Submitted:
26 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
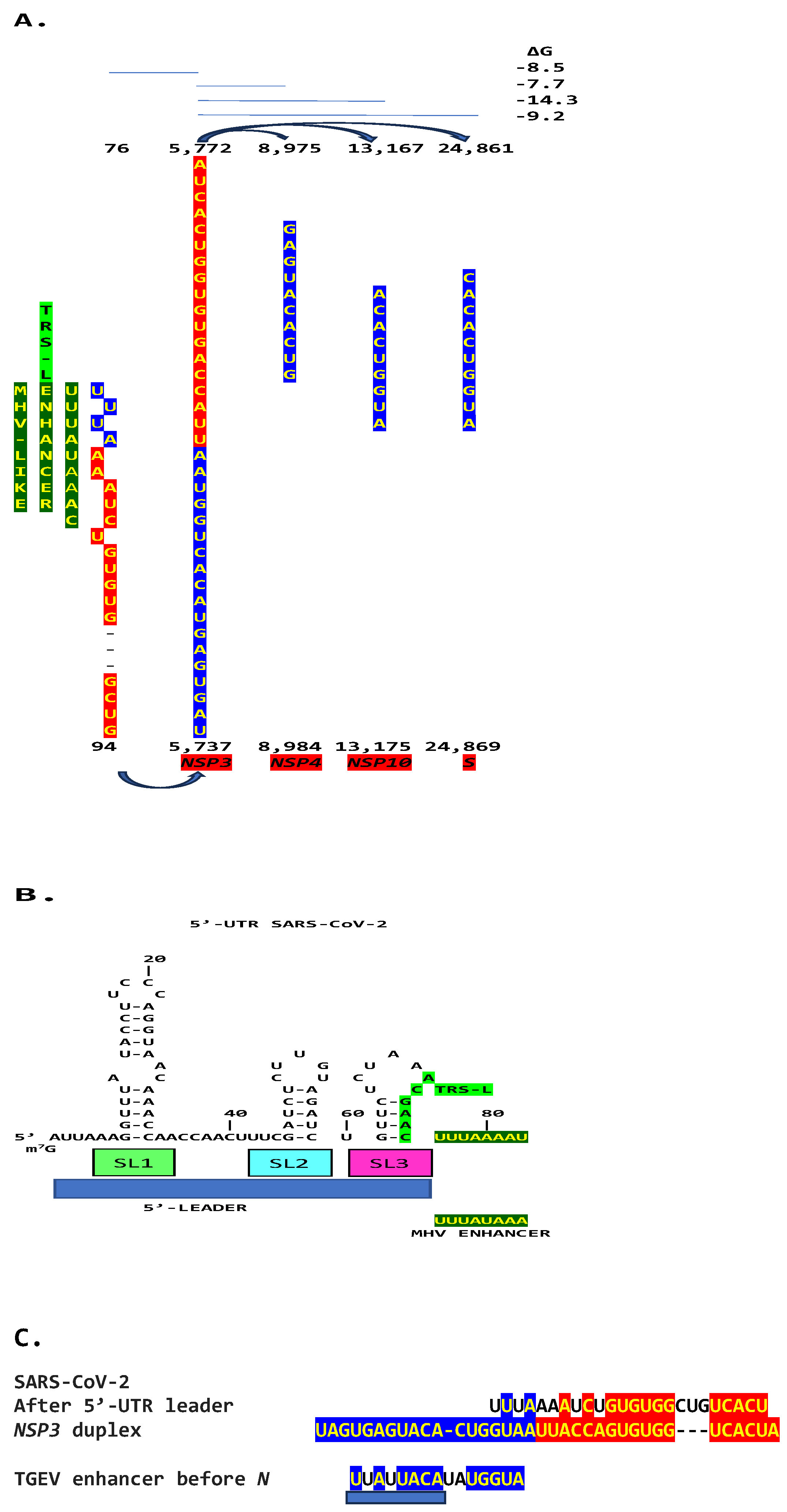
2. Results
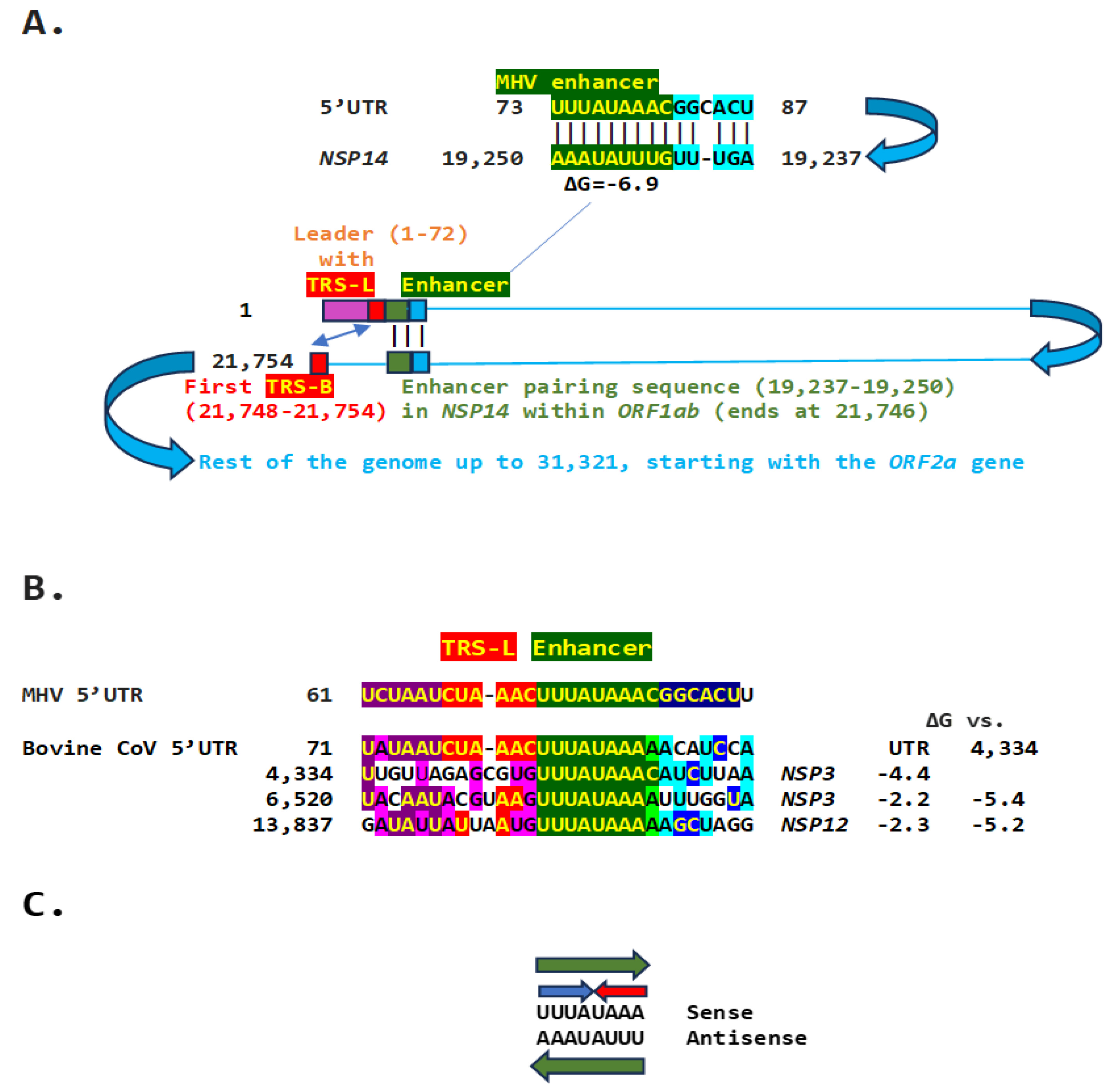
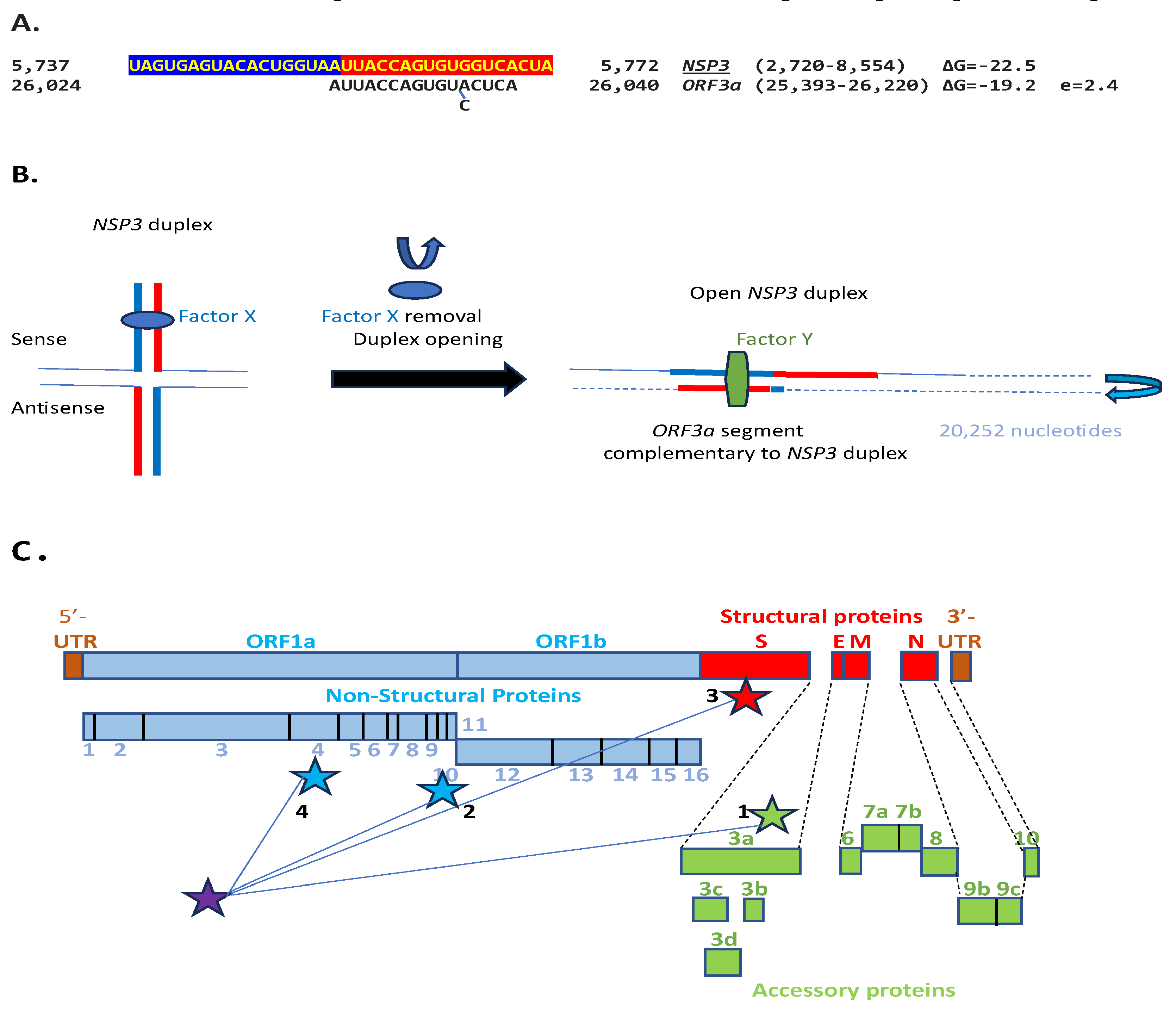
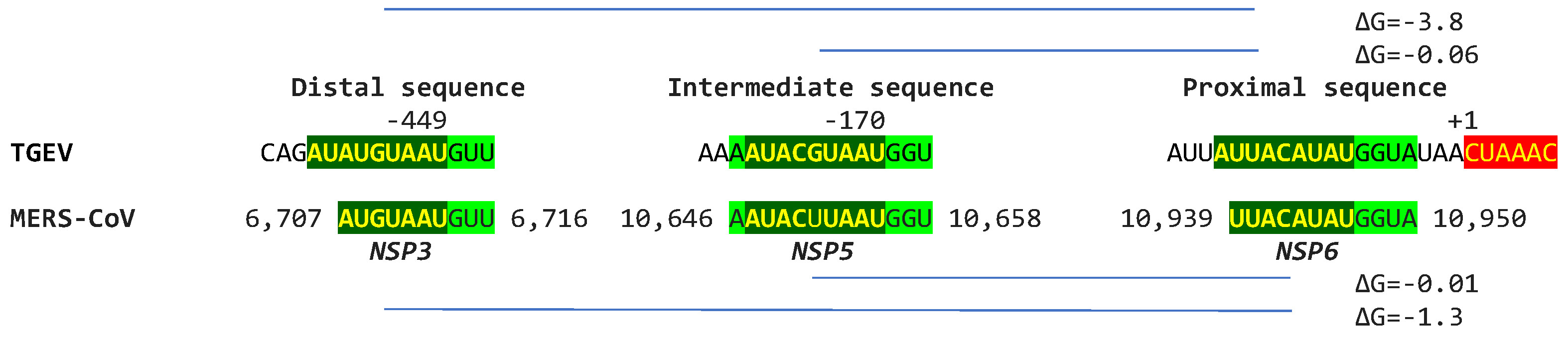
2.1. TGEV Enhancer-Based Model for MHV Enhancer and Potentially Bovine Coronavirus
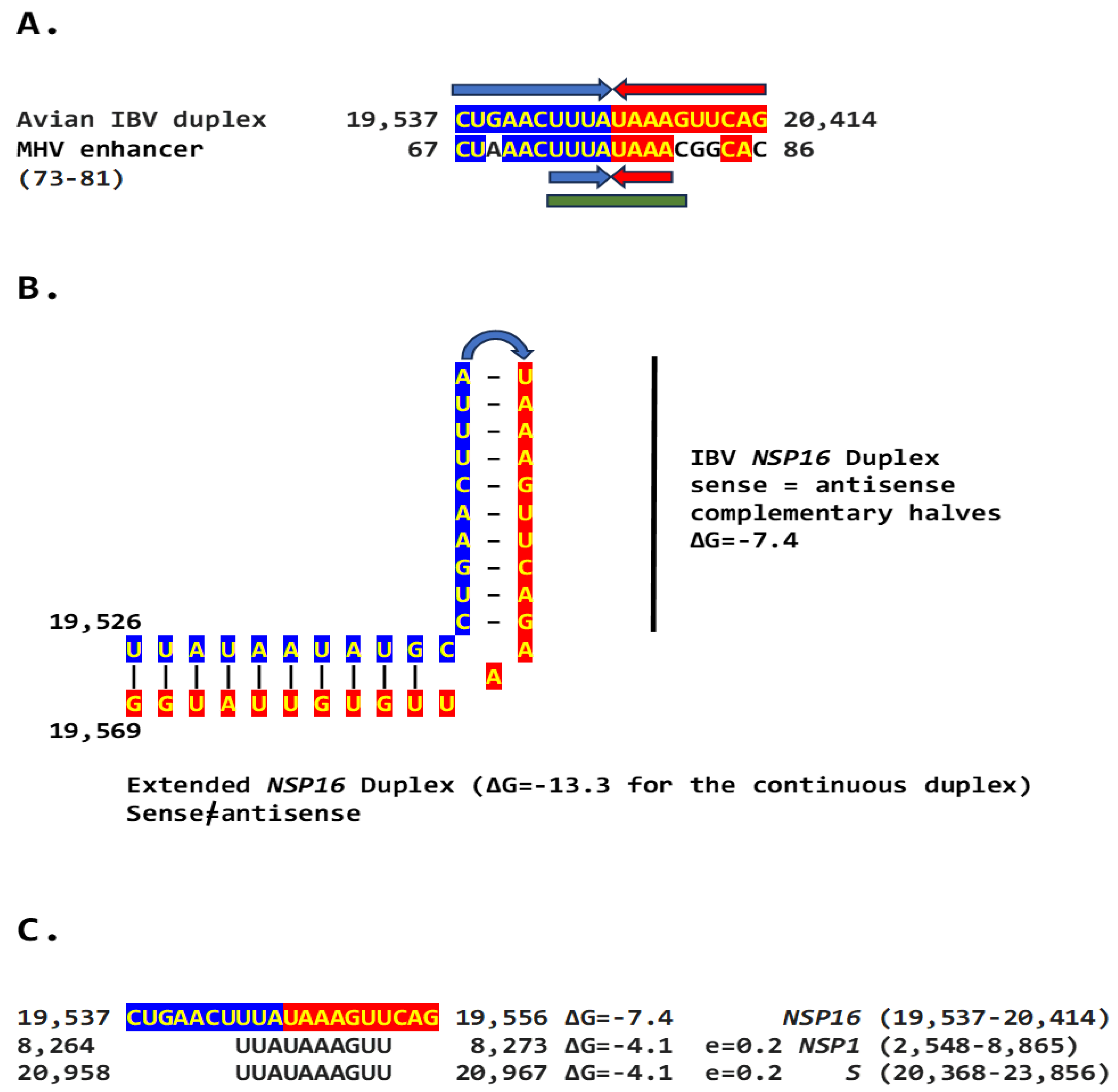
2.2. Potential Enhancer in the Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV)
2.2.1. Variation in NSP16 Duplex, Its Distal Binding Sequence in S, or Both Consistent with Reported Cases of Viral Attenuation or Its Reversal
2.2.2. Further Analysis of NSP16 Duplex Variation and Its Possible Association with Viral Attenuation or Its Reversal
2.2.3. Sequences Similar to the IBV NSP16 Extended Duplex are Present in the Rousettus Bat Betacoronaviruses (Nobecoviruses), Related to SARS-CoV-1/-2.
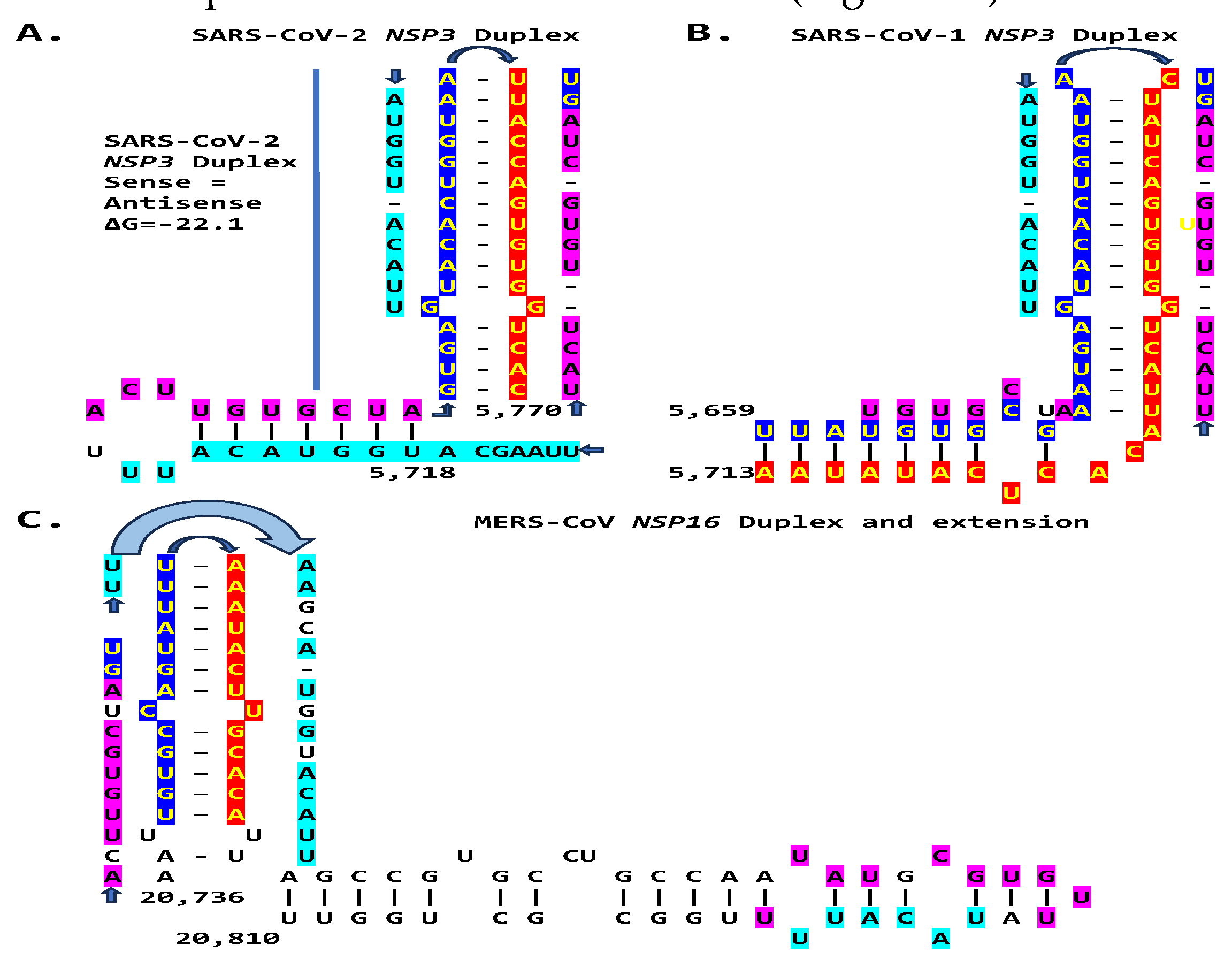
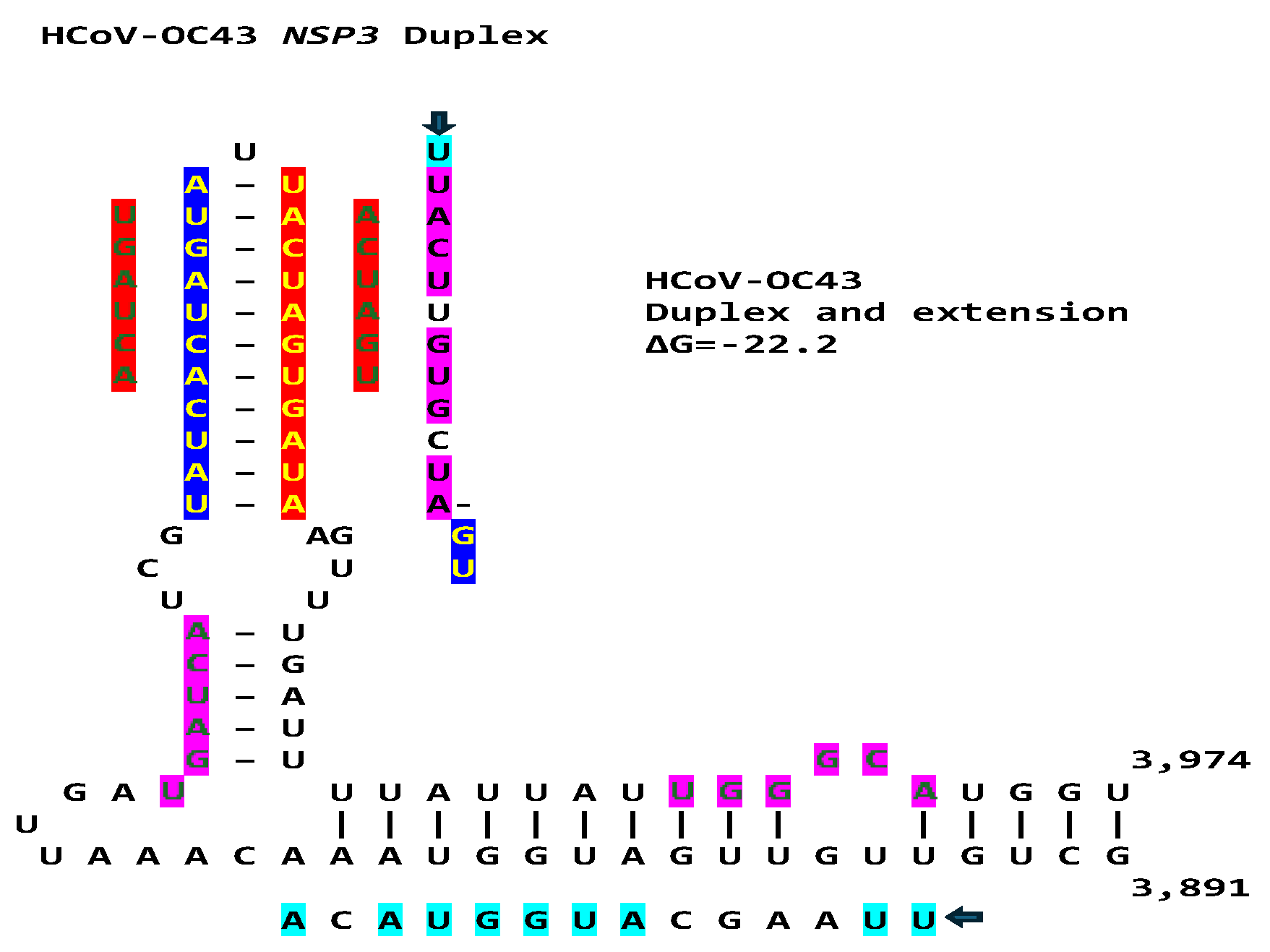
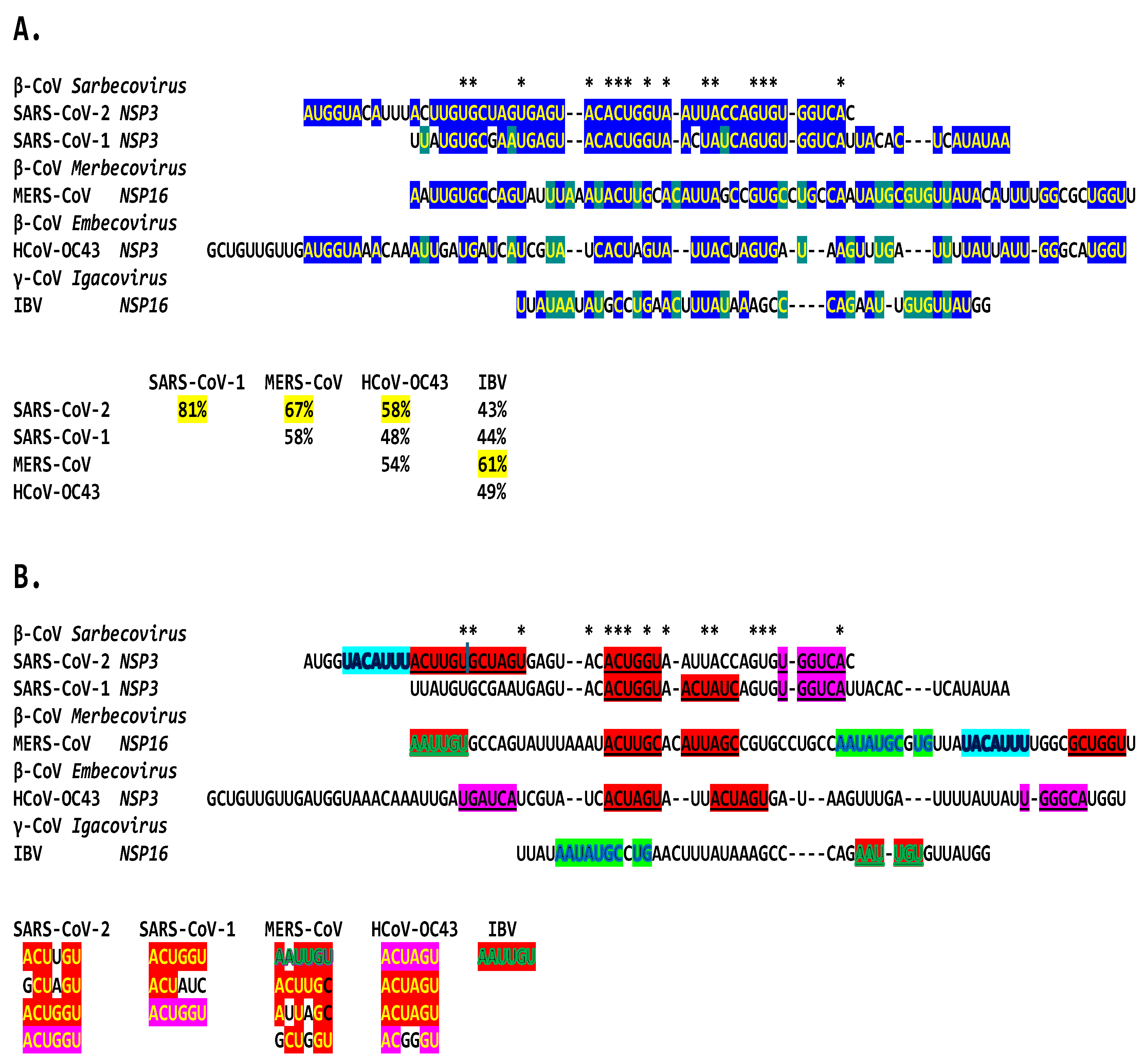
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 and Other Betacoronaviruses Infecting Humans
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Detection of Duplex-Forming Genomic Sequences Reading Similarly in the Sense and Antisense Directions with Complementary Halves as Potential Core Enhancer Elements
4.2. Detection of Coronaviral Genomic Sequences that Could Pair to a Core Enhancer Element
4.3. Characterization of Extended Duplexes and Visualization of RNA Secondary Structures and Estimation of Minimum Free Energies of Duplexes
4.4. Determination of Similarities between Coronaviral Extended Duplexes with Viridae Sequences in GenBank and Analysis of Possible Nucleotide and Amino Acid Sequence Variations Being Consistent with Attenuation
4.5. Assessment of Sequence Similarities in Multiple Alignments of Potential Coronaviral Extended Duplex Core Enhancer Elements
4.5. Assessment of Attenuation Status of IBV Strains
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorbalenya, A.E., Enjuanes, L., Ziebuhr, J., Snijder, E.J. Nidovirales: evolving the largest RNA virus genome. Virus Res 2006, 117, 17-37. [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C., Goeman, J.J., Parquet Mdel, C., Nga, P.T., Snijder, E.J., Morita, K., Gorbalenya, A.E. The footprint of genome architecture in the largest genome expansion in RNA viruses. PLoS Pathog 2013, 9, e1003500. [CrossRef]
- Masters, P.S. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv Virus Res 2006, 66, 193-292. [CrossRef]
- Forni, D., Cagliani, R., Clerici, M., Sironi, M. Molecular Evolution of Human Coronavirus Genomes. Trends Microbiol 2017, 25, 35-48. [CrossRef]
- Ziv, O., Gabryelska, M.M., Lun, A.T.L., Gebert, L.F.R., Sheu-Gruttadauria, J., Meredith, L.W., Liu, Z.Y., Kwok, C.K., Qin, C.F., MacRae, I.J., Goodfellow, I., Marioni, J.C., Kudla, G., Miska, E.A. COMRADES determines in vivo RNA structures and interactions. Nat Methods 2018, 15, 785-788. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C., Olsthoorn, RCL. Group-specific structural features of the 5′-proximal sequences of coronavirus genomic RNAs. Virology 2010, 401, 29-41. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D., Jiang, A., Feng, J., Li, G., Guo, D., Sajid, M., Wu, K., Zhang, Q., Ponty, Y., Will, S., Liu, F., Yu, X., Li, S., Liu, Q., Yang, X.L., Guo, M., Li, X., Chen, M., Shi, Z.L., Lan, K., Chen, Y., Zhou, Y. The SARS-CoV-2 subgenome landscape and its novel regulatory features. Molecular cell 2021, 81, 2135–2147.e5. [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, S., Cruz, J.L., Sola, I., Mateos-Gómez P.A., Palacio, L., Enjuanes, L. Coronavirus nucleocapsid protein facilitates template switching and is required for efficient transcription. Journal of virology 2010, 84, 2169-2175. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., Kang, H., Liu, P., Makkinje, N., Williamson, S.T., Leibowitz, J.L., Giedroc, D.P. Structural lability in stem-loop 1 drives a 5’ UTR-3’ UTR interaction in coronavirus replication. J Mol Biol 2008, 377, 790-803. [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z., Tidu, A., Eriani, G., Martin, F. Secondary structure of the SARS-CoV-2 5’-UTR. RNA biology 2021, 18, 447-456. [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.S., Hahn, Y.S., Rice, C.M., Lee, E., Dalgarno, L., Strauss, E.G., Strauss, J.H. Conserved elements in the 3’ untranslated region of flavivirus RNAs and potential cyclization sequences. J Mol Biol 1987, 198, 33-41. [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.Y., Tsai, T.L., Lin, C.N., Lin, C.H., Wu, H.Y. Interaction of coronavirus nucleocapsid protein with the 5’- and 3’-ends of the coronavirus genome is involved in genome circularization and negative-strand RNA synthesis. The FEBS journal 2019, 286, 3222-3239. [CrossRef]
- Goebel, S.J., Hsue, B., Dombrowski, T.F., Masters, P.S. Characterization of the RNA components of a putative molecular switch in the 3’ untranslated region of the murine coronavirus genome. J Virol 2004, 78, 669-682. [CrossRef]
- Xue, X., Yang, H., Shen, W., Zhao, Q., Li, J., Yang, K., Chen, C., Jin, Y., Bartlam, M., Rao, Z. Production of authentic SARS-CoV M(pro) with enhanced activity: application as a novel tag-cleavage endopeptidase for protein overproduction. Journal of molecular biology 2007, 366, 965-975. [CrossRef]
- Jonassen, C.M., Jonassen, T.O., Grinde, B. A common RNA motif in the 3’ end of the genomes of astroviruses, avian infectious bronchitis virus and an equine rhinovirus. The Journal of general virology 1998, 79, 715-718. [CrossRef]
- Robertson, M.P., Igel, H., Baertsch, R., Haussler, D., Ares, M. Jr., Scott, W.G. The structure of a rigorously conserved RNA element within the SARS virus genome. PLoS biology 2005, 3, e5. [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, J.F., Hogue, B.G. Host protein interactions with the 3’ end of bovine coronavirus RNA and the requirement of the poly(A) tail for coronavirus defective genome replication. Journal of virology 2000, 74, 5053-5065. [CrossRef]
- Tarun, S.Z. Jr., Wells, S.E., Deardorff, J.A., Sachs, A.B. Translation initiation factor eIF4G mediates in vitro poly(A) tail-dependent translation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1997, 94, 9046-9051. [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, T., Arya, S., Chan, S.H., Qi, S., Dai, N., Misra, A., Park, J.G., Oladunni, F., Kovalskyy, D., Hromas, R.A., Martinez-Sobrido, L., Gupta, Y.K. Structural basis of RNA cap modification by SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 3718. [CrossRef]
- Thiel, V., Ivanov, K.A., Putics, Á., Hertzig, T., Schelle, B., Bayer, S., Weißbrich, B., Snijder, E.J., Rabenau, H., Doerr, H.W., Gorbalenya, A.E., Ziebuhr, J.Á. Mechanisms and enzymes involved in SARS coronavirus genome expression. The Journal of general virology 2003, 84, 2305-2315. [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.M. Cellular factors in the transcription and replication of viral RNA genomes: a parallel to DNA-dependent RNA transcription. Virology 1998, 244, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Bentley, K., Keep, S.M., Armesto, M., Britton, P. Identification of a noncanonically transcribed subgenomic mRNA of infectious bronchitis virus and other gammacoronaviruses. Journal of virology 2013, 87, 2128-2136. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D., Jiang, A., Feng, J., Li, G., Guo, D., Sajid, M., Wu, K., Zhang, Q., Ponty, Y., Will, S., Liu, F., Yu, X., Li, S., Liu, Q., Yang, X.L., Guo, M., Li, X., Chen, M., Shi, Z.L., Lan, K., Chen, Y., Zhou, Y. The SARS-CoV-2 subgenome landscape and its novel regulatory features. Mol Cell 2021, 81, 2135-2147.e5. [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.L., Zúñiga, S., Enjuanes, L., Sola, I. Identification of a coronavirus transcription enhancer. J Virol 2008, 82, 3882-3893. [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Gómez, P.A., Morales, L., Zuñiga, S., Enjuanes, L., Sola, I. Long-distance RNA-RNA interactions in the coronavirus genome form high-order structures promoting discontinuous RNA synthesis during transcription. Journal of virology 2013, 87, 177-186. [CrossRef]
- Patarca, R, Haseltine, W.A. Bioinformatics Insights on Viral Gene Expression Transactivation: From HIV-1 to SARS-CoV-2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 3378. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Zhang, X. The leader RNA of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus contains an enhancer-like element for subgenomic mRNA transcription. J Virol 2000, 74, 10571-10580. [CrossRef]
- Lindenbach, B.D., Sgro, J.Y., Ahlquist, P. Long-distance base pairing in flock house virus RNA1 regulates subgenomic RNA3 synthesis and RNA2 replication. J Virol 2002, 76, 3905-3919. [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.R., White, K.A. An RNA activator of subgenomic mRNA1 transcription in tomato bushy stunt virus. J Biol Chem 2002, 277(5):3760-6. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.X., White, K.A. A complex network of RNA-RNA interactions controls subgenomic mRNA transcription in a tombusvirus. EMBO J 2004, 23, 3365-3374. [CrossRef]
- Wu, B., Grigull, J., Ore, M.O., Morin, S., White, K.A. Global organization of a positive-strand RNA virus genome. PLoS Pathog 2013, 9, e1003363. [CrossRef]
- Gong, T., Ju, F., Bu, D. Accurate prediction of RNA secondary structure including pseudoknots through solving minimum-cost flow with learned potentials. Commun Biol 2024, 7, 297. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Wimmer, E., Paul, A.V. Cis-acting RNA elements in human and animal plus-strand RNA viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009, 1789, 495-517. [CrossRef]
- Pathak, K.B., Pogany, J., Nagy, P.D. Non-template functions of the viral RNA in plant RNA virus replication. Curr Opin Virol 2011, 1, 332-338. [CrossRef]
- Sztuba-Solińska, J., Stollar, V., Bujarski, J.J. Subgenomic messenger RNAs: mastering regulation of (+)-strand RNA virus life cycle. Virology 2011, 412, 245-255. [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.A., Thornbrough, J.M., Zhang, R., Jha, B.K., Li, Y., Elliott, R., Quiroz-Figueroa, K., Chen, A.I., Silverman, R.H., Weiss, S.R. Lineage A Betacoronavirus NS2 Proteins and the Homologous Torovirus Berne pp1a Carboxy-Terminal Domain Are Phosphodiesterases That Antagonize Activation of RNase L. J Virol 2017, 91, e02201-16. [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.A., Elde, N.C. Recurrent viral capture of cellular phosphodiesterases that antagonize OAS-RNase L. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2024, 121, e2312691121. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L., Jha, B.K., Wu, A., Elliott, R., Ziebuhr, J., Gorbalenya, A.E., Silverman, R.H., Weiss, S.R. Antagonism of the interferon-induced OAS-RNase L pathway by murine coronavirus ns2 protein is required for virus replication and liver pathology. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 607-616. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G., Slowinski, V., White, K.A. Subgenomic mRNA regulation by a distal RNA element in a (+)-strand RNA virus. RNA 1999, 5, 550-561. [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, J.O., Chu, D.K., Peiris, J.S., Kosakovsky Pond, S.L., Poon, L.L. A case for the ancient origin of coronaviruses. J Virol 2013, 87, 7039-7045. [CrossRef]
- Peng, S., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Song, X., Zou, Y., Li, L., Zhao, X., Yin, Z. Current Knowledge on Infectious Bronchitis Virus Non-structural Proteins: The Bearer for Achieving Immune Evasion Function. Front Vet Sci 2022, 9, 820625. [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D., Casais, R., Armesto, M., Hodgson, T., Izadkhasti, S., Davies, M., Lin, F., Tarpey, I., Britton, P. Manipulation of the infectious bronchitis coronavirus genome for vaccine development and analysis of the accessory proteins. Vaccine 2007, 25, 5558-62. [CrossRef]
- Kint, J., Dickhout, A., Kutter, J., Maier, H.J., Britton, P., Koumans, J., Pijlman, G.P., Fros, J.J., Wiegertjes, G.F., Forlenza, M. Infectious Bronchitis Coronavirus Inhibits STAT1 Signaling and Requires Accessory Proteins for Resistance to Type I Interferon Activity. J Virol 2015, 89, 12047-12057. [CrossRef]
- de Wit, J.J.S., Cook, J.K.A. Spotlight on avian pathology: infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Pathol 2019, 48, 393-395. [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D. Coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. Vet Res 2007, 38, 281-297. [CrossRef]
- Ammayappan, A., Upadhyay, C., Gelb, J.Jr., Vakharia, V.N. Identification of sequence changes responsible for the attenuation of avian infectious bronchitis virus strain Arkansas DPI. Arch Virol 2009, 154, 495-499. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.T., Wu, H.Y., Wang, C.H. Genetic sequence changes related to the attenuation of avian infectious bronchitis virus strain TW2575/98. Virus Genes 2020, 56, 369-379. [CrossRef]
- Keep, S., StevensonLeggett, P., Dowgier, G., Foldes, K., Webb, I., Fones, A., Littolff, K., Everest, H., Britton, P., Bickerton, E. A Temperature-Sensitive Recombinant of Avian Coronavirus Infectious Bronchitis Virus Provides Complete Protection against Homologous Challenge. J Virol 2002, 96, e01100-22. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., Liang, R., Cheng, J., Zhao, J., Xue, J., Zhang, G. Attenuated Viral Replication of Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus with a Novel 82-Nucleotide Deletion in the 5a Gene Indicates a Critical Role for 5a in Virus-Host Interactions. Microbiol Spectr 2022, 10, e0140522. [CrossRef]
- Haijema, B.J., Volders, H., Rottier, P.J. Live, attenuated coronavirus vaccines through the directed deletion of group-specific genes provide protection against feline infectious peritonitis. J Virol 2004, 78, 3863-3871. [CrossRef]
- de Haan, C.A., Masters, P.S., Shen, X., Weiss, S., Rottier, P.J. The group-specific murine coronavirus genes are not essential, but their deletion, by reverse genetics, is attenuating in the natural host. Virology 2002, 296, 177-189. [CrossRef]
- Laconi, A., van Beurden, S.J., Berends, A.J., Krämer-Kühl, A., Jansen, C.A., Spekreijse, D., Chénard, G., Philipp, H.C., Mundt, E., Rottier, P.J.M., Hélène Verheije, M. Deletion of accessory genes 3a, 3b, 5a or 5b from avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus induces an attenuated phenotype both in vitro and in vivo. J Gen Virol 2018, 99, 1381–1390. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., Cheng, J., Yan, S., Jia, W., Zhang, K., Zhang, G. S gene and 5a accessory gene are responsible for the attenuation of virulent infectious bronchitis coronavirus. Virology 2019, 533, 12-20. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.P., Wang, C.H. Sequence changes of infectious bronchitis virus isolates in the 3’ 7.3 kb of the genome after attenuating passage in embryonated eggs. Avian Pathol 2007, 36, 59-67. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., Han, Z., Chen, J., Liu, X., Shao, Y., Kong, X., Tong, G., Rong, J. S1 gene sequence heterogeneity of a pathogenic infectious bronchitis virus strain and its embryo-passaged, attenuated derivatives. Avian Pathol 2007, 36, 231-234. [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, T., Casais, R., Dove, B., Britton, P., Cavanagh, D. Recombinant infectious bronchitis coronavirus Beaudette with the spike protein gene of the pathogenic M41 strain remains attenuated but induces protective immunity. J Virol 2004, 78, 13804-13811. [CrossRef]
- Armesto, M., Cavanagh, D., Britton, P. The replicase gene of avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus is a determinant of pathogenicity. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7384. [CrossRef]
- Jindal, G.A., Bantle, A.T., Solvason, J.J., Grudzien, J.L., D’Antonio-Chronowska, A., Lim, F., Le, S.H., Song, B.P., Ragsac, M.F., Klie, A., Larsen. R.O., Frazer, K.A., Farley, E.K. Single-nucleotide variants within heart enhancers increase binding affinity and disrupt heart development. Dev Cell 2023, 58, 2206-2216.e5. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.E., Jackwood, M.W., McKinley, E.T., Thor, S.W., Hilt, D.A., Acevedol, N.D., Williams, S.M., Kissinger, J.C., Paterson, A.H., Robertson, J.S., Lemke, C. Changes in nonstructural protein 3 are associated with attenuation in avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virus Genes 2012, 44, 63-74. [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, A., De Silva Senapathi, U., Abdul-Cader, M.S., Popowich, S., Marshall, F., Cork, S.C., van der Meer, F., Gomis, S., Abdul-Careem, M.F. Comparative features of infections of two Massachusetts (Mass) infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) variants isolated from Western Canadian layer flocks. BMC Vet Res 2018, 14, 391. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F., Han, Z., Zhang, T., Shao, Y., Kong, X., Ma, H., Liu, S. Genomic characteristics and changes of avian infectious bronchitis virus strain CK/CH/LDL/971 after serial passages in chicken embryos. Intervirology 2014, 57, 319-330. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L., Su, J.L., Zhao, J.X., Zhang, G.Z. Complete genome sequence analysis of a predominant infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) strain in China. Virus Genes 2009, 38, 56-65. [CrossRef]
- Han, Z., Sun, C., Yan, B., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Li, C., Zhang, Q., Ma, Y., Shao, Y., Liu, Q., Kong, X., Liu, S. A 15-year analysis of molecular epidemiology of avian infectious bronchitis coronavirus in China. Infect Genet Evol 2011, 11, 190-200. [CrossRef]
- McKinley, E.T., Jackwood, M.W., Hilt, D.A., Kissinger, J.C., Robertson, J.S., Lemke, C., Paterson, A.H. Attenuated live vaccine usage affects accurate measures of virus diversity and mutation rates in avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virus Res 2011, 158, 225-234. [CrossRef]
- Thor, S.W., Hilt, D.A., Kissinger, J.C., Paterson, A.H., Jackwood, M.W. Recombination in avian gamma-coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Viruses 2011, 3, 1777-1799. [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, M.W., Hall, D., Handel, A. Molecular evolution and emergence of avian gammacoronaviruses. Infect Genet Evol 2012, 12, 1305-1311. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.R., Theuns, S., Roukaerts, I.D., Zeller, M., Matthijnssens, J., Nauwynck, H.J. Genetic Characterization of the Belgian Nephropathogenic Infectious Bronchitis Virus (NIBV) Reference Strain B1648. Viruses 2015, 7, 4488-506. [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y., Li, Y.T., Chen, Y.T., Chen, T.C., Hu, C.J., Chen, H.W. Identification of an infectious bronchitis coronavirus strain exhibiting a classical genotype but altered antigenicity, pathogenicity, and innate immunity profile. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 37725. [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y., Chen, H.W. Infectious Bronchitis Virus Variants: Molecular Analysis and Pathogenicity Investigation. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18, 2030. [CrossRef]
- Bande, F., Arshad, S.S., Omar, A.R., Hair-Bejo, M., Mahmuda, A., Nair, V. Global distributions and strain diversity of avian infectious bronchitis virus: a review. Anim Health Res Rev 2017, 18, 70-83. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., Shao, Y., Ma, H., Sun, C., Zhang, X., Li, C., Han, Z., Yan, B., Kong, X., Liu, S. Comparative analysis of four Massachusetts type infectious bronchitis coronavirus genomes reveals a novel Massachusetts type strain and evidence of natural recombination in the genome. Infect Genet Evol 2013, 14, 29-38. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S., Tang, M., Jiang, Y., Chen, X., Shen, X., Li, J., Dai, Y., Zou, J. Complete genome sequence of a novel infectious bronchitis virus strain circulating in China with a distinct S gene. Virus Genes 2014, 49, 152-156. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T., Han, Z., Xu, Q., Wang, Q., Gao, M., Wu, W., Shao, Y., Li, H., Kong, X., Liu, S. Serotype shift of a 793/B genotype infectious bronchitis coronavirus by natural recombination. Infect Genet Evol 2015, 32, 377-387. [CrossRef]
- Jakhesara, S.J., Nath, B., Pal, J.K., Joshi, C.G., Kumar, S. Emergence of a genotype I variant of avian infectious bronchitis virus from Northern part of India. Acta Trop 2018, 183, 57-60. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L., Han, Z., Chen, Y., Zhao, W., Sun, J., Zhao, Y., Liu, S. Characterization of the complete genome, antigenicity, pathogenicity, tissue tropism, and shedding of a recombinant avian infectious bronchitis virus with a ck/CH/LJL/140901-like backbone and an S2 fragment from a 4/91-like virus. Virus Res 2018, 244:99-109. [CrossRef]
- Al-Jallad, T., Kassouha, M., Salhab, M., Alomar, A., Al-Masalma, M., Abdelaziz, F. Molecular characterization of isolated infectious bronchitis viruses from affected vaccinated broiler flocks in Syria. BMC Vet Res 2020, 16, 449. [CrossRef]
- Dinan, A.M., Keep, S., Bickerton, E., Britton, P., Firth, A.E., Brierley, I. Comparative Analysis of Gene Expression in Virulent and Attenuated Strains of Infectious Bronchitis Virus at Subcodon Resolution. J Virol 2019, 93, e00714-19. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.S.H., Ojkic, D., Coffin, C.S., Cork, S.C., van der Meer, F., Abdul-Careem, M.F. Delmarva (DMV/1639) Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV) Variants Isolated in Eastern Canada Show Evidence of Recombination. Viruses 2019, 11, 1054. [CrossRef]
- Goraichuk, I.V., Davis, J.F., Kulkarni, A.B., Afonso, C.L., Suarez, D.L. A 25-Year-Old Sample Contributes the Complete Genome Sequence of Avian Coronavirus Vaccine Strain ArkDPI, Reisolated from Commercial Broilers in the United States. Microbiol Resour Announc 2020, 9, e00067-20. [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M., Hidalgo, H. Live Attenuated Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccines in Poultry: Modifying Local Viral Populations Dynamics. Animals (Basel) 2020, 10, 2058. [CrossRef]
- Legnardi, M., Tucciarone, C.M., Franzo, G., Cecchinato, M. Infectious Bronchitis Virus Evolution, Diagnosis and Control. Vet Sci 2020, 7, 79. [CrossRef]
- Bali, K., Bálint, Á., Farsang, A., Marton, S., Nagy, B., Kaszab, E., Belák, S., Palya, V., Bányai, K. Recombination Events Shape the Genomic Evolution of Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Europe. Viruses 2021, 13, 535. [CrossRef]
- Quinteros, J.A., Ignjatovic, J., Chousalkar, K.K., Noormohammadi, A.H., Browning, G.F. Infectious bronchitis virus in Australia: a model of coronavirus evolution - a review. Avian Pathol 2021, 50, 295-310. [CrossRef]
- Quinteros, J.A., Noormohammadi, A.H., Lee, S.W., Browning, G.F., Diaz-Méndez, A. Genomics and pathogenesis of the avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Aust Vet J 2022, 100, 496-512. [CrossRef]
- Lisowska, A., Pikuła, A., Opolska, J., Jasik, A., Kycko, A., Domańska-Blicharz, K. Virulence Properties of GI-23 Infectious Bronchitis Virus Isolated in Poland and Efficacy of Different Vaccination strategies. Pathogens 2021, 10, 522. [CrossRef]
- Houta, M.H., Hassan, K.E., El-Sawah, A.A., Elkady, M.F., Kilany, W.H., Ali, A., Abdel-Moneim, A.S. The emergence, evolution and spread of infectious bronchitis virus genotype GI-23. Arch Virol 2021, 166, 9-26. [CrossRef]
- Lv, D., Dong, Z.H., Fan, W.S., Tang, N., Wang, L., Wei, L.P., Ji, Z.H., Tang, J.W., Lin, L.T., Wei, T.C., Huang, T., Wei, P., Mo, M.L. Identification of a novel avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus variant with three-nucleotide-deletion in nucleocapsid gene in China. J Vet Med Sci 2021, 83, 1608-1619. [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.P., Jude, R., Gallardo, R.A. Infectious Bronchitis Virus: A Comprehensive Multilocus Genomic Analysis to Compare DMV/1639 and QX Strains. Viruses 2022, 14, 1998. [CrossRef]
- Marandino, A., Mendoza-González, L., Panzera, Y., Tomás, G., Williman, J., Techera, C., Gayosso-Vázquez, A., Ramírez-Andoney, V., Alonso-Morales, R., Realpe-Quintero, M., Pérez, R. Genome Variability of Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Mexico: High Lineage Diversity and Recurrent Recombination. Viruses 2023, 15, 1581. [CrossRef]
- Rafique, S., Jabeen, Z., Pervaiz, T., Rashid, F., Luo, S., Xie, L., Xie, Z. Avian infectious bronchitis virus (AIBV) review by continent. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2024, 14, 1325346. [CrossRef]
- Rohaim, M.A., El Naggar, R.F., Abdelsabour, M.A., Mohamed, M.H.A., El-Sabagh, I.M., Munir, M. Evolutionary Analysis of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Reveals Marked Genetic Diversity and Recombination Events. Genes (Basel) 2020, 11, 605. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., Hou, B. A pathogenic and recombinant infectious bronchitis virus variant (CK/CH/GX/202109) with multiorgan tropism. Vet Res 2023, 54, 54. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., Liu, G., Zhou, Q., Yang, H., Zhou, C., Kong, W., Su, J., Li, G., Si, H., Ou, C. Which strain of the avian coronavirus vaccine will become the prevalent one in China next? Front Vet Sci 2023, 10, 1139089. [CrossRef]
- Fang SG, Shen S, Tay FP, Liu DX. Selection of and recombination between minor variants lead to the adaptation of an avian coronavirus to primate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005, 336, 417-423. [CrossRef]
- Lim, X.F., Lee, C.B., Pascoe, S.M., How, C.B., Chan, S., Tan, J.H., Yang, X., Zhou, P., Shi, Z., Sessions, O.M., Wang, L.F., Ng, L.C., Anderson, D.E., Yap, G. Detection and characterization of a novel bat-borne coronavirus in Singapore using multiple molecular approaches. J Gen Virol 2019, 100, 1363-1374. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Pan, Y.F., Yang, L.F., Yang, W.H., Lv, K., Luo, C.M., Wang, J., Kuang, G.P., Wu, W.C., Gou, Q.Y., Xin, G.Y., Li, B., Luo, H.L., Chen, S., Shu, Y.L., Guo, D., Gao, Z.H., Liang, G., Li, J., Chen, Y.Q., Holmes, E.C., Feng, Y., Shi, M. Individual bat virome analysis reveals co-infection and spillover among bats and virus zoonotic potential. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 4079. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y., Yang, R., Lee, I., Zhang, W., Sun, J., Wang, W., Meng, X. Characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 E Protein: Sequence, Structure, Viroporin, and Inhibitors. Protein Sci 2021, 30, 1114-1130. [CrossRef]
- Khare, S., Gurry, C.; Freitas, L.; Schultz, M.B.; Bach, G.; Diallo, A.; Akite, N; Ho, J.; Lee, R.T.; Yeo, W.; Curation Team GC; Maurer-Stroh, S. GISAID’s Role in Pandemic Response. China CDC Weekly 2021, 3, 1049-1051. [CrossRef]
- Elbe, S., Buckland-Merrett, G. Data, disease and diplomacy: GISAID’s innovative contribution to global health. Global Challenges 2017, 1, 33-46. [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y., McCauley, J. GISAID: from vision to reality. EuroSurveillance 2017, 22, . [CrossRef]
- Konno, Y., Kimura, I., Uriu, K., Fukushi, M., Irie, T., Koyanagi, Y., Sauter, D., Gifford, R.J.; USFQ-COVID19 Consortium; Nakagawa, S., Sato, K. SARS-CoV-2 ORF3b Is a Potent Interferon Antagonist Whose Activity Is Increased by a Naturally Occurring Elongation Variant. Cell Rep 2020, 32, 108185. [CrossRef]
- Lim, F., Solvason, J.J., Ryan, G.E., Le, S.H., Jindal, G.A., Steffen, P., Jandu, S.K., Farley, E.K. Affinity-optimizing enhancer variants disrupt development. Nature 2024, 626, 151-159. [CrossRef]
- Vo Ngoc, L., Wang, Y.L., Kassavetis, G.A., Kadonaga, J.T. The punctilious RNA polymerase II core promoter. Genes Dev 2017, 31, 1289-1301. [CrossRef]
- FANTOM Consortium and the RIKEN PMI and CLST (DGT). A promoter-level mammalian expression atlas. Nature 2014, 507, 462-470. [CrossRef]
- Xi, H., Yu, Y., Fu, Y., Foley, J., Halees, A., Weng, Z. Analysis of overrepresented motifs in human core promoters reveals dual regulatory roles of YY1. Genome Res 2007, 17, 798-806. [CrossRef]
- Dudnyk, K., Cai, D., Shi, C., Xu, J., Zhou, J. Sequence basis of transcription initiation in the human genome. Science 2024, 26, 384(6694):eadj0116. [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, K., Fukaya, T. Regulatory landscape of enhancer-mediated transcriptional activation. Trends Cell Biol 2024, Feb 13, S0962-8924(24)00020-5. [CrossRef]
- Han, Z., Li, W. Enhancer RNA: What we know and what we can achieve. Cell Prolif 2022, 55, e13202. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L., Cao, C., Ji, L., Cai, Z., Wang, D., Ye, R., Chen, J., Yu, X., Zhou, J., Bai, Z., Wang, R., Yang, X., Zhu, P., Xue, Y. Complementary Alu sequences mediate enhancer-promoter selectivity. Nature 2023, 619, 868-875. [CrossRef]
- Schoenfelder, S., Fraser, P. Long-range enhancer-promoter contacts in gene expression control. Nat Rev Genet 2019, 20, 437-455. [CrossRef]
- Pombo, A., Dillon, N. Three-dimensional genome architecture: players and mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2015, 16, 245-257. [CrossRef]
- Long, H.K., Prescott, S.L., Wysocka, J. Ever-Changing Landscapes: Transcriptional Enhancers in Development and Evolution. Cell 2016, 167, 1170-1187. [CrossRef]
- Furlong, E.E.M., Levine, M. Developmental enhancers and chromosome topology. Science 2018, 361, 1341-1345. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Zhu, X., Wu, L., Zhu, Y., Zhao, D., Xu, X., Chemparathy, A., Wang, H., Cao, Y., Nakamura, M., Noordermeer, J.N., La Russa, M., Wong, W.H., Zhao, K., Qi, L.S. Nested epistasis enhancer networks for robust genome regulation. Science 2022, 377, 1077-1085. [CrossRef]
- Mönttinen, H.A.M., Frilander, M.J., Löytynoja, A. Generation of de novo miRNAs from template switching during DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2310752120. [CrossRef]
- Lau, B., Kerr, K., Camiolo, S., Nightingale, K., Gu, Q., Antrobus, R., Suárez, N.M., Loney, C., Stanton, R.J., Weekes, M.P., Davison, A.J. Human Cytomegalovirus RNA2.7 Is Required for Upregulating Multiple Cellular Genes To Promote Cell Motility and Viral Spread Late in Lytic Infection. J Virol 2021, 95, e0069821. [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.H., Zimmer, A., Moutot, G., Mesnard, J.M., Chazal, N. Retroviral Antisense Transcripts and Genes: 33 Years after First Predicted, a Silent Retroviral Revolution? Viruses 2021, 13, 2221. [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, K., Matsuoka, M. Functional and Pathogenic Roles of Retroviral Antisense Transcripts. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 875211. [CrossRef]
- Lin, E., Panfil, A.R., Sandel, G., Jain, P. Novel perspectives on antisense transcription in HIV-1, HTLV-1, and HTLV-2. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 1042761. [CrossRef]
- Georg, J., Hess, W.R. Widespread Antisense Transcription in Prokaryotes. Microbiol Spectr 2018, 6. [CrossRef]
- Werner, A., Kanhere, A., Wahlestedt, C., Mattick, J.S. Natural antisense transcripts as versatile regulators of gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 2024, Apr 17. [CrossRef]
- Patarca R, Haseltine WA. Forty years of HIV research inspires the development of SARS-CoV-2 therapy. J Mol Cell Biol 2024, 15, mjad065. [CrossRef]
- Li, R., Caico, I., Xu, Z., Iqbal, M.S., Romerio, F. Epigenetic Regulation of HIV-1 Sense and Antisense Transcription in Response to Latency-Reversing Agents. Noncoding RNA 2023, 9, 5. [CrossRef]
- Ward, S., Childs, A., Staley, C., Waugh, C., Watts, J.A., Kotowska, A.M., Bhosale, R., Borkar, A.N. Integrating cryo-OrbiSIMS with computational modelling and metadynamics simulations enhances RNA structure prediction at atomic resolution. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 4367. [CrossRef]
- Enjuanes, L., Zuñiga, S., Castaño-Rodriguez, C., Gutierrez-Alvarez, J., Canton, J., Sola, I. Molecular Basis of Coronavirus Virulence and Vaccine Development. Adv Virus Res 2016, 96, 245-286. [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D., Gralinski, L.E., Mitchell, H.D., Dinnon, K.H.3rd, Leist, S.R., Yount, B.L.Jr, McAnarney, E.T., Graham, R.L., Waters, K.M., Baric, R.S. Combination Attenuation Offers Strategy for Live Attenuated Coronavirus Vaccines. J Virol 2018, 92, e00710-18. [CrossRef]
- van Beurden, S.J., Berends, A.J., Krämer-Kühl, A., Spekreijse, D., Chénard, G., Philipp, H.C., Mundt, E., Rottier, P.J.M., Verheije, M.H. A reverse genetics system for avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus based on targeted RNA recombination. Virol J 2017, 14, 109. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 2008, 36(Web Server issue): W5-W9. [CrossRef]
- ICTV Coronaviridae Study Group. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). 2021. Available from: https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports/ictv_9th_report/positive-sense-rna-viruses-2011/w/posrna_viruses/223/coronaviridae-figures.
- Kerpedjiev, P.; Hammer, S.; Hofacker, I.L. Forna (force-directed RNA): Simple and effective online RNA secondary structure diagrams. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3377-3379. [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.R.; Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Neuböck, R.; Hofacker, I.L. The Vienna RNA Websuite. Nucleic Acids Research 2008, 36, W70-W74. https://doi.org10.1093/nar/gkn188.
- Lorenz, R., Bernhart, S.H., Höner Zu Siederdissen, C., Tafer, H., Flamm, C., Stadler, P.F., Hofacker, IL. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol Biol 2011, 6, 26. [CrossRef]
- Bikandi, J., San Millán, R., Rementeria, A., Garaizar, J. In silico analysis of complete bacterial genomes: PCR, AFLP-PCR and endonuclease restriction. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 798-799. [CrossRef]
- Duvaud, S., Gabella, C., Lisacek, F., Stockinger, H., Ioannidis, V., Durinx, C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, W216-W227. [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Research 2022, 50, W276-W279. [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




