Submitted:
07 June 2024
Posted:
10 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
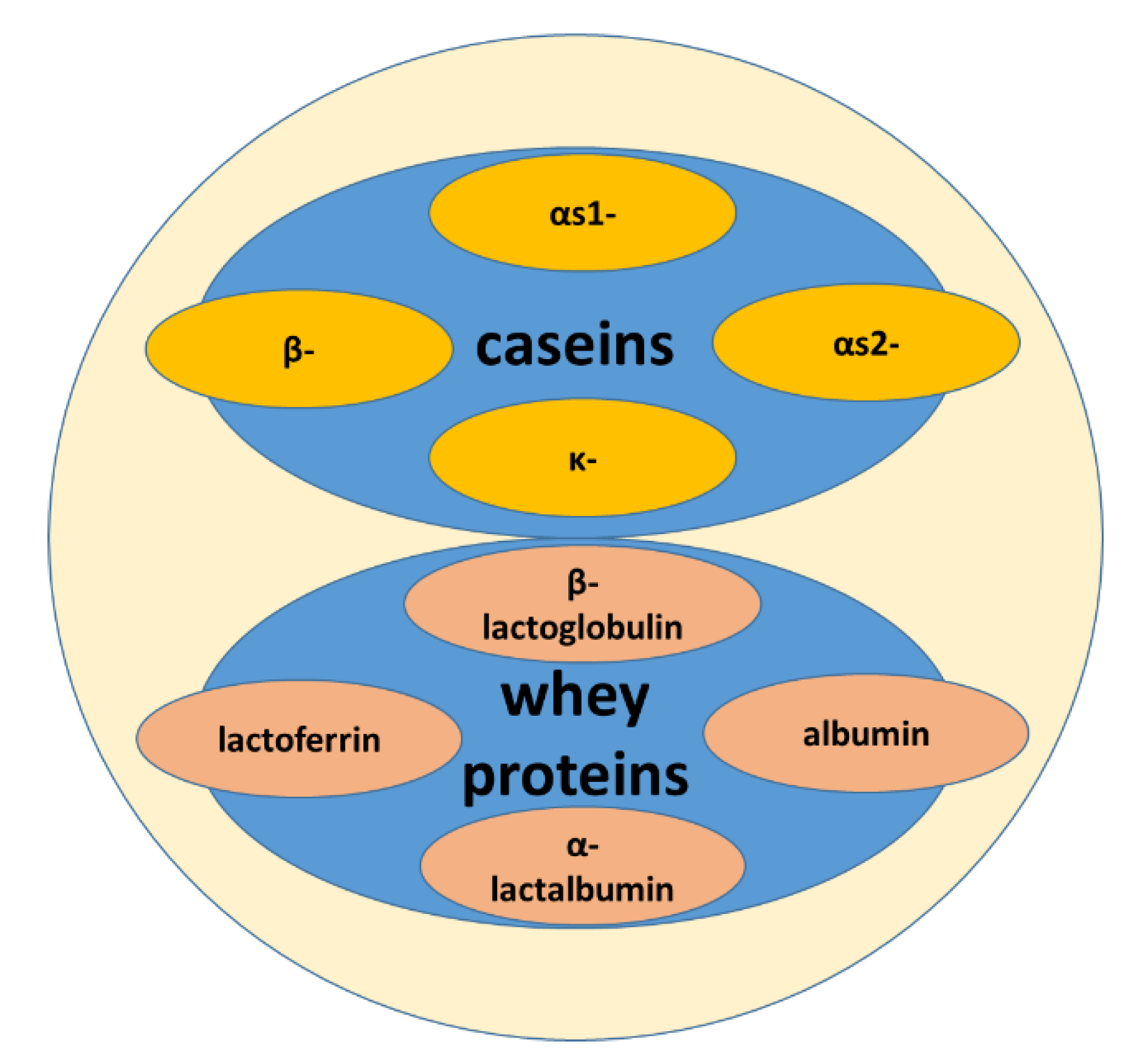
2. Milk and Whey
2.1. Milk
2.2. Whey
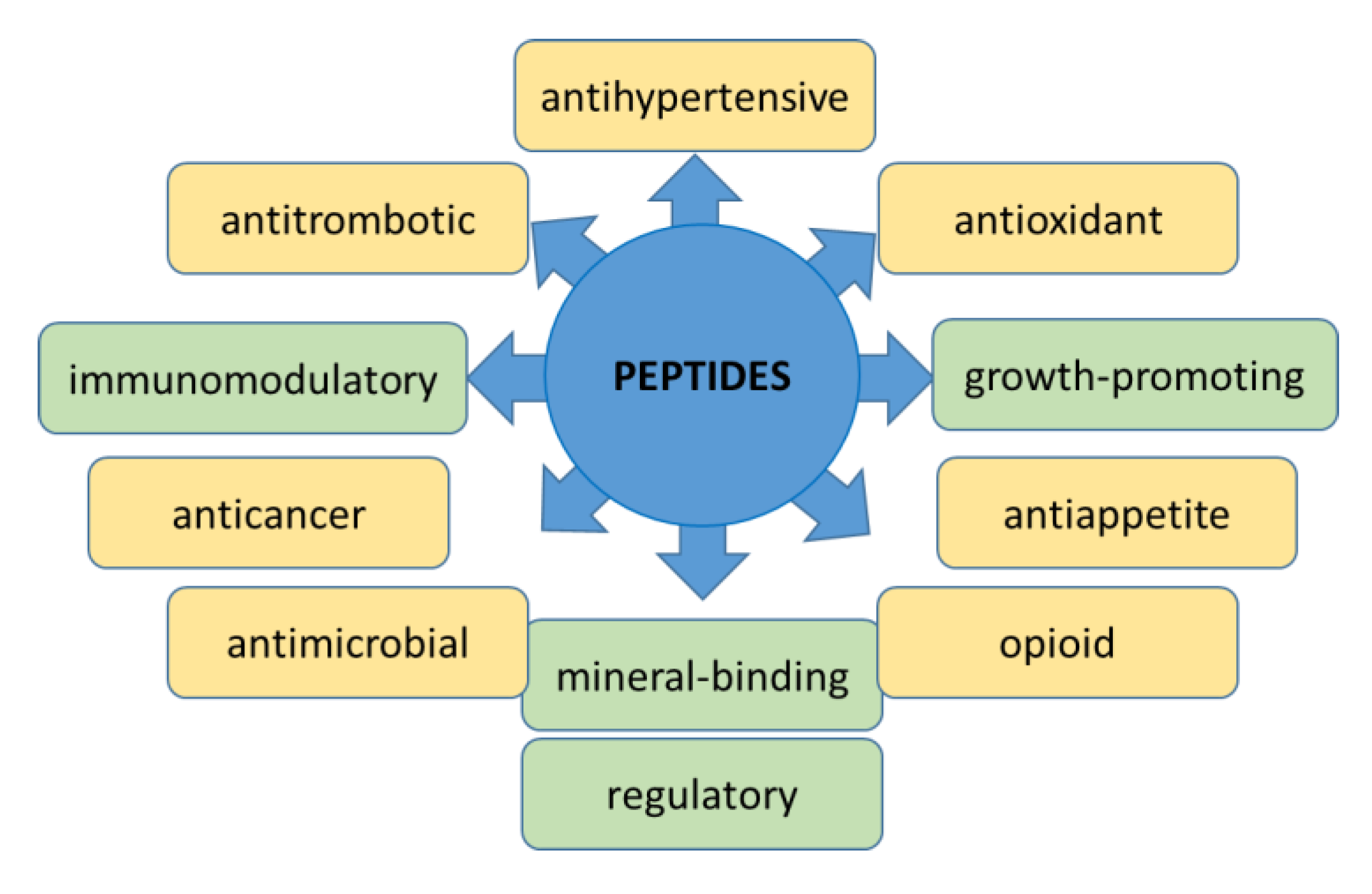
3. Peptides
4. Whey-Based Drinks
5. Proteolytic Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria
6. Perspectives
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- León-López, A.; Pérez-Marroquín, X.A.; Estrada-Fernández, A.G; Campos-Lozada, G.; Morales-Peñaloza, A.; Campos-Montiel, R.G; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Milk whey hydrolysates as high value-added natural polymers: functional properties and applications. Polymers 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Wei, J.; Hao, L.; Shan, Q.; Li, H.; Gao, D.; Jin, Y.; Sun, P. Bioactive proteins and their physiological functions in milk. Curr. Protein. Pept. Sc. 2019, 20(7), 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Shan, Q.; Wei, J.; Ma, F.; Sun, P. Lactoferrin: major physiological functions and applications. Curr. Protein. Pept. Sc. 2019, 20(2), 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minj, S.; Anand, S. Whey proteins and its derivatives: bioactivity, functionality, and current applications. Dairy 2020, 1(3), 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic peptides: current applications and future directions. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 14(1), 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Kamal, M.M.; Rahman, M.H.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Haque, M.A.; Saha, K.K.; Rahman, M.A. Functional dairy products as a source of bioactive peptides and probiotics: current trends and future prospectives. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59(4), 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodionov, I.S.; Evdokimov, I.A.; Abakumova, E.A. Biotechnological bases of a functional drink based on whey. Modern Science and Innovations 2023, 1, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.W.; Nam, M.S. Bioactive peptides in milk and dairy products: A Review. Korean J. Food Sci. An. 2015, 35(6), 831–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.T.; Bule, M.; Ullah, R.; Nadeem, M.; Asif, S.; Niaz, K. The antioxidant components of milk and their role in processing, ripening, and storage: Functional food. Vet. World 2019, 12(1), 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Givens, D.I. Milk and dairy foods: implications for cardio metabolic health. Cardiovasc. endocrinol. metab. 2018, 7(3), 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, J.T.; Ross, R.P.; Bolton, D.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Bioactive peptides from muscle sources: meat and fish. Nutrients 2011, 3, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Luchian, T.; Park, Y. New antimicrobial peptide kills drug-resistant pathogens without detectable resistance. Oncotarget 2018, 9(21), 15616–15634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, R.A. Poppitt, S. Milk protein for improved metabolic health: a review of the evidence. Nutr. Metab. (Lond) 2013, 10, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, S.K. Antioxidants capacity of milk, probiotics and postbiotics: a review. <italic>FSNT </italic><bold>2024</bold>, <italic>9(1)</italic>. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Han, S.; He, H. Lactoferrin alleviates inflammation and regulates gut microbiota composition in H5N1-infected mice. Nutrients 2023, 15(15), 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trybek, G.; Metlerski, M.; Szumilas, K.; Aniko-Włodarczyk, M.; Preuss, O. The biological properties of lactoferrin. Cent. Eur. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2016, 15, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, I.; Vignard, J.; Bouchenot, C.; Graikini, D.; Grasa. L.; Pérez M.D.; Mirey, G.; Sánchez, L. Dairy by-products and lactoferrin exert antioxidant and antigenotoxic activity on intestinal and hepatic cells. Foods 2023, 12(10), 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, E.S.; Christensen, B. Milk osteopontin and human health. Nutrients 2023, 15(11), 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldrá, F.; Reig, M.; Aristoy, M.C.; Mora, L. Generation of bioactive peptides during food processing. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán-Rodríguez, F.; Gómez-Ruizy, L.; Rodríguez-Serrano, G.; Alatorre-Santamaría, S.; García-Garibay, M.; Cruz-Guerrero, W.A. Iron binding and antithrombotic peptides released during the fermentation of milk by Lactobacillus casei shirota. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim. 2019, 18, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Liang, N.; Rathish, H.; Kim, B.J.; Lueangsakulthai, J.; Koh, J.; Qu, Y.; Schulz, H.J.; Dallas, D.C. Bioactive milk peptides: an updated comprehensive overview and database. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 28, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintieri, L.; Fanelli, F.; Monaci, L.; Fusco, V. Milk and its derivatives as sources of components and microorganisms with health-promoting properties: probiotics and bioactive peptides. Foods 2024, 13(4), 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive peptides derived from human milk proteins-mechanisms of action. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25(5), 503–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudkiewicz, M.; Berlowska, J.; Kregiel, D. Acid whey as a medium for cultivation of conventional and non-conventional yeasts. <italic>Biotechnol. Food Sci.</italic> <bold>2016</bold>, <italic>80 (2)</italic>, 75-82 http://www.bfs.p.lodz.pl.
- Chizhayeva, A.; Oleinikova, Y.; Saubenova, M.; Sadanov, A.; Amangeldi, A.; Aitzhanova, A.; Yelubaeva, M.; Alybaeva, A. Impact of probiotics and their metabolites in enhancement the functional properties of whey-based beverages. AIMS agric. food. 2020, 5(3), 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchik, P.; Zuber, T.; Zuber, A.; Moraru, C.I. Short communication: composition of coproduct streams from dairy processing: Acid whey and milk permeate. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 3978–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera Rodriguez, F.; Fernández-Martinez, A .; Muro Urista C. <italic>Whey: types, composition and health implications,</italic> 1st edition, R. Benitez, G. Ortero (Eds.), Nova science publishers Inc., Hauppauge, NY ,2012.
- Bylund, G. <italic>Dairy processing handbook, </italic>3rd. ed. Tetra Pak Processing Systems AB, Lund, Sweden. 2015.
- Zotta, T.; Solieri, L.; Iacumin, L.; Picozzi, C.; Gullo, M. Valorization of cheese whey using microbial fermentations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104(7), 2749–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B.; Athira, S.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, R.; Sarkar, P. Bioactive peptides from whey proteins. Whey Proteins 2019, 519–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Mendoza, D.; Kosmerl, E.; Krentz, A.; Zhang, L.; Badiger, S.; Miyagusuku-Cruzado, G.; Mayta-Apaza, A.; Giusti, M.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; García-Cano, I. Invited review: Acid whey trends and health benefits. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104(2), 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballatore, MB.; Bettiol, MDR.; Vanden Braber, NL.; Aminahuel, CA.; Rossi, YE.; Petroselli, G.; Erra-Balsells, R.; Cavaglieri, LR.; Montenegro, MA. Antioxidant and cytoprotective effect of peptides produced by hydrolysis of whey protein concentrate with trypsin. <italic>Food Chem.</italic><bold> 2020</bold>, <italic>319</italic>, 126472. [CrossRef]
- Dullius, A.; Goettert, MI.; Volken de Souza, CF. Whey protein hydrolysates as a source of bioactive peptides for functional foods – Biotechnological facilitation of industrial scale-up. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaver, EH.; Kempka, AP. Potential of milk-derived bioactive peptides as antidiabetic, antihypertensive, and xanthine oxidase inhibitors: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis and updated review. Amino Acids 2023, 55(12), 1829–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khavinson, V. Kh.; Popovich, I. G.; Linkova, N.S.; Mironova, E.S.; Ilina, A. R. Peptide regulation of gene expression: A systematic review. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcone, S.; Belton, O.; Fitzgerald, DJ. Milk-derived bioactive peptides and their health promoting effects: a potential role in atherosclerosis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 83(1), 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendse, LB.; Danser, AHJ.; Poglitsch, M.; Touyz, RM. Novel therapeutic approaches targeting the renin-angiotensin system and associated peptides in hypertension and heart failure. <italic>Pharmacol. Rev. </italic><bold>2019</bold>, <italic>71(4)</italic>, 539–570. [CrossRef]
- Rutherfurd-Markwick, KJ. Food proteins as a source of bioactive peptides with diverse functions. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 49–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.; Mudgil, P.; Palakkott, A.; Iratni, R.; Gan, CY., Maqsoo, S.; Ayoub, M.A. Molecular basis of the anti-diabetic properties of camel milk through profiling of its bioactive peptides on dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) and insulin receptor activity. <italic>J. Dairy Sci.</italic><bold> 2021</bold>, <italic>104(1)</italic>, 61-77. [CrossRef]
- Muttenthaler, M.; King, GF.; Adams, DJ.; Alewood, PF. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggag, Y.A.; Donia, A.A.; Osman M.A.; El-Gizawy, S.A. Peptides as drug candidates: limitations and recent development perspectives. <italic>Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res.</italic><bold> 2018</bold>, 8(4). [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Bin, Y.; Xia, J. PrMFTP: Multi-functional therapeutic peptides prediction based on multi-head self attention mechanism and class weight optimization. <italic>PLoS Comput. Biol.</italic> <bold>2022</bold>, <italic>18(9)</italic>. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, QY.; Yan, ZB.; Meng, YM.; Hong, XY.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.; Cheng, XR.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, CY. Antimicrobial peptides: mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8(1), 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, D.P.; Mohapatra, S.; Misra, S.; Sahu, P.S. Milk derived bioactive peptides and their impact on human health – A review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23(5), 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, I.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Hayat, S.; Aslam, B.; Sarfraz, M.H.; Yaseen, H.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Shah, A.A.; Khurshid, M. Prospects of antimicrobial peptides as an alternative to chemical preservatives for food safety. Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 45(2), 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.A.T.; Mantovani, H.C.; Jain, S. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria and their potential in the preservation of fruit products. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37(7), 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A. Physicochemical and sequence determinants of antiviral peptides. Biol. Futur. 2023, 74(4), 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Kumar, H.; Alghamdi, W.; Kateb, F.A.; Alarfaj, F.K. Recent advances in machine learning-based models for prediction of antiviral peptides. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefin, N.; Herrera-Belén, L.; Farias, J.G.; Beltrán, J.F. Review and perspective on bioinformatics tools using machine learning and deep learning for predicting antiviral peptides. Mol. Divers. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnepolsky, B.; Grigolava, M.; Gabrielian, A.; Rosenthal, A.; Hurt, D.; Tartakovsky, M.; Pirtskhalava, M. Analysis, modeling, and target-specific predictions of linear peptides inhibiting virus entry. <italic>ACS Omega</italic> <bold>2023</bold>, <italic>22;8(48)</italic>, 46218-46226. [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Raza, A.; Zou, Q. Deepstacked-AVPs: predicting antiviral peptides using tri-segment evolutionary profile and word embedding based multi-perspective features with deep stacking model. <italic>BMC Bioinformatics</italic> <bold>2024</bold>, <italic>7;25(1),</italic> 102. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Pei, H.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Zou, Q.; Lv, Z. FEOpti-ACVP: identification of novel anti-coronavirus peptide sequences based on feature engineering and optimization. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25(2), bbae037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Wu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xiang, C.; Huang, J. ACP-Dnnel: anti-coronavirus peptides’ prediction based on deep neural network ensemble learning. Amino Acids 2023, 55(9), 1121–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfi, R.; Kahaki, FA.; Ebrahimi, T.; Montazersaheb, S.; Eyvazi, S.; Babaeipour, V.; Tarhriz, V. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs): roles, functions and mechanism of action. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S.; Doull, F.; Rutherfurd, K.J.; Cross, M. Immunoregulatory peptides in bovine milk. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, S111–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto, A. Technological options for the production of health-promoting proteins and peptides derived from milk and colostrum. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13(8), 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matar, C.; LeBlanc, J.G.; Martin, L.; Perdigon, G. A<italic>ctive peptides released in fermented milk: role and functions</italic>. In: Farnworth ER, editor. Handbook of fermented functional foods. Functional foods and nutraceuticals series. CRC Press; Boca Raton, F. L., USA: 2003. pp. 177–201.
- Yuan, Q.; Chen, K.; Yu, Y.; Le, N.Q.K.; Chua, M.C.H. Prediction of anticancer peptides based on an ensemble model of deep learning and machine learning using ordinal positional encoding. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24(1), bbac630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J. MA-PEP: A novel anticancer peptide prediction framework with multimodal feature fusion based on attention mechanism. Prot. Sci. 2024, 33(4), e4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, H. ACPPfel: Explainable deep ensemble learning for anticancer peptides prediction based on feature optimization. Front. Genet. 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Hayat, M.; Tahir, M.; Khan, S.; Alarfaj, FK. cACP-DeepGram: Classification of anticancer peptides via deep neural network and skip-gram-based word embedding model. Artif. Intell. Med. 2022, 131, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanea, M.; Dukyil, AS.; Afnan.; Riaz, B.; Alebeisat, F.; Islam, M.; Habib, S. To assist oncologists: an efficient machine learning-based approach for anti-cancer peptides classification. <italic>Sensors (Basel)</italic> <bold>2022</bold>, <italic>22(11)</italic>, 4005. [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, O.; Kilimci, ZH. An efficient consolidation of word embedding and deep learning techniques for classifying anticancer peptides: FastText+BiLSTM. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, O.; Yousef, A.; Jumani, TA.; Armghan, A. Response score-based protein structure analysis for cancer prediction aided by the Internet of Things. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14(1), 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, YW. <italic>Bioactive components of goat milk In: Park Y. W.</italic>, editor. Bioactive components in milk and dairy products. Wiley-blackwell publishers; Ames, Iowa and Oxford, England: 2009a. pp. 43–82.
- Marcone, S.; Belton, O.; Fitzgerald, DJ. Milk-derived bioactive peptides and their health promoting effects: a potential role in atherosclerosis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83(1), 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, L.; Shah, NP. Release and identification of angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides as influenced by ripening temperatures and probiotic adjuncts in Cheddar cheeses. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopada, K.; Basaiawmoit, B.; Sakure, A.A.; Maurya, R.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Solanki, D.; Singh, B.P.; Padhi, S.; Rai, A.K.; Liu, Z.; Mishra, B.K.; Hati, S. Purification and characterization of novel antihypertensive and antioxidative peptides from whey protein fermentate: In Vitro, In Silico, and Molecular Interactions Studies. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2023, 42(6), 598–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, G.; Huang, J.; Bao, C.; Meng, J.; Chen, H.; Cao, J. Effect of different proteases on the degree of hydrolysis and angiotensin i-converting enzyme-inhibitory activity in goat and cow milk. Biomolecules 2018, 8(4), 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkçi, N.; Akdeniz, V.; Akalın, AS. Probiotic whey-based beverages from cow, sheep and goat milk: antioxidant activity, culture viability, amino acid contents. Foods 2023, 12(3), 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansi, M.S.; Iram, D.; Vij, S.; Kapila, S.; Meena, S. In vitro biosafety and bioactivity assessment of the goat milk protein derived hydrolysates peptides. J. Food Saf. 2023, 43, e13061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, E.I.; Bogdanova, E.V.; Koshevarova, I.B. Nutritional evaluation of whey protein hydrolysate: chemical composition, peptide profile, and osmolarity. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Kumar, H.; Kumar, N.; Ranvir, S.; Jana, A.; Buttar, HS.; Telessy, IG.; Awuchi, CG.; Okpala, C.O.R.; Korzeniowska, M.; Guiné, R.P.F. Whey proteins processing and emergent derivatives: An insight perspective from constituents, bioactivities, functionalities to therapeutic applications. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, J.K.; Sharma, P.K. Mini review on antimicrobial peptides, sources, mechanism and recent applications. Protein peptide lett. 2020, 27(1), 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucarini, M. Bioactive peptides in milk: from encrypted sequences to nutraceutical aspects. Beverages 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iukalo A. V.; Datsyshyn K. Ye.; Yukalo V. G. Bioactive peptides of the cow milk whey proteins (<italic>Bos taurus</italic>). <italic>Biotechnol. Acta</italic> <bold>2013</bold>, <italic>6(5)</italic>, 49-61. (in Ukrainian).
- Zhang, Q.; Ul Ain, Q.; Schulz, C.; Pircher, J. Role of antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin in thrombosis and thromboinflammation. Front. immunol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, P.; Li, X.; Zou, X.; Wang, K.; Yao, L.; Sun, Zh.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Tan, Y. Antihypertensive effects of whey protein hydrolysate involve reshaping the gut microbiome in spontaneously hypertension rats. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasin, G.; Comerford, KB. Dairy foods and dairy proteins in the management of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of the clinical evidence. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6(3), 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punia, H.; Tokas, J.; Malik, A.; Sangwan, S.; Baloda, S.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.; Bhuker, A.; Singh, P.; Yashveer, S.; Agarwal, S.; Mor, V. Identification and detection of bioactive peptides in milk and dairy products: remarks about agro-foods. Molecules 2020, 25(15), 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro, U.; Álvarez, F.; Rodriguez, R.; Cuenca, A.; Jurado, T. Review: production and functionality of active peptides from milk. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2011, 17, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Márquez-Hernández, RI.; Hernández-Castellano, LE. Bioactive peptides from milk: animal determinants and their implications in human health. J. Dairy Res. 2019, 86, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, S.; Huma, N.; Butt, MS.; Aleem, M.; Abbas, M. Therapeutic potential of dairy bioactive peptides: a contemporary perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58(1), 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.N.; Tang, S.H.; He, Q.; Hu, J.X.; Zheng, J. In vitro antioxidant and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of fermented milk with different culture combinations. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103(2), 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, L.S.; Santos, M.L.; Abreu, J.P.; Rocha, R.S.; Esmerino, E.A.; Freitas, M.Q.; Mársico, E.T.; Campelo, P.H.; Pimentel, T.C.; Cristina Silva, M.; Souza, A.A.; Nogueira, F.C.S.; Cruz, A.G.; Teodoro, A.J. Probiotic fermented whey-milk beverages: Effect of different probiotic strains on the physicochemical characteristics, biological activity, and bioactive peptides. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haj Mustafa, M.; Soleimanian-Zad, S.; Albukhaty, S. Whey protein concentrate hydrolyzed by microbial protease: process optimization and evaluation of its dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitory activity. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 15, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, J.; Arslan, A.A.; Fedorova, M.; Hoffmann, R.; Kucukcetin, A.; Pischetsrieder, M. Peptide profiling of bovine kefir reveals 236 unique peptides released from caseins during its production by starter culture or kefir grains. J. Proteom. 2015, 117, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Lv, J.; Gong, J.Y.; Xiao, G.N.; Zhu, R.Y.; Li, L.; Qiu, J.N. Secondary structures and their effects on antioxidant capacity of antioxidant peptides in yogurt. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21(1), 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievore, P.; Simões, D.R.; Silva, K.M.; Drunkler, N.L.; Barana, A.C.; Nogueira, A.; Demiate, I.M. Chemical characterisation and application of acid whey in fermented milk. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skryplonek, K.; Jasińska, M. Fermented probiotic beverages based on acid whey. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. 2015, 14, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skryplonek, K.; Dmytrów, I.; Mituniewicz-Małek, A. Probiotic fermented beverages based on acid whey. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7773–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal M. Value added products utilizing acid whey: Development of a fruit yogurt beverage and a sports drink. Master’s thesis. Department of Food Science, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences. Cornell University, Ithaca, NY. 2017.
- Oleinikova, Y.; Alybayeva, A.; Daugaliyeva, S.; Alimzhanova, M.; Ashimuly, K.; Yermekbay, Zh.; Khadzhibayeva, I.; Saubenova, M. Development of an antagonistic active beverage based on a starter including Acetobacter and assessment of its volatile profile. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 148, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, R.J.S.; Sato, H.H. Biologically active peptides: Processes for their generation, purification and identification and applications as natural additives in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Food Res. Int. 2015, 74, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescuma, M.; Hébert, E.M.; Mozzi, F.; de Valdez, G.F. Functional fermented whey-based beverage using lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, W.M.; Nobre, M.S.C.; Cavalcanti, M.T.; Olbrich Dos Santos, K.M.; Salles, H.O.; Alonso Buriti, F.C. Proteolysis of reconstituted goat whey fermented by Streptococcus thermophilus in co-culture with commercial probiotic Lactobacillus strains. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareb, O.; Aïder, M. Whey and its derivatives for probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and functional foods: a critical review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11(2), 348–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleinikova, Y.; Amangeldi, A.; Yelubaeva, M.; Alybaeva, A.; Sadanov, A.; Saubenova, M.; Chizhaeva, A.; Aitzhanova, A.; Berzhanova, R. Immobilization of dairy starter on wheat bran enhance viability under acid and bile stress. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2020, 7(4), 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barukčić, I.; Lisak Jakopović, K.; Božanić, R. Valorisation of whey and buttermilk for production of functional beverages - an overview of current possibilities. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57(4), 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Matos Reis, S.; Mendes, GDRL; Mesquita, BMAC.; Lima, WJN.; Pinheiro, CAFD.; Ruas, FAO.; Santos, GLM.; Brandi, IV. Development of milk drink with whey fermented and acceptability by children and adolescents. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2847–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.; Fidan, H.; Ozogul, F.; Rocha, JM. Industrial and health applications of lactic acid bacteria and their metabolites. Front. microbiol. 2023, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Jain, A.K.; Ghosh, M. Industrial whey utilization as a medium supplement for biphasic growth and bacteriocin production by probiotic Lactobacillus casei LA-1. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 2012, 4, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabo, SS.; Converti, A.; Ichiwaki, S.; Oliveira, R.P.S. Bacteriocin production by <italic>Lactobacillus plantarum</italic> ST16Pa in supplemented whey powder formulations. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102(1), 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitzhanova, A.; Oleinikova, Y.; Mounier, J.; Hymery, N.; Leyva Salas, M.; Amangeldi, A.; Saubenova, M.; Alimzhanova, M.; Ashimuly, K.; Sadanov, A. Dairy associations for the targeted control of opportunistic Candida. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveschot, C.; Cudennec, B; Coutte, F.; Flahaut, C.; Fremont, M.; Drider, D.; Dhulster, P. production of bioactive peptides by <italic>Lactobacillus</italic> species: from gene to application. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansinhbhai, CH.; Sakure, A.; Maurya, R.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, KK.; Das, S.; Hati, S. Significance of whey protein hydrolysate on anti-oxidative, ACE-inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities and release of peptides with biofunctionality: an in vitro and in silico approach. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59(7), 2629–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, Z.; Cakir-Kiefer, C.; Roux, E.; Perrin, C.; Miclo, L.; Dary-Mourot, A. Review Strategies of producing bioactive peptides from milk proteins to functionalize fermented milk products. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldrá, F.; Gallego, M.; Reig, M.; Aristoy, MC.; Mora, L. Bioactive peptides generated in the processing of dry-cured ham. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas-Ortega, M.G.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Martinez-Hernandez, J.L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Nevarez-Moorillon, G.V. Production of bioactive peptides from lactic acid bacteria: a sustainable approach for healthier foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alu’datt, M.H.; Al-U’datt, D.G.F.; Alhamad, M.N.; Tranchant, C.C.; Rababah, T.; Gammoh, S.; Althnaibat, R.M.; Daradkeh, M.G.; Kubow, S. Characterization and biological properties of peptides isolated from dried fermented cow milk products by RP-HPLC: Amino acid composition, antioxidant, antihypertensive, and antidiabetic properties. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86(7), 3046–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan., M.; Guo, T.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y.; Li, DXA.; Zhang, S. Isolation and identification of novel casein-derived bioactive peptides and potential functions in fermented casein with<italic> Lactobacillus helveticus</italic>. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2019, 8, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak, K.; Gustaw, W.; Fornal, E.; Kononiuk, A.; Michalak-Majewska, M.; Radzki, W.; Waśko, A. Functional and technological potential of whey protein isolate in production of milk beverages fermented by new strains of Lactobacillus helveticus. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10(20), 7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandelli, A.; Daroit, D.J.; Corrˆea, A.P.F. Whey as a source of peptides with remarkable biological activities. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeth, H.C.; Bansal, N. <italic>Whey proteins: From milk to medicine.</italic> Academic Press. UK, London, 2018, 746 pp.
- Dulliusa, A.; Goettert, M.I.; de Souza, C.F.V. Whey protein hydrolysates as a source of bioactive peptides for functional foods – Biotechnological facilitation of industrial scale-up. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 58–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Keskin Ulug, S.; Hong, H.; Wu, J. Regulatory requirements of bioactive peptides (protein hydrolysates) from food proteins. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 58, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.F.T. da.; Barbosa, M.A.P.; Marinho, T.A. de F.; Lima, G.C.; Santos, W.L. dos; Espindola, M.T.A.; Soares, L.B.F.; Gomes, J.E.G.; Moreira, K.A. Ten years of research on bioactive peptides in Brazil: a scientometric analysis. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruchinin, A.G.; Bolshakova, E.I.; Barkovskaya, I.A. Bioinformatic modeling (in silico) of obtaining bioactive peptides from the protein matrix of various types of milk whey. Fermentation 2023, 9(4), 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Beverly, R.L.; Qu, Y.; Dallas, D.C. Milk bioactive peptide database: A comprehensive database of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides and novel visualization. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, A.F.; Marnotes, N.G.; Rubio, O.D.; Garcia, A.C.; Pereira, C.D. Dairy by-products: a review on the valorization of whey and second cheese whey. Foods 2021, 10(5), 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krunic, T.; Rakin, M.; Bulatovic, M.; Zaric, D. Chapter 9 - The contribution of bioactive peptides of whey to quality of food products. <italic>Food Processing for Increased Quality and Consumption, Handbook of Food Bioengineering</italic><bold> 2018</bold>, 251-285. [CrossRef]
- Aman, F.; Masood, S. How nutrition can help to fight against COVID-19 pandemic. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, S121–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, A.; Sharma, S.; Kant, A.; Sevda, S.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Garlapati, V.K. Functional foods as a formulation ingredients in beverages: technological advancements and constraints. Bioengineered. 2021, 12(2), 11055–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.T.; Ali, Z.; Armitage, A.E.; Bonell, A.; Cerami, C.; Drakesmith, H.; Jobe, M.; Jones, K.S.; Liew, Z.; Moore, S.E.; Morales-Berstein, F.; Nabwera, H.M.; Nadjm, B.; Pasricha, S.R.; Scheelbeek, P.; Silver, M.J.; The, M.R.; Prentice, A.M. Could nutrition modulate COVID-19 susceptibility and severity of disease? A systematic review. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri, E.B.M.; Oh, D.H.; Lee, B.H. Bioactive peptides. Foods 2017, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Barrientos, L.M.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Torres-Llanez, M.J.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Córdoba, B. Invited review: Fermented milk as antihypertensive functional food. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, M.A.; Irfan, S.; Hafiz, I.; Ranjha, MM.A.N.; Rahaman, A.; Murtaza, M.S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Siddiqui, S.A. Conventional and novel technologies in the production of dairy bioactive peptides. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




