Submitted:
11 June 2024
Posted:
11 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We perform a systematic review of explainable AI techniques that can ensure trust-worthiness and transparency in the medical domain and present a forward-looking roadmap for XAI-based CDSS.
- We categorized various studies from traditional CDSS to state-of-the-art XAI-based CDSS by appropriate criteria and summarize the features and limitations of each CDSS to propose a new XAI-based CDSS framework.
- We propose a novel CDSS framework using the latest XAI technology and show that potential value by introducing areas that can be utilized most effectively.
2. Related Work
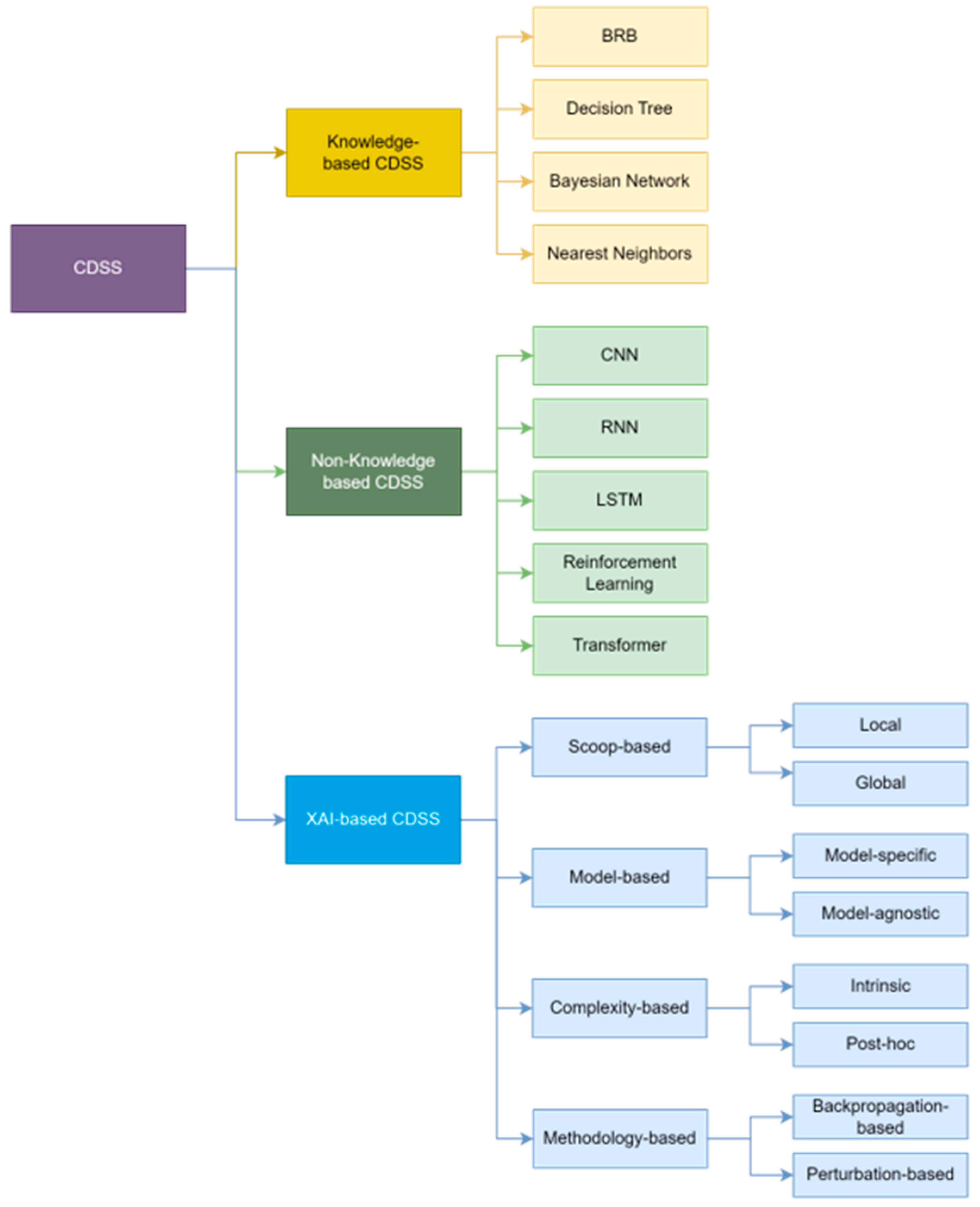
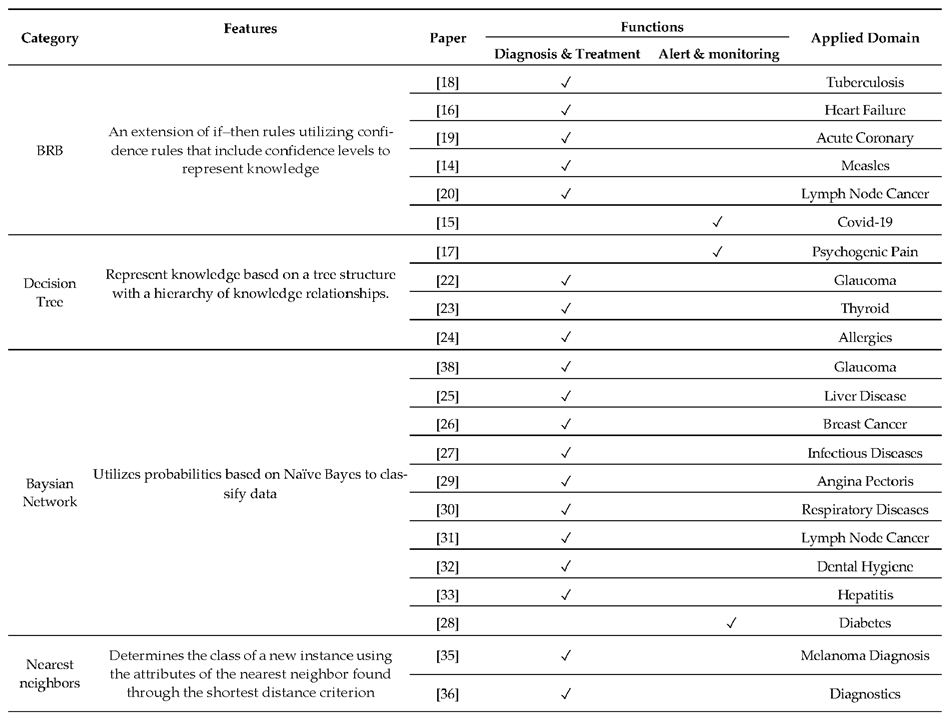
2.1. Knowledge-Based CDSS
2.2. Non-Knowledge-Based CDSS
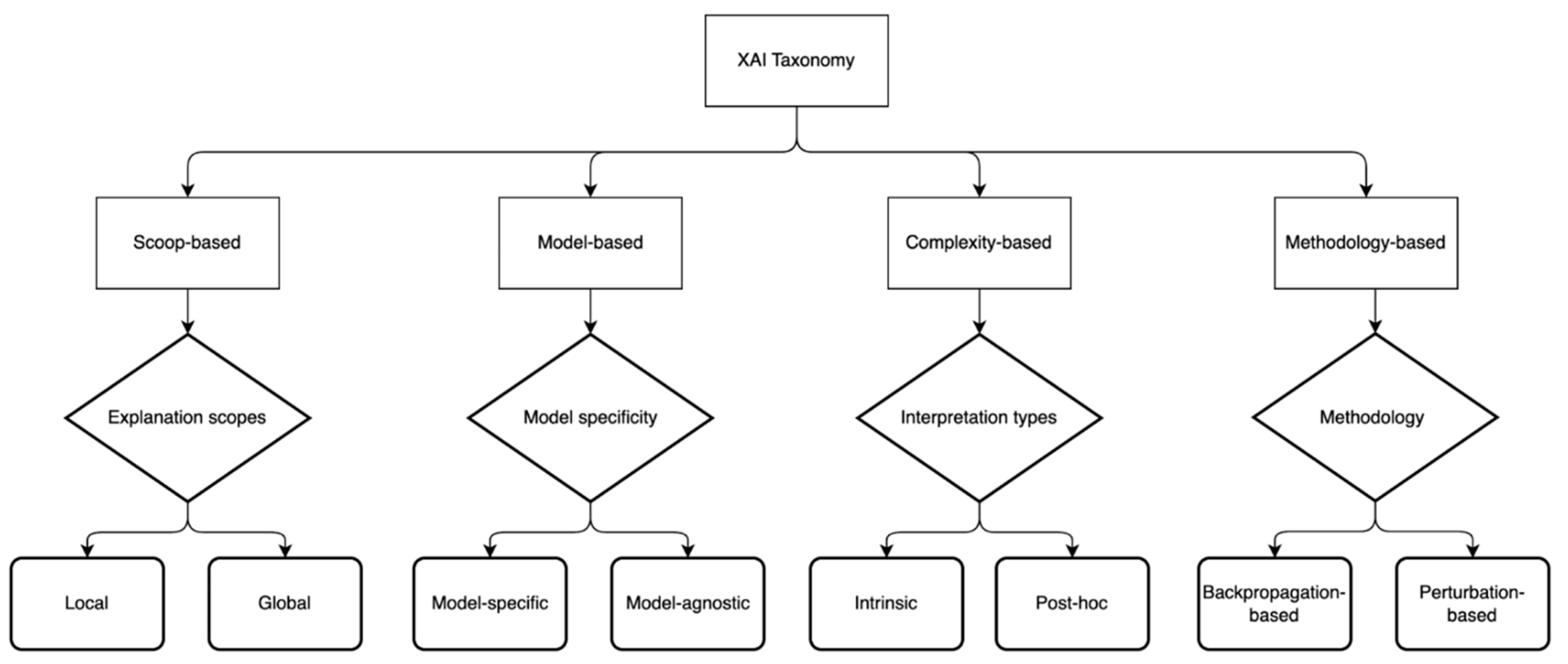
2.3. XAI-Based CDSS
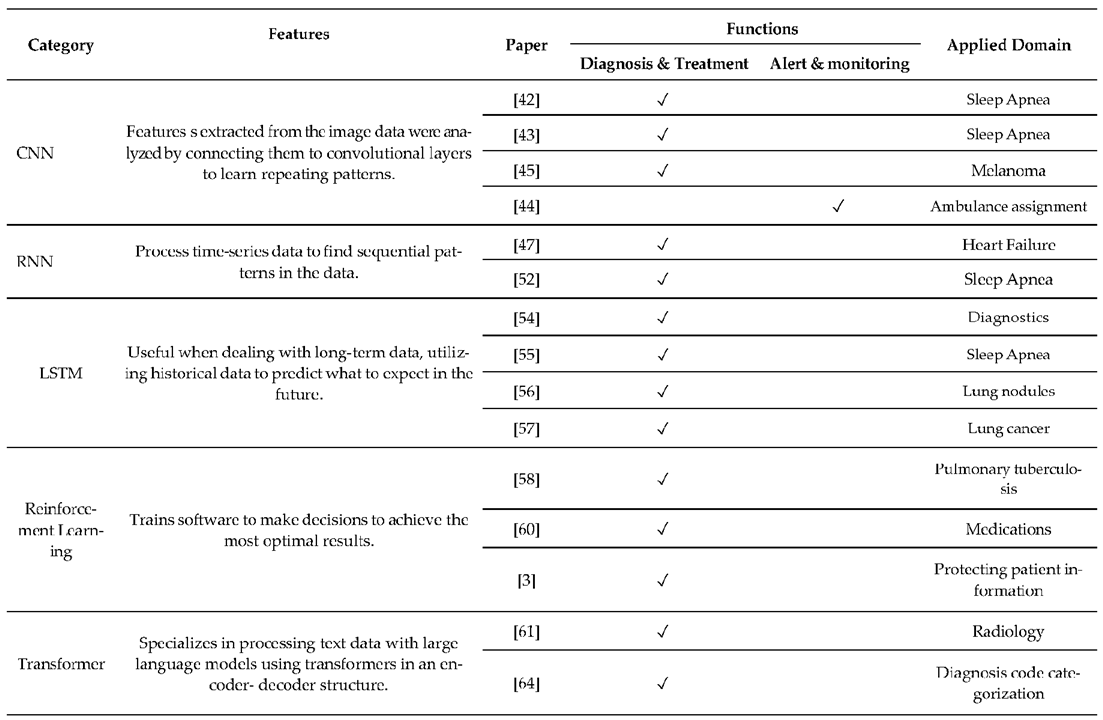
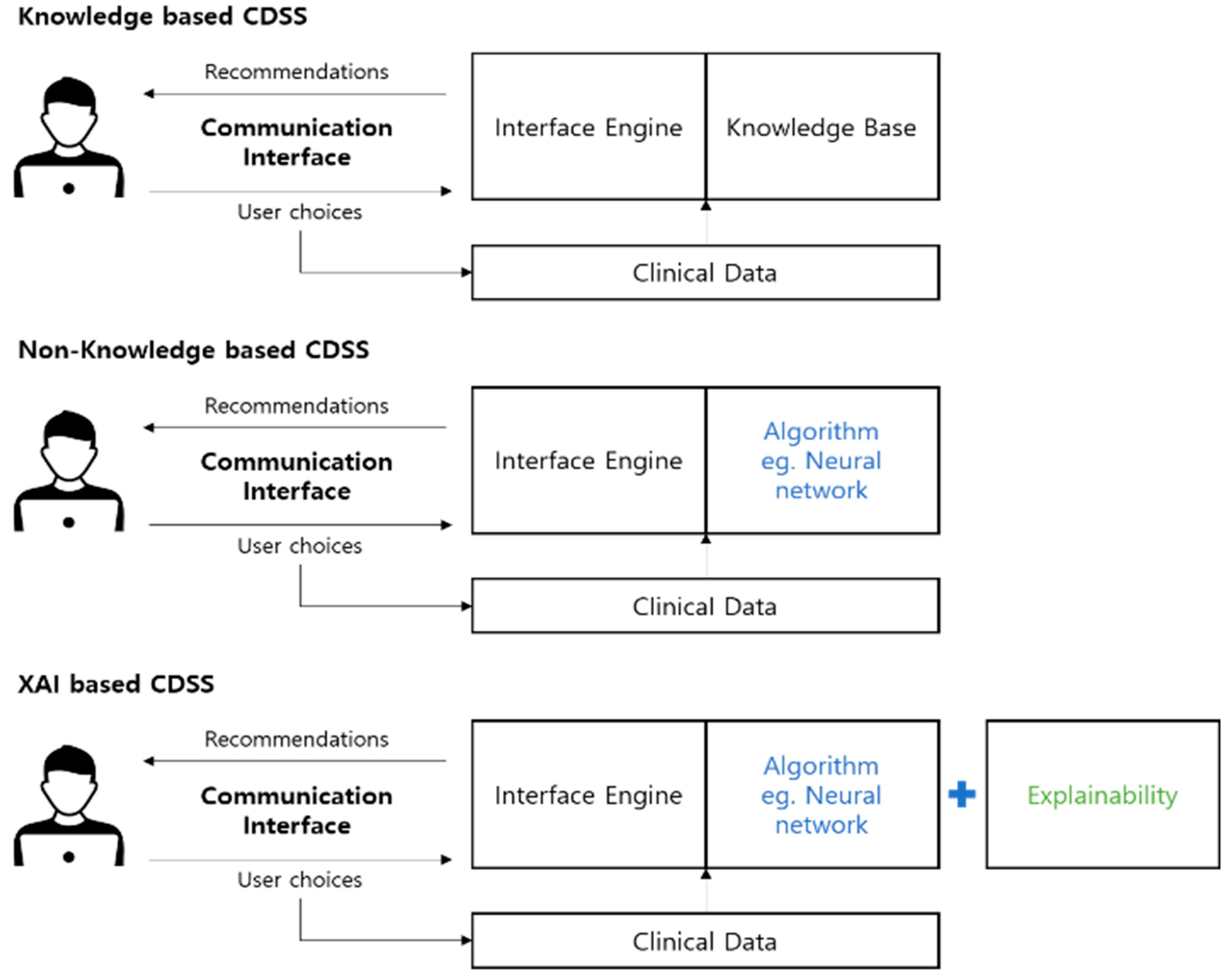
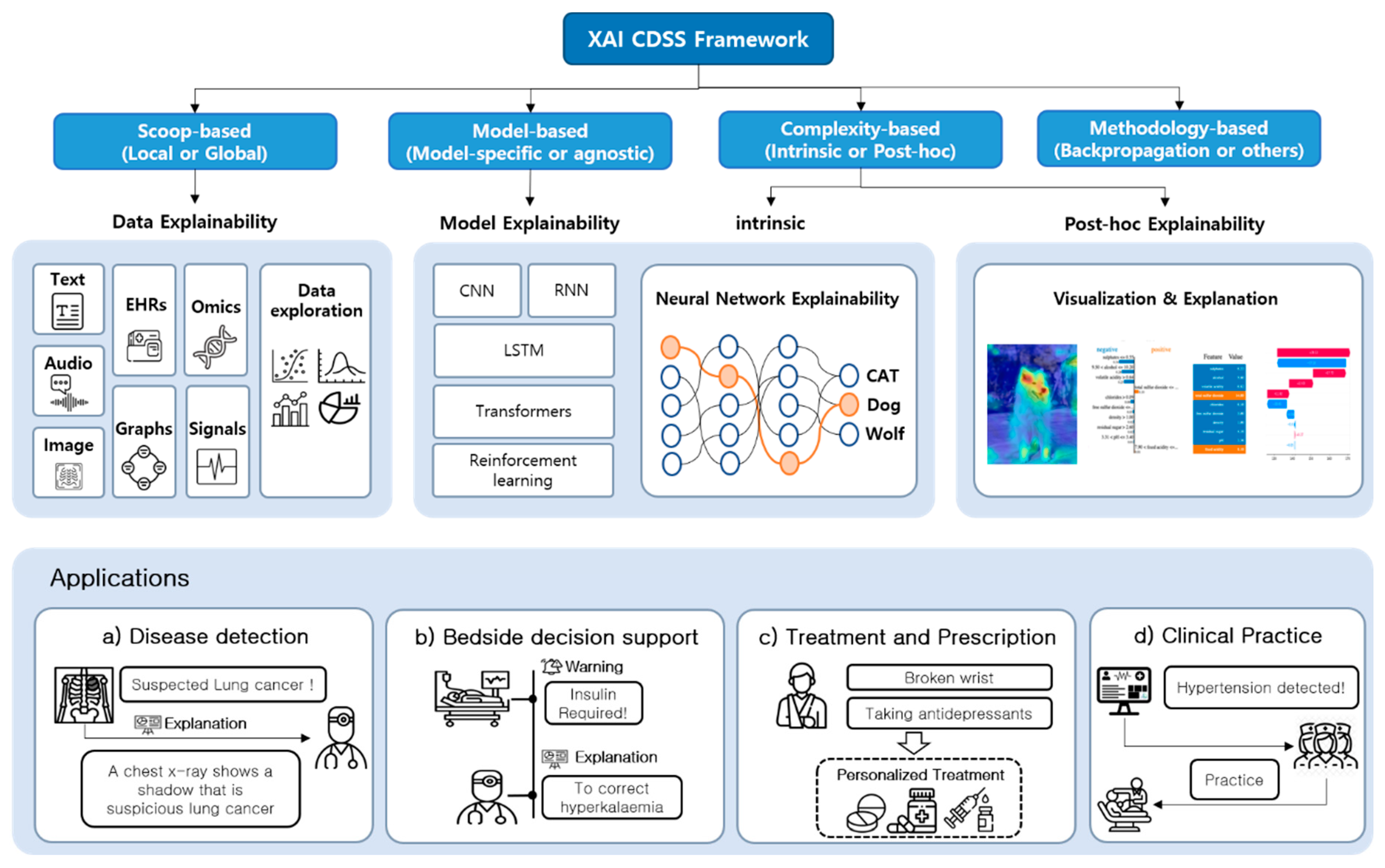
3. XAI CDSS Framework
3.1. Proposed Architecture
3.2. Dataset
3.2.1. Clinical Dataset
3.2.2. Knowledge Graph
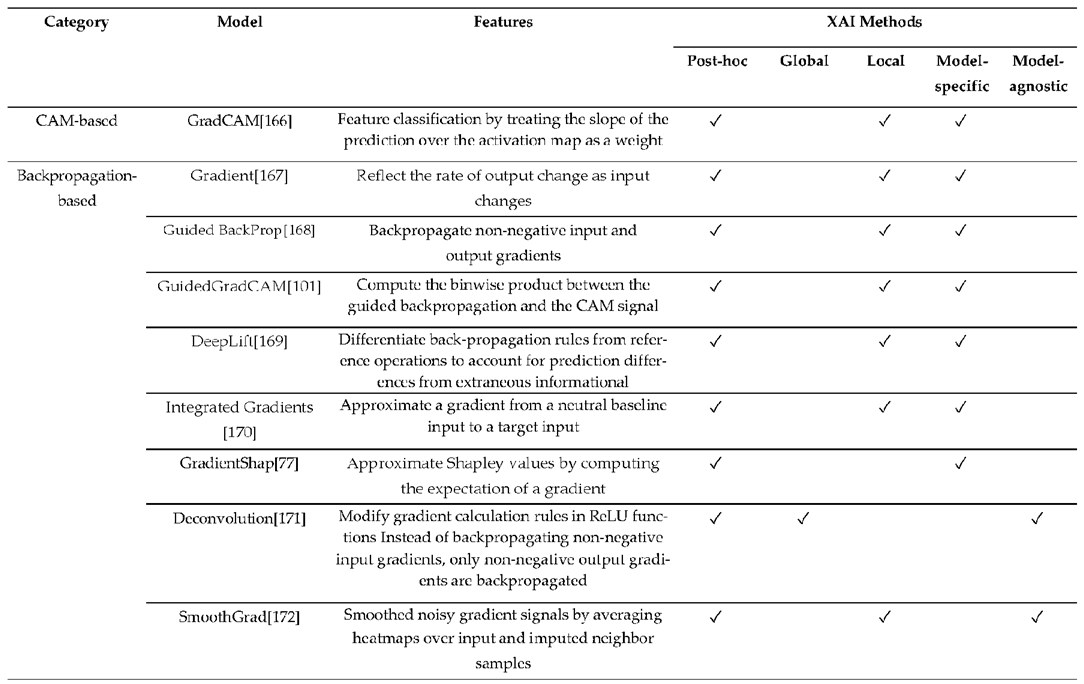
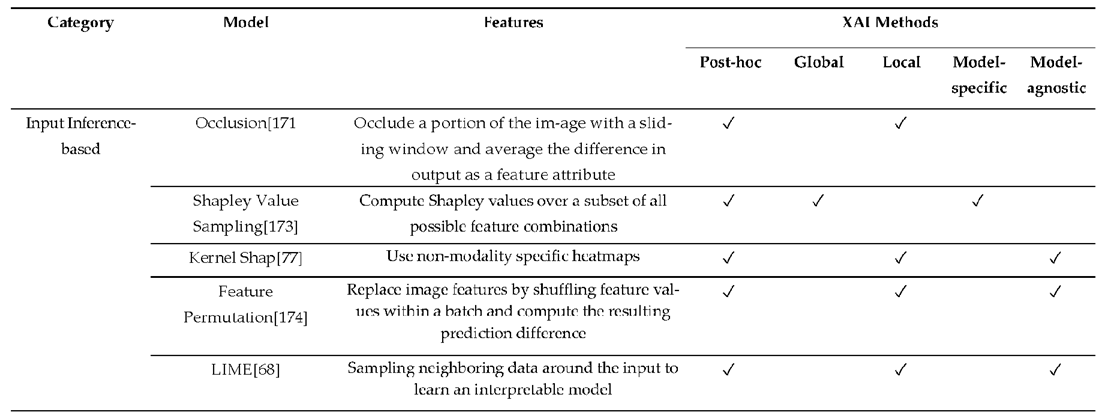
3.3. XAI Model
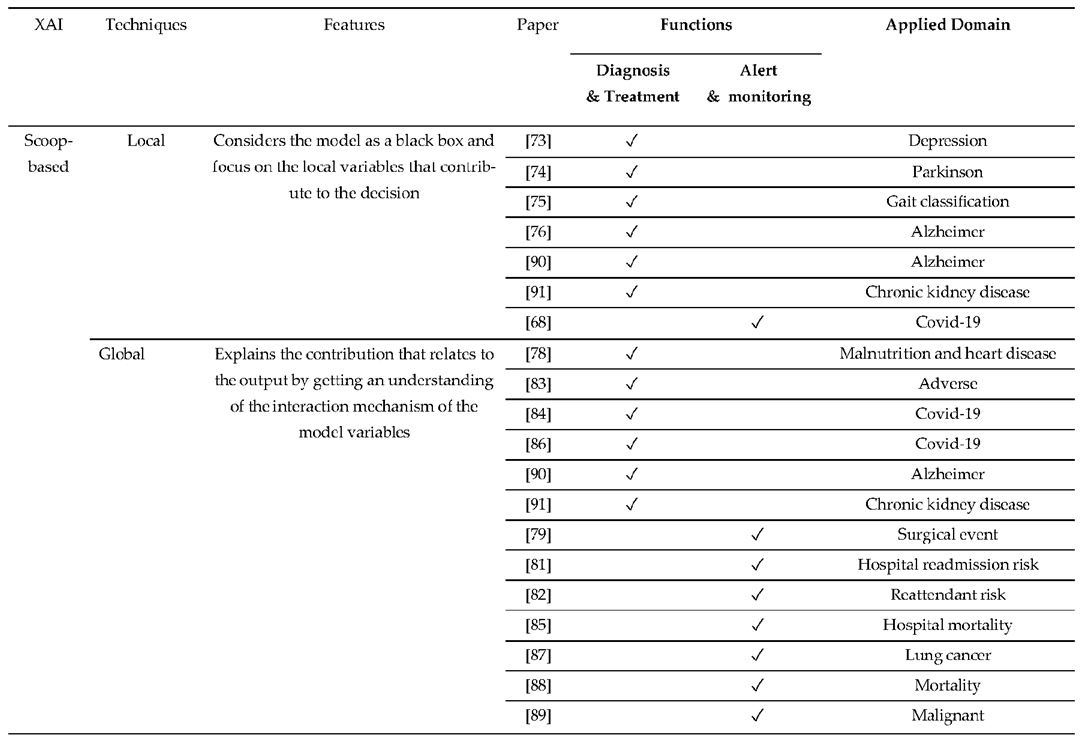
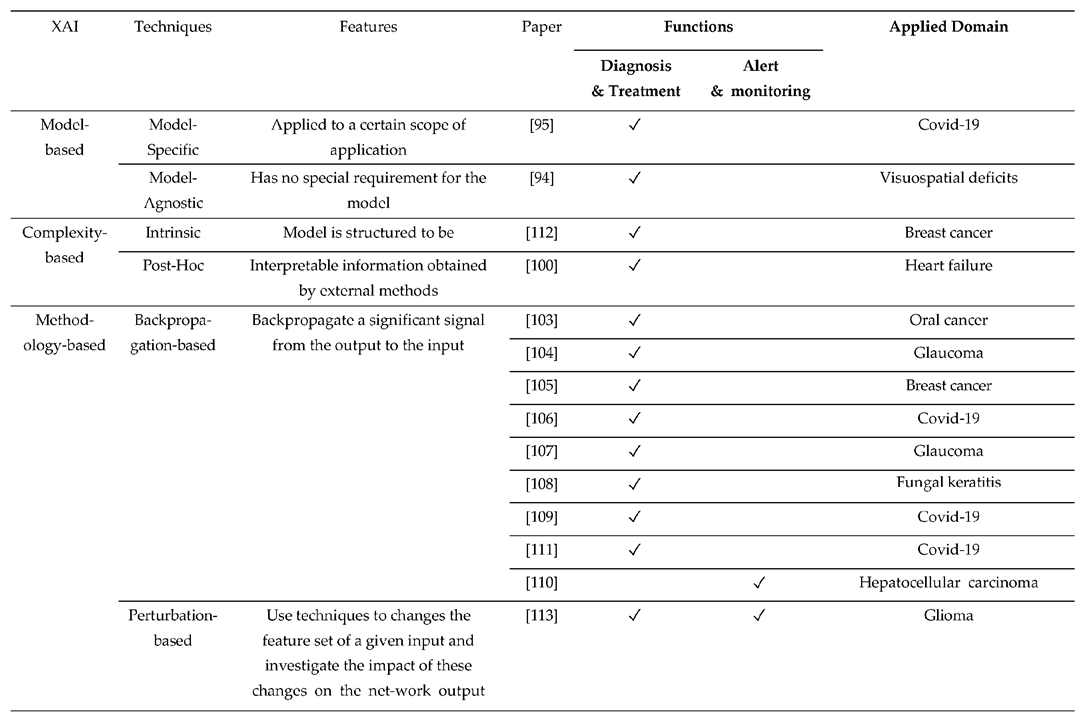
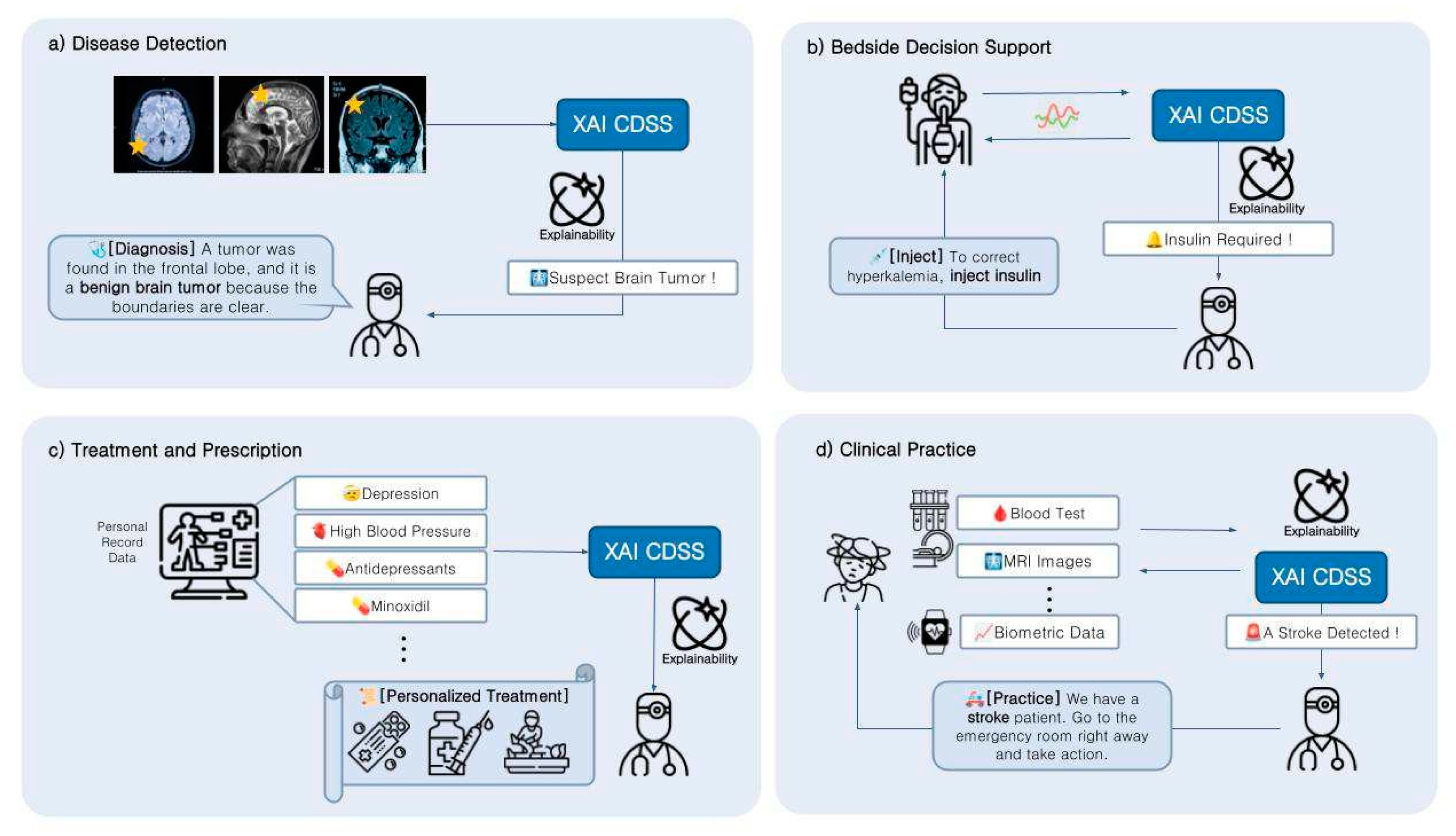
4. Applications
4.1. Function of CDSS
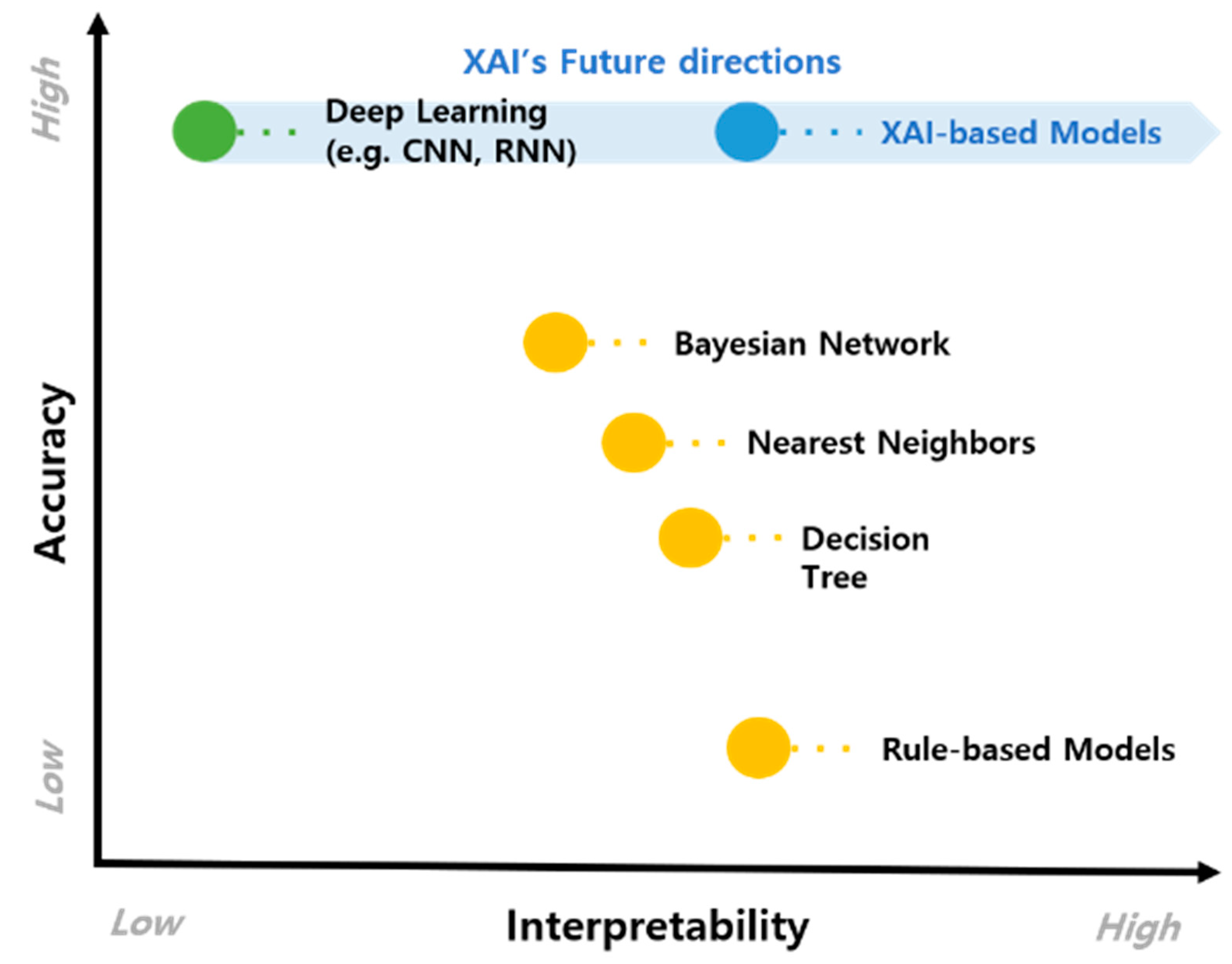
4.2. The Potential of XAI-Based CDSS
5. Discussion and Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalifa, M. Clinical decision support: Strategies for success. Procedia Computer Science 2014, 37, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.R.; Smith, D.H.; Feldstein, A.C.; Perrin, N.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Platt, R.; Soumerai, S.B. Computerized prescribing alerts and group academic detailing to reduce the use of potentially inappropriate medications in older people. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2006, 54, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Deng, R.H.; Choo, K.K.R.; Yang, Y. Privacy-preserving reinforcement learning design for patient-centric dynamic treatment regimes. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing 2019, 9, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fauw, J.; Ledsam, J.R.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Nikolov, S.; Tomasev, N.; Blackwell, S.; Askham, H.; Glorot, X.; O’Donoghue, B.; Visentin, D.; et al. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nature medicine 2018, 24, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, S.; Yan, C.; Li, M.; Jiang, C. Explaining the black-box model: A survey of local interpretation methods for deep neural networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 419, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi-Velez, F.; Kim, B. Towards a rigorous science of interpretable machine learning. arXiv e-prints 2017, arXiv-1702. [CrossRef]
- Syeda-Mahmood, T. Role of big data and machine learning in diagnostic decision support in radiology. Journal of the American College of Radiology 2018, 15(3), 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, I.; Gorman, P.; Greenes, R.A.; Haynes, R.B.; Kaplan, B.; Lehmann, H.; Tang, P.C. Clinical decision support systems for the practice of evidence-based medicine. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2001, 8(6), 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.B.; Singh, M.G. An evidential reasoning approach for multiple-attribute decision making with uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on systems, Man, and Cybernetics 1994, 24(1), 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.B. Rule and utility based evidential reasoning approach for multiattribute decision analysis under uncertainties. European journal of operational research 2001, 131(1), 31–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.B.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Sii, H.S.; Wang, H.W. Belief rule-base inference methodology using the evidential reasoning approach-RIMER. IEEE Transactions on systems, Man, and Cybernetics- part A: Systems and Humans 2006, 36(2), 266–285. [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.; Islam, M.M.; Hossain, M.S. A belief rule based clinical decision support system framework. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th international conference on computer and informa- tion technology (ICCIT). IEEE; 2014; pp. 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Xu, D.L.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.B. Applying a belief rule-base inference methodology to a guideline-based clinical decision support system. Expert Systems 2009, 26(5), 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Andersson, K.; Naznin, S. A belief rule based expert system to diagnose measles under uncertainty. In World Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering, and Applied Computing (WORLDCOMP’15): The 2015 International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Systems 2015, pp. 17–23.
- Ahmed, F.; Hossain, M.S.; Islam, R.U.; Andersson, K. An evolutionary belief rule-based clinical decision support system to predict COVID-19 severity under uncertainty. Applied Sciences 2021, 11(13), 5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, S.; Hossain, M.S. A belief rule based clinical decision support system to assess suspicion of heart failure from signs, symptoms and risk factors. 2013 International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision (ICIEV) 2013, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Xu, D.L.; Body, R.; Yang, J.B.; Mackway-Jones, K.; Carley, S. A belief rule-based decision support system for clinical risk assessment of cardiac chest pain. European Journal of Operational Research 2012, 219(3), 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Andersson, K. A belief rule based expert system to assess tuberculosis under uncertainty. Journal of medical systems 2017, 41(3), 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Rahaman, S.; Mustafa, R.; Andersson, K. A belief rule-based expert system to assess suspicion of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) under uncertainty. Soft Computing 2009, 22, 7571–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Liu, F.; Jiao, L.C.; Zhou, Z.J.; Yang, J.B.; Gong, M.G.; Zhang, X.P. A bi-level belief rule based decision support system for diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. Knowledge-based systems 2013, 54, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.; Hak, F.; Guimaraes, T.; Manuel, M.; Santos, M.F. Rule-based system for effective clinical decision support. Procedia Computer Science 2023, 220, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyungwon, Y.e.a. Clinical Knowledge Modeling for Thyroid Nodule Surgical Treatment CDSS Using Mind Maps and Iterative Decision Trees. Journal of The Korean Institute of Communication Sciences 2020, 37(9), 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.W.; Hussain, M.; Afzal, M.; Ali, T.; Choi, J.Y.; Han, H.S.; Lee, S. Use of mind maps and iterative decision trees to develop a guideline-based clinical decision support system for routine surgical practice: case study in thyroid nodules. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2019, 26(6), 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.W.e.a. Design and Implementation of a Clinical Decision Support System for Supporting Allergy Diagnosis and Treatment Decision Making for Pediatricians. Journal of Knowledge Information Technology and Systems 2023, 18(3), 5250535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasyluk, H.; Onisko, A.; Druzdzel, M. Support of diagnosis of liver disorders based on a causal Bayesian network model. Medical Science Monitor 2001, 7(1), 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Ramirez, N.; Acosta-Mesa, H.G.; Carrillo-Calvet, H.; Nava-Fernández, L.A.; Barrientos- Martinez, R.E. Diagnosis of breast cancer using Bayesian networks: A case study. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2007, 37(11), 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, P.J.; De Bruijn, N.C.; Schurink, K.; Hoepelman, A. A probabilistic and decision-theoretic approach to the management of infectious disease at the ICU. Artificial Intelligence in medicine 2000, 19, 251–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, S.; Benn, J.J.; Hovorka, R.; Olesen, K.G.; Carson, E.R. A probabilistic approach to glucose prediction and insulin dose adjustment: description of metabolic model and pilot evaluation study. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine 1994, 41(3-4), 153–165. [CrossRef]
- Vila-Francés, J.; Sanchis, J.; Soria-Olivas, E.; Serrano, A.J.; Martinez-Sober, M.; Bonanad, C.; Ventura, S. Expert system for predicting unstable angina based on Bayesian networks. Expert systems with applications 2013, 40, 5004–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edye, E.O.; Kurucz, J.F.; Lois, L.; Paredes, A.; Piria, F.; Rodríguez, J.; Delgado, S.H. Applying Bayesian networks to help physicians diagnose respiratory diseases in the context of COVID-19 pandemic. In 2021 IEEE URUCON 2021, pp. 368–371.
- Reijnen, C.; Gogou, E.; Visser, N.C.; Engerud, H.; Ramjith, J.; Van Der Putten, L.J.; Van de Vijver, K.; Santacana, M.; Bronsert, P.; Bulten, J.; et al. Preoperative risk stratification in endometrial cancer (ENDORISK) by a Bayesian network model: A development and validation study. PLoS medicine 2020, 17(5), e1003111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanathornwong, B.; Suebnukarn, S.; Ouivirach, K. Clinical Decision Support System for Geriatric Dental Treatment Using a Bayesian Network and a Convolutional Neural Network. Healthcare Informatics Research 2023, 29(1), 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riali, I.; Fareh, M.; Ibnaissa, M.C.; Bellil, M. A semantic-based approach for hepatitis C virus prediction and diagnosis using a fuzzy ontology and a fuzzy Bayesian network. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2023, 44(2), 2381–2395. [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Lingao, W.; Ji, R.; Wang, C.; Yao, L.; Kai, L.; Abdalla, A.N. Clinical Decision Support System Based on KNN/Ontology Extraction Method. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning 2020; pp. 56–62. [CrossRef]
- Abbes, W.; Sellami, D.; Marc-Zwecker, S.; Zanni-Merk, C. Fuzzy decision ontology for melanoma diagnosis using KNN classifier. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2021, 80, 25517–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comito, C.; Falcone, D.; Forestiero, A. Diagnosis Detection Support based on Time Series Similarity of Patients Physiological Parameters. In 2021 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI) 2021, pp. 1327–1331. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Park, Y.; Lee, W.S.; Lim, Y.; Kim, J.H. Clinical genome data model (cGDM) provides interactive clinical decision support for precision medicine. Scientific reports 2020, 10(1), 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DongJin, J.e.a. Natural language processing-based evolutionary clinical decision support systems: a case study in glaucoma diagnosis. Journal of The Korean Institute of Communication Sciences 2020, 37(9), 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Musarrat Hussain, e.a. Intelligent Medical Platform: IMP. Journal of The Korean Institute of Communication Sciences 2020, 37, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.T.; Pincock, D.; Baumgart, D.C.; Sadowski, D.C.; Fedorak, R.N.; Kroeker, K.I. An overview of clinical decision support systems: benefits, risks, and strategies for success. NPJ digital medicine 2020, 3(1), 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.O. CNN: A vision of complexity. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos 1997, 7(10), 2219–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, L.; Yu, Z.L.; Kluge, T.; Ser, W. Automatic system for obstructive sleep apnea events detection using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC). IEEE; 2018; pp. 3975–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Chaudhuri, S.; Munshi, S. Obstructive sleep apnoea detection using convolutional neural network based deep learning framework. Biomedical engineering letters 2018, 8, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueiro-Pequeño, J.; Casal-Guisande, M.; Comesaña-Campos, A.; Bouza-Rodríguez, J.B. Conceptual Design of a New Methodology Based on Intelligent Systems Applied to the Determination of the User Experience in Ambulances. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality (TEEM’21); 2021; pp. 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist- level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, Dipesh, e.a. Recurrent neural networks. Design and Applications 2001, 5(2), (64–67).
- Choi, E.; Schuetz, A.; Stewart, W.F.; Sun, J. Using recurrent neural network models for early detection of heart failure onset. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2017, 24, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthaharan, S. Machine learning models and algorithms for big data classification. Integr. Ser. Inf. Syst 2016, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Taud, H.; Mas, J.F. Multilayer perceptron (MLP). Geomatic approaches for modeling land change scenarios 2018, pp. 451–455. [CrossRef]
- LaValley, M.P. Logistic regression. Circulation 2020, 117(18), 2395–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, B. Machine learning algorithms-a review. nternational Journal of Science and Research (IJSR) 2020, 9(1), 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Sori, W.J.; Jiang, F.; Khan, A.; Liu, S. Recurrent neural network based classification of ECG signal features for obstruction of sleep apnea detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) and IEEE International Conference on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing (EUC); 2017; Volume 2, pp. 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPietro, R.; Hager, G.D. Deep learning: RNNs and LSTM. In Handbook of medical image computing and computer assisted intervention; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 503–519. [CrossRef]
- Lipton, Z.C.; Kale, D.C.; Elkan, C.; Wetzel, R. Learning to diagnose with LSTM recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.03677 2015. [CrossRef]
- ElMoaqet, H.; Eid, M.; Glos, M.; Ryalat, M.; Penzel, T. Deep recurrent neural networks for automatic detection of sleep apnea from single channel respiration signals. Sensors 2020, 20, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Goo, J.M.; Park, C.M.; Lee, H.J.; Jin, K.N. Computer-aided detection of malignant lung nodules on chest radiographs: effect on observers’ performance. Korean journal of radiology 2012, 13, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Obuchowski, N.; Phillips, M.; Risius, B.; Bazerbashi, B.; Meziane, M. Lung cancer screening with computer aided detection chest radiography: design and results of a randomized, controlled trial. PloS one 2013, 8, e59650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, T.; Cohen, C.; Pai, M.; Ahmad Khan, F. Computer-aided detection of pulmonary tuberculosis on digital chest radiographs: a systematic review. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2016, 20, 1226–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiering, M.A.; Van Otterlo, M. Reinforcement learning. Adaptation, learning, and optimization 2012, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Tan, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Ru, Y.; Jin, Y. A latent batch-constrained deep reinforcement learning approach for precision dosing clinical decision support. Knowledge-based systems 2022, 237, 107689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, D.; Sun, W.; Jin, J.; Dinov, I.D.; Cuneo, K.; Jamaluddin, J.; Matuszak, M.M.; Luo, Y.; Lawrence, T.S.; Jolly, S.; et al. A clinical decision support system for AI-assisted decision- making in response-adaptive radiotherapy (ARCliDS). Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, e.a. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transform- ers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 2018. [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Yao, H.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, X.; Hu, G.; Li, Y.; Xie, G. Embedding electronic health records to learn BERT-based models for diagnostic decision support. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 9th International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI). IEEE; 2021; pp. 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, K.e.a. Explainable AI in Industry. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 2019; KDD ’19. pp. 3203–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsen, T. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts and Challenges in Healthcare. AI 2023, 4, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.e.a. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): What we know and what is left to attain Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence. Information Fusion 2023, 99, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbay, F.e.a. A LIME-Based Explainable Machine Learning Model for Predicting the Severity Level of COVID-19 Diagnosed Patients. Applied Sciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. " Why should i trust you?" Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining; 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.R.e.a. Deterministic Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations for Stable Explainability. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction 2021, 3, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adadi, A.e.a. Peeking Inside the Black-Box: A Survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52138–52160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, H.W.e.a. Application of explainable artificial intelligence for healthcare: A systematic review of the last decade (2011–2022). Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2022, 226, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.Z.e.a. Deep learning for prediction of depressive symptoms in a large textual dataset. Neural Computing and Applications 2022, 34, 721–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, P.R.e.a. An Explainable Machine Learning Model for Early Detection of Parkinson’s Disease using LIME on DaTSCAN Imagery. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2020, 126, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dindorf, C.e.a. Interpretability of Input Representations for Gait Classification in Patients after Total Hip Arthroplasty. Sensors 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidulova, M.e.a. Towards Explainable Image Analysis for Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR); 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.e.a. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SShi, H.e.a. Explainable machine learning model for predicting the occurrence of postoperative malnutrition in children with congenital heart disease. Clinical Nutrition 2022, 41, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.e.a. Forecasting adverse surgical events using self-supervised transfer learning for physiological signals. NPJ Digital Medicine 2021, 4, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sappagh, S.e.a. A multilayer multimodal detection and prediction model based on ex- plainable artificial intelligence for Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.T.e.a. Predictive modeling for 14-day unplanned hospital readmission risk by using machine learning algorithms. BMC medical informatics and decision making 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmiel, F.P.e.a. Using explainable machine learning to identify patients at risk of reattendance at discharge from emergency departments. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 21513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NNguyen, S.e.a. Budget constrained machine learning for early prediction of adverse outcomes for COVID-19 patients. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 19543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.e.a. An Explainable System for Diagnosis and Prognosis of COVID-19. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 15839–15846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozenbaum, D.e.a. Personalized prediction of hospital mortality in COVID-19–positive patients. Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Innovations, Quality & Outcomes 2021, 5, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.A.e.a. Explaining machine learning based diagnosis of COVID-19 from routine blood tests with decision trees and criteria graphs. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2021, 132, 104335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAlsinglawi, B.e.a. An explainable machine learning framework for lung cancer hospital length of stay prediction. Scientific reports 2022, 12, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.A.e.a. Using a machine learning approach to predict mortality in critically ill influenza patients: a cross-sectional retrospective multicentre study in Taiwan. BMJ Open 2020, 10. Available online: https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/10/2/e033898.full.pdf. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FForoushani, H.M.e.a. Accelerating prediction of malignant cerebral edema after ischemic stroke with automated image analysis and explainable neural networks. Neurocritical care 2022, 36, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahim, S.M.e.a. Unlocking the Potential of XAI for Improved Alzheimer’s Disease Detection and Classification Using a ViT-GRU Model. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 8390–8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.K.e.a. Investigation on explainable machine learning models to predict chronic kidney diseases. Scientific Reports 2024, 14, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.e.a. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv preprint 2018. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.e.a. Learning Attentive Pairwise Interaction for Fine-Grained Classification. Proceed- ings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2020, 34, 13130–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksasat, R.e.a. Attentive pairwise interaction network for AI-assisted clock drawing test assessment of early visuospatial deficits. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 18113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambiar, A.e.a. Model-agnostic explainable artificial intelligence tools for severity predic- tion and symptom analysis on Indian COVID-19 data. Front Artif Intell 2023, 6, 1272506 PMC10726049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.F.; Kuflik, T.; Mocanu, I.G.; Najafian, S.; Shulner Tal, A. Recent studies of xai-review. In Proceedings of the Adjunct Proceedings of the 29th ACM Conference on User Modeling, Adaptation and Personalization, 2021, pp.; pp. 421–431. [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.e.a. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PMLR; 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, e.a. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, F.A.e.a. Brain tumor detection with mRMR-based multimodal fusion of deep learning from MR images using Grad-CAM. Iran Journal of Computer Science 2023, 6, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Hassan, M.M.; Bairagi, A.K.; Shariful Islam, S.M. NeuroNet19: an explainable deep neural network model for the classification of brain tumors using magnetic resonance imaging data. Scientific Reports 2024, 14, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, R.R.e.a. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision; 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahmunah, V.e.a. Explainable detection of myocardial infarction using deep learning models with Grad-CAM technique on ECG signals. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 146, 105550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, K.C.e.a. Interpretable deep learning approach for oral cancer classification using guided attention inference network. Journal of biomedical optics 2022, 27, 015001–015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.e.a. Explaining the Rationale of Deep Learning Glaucoma Decisions with Adversarial Examples. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QQian, X.e.a. Prospective assessment of breast cancer risk from multimodal multiview ul- trasound images via clinically applicable deep learning. Nature biomedical engineering 2021, 5, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.e.a. COVIDScreen: explainable deep learning framework for differential diagnosis of COVID-19 using chest X-rays. Neural Computing and Applications 2021, 33, 8871–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakoor, K.A.e.a. Robust and interpretable convolutional neural networks to detect glaucoma in optical coherence tomography images. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2020, 68, 2456–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.e.a. The Clinical Value of Explainable Deep Learning for Diagnosing Fungal Keratitis Using in vivo Confocal Microscopy Images. Frontiers in Medicine 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CChetoui, M.e.a. Explainable COVID-19 Detection on Chest X-rays Using an End-to-End Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture. Big Data and Cognitive Computing 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.e.a. Predicting microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: a deep learning model validated across hospitals. Cancer Imaging 2021, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.e.a. Explainable DCNN based chest X-ray image analysis and classification for COVID-19 pneumonia detection. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamy, J.B.e.a. Explainable artificial intelligence for breast cancer: A visual case-based reasoning approach. Artificial intelligence in medicine 2019, 94, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.e.a. Artificial intelligence in glioma imaging: challenges and advances. Journal of neural engineering 2020, 17, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, D, e. a. DARPA’s Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) Program. AI Magazine 2019, 40, 44–58. [CrossRef]
- Woodfield, R., e. a. Accuracy of electronic health record data for identifying stroke cases in large- scale epidemiological studies: a systematic review from the UK Biobank Stroke Outcomes Group. PloS one 2015, 10, e0140533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. China Kadoorie Biobank of 0.5 million people: survey methods, baseline characteristics and long-term follow-up. International Journal of Epidemiology 2011, 40, 1652– 1666. 2011, 40, 1652–1666, [https://academicoupcom/ije/article. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/ije/article-pdf/40/6/1652/2396544/dyr120.pdf. [CrossRef]
- Nagai, A. Overview of the BioBank Japan Project: Study design and profile. Journal of Epidemiology 2017, 27, S2–S8. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E. MIMIC-CXR, a de-identified publicly available database of chest radiographs with free-text reports. Scientific data 2019, 6, 317. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.G. The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America 2005, 15, 869. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berle, J.O. Actigraphic registration of motor activity reveals a more structured behavioural pattern in schizophrenia than in major depression. BMC research notes 2010, 3, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Bien, N.e.a. Deep-learning-assisted diagnosis for knee magnetic resonance imaging: devel- opment and retrospective validation of MRNet. PLoS medicine 2018, 15, e1002699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, G.e.a. Augmenting the national institutes of health chest radiograph dataset with expert annotations of possible pneumonia. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence 2019, 1, e180041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demner-Fushman, e.a. Preparing a collection of radiology examinations for distribution and retrieval. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2015, 23, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, D.S.e.a. Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS): Cross-sectional MRI Data in Young, Middle Aged, Nondemented, and Demented Older Adults. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 2007, 19, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. ChestX-Ray8: Hospital-Scale Chest X-Ray Database and Benchmarks on Weakly- Supervised Classification and Localization of Common Thorax Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Los Alamitos, CA, USA; 2017; pp. 3462–3471. [CrossRef]
- Armato III, S.G.e.a. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Medical physics 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.e.a. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): maintaining and operating a public informa- tion repository. Journal of digital imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.e.a. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Scientific data 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PPollard, T.J.e.a. The eICU Collaborative Research Database, a freely available multi-center database for critical care research. Scientific data 2018, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzuner, O.e.a. 2010 i2b2/VA challenge on concepts, assertions, and relations in clinical text. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2011, 18, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.e.a. Evaluating temporal relations in clinical text: 2012 i2b2 Challenge. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2013, 20, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, A.; Uzuner, Ö. Annotating longitudinal clinical narratives for de-identification: The 2014 i2b2/UTHealth corpus. Journal of biomedical informatics 2015, 58, S20–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.e.a. Identifying relations of medications with adverse drug events using recurrent convolutional neural networks and gradient boosting. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2019, 27, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczak, K.e.a. Review The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): an immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemporary Oncology/Współczesna Onkologia 2015, 2015, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Herrera, e.a. Overview of the medical tasks in ImageCLEF 2016. CLEF working notes Evora, Portugal 2016.
- Demner-Fushman, D.; Antani, S.; Simpson, M.; Thoma, G.R. Design and development of a mul- timodal biomedical information retrieval system. Journal of Computing Science and Engineering 2012, 6, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, A.L.e.a. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Weng, Y.; Xia, F.; Sun, B.; Li, S. VPAI_LAB at MedVidQA 2022: a two-stage cross-modal fusion method for medical instructional video classification. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 21st Workshop on Biomedical Language Processing; 2022; pp. 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Prkachin, K.M.; Solomon, P.E.; Matthews, I. Painful data: The UNBC- McMaster shoulder pain expression archive database. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE In- ternational Conference on Automatic Face I& Gesture Recognition (FG); 2011; pp. 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Attal, K.; Demner-Fushman, D. A dataset for medical instructional video classification and question answering. Scientific Data 2023, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic acids research 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [CrossRef]
- Bizon, C., e. a. ROBOKOP KG and KGB: integrated knowledge graphs from federated sources. Journal of chemical information and modeling 2019, 59, 4968–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, P. KnowLife: A knowledge graph for health and life sciences. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 30th International Conference on Data Engineering; 2014; pp. 1254–1257. [CrossRef]
- SSchriml, L.M. Disease Ontology: a backbone for disease semantic integration. Nucleic Acids Research 2011, 40, D940–D946. Available online: https://academicoupcom/nar/ARTICLE. [CrossRef]
- Su, C.e.a. Biomedical discovery through the integrative biomedical knowledge hub (iBKH). Iscience 2023, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nature genetics 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Shukla, S.; Datta, D.; Misra, R. Generating novel molecule for target protein (SARS- CoV-2) using drug–target interaction based on graph neural network. Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics 2022, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelstein, D.S.; Baranzini, S.E. Heterogeneous network edge prediction: a data integration approach to prioritize disease-associated genes. PLoS computational biology 2015, 11, e1004259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, H. Prediction of compound synthesis accessibility based on reaction knowledge graph. Molecules 2022, 27, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M. The KEGG database. In Proceedings of the ‘In silico’simulation of biological processes: Novartis Foundation Symposium 247. Wiley Online Library, 2002, Vol. 247, pp. 91–103. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Lee, N.; Shin, Y.; Shin, D. Intelligent generation of optimal synthetic pathways based on knowledge graph inference and retrosynthetic predictions using reaction big data. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 2022, 130, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hristovski, D.; Schutte, D.; Kastrin, A.; Fiszman, M.; Kilicoglu, H. Drug repurposing for COVID-19 via knowledge graph completion. Journal of biomedical informatics 2021, 115, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, L.M.; Duncan, W.D.; Diehl, A.D. An ontology for representing hematologic malignancies: the cancer cell ontology. BMC bioinformatics 2019, 20, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ding, P.; Xu, R. KG-Predict: A knowledge graph computational framework for drug repurposing. Journal of biomedical informatics 2022, 132, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandak, P.; Huang, K.; Zitnik, M. Building a knowledge graph to enable precision medicine. Scientific Data 2023, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Rao, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Fang, E.F.; Yang, Y.; Niu, Z. PharmKG: a dedicated knowledge graph benchmark for bomedical data mining. Briefings in bioinformatics 2021, 22, bbaa344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Che, C. Drug repurposing for Parkinson’s disease by integrating knowledge graph completion model and knowledge fusion of medical literature. Future Internet 2021, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.e.a. Large-scale multi-modal pre-trained models: A comprehensive survey. Machine Intelligence Research 2023, 20, 447–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C. Multimodal deep generative adversarial models for scalable doubly semi- supervised learning. Information Fusion 2021, 68, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Ieee; 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.e.a. GAN review: Models and medical image fusion applications. Information Fusion 2023, 91, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D. P. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6114. 2013. arXiv:1312.6114 2013. [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.e.a. Vatt: Transformers for multimodal self-supervised learning from raw video, audio and text. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, 34, 24206–24221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.e.a. What do you see? Evaluation of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in- terpretability through neural backdoors. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD conference on knowledge discovery & data mining; 2021; pp. 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.e.a. Grad-CAM: Why did you say that? arXiv:1611.07450 2016. [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep inside convolutional networks: Visualising image classification models and saliency maps. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6034. 2013. arXiv:1312.6034 2013. [CrossRef]
- Springenberg, J.T.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T.; Riedmiller, M. Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6806. 2014. arXiv:1412.6806.
- Shrikumar, A.; Greenside, P.; Kundaje, A. Learning important features through propagating activation differences. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PMLR; 2017; pp. 3145–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrikumar, A.; Greenside, P.; Shcherbina, A.; Kundaje, A. Not just a black box: Learning important features through propagating activation differences. arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.01713. 2016. arXiv:1605.01713 2016. [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part I 13. Springer, 2014, pp. 818–833. [CrossRef]
- Smilkov, D.; Thorat, N.; Kim, B.; Viégas, F.; Wattenberg, M. Smoothgrad: removing noise by adding noise. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.03825 2017. [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.; Gómez, D.; Tejada, J. Polynomial calculation of the Shapley value based on sampling. Computers & Operations Research 2009, 36, 1726–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Rudin, C.; Dominici, F. All models are wrong, but many are useful: Learning a variable’s importance by studying an entire class of prediction models simultaneously. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2019, 20, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Modality | Dataset | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single- modality | Image | MURA[120] | Musculoskeletal radiology images |
| MRNet[121] | MRI images | ||
| RSNA[122] | Chest X-ray images | ||
| Demner, F., 2016[123] | Chest X-ray images | ||
| OASIS[124] | MRI images | ||
| ADNI[119] | CT images | ||
| X. Wang, 2017[125] | Chest X-ray images | ||
| Armato III 2011[126] | CT images | ||
| TCIA[127] | Cancer tumor images | ||
| EHR | MIMIC-III[128] | Demographics, clinical history, diagnoses, prescrip- tions, physical information, etc | |
| eICU[129] | Management activities, clinical assessments, treat- ment plans, vital sign measurements, etc. | ||
| Text | 2010 i2b2/VA[130] | Discharge statements, progress reports, radiology reports, pathology reports | |
| 2012 i2b2[131] | Discharge statements | ||
| 2014 i2b2/UTHealth[132] | Longitudinal medical record | ||
| 2018 n2c2[133] | Discharge statements | ||
| Multi-Modality | Genome, Image | TCGA[134] | Genome, medical images |
| Genome, Image, EHR | UK Biobank[115] | Clinical information, genomic analysis, exon variant testing, whole genome sequencing testing, MRI, etc. | |
| Image, Text | ImageCLEFmed[135] | Diagnostic images, visible light images, signals, waves, etc. | |
| Openi[136] | Medical articles, images | ||
| Multiple signal | PhysiNet[137] | Biomedical signals | |
| Video | MedVidCL[138] | Medical instruction images | |
| UNBC-McMaster[139] | Patient with shoulder pain | ||
| MedVidOA[140] | Medical instruction images |
| CDSS | Bio-informatics | Medicine | Pharmaceutical Chemistry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HKG | DrugBank[141] | Gene Ontology[146] | GEFA[147] | HetioNet[148] |
| POBOKOP[142] | Reaction[149] | |||
| KnowLife[143] | KEGG[150] | ASICS[151] | DrKG[152] | |
| Disease Ontology[144] | Hetionet[152] | |||
| iBKH[145] | Cell Ontology[153] | GP-KG[154] | PrimeKG[155] | |
| PharmKG[156] | DRKF[157] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





