Submitted:
20 June 2024
Posted:
21 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Current Management of Coronary Stenosis
The Use of Hydrogen and Oxygen Nanobubbles as a Novel Treatment
Scientific Rationale
Potential Advantages over Traditional Therapies
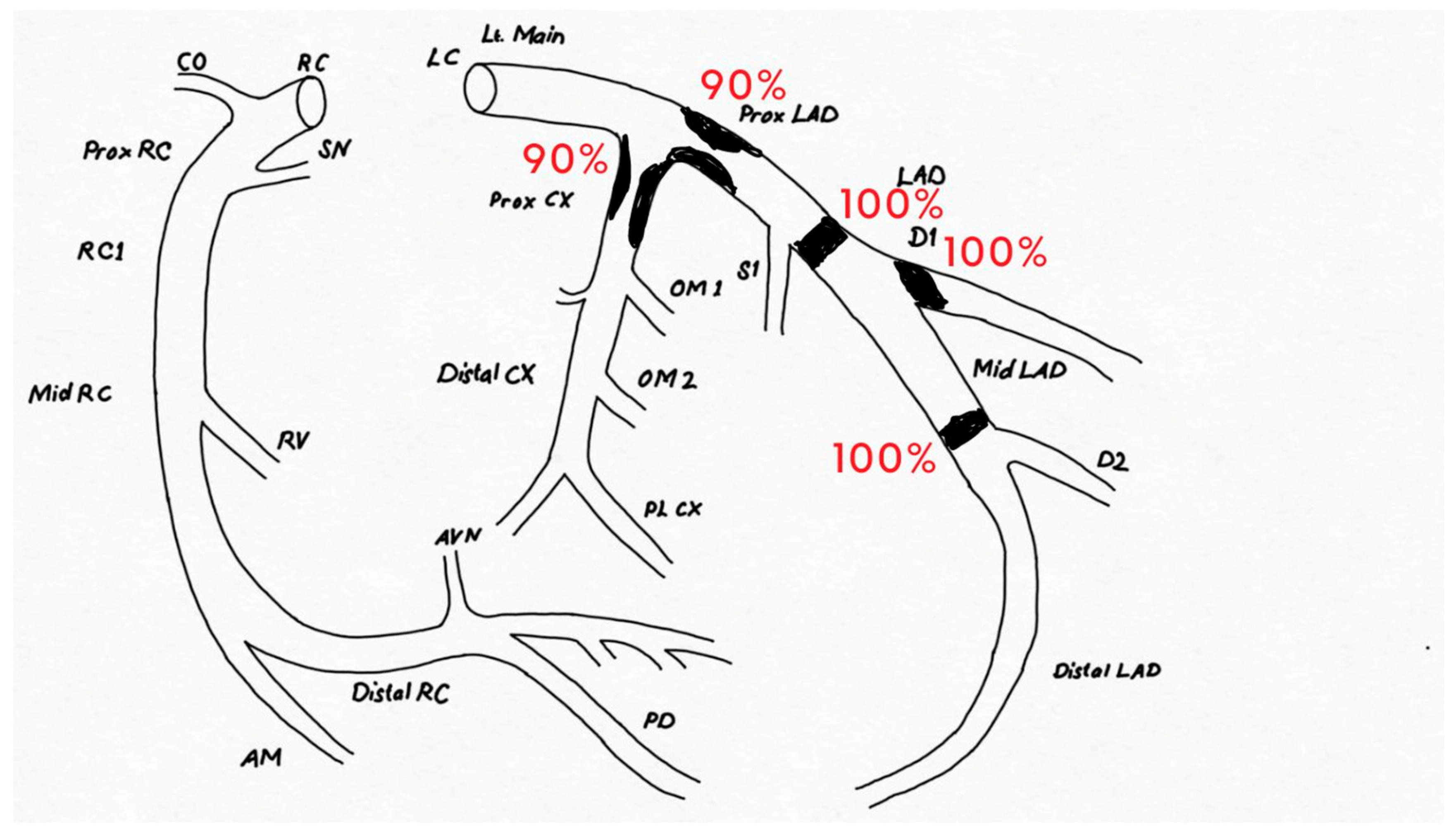
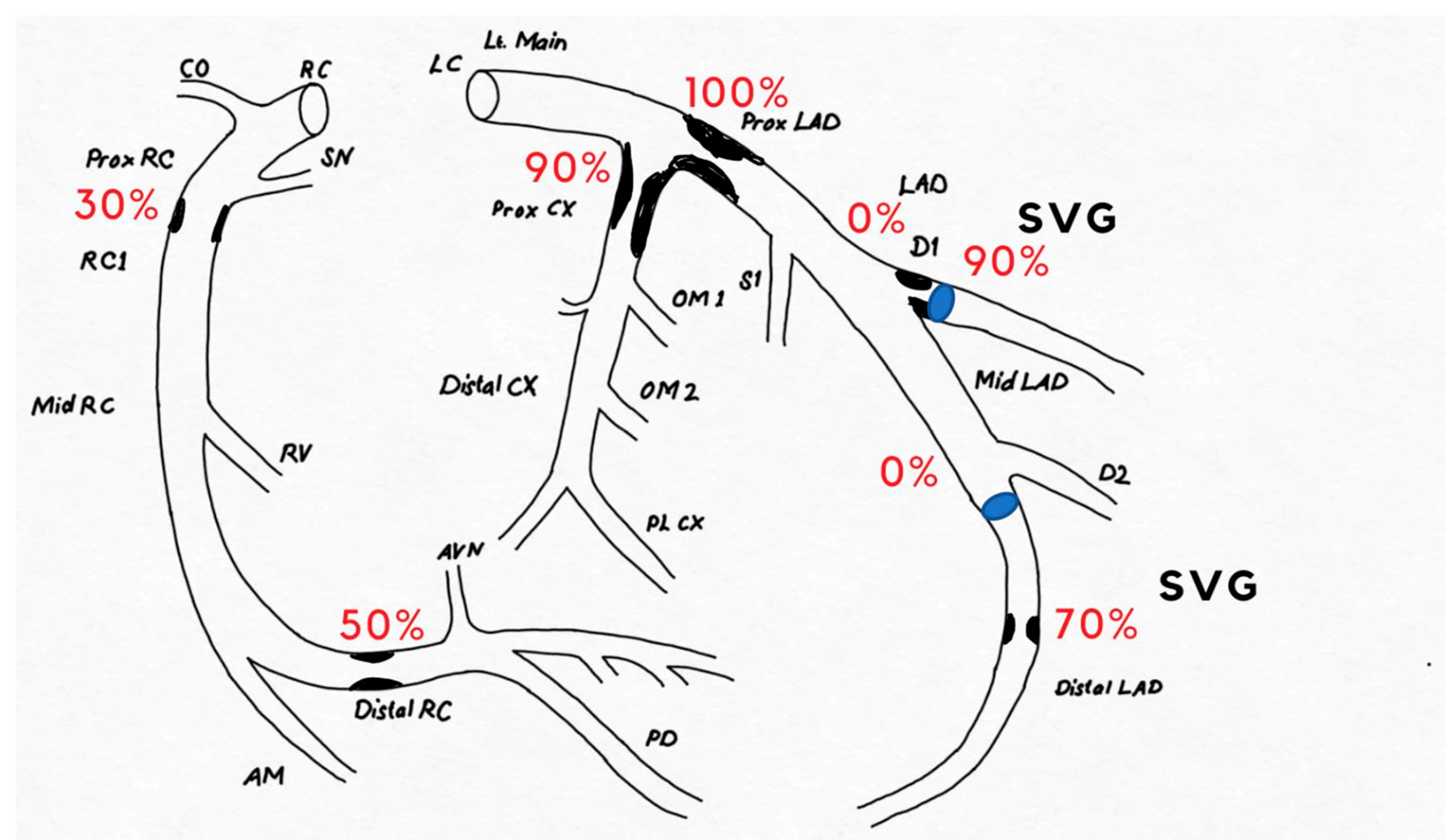
Case Presentation
Discussion
Conclusions
References
- Masuda, D.; Yamashita, S. Enhanced Intestinal Absorption of Cholesterol along with Increased Chylomicron Remnants for De novo Progression of Coronary Stenosis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Qin, M.; Zhang, B.; Lin, L.; Ma, Q.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Lai, W.; et al. Comprehensive Metabolomics Identified the Prominent Role of Glycerophospholipid Metabolism in Coronary Artery Disease Progression. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 632950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, P.V.; Tien, H.A.; Van Minh, H.; Valensi, P. Triglyceride glucose index for the detection of asymptomatic coronary artery stenosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graby, J.; Sellek, J.; Khavandi, A.; Loughborough, W.; Hudson, B.J.; Shirodaria, C.; Downie, P.; Antoniades, C.; Rodrigues, J.C.L. Coronary CT angiography derived pericoronary inflammation and bespoke cardiovascular risk prediction in the lipid clinic: beyond the calcium score. Eur. Hear. J. 2022, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichuum, S.; Chiang, S.-J.; Daimon, M.; Chang, S.-C.; Chan, C.-L.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Tseng, C.-L. Segmental Tissue Speckle Tracking Predicts the Stenosis Severity in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 832096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubero-Gallego, H.; Tizón-Marcos, H.; Vaquerizo, B.; Valero, I.M.C.; Pinel, a.A.C.; Borrego, J.C.; Blanco, B.J.M.S.; Martína, R.G.D.M. Current options for the management of calcified lesions. REC: Interv. Cardiol. (English Ed. 2020; 2, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bershtein, L.L.; Zbyshevskaya, E.V.; Gumerova, V.E. Optimum Treatment Strategy in Chronic Coronary Syndromes: the New Trials vs the Current Guidelines. Ration. Pharmacother. Cardiol. 2021, 17, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laricchia, A.; Colombo, A. New interventional solutions in calcific coronary atherosclerosis: drill, laser, shock waves. Eur. Hear. J. Suppl. 2020, 22, L49–L52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannaccone, G.; Scarparo, P.; Wilschut, J.; Daemen, J.; Dekker, W.D.; De Jaegere, P.; Zijlstra, F.; Van Mieghem, N.M.; Diletti, R. Current approaches for treatment of coronary chronic occlusions. Expert Rev. Med Devices 2019, 16, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doenst, T.; Thiele, H.; Haasenritter, J.; Wahlers, T.; Massberg, S.; Haverich, A. The Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease Current Status Six Decades After the First Bypass Operation. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2022, 119, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predescu, L.M.; Zarma, L.; Platon, P.; Postu, M.; Bucsa, A.; Croitoru, M.; Deleanu, D.E.; Ginghina, C. Current treatment of left main coronary artery disease. Cor et Vasa 2016, 58, e328–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolone, D.T.; Gallinoro, E.; Esposito, G.; Paolisso, P.; Bermpeis, K.; De Colle, C.; Fabbricatore, D.; Mileva, N.; Valeriano, C.; Munhoz, D.; et al. Contemporary Management of Stable Coronary Artery Disease. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2022, 29, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, G. , & Tekin, A. (2015). Current Medical Treatment of Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Arşiv Kaynak Tarama Dergisi, 24(4), 592-613.
- Desch, S.; Schuler, G.; Niebauer, J. [Conservative treatment of coronary heart disease--current options]. . 2005, 147, 45–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zwart, B.; Parker, W.A.E.; Storey, R.F. New Antithrombotic Drugs in Acute Coronary Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correale, M.; Tricarico, L.; Iacoviello, M.; Brunetti, N.D. SGLT2 Inhibitors: Statins or ACE-Inhibitors of the 21st Century? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, M.H.; Hall, A.S.; Narkiewicz, K. The Combination of Beta-Blockers and ACE Inhibitors Across the Spectrum of Cardiovascular Diseases. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2023, 37, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-Z.; Cao, L.-H.; Liu, H. ACE inhibitors in cardiac surgery: current studies and controversies. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndrepepa, G.; Braun, S.; Schömig, A.; Kastrati, A. Impact of therapy with statins, beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on plasma myeloperoxidase in patients with coronary artery disease. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2011, 100, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Lee, J.; Lee, S. ARB Superiority Over ACE Inhibitors in Coronary Heart Disease: An Alternative Viewpoint. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2019, 39, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.-S. Current Status of Coronary Stent. Korean J. Med. 2015, 89, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B. R. , & Hong, M. K. ( 2006). Medical Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease. Hanyang Medical Reviews, 39–51.
- Sim, H.W.; Zheng, H.; Richards, A.M.; Chen, R.W.; Sahlen, A.; Yeo, K.-K.; Tan, J.W.; Chua, T.; Tan, H.C.; Yeo, T.C.; et al. Beta-blockers and renin-angiotensin system inhibitors in acute myocardial infarction managed with inhospital coronary revascularization. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, H.; Olschewski, M.; Münzel, T.; Gori, T. Coronary In-Stent Restenosis: Predictors and Treatment. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2021, 118, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.-C.; Park, D.-W.; Park, S.-J. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention and Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting for the Treatment of Left Main Coronary Artery Disease. Korean Circ. J. 2019, 49, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towashiraporn, K.; Krittayaphong, R. Current Perspectives on Antithrombotic Therapy for the Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 2397–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Klusewitz, S.; Elefteriades, J.; Prescher, L. The Current State of Coronary Revascularization: Percutaneous Coronary Intervention versus Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery. Int. J. Angiol. 2021, 30, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushparaji, B. , Donisan, T. ( 25(6), 143–158. [PubMed]
- Garg, D. Regenerative Medicine and its Potential in Cardiovascular Disease. J. Stud. Res. 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, B.; Abedi, M.; Arabi, M.; Alavi-Moghadam, S.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Hadavandkhani, M.; Tayanloo-Beik, A.; Kordi, R.; Roudsari, P.P.; Larijani, B. Regenerative Medicine for the Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease; Status and Future Perspectives. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwinowicz, R. , Kapelak, B., Sadowski, J., Kędziora, A., & Bartus, K. (2018). The use of stem cells in ischemic heart disease treatment. Kardiochirurgia i Torakochirurgia Polska/Polish Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 15(3), 196-199.
- Amrutha, M.; Monaza, A.; Rithika, P.; Surya, S.; Kochoradze-Margishvili, T. Use of Stem Cells In Regenerative Cardiovascular Medicine (Review Article). Exp. Clin. Med. Ga. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, A.G.; Reidell, O.; Stachelscheid, H.; Klose, K.; Gossen, M.; Falk, V.; Röll, W.; Stamm, C. Regenerative Medicine/Cardiac Cell Therapy: Pluripotent Stem Cells. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 66, 053–062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, H.; Sakata, R. Cardiovascular surgery for realization of regenerative medicine. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 60, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behjati, M. Suggested indications of clinical practice guideline for stem cell-therapy in cardiovascular diseases: A stepwise appropriate use criteria for regeneration therapy. 2013, 9, 306–310.
- Nazari-Shafti, T.Z.; Kempfert, J.; Falk, V.; Röll, W.; Stamm, C. Regenerative Medicine/Cardiac Cell Therapy: Adult/Somatic Progenitor Cells. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 66, 042–052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolli, R.; Hare, J. Introduction to a Compendium on Regenerative Cardiology. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandaswamy, E.; Zuo, L. Recent Advances in Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease: Role of Science and Technology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksandric, S.; Banovic, M.; Beleslin, B. Challenges in Diagnosis and Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients With Severe Aortic Stenosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 849032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessey, B.; Pareek, N.; Macaya, F.; Yeoh, J.; Shlofmitz, E.; Gonzalo, N.; Hill, J.; Escaned, J. Contemporary percutaneous management of coronary calcification: current status and future directions. Open Hear. 2023, 10, e002182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghrairi, M.; Sulaiman, N.; Mutashar, S. Health Care Monitoring and Treatment for Coronary Artery Diseases: Challenges and Issues. Sensors 2020, 20, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekala, K.; Mehta, R.H.; Joumaa, M.; Yamasaki, H. Treatment of heavily calcified coronary artery stenosis using 3.5 mm peripheral intravascular lithotripsy balloon: case series. Eur. Hear. J. - Case Rep. 2020, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, E.; Sato, S.; Honda, S.; Nakazawa, A. All trans retinoic acid alleviates coronary stenosis by regulating smooth muscle cell function in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, C.W.; Dörr, O.; Woehrle, J.; Krackhardt, F.; Ince, H.; Zeus, T.; Berland, J.; Piot, C.; Roubille, F.; Schult, I.; et al. A multicentre, randomised controlled clinical study of drug-coated balloons for the treatment of coronary in-stent restenosis. EuroIntervention 2020, 16, e328–e334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Tian, J.; Yang, X.; Xing, H.; He, Y.; Song, X. Effects of Oral Drugs on Coronary Microvascular Function in Patients Without Significant Stenosis of Epicardial Coronary Arteries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Coronary Flow Reserve. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 580419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, R.; Akhavan, O.; Hamblin, M.R.; Varma, R.S. Review of Oxygenation with Nanobubbles: Possible Treatment for Hypoxic COVID-19 Patients. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 11386–11412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L. , & Miwa, N. (2021). Hydrogen nano-bubble water suppresses ROS generation, adipogenesis, and interleukin-6 secretion in hydrogen-peroxide-or PMA-stimulated adipocytes and three-dimensional subcutaneous adipose equivalents. Cells, 10(3), 626.
- Kurokawa, H., Matsui, H., Ito, H., Taninaka, A., Shigekawa, H., Dodbiba, G., ... & Fujita, T. (2019). Antioxidant effect of hydrogen nanobubble contributes to suppression of tumor cell growth. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res, 19, 14592-14594.
- Si, Y.; Tian, H.; Dong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Jia, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Qin, S. Effects of hydrogen as adjuvant treatment for unstable angina. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DU, Z.; Jia, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X. Protective effects of hydrogen-rich saline in uncontrolled hemorrhagic shock. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M. , Zhang, Z., Gao, B., Liu, L., & Hu, T. (2017). Hydrogen medicine therapy: an effective and promising novel treatment for multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) induced by influenza and other viral infections diseases. SOJ Microbiol Infect Dis, 5, 1-6.
- LeBaron, T.W.; Kura, B.; Kalocayova, B.; Tribulova, N.; Slezak, J. A New Approach for the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disorders. Molecular Hydrogen Significantly Reduces the Effects of Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W. C. , Zhang, Y. R., Yu, J. X., Yang, Y., Liu, X. N., Zhang, X.,... & Wang, Q. S. (2022). Hydrogen-oxygen therapy improves postoperative pulmonary functions and accelerates recovery through attenuating inflammatory reactions and oxidative stress in patients undergoing lung surgery.
- Zhang, J.H.; Matei, N.; Camara, R. Emerging mechanisms and novel applications of hydrogen gas therapy. Med Gas Res. 2018, 8, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Bajgai, J.; Fadriquela, A.; Sharma, S.; Trinh Thi, T.; Akter, R.; Goh, S.H.; Kim, C.-S.; Lee, K.-J. Redox Effects of Molecular Hydrogen and Its Therapeutic Efficacy in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Processes 2021, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghia, N.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Binh, P.T.; May, L.T.; Huy, T.T.; Giang, P.T.; St-Hilaire, S.; Van, P.T. Effect of nanobubbles (oxygen, ozone) on the Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei), Vibrio parahaemolyticus and water quality under lab conditions. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2022, 25, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluemke, E.; Young, L.A.J.; Owen, J.; Smart, S.; Kinchesh, P.; Bulte, D.P.; Stride, E. Determination of oxygen relaxivity in oxygen nanobubbles at 3 and 7 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Mater. Physics, Biol. Med. 2022, 35, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerschmidt, V.; Ren, W.; Tsipursky, M.; Irudayaraj, J. Characterization of Oxygen Nanobubbles and In Vitro Evaluation of Retinal Cells in Hypoxia. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 16–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verinda, S. B. , Yulianto, E., Gunawan, G., & Nur, M. (2021). Ozonated nanobubbles-a potential hospital waste water treatment during the COVID-19 outbreak in Indonesia to eradicate the persistent SARS-CoV-2 in HWWs. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health, 24, 24-197.
- Matsuki, N.; Ishikawa, T.; Ichiba, S.; Shiba, N.; Ujike, Y.; Yamaguchi, T. Oxygen supersaturated fluid using fine micro/nanobubbles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4495–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, P.; Novikova, G.; Goergen, C.J.; Irudayaraj, J. Ultrasound beam steering of oxygen nanobubbles for enhanced bladder cancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, P.N.; Cui, Y.; Elzey, B.D.; Goergen, C.J.; Long, C.M.; Irudayaraj, J. Oxygen nanobubbles revert hypoxia by methylation programming. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghia, N. H., Van, P. T., Giang, P. T., Hanh, N. T., St-Hilaire, S., & Domingos, J. A. (2021). Control of Vibrio parahaemolyticus (AHPND strain) and improvement of water quality using nanobubble technology. Aquaculture Research, 52(6), 2727-2739.
- Khan, M.S.; Hwang, J.; Seo, Y.; Shin, K.; Lee, K.; Park, C.; Choi, Y.; Hong, J.W.; Choi, J. Engineering oxygen nanobubbles for the effective reversal of hypoxia. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. 3), S318–S327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, R.; Marano, F.; Argenziano, M.; Varese, A.; Frairia, R.; Catalano, M.G. Combining Drug-Loaded Nanobubbles and Extracorporeal Shock Waves for Difficult-to-Treat Cancers. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2017, 15, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, G.; Kumar, J.A. Nanobubbles: a promising efficient tool for therapeutic delivery of antibacterial agents for the Staphylococcus aureus infections. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 6177–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T. , Zhou, J., Zhang, C., Zhi, X., Niu, J., Fu, H.,... & Cui, D. (2018). Surface-engineered nanobubbles with pH-/light-responsive drug release and charge-switchable behaviors for active NIR/MR/US imaging-guided tumor therapy. NPG Asia Materials, 10(11), 1046-1060.
- Tiwari, S.P. Nanobubbles as theranostic platforms for tumour-specific imaging and therapy. Int. J. Heal. Sci. 2022, 10944–10954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellow, C.; Abenojar, E.C.; Exner, A.A.; Zheng, G.; Goertz, D.E. Concurrent visual and acoustic tracking of passive and active delivery of nanobubbles to tumors. Theranostics 2020, 10, 11690–11706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. F. , Zhou, J., Chen, X. R., & Yu, J. (2018). Drug-loaded nanobubbles for ultrasound-mediated antitumor treatment. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents, 32(4), 923-929.
- Pal, P.; Joshi, A.; Anantharaman, H. Nanobubble ozonation for waterbody rejuvenation at different locations in India: A holistic and sustainable approach. Results Eng. 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Fang, K.; Lan, M.; Shen, D.; Liu, D.; Yu, Z.; Guo, Y. Preparation Of Nanobubbles Modified With A Small-Molecule CXCR4 Antagonist For Targeted Drug Delivery To Tumors And Enhanced Ultrasound Molecular Imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, ume 14, 9139–9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, P.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y. Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Delivery through Micro/Nanobubble-Assisted Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, D.; Fang, K.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Qiao, B.; Guo, Y. Multifunctional nanobubbles carrying indocyanine green and paclitaxel for molecular imaging and the treatment of prostate cancer. J. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigatelli, G.; Zuin, M.; Bilato, C.; Nguyen, T. Coronary artery cavitation as a trigger for atherosclerotic plaque progression: a simplified numerical and computational fluid dynamic demonstration. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, G.; Slevin, M.; Krupinski, J. Nanotechnology for the treatment of coronary in stent restenosis: a clinical perspective. Vasc. Cell 2011, 3, 8–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yang, L.; Zhong, L.; Kutty, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, K.; Xiu, J.; Cao, S.; Huang, Q.; Liao, W.; et al. Delivery of Hydrogen Sulfide by Ultrasound Targeted Microbubble Destruction Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetuga, I.A.; Olakoyejo, O.O.; Oluwatusin, O.; Adelaja, A.O.; Gbegudu, J.K.; Aderemi, K.S.; Adeyemi, E.A. Computational model of nano-pharmacological particles for the clinical management of stenotic and aneurysmatic coronary artery in the human body. Niger. J. Technol. Dev. 2023, 20, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Oshita, S.; Thuyet, D.Q.; Saito, M.; Yoshimoto, T. Antioxidant Activity of Hydrogen Nanobubbles in Water with Different Reactive Oxygen Species both in Vivo and in Vitro. Langmuir 2018, 34, 11878–11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, H.; Chi, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Yang, W.; Liu, W.; Yang, W. Hydrogen Gas Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Independent of Postconditioning in Rats by Attenuating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Autophagy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, X.; Wang, W.-X.; Liu, S. Enhanced Removal of Free Radicals by Aqueous Hydrogen Nanobubbles and Their Role in Oxidative Stress. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 15096–15107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y. Advances and applications of Nanotechnology to solve Coronary Heart Disease. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 36, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, Y.; Sano, F.; Abe, T.; Tamura, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Ueda, I.; Homma, K.; Suzuki, M.; et al. The Effects of Hydrogen Gas Inhalation on Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for ST-Elevated Myocardial Infarction ― First Pilot Study in Humans ―. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.F.; Yin, Y.P.; Cui, Y.L.; Chen, L.F.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, C.L.; Zhu, W.L.; Song, C.X.; Zhang, H.; She, M.P.; et al. [Efficacy and mechanism of local delivery of rapamycin and rapamycin-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles on coronary restenosis of injury-stenosis model of minipigs]. . 2016, 96, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, I.; Timcic, S.; Odanovic, N.; Otasevic, P.; Collet, C. Serial stenosis assessment—can we rely on invasive coronary physiology. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1172906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumata, Y.; Sano, F.; Abe, T.; Tamura, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Ueda, I.; Homma, K.; Suzuki, M.; et al. The Effects of Hydrogen Gas Inhalation on Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for ST-Elevated Myocardial Infarction ― First Pilot Study in Humans ―. Circ. J. 2017, 81, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Guo, Z.; Jia, G.; Ma, R.; Li, M. Influencing factors of coronary artery stenosis in patients with stable coronary heart disease and a correlation analysis. 2021, 13, 9522–9529.
- Tang, Y. Advances and applications of Nanotechnology to solve Coronary Heart Disease. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 36, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lv, T.; She, F.; Liu, F.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, B.; Xie, Y.; Geng, Y.; et al. Coronary stenosis is a risk marker for impaired cardiac function on cardiopulmonary exercise test. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Du, Y.; Chen, B.; Toorabally, M.B.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, N.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Tao, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Intracoronary Ad-HGF Administration for Treating Severe Coronary Disease: Results From Long-Term Follow-Up of a Phase I Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Trials 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, B.J.; Young, R.F.; Suzuki, G.; Fallavollita, J.A.; Canty, J.M. The physiological significance of a coronary stenosis differentially affects contractility and mitochondrial function in viable chronically dysfunctional myocardium. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2013, 108, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornish, D.; Scherwitz, L.W.; Billings, J.H.; Gould, K.L.; Merritt, T.A.; Sparler, S.; Armstrong, W.T.; Ports, T.A.; Kirkeeide, R.L.; Hogeboom, C.; et al. Intensive Lifestyle Changes for Reversal of Coronary Heart Disease. JAMA 1998, 280, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




