Submitted:
02 June 2024
Posted:
05 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
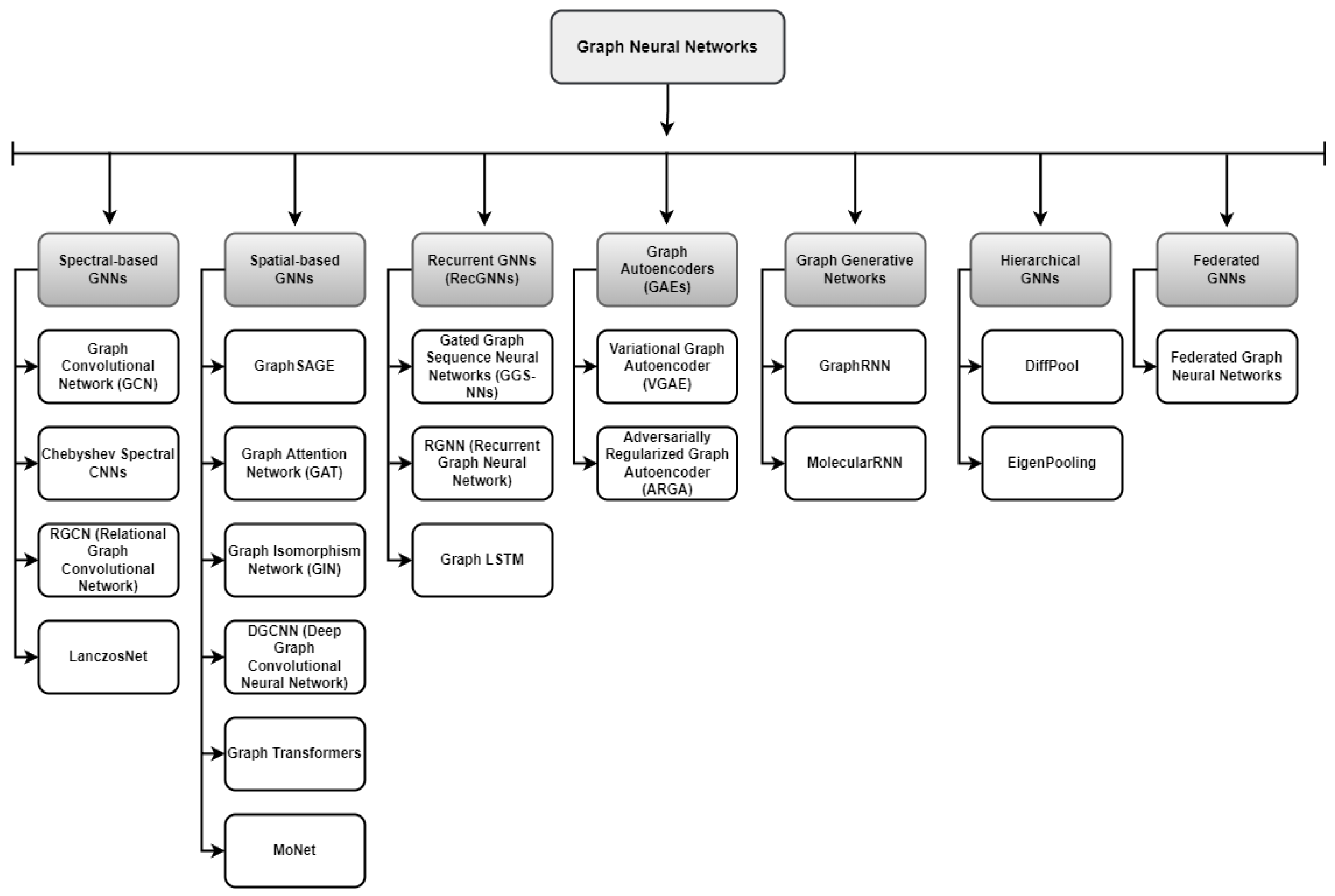
- GNN Basics and Theories: This paper presents the basic concepts of GNNs and their layers. Furthermore, Figure 2, proposes a taxonomy of GNNs according to their variations.
- Quantization Methods and Lightweight Models: This survey includes reviews of quantization methods aimed at building lightweight GNN models for embedded systems or GPU, CPU based applications.
- FPGA Based Hardware Accelerators: Our research describes in detail the work being done on hardware-based accelerators (typically FPGAs) that can be used in current or future embedded device applications.
- Discussion and Future Research Directions: The study discusses study outcomes for future research based on the findings and provides insights about possible research gaps.
2. Background
2.1. Graph Neural Networks
2.2. Graph Convolutional Networks
2.3. Graph Isomorphism Networks
2.4. Graph Attention Networks
2.5. GraphSAGE
3. Graph Neural Network Quantization
3.1. Quantization
3.1.1. Scalar Quantization
3.1.2. Vector Quantization
3.2. Quantization Approaches for GNNs
| Publication | Year | Targetted Problem | Quantized Parameters | Datasets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXACT [86] | 2021 | High memory need for training | Activations | Reddit, Flicker, Yelp, obgn-arxiv, obgn-products |
| VQ-GNN [88] | 2021 | Challenges of sampling based techniques | Convolution matrix, Node feature matrix | ogbn-arxiv, Reddit, PPI, ogbl-collab |
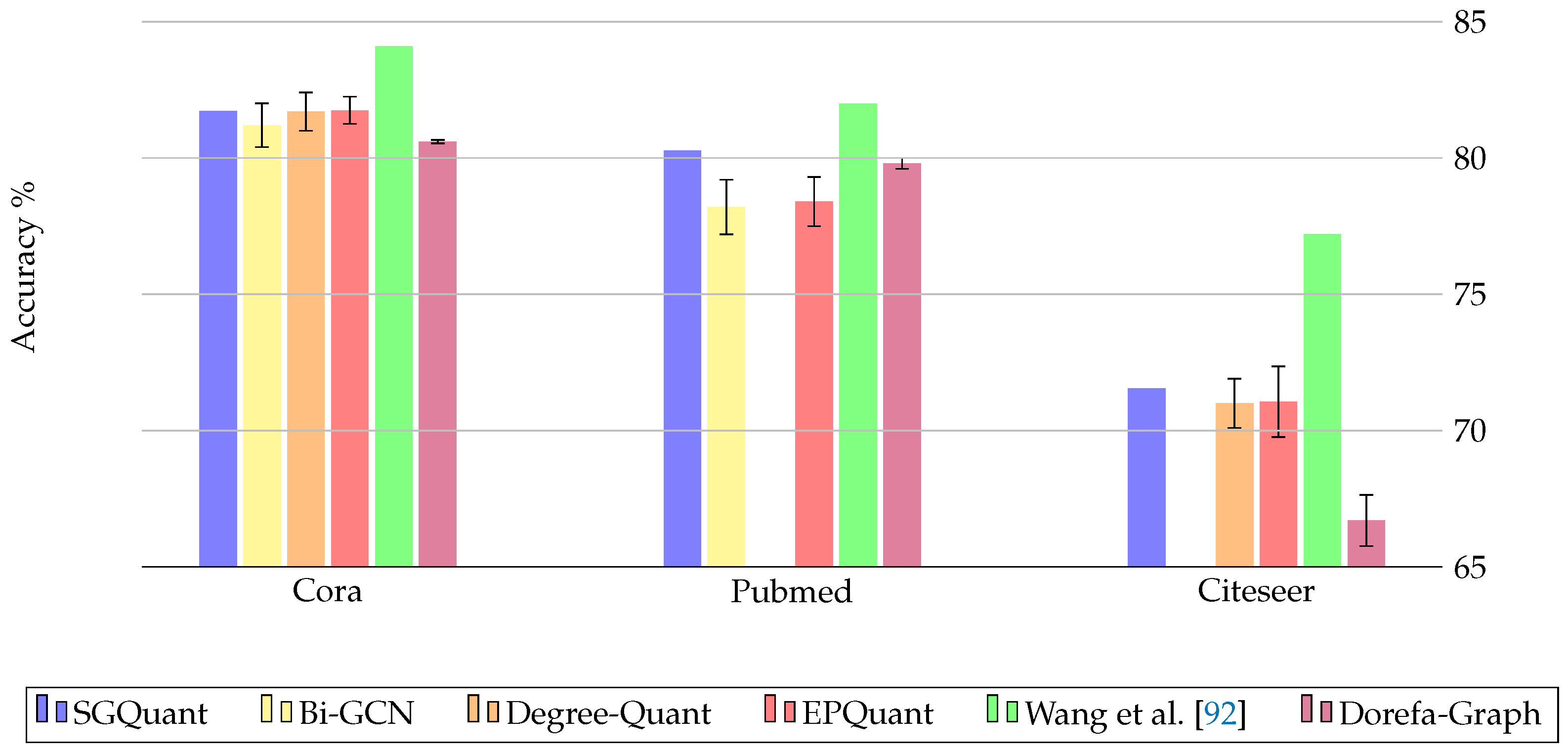
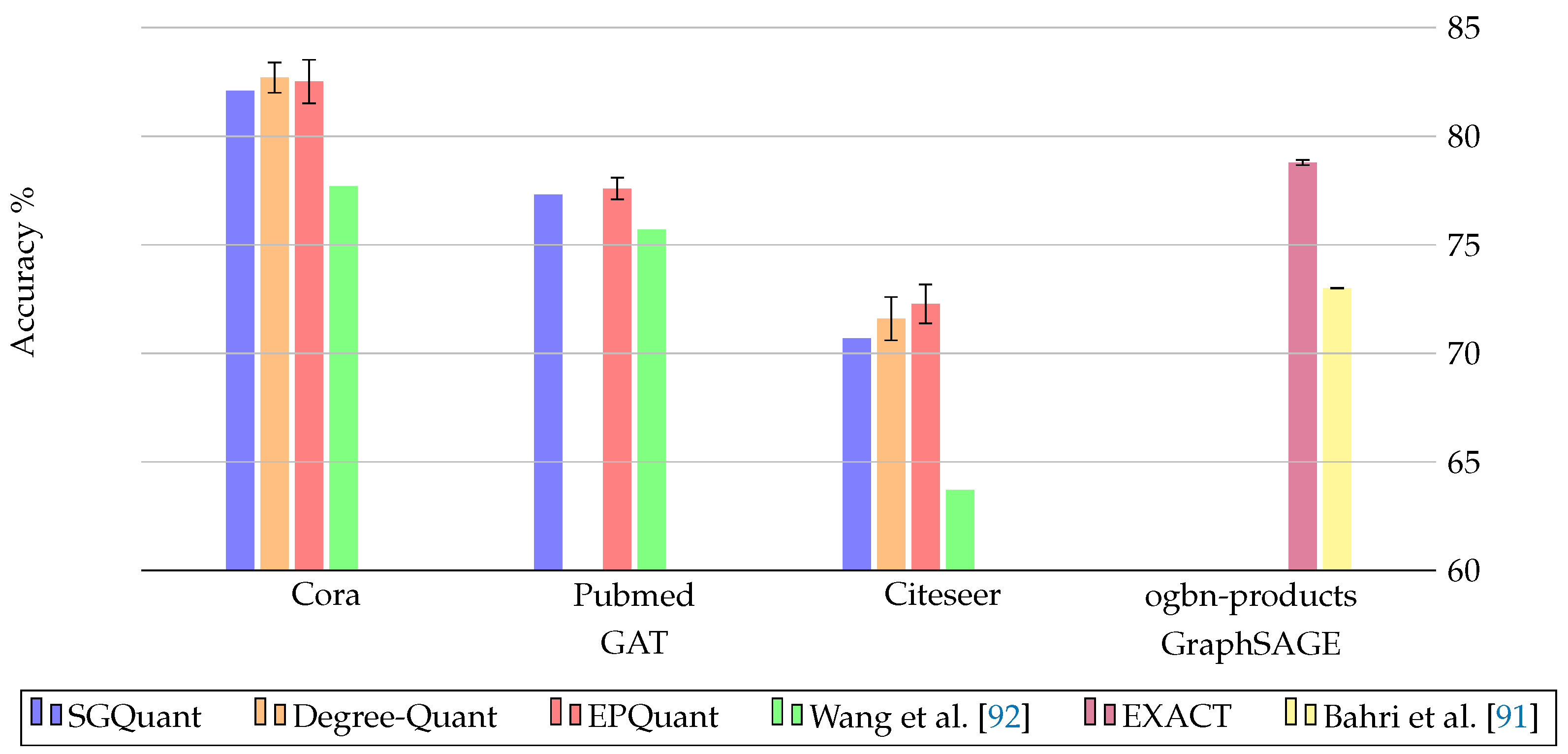
| SGQuant [89] | 2020 | High memory footprint for energy-limited devices | Feature matrix | Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed, Amazon-computer, Reddit |
| LPGNAS [90] | 2020 | Insufficient optimization research in the field | Weights, Activations | Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed, Amazon-Computers and Photos, Flicker, CoraFull, Yelp |
| Bahri et al. [91] | 2021 | Challenges in real-world applications due to model size and energy requirements | Weights, Feature matrix | obgn-Products, obgn-Protein |
| Wang et al. [92] | 2021 | Model inefficiency and scaling problems with inefficient real-valued parameters | Weights, Attention coefficients, Node embeddings | Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed, Facebook, wiki-vote, Brazil, USA |
| Degree-Quant [35] | 2020 | Inefficient training/inference time | Weights, Activations | Cora, Citeseer, ZINC, MNIST, CIFAR10, Reddit-Binary |
| EPQuant [93] | 2022 | Limited availability on edge devices due to high requirements | Input embeddings, Weights, Learnable parameters | Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed, Reddit, Amazon2M |
| Bi-GCN [94] | 2021 | High memory requirements of GNNs | Weights, Node features | Cora, Pubmed, Flicker, Reddit |
| Dorefa-Graph [95] | 2024 | Cost-effective computing on embedded systems | Feature matrix, Weights, Adjacency matrix, Activations | Cora, Pubmed, Citeseer |
4. Graph Neural Network Acceleration
4.1. Hardware-Based Accelerator Approaches
4.2. FPGA-Based Accelerators Approaches
4.3. FPGA-Based Heterogeneous Approaches
4.4. Frameworks for FPGA-Based Accelerators
4.5. FPGA-Based Accelerator Approaches with Quantization
| Publication | Hardware | Resource Consumption | Quantized Parameters | Baselines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
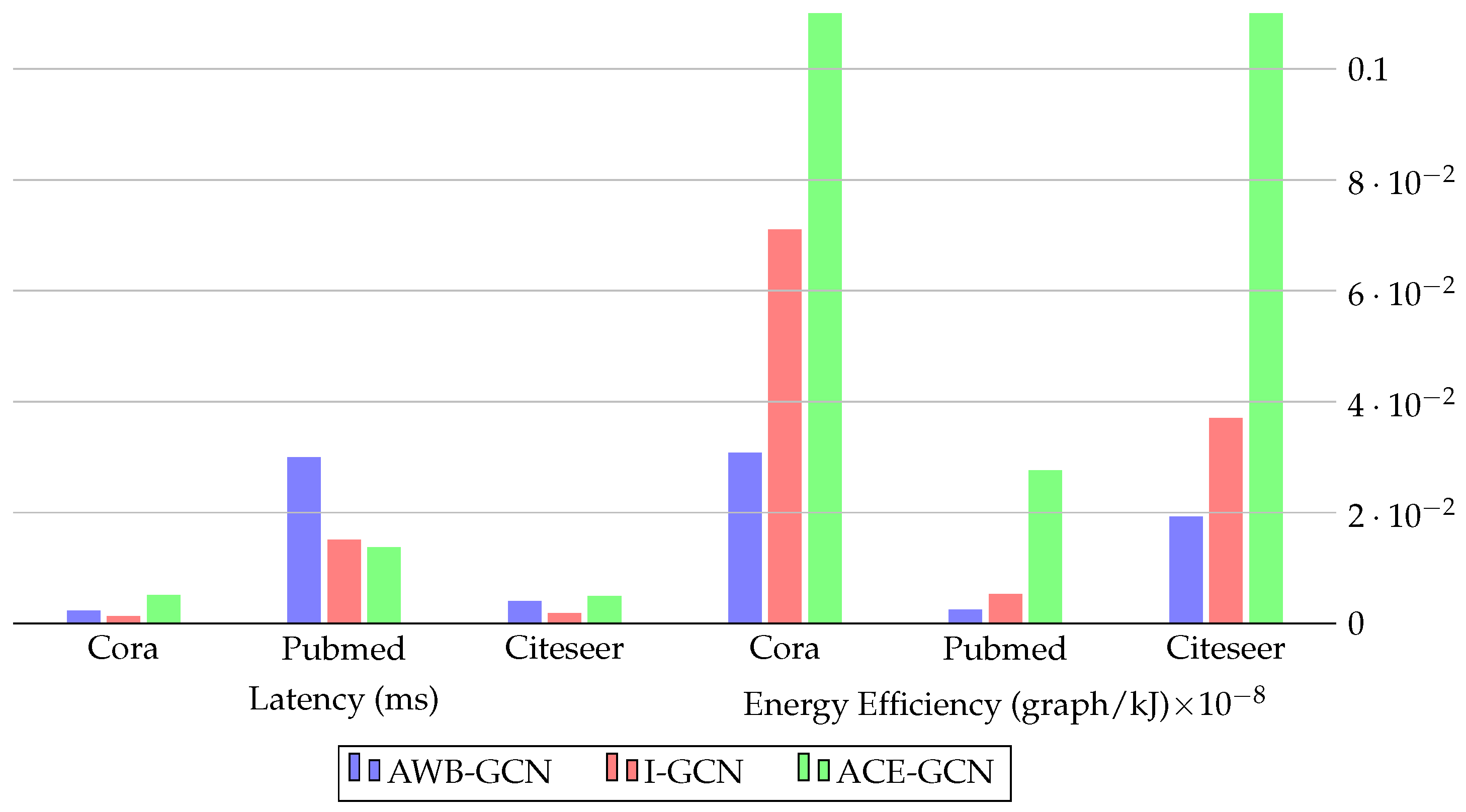
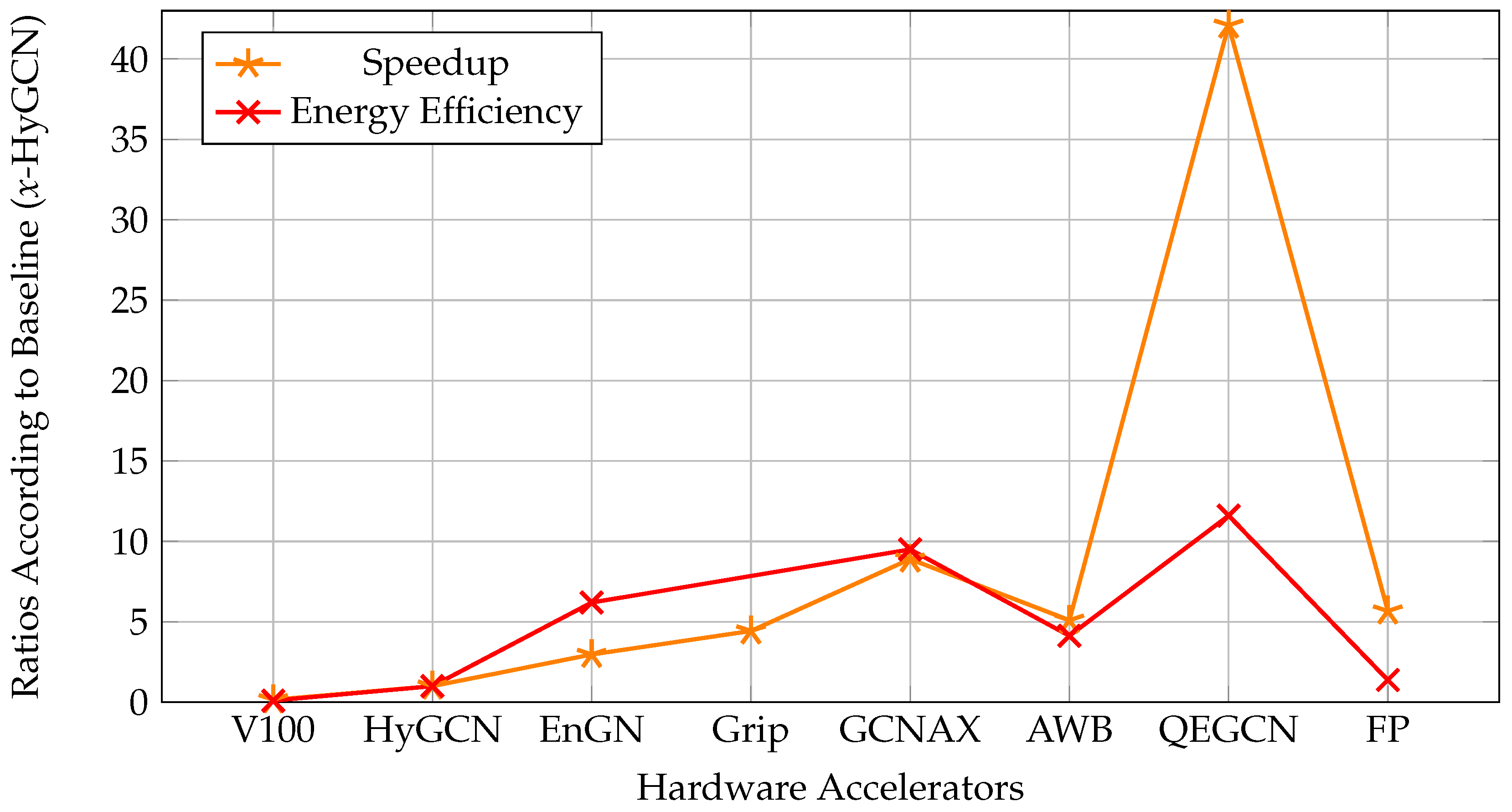
| FP-GNN [24] | VCU128 Freq:225 MHz | LUT: 717,578 FF: 517,428 BRAM: 1,792 DSP: 8,192 | Features, Weights 32-bit fixed point | PyG-CPU-GPU, HyGCN, GCNAX, AWB-GCN, I-GCN |
| FTW-GAT [127] | VCU128 Freq:225 MHz | LUT: 436.657 FF: 470,222 BRAM: 1,502 DSP: 1,216 | 8-bit int Features3-bit int Weights | PyG-CPU-GPU, FP-GNN |
| Wang et al. [128] | Alveo U200 Freq:250 MHz | LUT: 1,010,00 FF: 117,00 BRAM: 1,430 DSP: 392 | 1-bit integer Features, Weights 32-bit integer Adjacency matrix | PyG-CPU-GPU, ASAP [113] |
| LL-GNN [32] | Alveo U250 Freq:200 MHz | LUT: 815,000 FF: 139,000 BRAM: 37 DSP: 8,986 | Model Parameters 12-bit fixed point | PyG-CPU-GPU |
| Ran et al. [129] | Alveo U200 Freq:250 MHz | LUT: 427,438 FF: NI BRAM: 1,702 DSP: 33.7 | Features, Weights | PyG-CPU-GPU, HyGCN, ASAP [113], AWB-GCN, LW-GCN |
| SkeletonGCN [126] | Alveo U200 Freq:250 MHz | LUT: 1,021,386 FF: NI BRAM: 1,338 DSP: 960 | Feature, Adjacency matrices, Trainable parameters 16-bit signed integer | PyG-CPU-GPU, GraphACT |
| QEGCN [130] | VCU128 Freq:225 MHz | LUT: 21,935 FF: 9,201 BRAM: 22 DSP: 0 | Features, Weights 8-bit fixed point | PyG-CPU-GPU, DGL-CPU-GPU, HyGCN, EnGN, AWB-GCN, ACE-GCN |
| Yuan et al. [131] | VCU128 Freq:300 MHz | LUT: 3,244 FF: 345 BRAM: 102.5 DSP: 64 | Features, Weights 32-bit fixed point | PyG-CPU-GPU |
| FPGAN [125] | Arria10 GX1150 Freq:216 MHz | LUT: 250,570 FF: 338,490 BRAM: NI DSP: 148 | Features, Weights fixed point | PyG-CPU-GPU |
| LW-GCN [132] | Kintex-7 K325T Freq:200 MHz | LUT: 161,529 FF: 94,369 BRAM: 291.5 DSP: 512 | Features, Weights 16-bit signed fixed point | PyG-CPU-GPU, AWB-GCN |
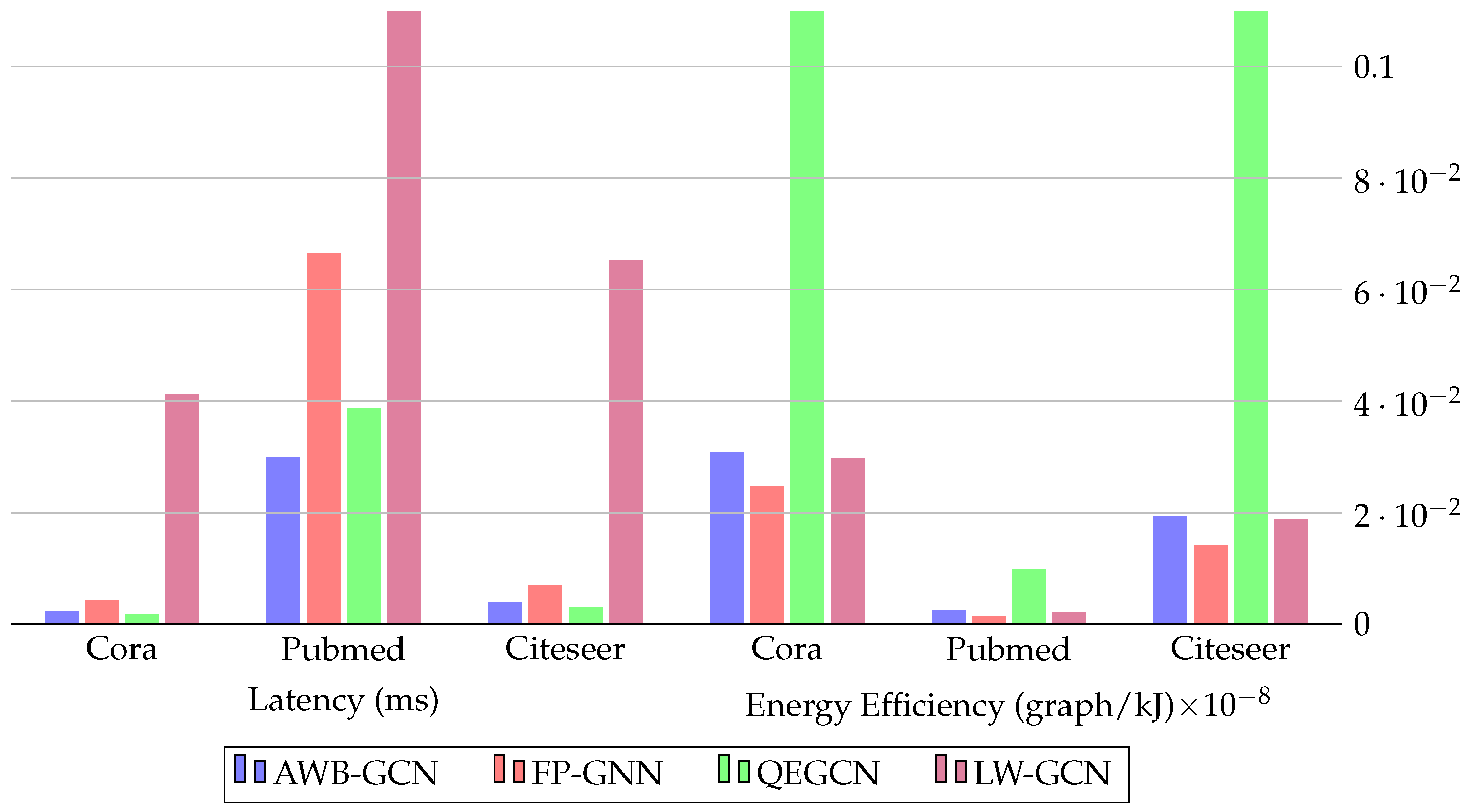
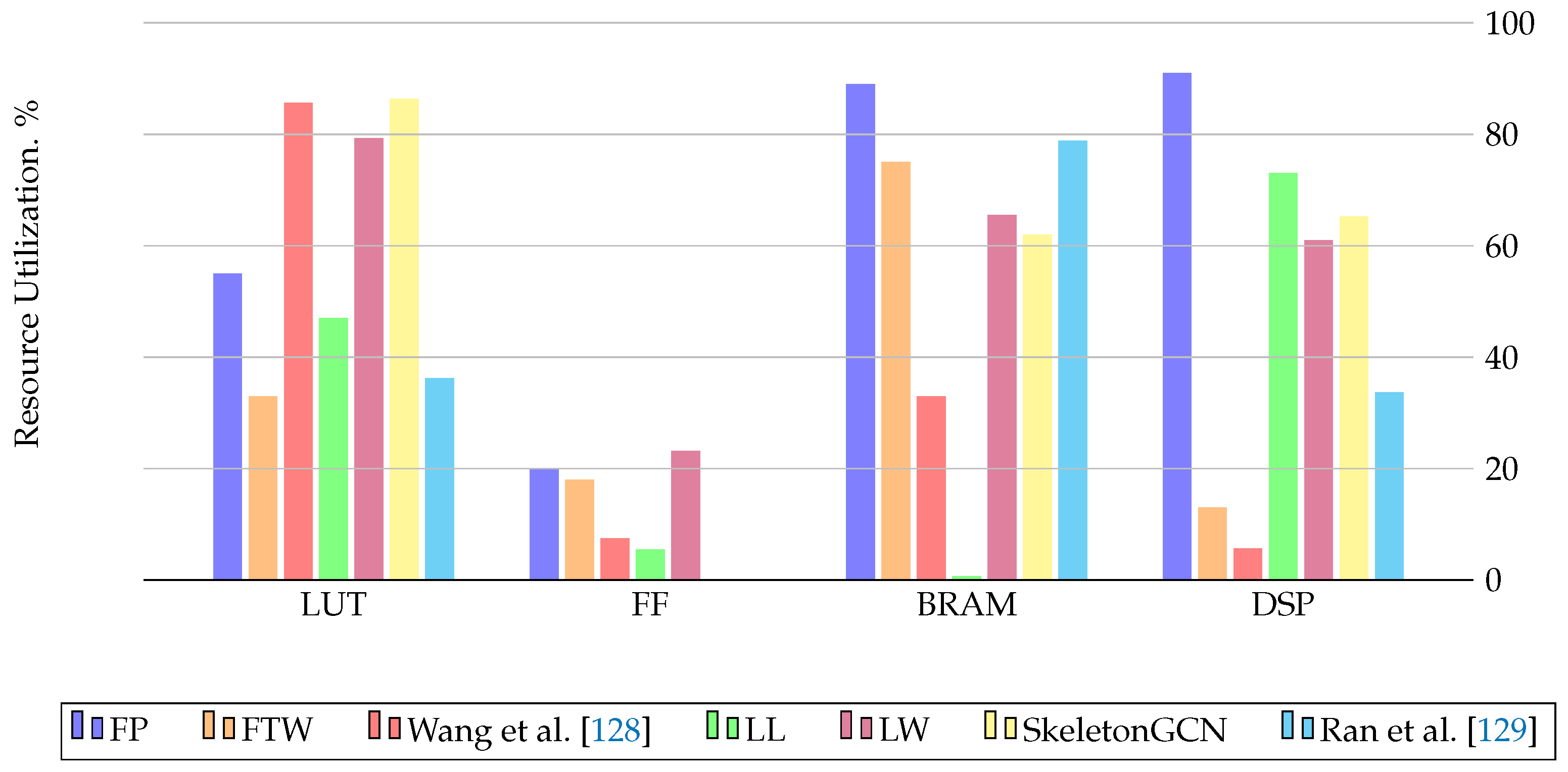
4.6. FPGA-Based Accelerators for Embedded Applications
| Study | Target Device | Datasets | Fixed-point representation |
|---|---|---|---|
| LW-GCN [132] | Xilinx Kintex-7 | Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed | ✔ |
| Zhou et al. [133] | Xilinx ZCU104, Alveo U200 | Wikipedia, Reddit, GDELT | - |
| gFADES [72] | Zynq Ultrascale+ XCZU28DR | Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed | - |
| Hansson et al. [134] | Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ | Cora, Citeseer, Pubmed | ✔ |
5. Discussion and Future Research Directions
5.1. Quantization and Future Directions
- Scalar quantization methods are prevalent in embedded systems due to their ease of implementation and the computational efficiency of integer arithmetic.
- Vector quantization provides higher compression ratios compared to scalar quantization by grouping multiple vectors together.
- Combining vector and scalar quantization offers the benefits of both integer arithmetic computational power and the high compression ratio of vector quantization, crucial for developing highly efficient low-dimensional models for hardware applications.
- Achieving a delicate balance between energy efficiency, training-output speed, and accuracy in unified approaches requires careful customization during the design phase according to the specific requirements of particular applications, highlighting the important role of future efforts in achieving this balance.
- Mixed precision approaches show the potential to maintain accuracy while reducing model size. However, different bit representations can introduce computational complexity from a hardware standpoint. As a result, there is growing interest in the development of fully quantized GNN models specifically designed for embedded system applications.
- Research shows that the accuracy achieved with 16-bit and 8-bit quantization values can be achieved with lower-bit numbers such as 4-bit and 2-bit. In this context, the adoption of aggressive methods involving low-bit representations to integrate large GNN models into embedded device applications will begin to attract the attention of more researchers.
5.2. Hardware Accelerators and Future Directions
- The current body of FPGA studies related to Graph Neural Network (GNN) models is still insufficient to comprehensively address the complexities of embedded system applications, and it underscores a significant research gap in the field of FPGA.
- While a significant portion of research efforts concentrate on GNN inference, there exists a critical need to expedite the training phase, particularly for dynamic graph structures, necessitating further exploration in this realm.
- The adaptive nature of FPGA accelerators exhibits notable efficacy in accommodating diverse application requirements, demonstrating their potential for widespread adoption in various domains.
- While the utilization of common datasets and network models provides an initial benchmark for researchers, the limited extension of studies to diverse application domains and the absence of the establishment of distinct baselines pose significant challenges requiring resolution.
- Although this work is focused on quantization and FPGA-based accelerators, additional techniques such as sampling, reordering, simplification, and knowledge distillation are currently being used with promising results. It is anticipated that interest in additional methods such as quantization and other approaches will grow in hardware-based applications.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bronstein, M.M.; Bruna, J.; LeCun, Y.; Szlam, A.; Vandergheynst, P. Geometric deep learning: going beyond euclidean data. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2017, 34, 18–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cui, G.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Sun, M. Graph neural networks: A review of methods and applications. AI open 2020, 1, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, F.; Isufi, E.; Leus, G.; Ribeiro, A. Graphs, convolutions, and neural networks: From graph filters to graph neural networks. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 2020, 37, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutino, M.; Isufi, E.; Leus, G. Advances in distributed graph filtering. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2019, 67, 2320–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, L.B.; Beferull-Lozano, B. Quantization in graph convolutional neural networks. 2021 29th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1855–1859.
- Zhu, R.; Zhao, K.; Yang, H.; Lin, W.; Zhou, C.; Ai, B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. Aligraph: A comprehensive graph neural network platform. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1902.08730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Farrell, S.; Calafiura, P.; Murnane, D.; Gray, L.; Klijnsma, T.; Pedro, K.; Cerati, G.; Kowalkowski, J.; Perdue, G.; others. Graph neural networks for particle reconstruction in high energy physics detectors. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2003.11603. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.; Murnane, D.; Calafiura, P.; Choma, N.; Conlon, S.; Farrell, S.; Xu, Y.; Spiropulu, M.; Vlimant, J.R.; Aurisano, A.; others. Performance of a geometric deep learning pipeline for HL-LHC particle tracking. The European Physical Journal C 2021, 81, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, K.; Guo, X.; Gao, H.; Li, S.; Pei, J.; Long, B.; others. Graph neural networks for natural language processing: A survey. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning 2023, 16, 119–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Luo, J. Graph neural network for traffic forecasting: A survey. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022; 117921. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, J.; Liang, J.; Kumar, V.; Raimondo, F.; Sun, X.; McConville, R.; Pasquier, T.; Piechocki, R.; Oikonomou, G.; Luo, B.; others. Resource-Interaction Graph: Efficient Graph Representation for Anomaly Detection. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2212.08525. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, W.; Ying, Z.; Leskovec, J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, T.; Rong, Y.; Huang, J. Adaptive sampling towards fast graph representation learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, R.; He, R.; Chen, K.; Eksombatchai, P.; Hamilton, W.L.; Leskovec, J. Graph convolutional neural networks for web-scale recommender systems. Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, 2018, pp. 974–983.
- Battaglia, P.W.; Hamrick, J.B.; Bapst, V.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Zambaldi, V.; Malinowski, M.; Tacchetti, A.; Raposo, D.; Santoro, A.; Faulkner, R.; others. Relational inductive biases, deep learning, and graph networks. arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1806.01261. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.Y. Deep graph library: Towards efficient and scalable deep learning on graphs. ICLR workshop on representation learning on graphs and manifolds, 2019.
- Lerer, A.; Wu, L.; Shen, J.; Lacroix, T.; Wehrstedt, L.; Bose, A.; Peysakhovich, A. Pytorch-biggraph: A large scale graph embedding system. Proceedings of Machine Learning and Systems 2019, 1, 120–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Philip, S.Y. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems 2020, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, P.; Zhu, W. Deep learning on graphs: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2020, 34, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Li, A.; Shi, R.; Wu, C.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Haghi, P.; Tumeo, A.; Che, S.; Reinhardt, S.; others. AWB-GCN: A graph convolutional network accelerator with runtime workload rebalancing. 2020 53rd Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO). IEEE, 2020, pp. 922–936.
- Fey, M.; Lenssen, J.E. Fast graph representation learning with PyTorch Geometric. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1903.02428. [Google Scholar]
- Ferludin, O.; Eigenwillig, A.; Blais, M.; Zelle, D.; Pfeifer, J.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Li, S.; Abu-El-Haija, S.; Battaglia, P.; Bulut, N.; others. TF-GNN: graph neural networks in TensorFlow. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2207.03522. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdanbakhsh, A.; Park, J.; Sharma, H.; Lotfi-Kamran, P.; Esmaeilzadeh, H. Neural acceleration for GPU throughput processors. Proceedings of the 48th international symposium on microarchitecture, 2015, pp. 482–493.
- Tian, T.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, W.; Jin, X. FP-GNN: adaptive FPGA accelerator for graph neural networks. Future Generation Computer Systems 2022, 136, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Yanez, J.; Hosseinabady, M. Sparse and dense matrix multiplication hardware for heterogeneous multi-precision neural networks. Array 2021, 12, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sit, M.; Kazami, R.; Amano, H. FPGA-based accelerator for losslessly quantized convolutional neural networks. 2017 International Conference on Field Programmable Technology (ICFPT). IEEE, 2017, pp. 295–298.
- Zhang, B.; Kuppannagari, S.R.; Kannan, R.; Prasanna, V. Efficient neighbor-sampling-based gnn training on cpu-fpga heterogeneous platform. 2021 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–7.
- Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; He, L.; Huawei, L.; Xu, D.; Li, X. Engn: A high-throughput and energy-efficient accelerator for large graph neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers 2020, 70, 1511–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sohrabizadeh, A.; Wan, C.; Huang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cong, J.; Sun, Y.; others. A Survey on Graph Neural Network Acceleration: Algorithms, Systems, and Customized Hardware. arXiv preprint 2023, arXiv:2306.14052. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Prasanna, V. GraphACT: Accelerating GCN training on CPU-FPGA heterogeneous platforms. Proceedings of the 2020 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, 2020, pp. 255–265.
- Kiningham, K.; Levis, P.; Ré, C. GReTA: Hardware optimized graph processing for GNNs. Proceedings of the Workshop on Resource-Constrained Machine Learning (ReCoML 2020), 2020.
- Que, Z.; Loo, M.; Fan, H.; Blott, M.; Pierini, M.; Tapper, A.D.; Luk, W. LL-GNN: low latency graph neural networks on FPGAs for particle detectors. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2209.14065. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Tian, T.; Wu, W.; Jin, X. HuGraph: Acceleration of GCN Training on Heterogeneous FPGA Clusters with Quantization. 2022 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1–7.
- Gholami, A.; Kim, S.; Dong, Z.; Yao, Z.; Mahoney, M.W.; Keutzer, K. A survey of quantization methods for efficient neural network inference. In Low-Power Computer Vision; Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2022; pp. 291–326.
- Tailor, S.A.; Fernandez-Marques, J.; Lane, N.D. Degree-quant: Quantization-aware training for graph neural networks. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2008.05000. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, P.; Ferrara, E. Graph embedding techniques, applications, and performance: A survey. Knowledge-Based Systems 2018, 151, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.; Xu, J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph convolutional networks: a comprehensive review. Computational Social Networks 2019, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.; Xu, J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph convolutional networks: Algorithms, applications and open challenges. Computational Data and Social Networks: 7th International Conference, CSoNet 2018, Shanghai, China, December 18–20, 2018, Proceedings 7. Springer, 2018, pp. 79–91.
- Quan, P.; Shi, Y.; Lei, M.; Leng, J.; Zhang, T.; Niu, L. A brief review of receptive fields in graph convolutional networks. IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence-Companion Volume, 2019, pp. 106–110.
- Asif, N.A.; Sarker, Y.; Chakrabortty, R.K.; Ryan, M.J.; Ahamed, M.H.; Saha, D.K.; Badal, F.R.; Das, S.K.; Ali, M.F.; Moyeen, S.I.; others. Graph neural network: A comprehensive review on non-euclidean space. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60588–60606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chami, I.; Abu-El-Haija, S.; Perozzi, B.; Ré, C.; Murphy, K. Machine learning on graphs: A model and comprehensive taxonomy. The Journal of Machine Learning Research 2022, 23, 3840–3903. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, P. Everything is connected: Graph neural networks. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2023, 79, 102538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, U.A.; Tang, H.; Wu, G.; Marjan, S.; Hussain, A. Deep learning with graph convolutional networks: An overview and latest applications in computational intelligence. International Journal of Intelligent Systems 2023, 2023, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wei, M.; Li, Z. A comprehensive review of graph convolutional networks: approaches and applications. Electronic Research Archive 2023, 31, 4185–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, N.; Wu, J.; Beheshti, A.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Foo, J.; Haghighi, V.; Hanif, A.; Shahabikargar, M. A comprehensive survey on graph summarization with graph neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Fang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Long, Q.; Qiao, Z.; Qin, Y.; Shen, J.; Sun, F.; Xiao, Z.; others. A comprehensive survey on deep graph representation learning. Neural Networks 2024, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Xing, P.; Deng, Z.; Li, A.; Guan, C.; Yu, H. Federated Graph Neural Networks: Overview, Techniques, and Challenges. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopera, D.S.; Servadei, L.; Kiprit, G.N.; Hazra, S.; Wille, R.; Ecker, W. A survey of graph neural networks for electronic design automation. 2021 ACM/IEEE 3rd Workshop on Machine Learning for CAD (MLCAD). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–6.
- Liu, X.; Yan, M.; Deng, L.; Li, G.; Ye, X.; Fan, D. Sampling methods for efficient training of graph convolutional networks: A survey. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica 2021, 9, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamis, I.; Michail, D.; Glykou, F.; Tsantilas, P. A survey on the use of graph convolutional networks for combating fake news. Future Internet 2022, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, Z.; Qin, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Feng, J.; Gu, Y.; Ju, W.; Luo, X.; Zhang, M. A survey on graph neural networks in intelligent transportation systems. arXiv preprint 2024, arXiv:2401.00713. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, L.C.; Garcez, A.; Gori, M.; Prates, M.; Avelar, P.; Vardi, M. Graph neural networks meet neural-symbolic computing: A survey and perspective. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2003.00330. [Google Scholar]
- Malekzadeh, M.; Hajibabaee, P.; Heidari, M.; Zad, S.; Uzuner, O.; Jones, J.H. Review of graph neural network in text classification. In 2021 IEEE 12th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), 2021.
- Ahmad, T.; Jin, L.; Zhang, X.; Lai, S.; Tang, G.; Lin, L. Graph convolutional neural network for human action recognition: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence 2021, 2, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Tang, M.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Guo, S.; Cai, L.; Gutierrez, R.; Campbel, B.; Barnes, L.E.; Boukhechba, M. Graph neural networks in IoT: a survey. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks 2023, 19, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Gabrys, B.; Musial, K. A Network Science perspective of Graph Convolutional Networks: A survey. IEEE Access 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Lu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Chang, X.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Fang, D. Graph convolutional networks in language and vision: A survey. Knowledge-Based Systems 2022, 251, 109250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Qin, E.; Martínez, F.M.; Guirado, R.; Jain, A.; Abadal, S.; Abellán, J.L.; Acacio, M.E.; Alarcón, E.; Rajamanickam, S.; others. A taxonomy for classification and comparison of dataflows for gnn accelerators. Technical report, Sandia National Lab.(SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States), 2021.
- Li, S.; Tao, Y.; Tang, E.; Xie, T.; Chen, R. A survey of field programmable gate array (FPGA)-based graph convolutional neural network accelerators: challenges and opportunities. PeerJ Computer Science 2022, 8, e1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yan, M.; Deng, L.; Li, G.; Ye, X.; Fan, D.; Pan, S.; Xie, Y. Survey on graph neural network acceleration: An algorithmic perspective. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2202.04822. [Google Scholar]
- Abadal, S.; Jain, A.; Guirado, R.; López-Alonso, J.; Alarcón, E. Computing graph neural networks: A survey from algorithms to accelerators. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. Advances in neural information processing systems 2016, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, R.; Zhao, Z.; Urtasun, R.; Zemel, R.S. Lanczosnet: Multi-scale deep graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1901.01484. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, V.P.; Bresson, X. A generalization of transformer networks to graphs. arXiv. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2012.09699. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, F.; Boscaini, D.; Masci, J.; Rodola, E.; Svoboda, J.; Bronstein, M.M. Geometric deep learning on graphs and manifolds using mixture model cnns (2016). Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.08402.
- Li, Y.; Tarlow, D.; Brockschmidt, M.; Zemel, R. Gated graph sequence neural networks. arXiv preprint 2015, arXiv:1511.05493. [Google Scholar]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Variational graph auto-encoders. arXiv preprint 2016, arXiv:1611.07308. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Hu, R.; Long, G.; Jiang, J.; Yao, L.; Zhang, C. Adversarially regularized graph autoencoder for graph embedding. arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1802.04407. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.; Ying, R.; Ren, X.; Hamilton, W.; Leskovec, J. Graphrnn: Generating realistic graphs with deep auto-regressive models. International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2018, pp. 5708–5717.
- Ying, Z.; You, J.; Morris, C.; Ren, X.; Hamilton, W.; Leskovec, J. Hierarchical graph representation learning with differentiable pooling. Advances in neural information processing systems 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Aggarwal, C.C.; Tang, J. Graph convolutional networks with eigenpooling. Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, 2019, pp. 723–731.
- Nunez-Yanez, J. Accelerating Graph Neural Networks in Pytorch with HLS and Deep Dataflows. International Symposium on Applied Reconfigurable Computing. Springer, 2023, pp. 131–145.
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Hu, W.; Leskovec, J.; Jegelka, S. How powerful are graph neural networks? arXiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1810.00826. [Google Scholar]
- Veličkovič, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv preprint 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Tang, E.; Yu, J.; Wang, K. Graph-OPU: A Highly Integrated FPGA-Based Overlay Processor for Graph Neural Networks. 2023 33rd International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL). IEEE, 2023, pp. 228–234.
- Novkin, R.; Amrouch, H.; Klemme, F. Approximation-aware and quantization-aware training for graph neural networks. Authorea Preprints 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C. Adaptive Message Quantization and Parallelization for Distributed Full-graph GNN Training. Proceedings of Machine Learning and Systems 2023, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Liang, H.; Wang, X.; Tao, L.; Tian, T.; Wang, T.; He, Z.; Wu, W.; Jin, X. GCINT: Dynamic Quantization Algorithm for Training Graph Convolution Neural Networks Using Only Integers 2022.
- Wang, Y.; Feng, B.; Ding, Y. QGTC: accelerating quantized graph neural networks via GPU tensor core. Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGPLAN symposium on principles and practice of parallel programming, 2022, pp. 107–119.
- Ma, Y.; Gong, P.; Yi, J.; Yao, Z.; Li, C.; He, Y.; Yan, F. Bifeat: Supercharge gnn training via graph feature quantization. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2207.14696. [Google Scholar]
- Eliasof, M.; Bodner, B.J.; Treister, E. Haar wavelet feature compression for quantized graph convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y. An efficient segmented quantization for graph neural networks. CCF Transactions on High Performance Computing 2022, 4, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, F.; Mo, Z.; Hu, Q.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Liang, X.; Cheng, J. A2Q: Aggregation-Aware Quantization for Graph Neural Networks. arXiv preprint 2023, arXiv:2302.00193. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Eravci, B.; Guliyev, R.; Ferhatosmanoglu, H. Low-bit quantization for deep graph neural networks with smoothness-aware message propagation. Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, 2023, pp. 2626–2636.
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, K.; Yang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, R.; Hu, X. EXACT: Scalable graph neural networks training via extreme activation compression. International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021.
- Eliassen, S.; Selvan, R. Activation Compression of Graph Neural Networks using Block-wise Quantization with Improved Variance Minimization. arXiv preprint 2023, arXiv:2309.11856. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Kong, K.; Li, J.; Zhu, C.; Dickerson, J.; Huang, F.; Goldstein, T. VQ-GNN: A universal framework to scale up graph neural networks using vector quantization. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, 34, 6733–6746. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Peng, X.; Ding, Y. Sgquant: Squeezing the last bit on graph neural networks with specialized quantization. 2020 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1044–1052.
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Bates, D.; Mullins, R.; Jamnik, M.; Lio, P. Learned low precision graph neural networks. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2009.09232. [Google Scholar]
- Bahri, M.; Bahl, G.; Zafeiriou, S. Binary graph neural networks. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2021, pp. 9492–9501.
- Wang, H.; Lian, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, L.; He, X.; Lin, Y.; Lin, X. Binarized graph neural network. World Wide Web 2021, 24, 825–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Du, Z.; Li, S.; Zheng, H.; Xie, Y.; Tan, N. EPQuant: A Graph Neural Network compression approach based on product quantization. Neurocomputing 2022, 503, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y. Bi-gcn: Binary graph convolutional network. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021, pp. 1561–1570.
- Kose, H.T.; Nunez-Yanez, J.; Piechocki, R.; Pope, J. Fully Quantized Graph Convolutional Networks for Embedded Applications.
- Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C. Topology-Aware Quantization Strategy via Personalized PageRank for Graph Neural Networks. 2022 IEEE Smartworld, Ubiquitous Intelligence & Computing, Scalable Computing & Communications, Digital Twin, Privacy Computing, Metaverse, Autonomous & Trusted Vehicles (SmartWorld/UIC/ScalCom/DigitalTwin/PriComp/Meta). IEEE, 2022, pp. 961–968.
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zou, X.; Yang, X.; Gu, Y. Algorithms and architecture support of degree-based quantization for graph neural networks. Journal of Systems Architecture 2022, 129, 102578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Peng, H.; Hasan, A.; Huang, S.; Zhao, J.; Fang, H.; Zhang, W.; Geng, T.; Khan, O.; Ding, C. Accel-gcn: High-performance gpu accelerator design for graph convolution networks. 2023 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD). IEEE, 2023, pp. 01–09.
- Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Miao, Y.; Xue, J.; Wu, M.; Zhou, L.; Dai, Y. {NeuGraph}: Parallel deep neural network computation on large graphs. 2019 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 19), 2019, pp. 443–458.
- Peng, H.; Xie, X.; Shivdikar, K.; Hasan, M.; Zhao, J.; Huang, S.; Khan, O.; Kaeli, D.; Ding, C. Maxk-gnn: Towards theoretical speed limits for accelerating graph neural networks training. arXiv preprint 2023, arXiv:2312.08656. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Deng, L.; Hu, X.; Liang, L.; Feng, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, D.; Xie, Y. Hygcn: A gcn accelerator with hybrid architecture. 2020 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA). IEEE, 2020, pp. 15–29.
- Yin, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H. Exploring architecture, dataflow, and sparsity for gcn accelerators: A holistic framework. Proceedings of the Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2023, 2023, pp. 489–495. [Google Scholar]
- Auten, A.; Tomei, M.; Kumar, R. Hardware acceleration of graph neural networks. 2020 57th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–6.
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Hu, X.; Basak, A.; Liang, L.; Yan, M.; Deng, L.; Ding, Y.; Du, Z.; others. Rubik: A hierarchical architecture for efficient graph neural network training. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 2021, 41, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Louri, A.; Karanth, A.; Bunescu, R. GCNAX: A flexible and energy-efficient accelerator for graph convolutional neural networks. 2021 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA). IEEE, 2021, pp. 775–788.
- Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, K.; Louri, A. SGCNAX: A scalable graph convolutional neural network accelerator with workload balancing. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 2021, 33, 2834–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiningham, K.; Levis, P.; Ré, C. GRIP: A graph neural network accelerator architecture. IEEE Transactions on Computers 2022, 72, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kannan, R.; Prasanna, V. BoostGCN: A framework for optimizing GCN inference on FPGA. 2021 IEEE 29th Annual International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines (FCCM). IEEE, 2021, pp. 29–39.
- Zhang, C.; Geng, T.; Guo, A.; Tian, J.; Herbordt, M.; Li, A.; Tao, D. H-gcn: A graph convolutional network accelerator on versal acap architecture. 2022 32nd International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL). IEEE, 2022, pp. 200–208.
- Romero Hung, J.; Li, C.; Wang, P.; Shao, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, G. ACE-GCN: A Fast data-driven FPGA accelerator for GCN embedding. ACM Transactions on Reconfigurable Technology and Systems (TRETS) 2021, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, C.; Xie, C.; You, H.; Herbordt, M.; Lin, Y.; Li, A. I-GCN: A graph convolutional network accelerator with runtime locality enhancement through islandization. MICRO-54: 54th annual IEEE/ACM international symposium on microarchitecture, 2021, pp. 1051–1063.
- Lin, Y.C.; Zhang, B.; Prasanna, V. Gcn inference acceleration using high-level synthesis. 2021 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–6.
- Zhang, B.; Zeng, H.; Prasanna, V. Hardware acceleration of large scale gcn inference. 2020 IEEE 31st International Conference on Application-specific Systems, Architectures and Processors (ASAP). IEEE, 2020, pp. 61–68.
- Sohrabizadeh, A.; Chi, Y.; Cong, J. SPA-GCN: Efficient and Flexible GCN Accelerator with an Application for Graph Similarity Computation. arXiv preprint 2021, arXiv:2111.05936. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, Y.; Wei, B.; Yuan, W.; Jin, X. Hardware Acceleration of Sampling Algorithms in Sample and Aggregate Graph Neural Networks. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2209.02916. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Niu, D.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, T.; Guan, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, L.; Du, Z.; others. Hyperscale FPGA-as-a-service architecture for large-scale distributed graph neural network. Proceedings of the 49th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, 2022, pp. 946–961.
- Chen, S.; Zheng, D.; Ding, C.; Huan, C.; Ji, Y.; Liu, H. TANGO: re-thinking quantization for graph neural network training on GPUs. Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis, 2023, pp. 1–14.
- Zhang, B.; Zeng, H.; Prasanna, V. Low-latency mini-batch gnn inference on cpu-fpga heterogeneous platform. 2022 IEEE 29th International Conference on High Performance Computing, Data, and Analytics (HiPC). IEEE, 2022, pp. 11–21.
- Lin, Y.C.; Zhang, B.; Prasanna, V. Hp-gnn: Generating high throughput gnn training implementation on cpu-fpga heterogeneous platform. Proceedings of the 2022 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, 2022, pp. 123–133.
- Sarkar, R.; Abi-Karam, S.; He, Y.; Sathidevi, L.; Hao, C. FlowGNN: A Dataflow Architecture for Real-Time Workload-Agnostic Graph Neural Network Inference. 2023 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1099–1112.
- Liang, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X. Deepburning-gl: an automated framework for generating graph neural network accelerators. Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, 2020, pp. 1–9.
- Chen, H.; Hao, C. Dgnn-booster: A generic fpga accelerator framework for dynamic graph neural network inference. 2023 IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines (FCCM). IEEE, 2023, pp. 195–201.
- Abi-Karam, S.; Hao, C. Gnnbuilder: An automated framework for generic graph neural network accelerator generation, simulation, and optimization. 2023 33rd International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL). IEEE, 2023, pp. 212–218.
- Lu, Q.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, M.; Hu, J.; Shi, Y. Hardware/Software Co-Exploration for Graph Neural Architectures on FPGAs. 2022 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI). IEEE, 2022, pp. 358–362.
- Yan, W.; Tong, W.; Zhi, X. FPGAN: an FPGA accelerator for graph attention networks with software and hardware co-optimization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 171608–171620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Tao, Z.; Wang, K.; He, L. Skeletongcn: a simple yet effective accelerator for gcn training. 2022 32nd International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL). IEEE, 2022, pp. 445–451.
- He, Z.; Tian, T.; Wu, Q.; Jin, X. FTW-GAT: An FPGA-based accelerator for graph attention networks with ternary weights. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Que, Z.; Luk, W.; Fan, H. Customizable FPGA-based Accelerator for Binarized Graph Neural Networks. 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1968–1972.
- Ran, S.; Zhao, B.; Dai, X.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Y. Software-hardware co-design for accelerating large-scale graph convolutional network inference on FPGA. Neurocomputing 2023, 532, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Tian, T.; Wu, Q.; Jin, X. QEGCN: An FPGA-based accelerator for quantized GCNs with edge-level parallelism. Journal of Systems Architecture 2022, 129, 102596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Tian, T.; Liang, H.; Jin, X. A gather accelerator for GNNs on FPGA platform. 2021 IEEE 27th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS). IEEE, 2021, pp. 74–81.
- Tao, Z.; Wu, C.; Liang, Y.; Wang, K.; He, L. LW-GCN: A lightweight FPGA-based graph convolutional network accelerator. ACM Transactions on Reconfigurable Technology and Systems 2022, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, B.; Kannan, R.; Prasanna, V.; Busart, C. Model-architecture co-design for high performance temporal gnn inference on fpga. 2022 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1108–1117.
- Hansson, O.; Grailoo, M.; Gustafsson, O.; Nunez-Yanez, J. Deep Quantization of Graph Neural Networks with Run-Time Hardware-Aware Training. International Symposium on Applied Reconfigurable Computing. Springer, 2024, pp. 33–47.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





