1. Introduction
On account of the overall lack of land resources and the large population base in China, the agricultural production is faced with enormous challenges. In this case, the protection of cultivated land under the premise of ensuring grain security has become an important measure [
1,
2,
3]. The cultivated land protection policy of China has accumulated successful experiences from the historical evolution and also reflected a certain trend in local evolution. How to keep policy implementation does not deviate is the important part to cultivated land protection. Improving the sustainable use of cultivated land [
4], enhancing farmers' understanding and protection awareness of cultivated land protection policies, and strengthening the enthusiasm for agricultural production are the fatal measures to promote higher grain production efficiency of cultivated land under the guarantee of grain security [
5]. With the renewal and improvement of Chinese cultivated land protection policy, the focus of cultivated land protection in China has shifted to quantity-quality-ecology from the historical evolution of cultivated land protection policy [
6]. Compared with the focus on the implementation of the cultivated land protection policy, more scholars only focus on the historical evolution of the cultivated land protection policy, implying the overall perspective is macro. Niu et al. researched the path optimization from the historical evolution and practical exploration of cultivated land protection policy [
7]. Wang et al. found the future trend from the historical evolution and protection effect of cultivated land protection policy [
8]. Lu et al. gave suggestions for improving the system in the new era directly from the logic of the evolution of cultivated land protection [
9]. Yu et al. discovered the countermeasures to strengthen cultivated land protection from the problems of cultivated land protection based on the bottom-line thinking of grain security [
10]. Liu et al. summarized the historical evolution and optimization transformation of Chinese cultivated land protection strategy from the perspective of ecological civilization [
11]. Nevertheless, there are few researches on the implementation perspective of the historical evolution of cultivated land protection policy. What’s more, the researches on farmers and the key implementation subject of Smith policy implementation model are mostly based on empirical analysis, which is lack of exploration on the policy evolution of cultivated land protection policy from the perspective of policy implementation. Regarding the protection of cultivated land, there are more work could be carry out in the future [
12]. As most previous studies have made policies based on the historical evolution of cultivated land protection policies, this paper uses the Smith policy implementation model to introduce new concerns about the perspective of cultivated land protection policy implementation from the historical and local evolution of Chinese cultivated land protection policies, and obtain countermeasures for improving cultivated land protection policies. In addition, this work summarized the historical experiences and the trend of the local cultivated land protection policy. On account of the insufficient total cultivated land, low quality and ambiguous implementation of the trinity in China, the supplementary direction of the evolution of cultivated land protection policy from the perspective of policy implementation by the Smith policy implementation model was explored.
2. Evolution Characteristics of Cultivated Land Protection Policy in China
Through the Chinese literature management website
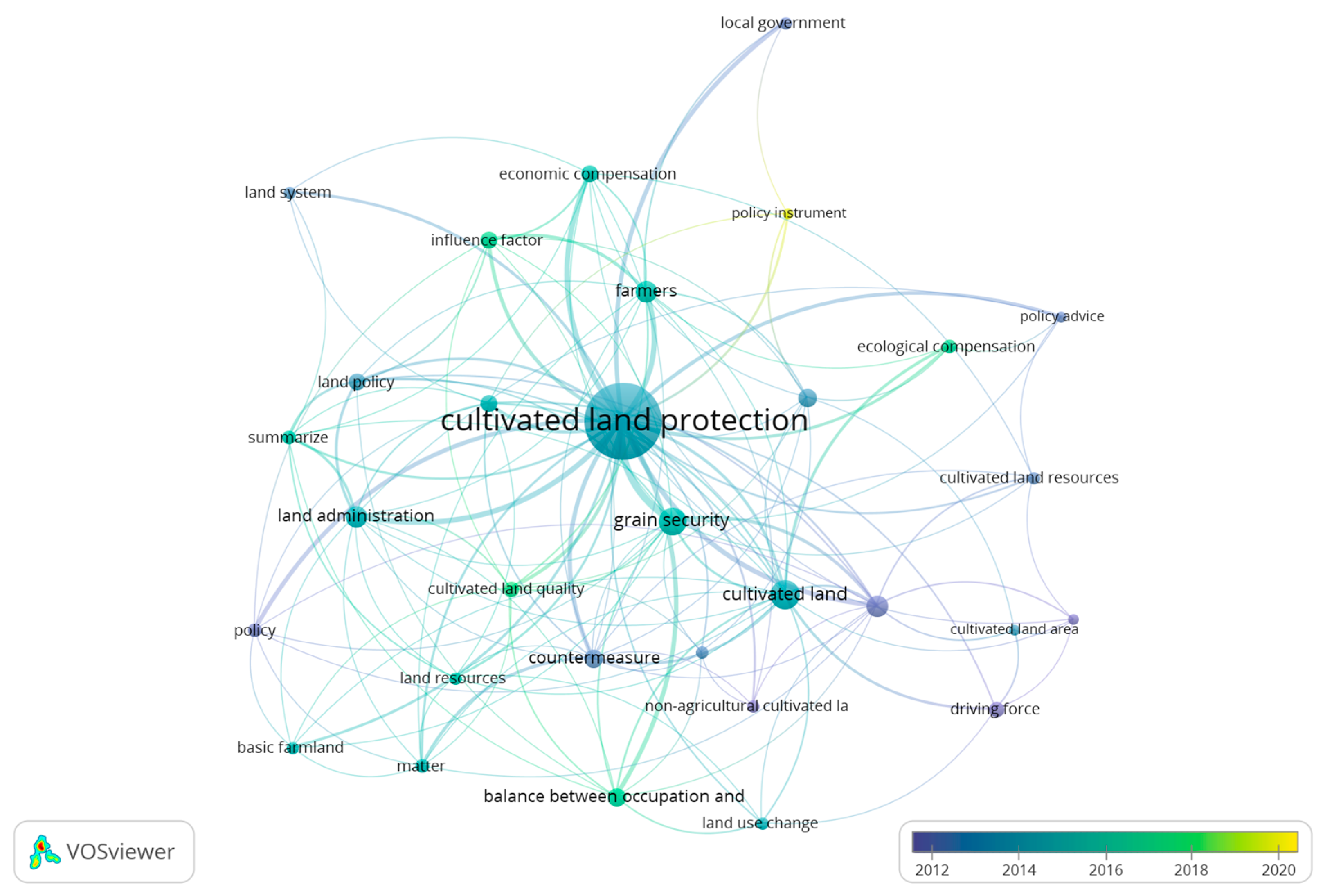
https://www.cnki.net/, the literature on Cultivated Land Protection Policy was studied. Authors used VOSviewer software to cluster and integrate the collected literature and find the keywords related to farmland protection (
Figure 1). It can be seen that the farmers, economic compensation, policy instrument, local government are the key factors of the same kind of influence, and also the necessary link closely related to the cultivated land protection policy. Moreover, with the development of time, the maturity of the research on cultivated land protection is starting around the cultivated land protection itself. In recent years, the overall dynamic range of its literature has not changed much, indicating that the research on cultivated land protection still needs attention. In particular, the policy research based on the peasant household dimension still needs to be updated.
Most of the literature with respect to the cultivated land protection policy is based on the level of policy formulation by the government. From the logic of time development sequence, the historical evolution of cultivated land protection policy is sorted out in time order. On this basis, the focus shift of the development history of cultivated land protection policy is summarized [
13]. As the basic resources and production factors of agriculture, cultivated land is the fundamental source of grain security, which must be strengthened in the country's vigorous implementation of the strategy of "storing grain in the land" [
14]. To do a good job in the protection of cultivated land, under the promotion of the goal of sustainable development, the core concept of ecological civilization construction is injected into the sustainable use of cultivated land, which is conducive to the long-term development of grain security and an important direction of agricultural development. After 1949, the cultivated land protection system has become increasingly perfect. Then after the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, socialism with Chinese characteristics has entered a new era, the inherent meaning of cultivated land protection policy has been richer and deeper, and the evolution of cultivated land protection policy has become increasingly mature. Cultivated land protection is a sustainable project, meanwhile each generation has its mission and responsibility. The foundation of successful experience will provide a clearer direction for the future direction of cultivated land protection. According to the data collected by this work, the evolution of the successful experience of cultivated land protection policy is mainly based on the change from 1949 to 2012. The core value orientation of main cultivated land protection has three aspects. First, the pursuit of cultivated land quantity control is the basis of cultivated land protection. Secondly, keeping the quality of cultivated land management is the guarantee of cultivated land protection. At last, the key of cultivated land protection is to coordinate the quantity-quality-ecology of cultivated land.
2.1. Basic Stage of the Evolution of Cultivated Land Protection Policies
After 1949, the pursuit of cultivated land quantity has laid a solid foundation for the comprehensive protection and utilization of cultivated land. Agricultural production, which dominated rural economic construction, was closely dependent on cultivated land, and the cultivated land protection policy based on the protection of cultivated land quantity became the main focus. By the 1960s, the emphasis of non-agricultural construction on the occupation of cultivated land was mentioned several times in the relevant regulations, policies and reports, to pursue the agricultural production mode of cultivated land quantity construction. To a certain extent, the cultivated land protection has been preliminarily explored. The evolution of Chinese cultivated land protection policy has obvious epochal characteristics. Based on the requirements of economic development in different periods, cultivated land protection mainly pursued the control of cultivated land quantity from 1949.
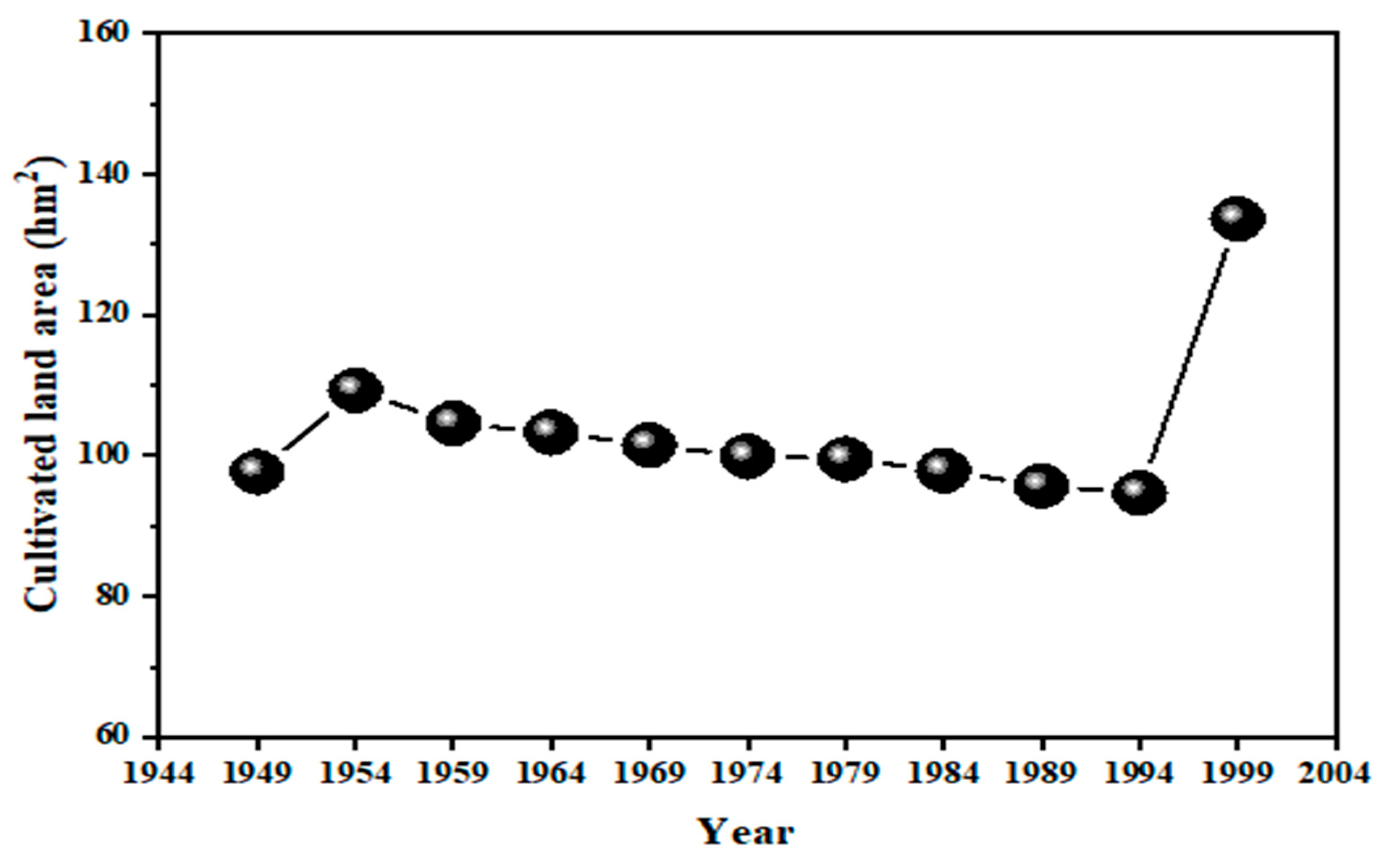
After 1979, becasue of a large number of engineering projects making concessions to cultivated land, the obvious loss of rural farmers, and the increase in the occupation of cultivated land by township workshops and farmers' housing, the area of cultivated land declined and the overall trend of cultivated land protection declined significantly (
Figure 2). From the trend of the change of the national cultivated land area from 1949 to 1999, in the long and tortuous historical development, the relevant cultivated land protection system pursuing the cultivated land quantity accumulated experience for the subsequent cultivated land protection policy. In the updating of the cultivated land protection policy with the farmer, the consensus premise of implementing the policy was not to reduce the total amount of cultivated land and permanent basic farmland.
To ease the decline of the cultivated land quantity, the "Notice on Strengthening Land Administration and Preventing Unauthorized Occupation of Cultivated Land" issued by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and The State Council in March 1986 indicated the importance attached to the protection of cultivated land quantity. On June 25 of the same year, "the Land Management Law" of the People's Republic of China was deliberated and passed by the Standing Committee of the 6th National People's Congress, marking that Chinese land management and cultivated land protection entered the stage of the rule of law. In the stage of the pursuit of cultivated land protection and security, since the protection of basic farmland in 1994, the pursuit of cultivated land protection is the original core orientation of the history of cultivated land protection policy, and it is also an inevitable response to the reduction of cultivated land area (
Table 1).
Since 1949, agriculture has been a pillar industry in the development of the national economy. Moreover, the protection of cultivated land with the promotion of grain production as the main theme is the top priority of rural economic work [
15]. Taking the protection of basic farmland as the beginning of cultivated land protection is an inevitable product under the historical background of vigorously developing economy from 1949. Chinese cultivated land protection policy is based on the "Basic Farmland Protection Regulations" issued by The State Council on August 18, 1994, so that the protection of basic farmland becomes the beginning of the protection policy of cultivated land. The amount of cultivated land is directly reflected in the area of basic farmland, and the protection of basic farmland is the core part of the protection of cultivated land in sustainable utilization. The control of the red line of basic farmland area is maintained and the increase of farmland output is driven, which not only meets the needs of grain production but also does a good job in the basic measures of "storing grain in the land" for the sustainable utilization of cultivated land. On the road to the rapid development of China, improving the awareness of the red line of the cultivated land quantity, ensuring the increase of the cultivated land quantity in the development, and doing a good job in guaranteeing the cultivated land quantity are the basises for sustainable utilization of cultivated land.
Then, the evolution of Chinese cultivated land protection policy came to the second stage from 2004 to 2011. Excellent completion of cultivated land protection work is essentially to ensure the quality of cultivated land and maintain the productivity of cultivated land. At present, the construction of cultivated land quality in our country is mainly in the implementation of high-standard farmland construction projects. The history of cultivated land protection policy in China reflects the increasingly high requirements for high-standard farmland construction. Through the improvement of production conditions in accordance with local conditions and the scientific allocation of farmland infrastructure, the quality of cultivated land is significantly improved, and the cultivated land is controlled, which providing a practical guarantee for cultivated land protection.
Chinese urbanization entered a period of rapid development in 2004. In the process of administrative allocation of resources and market, forces are biased towards the development of urbanization [
16]. The improvement of cultivated land quality and the guarantee of rural agricultural development mainly relies on the construction of high-standard farmland. In 2008, "the permanent basic farmland" was put forward in the Third Plenary Session of the 17th Communist Party of China Central Committee, which clearly emphasized the requirements of cultivated land quality, cultivated land contiguous degree, and cultivated land stability. As a unique concept in the development of Chinese cultivated land protection policy, the permanent basic farmland has clear guidance for the policy formulation direction of cultivated land protection and has more stringent requirements for the quality of cultivated land protection. It means that Chinese cultivated land protection has officially entered the stage of permanent basic farmland protection with characteristic policy measures for cultivated land protection. In addition, the cultivated land protection policy focused on the quality and quantity of cultivated land protection (
Table 2).
In the safeguarding stage of cultivated land protection, it is important to maintain the quality of cultivated land and ensure its production capacity in order to strengthen agricultural infrastructure. From the perspective of cultivated land protection policies from 2004 to 2011, the safeguarding stage of cultivated land protection mainly focused on ensuring the steady progress of rural agriculture in fast-paced urbanization. The implementation of the strictest cultivated land protection policies, increasing the construction of high-standard farmland, and improving cultivated land quality and production capacity are currently the main measures to ensure cultivated land protection in China.
2.2. A New Stage of the Evolution of Cultivated Land Protection Policy
Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, the "five-sphere integrated plan": a plan to promote coordinated economic, political, cultural, social and ecological advancement, and the new development concept have made the construction of ecological civilization the top priority under the new historical starting point [
17]. For the protection of cultivated land, under the guidance of the concept of ecological civilization construction, China has formed a cultivated land protection and management system of "quantity protection, quality construction and ecological maintenance". Socialism with Chinese characteristics has entered a new era [
18]. A more comprehensive policy system has gradually been formed for the protection of cultivated land. Based on the previous mechanism of constructing the quantity and quality of farmland, the dimension of cultivated land protection and utilization has added the key indicator of "ecology". The implementation of cultivated land protection policies has transitioned from the requirement of "permanent basic farmland" to the construction of "high-standard farmland", meaning that the requirements for farmland construction have been raised to higher standards. Through measures such as land consolidation, improvement, and supporting facility construction, farmland has been made more productive ecological benefits and disaster resistance.
After the 18th National Congress, the concept of ecological civilization construction runs through the construction of the new era. Advancing the dimension of cultivated land protection to the trinity of quantity-quality-ecology, is the key to cultivated land protection. As a part of the ecosystem, cultivated land should be an essential part of ecological civilization construction. In the division of the "three zones and three lines", agricultural space with cultivated land is the core. The urban and ecological space are delineated by three departments, indicating the spatial overlap is inevitable. Hence, strictly defining the permanent basic farmland protection red line is the key to cultivated land protection. Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, under the call of ecological civilization construction, cultivated land has been regarded as an important land resource. China has divided cultivated land into "mountains, waters, forests, fields, lakes, grasslands, and sands" through the release of the "Plan for Cultivated Land, Grassland, Rivers, Lakes, and Livelihoods (2016-2030)" and the "National Land Planning Outline (2016-2030)", The land resources were protected and utilized through an integrated mechanism and systematic governance. This is another step forward in the protection of cultivated land (
Table 3).
Under the prevailing ecological civilization construction, the ecological governance system of cultivated land and "mountains, waters, forests, fields, lakes, and grasses" complement each other. Once the government pays more attention to the production capacity of cultivated land, sustainable utilization and development of cultivated land would achieved. The essence of cultivated land protection is to protect the production capacity of cultivated land. In terms of the long-term use and protection of cultivated land production capacity, it is necessary to recognize the current difficulties in the construction of high-standard farmland [
19]. The 20th National Congress once again mentioned firmly holding the red line of 1.8 billion mu of cultivated land and gradually turning all permanent basic farmland into high-standard farmland, which is a profound expectation for the construction of high-standard farmland. In policy operation, countries need to explore the possibility of realizing it to achieve the protection and utilization of cultivated land production capacity.
2.3. The Evolution Trend of Local
In the report of the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, comprehensively consolidating the foundation of grain security is an inevitable requirement in line with the basic pattern of grain transportation and sales in China, and it is also an unchanged goal in adhering to the strictest cultivated land protection policies.To solve the problem of grain security [
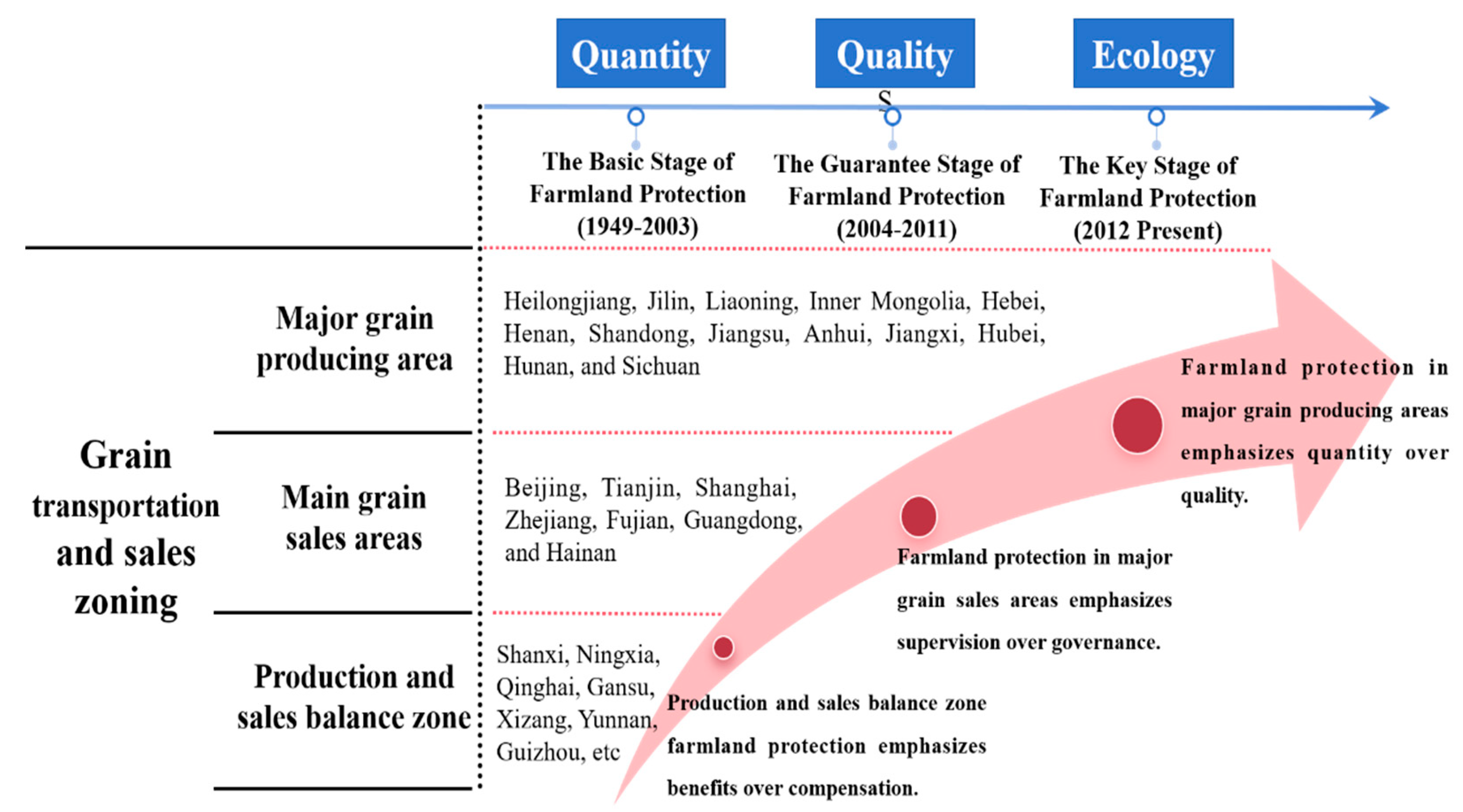
20], various provinces in China are divided into three major regions- the main grain production area, the main sales area, and the production and sales balance area according to the grain transportation and sales pattern. Among them, the main grain production area can ensure self-sufficiency while also transferring a large amount of commodity grain. The economy of the main grain sales areas is relatively developed, but there are more people and less land, resulting in a large gap in grain production and demand. And the production and sales balance zone has limited contribution to the national grain production, but can maintain self-sufficiency. To comply with the evolution logic of cultivated land protection policies in implementation, and to achieve the protection of sustainable utilization of farmland under the primary premise of ensuring grain security, it is particularly important to do a good job in cultivated land protection according to local conditions for the three basic patterns of grain transportation and sales. On account of the experience of the evolution of cultivated land protection policies, this study compared the effectiveness of cultivated land protection policies in the three major regions represented by Heilongjiang, Zhejiang, and Guizhou provinces. Furthermore, the implementation effect of grain transportation and sales zoning in cultivated land protection policies were summarized to identify possible trends in the local evolution of cultivated land protection policies in China (
Figure 3).
In the first place, cultivated land protection in major grain-producing areas emphasizes quantity over quality. After the reform and opening up, the southern part of China has focused on economic construction with the strong promotion of economic development. The heavy responsibility of national grain production had gradually transitioned from the traditional grain-producing areas in the south to the relatively slow economic central and western regions. The grain transportation and sales pattern had changed from the previous "southern grain transportation to the north" to the current "northern grain transportation to the south". Especially as a world-class grain warehouse, the Northeast region needs to implement the black land protection project and strengthen the construction of the cultivated land protection system [
21]. Heilongjiang is a major agricultural province in China with major grain production areas. It is an important "world-class granary". Taking Heilongjiang as an example, the typical black soil cultivated land area is 156 million mu, accounting for 56.1% of the typical black soil area in Northeast China. Under the framework of existing national cultivated land protection policies, to ensure the quantity of cultivated land, the red line of cultivated land is strictly defined. Hence, the government of Heilongjiang Province attaches great importance to the protection of cultivated land. According to Chinese third National Land Survey, the cultivated land area in Heilongjiang is about 257 million mu, an increase of nearly 19 million mu compared with the second National Land Survey. It can be clearly seen from the data that the pursuit of emphasis on the amount of cultivated land protection is the basic trend of grain producing areas to ensure the effective utilization of cultivated land resources and the security of grain security.
However, in promoting the implementation of cultivated land protection policy, there has been a problem in the main grain-producing areas where cultivated land protection is relatively focused on quantity while neglecting quality improvement. Taking Heilongjiang as an example, there is a lack of further tracking and improvement of relevant policies to ensure the quality of cultivated land [
22]. Due to the long-term need to ensure grain output, cultivated land has been heavily developed and utilized, relying on a large amount of fertilizers and pesticides for a long time. The black soil, known as the "giant panda" in cultivated land, has been destroyed in its original micro-ecology. After 60 to 70 years of cultivation, the thickness of the black soil layer has decreased from the original 60-70 cm to 20-30 cm. In some plots, the thickness of the cultivated layer is only 5 cm, resulting in a phenomenon of "broken skin and yellow". The fertile black soil continues to be "thin and hard" [
23]. These are the problems that major grain producing areas pay more attention to quantity in the protection of cultivated land, but ignore quality improvement.
Next in importance, cultivated land protection in major grain sales areas emphasizes supervision over governance. The pattern of grain transportation and marketing has shifted from the reform and development of China, and the main grain marketing areas basically pay more attention to economic development than that of agricultural production. However, due to the overall situation of the lack of cultivated land resources, the main grain marketing area attaches great importance to the supervision and administrative work of cultivated land protection work. Taking Zhejiang Province as an example, under the attention of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council to cultivated land protection work, high attention has been paid to the development of cultivated land protection work in administrative work, and strict institutional regulations have been established for the supervision of cultivated land protection policy. In order to comprehensively protect cultivated land, Zhejiang has established a "field chief system" and village-level inspectors at the provincial, municipal, county, and rural levels in recent years. At the same time, we will strengthen supervision in digital technology, develop and apply a "smart protection of farmland" digital system, build a "civil defense&technical defense" cultivated land protection model, and fully protect 19.53 million mu of farmland. We have strict construction goals in the supervision of cultivated land protection policies.
However, in promoting the implementation of cultivated land protection policy, there has been a problem in the main grain-producing areas. The cultivated land protection is relatively valued and regulatory systems are established while neglecting the joint governance of farmers. Take Zhejiang Province as an example, it is a city with the theme of economic development. In the "seventh National Population Census", the number of its floating population ranked the second in the country. Therefore, in the competition of economic development in Zhejiang province, there are some disputes over the main body of its cultivated land. At the same time, the scarcity of cultivated land resources within the province, coupled with the scattered distribution, remote location, and poor farming conditions of cultivated land, is not enough to stimulate the enthusiasm of farmers for farming and promote joint governance among farmers. Therefore, under the strict supervision system of "military order" cultivated land protection policy, the incentive for farmers to cultivate independently is insufficient. This is a problem of heavy supervision and light governance in cultivated land protection in the main grain sales area.
At length, production and sales balance zone cultivated land protection emphasizes benefits over compensation. With the acceleration of industrialization and urbanization, if the grain production and sales balance zone cannot be self-sufficient in grain production, it will increase regional development costs in the cross regional flow of grain. While maintaining basic grain production, it will also promote regional development work, which puts higher requirements on the effectiveness of local protection work in the grain production and sales balance zone. Taking Guizhou Province as an example, rocky desertification in the typical Karst Landform has made the ecological environment fragile, which has been an innegligible issue in development of Guizhou [
24]. The implementation of cultivated land protection policies by the Guizhou government is on par with the governance of the ecological environment. During the 13th Five Year Plan period, Guizhou added 564,200 mu of farmland and 309,700 mu of paddy fields, accumulating 16.77 million mu of high-standard farmland. The benefits of supplementing and coordinating farmland have significantly improved, and combined with its geographical environment and ecological advantages. These measures vigorously developed the rural industrial revolution, develop selenium and germanium rich characteristic farmland resources, implemented ecological protection benefits through a series of cultivated land protection policies, avoided economic and environmental costs [
25], and achieved the higher pursuit of cultivated land protection benefits.
However, in promoting the implementation of cultivated land protection policy, there has been a problem in the production and sales balance zone. The cultivated land protection is relatively focused on the establishment of policy implementation benefits and neglects, which meeting the compensation needs of farmers. Taking Guizhou Province as an example, the funding for cultivated land protection mainly comes from financial support. When providing economic compensation for cultivated land protection to farmers, it is difficult to achieve fairness in coordinating regional development due to the uneven development speed within the province. With the development of urbanization in Guizhou Province, the demand for cultivated land and industrial land is increasing within the province. However, the government’s financial investment is limited. There is a lack of multi-channel economic compensation and financing methods for cultivated land protection. The incentive effect of cultivated land protection is not obvious, which is a problem of prioritizing benefits overcompensation in the production and sales balance zone.
3. Based on Smith Policy Implementation
In the historical evolution of cultivated land protection policy, the evolution of policy core values has laid the foundation for successful experiences. However, in the specific process of policy implementation, it is still difficult to avoid practical implementation problems, which may lead to policy deviations. How to ensure that the issued cultivated land protection policy does not deviate from the actual policy environment and the empirical logic of policy evolution in the process of policy implementation has become an urgent problem to be solved. In the running path of Smith model, the policy difficulties focusing on farmer feedback makes the direction of future improvement and supplement of cultivated land protection policies more clear.
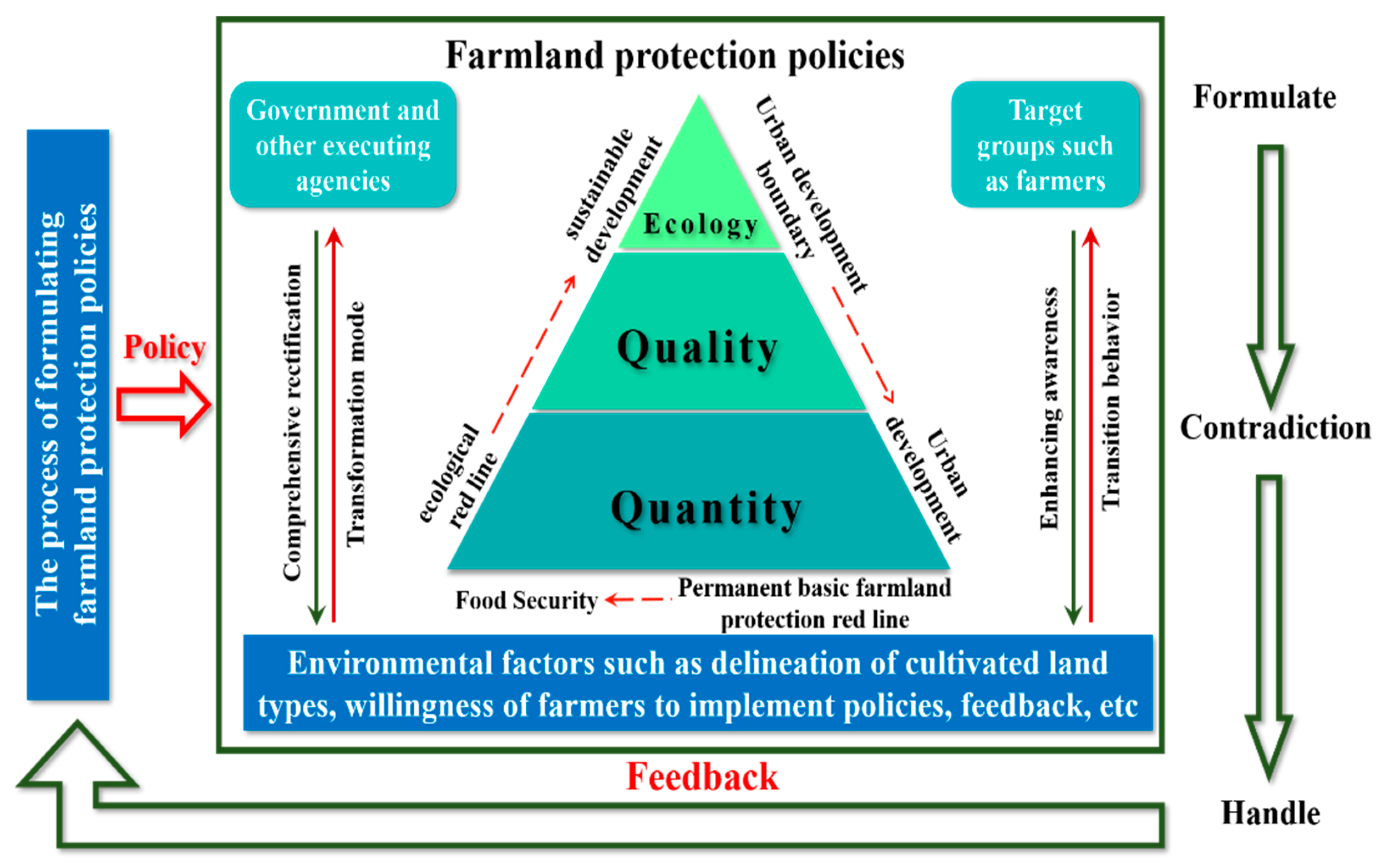
The formulation and implementation of policies are a dynamic process of interrelated policy cycles. In the direction of improving and supplementing cultivated land protection policies, it is necessary to combine the operational characteristics of the policies themselves to ensure the implementation of policies to achieve policy objectives. In the entire system of cultivated land protection policy operation, the government must find experience from the overall macro perspective and evolutionary logic, as well as for the policy target group to actively cooperate in the policy operation environment, timely feedback on the success of policy implementation and related issues, to make further policy adjustments. Among them, the government’s control of the policy intention of the target group is the top priority. It not only involves complex elements and diverse links but also considers the practical interests of the policy target group, which is directly related to whether the policy can proceed. However, in the current literature analysis of cultivated land protection policy, the consideration of the target group involved in the policy is far from sufficient for the government and the cultivated land protection policy itself. Based on the Smith policy execution model, we put farmers as the policy target group in the same important position as the cultivated land protection policy, the government implementation mechanism and environmental factors. The focus is on the farmers who are the main target group of cultivated land protection policies. From the perspective of the impact of farmland policies on farmers, Sort out the direction of improving cultivated land protection policy.
The most prominent feature of Smith policy implementation model is that it integrates the other three elements of policy implementation, namely the executing agency, target group, and environmental factors, into a unified system with idealized policies. These three elements play an equally important role in cultivated land protection policies, and the interactive factors between them are the key to smooth policy implementation. In the protection of cultivated land, the idealized policy of cultivated land protection is always carried out in the interaction reaction between the government, farmers, and environmental factors (
Figure 4).
3.1. The Limited Amount of Cultivated Land
The insufficient total per capita cultivated land area in China is currently the primary issue in the protection of cultivated land. China, which ranks fourth in the world in terms of total population and cultivated land area, firmly adheres to the red line of 1.8 billion mu of cultivated land protection policy in terms of per capita cultivated land area, which is unshakable. From the historical experience of the basic stage of cultivated land protection policies, the faster the economy develops, the more it is necessary to lay a solid foundation for protecting the total area of farmland. At present, the total amount of reserve cultivated land resources in China is about 80.2915 million mu, but most of them are in the central and western edge areas, and scattered cultivated land accounts for the main component, with only 35.3% of contiguous cultivated land, and only concentrated in a few major grain-producing areas such as Xinjiang, Jilin, and Heilongjiang [
26].
Based on the Smith policy implementation model, farmers are unclear about the classification of land use types, which is an urgent problem to be solved in the context of insufficient total cultivated land. For farmers, there is a certain difficulty in understanding the boundary between "general farmland", "permanent basic farmland", and then "high-standard farmland" [
27]. There are practical difficulties in clearly dividing the utilization and classification of farmland, which is based on the cultural level of farmers themselves, and there is a certain degree of universality difficulty. Based on the ambiguity left by the government in dividing the types of cultivated land, there is a problem of insufficient communication with farmers. For example, in village organizational life, village chiefs do not strictly distinguish the specific types of use of cultivated land and do not timely promote it in the communication with farmers, resulting in natural policy cognitive biases among farmers.
3.2. Low Quality of Cultivated Land
The low quality of cultivated land in our country is currently the main problem in the implementation of cultivated land protection work. The essence of farmland protection lies in ensuring farmland production capacity and improving farmland quality. According to the current national survey data on the quality level of cultivated land in China, the quality of cultivated land in the main grain producing areas weakens with the increase of development efforts. The black soil layer in the black soil area of Northeast China is gradually thinning, and insufficient organic fertilizer input leads to soil degradation, which cannot be solved. The cultivated layer in the tidal soil areas of North China and the Huanghuai Plain is also gradually thinning, with a great risk of soil fertility decline, and there is no technical reduction in soil salinization. Heavy metal pollution is serious in some soils of the Middle and Lower Yangtze Valley Plain. The poor water retention and lack of technical solutions to soil salinization and desertification in the northwest arid region have led to a lower overall quality of cultivated land, which is a background factor that must be taken seriously in carrying out cultivated land protection.
Based on the Smith policy implementation model, unscientific farming by farmers during the cultivation process is an urgent problem to be solved in the context of low farmland quality. For farmers, the quality of cultivated land is low and the harvest is poor. To ensure the family's grain output, there is inevitably a tendency to strengthen the intensity of cultivation. Therefore, due to the lack of scientific and urgent cultivation methods by farmers, the process of protecting cultivated land tends to "push the seedlings too far". In the process of cultivated land protection, if farmers cannot use scientific farming concepts and equipment for grain crop production, it will further increase the problem of low farmland quality in China [
28]. This is not only based on the labor capacity and agricultural capital of farmers themselves but also on the government's support for farmers to purchase farming equipment and the implementation of scientific farming technology guidance and training in the process of implementing cultivated land protection policies [
29].
3.3. The Implementation of the Trinity Is Vague
In the process of achieving sustainable utilization of cultivated land in China, achieving the integration of quantity-quality-ecology is currently a key issue in the protection of cultivated land. At present, in the division of "three zones and three lines" in China, cultivated land is delineated by three departments respectively with urban space and ecological space, and spatial overlap is inevitable. Strictly defining the permanent basic farmland protection red line is not only for protecting cultivated land but also for protecting the basic benefits of farmers. However, in the implementation of ecological compensation mechanisms, some interests of farmers may be limited. The implementation of the system of cultivating and recuperating farmland requires farmers to obtain direct benefits from government subsidies. How to clarify the standards and boundaries in implementation has become a thorny problem that must be solved [
30].
Based on the Smith policy implementation model, the interests of farmers are limited in the mechanism of cultivated land protection and ecological compensation, which is an urgent problem to be solved in the context of implementing the "quantity-quality-ecology" trinity of cultivated land protection. For farmers, the "three zones and three lines" lack clear boundary delineation in government orders, and their lack of timely and sensitive grasp of "red line awareness" makes their interests the main driving force to constrain their behavior. If the interests of farmers cannot be guaranteed to meet their expectations for farmland labor, achieving the implementation of the "quantity-quality-ecology" trinity of cultivated land protection is always flowing water without a source. In the process of protecting farmland, if the interests of farmers cannot be guaranteed to be unrestricted in the mechanism of ecological restoration compensation, the implementation of the three-in-one system will become even more distant [
31]. This is not only based on the value orientation of farmers themselves but also on the on-site research of the government on the ecological civilization construction of characteristic industries in towns and villages during the process of issuing cultivated land protection policies, as well as the practical understanding of the policy orientation of farmers.
4. Discussion
In the implementation of cultivated land protection policies, how to grasp the policy execution intentions of target groups such as farmers, further optimize cultivated land protection policies through farmer supervision feedback, and encourage more social participation to support the systematic engineering of cultivated land protection, is a feasible direction for the improvement and supplementation of future cultivated land protection policies. Based on the Smith policy execution model, this paper divides the structure of cultivated land protection policies and proposes directions for improving and supplementing future cultivated land protection policies.
4.1. Strictly Classification of Cultivated Land Types
Farmers are the primary target group of cultivated land protection policy. For farmers, the understanding degree of cultivated land protection directly affects whether the implementation of cultivated land protection policy can be sustained for a long time. Their dissatisfaction with farmland conservation policies can directly address key issues. Based on the overall low education level of Chinese farmers, in the process of policy implementation, the form and standard of cultivated land division are scientifically sorted out under the premise of multifunctional farmland [
32]. In the strict division of cultivated land types, strengthening the farmers' understanding of the types of cultivated land utilization can greatly strengthen the recognition degree of farmers in the protection of cultivated land [
33].
At present, the classification of farmland types in cultivated land protection policies is based on farmland quality, mainly divided into general farmland, permanent basic farmland, and high-standard farmland [
34]. Under the red line standard of three zones and three lines, the classification of farmland types should be more strict. Based on the three control lines of urban development boundary, permanent basic farmland protection red line, and ecological protection red line, it is a practical problem to clearly define the classification of permanent basic farmland [
35]. How to transition permanent basic farmland to high-standard farmland construction is a systematic and long-term project in the current context of accelerating urbanization and deepening the concept of ecological civilization construction. The cultivated land designated as permanent basic farmland needs to strengthen the awareness of farmers not to occupy or idle it through personal actions. In the form of a "field chief system", local administrative officials should be held responsible for the designated farmland, and farmers should have a clear sense of boundaries for their land. Enable farmers to have greater autonomy under their annual farming arrangements, thereby enhancing their recognition of cultivated land protection. The education level of farmers varies, but based on their life experience in cultivating farmland, their utilization and protection of their land are still evident. It is necessary to issue cultivated land protection policies at the level of farmers' understanding to provide them with a model to exercise.
4.2. Stimulate the Enthusiasm of Farmers
The enthusiasm of farmers in the construction of farmland is directly related to the efficiency of cultivation and plays a key role in ensuring the sustainable development of farmland while ensuring the production capacity of agricultural products. For farmers, improving the scientific cultivation methods, techniques, and equipment can also drive the greater production capacity of farmland and achieve a higher crop economy. This is a policy measure that is beneficial and harmless. Government investment in the construction of scientific cultivation has greatly increased the enthusiasm of farmers for building farmland.
In the high requirements of constructing high-standard farmland, protective tillage technology is the equipment support to ensure high yield in standard farmland [
36]. With the development of new urbanization, the serious loss of rural working population with cultivated land and good farming ability has become the mainstream form. Only by vigorously developing conservation tillage technology and improving the scientific conservation tillage, can farmers have great enthusiasm for farmland construction from the technical level. Taking farmers as the popularization and service object of conservation tillage technology and equipment, it requires the government to issue special policy documents on improving the science of conservation tillage. The government needs to implement the scientific improvement of tillage into the research and development tasks, and implement conservation tillage methods according to local conditions. At the same time, preferential measures and subsidy funds are guided for conservation tillage equipment, so that farmers can apply conservation tillage equipment in actual farming. Different cultivation methods have varying degrees of impact on the soil texture of cultivated land [
37], and scientific conservation tillage is more conducive to the sustainable development of cultivated land [
38].
4.3. Protect the Interests of All Parties
For the sustainable development of cultivated land in China, policies such as ecological fallow are usually adopted [
39]. Therefore, whether the ecological compensation mechanism can make subsidies attractive enough to farmers is the root cause of determining whether fallow can be carried out [
40]. Based on pursuing ecological civilization construction and integrating sustainable development of various resources, farmers, as the main policy target group for cultivated land protection [
41], are closely related to the utilization of farmland and their own cost of living guarantee. The authors believe that in the absence of achieving the ideal compensation benefits for farmers, excessive cultivation of cultivated land is a better choice for farmers or developers who contract agricultural product projects. Therefore, how to make the ecological compensation mechanism satisfactory to farmers, developers, and even the government requires a joint decision based on the interests and opinions of multiple stakeholders.
In the continuous promotion of ecological civilization construction, policies such as returning farmland to forests focus on long-term development benefits. However, based on the assumption of rational economic man, farmers mainly pay attention to the immediate economic interests in their actual work. Therefore, it is difficult for farmers to play their subjective initiative in the series of policies related to cultivated land protection and ecological protection. The scope of the participants of cultivated land protection is related to the general premise of ecology, but in fact, it is related to a wide range of groups. As a target group with economic interests related to the protection of cultivated land, the related economic compensation should be based on the ideal expectations of farmers. The government guarantees the economic interests of farmers through simple and direct subsidies, so that the cultivated land protection policy is in operation and does not lag behind in ecological problems.
5. Conclusions
The protection of cultivated land is a systematic project that benefits the present and the future. Under the concept of ecological civilization construction, the sustainable development of cultivated land is equally important as the sustainable development of other ecological resources. In the historical evolution of Chinese cultivated land protection policy, the evolution of successful experiences is mainly based on the new era transition from 1949 to 2012. Firstly, from 1949 to 2003, the basic stage was to pursue the control of the quantity of farmland, which was the foundation of cultivated land protection. In the protection stage from 2004 to 2011, maintaining the quality of cultivated land was the guarantee of cultivated land protection. Furthermore, after 2012, the integration of the quantity-quality-ecology of cultivated land is the key to protecting cultivated land. From the establishment of the People's Republic of China to the convening of the 18th National Congress, there was a process of shifting the focus of cultivated land protection, which was also in line with the mature development of the economy, environment, and society. It is a continuous process. At the same time, comparing the implementation effect of Chinese cultivated land protection policies, each province is divided into regions based on grain transportation and sales. The development trend of local cultivated land protection policies is mainly as follows: the protection of farmland in major grain producing areas emphasizes quantity over quality; the protection of cultivated land in the main grain sales areas emphasizes supervision over governance; the protection of cultivated land in the production and sales balance zone emphasizes benefits overcompensation. The specific implementation of cultivated land protection policies always focuses on the process of policy implementation. We use the Smith policy implementation model as the main model, and through induction, deduction, and comprehensive analysis, sort out the multi-source obstacles in the practice of cultivated land protection policies based on historical experience of cultivated land protection policies. In the context of insufficient total farmland, the classification of farmer utilization is unclear. Under the background of low farmland quality, farmers cultivate unscientific crops. Starting from the three aspects of limited interests of farmers in the context of the implementation of the Three in One approach, combined with the Smith model, corresponding directions for improving future cultivated land protection policies are proposed.
Under the tide of socialism with Chinese characteristics entering a new era, the policy of protecting cultivated land is based on its historical evolution. In the division of the "three zones and three lines", different requirements have been put forward for the construction of general cultivated land, permanent basic farmland, and high-standard farmland. The overall situation is still to supplement general cultivated land with permanent basic farmland, allowing permanent basic farmland to transition to high-standard farmland. In terms of cultivation methods and techniques with the scientific improvement of farming equipment, focus on the immediate interests of farmers is more conducive to cultivated land protection policies. Exploring the feasibility of cultivated land protection policies in the policy environment, starting from Smith policy implementation model, it is particularly important to pay attention to farmers as the target group of policies. In the specific implementation of cultivated land protection policies, directly utilizing feedback from farmers as stakeholders will also contribute to the maturity and improvement of cultivated land protection policies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.C. and N.Y.; writing original draft preparation, N.Y.; writing-reviewing and editing, B.C. and N.Y.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number: 41807366]; and the Guizhou Provincial Key Technology R&D Program (Grant No. [2021]456).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the author.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number: 41807366]; and the Guizhou Provincial Key Technology R&D Program (Grant No. [2021]456).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WANG Jun, LI Ping, ZHAN Yunqiu, et al.,2019. Study on the protection and improvement of cultivated land quality in China. China population,resources and environment. 29(4):87-93.
- Yang H, Shen X, Lai L, et al.,2017. Spatio-temporal variations of health costs caused by chemical fertilizer utilization in China from 1990 to 2012. Sustainability. 9(9):1505. [CrossRef]
- KONG Xiangbin, CHEN Wenguang, WEN Liangyou.,2022. Building the Foundation of grain Security for Great Countries through Three Security Measures of Cultivated Land Resources. Agricultural Economy and Management. (03):1-12.
- ZHANG Zhengfeng.,2019. Sustainable Land Use Goals, Challenges, and Response Strategies for SDGs. China Land Science. 33(10):48-55.
- CHEN Meiqiu, WU Yuehong, LIU Taoju.,2012. Research and prospects on farmland protection in China based on farmer behavior. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University (Social Science Edition). 12(3):66-72.
- LIU Mengpao, ZHANG Anlu.,2021. The Historical Logic and Optimization Path of the Changes in Chinese Farmland Use Policy since the Founding of the Communist Party of China in the Century. China Land Science. 35(12):19-28.
- NIU Shandong, FANG Bin.,2019. 70 Years of Chinese Farmland Protection System: Historical Evolution, Realistic Exploration, and Path Optimization. China Land Scienc. 33(10):1-12.
- WANG Wenxu, CAO Yingui, SU Ruiqing, et al.,2020. Research on Chinese Farmland Protection Policy: Based on Background, Effects, and Future Trends. China Agricultural Resources and Regionalization. 41(10):40-51.
- LU Yanxia, WANG Boyuan.,2022. Evolution and Logic of Farmland Protection System and Policy. China Land. (02):4-8.
- YU Fawen, DAI Minghui, LIN Shan.,2022. Farmland protection based on the bottom line thinking of grain security: current situation, difficulties, and countermeasures. Economic Review. (12):9-16.
- LIU Kui, WANG Jian.,2021. Research on the Historical Evolution and Optimization Transformation of Chinese Farmland Protection Strategy. Agricultural Economy. (07):82-84.
- Gesang B.,2022. Protecting our future: What contribution can I make? PLOS Sustainability and Transformation. 1(6): e0000014.
- QU Futian, MA Xianlei, GUO Guancheng.,2021. From Political Order, Economic Development to National Governance: Institutional Logic and Basic Experience of Centennial Land Policy. Management World. 37(12):1-15.
- NIU Shandong, FANG Bin.,2019. 70 Years of Chinese Farmland Protection System: Historical Evolution, Realistic Exploration, and Path Optimization. China Land Science. 33(10):1-12.
- WANG Wenxu, CAO Yingui, SU Ruiqing, et al.,2020. The evolution process of Chinese cultivated land protection policy based on policy quantification. China Land Science. 34 (07):69-78.
- WEI Houkai.,2014. Polarization Tendency and Scale Pattern Reconstruction in Chinese Urbanization Process. China Industrial Economy. (03):18-30.
- CHEN Guishen, ZHANG Rena, CHENG Feng, et al.,2009. A study on cultivated land protection policies that prioritize both quantity and quality management. China Land Science. 23(12):39-43.
- QI Xinxian, ZHANG Zhihong, HUANG Xianjin.,2018. Contradictions and innovative responses to cultivated land protection in the new era. China Land Science. 32(08):9-15.
- LIANG Xiaoling, WANG Lu, LI Cheng, et al.,2021. A study on the rapid optimization layout of permanent basic farmland based on the integration of quantity, quality, and ecology. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment. 38(06):946-956.
- FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, et al.,2022. The State of Grain Security and Nutrition in the World 2022: Repurposing Grain and Agricultural Policies to Make Healthy Diets more Affordable. Rome: FAO. 2022:14.
- HAN Yang.,2022. Evolution, Vision Goals, and Implementation Paths of Chinese Cultivated Land Protection and Utilization Policy. Management World. 38(11):121-131.
- JIN Xin.,2020. Research on the Implementation Issues and Countermeasures of Cultivated Land Protection Policies in Heilongjiang Province. Harbin: Harbin University of Commerce.
- DI Yanshun, SUN Jiali.,2020. Problems and Countermeasures for the Protection of Black Soil Farmland in Heilongjiang Province. Modern Agriculture. (10):53-56.
- REN Hongyu, ZHAO Yuluan, GE Yujuan.,2020. Spatial correlation between farmland fragmentation and geomorphic types in karst mountainous areas: A case study of Xiuwen County, Guizhou. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Science Edition). 38 (04):1-9.
- LI D M, YANG Y Y, DU G M, et al.,2021. Understanding the contradiction between rural poverty and rich cultivated land resources:a case study of Heilongjiang Province in Northeast China. Land Use Policy. 108.
- WANG Yue, ZHU Fanglin, ZHONG Yu.,2023. The Evolution, Logic, and Prospects of the "Grain Storage in the Land" Strategy. Agricultural Economics and Management. (01):33-44.
- ZHENG Qingyu, SHANG Xudong, WANG Yu.,2023. Why is cultivated land protection difficult: goals, practices, and countermeasures-observations from the main grain producing areas in the western region. Economist. (04):98-107.
- XU Zijin, ZHAO Cuiwei, LUO Mingfei.,2013. Research on the Impact of Farmer Input Behavior on Farmland Quality: A Case Study of Qianjin and Fana Village in Guanling, Guizhou Province. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Science Edition). 31(04):1-3.
- CHEN Wenguang, KONG Xiangbin.,2023. Exploration of Chinese Agricultural Land Protection Science and Technology Innovation Strategy. Soil Bulletin. 54(04):947-954.
- SHI Fei, YANG Qingyuan, WANG Cheng, et al.,2021. Farmland fallow management model in ecologically degraded areas from the perspective of actor networks: A case study of Songtao County, Guizhou Province. Journal of Natural Resources 36(11):2892-2912.
- OU Minghao, WANG Kunpeng, GUO Jie.,2019. Research progress on ecological compensation mechanisms for cultivated land protection. Agricultural Modernization Research. 40(03):357-365.
- JIANG G H, WANG M Z, QU Y B, et al.,2020. Towards cultivated land multifunction assessment in China: applying the"influencing factors-functions-products-demands" integrated framework. Land Use Policy. 99.
- Boufous S, Hudson D, Carpio C.,2023 Farmers’ willingness to adopt sustainable agricultural practices: A meta-analysis. PLOS Sustainability and Transformation. 2(1): e0000037. [CrossRef]
- CHEN Wenguang, ZHANG Qingpu, KONG Xiangbin, et al.,2021. Optimization Rules and Empirical Study of Provincial Permanent Basic Farmland Layout Based on "Three Lines" Coordination. Journal of Agricultural Engineering. 37(15):248-257.
- LIANG Xiaoling, WANG Lu, LI Cheng, et al.,2021. A study on the rapid optimization layout of permanent basic farmland based on the integration of quantity, quality, and ecology. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment. 38(06):946-956.
- CUI Zhaoda, YU Zhigang, ZHANG Peige.,2021. Does the adoption of conservation tillage technology help improve the efficiency of grain production technology-Taking Corn as an Example. Journal of Agriculture and Forestry Economics and Management. 20(04):458-467.
- XU Yingying, SUN Shiming, JIN Xiaoyan, et al.,2022. Effects of Different Cultivation Measures on Soil Texture and Corn Yield. Corn Science. 30(04):97-106.
- PENG Wenlong, LV Xiao, XIN Zongfei, et al.,2020. International experience in sustainable intensive development and its implications for the protection of arable land in China. China Land Science. 34(04):18-25.
- LV Tiangui, XIE Hualin, LI Hongyi, et al.,2019. Research on the Deviation Risk, Formation Path, and Prevention System of the Implementation of Fallow Farming Policy. China Land Science. 33(04):51-58.
- ZHONG Yuan, ZHANG Xiaoning.,2018. Problems and Countermeasures in the Policy of Fallow Farming. Agricultural Economic Issues. (09):76-84.
- LIU Weibo, YANG Shengsu, LI Zhong, et al.,2021. Satisfaction and influencing factors of farmers in pilot areas for heavy metal pollution control with fallow land policies. Economic Geography. 41(01):158-164.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).