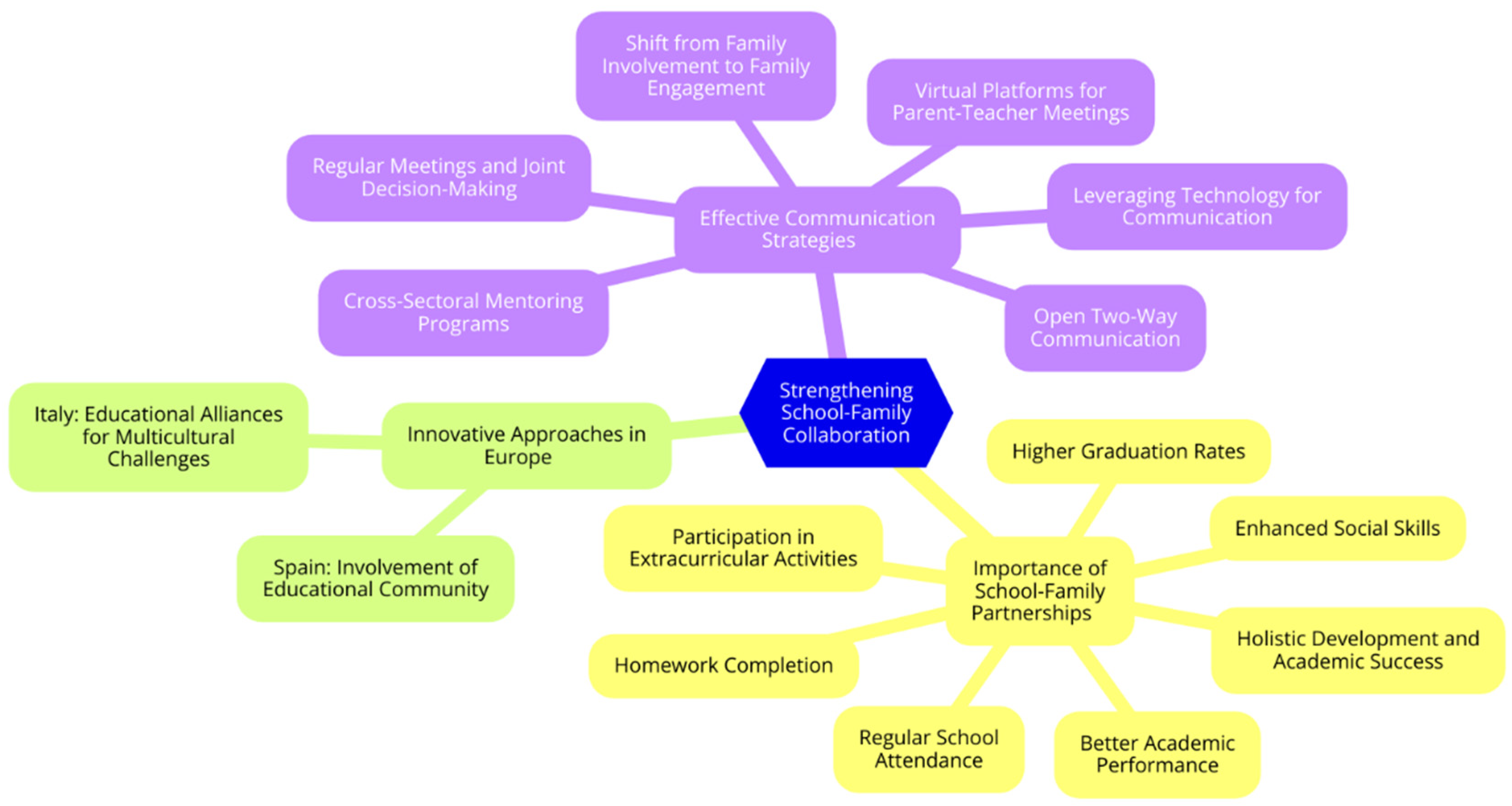
Strengthening School-Family Collaboration
Importance of School-Family Partnerships
Effective Communication Strategies
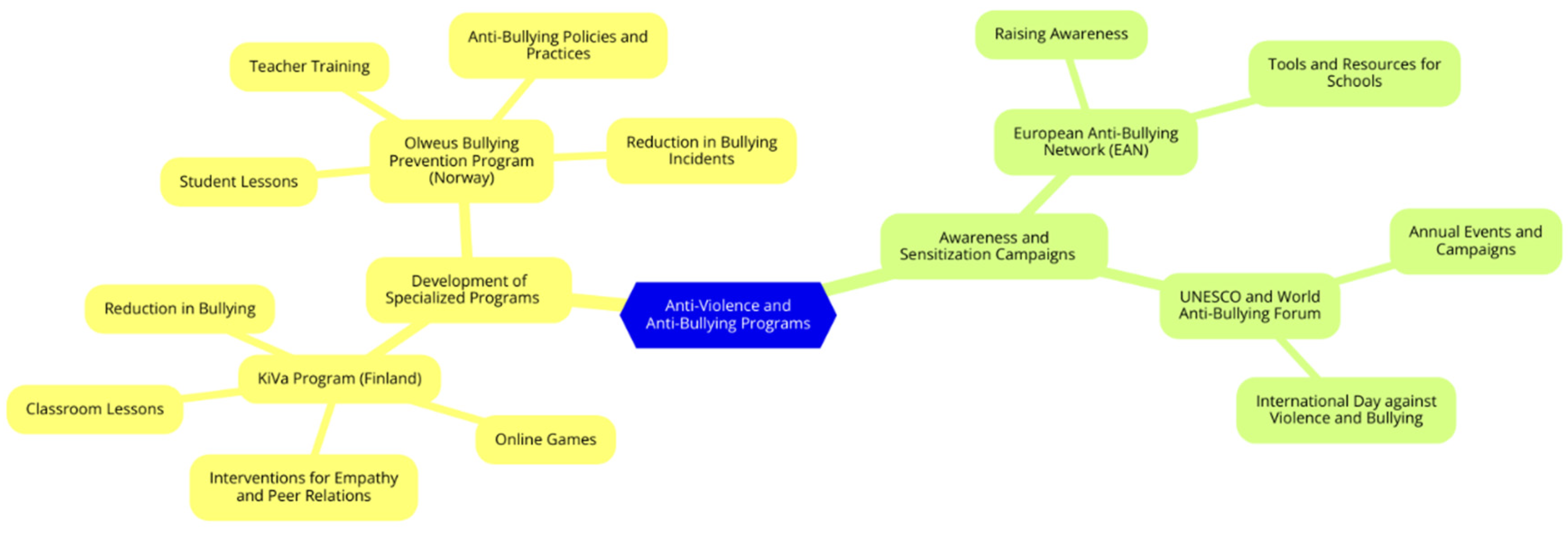
Anti-Violence and Anti-Bullying Programs
Development of Specialized Programs
Awareness and Sensitization Campaigns
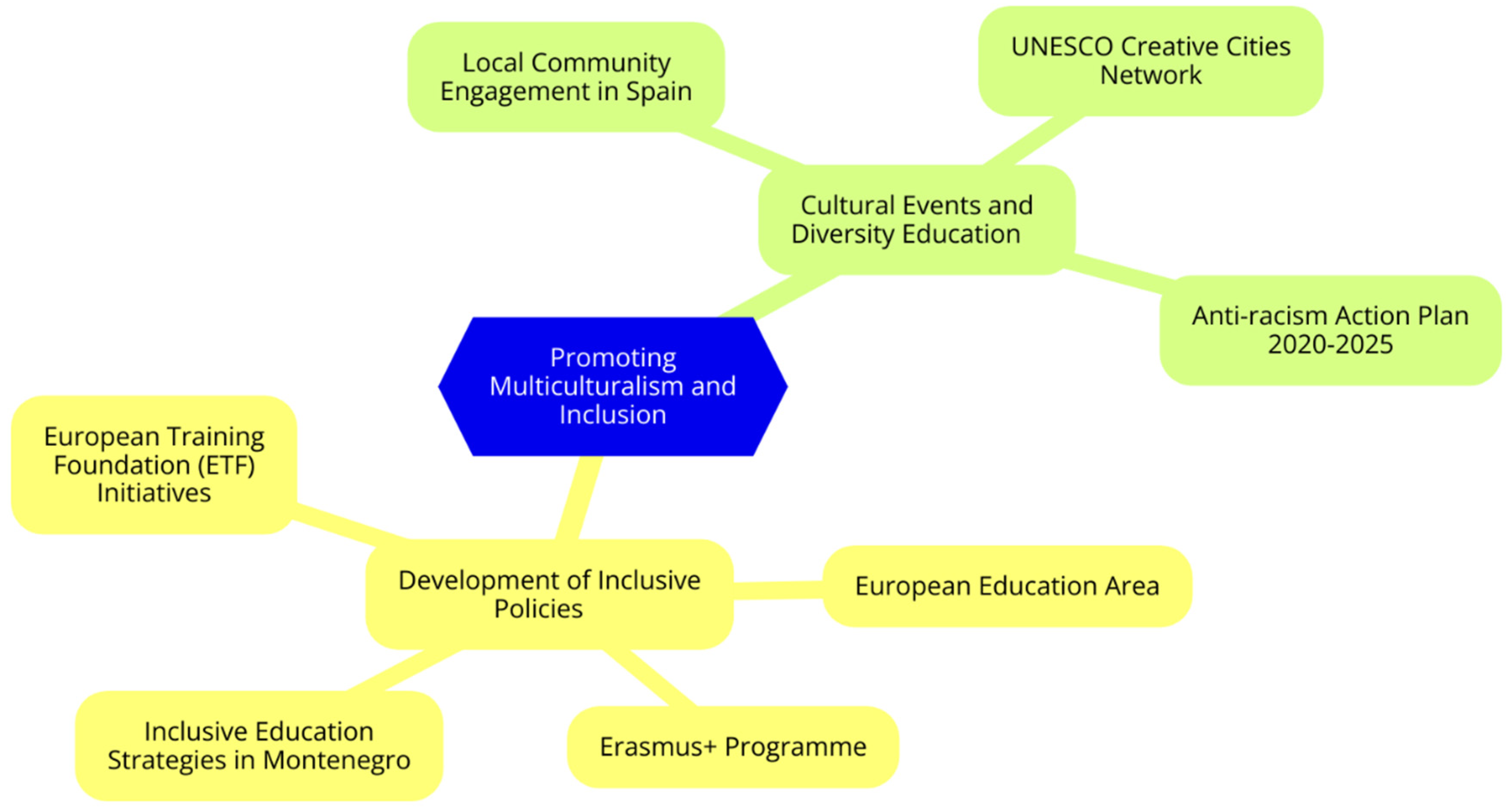
Promoting Multiculturalism and Inclusion
Development of Inclusive Policies
Cultural Events and Diversity Education
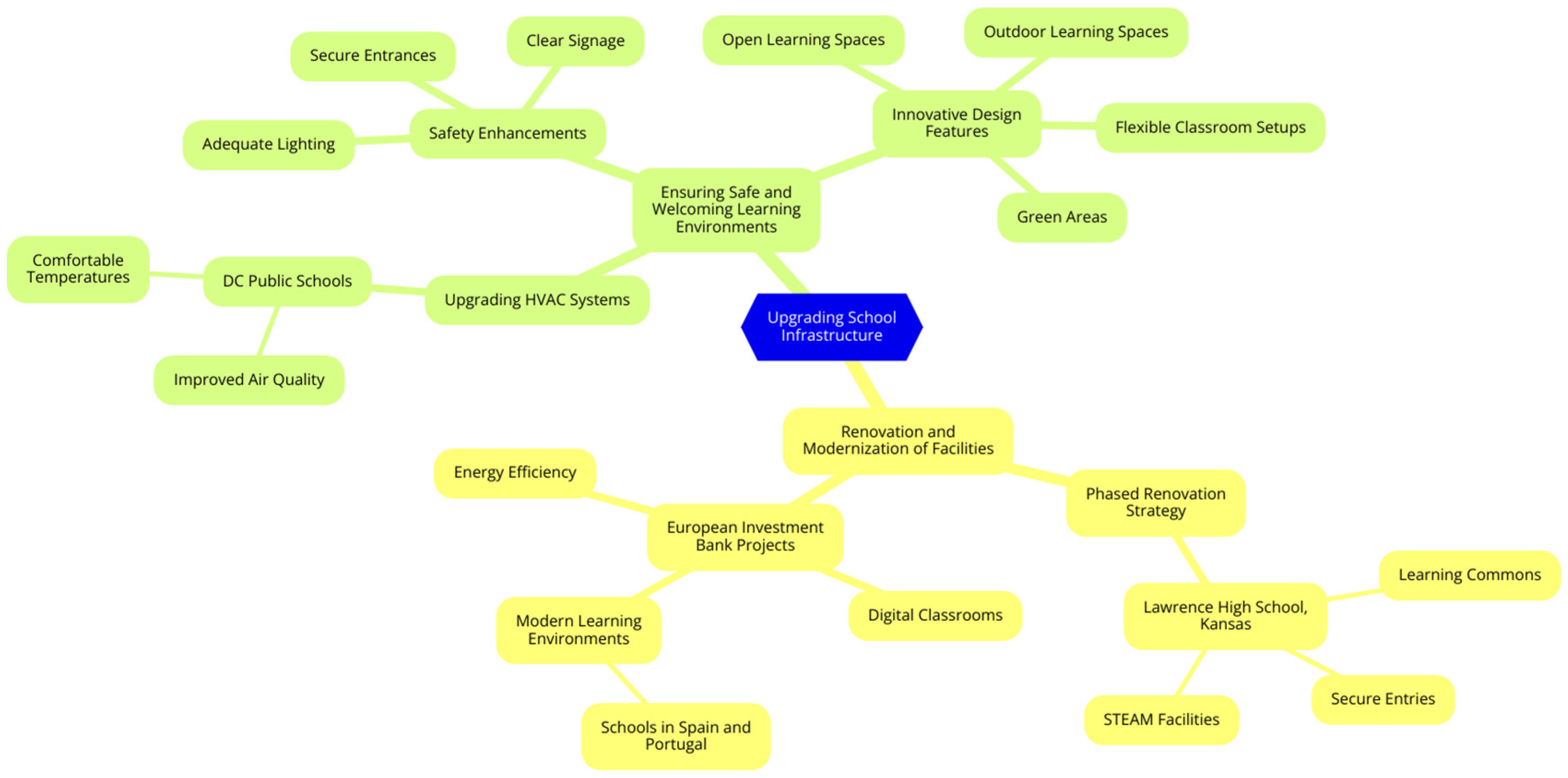
Upgrading School Infrastructure
Renovation and Modernization of Facilities
Ensuring Safe and Welcoming Learning Environments
Introduction of Extracurricular Activities
Benefits of Extracurricular Engagement
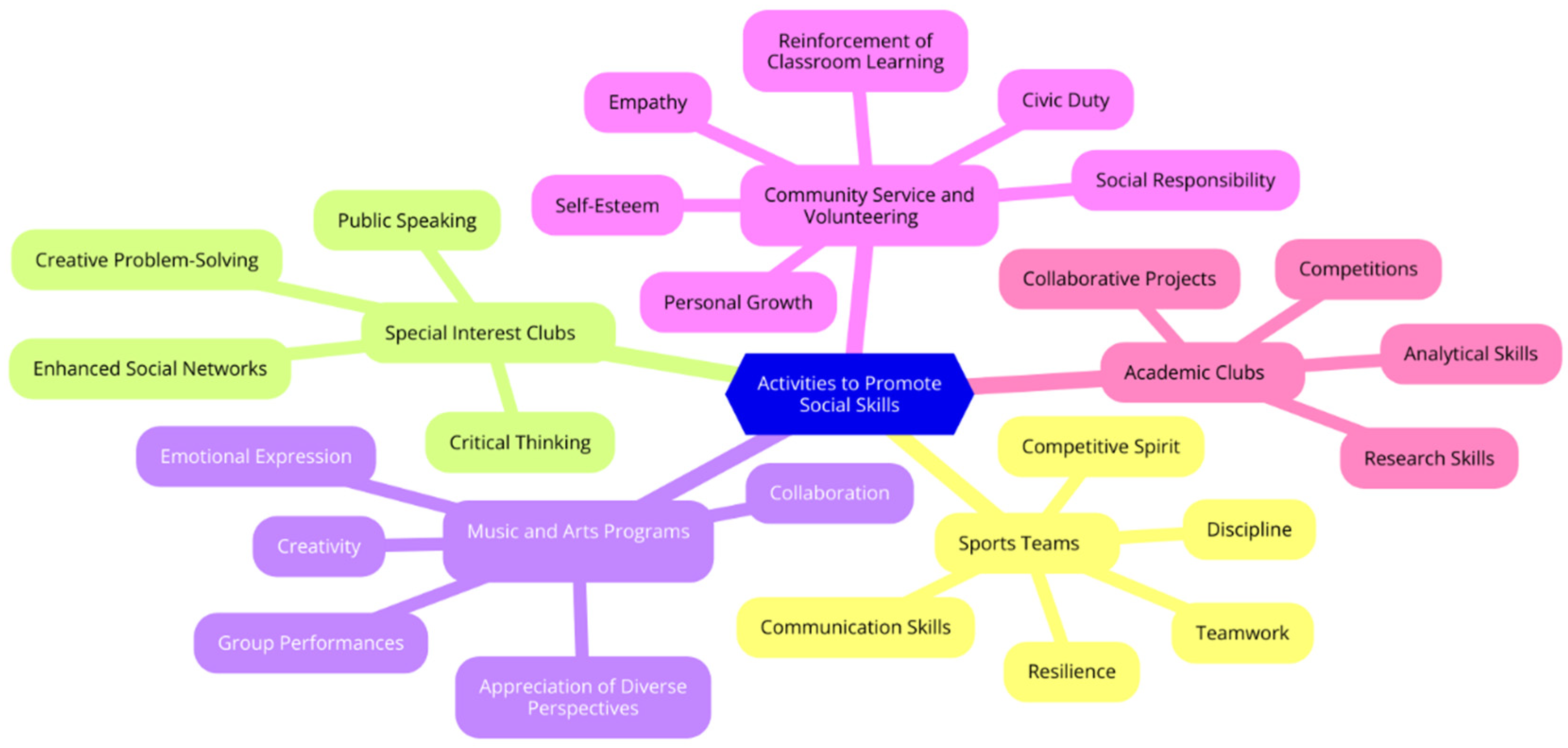
Types of Activities to Promote Social Skills
- Sports Teams: Participating in team sports helps students develop teamwork, discipline, and communication skills. It also teaches them about resilience and the dual aspects of victory and defeat, fostering a healthy competitive spirit and camaraderie among peers (Connections Academy, 2022).
- Special Interest Clubs: Special interest clubs, such as debate, drama, or chess clubs, provide platforms for students to develop critical thinking, public speaking, and creative problem-solving skills. These clubs also offer opportunities for students to connect with others who share similar passions, enhancing their social networks and interpersonal skills. For instance, at the University of California, Irvine (UCI), special interest clubs like Anteater Gaming and the Ballroom Club allow students to pursue their passions and hobbies outside of the classroom (Admissionsight, 2023). Similarly, at the University of Florida (UF), special interest clubs such as the Gator Chess Club provide students with opportunities to engage in activities they are passionate about, further developing their skills and social connections (Admissionsight, 2023). Engaging in these clubs allows students to explore new interests, develop new skills, and build meaningful connections with their peers, contributing to a well-rounded college experience.
- Music and Arts Programs: Engaging in music, theater, or visual arts can enhance students' creativity and emotional expression. These activities often involve group performances and collaborations, helping students learn to work together harmoniously and appreciate diverse perspectives (RAND Corporation, 2021).
- Community Service and Volunteering: Engaging in community service and volunteering offers students numerous benefits, including personal growth, skill development, and enhanced social connections. Participating in community service activities allows students to develop professional skills such as following instructions, cooperating with others, and giving their best effort, which are valuable in the professional world (Honor Society, 2023).
- Academic Clubs: Clubs that focus on subjects like science, math, or literature allow students to deepen their knowledge in specific areas while developing research and analytical skills. These clubs often involve collaborative projects and competitions, which promote teamwork and intellectual engagement (Connections Academy, 2022).
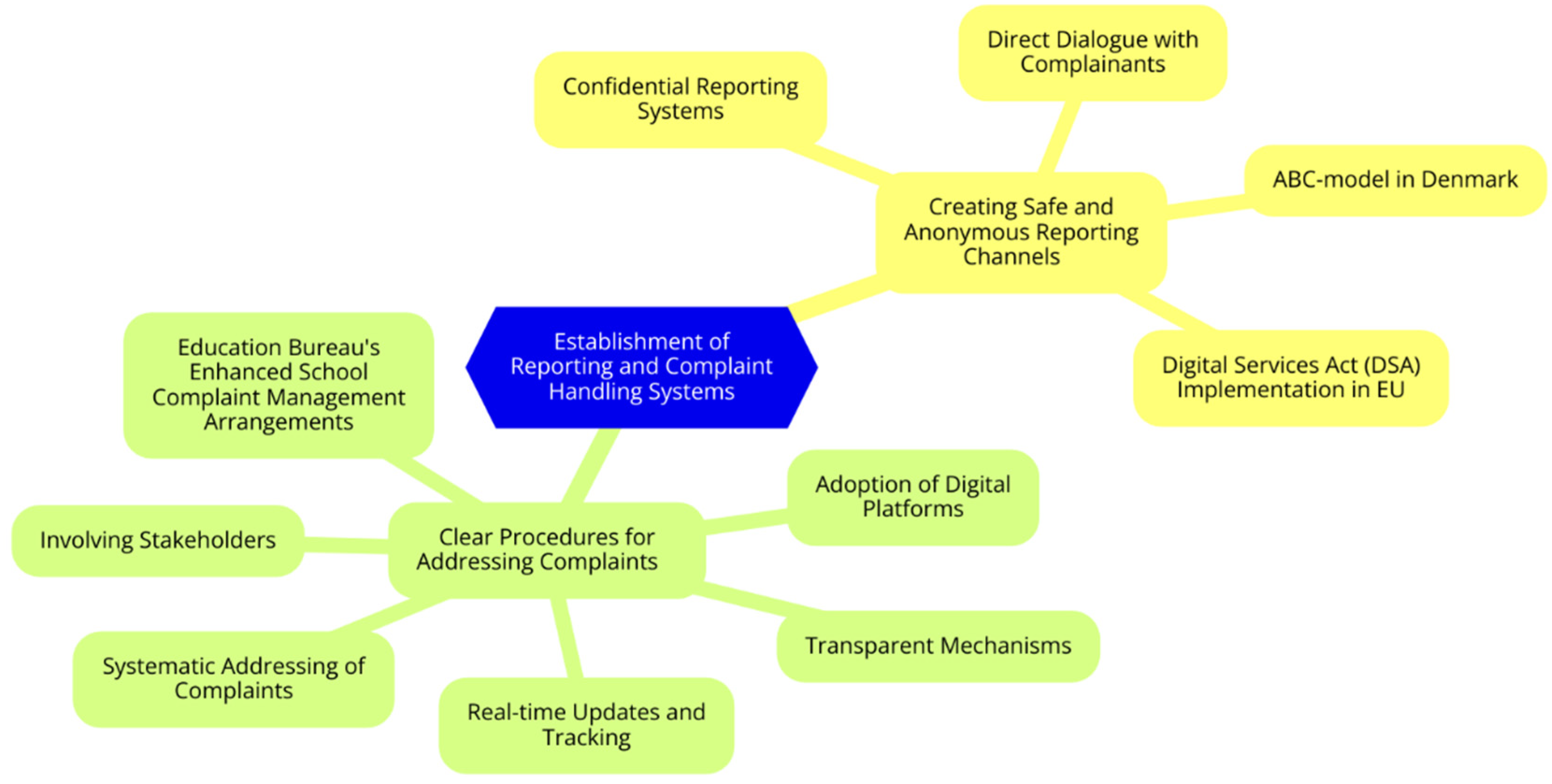
Establishment of Reporting and Complaint Handling Systems
Creating Safe and Anonymous Reporting Channels
Clear Procedures for Addressing Complaints
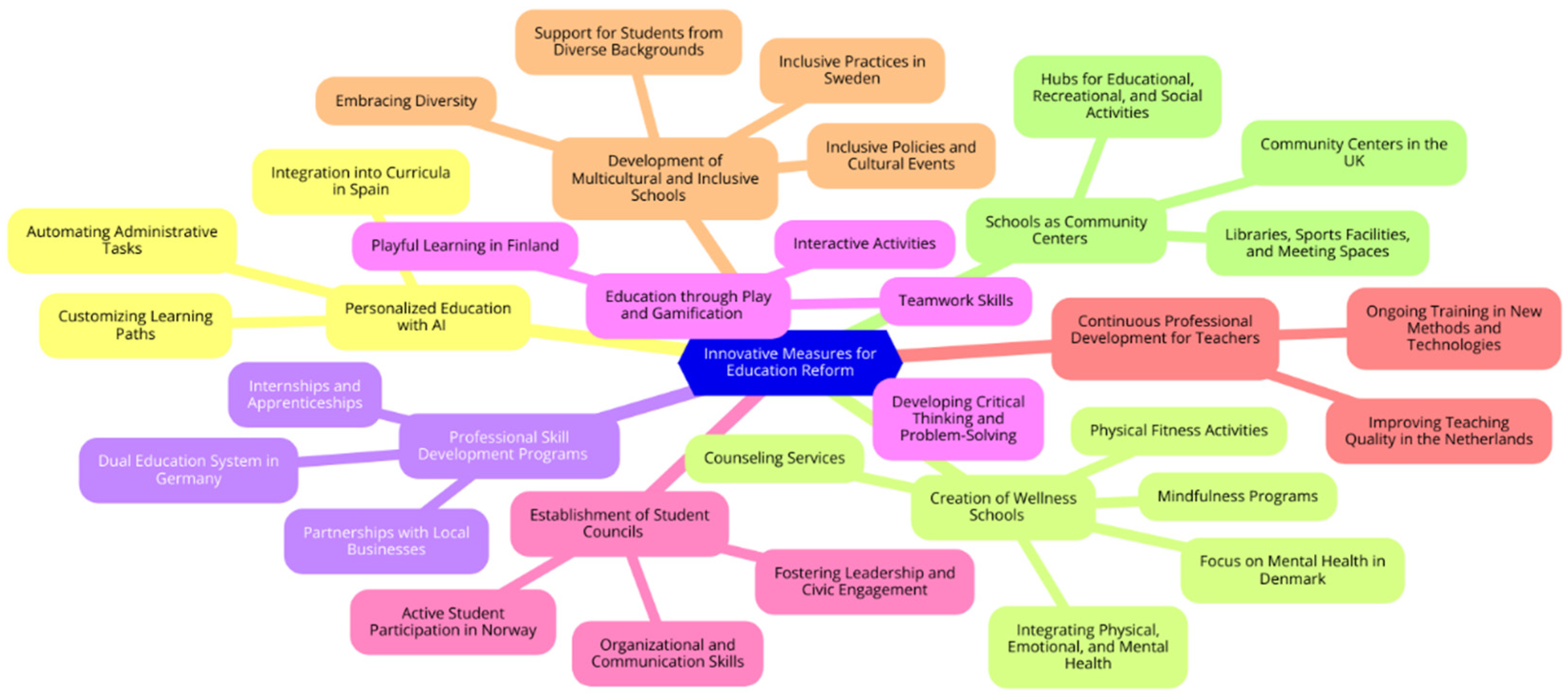
Innovative Measures for Education Reform
Personalized Education with AI
Creation of Wellness Schools
Professional Skill Development Programs
Education through Play and Gamification
Establishment of Student Councils
Continuous Professional Development for Teachers
Development of Multicultural and Inclusive Schools
Schools as Community Centers
Conclusion
Key Reforms and Their Impacts:
- Personalized Education with AI: Utilizing AI to tailor learning experiences to individual students’ needs enhances personalized interactions and instructional strategies, ensuring that every student receives the support they need to succeed.
- Creation of Wellness Schools: These schools integrate physical, emotional, and mental health resources, promoting overall student well-being and engagement. This holistic approach supports higher student engagement and academic success.
- Professional Skill Development Programs: Implementing programs such as internships, apprenticeships, and partnerships with local businesses equips students with essential skills for the modern workforce, bridging the gap between education and employment.
- Education through Play and Gamification: Incorporating games and interactive activities into the curriculum makes learning more engaging and effective, fostering critical thinking and teamwork skills.
- Establishment of Student Councils: Providing students with a voice in school governance fosters leadership, civic engagement, and a sense of responsibility, preparing them for active participation in society.
- Continuous Professional Development for Teachers: Ongoing training in new teaching methods, technologies, and subject matter expertise ensures high educational standards and improves student outcomes.
- Development of Multicultural and Inclusive Schools: Embracing diversity through inclusive policies, cultural events, and providing resources for students from diverse backgrounds ensures all students feel valued and supported, creating equitable educational environments.
- Schools as Community Centers: Transforming schools into hubs for educational, recreational, and social activities benefits both students and the broader community, fostering a sense of shared responsibility and support.
Declarations
Availability of Data and Materials
Funding
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| SEL | Social and Emotional Learning |
| CPD | Continuous Professional Development |
| OECD | Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| EAN | European Anti-Bullying Network |
| DSA | Digital Services Act |
| PROSPER | Promoting Optimal Support for Everyday Resilience |
| ETF | European Training Foundation |
| GSE | Graduate School of Education |
| UNICEF | United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund |
| HVAC | Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning |
| RAND | RAND Corporation |
References
- Admissionsight, (2023). An In-Depth Look at Extracurricular Activities at the University of California-Irvine.
- Admissionsight, (2023) Extracurricular Activities at the University of Florida: Opportunities Abound!
- American India Foundation. (2018). Handbook of Activities on Life Skills.
- Andersen, L. R., & Björkman, T. (2017). The Nordic Secret: A European Story of Beauty and Freedom.
- Bridgeland, J. M., Bruce, M., & Hariharan, A. (2013). The Missing Piece: A National Teacher Survey on How Social and Emotional Learning Can Empower Children and Transform Schools. Civic Enterprises.
- CASEL. (2023). Collaborative for Academic Social and Emotional Learning.
- Connections Academy. (2022). 5 Common Extracurricular Activities and Why They’re Important.
- Dusi, P. (2012). The Family-School Relationships in Europe: A Research Review. Center for Educational Policy Studies Journal, 2(1), 13-33. [CrossRef]
- EdSurge. (2023). Continuous Professional Development for Educators.
- Education Bureau. (2023). Enhanced School Complaint Management Arrangements.
- Egelund, N., Haug, P., & Schwab, S. (2016). Educational Reforms and Teacher Training in Denmark. Journal of Education Policy.
- Edutopia. (2023). Key elements of SEL implementation: Creating an SEL team for planning and sustainability.
- European Anti-Bullying Network. (2021). European Anti-Bullying Network: A policy paper.
- European Commission. (2023). Inclusive Education as a Cornerstone for Social Cohesion and Equity.
- European Union. (2022) Regulation (EU) 2022/2065 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 October 2022 on a Single Market For Digital Services (Digital Services Act) and amending Directive 2000/31/EC. Official Journal of the European Union, L 277.
- ETF. (2023). Social Inclusion through Education and Skills Development.
- Frontiers (2021). Crafting personalized learning paths with AI for lifelong learning: a systematic literature review.
- Frontiers. (2023). Playfulness, games and playful learning to promote good.
- Grant, S., Meyer, L., & Strambler, M. J. (2023). Measuring social and emotional learning implementation in a research-practice partnership. Frontiers in Psychology, Volume 14 - 2023 |. [CrossRef]
- Gunnulfsen, A.E., Skedsmo, G. (2023). School Leadership in Norway: Key Characteristics and Current Challenges. In: Gunnulfsen, A.E., Ärlestig, H., Storgaard, M. (eds) Education and Democracy in the Nordic Countries. Educational Governance Research, vol 21. Springer, Cham.
- Harvard University. (2020). REPORT OF THE TASK FORCE ON MANAGING STUDENT MENTAL HEALTH.
- Hooks, b. (2003). Teaching Community: A Pedagogy of Hope.
- Honor Society. (2023). The Impact of Extracurricular Activities on Academic Success.
- IQVIA. (2023). Environmental, Social, and Governance Report.
- Williford, A., Boulton, A., Noland, B. et al. Effects of the KiVa Anti-bullying Program on Adolescents’ Depression, Anxiety, and Perception of Peers. J Abnorm Child Psychol 40, 289–300 (2012).
- Kohn, A. (2020). What Does It Mean to Be Well Educated?
- Learning Policy Institute. (2023). Evidence for Social and Emotional Learning in Schools.
- NSBA, 2021. From Changing Learning Space to Changing Curriculum.
- NSBA, 2022, Playground Power.
- OECD. (2003). Learning for Tomorrow's World: First Results from PISA 2003,Student Learning,Attitudes, Engagement and Strategies.
- Pleshakova, A. Yu. (2019). Germany's Dual Education System: The Assessment by Its Subjects. [CrossRef]
- Wang Yan. (2013). Education Policy Reform Trends in G20 Members.Springer 2013.
- OECD. (2019). Fostering Creativity and Critical Thinking: What it Means in the Educational Context.
- OECD. (2022). Trends Shaping Education 2022.
- Olweus, D. (2009). The Olweus Bullying Prevention Program: Implementation and evaluation over two decades.
- Pesovski, I., Santos, R., & Henriques, R. (2024). Generative AI for Customizable Learning Experiences. [CrossRef]
- Kevin A. Gee, Vigdis Asmundson, Tseng Vang, Educational impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States: Inequities by race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K. A., Borrego, M., Finelli, C. J., DeMonbrun, M., Crockett, C., Tharayil, S., Shekhar, P., Waters, C., & Rosenberg, R. (2021). Instructor strategies to aid implementation of active learning: A systematic literature review. International Journal of STEM Education, 8(1), Article 9. [CrossRef]
- Noble, T., McGrath, H. PROSPER: A New Framework for Positive Education. Psych Well-Being 5, 2 (2015). [CrossRef]
- RAND Corporation. (2021). Benefits of Extracurricular Activities for Children.
- RAND Corporation. (2023). Educational Reform.
- Ravitch, D. (2016). The Death and Life of the Great American School System: How Testing and Choice Are Undermining Education.
- Rosen, J. A., Glennie, E. J., Dalton, B. W., Lennon, J. M., & Bozick, R. N. (2010). Noncognitive Skills in the Classroom: New Perspectives on Educational Research.
- Solhaug, T. (2018). Social science education (samfunnsfag) in Norway: A country report.
- School Construction News. (2023). Undertaking Successful Phased Modernizations of K-12 Schools.
- School Construction News. (2018). Trendspotting: Creating Outdoor & Extended Learning Areas.
- Smith, T. E., Holmes, S. R., Romero, M. E., & Sheridan, S. M. (2022). Evaluating the Effects of Family–School Engagement Interventions on Parent–Teacher Relationships: A Meta-analysis. School Mental Health, 14(2), 278-293. [CrossRef]
- Thies T. & Falk S. 2021.International Students in Higher Education: Extracurricular Activities and Social Interactions as Predictors of University Belonging.
- UNICEF. (2019-2025). Montenegro Inclusive Education Strategy.
- Winthrop, R. (2022). Transforming Education Systems: Why What and How. Brookings Institution.
- Winthrop, R., Barton, A., Ershadi, M., & Ziegler, L. (2021). Collaborating to transform and improve education systems: A playbook for family-school engagement. The Brookings Institution.
- Wilson A. Shaari A. 2023. A REVIEW ON THE STRUCTURE AND PRIORITIES OF THE SWEDISH EDUCATION SYSTEM. [CrossRef]
- World Bank. (2024). Educational Infrastructure and Modern Methods of Construction: Analysis of Off-site Technology for the Construction of School Buildings.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




