Submitted:
13 June 2024
Posted:
13 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Respiratory Tract Infections and Mucosal Immune Responses
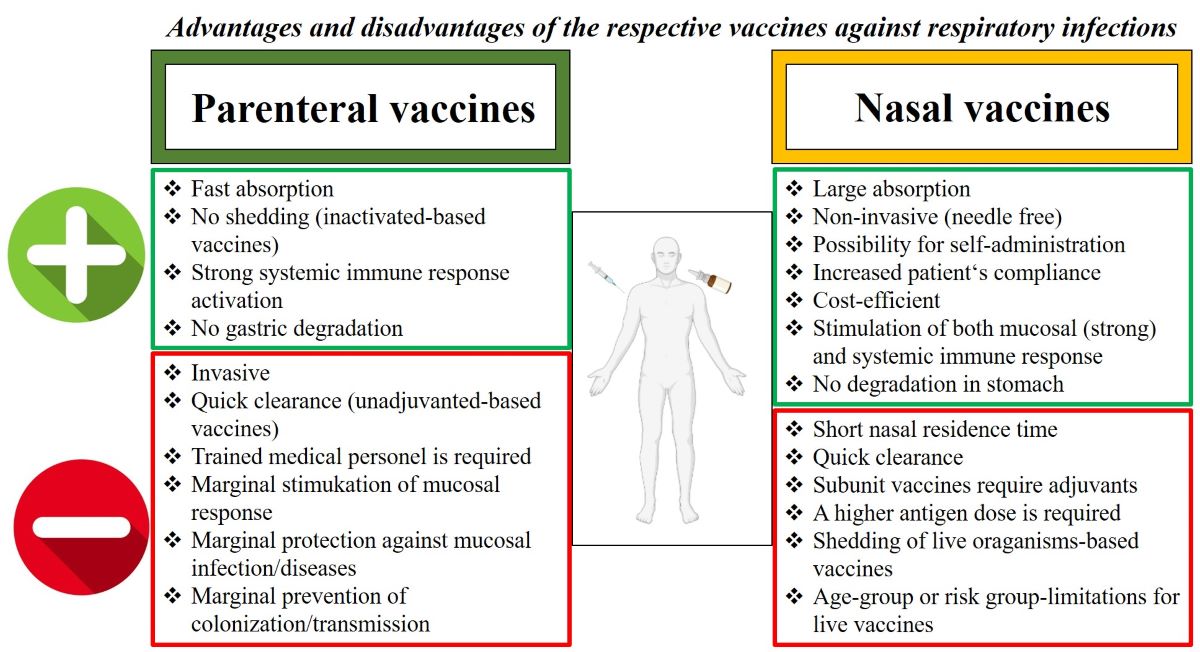
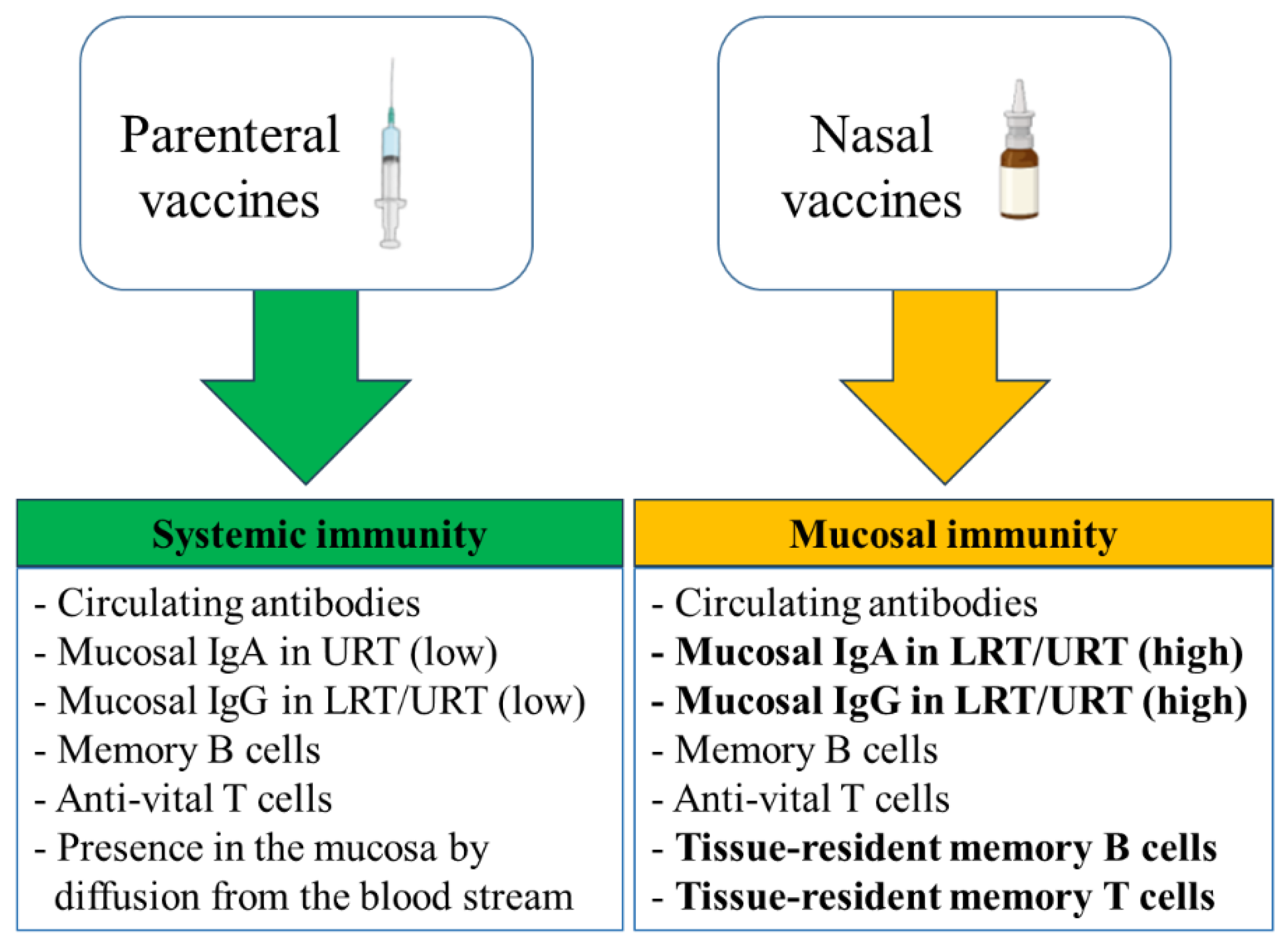
2. Mucosal versus Systemic Vaccines
3. SARS-CoV-2
3.1. Pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2
3.2. Virulence Factors of SARS-CoV-2
3.3. SARS-CoV-2 Variants
3.4. Immunity against SARS-CoV-2
4. Treatments against SARS-CoV-2 by Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) and Vaccination
4.1. Therapeutic mAbs
4.2. Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2
4.2.1. Systemic Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2
| Vaccine type/ platform |
Expressed SARS-CoV-2 component | Approved COVId-19 vaccine | Developer | Dosage number and schedule | Reference |
|
Nucleoside |
modified mRNA encoding S protein |
COMIRNATY (BNT162b2) |
BioNTech SE, Pfizer Inc. | Two doses, 3 weeks apart | [155] |
| modified mRNA encoding S protein |
Moderna vaccine (mRNA-1273) |
Moderna | Two doses, 4 weeks apart | [156] | |
|
Modified adenovirus vector |
Encoding S protein |
VAXZEVRIA (ChAdOx1-nCoV-19) |
AstraZeneca, University of Oxford |
Two doses given 4 to 12 weeks Apart |
[157] |
| Covishield (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) |
Serum Institute of India | Two doses given 12 weeks apart | [158] | ||
| Ad26CoV2.S | Johnson & Johnson |
One time dose | [159] | ||
| CONVIDECIA (Ad5-nCoV) |
CanSino Biologics Inc. |
One time dose | [160] | ||
| Sputnik V | Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology |
Two doses given 3 weeks apart | [161] | ||
|
Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 |
BBIBP-CorV | Sinopharm | Two doses, 3 weeks apart | [162] | |
| CoviVac | Russian Academy of Sciences |
Two doses given two weeks apart | [163] | ||
| CoronaVac | Sinovac Biotech Ltd. | Two doses given 2 weeks apart | [164] | ||
| COVAXIN (BBV152) |
Bharat Biotech | Two doses given 4 weeks apart | [165] | ||
| VLA2001 | Valneva | Two doses given 4 weeks apart | [166] | ||
| Adjuvanted protein subunit |
Dimeric RBD (with squalene-based oil-in-water adjuvant, Sepivac SWE™) | ZF2001 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | Three doses given 30 days apart | [167] |
| Recombinant RBD fusion heterodimer of the Beta and the Alpha variants of SARS-CoV-2 (with an oil-in-water emulsion based on squalene (SQBA)) | PHH-1V (Bimervax) | HIPRA | Booster dose (for 16 years and older age group) | [168] | |
| Peptide Subunit |
A peptide vaccine composed of three short peptides derived from SARS-2-S (S454–478, S1181–1202, and S1191–1211) conjugated to SARS-2 nucleocapsid protein | EpiVacCorona | Vektor State Research Centre, Russia | Two doses, 3-4 weeks apart | [169] |
|
Recombinant protein |
S protein nanoparticle | NUVAXOVID (Nvx-CoV-2373) |
Novavax | Two doses, 3 weeks apart | [170] |
| Covovax | Serum Institute of India |
Two doses, 3 weeks apart | [163] | ||
4.2.2. Mucosal Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2
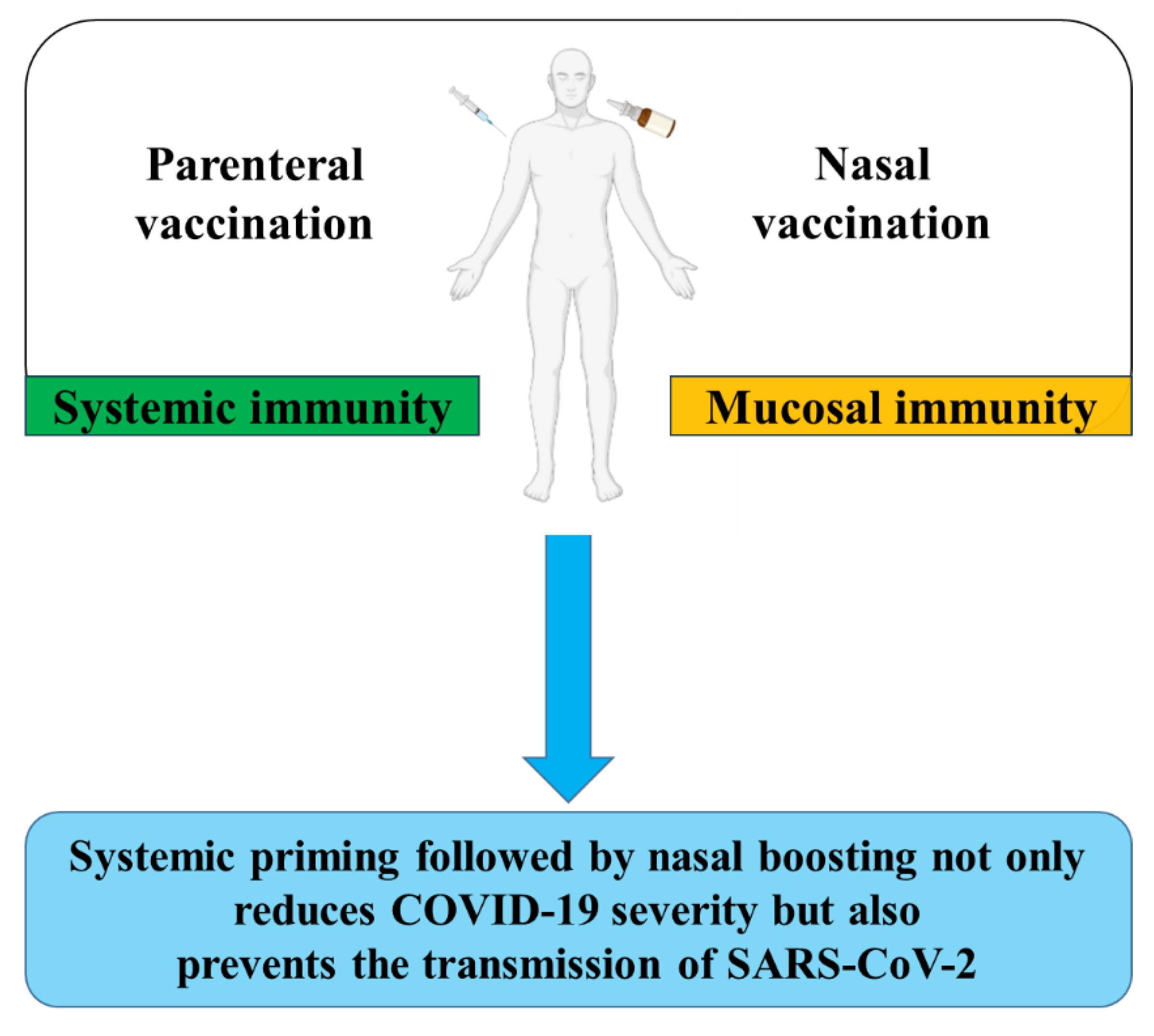
5. Prime-Boost Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2
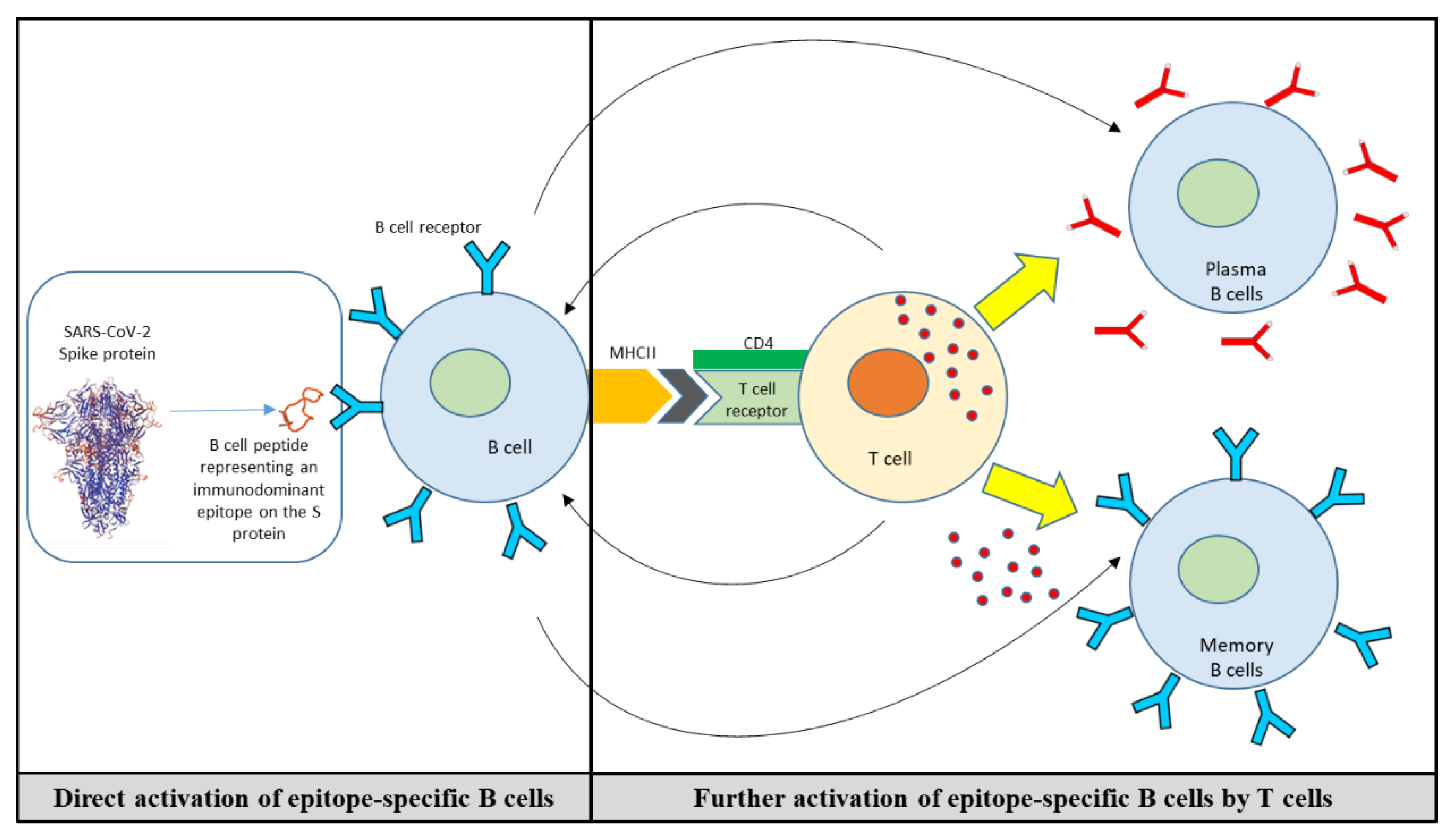
6. B Cell Peptide/Mimotope-Based Vaccine
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Collaborators, G.B.D.A.R. Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2022, 400, 2221-2248. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Ren, J.; Li, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, G. Global burden of upper respiratory infections in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to 2019. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100986. [CrossRef]
- Mettelman, R.C.; Allen, E.K.; Thomas, P.G. Mucosal immune responses to infection and vaccination in the respiratory tract. Immunity 2022, 55, 749-780. [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, J.; Czerkinsky, C. Mucosal immunity and vaccines. Nat Med 2005, 11, S45-53. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Xie, F. Innate and adaptive immune response in SARS-CoV-2 infection-Current perspectives. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1053437. [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.; Ojha, V.; Fricke, I.; Al-Sheboul, S.A.; Imarogbe, C.; Gravier, T.; Green, M.; Peterson, L.; Koutsaroff, I.P.; Demir, A.; et al. Innate and Adaptive Immunity during SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Biomolecular Cellular Markers and Mechanisms. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Twigg, H.L., 3rd. Humoral immune defense (antibodies): recent advances. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2005, 2, 417-421. [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, B.; Tomela, K.; Olejnik-Schmidt, A.; Mackiewicz, A.; Schmidt, M. Secretory IgA in Intestinal Mucosal Secretions as an Adaptive Barrier against Microbial Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Brandtzaeg, P. Secretory IgA: Designed for Anti-Microbial Defense. Front Immunol 2013, 4, 222. [CrossRef]
- Steffen, U.; Koeleman, C.A.; Sokolova, M.V.; Bang, H.; Kleyer, A.; Rech, J.; Unterweger, H.; Schicht, M.; Garreis, F.; Hahn, J.; et al. IgA subclasses have different effector functions associated with distinct glycosylation profiles. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 120. [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.E.; Liu, M.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; de Vries, E.; de Haan, C.A.M. Respiratory mucus as a virus-host range determinant. Trends Microbiol 2021, 29, 983-992. [CrossRef]
- Woodland, D.L. Vaccine Development. Viral Immunol 2017, 30, 141. [CrossRef]
- Orenstein, W.A.; Ahmed, R. Simply put: Vaccination saves lives. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, 4031-4033. [CrossRef]
- Bourouiba, L. Turbulent Gas Clouds and Respiratory Pathogen Emissions: Potential Implications for Reducing Transmission of COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 323, 1837-1838. [CrossRef]
- Le Sage, V.; Lowen, A.C.; Lakdawala, S.S. Block the Spread: Barriers to Transmission of Influenza Viruses. Annu Rev Virol 2023, 10, 347-370. [CrossRef]
- Azegami, T.; Yuki, Y.; Kiyono, H. Challenges in mucosal vaccines for the control of infectious diseases. Int Immunol 2014, 26, 517-528. [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, E.C.; Ward, R.W. Mucosal vaccines - fortifying the frontiers. Nat Rev Immunol 2022, 22, 236-250. [CrossRef]
- Lund, F.E.; Randall, T.D. Scent of a vaccine. Science 2021, 373, 397-399. [CrossRef]
- Bladh, O.; Aguilera, K.; Marking, U.; Kihlgren, M.; Greilert Norin, N.; Smed-Sorensen, A.; Sallberg Chen, M.; Klingstrom, J.; Blom, K.; Russell, M.W.; et al. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific IgA and IgG in nasal secretions, saliva and serum. Front Immunol 2024, 15, 1346749. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J. Harnessing Nasal Immunity with IgA to Prevent Respiratory Infections. Immuno 2022, 2, 571-583. [CrossRef]
- Tokunoh, N.; Tamiya, S.; Watanabe, M.; Okamoto, T.; Anindita, J.; Tanaka, H.; Ono, C.; Hirai, T.; Akita, H.; Matsuura, Y.; et al. A nasal vaccine with inactivated whole-virion elicits protective mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in mice. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1224634. [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, H.; Kett, V. Current prospects and future challenges for nasal vaccine delivery. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2017, 13, 34-45. [CrossRef]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claer, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Sci Transl Med 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Tamiya, E.; Osaki, S.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Ushijima, H.; Tsukinoki, K. Point-of-Care Diagnostic Biosensors to Monitor Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing IgG/sIgA Antibodies and Antioxidant Activity in Saliva. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E.; Vidarsson, G. Antibodies and their receptors: different potential roles in mucosal defense. Front Immunol 2013, 4, 200. [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.W.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Ogra, P.L.; Mestecky, J. Mucosal Immunity in COVID-19: A Neglected but Critical Aspect of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 611337. [CrossRef]
- Jarlhelt, I.; Nielsen, S.K.; Jahn, C.X.H.; Hansen, C.B.; Perez-Alos, L.; Rosbjerg, A.; Bayarri-Olmos, R.; Skjoedt, M.O.; Garred, P. SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Mediate Complement and Cellular Driven Inflammation. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 767981. [CrossRef]
- Markiewski, M.M.; Lambris, J.D. The role of complement in inflammatory diseases from behind the scenes into the spotlight. Am J Pathol 2007, 171, 715-727. [CrossRef]
- Pollard, A.J.; Bijker, E.M. A guide to vaccinology: from basic principles to new developments. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 83-100. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, S. Effect of vaccine administration modality on immunogenicity and efficacy. Expert Rev Vaccines 2015, 14, 1509-1523. [CrossRef]
- Spiekermann, G.M.; Finn, P.W.; Ward, E.S.; Dumont, J.; Dickinson, B.L.; Blumberg, R.S.; Lencer, W.I. Receptor-mediated immunoglobulin G transport across mucosal barriers in adult life: functional expression of FcRn in the mammalian lung. J Exp Med 2002, 196, 303-310. [CrossRef]
- Dotiwala, F.; Upadhyay, A.K. Next Generation Mucosal Vaccine Strategy for Respiratory Pathogens. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Pabst, R. Mucosal vaccination by the intranasal route. Nose-associated lymphoid tissue (NALT)-Structure, function and species differences. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4406-4413. [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.P.S.; St John, A.L. Promises and challenges of mucosal COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccine 2023, 41, 4042-4049. [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.R.; Flannery, B.; Ambrose, C.S.; Begue, R.E.; Caspard, H.; DeMarcus, L.; Fowlkes, A.L.; Kersellius, G.; Steffens, A.; Fry, A.M.; et al. Live Attenuated and Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness. Pediatrics 2019, 143. [CrossRef]
- Ilyushina, N.A.; Haynes, B.C.; Hoen, A.G.; Khalenkov, A.M.; Housman, M.L.; Brown, E.P.; Ackerman, M.E.; Treanor, J.J.; Luke, C.J.; Subbarao, K.; et al. Live attenuated and inactivated influenza vaccines in children. J Infect Dis 2015, 211, 352-360. [CrossRef]
- Mohn, K.G.; Brokstad, K.A.; Pathirana, R.D.; Bredholt, G.; Jul-Larsen, A.; Trieu, M.C.; Lartey, S.L.; Montomoli, E.; Tondel, C.; Aarstad, H.J.; et al. Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine in Children Induces B-Cell Responses in Tonsils. J Infect Dis 2016, 214, 722-731. [CrossRef]
- Mohn, K.G.; Smith, I.; Sjursen, H.; Cox, R.J. Immune responses after live attenuated influenza vaccination. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2018, 14, 571-578. [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Brokstad, K.A.; Cox, R.J. Influenza Vaccination Strategies: Comparing Inactivated and Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines (Basel) 2015, 3, 373-389. [CrossRef]
- Kawai, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nogimori, T.; Takeshita, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Yoshioka, Y. The Potential of Neuraminidase as an Antigen for Nasal Vaccines To Increase Cross-Protection against Influenza Viruses. J Virol 2021, 95, e0118021. [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, C.M.; Kistner, O.; Montomoli, E.; Viviani, S.; Marchi, S. Influenza Viruses and Vaccines: The Role of Vaccine Effectiveness Studies for Evaluation of the Benefits of Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.J.; Huo, Z.; Barnett, S.; Kromann, I.; Giemza, R.; Galiza, E.; Woodrow, M.; Thierry-Carstensen, B.; Andersen, P.; Novicki, D.; et al. Transient facial nerve paralysis (Bell's palsy) following intranasal delivery of a genetically detoxified mutant of Escherichia coli heat labile toxin. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6999. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Diaz-Arevalo, D.; Guan, H.; Zeng, M. Noninvasive vaccination against infectious diseases. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2018, 14, 1717-1733. [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Williams, C.M.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Furuya, Y. Impact of Pre-Existing Immunity to Influenza on Live-Attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV) Immunogenicity. Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8. [CrossRef]
- Mok, D.Z.L.; Chan, K.R. The Effects of Pre-Existing Antibodies on Live-Attenuated Viral Vaccines. Viruses 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Coelingh, K.L.; Wu, X.W.; Mallory, R.M.; Ambrose, C.S. An integrated multi-study analysis of serum HAI antibody responses to Ann Arbor strain live attenuated influenza vaccine in children and adults. Trials in Vaccinology 2014, 3, 150-153. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ni, W.J.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Cai, M.; Sun, Y.C. Advances in Pathogenesis, Progression, Potential Targets and Targeted Therapeutic Strategies in SARS-CoV-2-Induced COVID-19. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 834942. [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.W.; Tian, J.H.; Pei, Y.Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265-269.
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270-273. [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Zumla, A.; Locatelli, F.; Ippolito, G.; Kroemer, G. Coronavirus infections: Epidemiological, clinical and immunological features and hypotheses. Cell Stress 2020. [CrossRef]
- Tsatsakis, A.; Calina, D.; Falzone, L.; Petrakis, D.; Mitrut, R.; Siokas, V.; Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Libra, M.; Doukas, S.G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 pathophysiology and its clinical implications: An integrative overview of the pharmacotherapeutic management of COVID-19. Food Chem Toxicol 2020, 146, 111769. [CrossRef]
- Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L. SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 2022, 20, 270-284. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497-506. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R.; Li, T.; Zeng, D.; Li, M. Clinical features of familial clustering in patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Virus Res 2020, 286, 198043. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Z.; Yu, Y.; Huang, B.; Fu, S.; Tan, Y.; Sun, J.; et al. Clinical Features of Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2020, 15, 1139-1145. [CrossRef]
- Alefishat, E.; Jelinek, H.F.; Mousa, M.; Tay, G.K.; Alsafar, H.S. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 variants: A focus on severity, susceptibility, and preexisting immunity. J Infect Public Health 2022, 15, 277-288. [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.J.; Uyeki, T.M.; Chu, H.Y. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on community respiratory virus activity. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023, 21, 195-210. [CrossRef]
- Ragab, D.; Salah Eldin, H.; Taeimah, M.; Khattab, R.; Salem, R. The COVID-19 Cytokine Storm; What We Know So Far. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 1446. [CrossRef]
- Elkoshi, Z. The Binary Model of Chronic Diseases Applied to COVID-19. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 716084. [CrossRef]
- Manjili, R.H.; Zarei, M.; Habibi, M.; Manjili, M.H. COVID-19 as an Acute Inflammatory Disease. J Immunol 2020, 205, 12-19. [CrossRef]
- Brodin, P. Immune determinants of COVID-19 disease presentation and severity. Nat Med 2021, 27, 28-33. [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, N.; Di Napoli, M.; Biller, J.; Siegler, J.E.; Shekhar, R.; McCullough, L.D.; Harkins, M.S.; Hong, E.; Alaouieh, D.A.; Mansueto, G.; et al. The Neurological Manifestations of Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2021, 21, 44. [CrossRef]
- Dale, L. Neurological Complications of COVID-19: A Review of the Literature. Cureus 2022, 14, e27633. [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023, 21, 133-146. [CrossRef]
- Minotti, C.; McKenzie, C.; Dewandel, I.; Bekker, C.; Sturniolo, G.; Doni, D.; Giaquinto, C.; Van Der Zalm, M.M.; Dona, D. How does post COVID differ from other post-viral conditions in childhood and adolescence (0-20 years old)? A systematic review. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 68, 102436. [CrossRef]
- Pleasure, S.J.; Green, A.J.; Josephson, S.A. The Spectrum of Neurologic Disease in the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Pandemic Infection: Neurologists Move to the Frontlines. JAMA Neurol 2020, 77, 679-680. [CrossRef]
- Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; Simani, L. Central nervous system manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review. J Neurol Sci 2020, 413, 116832. [CrossRef]
- Caronna, E.; Alpuente, A.; Torres-Ferrus, M.; Pozo-Rosich, P. Toward a better understanding of persistent headache after mild COVID-19: Three migraine-like yet distinct scenarios. Headache 2021, 61, 1277-1280. [CrossRef]
- Orendacova, M.; Kvasnak, E. Possible Mechanisms Underlying Neurological Post-COVID Symptoms and Neurofeedback as a Potential Therapy. Front Hum Neurosci 2022, 16, 837972. [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.; Kevadiya, B.D.; Gendelman, H.E.; Byrareddy, S.N. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Leads to Neurological Dysfunction. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2020, 15, 167-173. [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Du, T.; Hong, W.; Chen, L.; Que, H.; Lu, S.; Peng, X. Neurological complications and infection mechanism of SARS-COV-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 406. [CrossRef]
- Molaverdi, G.; Kamal, Z.; Safavi, M.; Shafiee, A.; Mozhgani, S.H.; Ghobadi, M.Z.; Goudarzvand, M. Neurological complications after COVID-19: A narrative review. eNeurologicalSci 2023, 33, 100485. [CrossRef]
- Collantes, M.E.V.; Espiritu, A.I.; Sy, M.C.C.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; Jamora, R.D.G. Neurological Manifestations in COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Can J Neurol Sci 2021, 48, 66-76. [CrossRef]
- Delorme, C.; Houot, M.; Rosso, C.; Carvalho, S.; Nedelec, T.; Maatoug, R.; Pitron, V.; Gassama, S.; Sambin, S.; Bombois, S.; et al. The wide spectrum of COVID-19 neuropsychiatric complications within a multidisciplinary centre. Brain Commun 2021, 3, fcab135. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-de-Las-Penas, C.; Palacios-Cena, D.; Gomez-Mayordomo, V.; Cuadrado, M.L.; Florencio, L.L. Defining Post-COVID Symptoms (Post-Acute COVID, Long COVID, Persistent Post-COVID): An Integrative Classification. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18. [CrossRef]
- Cabanes-Martinez, L.; Villadoniga, M.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, L.; Araque, L.; Diaz-Cid, A.; Ruz-Caracuel, I.; Pian, H.; Sanchez-Alonso, S.; Fanjul, S.; Del Alamo, M.; et al. Neuromuscular involvement in COVID-19 critically ill patients. Clin Neurophysiol 2020, 131, 2809-2816. [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Chang, J.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol 2020, 77, 683-690. [CrossRef]
- Le, K.; Kannappan, S.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, K.K. Structural understanding of SARS-CoV-2 virus entry to host cells. Front Mol Biosci 2023, 10, 1288686. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Zhao, R.; Gao, L.J.; Gao, X.F.; Wang, D.P.; Cao, J.M. SARS-CoV-2: Structure, Biology, and Structure-Based Therapeutics Development. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 587269. [CrossRef]
- Baig, A.M.; Khaleeq, A.; Ali, U.; Syeda, H. Evidence of the COVID-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms. ACS Chem Neurosci 2020, 11, 995-998. [CrossRef]
- Kyrou, I.; Randeva, H.S.; Spandidos, D.A.; Karteris, E. Not only ACE2-the quest for additional host cell mediators of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) as a novel SARS-CoV-2 host cell entry mediator implicated in COVID-19. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 21. [CrossRef]
- Paniz-Mondolfi, A.; Bryce, C.; Grimes, Z.; Gordon, R.E.; Reidy, J.; Lednicky, J.; Sordillo, E.M.; Fowkes, M. Central nervous system involvement by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). J Med Virol 2020, 92, 699-702. [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, P.; Hao, J.; Han, Z. Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front Med 2020, 14, 185-192. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Du, L.; Shi, Z. An emerging coronavirus causing pneumonia outbreak in Wuhan, China: calling for developing therapeutic and prophylactic strategies. Emerg Microbes Infect 2020, 9, 275-277. [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, M.T.; Mermelstein, A.G.; Parker Miller, E.; Seth, P.C.; Stancofski, E.D.; Fera, D. Structural Analysis of Neutralizing Epitopes of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike to Guide Therapy and Vaccine Design Strategies. Viruses 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M. Proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Microbiol Immunol 2022, 66, 15-23. [CrossRef]
- Samavati, L.; Uhal, B.D. ACE2, Much More Than Just a Receptor for SARS-COV-2. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 317. [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 183, 1735. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271-280 e278. [CrossRef]
- Benton, D.J.; Wrobel, A.G.; Xu, P.; Roustan, C.; Martin, S.R.; Rosenthal, P.B.; Skehel, J.J.; Gamblin, S.J. Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion. Nature 2020, 588, 327-330. [CrossRef]
- Almagro, J.C.; Mellado-Sanchez, G.; Pedraza-Escalona, M.; Perez-Tapia, S.M. Evolution of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Antibodies. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Bhattacharya, M.; Nag, S.; Dhama, K.; Chakraborty, C. A Detailed Overview of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron: Its Sub-Variants, Mutations and Pathophysiology, Clinical Characteristics, Immunological Landscape, Immune Escape, and Therapies. Viruses 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Zappa, M.; Verdecchia, P.; Angeli, F. Is the competition between variants the end of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pandemic? A journey from Wuhan to XBB.1.16. Eur J Intern Med 2023, 113, 13-15. [CrossRef]
- Andre, M.; Lau, L.S.; Pokharel, M.D.; Ramelow, J.; Owens, F.; Souchak, J.; Akkaoui, J.; Ales, E.; Brown, H.; Shil, R.; et al. From Alpha to Omicron: How Different Variants of Concern of the SARS-Coronavirus-2 Impacted the World. Biology (Basel) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Lyngse, F.P.; Kirkeby, C.T.; Denwood, M.; Christiansen, L.E.; Molbak, K.; Moller, C.H.; Skov, R.L.; Krause, T.G.; Rasmussen, M.; Sieber, R.N.; et al. Household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant of concern subvariants BA.1 and BA.2 in Denmark. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 5760. [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zou, J.; Kurhade, C.; Cai, H.; Yang, Q.; Cutler, M.; Cooper, D.; Muik, A.; Jansen, K.U.; Xie, X.; et al. Neutralization and durability of 2 or 3 doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine against Omicron SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 485-488 e483. [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, R.K.; Chen, I.P.; Ma, T.; Syed, A.M.; Brazer, N.; Saldhi, P.; Simoneau, C.R.; Ciling, A.; Khalid, M.M.; Sreekumar, B.; et al. Limited cross-variant immunity from SARS-CoV-2 Omicron without vaccination. Nature 2022, 607, 351-355. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Duan, M.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, X.; Xu, K.; Gao, G.F. Neutralization of BQ.1, BQ.1.1, and XBB with RBD-Dimer Vaccines. N Engl J Med 2023, 388, 1142-1145. [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Xu, K.; Faraone, J.N.; Goodarzi, N.; Zheng, Y.M.; Carlin, C.; Bednash, J.S.; Horowitz, J.C.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Saif, L.J.; et al. Immune Evasion, Infectivity, and Fusogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.86 and FLip Variants. bioRxiv 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S. SARS-CoV-2 evolution from the BA.2.86 to JN.1 variants: unexpected consequences. Trends Immunol 2024, 45, 81-84. [CrossRef]
- Sievers, B.L.; Cheng, M.T.K.; Csiba, K.; Meng, B.; Gupta, R.K. SARS-CoV-2 and innate immunity: the good, the bad, and the "goldilocks". Cell Mol Immunol 2024, 21, 171-183. [CrossRef]
- Sunagar, R.; Singh, A.; Kumar, S. SARS-CoV-2: Immunity, Challenges with Current Vaccines, and a Novel Perspective on Mucosal Vaccines. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Abebe, E.C.; Dejenie, T.A. Protective roles and protective mechanisms of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 infection and their potential clinical implications. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1055457. [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. Neutralizing antibodies for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Cell Mol Immunol 2021, 18, 2293-2306. [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ryu, D.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.I.; Seo, J.M.; Kim, Y.G.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, P.; et al. A therapeutic neutralizing antibody targeting receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 288. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Yu, J.; Rapp, M.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Chan, J.F.; Sahi, V.; Figueroa, A.; et al. Potent Neutralizing Antibodies Directed to Multiple Epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 Spike. bioRxiv 2020. [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping Neutralizing and Immunodominant Sites on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain by Structure-Guided High-Resolution Serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024-1042 e1021. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Guzek, A.; Ruff, J.; Jasinska, J.; Scheikl, U.; Zwazl, I.; Kundi, M.; Stockinger, H.; Farcet, M.R.; Kreil, T.R.; et al. Neutralising SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific antibodies persist for at least six months independently of symptoms in adults. Commun Med (Lond) 2021, 1, 13. [CrossRef]
- Joyner, M.J.; Senefeld, J.W.; Klassen, S.A.; Mills, J.R.; Johnson, P.W.; Theel, E.S.; Wiggins, C.C.; Bruno, K.A.; Klompas, A.M.; Lesser, E.R.; et al. Effect of Convalescent Plasma on Mortality among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: Initial Three-Month Experience. medRxiv 2020. [CrossRef]
- Weinreich, D.M.; Sivapalasingam, S.; Norton, T.; Ali, S.; Gao, H.; Bhore, R.; Musser, B.J.; Soo, Y.; Rofail, D.; Im, J.; et al. REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021, 384, 238-251. [CrossRef]
- Wellinghausen, N.; Plonne, D.; Voss, M.; Ivanova, R.; Frodl, R.; Deininger, S. SARS-CoV-2-IgG response is different in COVID-19 outpatients and asymptomatic contact persons. J Clin Virol 2020, 130, 104542. [CrossRef]
- Wolfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Muller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465-469. [CrossRef]
- Moss, P. The T cell immune response against SARS-CoV-2. Nat Immunol 2022, 23, 186-193. [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J. Passive antibody therapy in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol 2020, 20, 401-403. [CrossRef]
- Fragkou, P.C.; Belhadi, D.; Peiffer-Smadja, N.; Moschopoulos, C.D.; Lescure, F.X.; Janocha, H.; Karofylakis, E.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Mentre, F.; Skevaki, C.; et al. Review of trials currently testing treatment and prevention of COVID-19. Clin Microbiol Infect 2020. [CrossRef]
- Bloch, E.M.; Shoham, S.; Casadevall, A.; Sachais, B.S.; Shaz, B.; Winters, J.L.; van Buskirk, C.; Grossman, B.J.; Joyner, M.; Henderson, J.P.; et al. Deployment of convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. J Clin Invest 2020. [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zost, S.J.; Greaney, A.J.; Starr, T.N.; Dingens, A.S.; Chen, E.C.; Chen, R.E.; Case, J.B.; Sutton, R.E.; Gilchuk, P.; et al. Genetic and structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 variant neutralization by a two-antibody cocktail. Nat Microbiol 2021, 6, 1233-1244. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Adams, A.C.; Hufford, M.M.; de la Torre, I.; Winthrop, K.; Gottlieb, R.L. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 382-393. [CrossRef]
- Bhimraj, A.; Morgan, R.L.; Shumaker, A.H.; Baden, L.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Edwards, K.M.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gandhi, R.T.; Muller, W.J.; Nakamura, M.M.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. Clin Infect Dis 2022. [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Geiger, C.; Jessop, N.; Pedotti, R.; Raposo, C.; Whitley, L.; Brown, J.S.; Muros-Le Rouzic, E. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in multiple sclerosis: A retrospective cohort study. Mult Scler Relat Disord 2023, 79, 104943. [CrossRef]
- Quiros-Roldan, E.; Amadasi, S.; Zanella, I.; Degli Antoni, M.; Storti, S.; Tiecco, G.; Castelli, F. Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2: Current Scenario and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2021, 14. [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wu, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Chai, Y.; Zheng, A.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, S.; Huang, M.; et al. An updated atlas of antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sub-variants including BQ.1.1 and XBB. Cell Rep Med 2023, 4, 100991. [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Whitley, R.; De Clercq, E. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2023, 22, 449-475. [CrossRef]
- Touret, F.; Giraud, E.; Bourret, J.; Donati, F.; Tran-Rajau, J.; Chiaravalli, J.; Lemoine, F.; Agou, F.; Simon-Loriere, E.; van der Werf, S.; et al. Enhanced neutralization escape to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 omicron sub-lineages. iScience 2023, 26, 106413. [CrossRef]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schafer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567-571. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Bhattacharya, M.; Dhama, K. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines, Vaccine Development Technologies, and Significant Efforts in Vaccine Development during the Pandemic: The Lessons Learned Might Help to Fight against the Next Pandemic. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Fiolet, T.; Kherabi, Y.; MacDonald, C.J.; Ghosn, J.; Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: a narrative review. Clin Microbiol Infect 2022, 28, 202-221. [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, N.; Ghasemiyeh, P.; Moradishooli, F.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Update on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines on different variants of SARS-CoV-2. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 117, 109968. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Masum, M.H.U.; Wajed, S.; Talukder, A. A comprehensive review on COVID-19 vaccines: development, effectiveness, adverse effects, distribution and challenges. Virusdisease 2022, 33, 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Rotshild, V.; Hirsh-Raccah, B.; Miskin, I.; Muszkat, M.; Matok, I. Comparing the clinical efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 22777. [CrossRef]
- Garner-Spitzer, E.; Wagner, A.; Kundi, M.; Stockinger, H.; Ohradanova-Repic, A.; Gebetsberger, L.; Schoetta, A.M.; Gudipati, V.; Huppa, J.B.; Kunert, R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody (Ab) Levels and the Kinetic of Ab Decline Determine Ab Persistence Over 1 Year. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 822316. [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Hamada, K.; Jubishi, D.; Hashimoto, H.; Okamoto, K.; Hisasue, N.; Sunohara, M.; Saito, M.; Shinohara, T.; Yamashita, M.; et al. Waning cellular immune responses and predictive factors in maintaining cellular immunity against SARS-CoV-2 six months after BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 9607. [CrossRef]
- Israel, A.; Merzon, E.; Schaffer, A.A.; Shenhar, Y.; Green, I.; Golan-Cohen, A.; Ruppin, E.; Magen, E.; Vinker, S. Elapsed time since BNT162b2 vaccine and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection: test negative design study. BMJ 2021, 375, e067873. [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, e84. [CrossRef]
- Vattiatio, G.; Lustig, A.; Maclaren, O.J.; Plank, M.J. Modelling the dynamics of infection, waning of immunity and re-infection with the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 in Aotearoa New Zealand. Epidemics 2022, 41, 100657. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Garner-Spitzer, E.; Schotta, A.M.; Orola, M.; Wessely, A.; Zwazl, I.; Ohradanova-Repic, A.; Weseslindtner, L.; Tajti, G.; Gebetsberger, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-mRNA Booster Vaccination Reverses Non-Responsiveness and Early Antibody Waning in Immunocompromised Patients - A Phase Four Study Comparing Immune Responses in Patients With Solid Cancers, Multiple Myeloma and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 889138. [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Suarez, C.; Murillo-Zamora, E. Waning immunity to SARS-CoV-2 following vaccination or infection. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 972083. [CrossRef]
- Van Egeren, D.; Stoddard, M.; White, L.F.; Hochberg, N.S.; Rogers, M.S.; Zetter, B.; Joseph-McCarthy, D.; Chakravarty, A. Vaccines Alone Cannot Slow the Evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Huo, N.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; Hou, L.; Chen, W. Monovalent XBB.1.5 booster vaccination induces a broad spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Emerg Microbes Infect 2024, 13, 2286260. [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, H.G.; Wallace, M.; Godfrey, M.; Roper, L.E.; Hall, E.; Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Link-Gelles, R.; Pilishvili, T.; Williams, J.; Moulia, D.L.; et al. Interim Recommendations from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices for the Use of Bivalent Booster Doses of COVID-19 Vaccines - United States, October 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022, 71, 1436-1441. [CrossRef]
- Carreno, J.M.; Singh, G.; Simon, V.; Krammer, F.; group, P.V.I.s. Bivalent COVID-19 booster vaccines and the absence of BA.5-specific antibodies. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e569. [CrossRef]
- Blankson, J.N. Bivalent COVID-19 Vaccines: Can the Original Antigenic Sin Be Forgiven? J Infect Dis 2023, 227, 1221-1223. [CrossRef]
- Palanica, A.; Jeon, J. Initial Mix-and-Match COVID-19 Vaccination Perceptions, Concerns, and Side Effects across Canadians. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, R.; Samieefar, N.; Masoumi, N.; Mohseni, S.; Rezaei, N. COVID-19 vaccines mix-and-match: The concept, the efficacy and the doubts. J Med Virol 2022, 94, 1294-1299. [CrossRef]
- Garg, I.; Sheikh, A.B.; Pal, S.; Shekhar, R. Mix-and-Match COVID-19 Vaccinations (Heterologous Boost): A Review. Infect Dis Rep 2022, 14, 537-546. [CrossRef]
- Deming, M.E.; Lyke, K.E. A 'mix and match' approach to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. Nat Med 2021, 27, 1510-1511. [CrossRef]
- Lasrado, N.; Barouch, D.H. SARS-CoV-2 Hybrid Immunity: The Best of Both Worlds. J Infect Dis 2023, 228, 1311-1313. [CrossRef]
- Samoud, S.; Bettaieb, J.; Gdoura, M.; Kharroubi, G.; Ben Ghachem, F.; Zamali, I.; Ben Hmid, A.; Salem, S.; Gereisha, A.A.; Dellagi, M.; et al. Immunogenicity of Mix-and-Match CoronaVac/BNT162b2 Regimen versus Homologous CoronaVac/CoronaVac Vaccination: A Single-Blinded, Randomized, Parallel Group Superiority Trial. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Yao, H.; Wu, N. Immune interference in effectiveness of influenza and COVID-19 vaccination. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1167214. [CrossRef]
- Schultz-Cherry, S.; McGargill, M.A.; Thomas, P.G.; Estepp, J.H.; Gaur, A.H.; Allen, E.K.; Allison, K.J.; Tang, L.; Webby, R.J.; Cherry, S.D.; et al. Cross-reactive Antibody Response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine After Recent COVID-19-Specific Monoclonal Antibody Therapy. Open Forum Infect Dis 2021, 8, ofab420. [CrossRef]
- Bobrovitz, N.; Ware, H.; Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Hosseini, R.; Cao, C.; Selemon, A.; Whelan, M.; Premji, Z.; Issa, H.; et al. Protective effectiveness of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection and hybrid immunity against the omicron variant and severe disease: a systematic review and meta-regression. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2023, 23, 556-567. [CrossRef]
- Spinardi, J.R.; Srivastava, A. Hybrid Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 from Infection and Vaccination—Evidence Synthesis and Implications for New COVID-19 Vaccines. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 370. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Garner-Spitzer, E.; Auer, C.; Gattinger, P.; Zwazl, I.; Platzer, R.; Orola-Taus, M.; Pichler, P.; Amman, F.; Bergthaler, A.; et al. Breakthrough Infections in SARS-CoV-2-Vaccinated Multiple Myeloma Patients Improve Cross-Protection against Omicron Variants. Vaccines 2024, 12, 518. [CrossRef]
- Rodda, L.B.; Morawski, P.A.; Pruner, K.B.; Fahning, M.L.; Howard, C.A.; Franko, N.; Logue, J.; Eggenberger, J.; Stokes, C.; Golez, I.; et al. Imprinted SARS-CoV-2-specific memory lymphocytes define hybrid immunity. Cell 2022, 185, 1588-1601 e1514. [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 2603-2615. [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N Engl J Med 2021, 384, 403-416. [CrossRef]
- Voysey, M.; Costa Clemens, S.A.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Single-dose administration and the influence of the timing of the booster dose on immunogenicity and efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine: a pooled analysis of four randomised trials. Lancet 2021, 397, 881-891. [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Goel, A.; Katiyar, H.; Tiwari, P.; Mayank; Sana, A.; Khetan, D.; Bhadauria, D.S.; Raja, A.; Khokher, N.; et al. Durability of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (Covishield((R))) Vaccine Induced Antibody Response in Health Care Workers. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Ledford, H. J&J's one-shot COVID vaccine offers hope for faster protection. Nature 2021. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.C.; Guan, X.H.; Li, Y.H.; Huang, J.Y.; Jiang, T.; Hou, L.H.; Li, J.X.; Yang, B.F.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.J.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a recombinant adenovirus type-5-vectored COVID-19 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18 years or older: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 479-488. [CrossRef]
- Logunov, D.Y.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Shcheblyakov, D.V.; Tukhvatulin, A.I.; Zubkova, O.V.; Dzharullaeva, A.S.; Kovyrshina, A.V.; Lubenets, N.L.; Grousova, D.M.; Erokhova, A.S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia. Lancet 2021, 397, 671-681. [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Tan, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, M.; Lou, Z.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BBIBP-CorV: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2021, 21, 39-51. [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskaya, L.I.; Piniaeva, A.N.; Ignatyev, G.M.; Gordeychuk, I.V.; Volok, V.P.; Rogova, Y.V.; Shishova, A.A.; Kovpak, A.A.; Ivin, Y.Y.; Antonova, L.P.; et al. Long-term humoral immunogenicity, safety and protective efficacy of inactivated vaccine against COVID-19 (CoviVac) in preclinical studies. Emerg Microbes Infect 2021, 10, 1790-1806. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Jin, H.; Cui, G.; Chen, P.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in healthy adults aged 60 years and older: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2021, 21, 803-812. [CrossRef]
- Ella, R.; Vadrevu, K.M.; Jogdand, H.; Prasad, S.; Reddy, S.; Sarangi, V.; Ganneru, B.; Sapkal, G.; Yadav, P.; Abraham, P.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BBV152: a double-blind, randomised, phase 1 trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2021, 21, 637-646. [CrossRef]
- Wressnigg, N.; Taucher, C.; Eder-Lingelbach, S.; Querton, B.; Krammer, M.; Lilja, A.; Hochreiter, R.; Hoffmann, M.; Pöhlmann, S.; Jaramillo, J.C. Effects of Homologous and Heterologous Booster Vaccinations of the Inactivated Dual-Adjuvanted Vaccine Vla2001 against Covid-19 Including Variants of Concern: A Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2023, 130, S25. [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Gao, L.; Tao, L.; Hadinegoro, S.R.; Erkin, M.; Ying, Z.; He, P.; Girsang, R.T.; Vergara, H.; Akram, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the RBD-Dimer-Based Covid-19 Vaccine ZF2001 in Adults. N Engl J Med 2022, 386, 2097-2111. [CrossRef]
- Prenafeta, A.; Bech-Sabat, G.; Moros, A.; Barreiro, A.; Fernandez, A.; Canete, M.; Roca, M.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, L.; Garriga, C.; Confais, J.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of PHH-1V vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 in non-human primates. iScience 2023, 26, 107224. [CrossRef]
- Shalash, A.O.; Toth, I.; Skwarczynski, M. The potential of developing a protective peptide-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Drug Dev Res 2022, 83, 1251-1256. [CrossRef]
- Dunkle, L.M.; Kotloff, K.L.; Gay, C.L.; Anez, G.; Adelglass, J.M.; Barrat Hernandez, A.Q.; Harper, W.L.; Duncanson, D.M.; McArthur, M.A.; Florescu, D.F.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of NVX-CoV2373 in Adults in the United States and Mexico. N Engl J Med 2022, 386, 531-543. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhuang, C.; Chu, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Huang, S.; Su, Y.; Lin, H.; Yang, C.; Jiang, H.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a live-attenuated influenza virus vector-based intranasal SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in adults: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 and 2 trials. Lancet Respir Med 2022, 10, 749-760. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Huang, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhuang, C.; Zhao, H.; Han, J.; Jaen, A.M.; Do, T.H.; Peter, J.G.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the intranasal spray SARS-CoV-2 vaccine dNS1-RBD: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med 2023, 11, 1075-1088. [CrossRef]
- Tioni, M.F.; Jordan, R.; Pena, A.S.; Garg, A.; Wu, D.; Phan, S.I.; Weiss, C.M.; Cheng, X.; Greenhouse, J.; Orekov, T.; et al. Mucosal administration of a live attenuated recombinant COVID-19 vaccine protects nonhuman primates from SARS-CoV-2. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 85. [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.; Verma, M.; Shin, A.; Zakin, L.; Sieling, P.; Tanaka, S.; Balint, J.; Dinkins, K.; Adisetiyo, H.; Morimoto, B.; et al. Intranasal plus subcutaneous prime vaccination with a dual antigen COVID-19 vaccine elicits T-cell and antibody responses in mice. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 14917. [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Verma, S.; Reddy, P.; Diamond, M.S.; Curiel, D.T.; Patel, C.; Jain, M.K.; Redkar, S.V.; Bhate, A.S.; Gundappa, V.; et al. Phase III Pivotal comparative clinical trial of intranasal (iNCOVACC) and intramuscular COVID 19 vaccine (Covaxin((R))). NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 125. [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Li, K.; Rowe, D.K.; Diaz, M.C.H.; Griffin, E.F.; Beavis, A.C.; Johnson, S.K.; Padykula, I.; Jones, C.A.; Briggs, K.; et al. Protection of K18-hACE2 mice and ferrets against SARS-CoV-2 challenge by a single-dose mucosal immunization with a parainfluenza virus 5-based COVID-19 vaccine. Sci Adv 2021, 7. [CrossRef]
- Chavda, V.P.; Bezbaruah, R.; Valu, D.; Patel, B.; Kumar, A.; Prasad, S.; Kakoti, B.B.; Kaushik, A.; Jesawadawala, M. Adenoviral Vector-Based Vaccine Platform for COVID-19: Current Status. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Emary, K.R.W.; Golubchik, T.; Aley, P.K.; Ariani, C.V.; Angus, B.; Bibi, S.; Blane, B.; Bonsall, D.; Cicconi, P.; Charlton, S.; et al. Efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern 202012/01 (B.1.1.7): an exploratory analysis of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 1351-1362. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Fan, P.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an aerosolised adenovirus type-5 vector-based COVID-19 vaccine (Ad5-nCoV) in adults: preliminary report of an open-label and randomised phase 1 clinical trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2021, 21, 1654-1664. [CrossRef]
- Tukhvatulin, A.I.; Gordeychuk, I.V.; Dolzhikova, I.V.; Dzharullaeva, A.S.; Krasina, M.E.; Bayurova, E.O.; Grousova, D.M.; Kovyrshina, A.V.; Kondrashova, A.S.; Avdoshina, D.V.; et al. Immunogenicity and protectivity of intranasally delivered vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine Sputnik V in mice and non-human primates. Emerg Microbes Infect 2022, 11, 2229-2247. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Song, Y.; Coleman, J.R.; Stawowczyk, M.; Tafrova, J.; Tasker, S.; Boltz, D.; Baker, R.; Garcia, L.; et al. Scalable live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate demonstrates preclinical safety and efficacy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118. [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, J.K.; Wyllie, K.; Zhao, Y.; Tea, L.; Tasker, S.; Yeolekar, L.R.; Dhere, R.; Mueller, S. 1938. CoviLiv™, a Novel Intranasal Live-Attenuated COVID-19 Vaccine Candidate, Induces Robust Humoral and Cellular Immunity in First-In-Human Clinical Trial CDX-CoV-001. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2023, 10. [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.; Limonta, M.; Muzio, V.; Lemos, G.; Hernández-Bernal, F.; Chinea, G.; Gonzalez-Roche, D.; Martin, A.; Bequet, M.; Marques, G.; et al. Cuban Vaccines Abdala and Mambisa against Covid-19. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2023, 130, S9-S10. [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.H.; Shivhare, D.; Chia, T.W.; Chew, S.L.; Sinsinbar, G.; Aw, T.Y.; Wong, S.; Venkataraman, S.; Lim, F.W.I.; Vandepapeliere, P.; et al. Artificial Cell Membrane Polymersome-Based Intranasal Beta Spike Formulation as a Second Generation Covid-19 Vaccine. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16757-16775. [CrossRef]
- Mohazzab, A.; Fallah Mehrabadi, M.H.; Es-Haghi, A.; Kalantari, S.; Mokhberalsafa, L.; Setarehdan, S.A.; Sadeghi, F.; Rezaei Mokarram, A.; Haji Moradi, M.; Razaz, S.H.; et al. Phase II, Safety and Immunogenicity of RAZI Cov Pars (RCP) SARS Cov-2 Vaccine in Adults Aged 18-70 Years; A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. J Pharm Sci 2023, 112, 3012-3021. [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Israelow, B.; Pena-Hernandez, M.A.; Suberi, A.; Zhou, L.; Luyten, S.; Reschke, M.; Dong, H.; Homer, R.J.; Saltzman, W.M.; et al. Unadjuvanted intranasal spike vaccine elicits protective mucosal immunity against sarbecoviruses. Science 2022, 378, eabo2523. [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.; Polacek, C.; Sheward, D.J.; Hanke, L.; Moliner-Morro, A.; McInerney, G.; Murrell, B.; Hartmann, K.T.; Jensen, H.E.; Jungersen, G.; et al. Protection against SARS-CoV-2 transmission by a parenteral prime-Intranasal boost vaccine strategy. EBioMedicine 2022, 84, 104248. [CrossRef]
- Rioux, M.; McNeil, M.; Francis, M.E.; Dawe, N.; Foley, M.; Langley, J.M.; Kelvin, A.A. The Power of First Impressions: Can Influenza Imprinting during Infancy Inform Vaccine Design? Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8. [CrossRef]
- Dangi, T.; Sanchez, S.; Lew, M.H.; Awakoaiye, B.; Visvabharathy, L.; Richner, J.M.; Koralnik, I.J.; Penaloza-MacMaster, P. Pre-existing immunity modulates responses to mRNA boosters. Cell Rep 2023, 42, 112167. [CrossRef]
- Pulendran, B.; P, S.A.; O'Hagan, D.T. Emerging concepts in the science of vaccine adjuvants. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2021, 20, 454-475. [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, B.M.; Feavers, I.M. Mimotope vaccines. J Med Microbiol 2001, 50, 937-939. [CrossRef]
- Pashov, A.D.; Plaxco, J.; Kaveri, S.V.; Monzavi-Karbassi, B.; Harn, D.; Kieber-Emmons, T. Multiple antigenic mimotopes of HIV carbohydrate antigens: relating structure and antigenicity. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 29675-29683. [CrossRef]
- Steward, M.W. The development of a mimotope-based synthetic peptide vaccine against respiratory syncytial virus. Biologicals 2001, 29, 215-219. [CrossRef]
- Chames, P.; Van Regenmortel, M.; Weiss, E.; Baty, D. Therapeutic antibodies: successes, limitations and hopes for the future. Br J Pharmacol 2009, 157, 220-233. [CrossRef]
- Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Bakhshinejad, B.; Baradaran, B.; Motallebnezhad, M.; Aghebati-Maleki, A.; Nickho, H.; Yousefi, M.; Majidi, J. Phage display as a promising approach for vaccine development. Journal of biomedical science 2016, 23, 66. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Strych, U.; Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E. The SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Pipeline: an Overview. Current tropical medicine reports 2020, 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Wiedermann, U.; Davis, A.B.; Zielinski, C.C. Vaccination for the prevention and treatment of breast cancer with special focus on Her-2/neu peptide vaccines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013, 138, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.; Battin, C.; Linhares, A.D.; Karin, B.; AMbroye, K.; Drinic, M.; Garner-Spitzer, E.; Zielinski, C.; Kundi, M.; Steinberger, P.; et al. Identification of PD1 B cell mimotopes with functional PD1-PDL1 blocking capacity: New strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Res 2019, 79. [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.; Garner-Spitzer, E.; Drinic, M.; Wiedermann, U. Vaccination against Her-2/neu, with focus on peptide-based vaccines. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100361. [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.; Drinic, M.; Hogler, S.; Ambroz, K.; Baier, K.; Kodajova, P.; Tomasich, E.; Berghoff, A.S.; Schmid, A.; Garner-Spitzer, E.; et al. Active immunization with a Her-2/neu-targeting Multi-peptide B cell vaccine prevents lung metastases formation from Her-2/neu breast cancer in a mouse model. Transl Oncol 2022, 19, 101378. [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.; Drinic, M.; Schmid, A.; Hladik, A.; Watzenbock, M.L.; Battin, C.; Garner-Spitzer, E.; Steinberger, P.; Kundi, M.; Knapp, S.; et al. Combined Vaccination with B Cell Peptides Targeting Her-2/neu and Immune Checkpoints as Emerging Treatment Option in Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J.; Jasinska, J.; Baier, K.; Kundi, M.; Ede, N.; Zielinski, C.; Wiedermann, U. Enhanced and long term immunogenicity of a Her-2/neu multi-epitope vaccine conjugated to the carrier CRM197 in conjunction with the adjuvant Montanide. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 118. [CrossRef]
- Lollini, P.L.; Cavallo, F.; Nanni, P.; Forni, G. Vaccines for tumour prevention. Nat Rev Cancer 2006, 6, 204-216. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Lindstrom, A.R.; Lin, T.Y.; Lam, K.S.; Li, Y. Peptide-based materials for cancer immunotherapy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7807-7825. [CrossRef]
- Malito, E.; Bursulaya, B.; Chen, C.; Lo Surdo, P.; Picchianti, M.; Balducci, E.; Biancucci, M.; Brock, A.; Berti, F.; Bottomley, M.J.; et al. Structural basis for lack of toxicity of the diphtheria toxin mutant CRM197. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, 5229-5234. [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, K.K.; King, C.L.; Greenspan, N.S.; Kirchner, H.L.; Schreiber, J.R. Immunization with Haemophilus influenzae type b-CRM(197) conjugate vaccine elicits a mixed Th1 and Th2 CD(4+) T cell cytokine response that correlates with the isotype of antipolysaccharide antibody. J Infect Dis 2001, 184, 931-935. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cao, J.; Lin, X.; Yue, J.; Zieneldien, T.; Kim, J.; Wang, L.; Fang, J.; Huang, R.P.; Bai, Y.; et al. Developing an Effective Peptide-Based Vaccine for COVID-19: Preliminary Studies in Mice Models. Viruses 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Telenti, A.; Arvin, A.; Corey, L.; Corti, D.; Diamond, M.S.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Garry, R.F.; Holmes, E.C.; Pang, P.S.; Virgin, H.W. After the pandemic: perspectives on the future trajectory of COVID-19. Nature 2021, 596, 495-504. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.J.; Pade, C.; Gibbons, J.M.; Butler, D.K.; Otter, A.D.; Menacho, K.; Fontana, M.; Smit, A.; Sackville-West, J.E.; Cutino-Moguel, T.; et al. Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection rescues B and T cell responses to variants after first vaccine dose. Science 2021, 372, 1418-1423. [CrossRef]
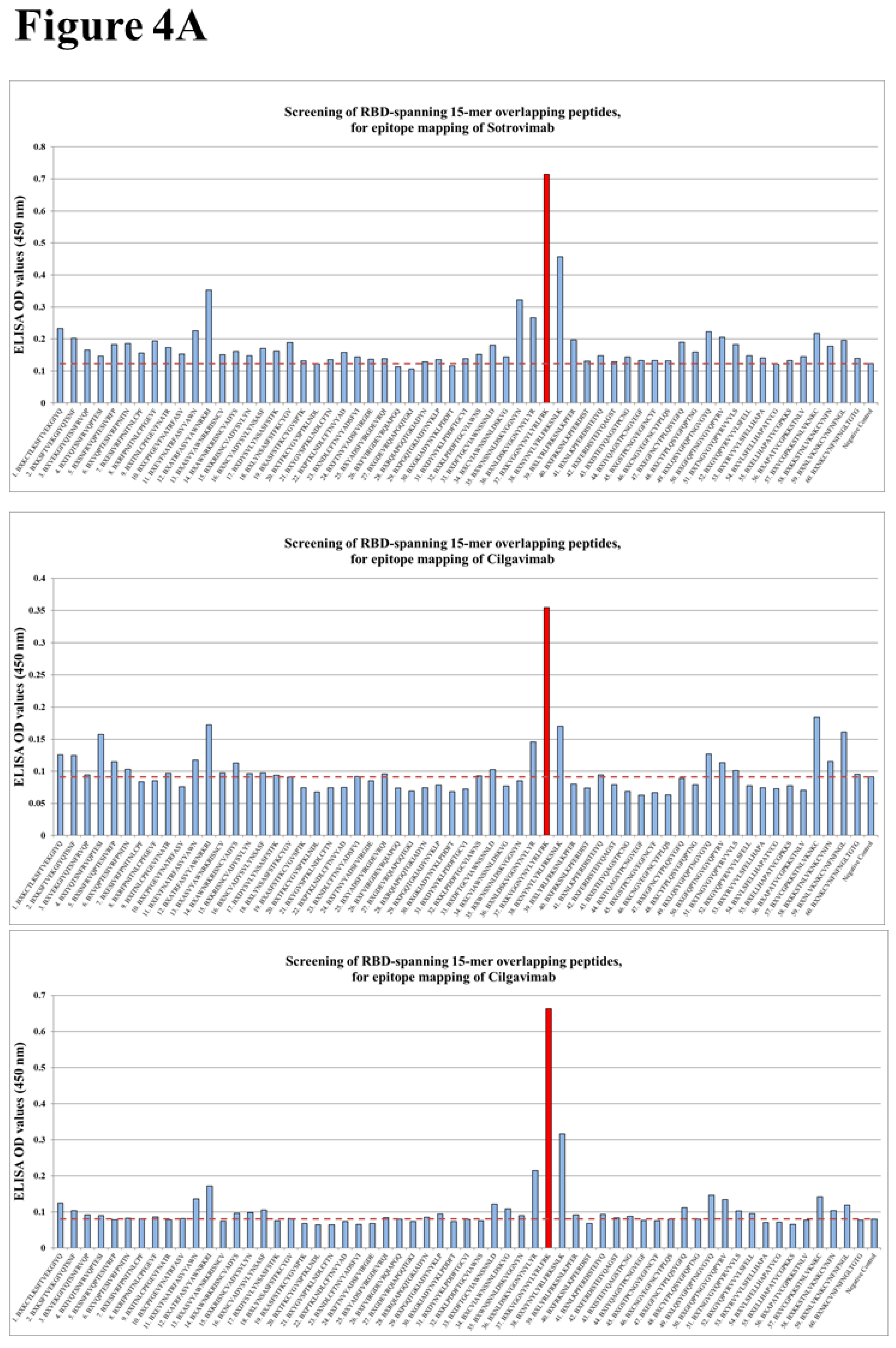
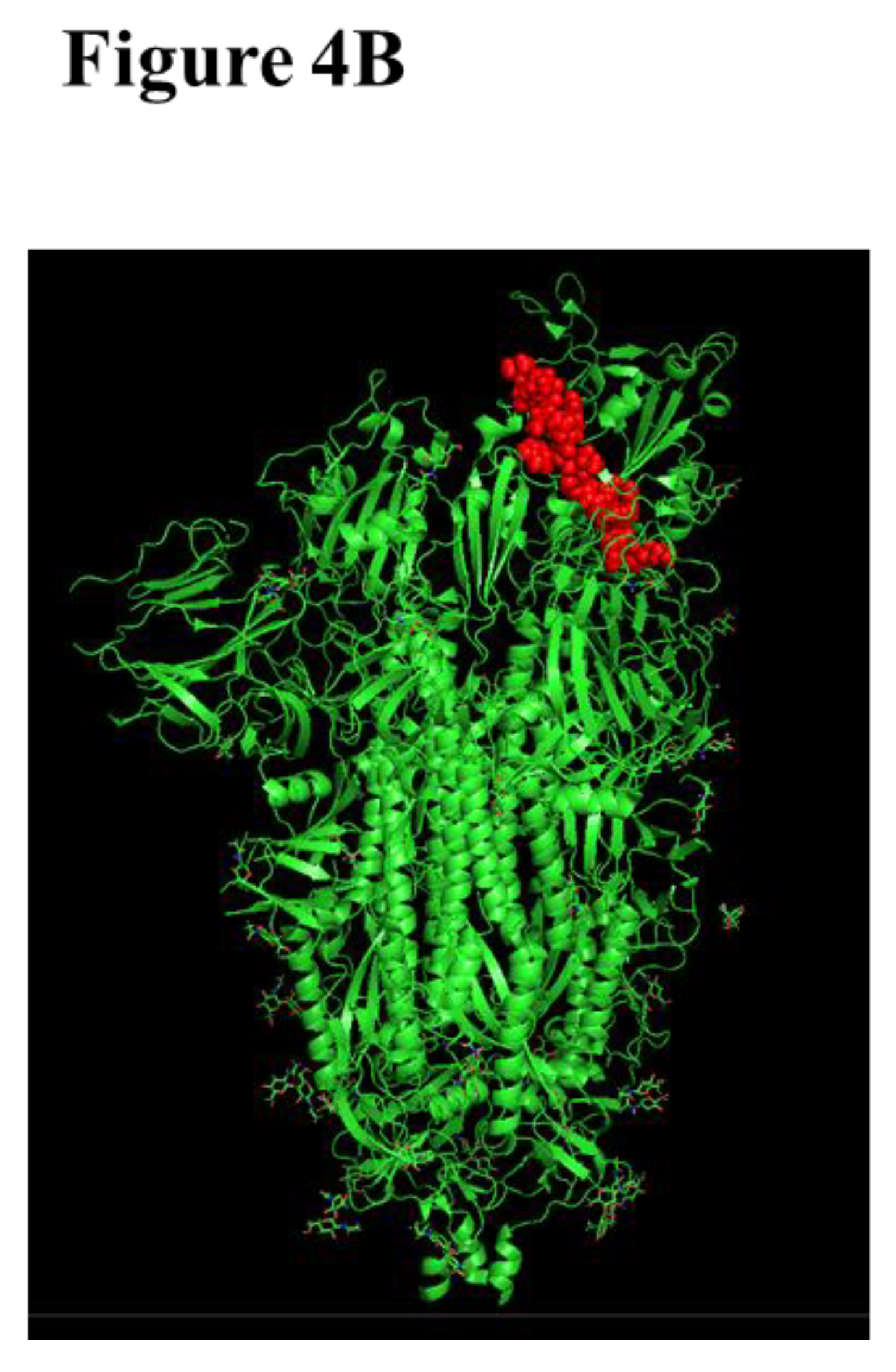
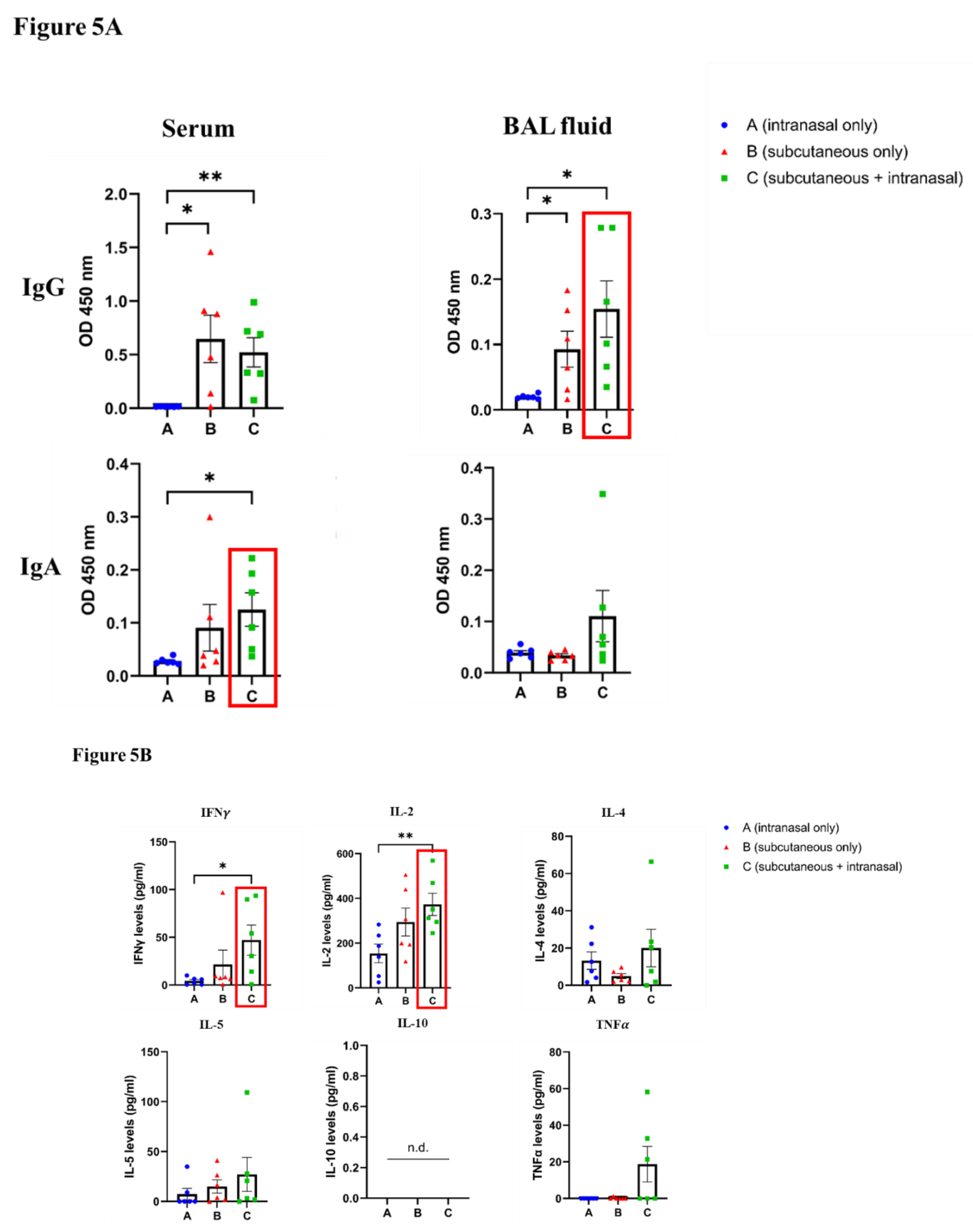
| Activity of therapeutic/prophylactic antibodies against Delta (EC50, ng/ml) and BA.2, BA.5, BA.2.75.2, XBB, BQ.1, and BQ.1.1 variants (fold-reduction) [124]* | |||||||||||
| Name | Treatment | Date of approval |
Effect, Targeting epitope |
Route of administration | Delta | BA.2 | BA.2.75.2 | BA.5 | BQ.1 | BQ.1.1 | XBB |
| Bebtelovimab | Therapeutic |
February, 2022 | Therapeutic, RBD |
Intravenous | 0.4 | ||||||
| Sotrovimab | May, 2021 | Intravenous |
98.6 | ||||||||
| Casirivimab | Treatment Or Post-exposure prophylaxis |
November, 2020 | Treatment Or Post-exposure prophylaxis, RBM |
Intravenous or sub-cutaneous |
14.7 | ||||||
| Imdevimab | 20.1 | ||||||||||
| Cilgavimab | Pre-exposure prophylaxis | December, 2021 | Pre-exposure prophylaxis | Intramuscular | 21.7 | ||||||
| Tixagevimab | 12.4 | ||||||||||
| 1-5 fold | 6-10 fold | 11-15 fold | 16-20 fold | Non-neutralizing |
| Vaccine type/ platform |
Expressed SARS-CoV-2 component | Vaccine name | Developer | Phase | Clinical trial identifier | Application | Reference |
|
Viral Vector (Replicating) |
live-attenuated influenza virus vector-based expressing SARS-CoV-2 RBD |
dNS1-RBD | Beijing Wantai | Approved | ChiCTR2000037782 ChiCTR2000039715 ChiCTR2100048316 | Two intranasal doses, 14 or 21 days apart |
[171] |
| Replication deficient Influenza A (CA4-DelNS1) virus expressing RBD domain of S protein |
DelNS1-2019-nCoV-RBDOPT1 | University of Hong Kong, Xiamen University and Beijing Wantai Biological Pharmacy |
Phase 3 | ChiCTR2100051391 | Two intranasal doses, 14 days apart |
[172] | |
| Respiratory Syncytial virus expressing S protein |
MV-014-212 | Meissa Vaccines, Inc | Phase 1 | NCT04798001 | Single intranasal dose, or 2 intranasal doses 36 days apart |
[173] | |
| Human adenovirus serotype 5 expressing S protein and nucleocapsid |
hAd5-S-Fusion + N-ETSD | ImmunityBio Inc | Phase 1b | NCT04591717 | Single subcutaneous dose followed by single sublingual dose, 21 days apart |
[174] | |
| Adenoviral vector expressing WA1 S protein |
BBV154 | Bharat Biotech International Limited |
Approved | NCT05522335 | Two intranasal doses, 28 days apart |
[175] | |
|
Viral Vector (Non-replicating) |
Parainfluenza virus 5 expressing WA1 S protein |
CVXGA1/PIV5-SARS-CoV-2 | CyanVac LLC | Phase 1 | NCT04954287 | Single intranasal dose | [176] |
| Adenoviral vector expressing S protein |
SC-Ad6-1 | Tetherex Pharmaceuticals Corporation |
Phase 1 | NCT04839042 | Single intranasal dose, or 2 intranasal doses one month apart |
[177] | |
| Adenoviral vector expressing S protein |
ChAdOx1/AZD1222 | University of Oxford and AstraZeneca Biopharmaceuticals |
Phase 1 | NCT04816019 | Single intranasal dose | [178] | |
| Adenoviral vector expressing WA1 S protein |
Ad5-nCoV-IH (Convidecia Air) |
CanSinoBio | Approved | NCT04552366 | Two doses with different administration routes (2 intranasal doses, 1 intramuscular and 1 intranasal dose, 28 days apart | [179] | |
| Adenoviral vector | Sputnik V/Gam-COVIDVac | The Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology |
Approved | NCT04954092 NCT05248373 |
Single intranasal dose | [180] | |
| Attenuated SARS-CoV-2 WA1 strain | CoviLiv | Codagenix/Serum Institute of India |
Phase 3 | ISRCTN15779782 | Two intranasal doses, 28 days apart | [181] [182] |
|
| Live attenuated virus |
RBD adjuvanted with aluminium hydroxide |
CIGB-669 (RBD + AgnHB) (Mambisa) |
Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (CIGB) |
Phase 2 | RPCEC00000345 | Two intranasal dose, 28 days apart, or One intramuscular dose followed by 2 intranasal doses, 28 days apart |
[183] (https://covid-19.cochrane.org/studies/crs-16897005) |
|
Protein subunit |
S protein encapsulated by an artificial cell membrane |
ACM Biolabs ACM-SARS-CoV-2- beta ACM CpG vaccine candidate (ACM-001) |
ACM Biolabs | Phase 1 | NCT05385991 | Single dose, after full vaccination with any registered and commercial SARS-CoV-2 vaccines | [184] |
| Recombinant S protein |
RAZI-COV PARS | Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute |
Approved | IRCT20201214049709N2 | Two intramuscular doses, followed by 1 intranasal dose | [185] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





