Submitted:
27 May 2024
Posted:
29 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population and Sample Size Calculations
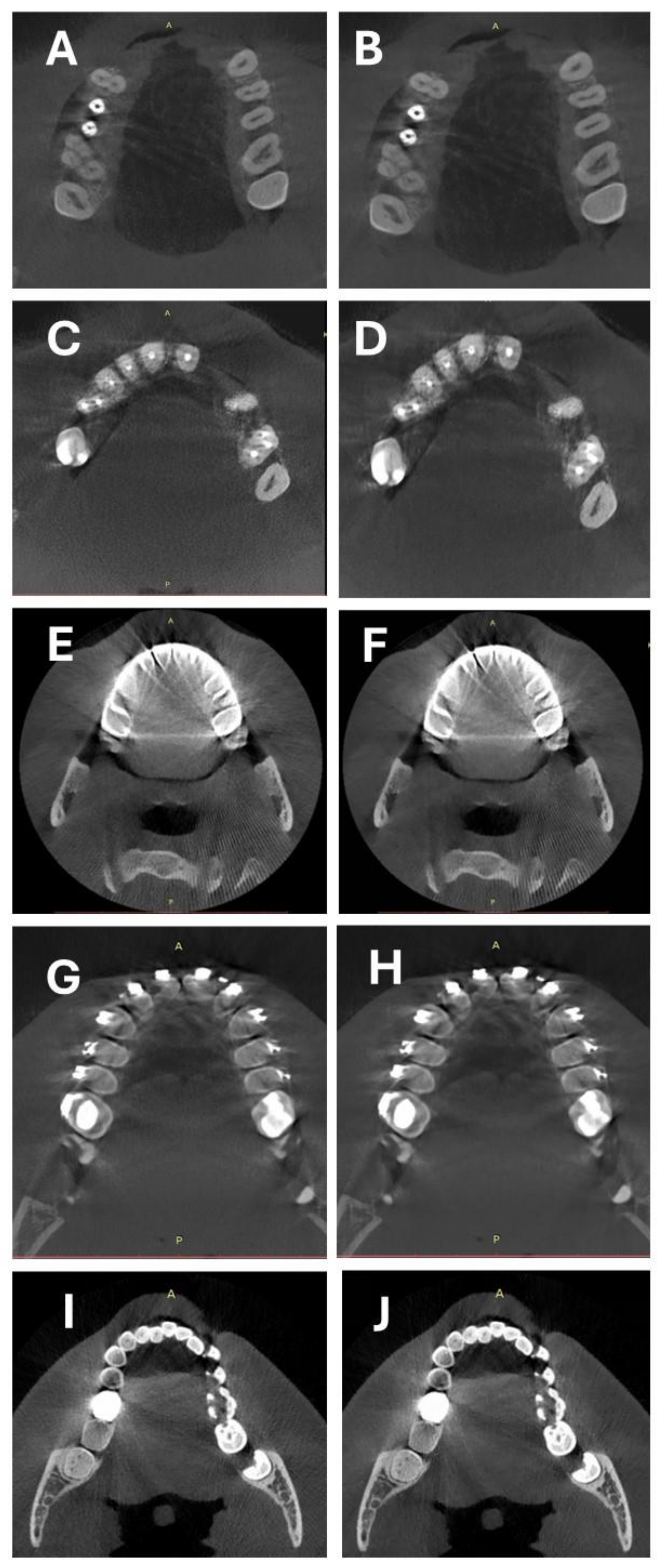
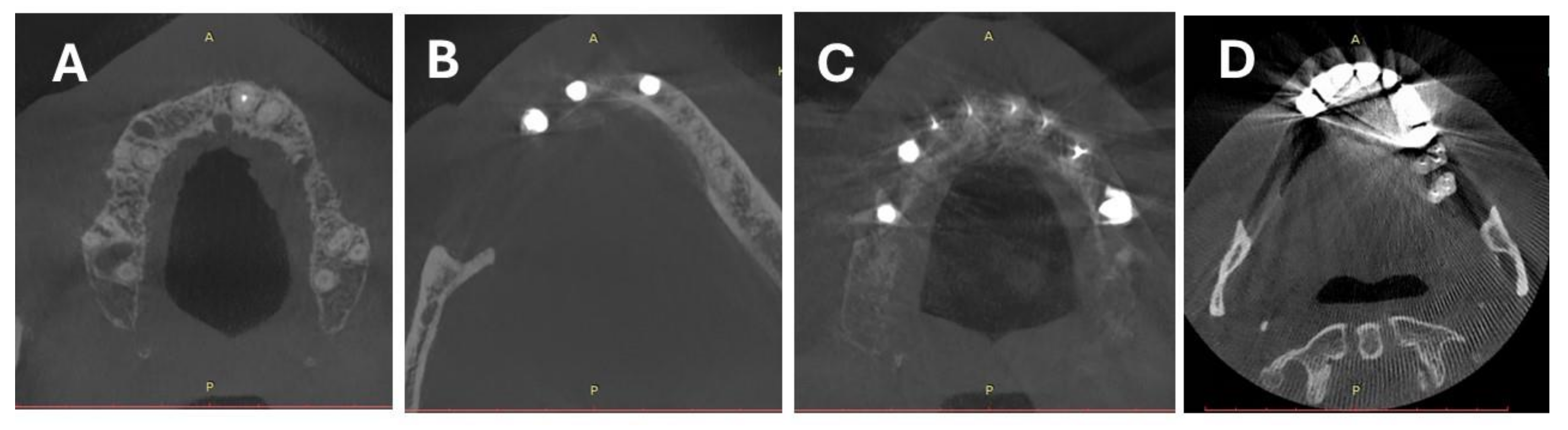
2.2. CBCT Scanning Protocol and Image Reconstruction
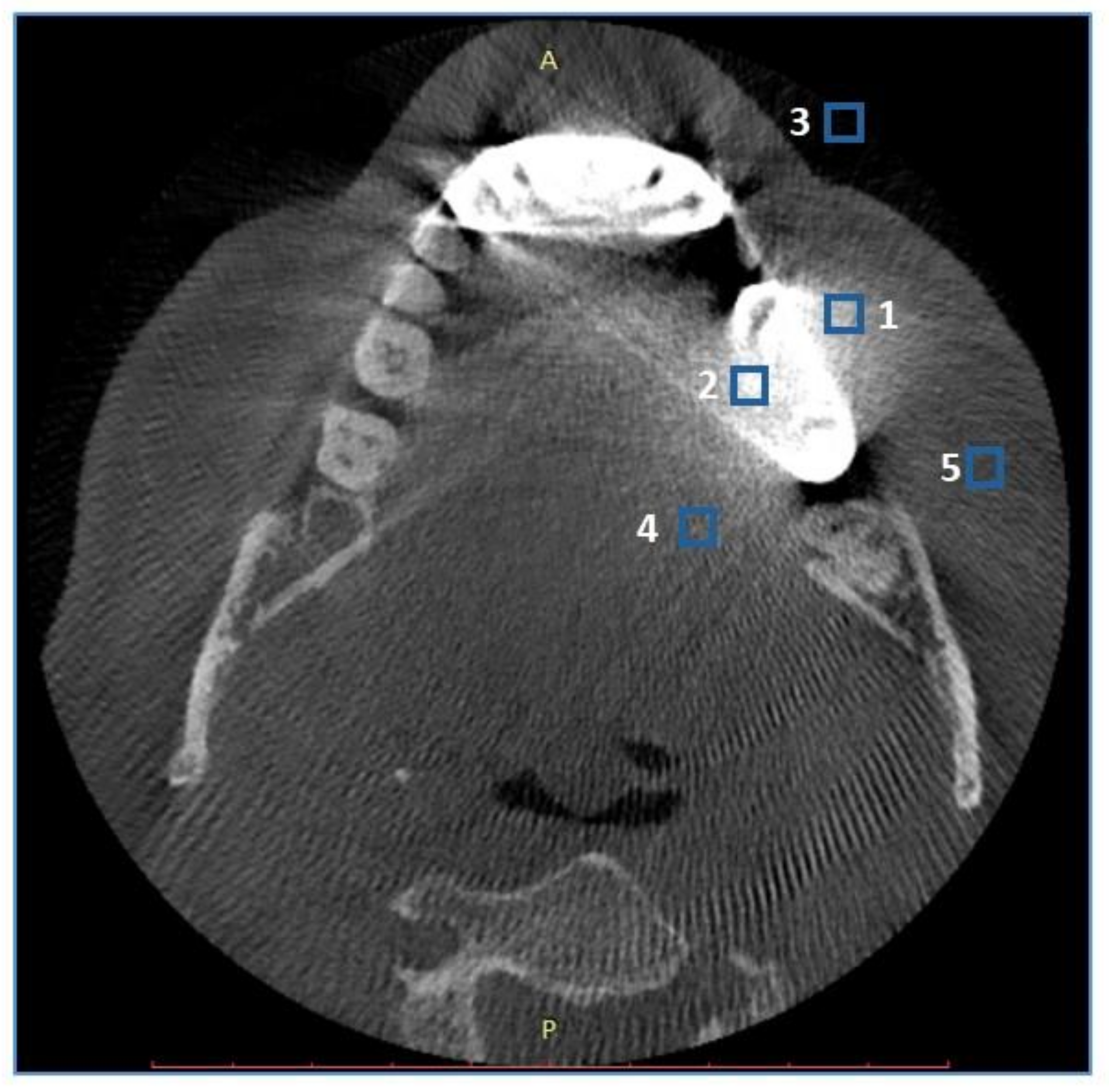
2.3. Objective Image Quality Assessment
2.4. Subjective Image Quality Assessment
2.5. Inter- and Intrareader Agreement
2.6. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population and Sample Size
3.2. Objective Image Quality
3.3. Subjective Image Quality
3.4. Intrareader, Interreader Reliability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
References
- Dawood, A.; Patel, S.; Brown, J. Cone Beam CT in Dental Practice. Br Dent J 2009, 207, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaêta-Araujo, H.; Leite, A.F.; de Faria Vasconcelos, K.; Jacobs, R. Two Decades of Research on CBCT Imaging in DMFR - An Appraisal of Scientific Evidence. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2021, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaasalainen, T.; Ekholm, M.; Siiskonen, T.; Kortesniemi, M. Dental Cone Beam CT: An Updated Review. Physica Medica 2021, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.H.; Fardim, K.A.C.; de Souza, C.F.; Sotto-Maior, B.S.; Assis, N.M.S.P.; Devito, K.L. Effect of Anatomical Region on the Formation of Metal Artefacts Produced by Dental Implants in Cone Beam Computed Tomographic Images. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2018, 47, 20170281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, R.; Heil, U.; Groß, D.; Bruellmann, D.D.; Dranischnikow, E.; Schwanecke, U.; Schoemer, E. Artefacts in CBCT: A Review. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2011, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrabuio, B.R.; Carvalho, C.G.; Peralta-Mamani, M.; da Silva Santos, P.S.; Rubiran Bullen, I.R.F.; Fische Rubira, C.M. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Artifacts in the Presence of Dental Implants and Associated Factors: An Integrative Review. Imaging Sci Dent 2021, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirturk Kocasarac, H.; Helvacioglu Yigit, D.; Bechara, B.; Sinanoglu, A.; Noujeim, M. Contrast-to-Noise Ratio with Different Settings in a CBCT Machine in Presence of Different Root-End Filling Materials: An in Vitro Study. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2016, 45, 20160012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Man, B.; Nuyts, J.; Dupont, P.; Marchal, G.; Suetens, P. Metal Streak Artifacts in X-Ray Computed Tomography: A Simulation Study. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1999, 46, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, B.; A. McMahan, C.; S. Moore, W.; Noujeim, M.; Geha, H.; B. Teixeira, F. Contrast-to-Noise Ratio Difference in Small Field of View Cone Beam Computed Tomography Machines. J Oral Sci 2012, 54, 227–232. [CrossRef]
- Kalender, W.A.; Hebel, R.; Ebersberger, J. Reduction of CT Artifacts Caused by Metallic Implants. Radiology 1987, 164, 576–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.J.; Mao, W.; Liu, C.; Aref, I.; Elshaikh, M.; Lee, J.K.; Pradhan, D.; Movsas, B.; Chetty, I.J.; Siddiqui, F. Improvements in CBCT Image Quality Using a Novel Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: A Clinical Evaluation. Adv Radiat Oncol 2019, 4, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washio, H.; Ohira, S.; Funama, Y.; Morimoto, M.; Wada, K.; Yagi, M.; Shimamoto, H.; Koike, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Karino, T.; et al. Metal Artifact Reduction Using Iterative CBCT Reconstruction Algorithm for Head and Neck Radiation Therapy: A Phantom and Clinical Study. Eur J Radiol 2020, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Lin, Y.B.; Jiang, S.D.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Bao, X.D. A New Dental CBCT Metal Artifact Reduction Method Based on a Dual-Domain Processing Framework. Phys Med Biol 2023, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Convolutional Neural Network Based Metal Artifact Reduction in X-Ray Computed Tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierczak, N.; Kazimierczak, W.; Serafin, Z.; Nowicki, P.; Nożewski, J.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J. AI in Orthodontics: Revolutionizing Diagnostics and Treatment Planning—A Comprehensive Review. J Clin Med 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Luo, H.; Su, C.; Yao, Y.; Liao, W. Machine Learning in Dental, Oral and Craniofacial Imaging: A Review of Recent Progress. PeerJ 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abesi, F.; Jamali, A.S.; Zamani, M. Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in the Detection and Segmentation of Oral and Maxillofacial Structures Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Images: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pol J Radiol 2023, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koetzier, L.R.; Mastrodicasa, D.; Szczykutowicz, T.P.; van der Werf, N.R.; Wang, A.S.; Sandfort, V.; van der Molen, A.J.; Fleischmann, D.; Willemink, M.J. Deep Learning Image Reconstruction for CT: Technical Principles and Clinical Prospects. Radiology 2023, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetzier, L.R.; Mastrodicasa, D.; Szczykutowicz, T.P.; van der Werf, N.R.; Wang, A.S.; Sandfort, V.; van der Molen, A.J.; Fleischmann, D.; Willemink, M.J. Deep Learning Image Reconstruction for CT: Technical Principles and Clinical Prospects. Radiology 2023, 306, e221257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.G.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, D.S.; Oh, J.; Goo, J.M. Deep Learning Reconstruction for Contrast-Enhanced CT of the Upper Abdomen: Similar Image Quality with Lower Radiation Dose in Direct Comparison with Iterative Reconstruction. Eur Radiol 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Chang, W.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, C.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.Y.; Cho, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H. Dose Reduction Potential of Vendor-Agnostic Deep Learning Model in Comparison with Deep Learning–Based Image Reconstruction Algorithm on CT: A Phantom Study. Eur Radiol 2022, 32, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Park, E.-A.; Lee, W.; Ahn, C.; Kim, J.-H. Incremental Image Noise Reduction in Coronary CT Angiography Using a Deep Learning-Based Technique with Iterative Reconstruction. Korean J Radiol 2020, 21, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, S.L.; Trout, A.T.; Somasundaram, E.; Anton, C.G.; Li, Y.; Dillman, J.R. Improving Image Quality and Reducing Radiation Dose for Pediatric CT by Using Deep Learning Reconstruction. Radiology 2020, 298, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racine, D.; Brat, H.G.; Dufour, B.; Steity, J.M.; Hussenot, M.; Rizk, B.; Fournier, D.; Zanca, F. Image Texture, Low Contrast Liver Lesion Detectability and Impact on Dose: Deep Learning Algorithm Compared to Partial Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction. Eur J Radiol 2021, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierczak, W.; Kędziora, K.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Kazimierczak, N.; Serafin, Z. Noise-Optimized CBCT Imaging of Temporomandibular Joints—The Impact of AI on Image Quality. J Clin Med 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierczak, W.; Kazimierczak, N.; Wilamowska, J.; Wojtowicz, O.; Nowak, E.; Serafin, Z. Enhanced Visualization in Endoleak Detection through Iterative and AI-Noise Optimized Spectral Reconstructions. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.G.; Ahn, C.; Choi, H.; Hong, W.; Park, J.; Kim, J.H.; Goo, J.M. Image Quality of Ultralow-Dose Chest CT Using Deep Learning Techniques: Potential Superiority of Vendor-Agnostic Post-Processing over Vendor-Specific Techniques. Eur Radiol 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; Rasband, W.; Eliceiri, K. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat Methods 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Tao, X.; Xi, Y. Evaluation of the Dental Spectral Cone Beam CT for Metal Artefact Reduction. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2019, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenele, R.C.; Nascimento, E.H.L.; Vasconcelos, T.V.; Noujeim, M.; Freitas, D.Q. Magnitude of Cone Beam CT Image Artifacts Related to Zirconium and Titanium Implants: Impact on Image Quality. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2018, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, W.; Kazimierczak, N.; Serafin, Z. Review of Clinical Applications of Dual-Energy CT in Patients after Endovascular Aortic Repair. J Clin Med 2023, 12, 7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Große Hokamp, N.; Hellerbach, A.; Gierich, A.; Jordan, D.W.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Maintz, D.; Haneder, S. Reduction of Artifacts Caused by Deep Brain Stimulating Electrodes in Cranial Computed Tomography Imaging by Means of Virtual Monoenergetic Images, Metal Artifact Reduction Algorithms, and Their Combination. Invest Radiol 2018, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, V.; Große Hokamp, N.; Abdullayev, N.; Rau, R.; Mpotsaris, A.; Maintz, D.; Borggrefe, J. Metal Artifact Reduction by Dual-Layer Computed Tomography Using Virtual Monoenergetic Images. Eur J Radiol 2017, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Spronk, D.; Luo, Y.; Puett, C.; Inscoe, C.R.; Tyndall, D.A.; Lee, Y.Z.; Lu, J.; Zhou, O. Feasibility of Dual-Energy CBCT by Spectral Filtration of a Dual-Focus CNT x-Ray Source. PLoS ONE 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Snyder, D.L.; O’Sullivan, J.A.; Vannier, M.W. Iterative Deblurring for CT Metal Artifact Reduction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1996, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boas, F.E.; Fleischmann, D. Evaluation of Two Iterative Techniques for Reducing Metal Artifacts in Computed Tomography. Radiology 2011, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Crop, A.; Casselman, J.; van Hoof, T.; Dierens, M.; Vereecke, E.; Bossu, N.; Pamplona, J.; D’Herde, K.; Thierens, H.; Bacher, K. Analysis of Metal Artifact Reduction Tools for Dental Hardware in CT Scans of the Oral Cavity: KVp, Iterative Reconstruction, Dual-Energy CT, Metal Artifact Reduction Software: Does It Make a Difference? Neuroradiology 2015, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, D.; Wilcox, C.; Heidinger, B.; Raptopoulos, V.; Brook, A.; Brook, O.R. Metal Implants on CT: Comparison of Iterative Reconstruction Algorithms for Reduction of Metal Artifacts with Single Energy and Spectral CT Scanning in a Phantom Model. Abdominal Radiology 2017, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayer, D.R.; Kim, N.Y.; Otto, B.J.; Grayev, A.M.; Kuner, A.D. Unintended Consequences: Review of New Artifacts Introduced by Iterative Reconstruction CT Metal Artifact Reduction in Spine Imaging. Proc. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierczak, W.; Nowak, E.; Kazimierczak, N.; Jankowski, T.; Jankowska, A.; Serafin, Z. The Value of Metal Artifact Reduction and Iterative Algorithms in Dual Energy CT Angiography in Patients after Complex Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjesteby, L.; Yang, Q.; Xi, Y.; Claus, B.E.H.; Jin, Y.; De Man, B.; Wang, G.; Shan, H. Deep Learning Methods for CT Image-Domain Metal Artifact Reduction.; 2017.
- Park, H.S.; Seo, J.K.; Hyun, C.M.; Lee, S.M.; Jeon, K. A Fidelity-Embedded Learning for Metal Artifact Reduction in Dental CBCT. Med Phys 2022, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song Tianyi and Peng Shengwang and Zhu Manman and Meng Ming Qiang and Ma Jianhua and Zeng Dong and Huang Jing and Wang Yongbo and Bian Zhaoying, Y. and Y. B-MAR: Bidirectional Artifact Representations Learning Framework for Metal Artifact Reduction in Dental CBCT. Phys Med Biol 2024.
- Rohleder, M.; Gottschalk, T.M.; Maier, A.; Kreher, B. Cross-Domain Metal Segmentation for CBCT Metal Artifact Reduction.; 2022.
- Hu, Z.; Jiang, C.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Liang, D. Artifact Correction in Low-Dose Dental CT Imaging Using Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks. Med Phys 2019, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramage, A.; Lopez Gutierrez, B.; Fischer, K.; Sekula, M.; Santaella, G.M.; Scarfe, W.; Brasil, D.M.; de Oliveira-Santos, C. Filtered Back Projection vs. Iterative Reconstruction for CBCT: Effects on Image Noise and Processing Time. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.A.A.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, S.Y. Image Denoising by Transfer Learning of Generative Adversarial Network for Dental CT. Biomed Phys Eng Express 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.A.A.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, S.Y. Half-Scan Artifact Correction Using Generative Adversarial Network for Dental CT. Comput Biol Med 2021, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierczak, W.; Kędziora, K.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Kazimierczak, N.; Serafin, Z. Noise-Optimized CBCT Imaging of Temporomandibular Joints—The Impact of AI on Image Quality. J Clin Med 2024, 13, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, B.; Yang, Z.; Kang, W. A Novel Reconstruction of the Sparse-View CBCT Algorithm for Correcting Artifacts and Reducing Noise. Mathematics 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S. Self-Supervised Denoising of Projection Data for Low-Dose Cone-Beam CT. Med Phys 2023, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liang, X.; Shen, C.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J. Synthetic CT Generation from CBCT Images via Deep Learning. Med Phys 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Park, C.; Lim, Y.; Cho, H. A Metal Artifact Reduction Method Using a Fully Convolutional Network in the Sinogram and Image Domains for Dental Computed Tomography. J Digit Imaging 2020, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codari, M.; de Faria Vasconcelos, K.; Ferreira Pinheiro Nicolielo, L.; Haiter Neto, F.; Jacobs, R. Quantitative Evaluation of Metal Artifacts Using Different CBCT Devices, High-Density Materials and Field of Views. Clin Oral Implants Res 2017, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, R.; Stamatakis, H.; Bosmans, H.; Bogaerts, R.; Jacobs, R.; Horner, K.; Tsiklakis, K. Quantification of Metal Artifacts on Cone Beam Computed Tomography Images. Clin Oral Implants Res 2013, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, A.H.; Fardim, K.A.C.; De Souza, C.F.; Sotto-Maior, B.S.; Assis, N.M.S.P.; Devito, K.L. Effect of Anatomical Region on the Formation of Metal Artefacts Produced by Dental Implants in Cone Beam Computed Tomographic Images. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2018, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Measurement | Mean | SD | Median | Min | Max | Q1 | Q3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔVV | Native | 174,41 | 266,69 | 73,25 | 0,0 | 1534,30 | 27,75 | 178,62 | p=0.094 |
| DLM | 174,07 | 263,69 | 71,75 | 0,1 | 1506,00 | 30,47 | 177,12 | ||
| AIx | Native | 166,65 | 218,96 | 73,89 | 0,0 | 1426,54 | 27,05 | 204,14 | p=0.001 * |
| DLM | 158,31 | 199,10 | 68,23 | 0,0 | 1215,26 | 25,48 | 205,84 | ||
| CNR | Native | 0,79 | 1,05 | 0,52 | 0,0 | 14,13 | 0,23 | 1,07 | p<0.001 * |
| DLM | 0,93 | 1,52 | 0,61 | 0,0 | 23,11 | 0,26 | 1,15 |
| Parameter | Measurement | Mean | SD | Median | Min | Max | Q1 | Q3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔVV | Native | 339,64 | 341,88 | 205,95 | 3,60 | 1534,30 | 104,20 | 462,15 | p=0.785 |
| DLM | 341,04 | 335,61 | 214,25 | 7,90 | 1506,00 | 106,07 | 449,28 | ||
| AIx | Native | 379,50 | 342,29 | 280,71 | 0,00 | 2374,64 | 159,29 | 491,80 | p=0.214 |
| DLM | 350,92 | 254,12 | 281,25 | 35,19 | 1301,66 | 170,38 | 469,82 | ||
| CNR | Native | 0,70 | 0,62 | 0,54 | 0,00 | 3,83 | 0,23 | 1,01 | p=0.001 * |
| DLM | 0,72 | 0,63 | 0,55 | 0,01 | 3,72 | 0,25 | 1,04 |
| Parameter | Type of object | Reconstruction | Mean | SD | Median | Min | Max | Q1 | Q3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔVV | Implants | Native | 119,70 | 164,77 | 53,30 | 4,60 | 919,40 | 23,98 | 135,80 | p=0,125 |
| DLM | 121,27 | 165,82 | 53,60 | 2,10 | 939,00 | 26,15 | 138,43 | |||
| Amalgam fillings | Native | 215,32 | 276,75 | 108,90 | 9,40 | 1231,40 | 49,00 | 274,40 | p=0,699 | |
| DLM | 213,79 | 281,48 | 105,90 | 7,90 | 1233,30 | 46,30 | 314,50 | |||
| Orthodontic appliances | Native | 224,82 | 352,62 | 70,25 | 0,30 | 1505,00 | 24,45 | 222,58 | p=0,567 | |
| DLM | 230,54 | 352,02 | 68,50 | 0,20 | 1506,00 | 33,37 | 357,38 | |||
| Root canal fillings | Native | 161,16 | 212,14 | 82,75 | 1,10 | 1177,90 | 29,70 | 186,93 | p=0,356 | |
| DLM | 160,54 | 209,45 | 85,25 | 0,90 | 1177,50 | 31,80 | 185,95 | |||
| Crown | Native | 227,84 | 389,47 | 64,00 | 0,00 | 1534,30 | 15,90 | 160,25 | p=0,195 | |
| DLM | 222,89 | 379,95 | 63,70 | 0,10 | 1486,80 | 22,60 | 157,65 | |||
| CNR | Implants | Native | 0,97 | 1,72 | 0,60 | 0,05 | 14,13 | 0,26 | 1,15 | p=0,350 |
| DLM | 1,22 | 2,76 | 0,74 | 0,03 | 23,11 | 0,31 | 1,33 | |||
| Amalgam fillings | Native | 0,81 | 0,65 | 0,62 | 0,01 | 2,87 | 0,42 | 1,03 | p=0,156 | |
| DLM | 0,90 | 0,80 | 0,64 | 0,01 | 3,44 | 0,38 | 1,12 | |||
| Orthodontic appliances | Native | 0,60 | 0,77 | 0,38 | 0,00 | 3,83 | 0,08 | 0,71 | p=0,656 | |
| DLM | 0,64 | 0,76 | 0,44 | 0,00 | 3,72 | 0,13 | 0,74 | |||
| Root canal fillings | Native | 0,74 | 0,69 | 0,52 | 0,02 | 4,59 | 0,28 | 1,03 | p=0,003* | |
| DLM | 0,85 | 0,80 | 0,60 | 0,01 | 4,47 | 0,31 | 1,11 | |||
| Crown | Native | 0,78 | 0,84 | 0,41 | 0,00 | 3,82 | 0,18 | 1,14 | p=0,097 | |
| DLM | 0,89 | 0,99 | 0,55 | 0,02 | 4,24 | 0,18 | 1,21 | |||
| AIx | Implants | Native | 105,00 | 172,18 | 34,19 | 5,17 | 852,14 | 17,23 | 133,07 | p=0,641 |
| DLM | 105,73 | 168,95 | 39,54 | 2,64 | 842,48 | 18,77 | 128,38 | |||
| Amalgam fillings | Native | 178,87 | 165,61 | 146,87 | 8,01 | 570,81 | 59,14 | 233,52 | p=0,474 | |
| DLM | 168,42 | 165,18 | 128,50 | 0,00 | 550,87 | 43,39 | 222,61 | |||
| Orthodontic appliances | Native | 285,51 | 355,50 | 138,01 | 20,56 | 1426,54 | 61,63 | 338,19 | p=0,157 | |
| DLM | 242,02 | 282,87 | 123,68 | 9,54 | 1215,26 | 47,12 | 356,00 | |||
| Root canal fillings | Native | 167,04 | 199,54 | 65,43 | 0,00 | 996,37 | 30,91 | 221,97 | p=0,155 | |
| DLM | 162,46 | 191,93 | 71,11 | 4,14 | 1025,77 | 30,29 | 234,94 | |||
| Crown | Native | 173,85 | 217,91 | 103,15 | 0,57 | 972,66 | 25,05 | 204,70 | p=0,247 | |
| DLM | 165,63 | 198,34 | 85,15 | 1,31 | 796,04 | 25,27 | 204,76 |
| Parameter | Measurement | N | Mean | SD | Median | Min | Max | Q1 | Q3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall image quality | Native | 244 | 3,16 | 0,63 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 4 | p<0.001 * |
| DLM | 244 | 3,86 | 0,82 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Intensity of artifacts | Native | 244 | 3,55 | 0,67 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 4 | p<0.001 * |
| DLM | 244 | 3,22 | 0,76 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| Reconstruction | Parameter | ICC | 95% CI | Agreement (Cicchetti) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | Overall image quality | 0,515 | 0,371 | 0,634 | Fair |
| Intensity of artifacts | 0,757 | 0,670 | 0,824 | Excelent | |
| DLM | Overall image quality | 0,515 | 0,372 | 0,634 | Fair |
| Intensity of artifacts | 0,681 | 0,572 | 0,767 | Good | |
| Reconstruction | Parameter | ICC | 95% CI | Agreement (Cicchetti) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | Overall image quality | 0,477 | 0,326 | 0,604 | Fair |
| Intensity of artifacts | 0,721 | 0,624 | 0,797 | Good | |
| DLM | Overall image quality | 0,478 | 0,330 | 0,604 | Fair |
| Intensity of artifacts | 0,573 | 0,429 | 0,686 | Fair | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





