Submitted:
05 June 2024
Posted:
12 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Machine Learning Based Diabetes Prediction Models
2.2. Outlier Detection Method
2.3. Oversampling Method for Solving Class Imbalance Issue
3. Data and Prediction Model
3.1. Description of the Dataset
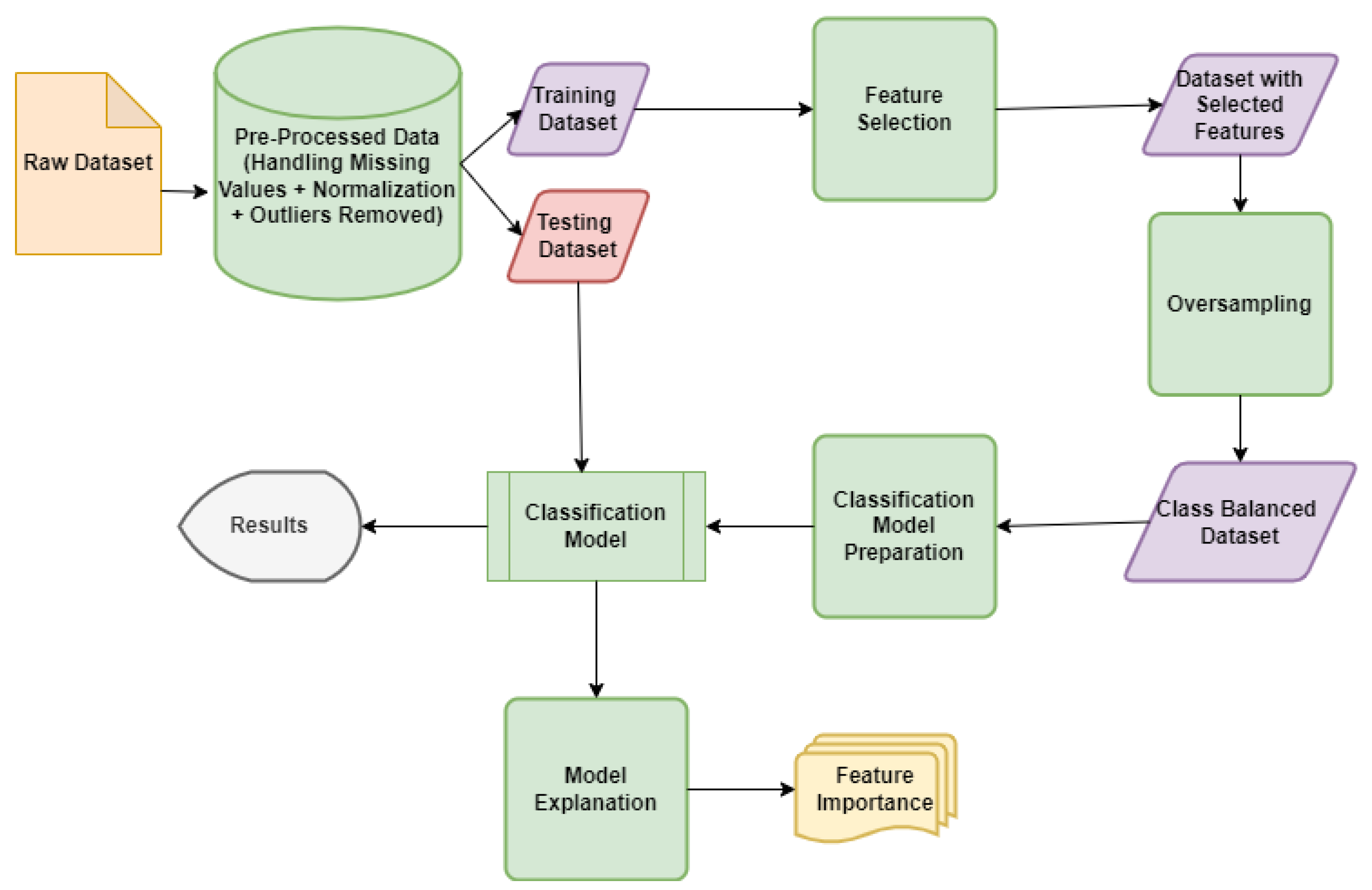
3.2. Proposed Model for Diabetes Prediction
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Min-Max Normalization
3.3.2. Isolation Forest
3.3.3. Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE)
3.3.4. Chi-Square Test
3.3.5. Minimum Redundancy and Maximum Relevancy (mRMR) Test
3.3.6. Recursive Feature Elimination based Random Forest (RFE-RF) Test
3.3.7. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
3.3.8. K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
3.3.9. Naive Bayes (NB)
3.3.10. SHAP
3.3.11. Performance Metrics
4. Experimental Analysis
5. Result Analysis
6. Conclusion and Future Work
References
- R. Thomas, S. Halim, S. Gurudas, S. Sivaprasad, and D. Owens, “Idf diabetes atlas: A review of studies utilizing retinal photography on the global prevalence of diabetes related retinopathy between 2015 and 2018,” Diabetes research and clinical practice, vol. 157, p. 107840, 2019. [CrossRef]
- G. D. Kalyankar, S. R. Poojara and N. V. Dharwadkar, “Predictive analysis of diabetic patient data using machine learning and Hadoop,” 2017 International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (ISMAC), Palladam, India, 2017, pp. 619–624. [CrossRef]
- S. Wild, G. Roglic, A. Green, R. Sicree, and H. King, “Global prevalence of diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030,” Diabetes Care, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 104–1053, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Newsletter. Issue 100 February 2023., 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.dab-bd.org/diabetes_newsletter.php. Accessed on: May 13, 2023.
- W. H. Organization, “Diabetes fact sheet N 312. October 2013,” Archived from the original on, vol. 26, 2013.
- E. Saedi, M. R. Gheini, F. Faiz, and M. A. Arami, “Diabetes mellitus and cognitive impairments,” World journal of diabetes, vol. 7, no. 17, p. 412, 2016. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. (2016). Projections of Mortality and Causes of Death, 2016 to 2060. [Online]. Available: https://www.who. int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/projections/en/.
- A. D. Association, “Economic costs of diabetes in the us in 2017,” Diabetes care, vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 917–928, 2018. [CrossRef]
- B.M. Patil, R.C. Joshi, and D. Toshniwal, "Hybrid prediction model for Type-2 diabetic patients", Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 37, no. 12, pp. 8102–8108, 2010. [CrossRef]
- H. Wu, S. Yang, Z. Huang, J. He, and X. Wang, “Type 2 diabetes mellitus prediction model based on data mining,” Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, vol. 10, pp. 100–107, 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. Domingues, M. Filippone, P. Michiardi, and J. Zouaoui, “A comparative evaluation of outlier detection algorithms: Experiments and analyses,” Pattern Recognit., vol. 74, pp. 406–421, Feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Douzas, F. Bacao, and F. Last, “Improving imbalanced learning through a heuristic oversampling method based on k-means and SMOTE,” Information Sciences, vol. 465, pp. 1–20, 2018. [CrossRef]
- B. Yan, G. Han, M. Sun and S. Ye, "A novel region adaptive SMOTE algorithm for intrusion detection on imbalanced problem," 2017 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2017, pp. 1281-1286. [CrossRef]
- A. Alloubani, A. Saleh, and I. Abdelhafiz, "Hypertension and diabetes mellitus as a predictive risk factors for stroke," Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome, Clin. Res. Rev., vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 577–584, Jul. 2018. [CrossRef]
- B.M. Patil, R.C. Joshi, and D. Toshniwal, "Hybrid prediction model for Type-2 diabetic patients," Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 37, nn. 12, pp. 8102–8108, 2010. [CrossRef]
- B. Farran, A.M. Channanath, K. Behbehani, and T.A. Thanaraj,“Predictive models to assess risk of type 2 diabetes, hypertension and comorbidity: machine-learning algorithms and validation using national health data from Kuwait–a cohort study.” BMJ open, vol. 3, May, 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. Wu, S. Yang, Z. Huang, J. He, and X. Wang, "Type 2 diabetes mellitus prediction model based on data mining,"Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, vol. 10, pp. 100–107, 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. M. Alam, M. A. Iqbal, Y. Ali, A. Wahab, S. Ijaz, T. I. Baig, A. Hussain, M. A. Malik, M. M. Raza, S. Ibrar, Z. Abbas, "A model for early prediction of diabetes,"Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, vol. 16, pp. 100204, 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. L. Fitriyani, M. Syafrudin, G. Alfian, and J. Rhee, “Development of disease prediction model based on ensemble learning approach for diabetes and hypertension,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, p. 144777, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Islam, R. Ferdousi, S. Rahman, and H. Y. Bushra, “Likelihood prediction of diabetes at early stage using data mining techniques,” Computer Vision and Machine Intelligence in Medical Image Analysis, Springer, pp. 113–125, 2020.
- M. M. Islam, M. J. Rahman, M. M. Abedin, B. Ahammed, M. Ali, N. F. Ahmed and M. Maniruzzaman, “Identification of the risk factors of type 2 diabetes and its prediction using machine learning techniques”, Health Systems, Taylor & Francis, pp. 1-12, 2022.
- H. M. Deberneh, and I. Kim. "Prediction of Type 2 diabetes based on machine learning algorithm." International journal of environmental research and public health, MDPI, no. 6, p. 3317, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. H. Syed, and T. Khan. "Machine learning-based application for predicting risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Saudi Arabia: a retrospective cross-sectional study." IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 199539-199561, 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. T. Liu, K. M. Ting and Z. -H. Zhou, "Isolation Forest," 008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Pisa, Italy, 2008, pp. 413-422. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Ijaz, M. Attique, and Y. Son, “Data-Driven Cervical Cancer Prediction Model with Outlier Detection and Over-Sampling Method”,Sensors, vol. 20, no. 10, 2020, Art. no. 2809. [CrossRef]
- R. Bharti, A. Khamparia, M. Shabaz, G. Dhiman, S. Pande, and P. Singh, "Prediction of Heart Disease Using a Combination of Machine Learning and Deep Learning", Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, vol. 2021, 2021, Art. no. 8387680. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Rezaei, J. R. Woodward, J. Ramirez and P. Munroe, "Combination of Isolation Forest, SMOTE and Ensemble Learning for the classification of Atrial Fibrillation and Ventricular Arrhythmia," 2021 International Conference on Biomedical Innovations and Applications (BIA), Varna, Bulgaria, 2022, pp. 45-50. [CrossRef]
- N. V. Chawla, K. W. Bowyer, L. O. Hall, and W. P. Kegelmeyer, "SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique," Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, vol. 16, pp.321-57, 2002.
- M. F. Ijaz, G. Alan, M. Syafrudin, and J. Rhee, “Hybrid prediction model for type 2 diabetes and hypertension using dbscan-based outlier detection, synthetic minority over-sampling technique (smote), and random forest,” Applied Sciences, vol. 8, no. 8, Aug. 2018, Art. no. 1325. [CrossRef]
- S. Wang, S. Liu, J. Zhang, X. Che, Y. Yuan, Z. Wang, D. Kong, "A new method of diesel fuel brands identification: SMOTE oversampling combined with XGBoost ensemble learning," Fuel, vol. 282, p. 118848, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Sridhar and S. Sanagavarapu, "Handling Data Imbalance in Predictive Maintenance for Machines using SMOTE-based Oversampling," 2021 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Lima, Peru, 2021, pp. 44-49. [CrossRef]
- J. P.Willems, J. T. Saunders, D. E. Hunt, and J. B. Schorling,"Prevalence of coronary heart disease risk factors among rural blacks: A community based study," Southern Medical Journal, vol. 90, no. 8, pp. 814–820, Aug. 1997. [CrossRef]
- A. Ugoni, and B.F. Walker, "The Chi square test: an introduction," COMSIG review, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 61–64, 1995.
- H. Peng, F. Long and C. Ding, "Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy," IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 1226–1238, Aug. 2005. [CrossRef]
- P.M. Granitto, C. Furlanello, F. Biasioli, F. Gasperi, "Recursive feature elimination with random forest for PTR-MS analysis of agroindustrial products." Chemometrics and intelligent laboratory systems, vol. 83, no. 2, pp. 83-90, 2006. [CrossRef]
- C. Corinna and V. Vapnik, "Support-Vector Networks," Machine Learning, Vol. 20, No. 3, pp. 273-297, 1995. [CrossRef]
- T. Cover and P. Hart, "Nearest neighbor pattern classification," IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 21–27, January 1967. [CrossRef]
- P. Langley, W. Iba, and K. Thompson, "An analysis of Bayesian classifiers," Aaai, vol. 90, pp. 223–228, 1992.
- S. M. Lundberg, and S.-L. Lee, "A unified approach to interpreting model predictions", Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017.
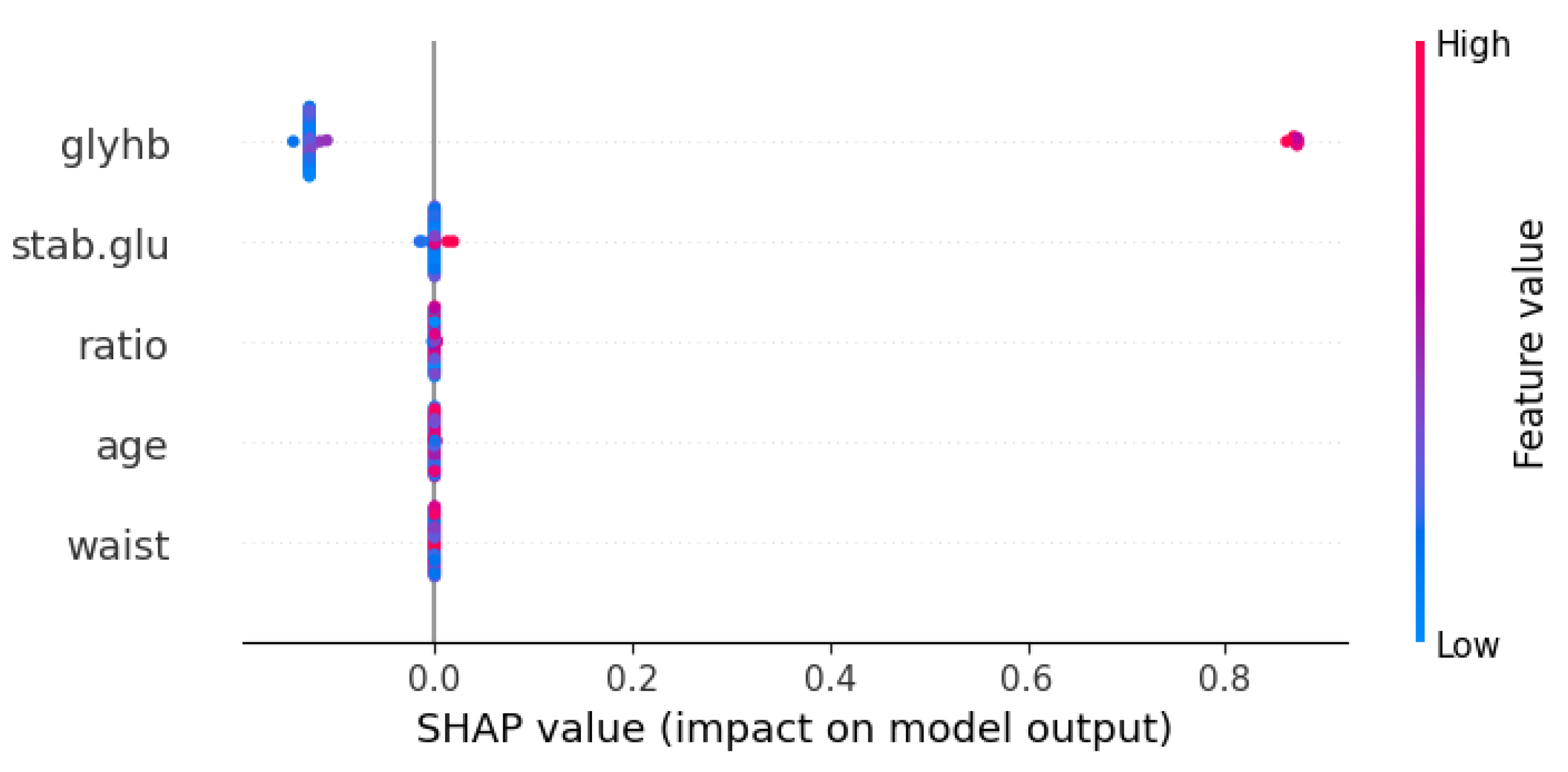
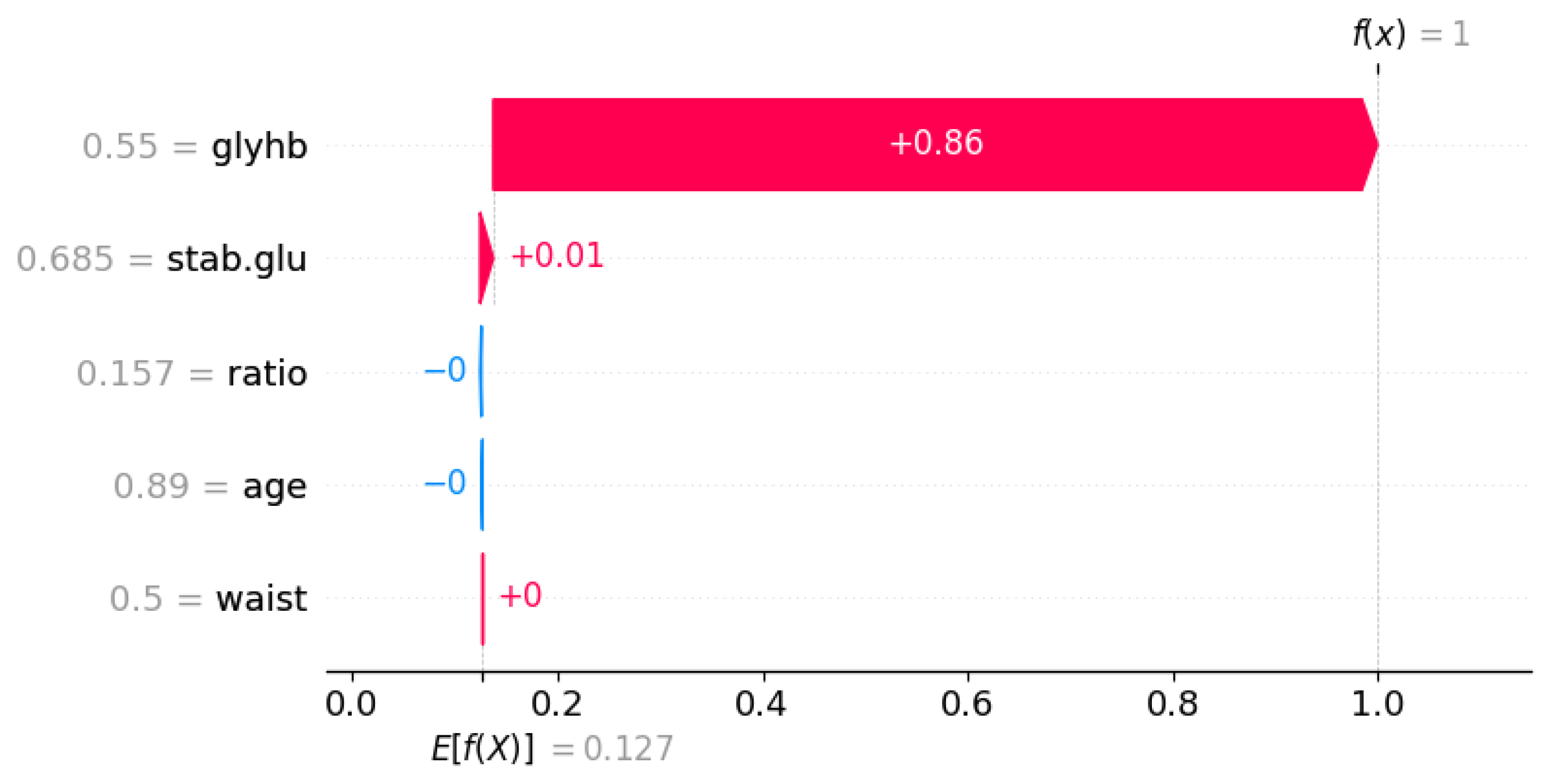
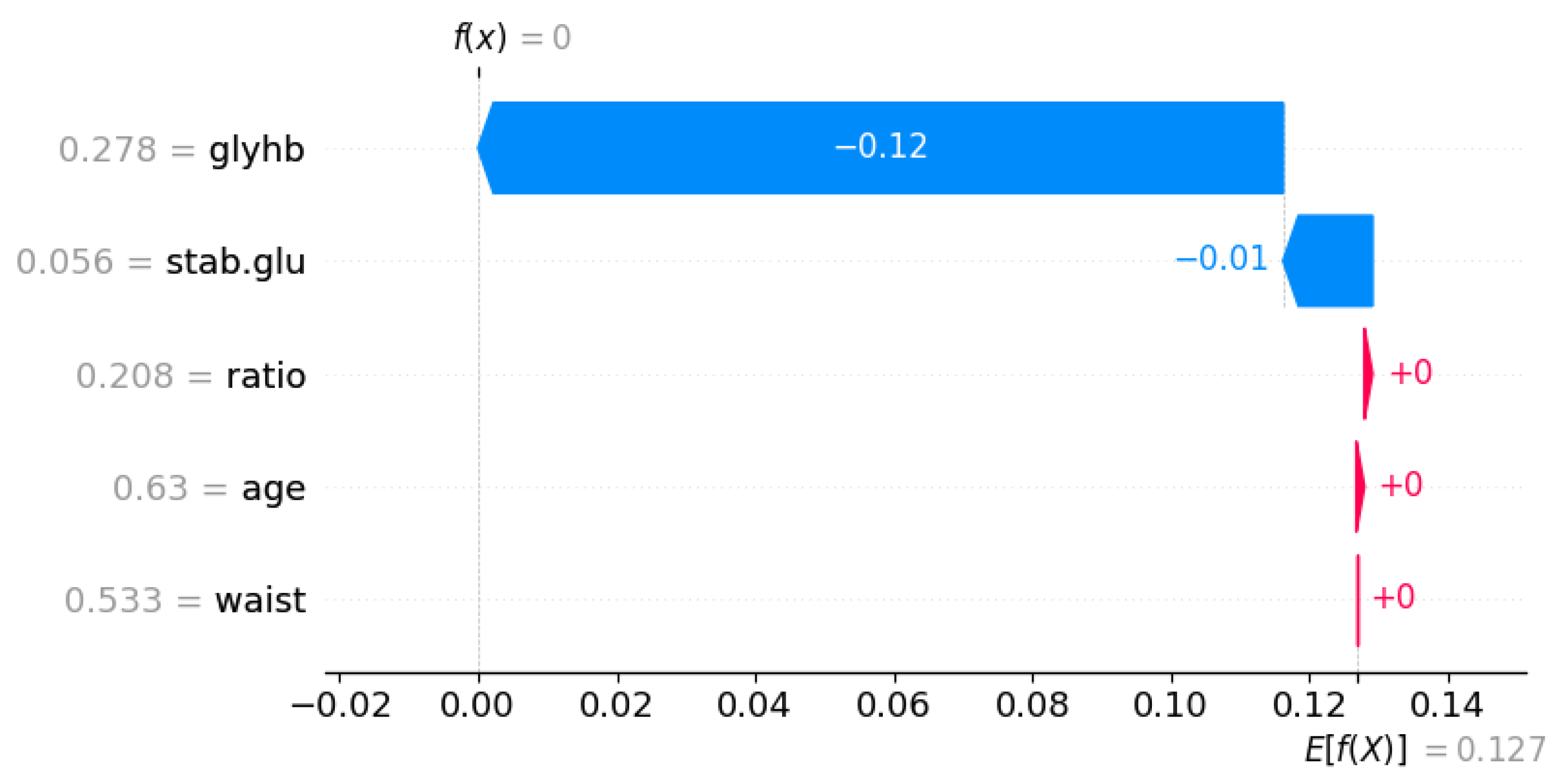
| Symbol | Attribute Name | Data Type | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chol | Total cholesterol | Numeric | 207.604 | 44.757 | 78.000 | 443.000 |
| stab.glu | Stabilized glucose | Numeric | 107.684 | 54.139 | 48.000 | 385.000 |
| hdl | High density lipoprotein | Numeric | 50.414 | 17.463 | 12.000 | 120.000 |
| ratio | Cholesterol/hdl ratio | Numeric | 4.528 | 1.757 | 1.500 | 19.299 |
| glyhb | Glycosylated hemoglobin | Numeric | 5.606 | 2.219 | 2.680 | 16.110 |
| location | Location | Nominal | - | - | - | - |
| age | Age | Numeric | 46.898 | 16.615 | 19.000 | 92.000 |
| gender | Gender | Nominal | - | - | - | - |
| height | Height | Numeric | 66.000 | 3.920 | 52.000 | 76.000 |
| weight | Weight | Numeric | 177.957 | 40.604 | 99.000 | 325.000 |
| frame | A factor | Nominal | - | - | - | - |
| bp.1s | First systolic blood pressure | Numeric | 137.396 | 23.185 | 90.000 | 250.000 |
| bp.1d | First diastolic blood pressure | Numeric | 83.393 | 13.559 | 48.000 | 124.000 |
| waist | Waist | Numeric | 37.957 | 5.785 | 26.000 | 56.000 |
| hip | Hip | Numeric | 43.093 | 5.649 | 30.000 | 64.000 |
| time.ppn | Postprandial time when labs were drawn | Numeric | 335.589 | 309.270 | 5.000 | 1560.000 |
| Classifiers Name | Acc | Sen | Spe | MCC | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN(K=5) | 0.88 | 0.33 | 0.98 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.66 |
| NB | 0.97 | 1 | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.98 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.962 | 0.7625 | 1 | 0.854 | 0.8649 | 0.8813 |
| Classifiers Name | Acc | Sen | Spe | MCC | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KNN(K=5) | 0.9 | 0.22 | 1 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 0.61 |
| NB | 0.972 | 1 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0.9 | 0.984 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.9782 | 0.85 | 0.9968 | 0.8983 | 0.9073 | 0.9234 |
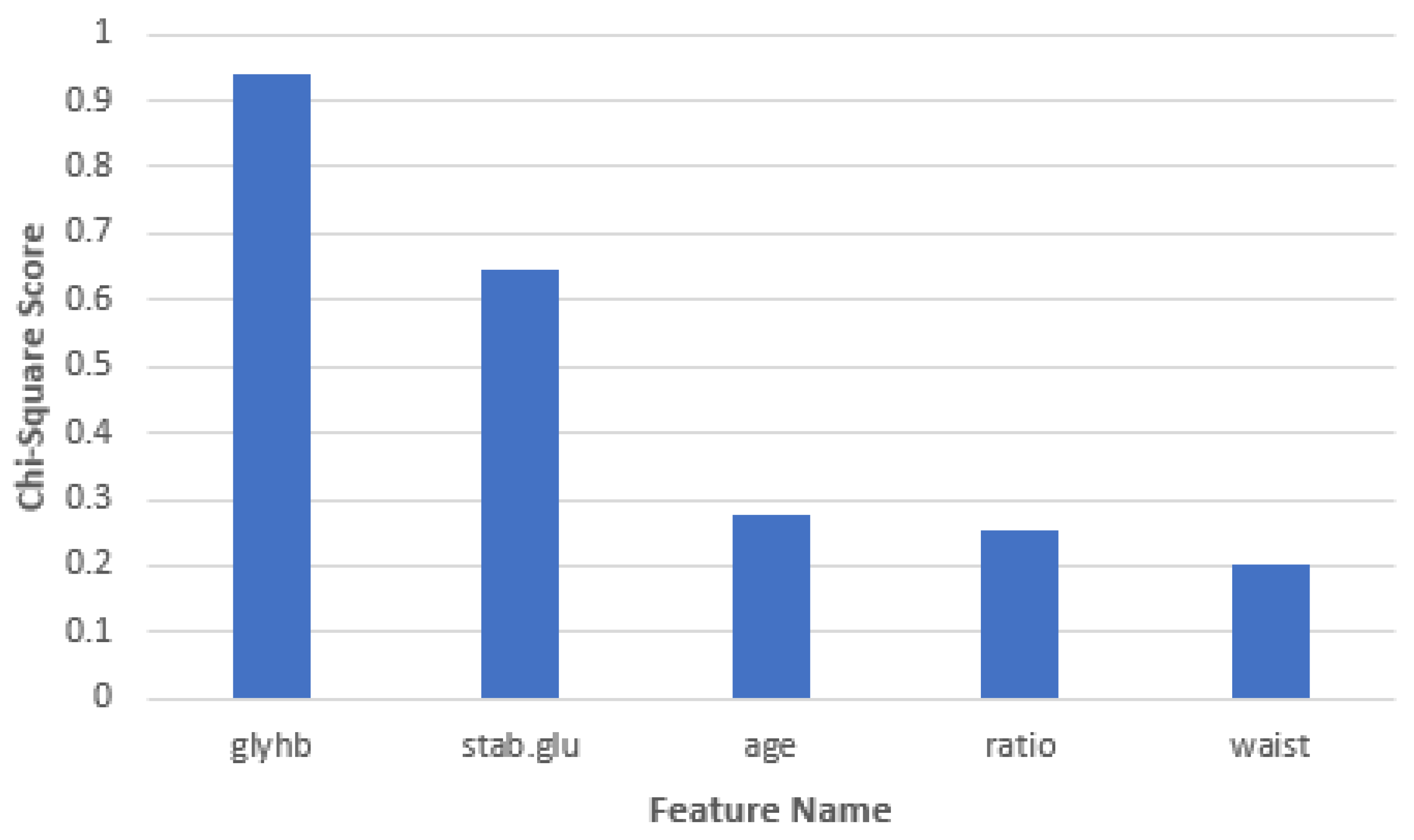
| Feature Name | Chi-Square Score |
|---|---|
| Glycosylated hemoglobin | 0.942140826 |
| Stabilized glucose | 0.648116177 |
| Age | 0.276345332 |
| Cholesterol/hdl ratio | 0.253842938 |
| Waist | 0.204076578 |
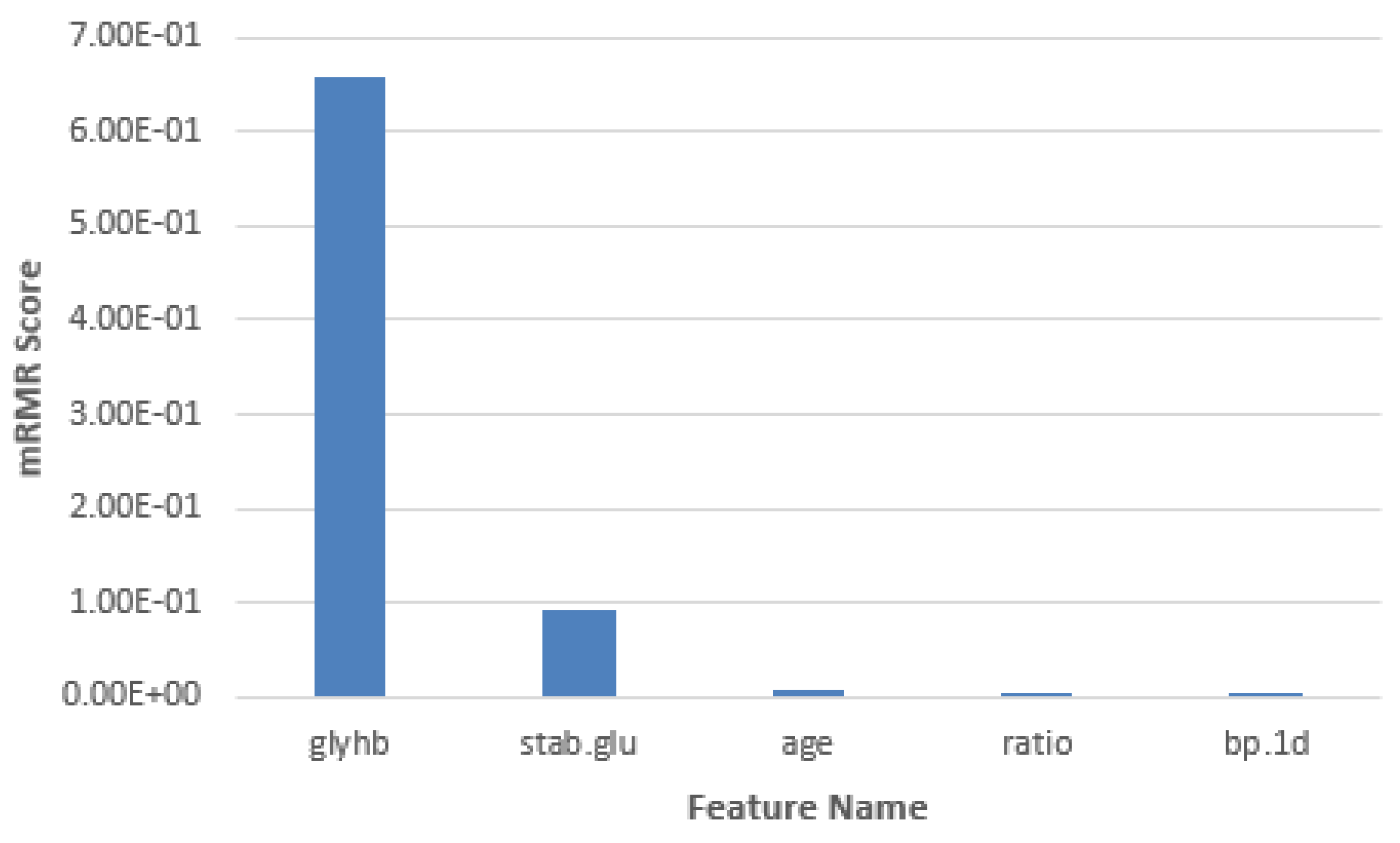
| Feature Name | Chi-Square Score |
|---|---|
| Glycosylated hemoglobin | 0.6569431 |
| Stabilized glucose | 0.09282437 |
| Age | 0.005962992 |
| Cholesterol/hdl ratio | 0.004957832 |
| First diastolic blood pressure | 0.00004741571 |
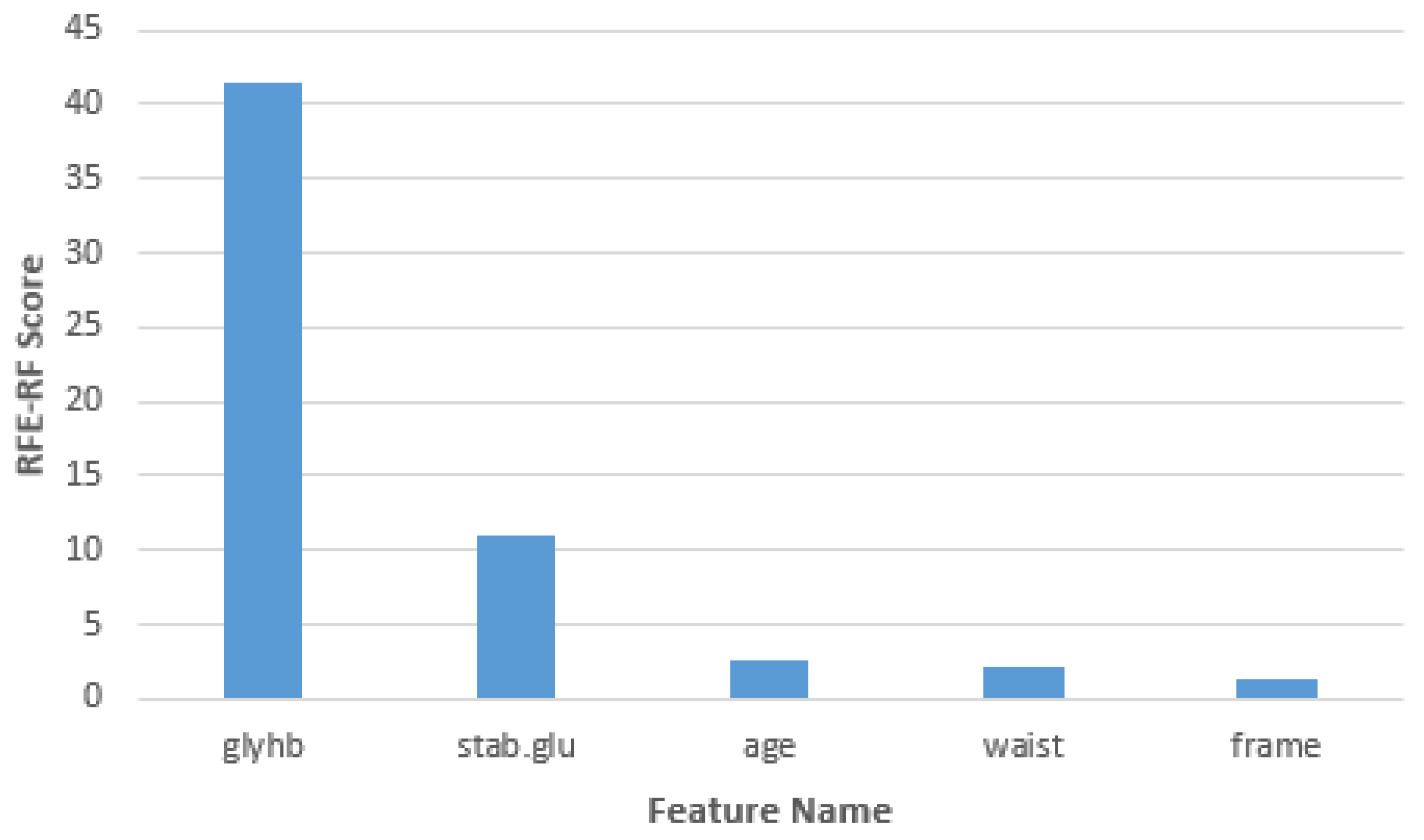
| Feature Name | Chi-Square Score |
|---|---|
| Glycosylated hemoglobin | 41.55193166 |
| Stabilized glucose | 10.90469737 |
| Age | 2.606353872 |
| Waist | 2.215980719 |
| Frame | 1.327181895 |
| Classifiers Name | Acc | Sen | Spe | MCC | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chi-square Test | ||||||
| KNN(K=5) | 0.9577465 | 0.7777778 | 0.983871 | 0.8014133 | 0.8235294 | 0.8808 |
| NB | 0.971831 | 1 | 0.9677419 | 0.8898252 | 0.9 | 0.9839 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.9950704 | 0.9777778 | 0.9975806 | 0.9776788 | 0.9803922 | 0.9876792 |
| mRMR Test | ||||||
| KNN(K=5) | 0.9577465 | 0.7777778 | 0.983871 | 0.8014133 | 0.8235294 | 0.8808 |
| NB | 0.971831 | 1 | 0.9677419 | 0.8898252 | 0.9 | 0.9839 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.9943662 | 0.9777778 | 0.9967742 | 0.974552 | 0.9777778 | 0.987276 |
| RFE-RF Test | ||||||
| KNN(K=5) | 0.915493 | 0.444444 | 0.983871 | 0.5569598 | 0.5714286 | 0.7142 |
| NB | 0.971831 | 1 | 0.9677419 | 0.8898252 | 0.9 | 0.9839 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.993662 | 0.9666667 | 0.9975806 | 0.9695377 | 0.9722222 | 0.9821237 |
| Classifiers Name | Acc | Sen | Spe | MCC | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Features | ||||||
| KNN(K=5) | 0.8591549 | 0.6666667 | 0.8870968 | 0.4763824 | 0.5454545 | 0.7769 |
| NB | 0.9577465 | 1 | 0.9516129 | 0.8448134 | 0.8571429 | 0.9758 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.9823944 | 0.8611111 | 1 | 0.9184793 | 0.9246324 | 0.9305556 |
| Chi-square Test | ||||||
| KNN(K=5) | 0.9577465 | 1 | 0.9516129 | 0.8448134 | 0.8571429 | 0.9758 |
| NB | 0.971831 | 1 | 0.9677419 | 0.8898252 | 0.9 | 0.9839 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.9957746 | 0.9777778 | 0.9983871 | 0.9801413 | 0.9823529 | 0.9880824 |
| mRMR Test | ||||||
| KNN(K=5) | 0.9577465 | 1 | 0.9516129 | 0.8448134 | 0.8571429 | 0.9758 |
| NB | 0.9577465 | 1 | 0.9516129 | 0.8448134 | 0.8571429 | 0.9758 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.9953052 | 0.962963 | 1 | 0.9784322 | 0.9803922 | 0.9814815 |
| RFE-RF Test | ||||||
| KNN(K=5) | 0.9577465 | 1 | 0.9516129 | 0.8448134 | 0.8571429 | 0.9758 |
| NB | 0.943662 | 1 | 0.9354839 | 0.8047625 | 0.8181818 | 0.9677 |
| SVM(RBF) | 0.9906103 | 0.9259259 | 1 | 0.9560093 | 0.9583333 | 0.962963 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




