Submitted:
22 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. General Metamorphic Working Process and Structure Composition Principle of Constrained Metamorphic Mechanisms
2.1. General Working Process of Constrained Metamorphic Mechanisms
2.2. Structure Composition Principle of Constrained Metamorphic Mechanisms
x (0-DOF group)
3. Modularized Force Analysis of Constrained Metamorphic Mechanisms and Structural Design of Metamorphic Revolute Joints
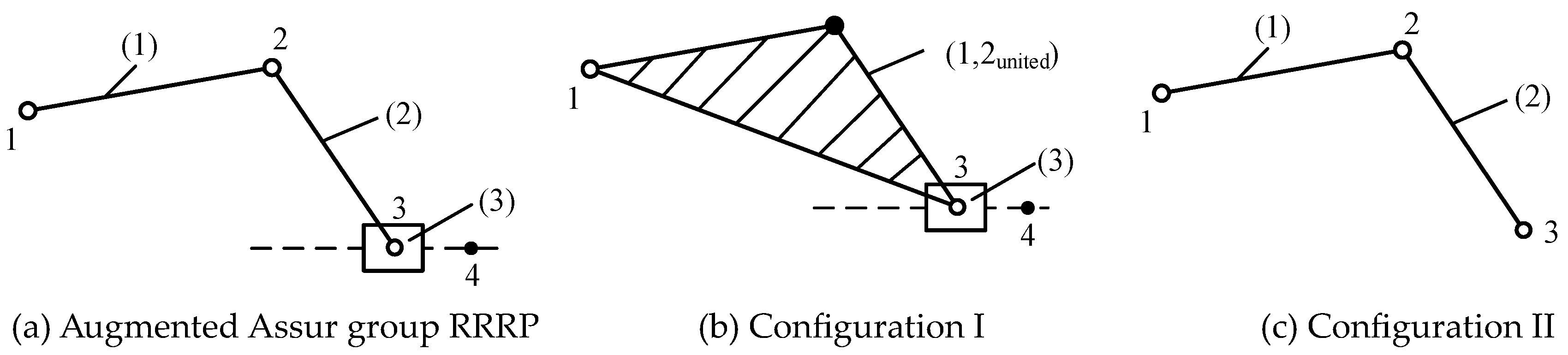
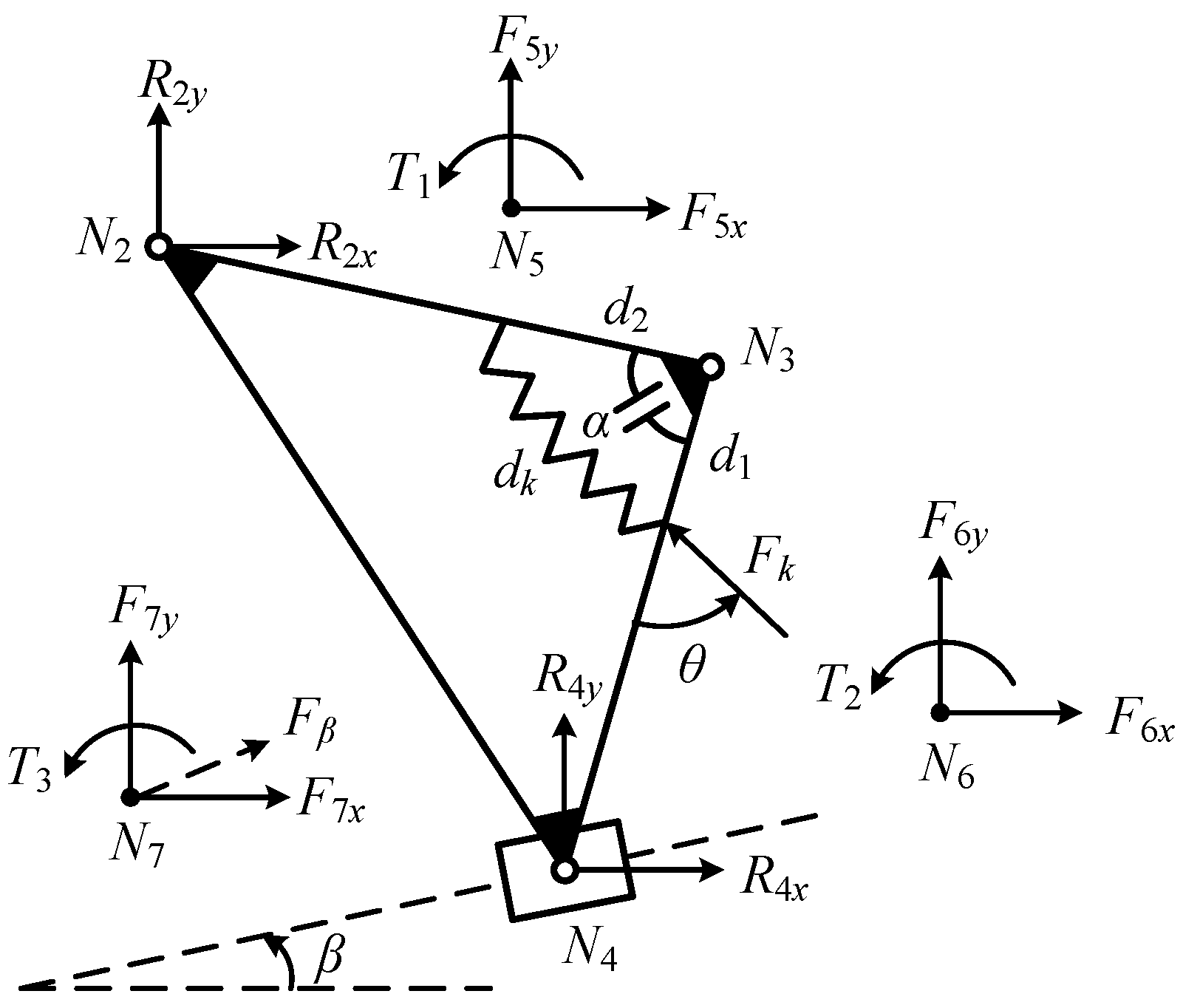
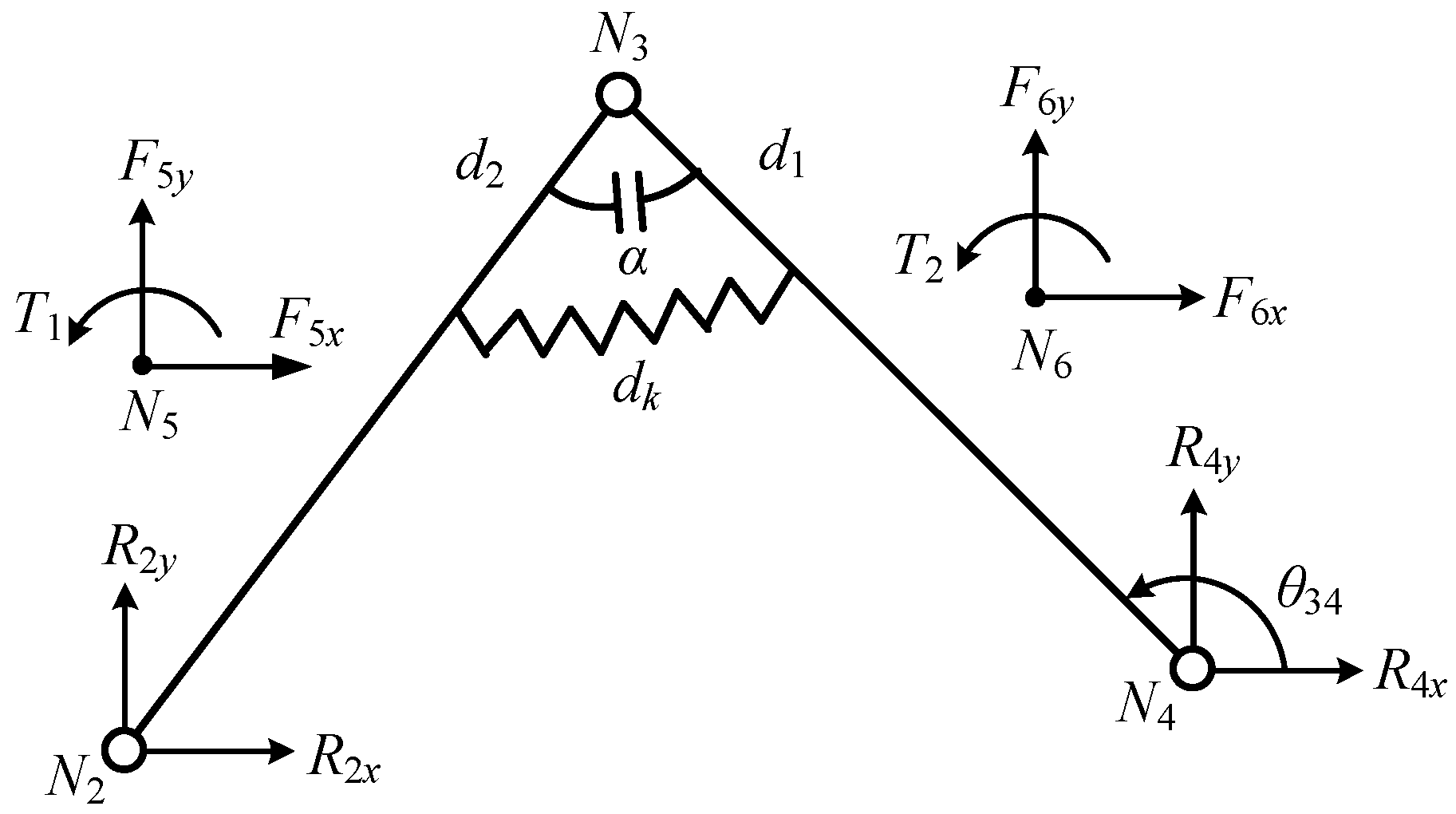
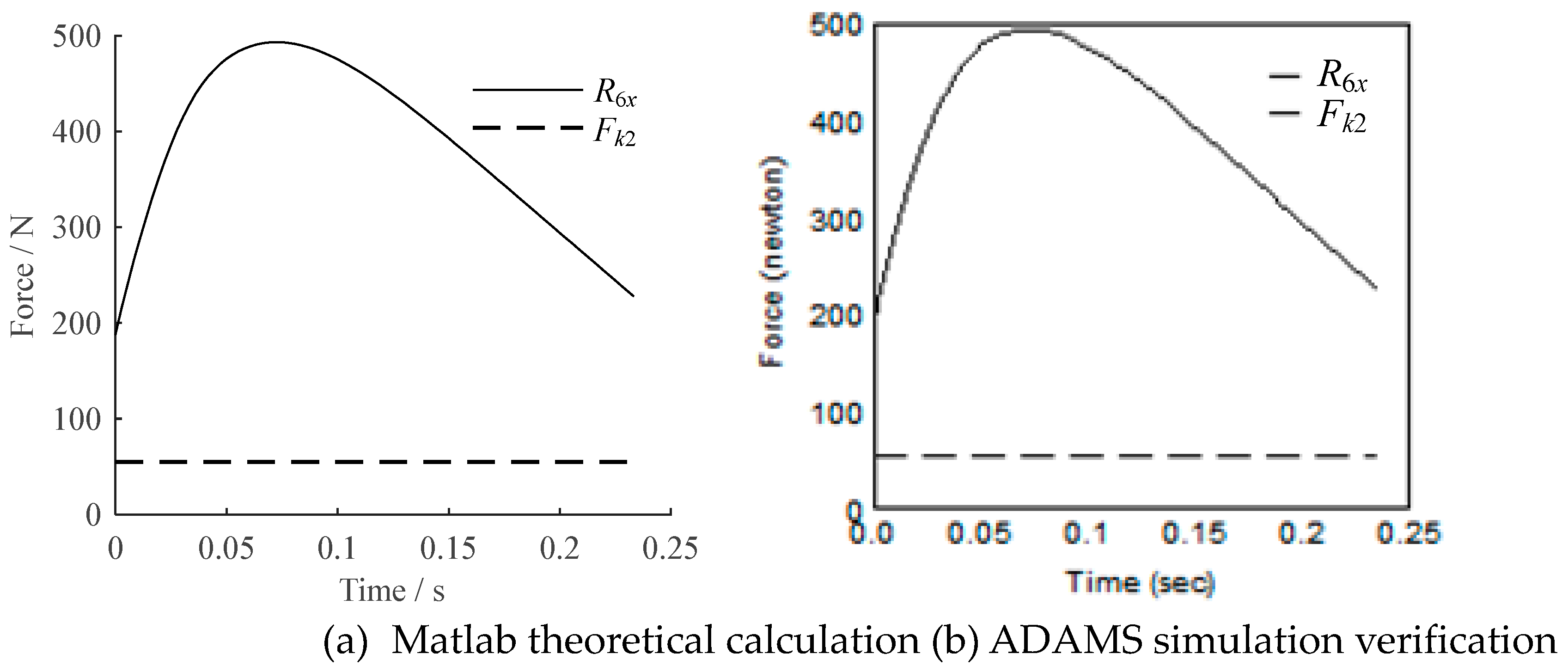
3.1. Modularized Force Analysis of AGGs
3.2. Structure Design of Metamorphic Revolute Joint according to Constraint Parameters Calculated in Modularized Force Analysis
4. Probabilistic Evaluation Model for the Configuration Transformation Ability of Constrained Metamorphic Mechanisms
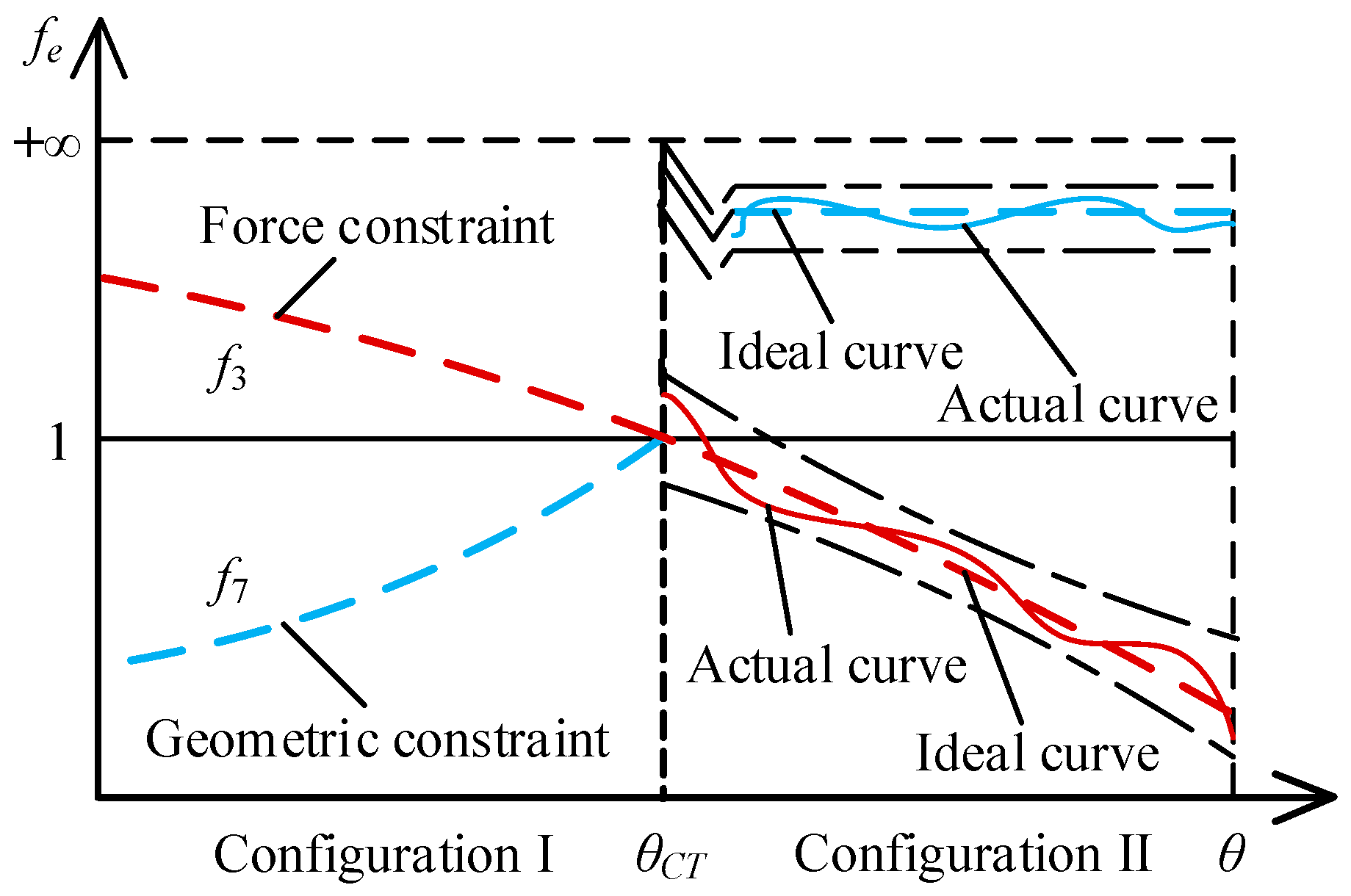
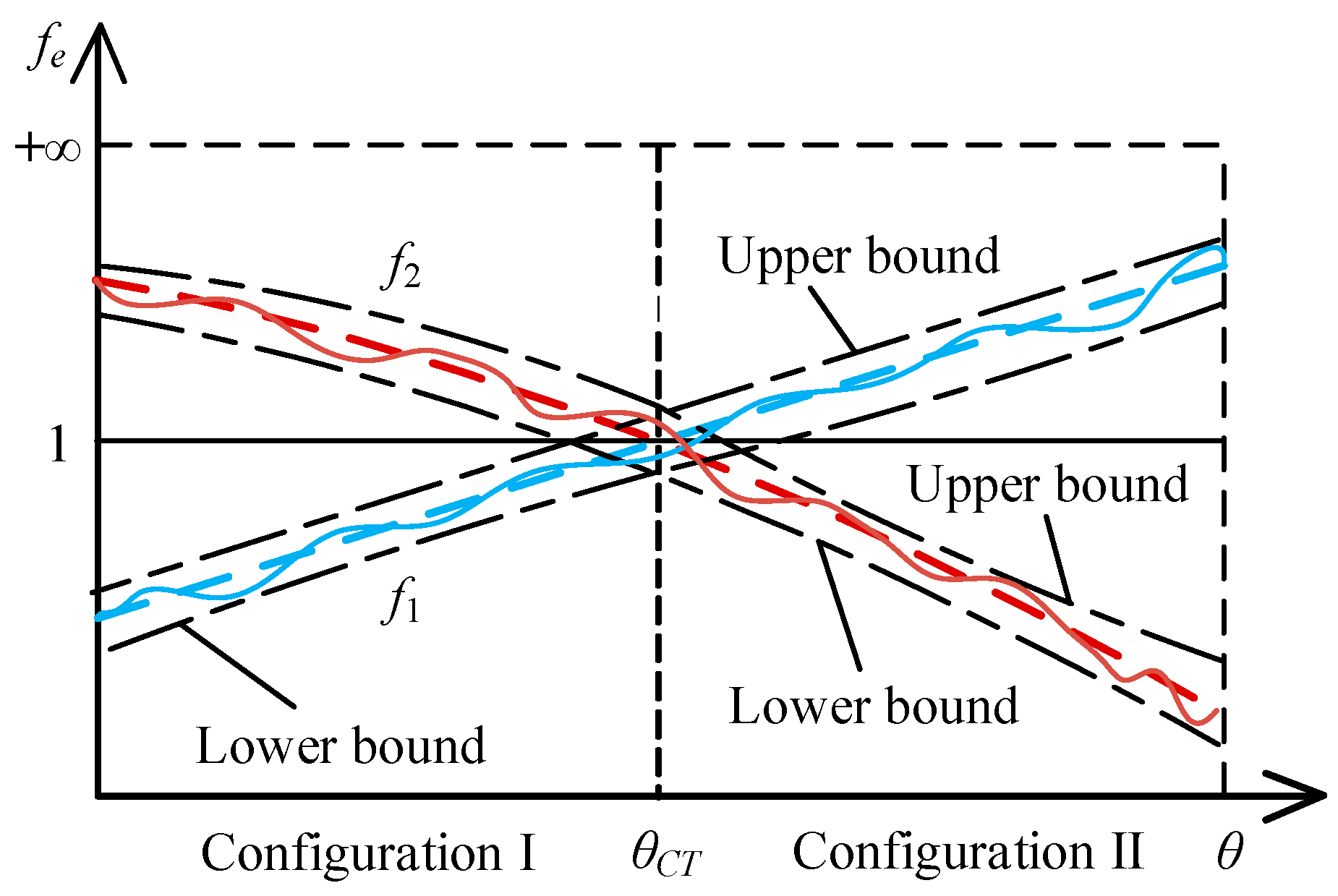
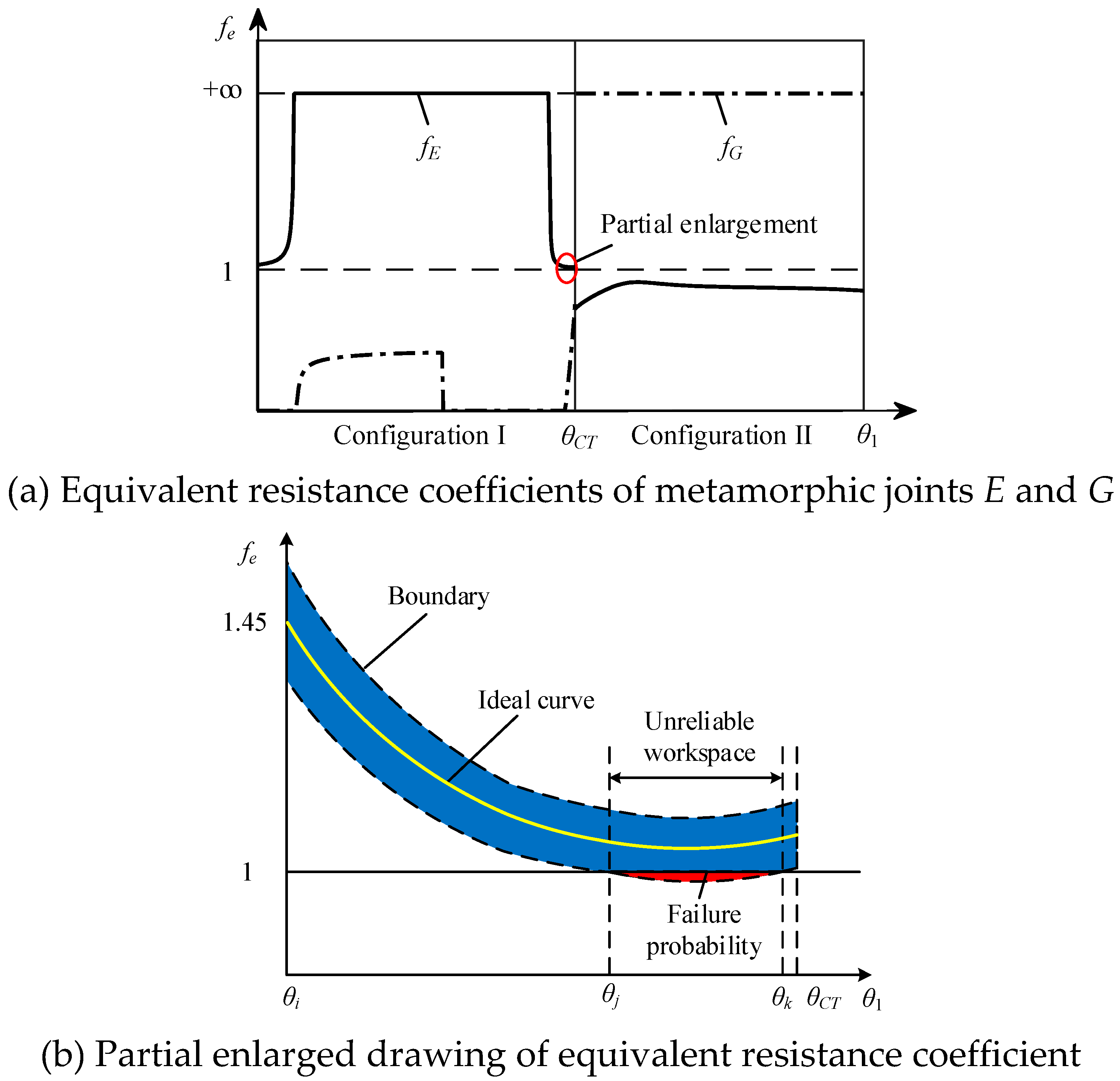
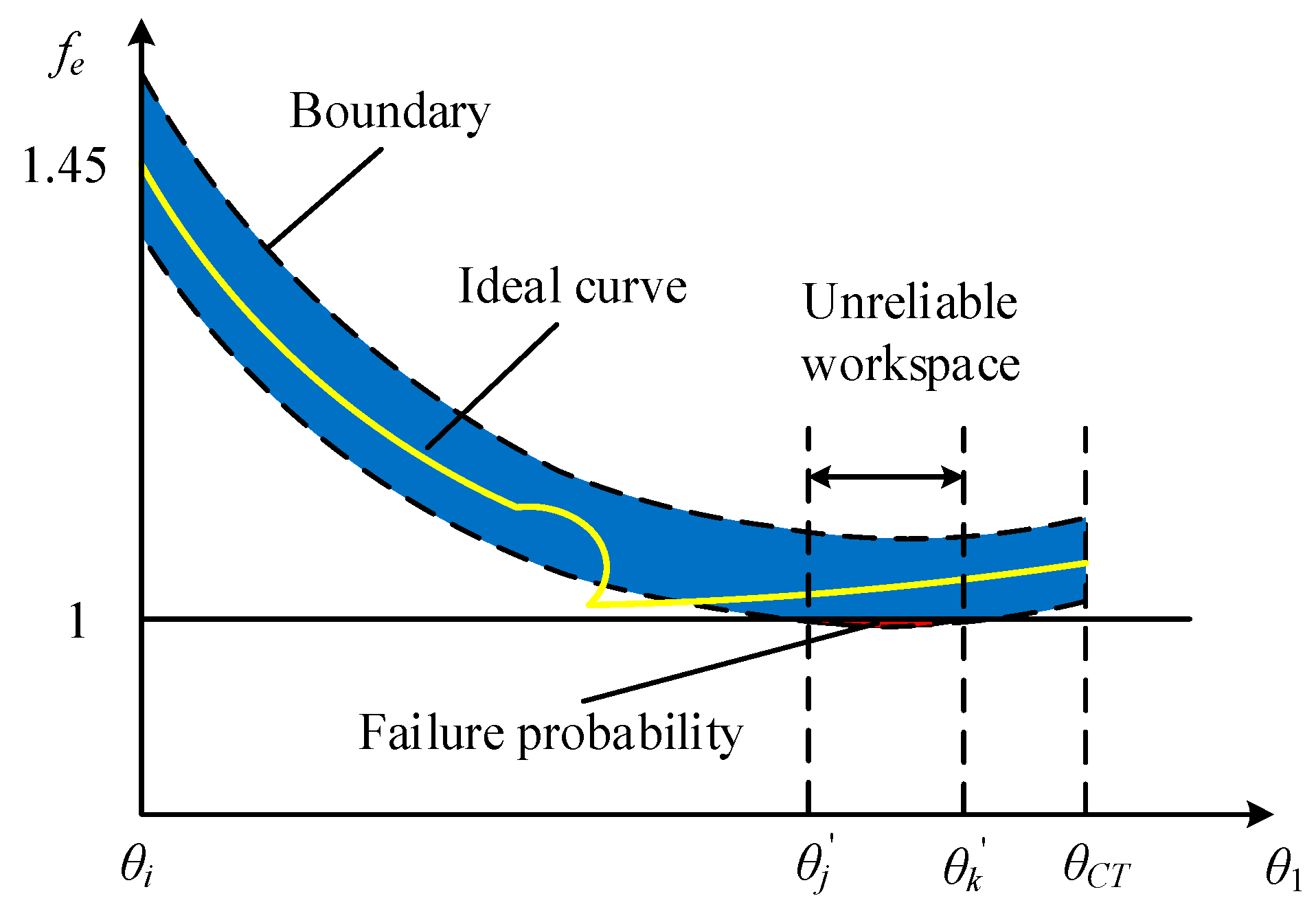
4.1. Evaluation of Configuration Transformation Ability Based on Equivalent Resistance Gradient Model
4.2. Random analysis of Configuration Transformation of Constrained Metamorphic Mechanisms
4.3. Reliability Evaluation Model of Configuration Transformation Ability
5. Reliability Optimization Design Method Oriented to the Stability of Configuration Transformation
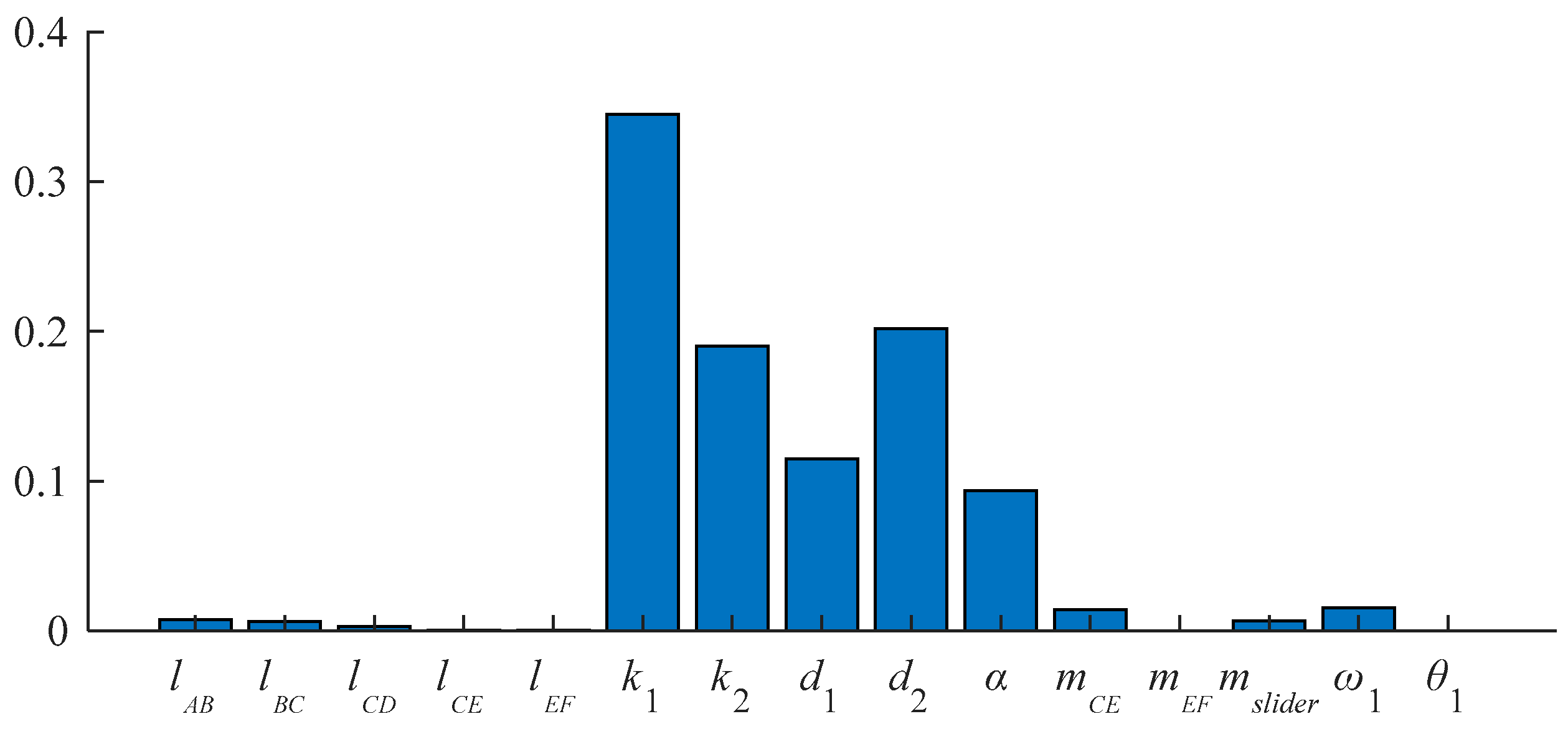
5.1. Determination of Optimization Design Parameters Based on Reliability Sensitivity Analysis
5.2. Objective Function
5.3. Constraint Condition
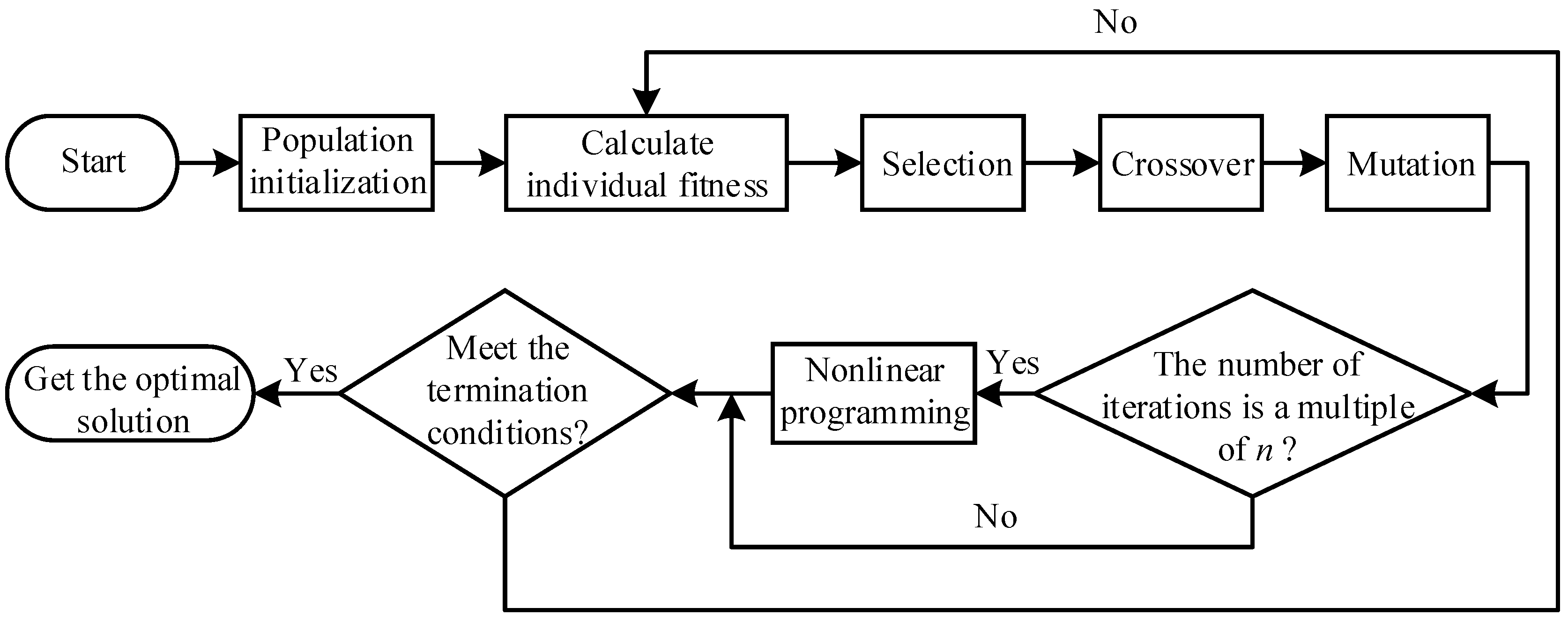
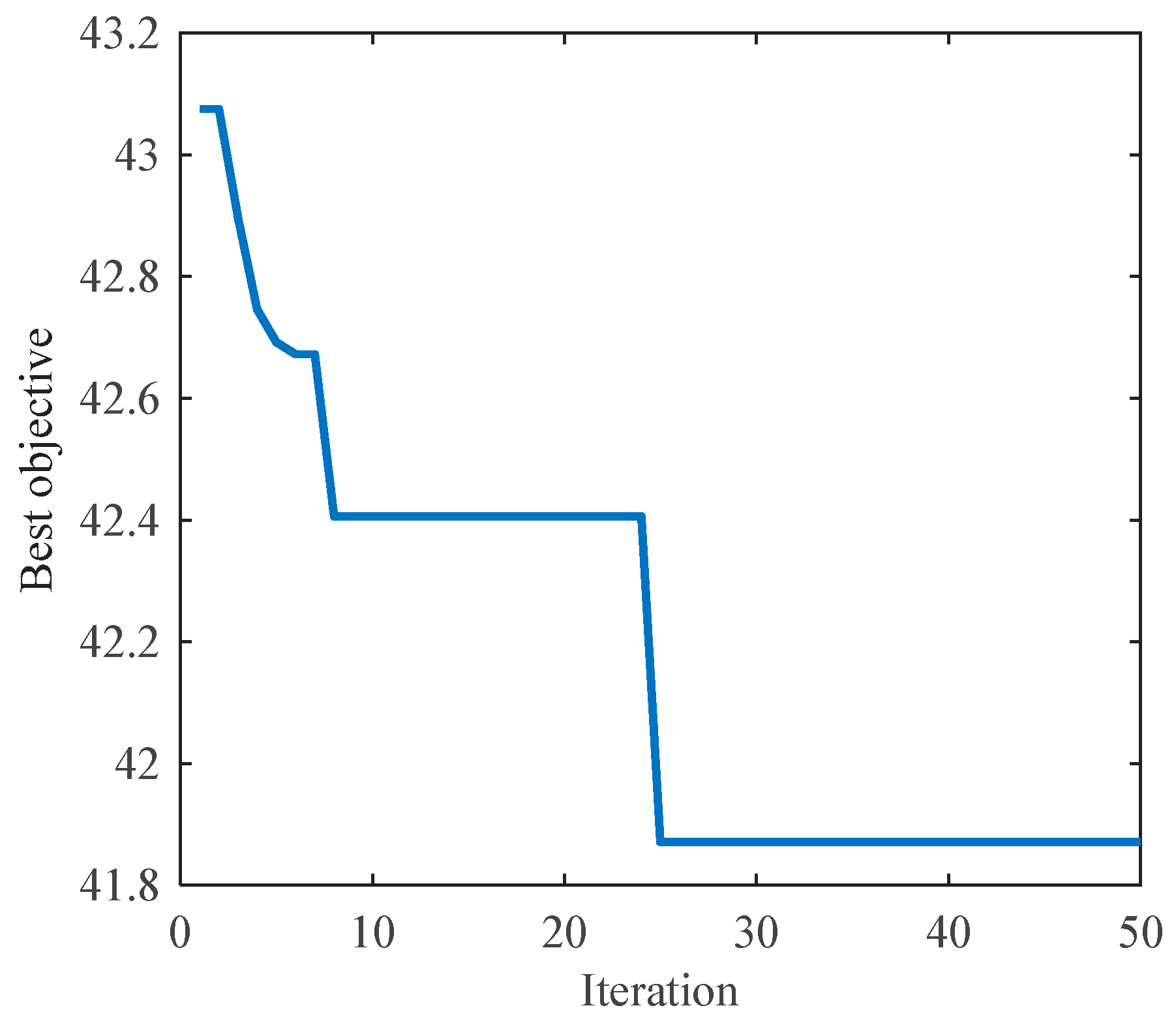
5.4. Reliability Optimization Design Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm
6. Calculation Example of the Paper Folding Metamorphic Mechanism
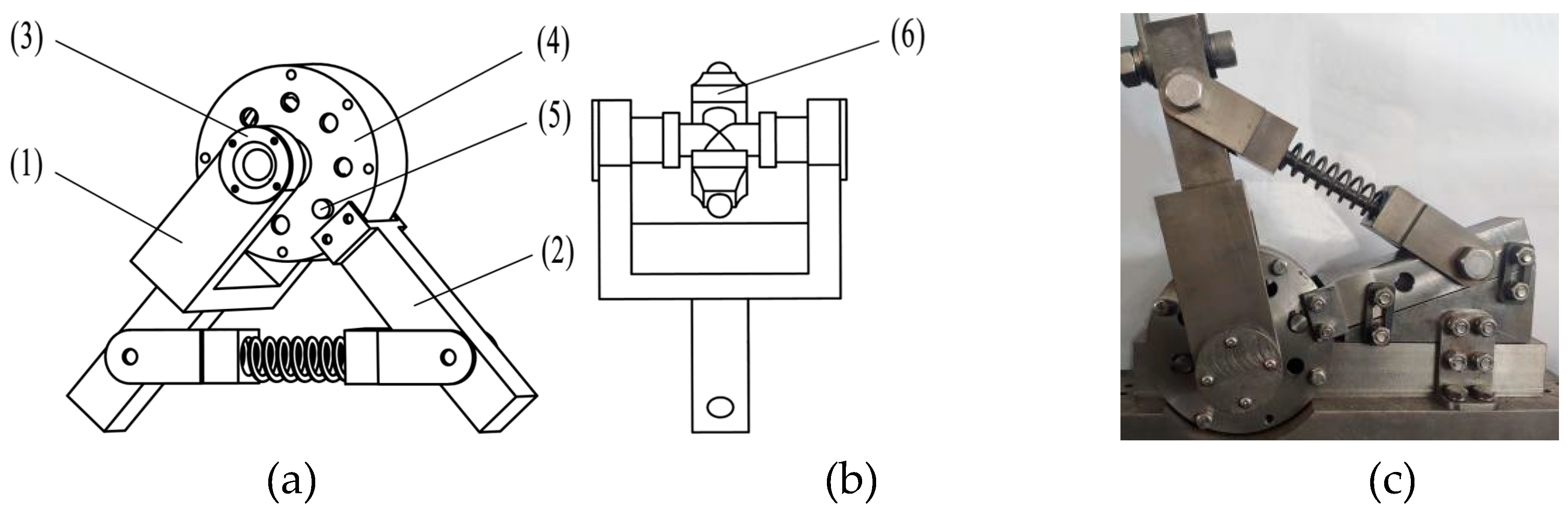
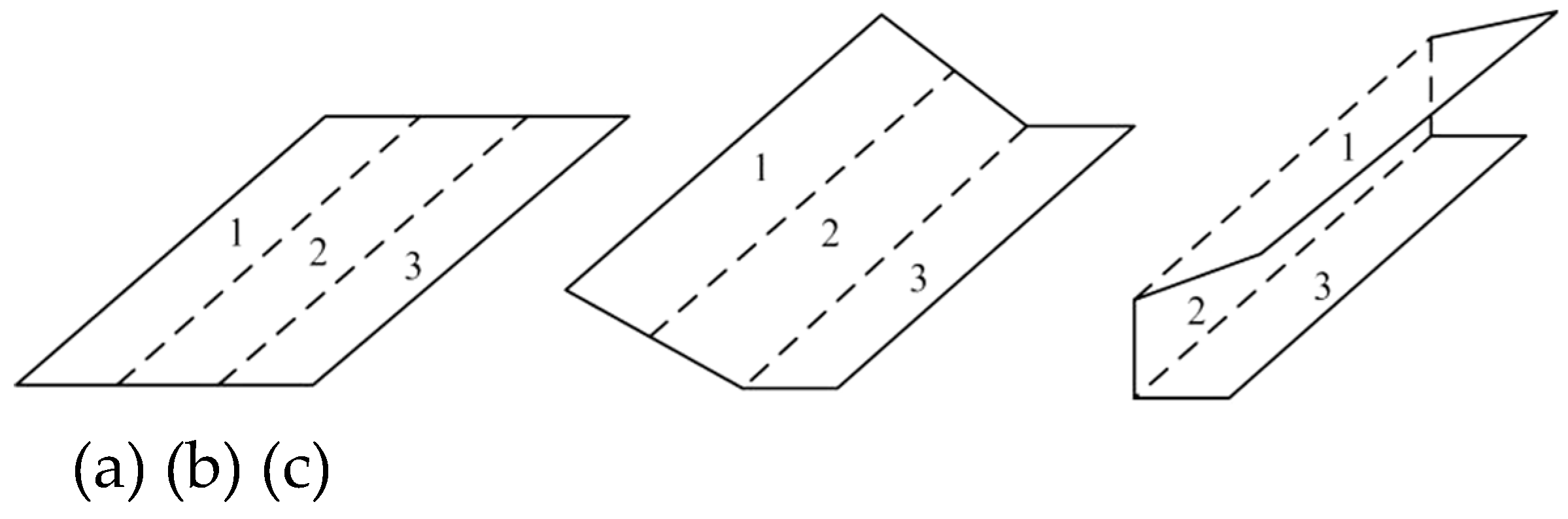
6.1. Type Synthesis of the Paper Folding Mechanism
6.2. Reliability Calculation of the Configuration Transformation Ability of the Paper Folding Mechanism
6.3. The Optimization Design of Reliability for Configuration Transformation of the Paper Folding Mechanism
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Dai, J. S., and Jones, J. R., 1999, “Mobility in Metamorphic Mechanisms of Foldable/Erectable Kinds,” Journal of Mechanical Design, 121(3), 375-382. [CrossRef]
- Jin, G. G., Zhang, Q. X., Dai, J. S., and Li, D.L., 2003 “Dynamic modeling of metamorphic mechanism,” Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 16(1), 94-99.
- Dai, J. S., Ding, X. L., and Zou, H. J., 2005, “Fundamentals and categorization of metamorphic mechanism,” Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, (06), 7-12.
- Guo, Z. H., Ma, L. Z., and Yang, Q. Z., 2005, “Topological type analysis of the variable freedom mechanism based on the metamorphic principle,” China Mechanical Engineering, 016(001), 3-5+9.
- Lan, Z. H., and Du, R., 2008, “Representation of Topological Changes in Metamorphic Mechanisms With Matrices of the Same Dimension,” Journal of Mechanical Design, 130(7), 074501-1-4. [CrossRef]
- Li, S. J., and Dai, J. S., 2012, “Structure synthesis of single—driven metamorphic mechanisms based on the augmented Assur groups,” Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 4(3), 031004-1-8. [CrossRef]
- Li, S. J., and Dai, J. S., 2012, “Advances in reconfigurable mechanisms and robotics Ⅰ,” Tianjin, Springer Press, 53-62.
- Kanner, O., and Dollar, A., 2013, “Kinematic Design of an Underactuated Robot Leg for Passive Terrain Adaptability and Stability,” Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 5(3), 031006-1-9. [CrossRef]
- Coppola, G., Zhang, D., Liu, K. F., and Gao, Z., 2013, “Design of Parallel Mechanisms for Flexible Manufacturing With Reconfigurable Dynamics,” Journal of mechanical design, 135(7), 071011-1-10. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. G., Chen, H. Q., Li, Y. X., Zou, Q. M., and Zheng, A. P., 2014, “Nonlinear dynamic model and simulation of a novel controllable metamorphic palletizing robot mechanism,” Proc. 2014 IFToMM Asian Conference on Mechanism and Machine Science, DYMl-4.
- Yang, Q., Wang, H. G., Li, S. J., and Dai, J. S., 2014, “Type synthesis of constrained metamorphic mechanisms with structural forms of the metamorphic joints,” Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 50(013), 1-8.
- Li, S. J., Wang, H. G., and Yang, Q., 2015, “Constraint Force Analysis of Metamorphic Joints Based on the Augmented Assur Groups,” Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 28(04), 747-755. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. C., Quan, Q. Q., Deng, Z. Q., and Hou, H. Y., 2016, “An Underactuated Robotic Arm Based on Differential Gears for Capturing Moving Targets: Analysis and Design,” Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 8(4), 041012-1-13. [CrossRef]
- Aimedee, F., Gogu, G., Dai, J. S., Bouzgarrou, C., and Bouton, N., “Systematization of morphing in reconfigurable mechanisms,” Mechanism and machine theory, 96, 215-224. [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. S., and Kuo, C. H., 2006, ‘Topological Representations and Characteristics of Variable Kinematic Joints,” Journal of Mechanical Design, 128(2), 384-391. [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. S., and Kang C. H., 2009, “Configuration synthesis of mechanisms with variable topologies,” Mechanism and Machine Theory, 44(5), 896-911.
- Gan, D. M., and Dai J. S., 2013, “Geometry constraint and branch motion evolution of 3-PUP parallel mechanisms with bifurcated motion,” Mechanism and Machine Theory, 61, 168-183.
- Zhang, K. T., Dai, J. S., and Fang, Y. F., 2013, “Geometric constraint and mobility variation of two 3SvPSv metamorphic parallel mechanisms,” Journal of Mechanical Design, 135(1), 011001-1-8. [CrossRef]
- Zlatanov, D. S., Bonev, I., and Gosselin, C., 2002, “Constraint singularities as configuration space singularities,” Advances in Robot Kinematics: Theory and Applications, 183-192.
- Gan, D. M., Dai, J. S., Dias, J., and Seneviratne, L., 2013, “Unified kinematics and singularity analysis of a metamorphic parallel mechanism with bifurcated motion,” Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 5(3), 031004-1-11. [CrossRef]
- Tian, H. B., Ma, H. W., and Ma, K., 2018, “Method for configuration synthesis of metamorphic mechanisms based on functional analyses,” Mechanism and Machine Theory, 123 (6), 27–39. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S. L., Guo, H. W, Liu, R. Q., and Deng, Z. Q., 2019, “Self-adaptive grasp process and equilibrium configuration analysis of a 3-DOF UACT robotic finger,” Mechanism and Machine Theory, 133, 250-266. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y. Y., Chang, B. Y., Jin, G. G., Wei, Z., Li, B., and Zhu, Y. J., “Research on Dynamics Modeling and Simulation of Constrained Metamorphic Mechanisms,” Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, 45(2), 321-336. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q., Hao, G. B., Li, S. J., Wang, H. G., and Li, H. Y., 2020, “Practical Structural Design Approach of Multicon guration Planar Single-Loop Metamorphic Mechanism with a Single Actuator,” Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 33(05), 29-43.
- Liu, S. L., Wang, X. D., Kong, J. Y., Zeng, T., and Tang, W., 2021, “Kinematic Reliability Analysis of Planar Metamorphic Mechanism with Multi-source Uncertainties,” Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 57(17), 64-75.
- Liao, P., and Lu, J. S., 1999, “A Calculating Metod of Circle Error Using Genetic Algorithms,” Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 31(4), 393-397.
- Pan, F. W., 2006, “Accuracy synthesis of new typed 6 DOF parallel robot based on self-adaptive genetic algorithm,” Journal of Machine Design, 26(8), 28-31.
- Pan, F. W., Lu, J. H., and He L. L., 2009, “Analysis of Kinematics of a Novel 6-DOF Parallel Platform Based on Genetic Algorithm,” Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 37(1), 37-40.
- Chen, X. L., and Sun, X. Y., 2012, “Dexterity analysis of a 4-ups-rps parallel mechanism,” International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 144(9), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Chen X. L., Jiang, D. Y., Chen, L. L, and Wang, Q., 2016, “Kinematics Performance Analysis and Optimal Design of Redundant Actuation Parallel Mechanism,” Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 47(6), 340-347.
- Ni, Y. B., Shao, C. Y., Zhang, B., and Guo, W., X., 2016, “Error modeling and tolerance design of a parallel manipulator with full-circle rotation,” Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 8(5), 1687814016649300. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y., 2017, “Optimal Design of Double-stage Wheel Hub Reducer System based on Fuzzy Theory,” Journal of Mechanical Transmission, 41(07), 180-187.
- Kang, X., and Dai, J. S., 2020, “Theoretical Difficulties and Research Progresses of Mechanism Reconfiguration in Mechanisms——Evolution Connotation, Furcation Principle, Design Synthesis and Application of Metamorphic Mechanisms,” China Mechanical Engineering, 31 (01), 57-71.
- Yu, J. J., Liu, K., and Kong X. W., 2020, “State of the Art of Multi-mode Mechanisms,” Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 56(19), 14-27.
- Wang, R. G., Chen, and H. Q., 2021, “Analysis and Optimization on Kinematic Reliability of Metamorphic Mechanisms with Multiple Failure Modes,” Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 57(11), 184-194.
- Li, S. J., 1995, “A Method of Disassembling Assur-Groups for IDENTIFYING and Modelling by Computer,” Journal of Northeastern University, (2): 198-201.
- Huang, P., and Ding H. F., 2019, “Structural synthesis of Assur groups with up to 12 links and creation of their classified databases,” Mechanism and Machine Theory, 145(C): 103668.
- Simionescu, P. A., 2019, “Kinematics of the RRR, RRT (Passive) and RRRR, RRRT (Active) Linkage-Mechanism Building Blocks with Applications and Reporting of New Findings,” Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 11(6), 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Xie, L. Y., 2014, “Issues and Commentary on Mechanical Reliability Theories, Methods and Models,” Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 50(14), 27-35.
- Shan, S., and Wang, G. G., 2008, “Reliable design space and complete single-loop reliability-based design optimization,” Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 93(8), 1218-1230. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. M., Huang, X. Z., He X. D., and Song X. Q., 2008, “Reliable sensitivity design for kinematics accuracy of planar linkage mechanism,” Journal of Engineering Design, 2008(01), 25-28.
- Zhang, Y. M., Zhu, L. S., Tang, L., and Lu, H., 2011, “Dynamical Stress Reliability and Sensitivity Analysis of Nonlinear Rotor System with Rigid-flexible Structure,” Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 047(002), 159-165.
- Yan, Z., and Guo R. L., 2013, “Precision optimization design of plane mechanism with gap,” Machinery, 51(10), 42-44.
- Li, X. P., Mao X., Gao J. Z., and Wang B. B., 2017, “Impact Analysis of the Parameters Variation on the Dynamic Performance of the Constraints Metamorphic Mechanism,” Mechanical design & manufacturing, 2017(12), 90-93.
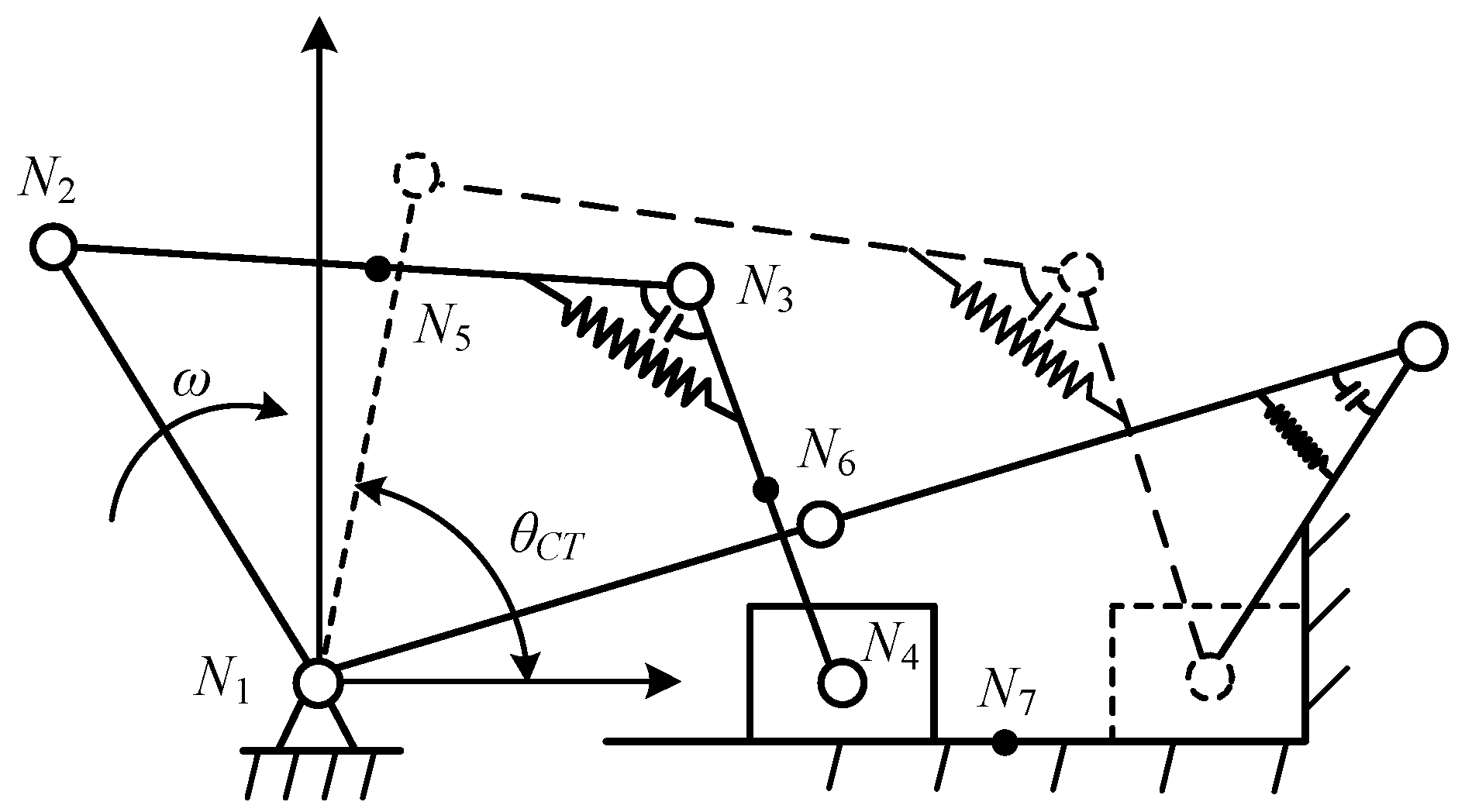
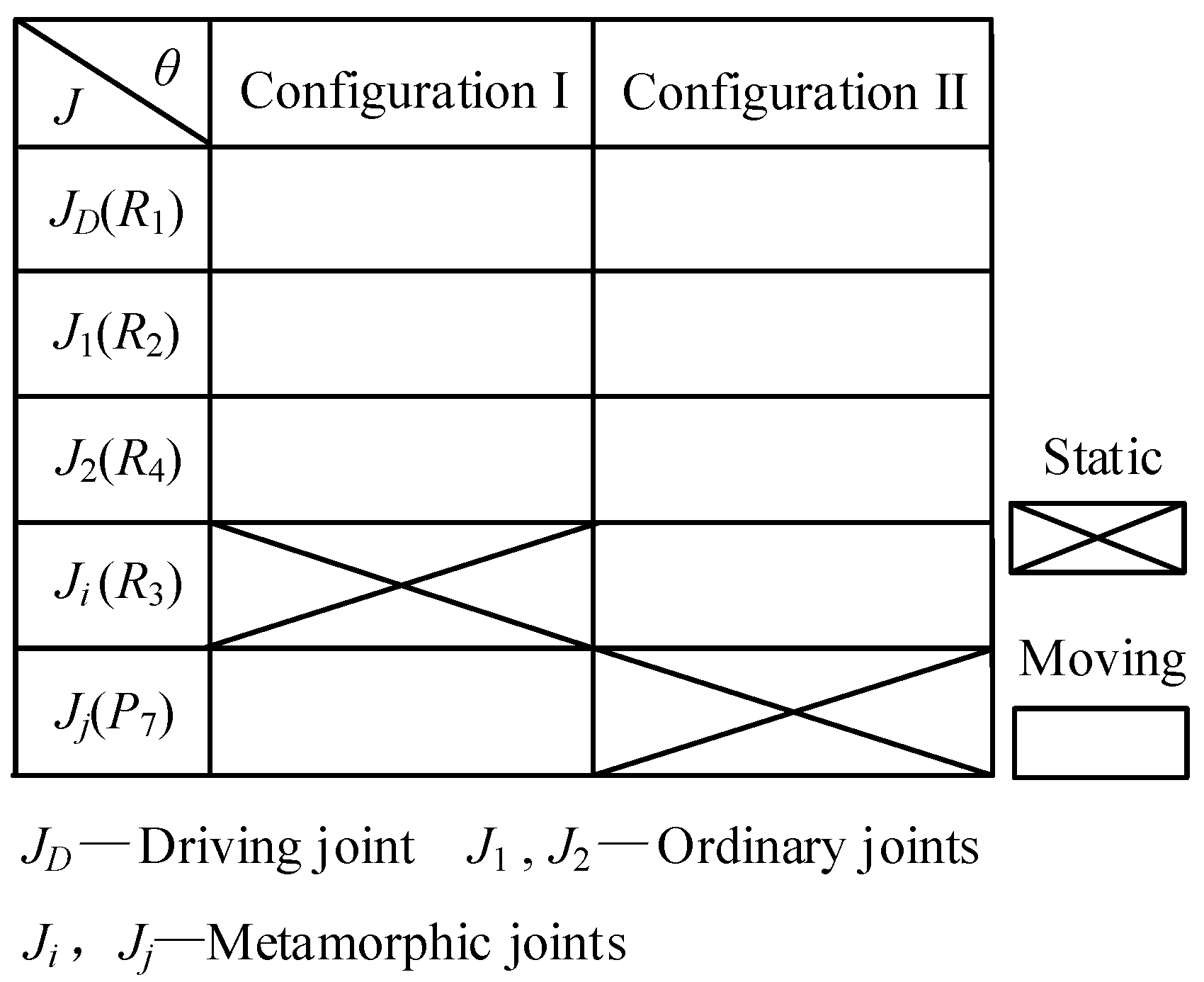
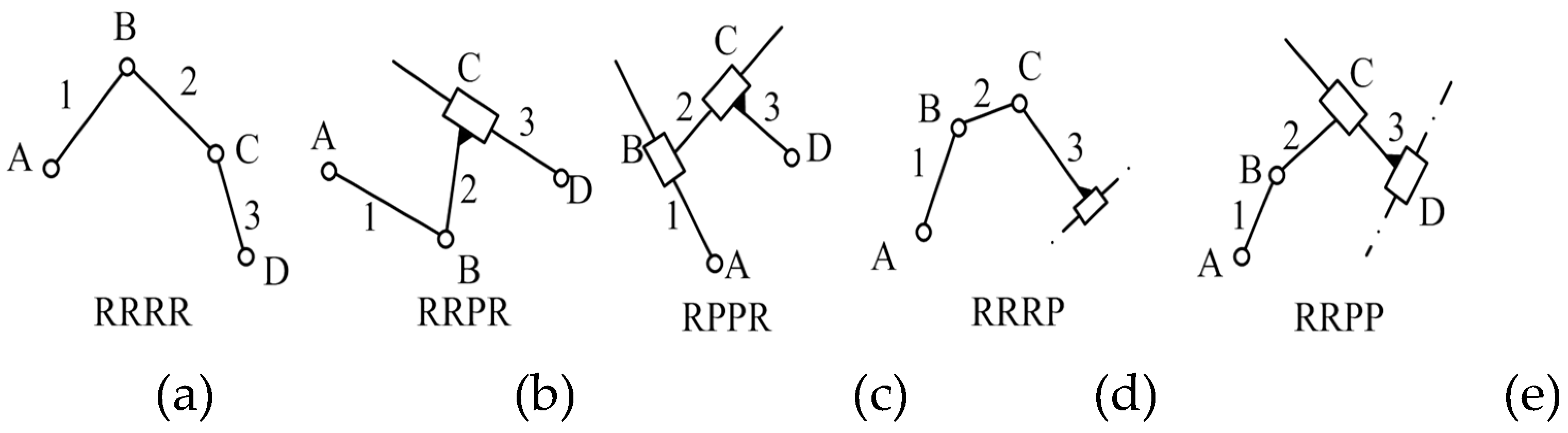
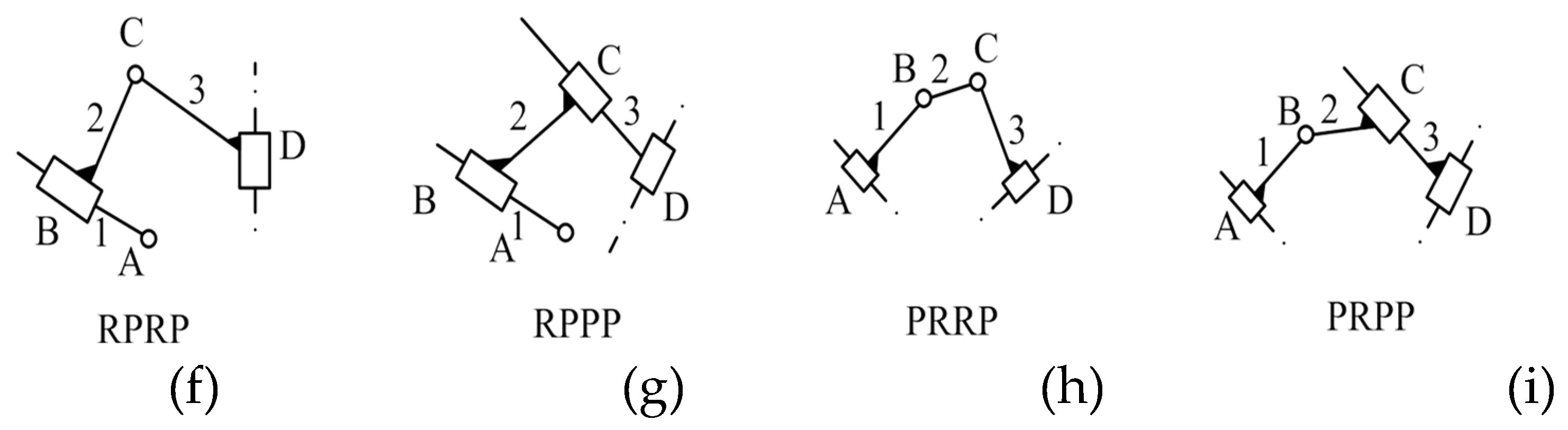
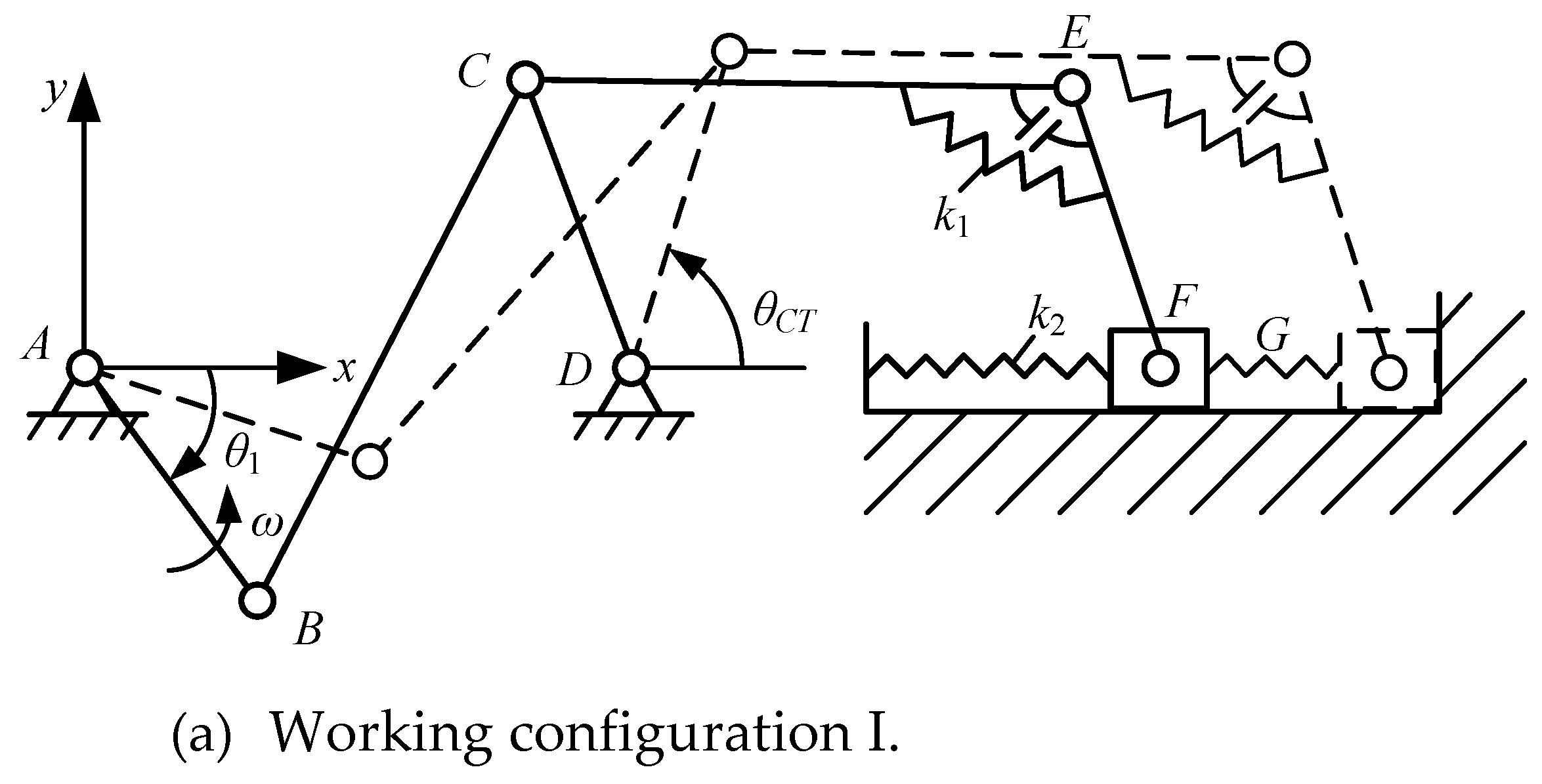
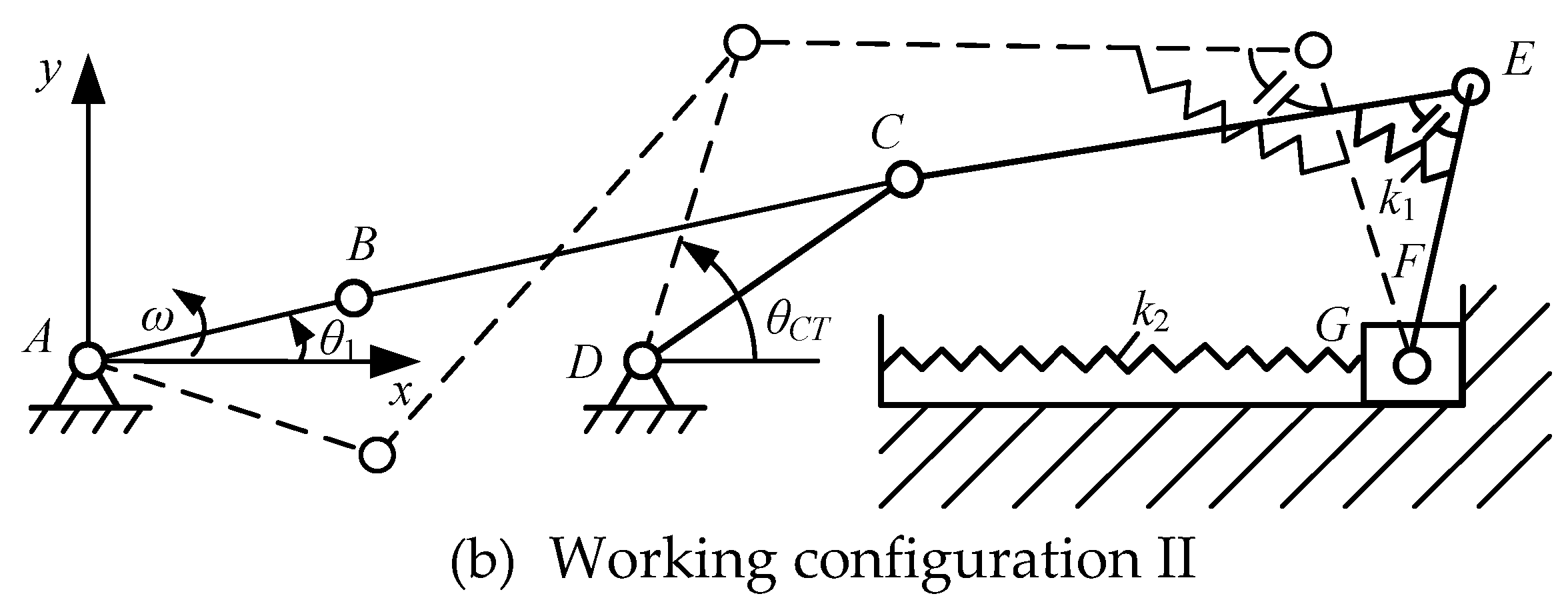
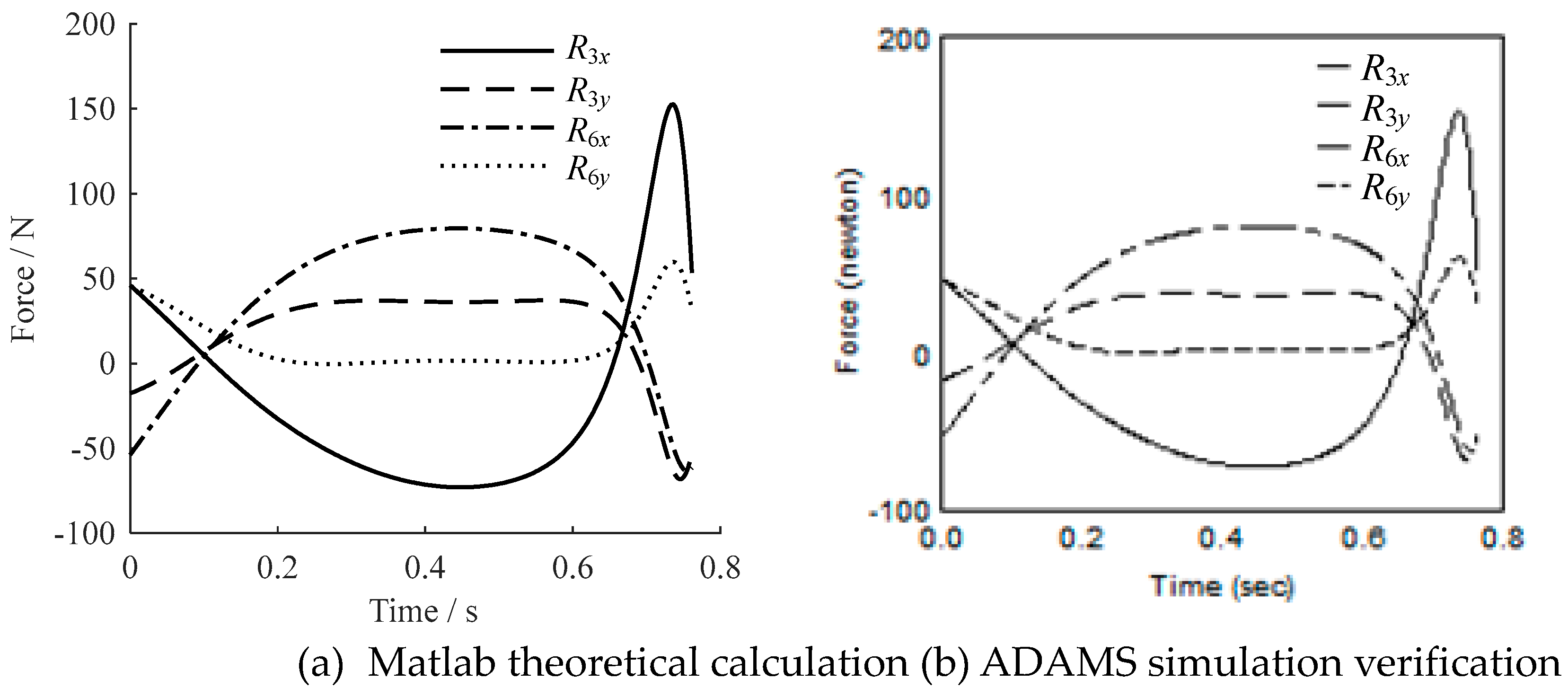
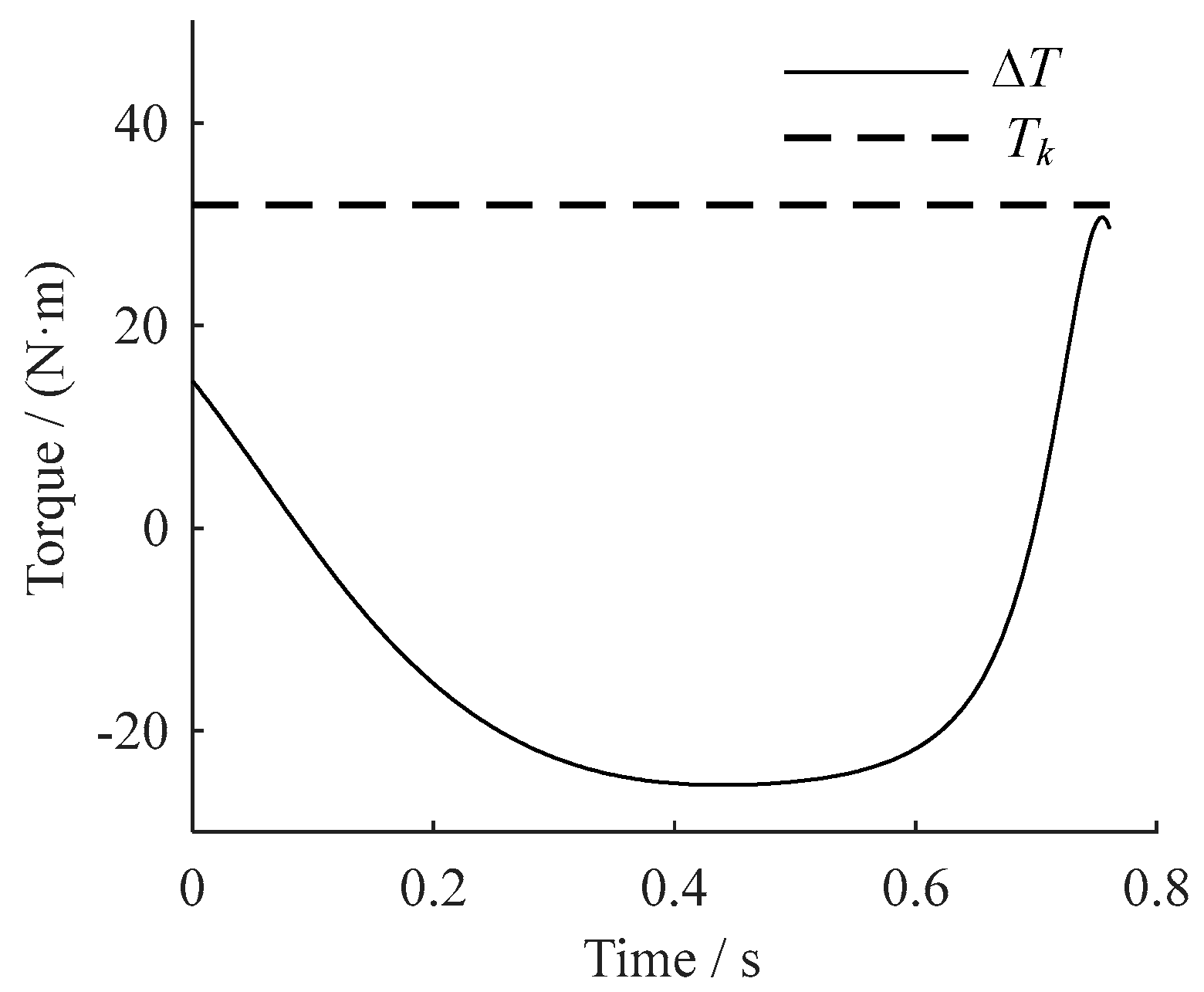
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
| lAB/mm | 180±0.125 | lBC/mm | 360±0.18 | lCD/mm | 240±0.145 |
| lCE/mm | 360±0.18 | lEF/mm | 210±0.145 | lAD/mm | 315 |
| maxlAF/mm | 870 | mAB/kg | N~(1,0.007) | mBC/kg | N~(1.5,0.01) |
| mCD/kg | N~(1,0.007) | mCE/kg | N~(1.5,0.01) | mEF/kg | N~(2,0.013) |
| mslider/kg | N~(1,0.007) | JAB/(kg·m2) | 0.0027 | JBC/(kg·m2) | 0.0162 |
| JCD/(kg·m2) | 0.0048 | JCE/(kg·m2) | 0.0162 | JEF/(kg·m2) | 0.00735 |
| a/mm | 250 | k1/(N/mm) | N~(10,0.1) | d1/mm | N~(100,0.667) |
| d2/mm | N~(120,0.667) | b/mm | 76 | k2/(N/mm) | N~(0.5,0.01) |
| ω1/(rad/s) | N~(2π,0.01) | α/° | N~(120.3,0.167) | Δθ1/° | N~(0,0.067) |
| Configuration I | Configuration II | |
| Type of mechanism | Crank slider | Crank rocker |
| Driving link angle | -290.2°~-15.2° | -15.2°~69.8° |
| Angle of joint E | Static(120.3°) | 120.3°~72.5° |
| Position of slider | 598.5mm~870mm | Static(870mm) |
| Angle of rocker | Static(115.9°) | 115.9°~88.8° |
| Configuration | Angle | μZ | σZ | β | Reliability | MCS |
| Conf. I | -21° | 2.5817 | 0.5194 | 4.9705 | 1 | 1 |
| Conf. I | -20° | 1.7918 | 0.5256 | 3.4088 | 0.9997 | 0.9996 |
| Conf. I | -19° | 1.3314 | 0.5337 | 2.4947 | 0.9937 | 0.9633 |
| Conf. I | -18° | 1.2474 | 0.5440 | 2.2930 | 0.9891 | 0.9886 |
| Conf. I | -17° | 1.5846 | 0.5570 | 2.8449 | 0.9978 | 0.9981 |
| Conf. I | -16° | 2.3832 | 0.5729 | 4.1599 | 1 | 1 |
| Transformation moment | -15.2° | 42.1336 | 1.0606 | 39.7262 | 1 | 1 |
| Conf. II | -15° | 132.4779 | 3.8848 | 34.1016 | 1 | 1 |
| Parameter | Sensitivity coefficient | Parameter | Sensitivity coefficient | Parameter | Sensitivity coefficient |
| lAB | 0.0075 | lBC | 0.0065 | lCD | 0.0030 |
| lCE | 0.0003 | lEF | 0.0003 | k1 | 0.3449 |
| k2 | 0.1904 | d1 | 0.1149 | d2 | 0.2019 |
| α | 0.0937 | mCE | 0.0142 | mEF | 0.0001 |
| mslider | 0.0067 | ω1 | 0.0155 | θ1 | 0.0002 |
| Moment | Equivalent resistance coefficient fe | Before optimization | After optimization |
| -17° | Mean value | 1.0522 | 1.0522 |
| Fluctuation range | 14.27% | 9.64% | |
| Failure probability | 0.21% | 0 | |
| -18° | Mean value | 1.0406 | 1.0406 |
| Fluctuation range | 13.84% | 9.41% | |
| Failure probability | 1.09% | 0.03% | |
| -19° | Mean value | 1.0435 | 1.0435 |
| Fluctuation range | 13.53% | 9.30% | |
| Failure probability | 0.63% | 0.01% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




