1. Introduction
The subjective perception of “time flow” is one of the most important cognitive capabilities in everyday life. For this subjectivity, objective time meters such as sundials, hourglasses, clocks, calendars, etc. are necessary. French psychologist Paul Fraisse (1911-1996) has suggested that human processing of time has three functionally distinct components: periods shorter than 0.1 s are perceived as “instantaneous”; periods between 0.1 s and approximately 5 s delimit the “perceived present” or “psychological present”. Periods longer than 5 s are thought to involve long-term memory [
1]. Kinsbourne and Hicks [
2] defined this period as the “extended present” and estimated its duration to be longer than 30 s.
The data available in the literature seem to indicate that two different modalities are used in the evaluation of time flow. In a first type, which can be defined “mental” or “verbal” counting, the subject is conscious of the time flow and tries to measure it by mentally counting. It has been observed that, during this type of “mental” timing, which undoubtedly involves working memory [
3], there is an involvement of motor structures such as the anterior lobe of the cerebellum of both sides, the supplementary motor area, and the left prefrontal cortex [
4]. However, when the subject's attention is polarized on another target and the mental counting is no longer possible, the subject estimates the time flow unconsciously, probably by using the same processes involved in the reversal learning, i.e. the adaptation of behavior according to changes in stimulus–reward conditions [
5] and/or delay discounting, i.e. how long a person is willing to wait for a reward [
6]. Therefore, motor and non–motor aspects seem to be implicated in temporal processing.
Ever since the pioneering work of Harold Gulliksen [
7] an alteration in the perception of time flow after physical activity has been observed [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. However, all these studies have only considered the "mental" mode for time flow assessment. To better understand the role of physical activity in these two different ways of estimating the flow of time, we compared the capability of estimating time intervals from 1s to 5 s, i.e. in the range of “present” [
1], in subjects performing an exhaustive exercise, by using tasks requiring mental count, presumably related with a motor activation, and tasks that did not allow it. Moreover, with the present study we wanted to verify if there is a correlation between the ability to estimate the time flow and blood lactate levels. In fact, a relationship between blood lactate levels and cognitive domains has been highlighted [
13].
2. Materials and Methods
Participants. Subjects who agreed to participate in the present study were 24 healthy adults, aging between 19 and 25 years. Out of these, 12 were women, aging between 19 and 24 years (mean age 22.0 years ± 1.86 SD), with a mean height of 1,66 m ( ± 0.04 SD) and a mean weight of 58.4 kg ( ± 3.73 SD). All the women who participated in the study had a regular menstrual cycle. The remaining 12 volunteers were men aging between 19 and 25 years (mean age 22.4 years ± 1.72 SD), with a mean height of 1,73 cm ( ± 0.03 SD) and a mean weight of 71.8 kg ( ± 5.81 SD). All participants practiced amateur sports for at least one year and had medical authorization to practice non-competitive sport activities. The T-test showed no statistically significant differences in age, height and weight between women and men.
The study was approved by the Ethical committee of the Kore University of Enna (number 538, 11 January 2024).
All participants were informed about the trials of the study and the anonymity of their answers before providing their written consent to participate, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Experimental Design. The tests were executed between 9 am and 1 pm, with participants who had a breakfast before 8 am [
14] and had a regular night's sleep prior to the testing sessions. Each subject had to participate in 2 different experimental sessions:
Session 1: each subject performed the task for time estimation (mental or non-mental, randomly selected) at rest and blood lactate was measured (pre); each subject executed the acute exhaustive exercise and, at the end, executed once more the task for time estimation; blood lactate was measured at the end of the exhaustive exercise, as well as after 5 min and 15 min.
Session 2 the day after session 1: each subject performed the second task for time estimation (mental or non-mental, randomly selected) at rest and blood lactate was measured (pre); each subject executed the acute exhaustive exercise and, at the end, executed once more the task for time estimation; blood lactate was measured at the end of the exhaustive exercise, as well as after 5 min and 15 min.
The overall duration of both tests did not exceed 3 minutes.
Exercise. The participants performed a maximal incremental cycloergometer test on a cycloergometer (Monark, Sweden), at a pedaling rate of 60 rpm, while electrocardiogram was monitored. Each subject started with unloaded cycling during 3 min, and the load was increased by 30 W every 3 min until volitional exhaustion or the required pedaling frequency of 60 rpm could not be maintained [
16].
Blood Lactate. Blood lactate was measured before as well as at the end and 15 min after the conclusion of the exercise, using a “Lactate Pro 2” portable lactate analyzer (Arkray Inc, Japan), since this automated lactate analyzer has a good reliability [
17].
Experiments. We tested the ability to make temporal discriminations in the range of the psychological “present”, i. e. around 1 to 5 seconds [
1]. Time estimation was assessed using two different experimental conditions, exploring either quantitative (mental count) or qualitative (comparison of different frames) estimation methods [
18].
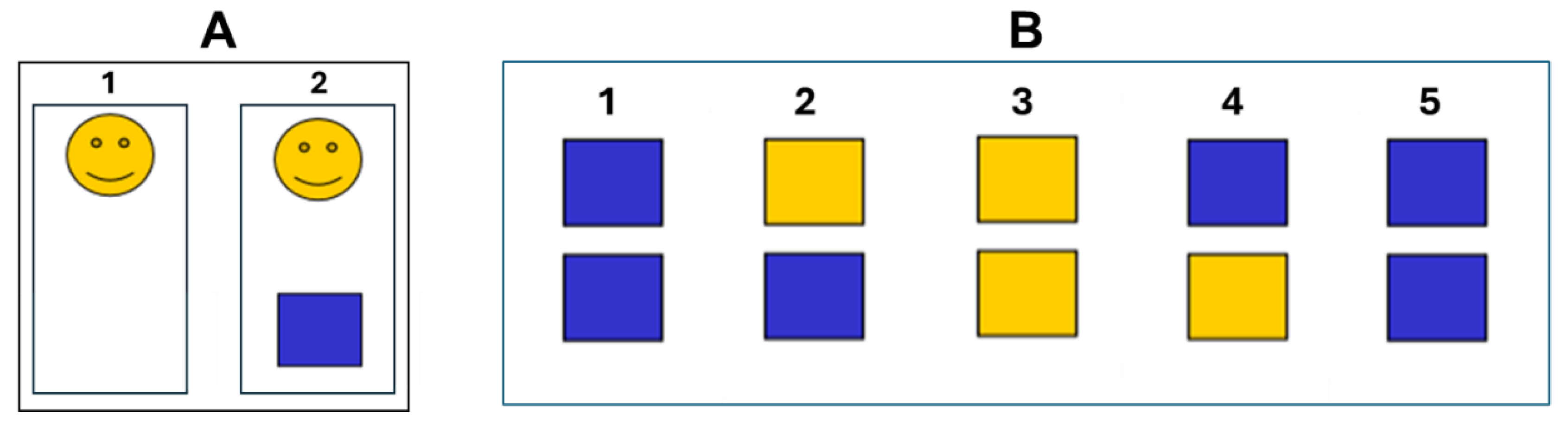
Figure 1 outline the two experiments.
Experiment 1. In this condition (
Figure 1A), subjects view a computer screen where a smiling yellow face firstly appeared and, after an interval randomly ranging from 1 to 5 s, a blue square. The subject was instructed to mentally count for the estimation of the interval between the two visual stimuli. The task was repeated 10 times for each session. The estimation of time was calculated as the percent variation with the respect to the considered interval.
Experiment 2. In this condition (
Figure 1B), we adapted the task described by Riesen and Schneider [
19]. The subjects saw on the computer screen two vertically arranged blue squares (1). Following examiner command, one of the squares turned yellow (2). After a variable time also the second square turned yellow (3). Then the first one turned blue again (4), then the second (5). Subjects were asked to indicate verbally which square had been yellow for a longer period (the upper or the lower). Within a test series the interval duration was constantly 1 or 2 s. However, the duration of the yellow phase of the two squares was randomly arranged to obtain differences in duration of 15%, 20%, 25%, 33% or 50%, with 15% indicating the most difficult condition (minimal difference between the two intervals) and 50% being the easiest condition (maximal difference between the two intervals). The number of trials with the first or second interval being longer was equal (5 times first, 5 times second square longer for each discriminative factor) because it was considered possible that the order might influence the subjects’ responses. Whether the upper or lower square was longer was fully randomized. In this experiment the number of correct answers was considered for the estimation of time.
Statistical analysis. Data was collected and averaged, and then compared with the paired t test (2-tailed) or 1-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA; Kruskal-Wallis test), followed by Dunn's Multiple Comparison Test. Correlations were analyzed as Simple Linear Regressions. Significance was set at p < 0.05. All analyses were performed by using GraphPad Prism version 9.5.1 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
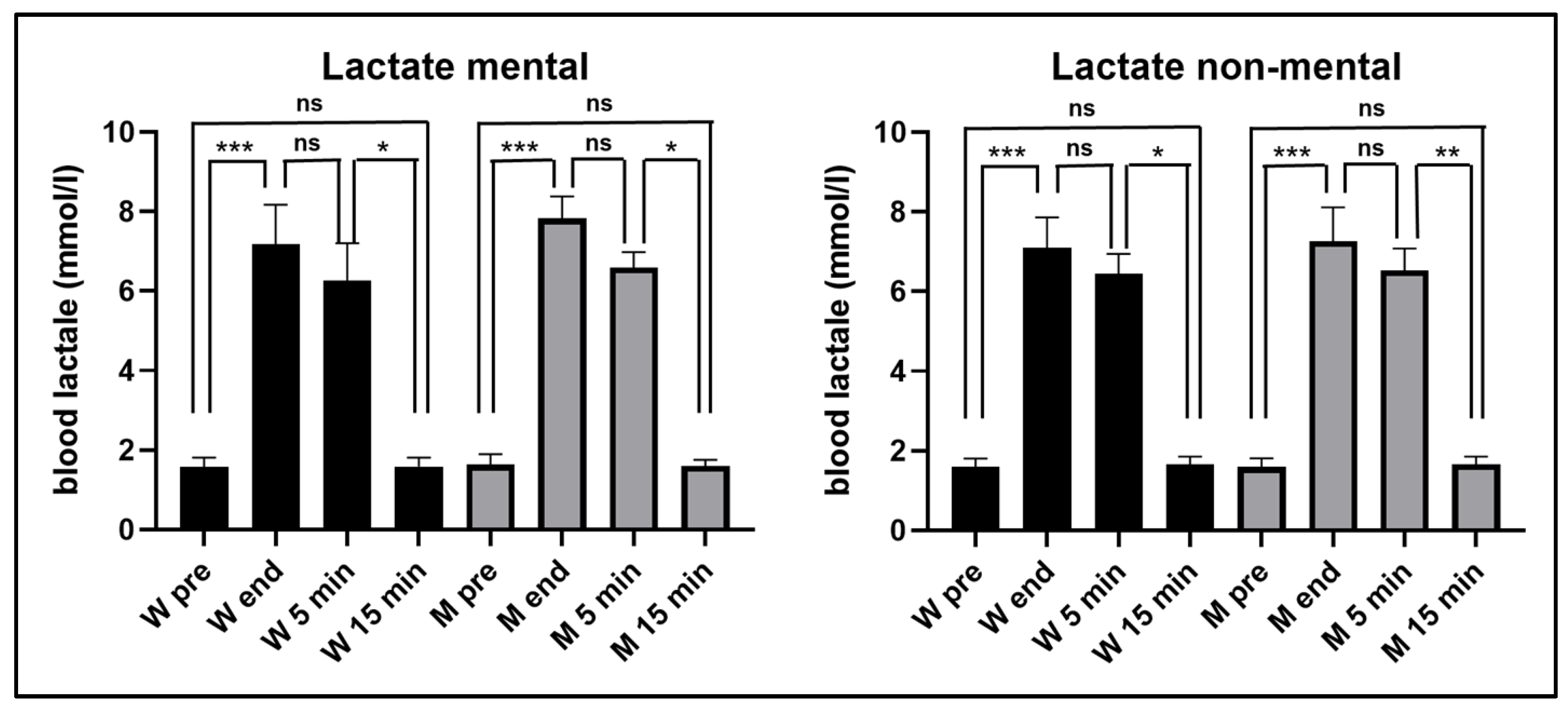
As can be seen in
Figure 2, in both experimental conditions the blood lactate increased significantly at the end of the exhaustive exercise, remained significantly higher 5 min after the end of the exercise and returned to the pre-exercise values 15 min after its end, without significant differences between women and men.
In the first experiment, in women blood lactate levels increased from 1.6 mmol/ml (±0.25 SD) before the exercise, to 7.2 mmol/l (±1.00 SD) at its end, and in men from (1.6 mmol/l ± 0.26 SD) before the exercise to 7.8 mmol/l (±0.56 SD) at its end. In the second experiment, in women blood lactate levels increased from 1.6 mmol/ml (±0.20 SD) before the exercise, to 7.1 mmol/l (±0.77 SD) at its end, and in men from (1.6 mmol/l ± 0.22 SD) before the exercise to 7.3 mmol/l (±0.85 SD) at its end. It should be noted that in both women and men, blood lactate levels showed no significant differences between those measured at the end of exercise and those measured 5 min after its conclusion.
3.1. Experiment 1
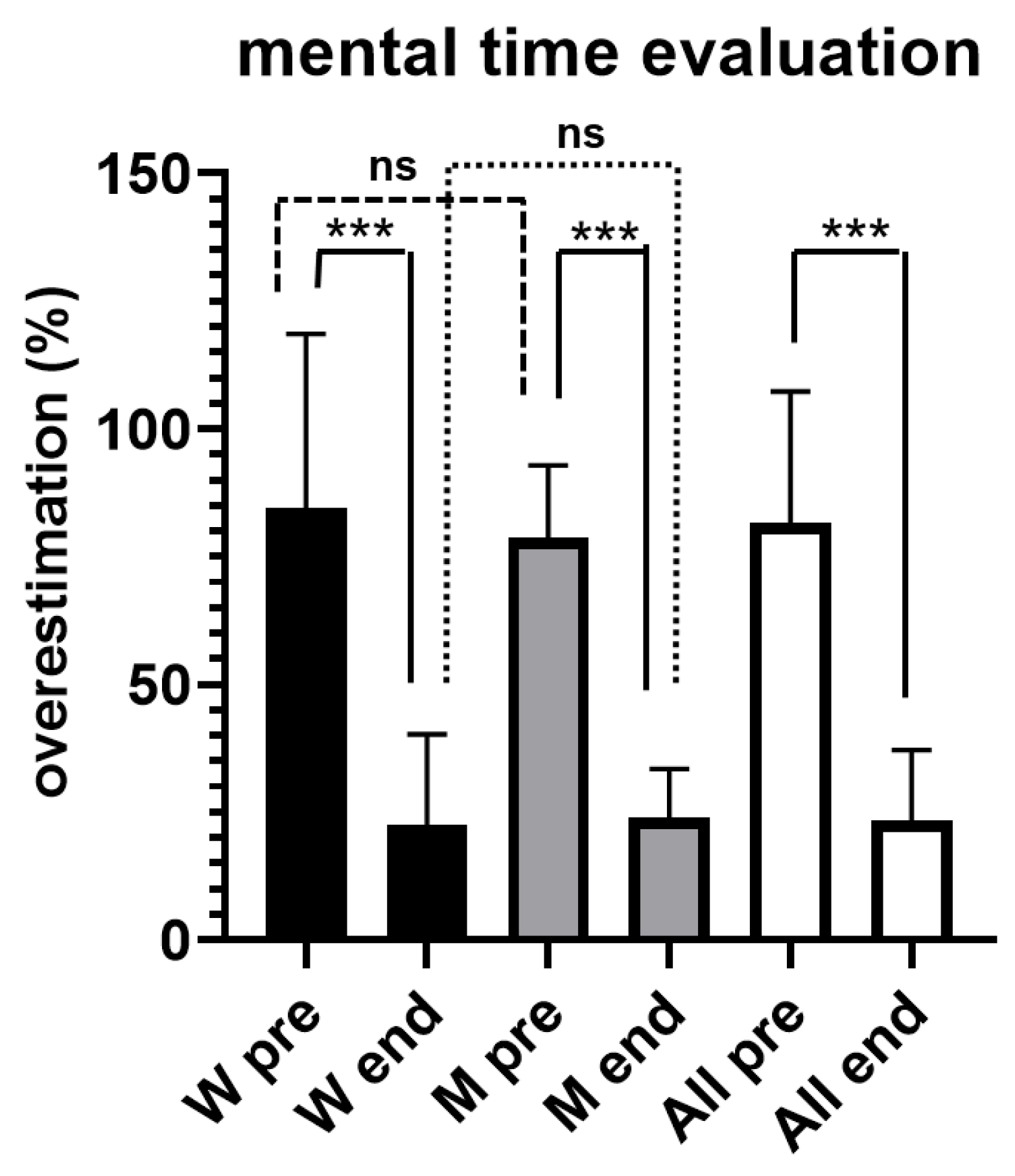
Figure 3 illustrates results obtained from both women and men during the evaluation of short time intervals, by using mental counting.
All participants overestimated the time durations, without significant differences between women and men; for the whole sample the overestimation was of + 81.6% ± 25.69 SD before the exercise (pre). However, at the conclusion of the exercise (end) the overestimation was significantly lower (p < 0.001), being equal to +23.3% ± 13.82 SD.
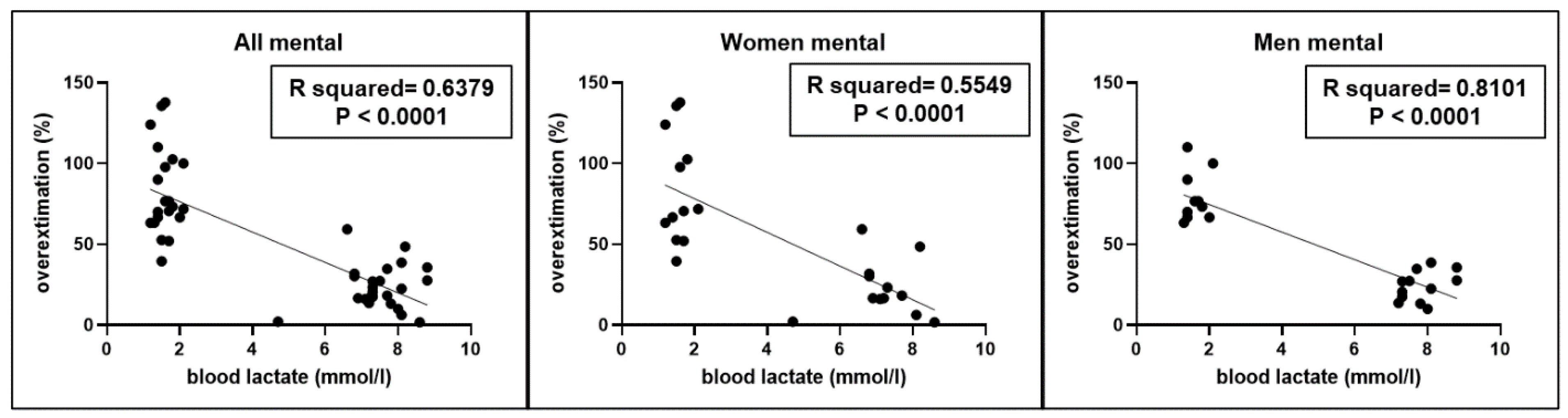
A significant correlation (r2=0.6379, p < 0.0001) was found between the overestimation of short intervals performed by participants and blood lactate levels (
Figure 4), without gender differences.
3.2. Experiment 2
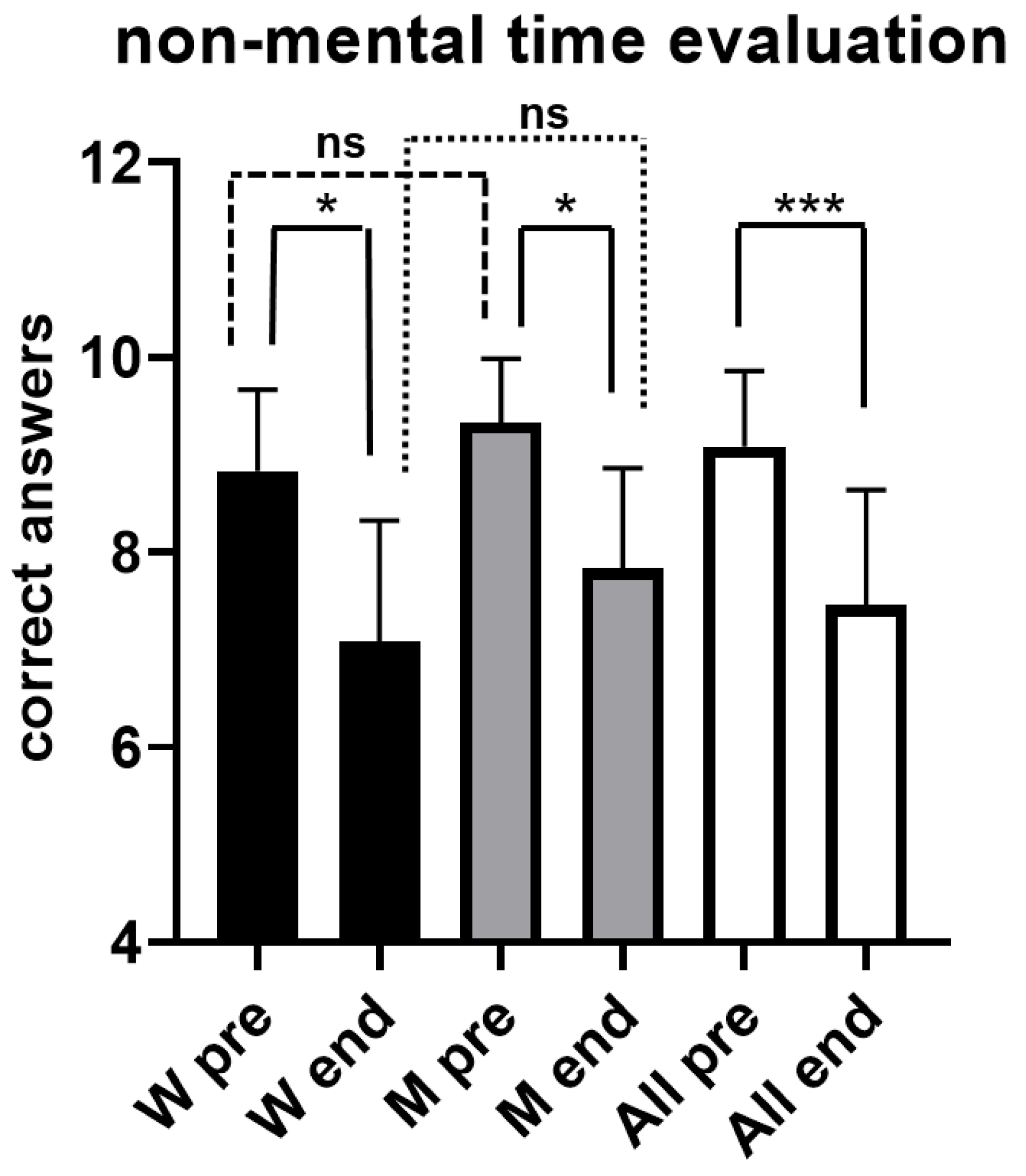
Figure 5 illustrates results obtained from both women and men during the evaluation of short time intervals, without the possibility to use mental counting. As can be seen, for the whole sample the number of correct answers decreased significantly (p < 0.001) after the exhaustive exercise, going from 9.1 ± 0.78 SD before the exhaustive exercise (pre) to 7.5 ± 1.18 SD at the conclusion (end). A statistically significant decrease (p < 0.05) was also observed in men, the number of correct answers going from 9.3 ± 0.65 SD before the exhaustive exercise (pre) to 7.8 ± 1.03 SD at the conclusion (end), and in women (p < 0.05), with the number of correct answers going from 8.8 ± 0.83 SD before the exhaustive exercise (pre) to 7.1 ± 1.24 SD at the conclusion (end).
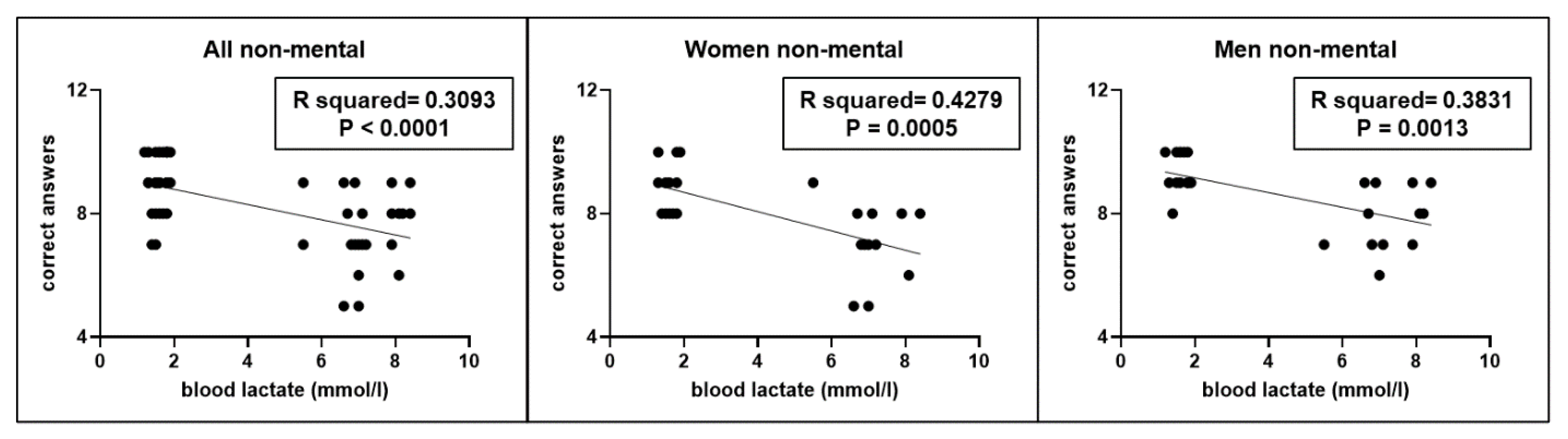
Moreover, even in this second experiment, a significant correlation (r2=0.3093, p < 0.0001) was found between the correct answers performed by participants and blood lactate levels (
Figure 6), without gender differences.
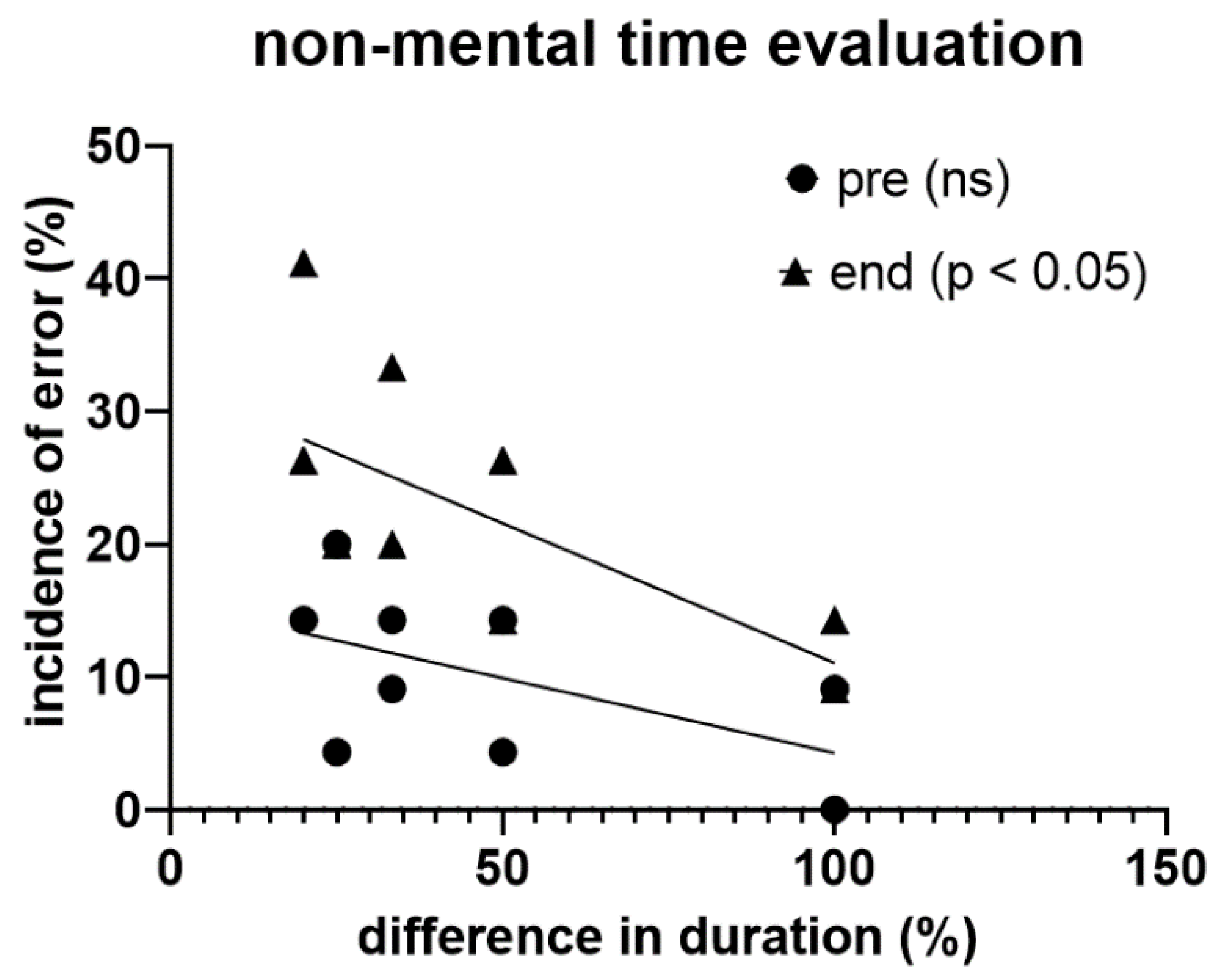
In this experiment, participants tended to show a higher probability of getting the temporal assessment wrong the more the difference in the duration of the two visual stimuli decreased, a trend that became statistically significant (p < 0.05) at the end of the exhaustive exercise (
Figure 7).
4. Discussion
In the evaluation of short intervals (between 1s and 5 s), individuals who have just performed an exhaustive exercise exhibited significant changes in their perception of time. These changes were detectable both when the participant estimates the time interval by counting mentally (verbal or quantitative estimation) and when he evaluates the time interval in a condition where this was not possible (non-verbal or qualitative estimation). In the mental counting, the subject is conscious of the time flow and tries to measure it by mentally counting. However, when the subject's attention is polarized on another target and the mental counting is no longer possible, the subject estimates the time flow unconsciously, probably by using the same processes involved in the reversal learning, i.e. the adaptation of behavior according to changes in stimulus–reward conditions [
5].
It is worth noting that time estimation by mental count is a procedure of which the subject has awareness, i.e. could be considered an explicit cognitive process, whereas time estimation without mental count could represent an implicit process. Since there is evidence for dissociation between the neural substrates that support explicit and implicit cognitive processes [
20], it can be further suggested that the two “timers” are in different part of the brain.
In the present study, where time intervals between 1 and 5 s were studied, a significant overestimation of time (+ 81.6% ± 25.69 SD), measured with mental count was detected in subjects at rest, without gender difference. This observation is in line with what was described by the German physiologist Karl von Vierordt (1818 –1884) in what is now called Vierordt's law i.e. "short" intervals of time tend to be overestimated, and "long" intervals of time tend to be underestimated [
21].
The difference in time perception in the two types of experiments used in the present research is in line with several studies that have shown a reduction in perceived time as the complexity of a task performed simultaneously increases [
22,
23]. In fact, it has been seen that, while when attention is devoted only to time there is an overestimation of time, there is an underestimation of time when attention is diverted from time [24).
In the present study, the marked overestimation of time observed at rest with mental counting was significantly reduced (p < 0.0001) at the end of the exhaustive exercise (+ 23.3% ± 13.83 SD), also in this case without gender difference. From these results it seems that an exhaustive exercise accelerated the mental count used to estimate time, with the result of greatly reducing the overestimation observed at rest. These observations seem to be in line with those found by Goudini et al. [
11] who observed significant underestimates in the evaluation of time intervals of 5, 10, 20 and 30 s after physical fatigue. In addition, the present results are congruent with Graham et al. [
25], as their results showed an underestimation of time (5, 10, 20 and 30 s) after 30 s of isometric exercises with knee extensors at 100%, 60%, and 10% of maximum voluntary contraction with respect to the control condition. The present results are also in line with those observed by Edwards and McCormick [
26] who asked participants to estimate the completion of 25%, 50%, 75% and 100% of a 30 s test on Wingate cycles and of 20 min on a rowing ergometer, under various rating of perceived exertion conditions. They observed that at the 75% and 100% intervals, estimates of time under maximal perceived exertion were significantly shorter than those performed under mild and moderate perceived exertion conditions.
There are two main models in the literature to describe the process of time perception; the Scalar Expectancy Theory, also called Pacemaker Accumulator Model, and the Striatal Beat Frequency Model [
27,
28].
The Scalar Expectancy Theory divides the system of measuring time into three successive moments [
29]. The process begins with the arrival of a signal that closes a switch and the pulses generated by a Poisson-variable pacemaker are collected in an accumulator. At some point, if an event interrupts the accumulation process, the contents of the accumulator are transferred from working memory to reference memory for long-term storage [
27], and the accumulator is reset to zero [
30]. When a new event occurs, the stored duration is compared to a new occurrence to determine whether the content that is in the accumulator at that moment is less, equal or greater than the stored event [
27,
28,
29].
The Striatal Beat Frequency Model attempts to identify neural regions involved in the process of timing [
31]. The model predicts that in the cerebral cortex there are cortico-striatal neurons that function as oscillators, real pacemakers. These neurons send their impulses to striatal spiny neurons which, in this way, monitor the activity of cortical oscillators. When a target duration is reached, dopamine is released from mesencephalic dopaminergic structures (Substantia Nigra pars compacta and the Ventral Tegmental Area) onto striatal neurons, which strengthens the cortico-striatal synapses that are active at that moment and, thus, stores the elapsed time interval [
32]. Subsequently, when an event occurs, striatal spiny neurons compare the current firing with the stored pattern to identify when the duration has been reached; when the two values match, spiny neurons fire to indicate that the interval has elapsed [
31,
32,
33].
The findings that physical fatigue can distort the subjective perception of time measured with mental counting can be explained in terms of the Scalar Expectancy Theory. In the present study all participants at the end of an exhaustive exercise had a significant increase in blood lactate. The observed levels were well above 4 mmol/l, value called OBLA (Onset of Blood Lactate Accumulation) [
34] and used to express the anaerobic threshold [
35].
In the present study, we cannot say that the observed changes in the ability to estimate the flow of time after an exhaustive exercise are dependent on the increase in blood lactate. However, in previous studies it has been observed that intravenous infusion of lactate in comfortably seated individuals was able to induce changes equal to those observed, in the same persons, after an exhaustive exercise on both attentional processes [
36] and excitability of the motor cortex [
37].
Therefore, it could be hypothesized that an increase in blood lactate above the OBLA, acting as a type of physiological arousal [
38,
39,
40], would increase the speed of the pacemaker, resulting in an increase in the number of pulses collected in the accumulator [41]. As a result, a rise in blood lactate levels, and the consequent enhanced arousal, could contribute to distortion of perceived time intervals.
On the other hand, it does not yet seem possible to propose a model to explain the worsening of the perception of time when the mental count is not possible.
5. Conclusions
Preliminary, it should be noted that the present study was conducted on a sample of only 24 subjects and that the participants were 12 women and 12 men aged between 19 and 25 years. Even with these limitations, this study found that the perception of time intervals between 1 and 5 s was affected at the end of an exhaustive exercise. The observed effects, associated with a significant increase in blood lactate levels, were different in the two types of time estimation used in the present study. In experimental conditions in which participants were asked to evaluate the duration of the time interval to be assessed by mental counting, a significant reduction in the overestimation of time made at rest was observed at the end of exercise. On the other hand, when participants had to evaluate the difference in duration between two events without the possibility to mentally count, a significant deterioration in performance was observed at the end of the exercise. In both cases, no gender differences were highlighted. Future research should aim to investigate in what way lactate might affect the perception of short-time intervals (≤ 5s), and how the perception of time can be achieved when it is not possible to mentally count.
Author Contributions
TM, M.S., and V.P.: conceptualization and supervision. T.M., S.R., and M.C.P.: methodology and software. T.M., G.R., S.M., and V.P.: writing—origin draft preparation. T.M. and V.P.: writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Kore University of Enna. Approval code: 538; approval date: 11 January 2024.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study can be obtained by the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fraisse, P. Perception and estimation of time. Ann. Rev. Psychol. 1984, 35, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsbourne, M.; Hicks, R.E. The extended present: evidence from time estimation from amnesics and normals. In Neuropsychological Impairment of short-term memory, Vallar, G., Shallice, T. Eds; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; pp. 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, M.B.; Sanderson, P.M. Multisensory integration with a head-mounted display: Sound delivery and self-motion. Hum. Factors 2008, 50, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, R.; Okuda, J.; Umetsu, A.; Sugiura, M.; Inoue, K.; Suzuki, K.; Tabuchi, M.; Tsukiura, T.; Narayan, S.L.; Nagasaka, T.; Yanagawa, I.; Fujii, T.; Takahashi, S.; Fukuda, H.; Yamadori, A. Human cerebellum plays an important role in memory-timed finger movement: an fMRI study. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, E.T. The functions of the orbitofrontal cortex. Brain Cogn. 2004, 55, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickel, W.K.; Jarmolowicz, D.P.; Mueller, E.T.; Koffarnus, M.N.; Gatchalian, K.M. Excessive discounting of delayed reinforcers as a trans-disease process contributing to addiction and other disease-related vulnerabilities: emerging evidence. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 287–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulliksen, H. The influence of occupation upon the perception of time. J. Exp. Psychol. 1927, 10, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, M.; Jakobson, A.; Havik, M.; Timpmann, S.; Burk, A.; Ööpik, V.; Allik, J.; Kreegipuu, K. Effects of heat acclimation on time perception. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 95, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, A.; Lunghi, C.; Gori, M. Moderate physical activity alters the estimation of time, but not space. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1004504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, H.R.; Konrad, A.; Alizadeh, S.; Graham, A.; Behm, D.G. Temporal perception is distorted by submaximal and maximal isometric contractions of the knee extensors in young healthy males and females. Front. Sports Act. Living 2023, 5, 1185480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudini, R.; Zahiri, A.; Alizadeh, S.; Drury, B.; Anvar, S.H.; Daneshjoo, A.; Behm, D.G. The effects of physical and mental fatigue on time perception. Sports (Basel) 2024, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.M.; Menting, S.G.P.; Elferink-Gemser, M.T.; Hettinga, F.J. The perception of time is slowed in response to exercise, an effect not further compounded by competitors: behavioral implications for exercise and health. Brain Behav. 2024; 14, e3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco, M.; Buscemi, A.; Ramaci, T.; Tusak, M.; Di Corrado, D.; Perciavalle, V.; Maugeri, G.; Perciavalle, Va.; Musumeci, G. Influences of blood lactate levels on cognitive domains and physical health during a sports stress. Brief Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coco, M.; Perciavalle, V.; Cavallari, P.; Perciavalle, Va. Effects of an Exhaustive Exercise on Motor Skill Learning and on the Excitability of Primary Motor Cortex and Supplementary Motor Area. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, 11–e2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perciavalle, Va.; Maci, T.; Perciavalle, V.; Massimino, S.; Coco, M. Working memory and blood lactate levels. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 2129–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, J.D.; Bourdon, P.C.; Woolford, S.M. Effect of measuring blood lactate concentrations using different automated lactate analysers on blood lactate transition thresholds. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2003, 6, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maci, T.; Le Pira, F.; Marturano, L.; Zappia, M. Time estimation in patients with parkinson’s disease. In Proceedings of the 38th Congress of Italian Neurological Society, Firenze, Italy, 13-17 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Riesen, J.M.; Schnider, A. Time estimation in Parkinson’s disease: normal long duration estimation despite impaired short duration discrimination. J. Neurol. 2001, 248, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destrebecqz, A.; Peigneux, P.; Laureys, S.; Degueldre, C.; Del Fiore, G.; Aerts, J.; Luxen, A.; Van Der Linden, M.; Cleeremans, A.; Maquet, P. The neural correlates of implicit and explicit sequence learning: Interacting networks revealed by the process dissociation procedure. Learn. Mem. 2005, 12, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierordt, K. Der Zeitsinn nach Versuchen (The Sense of Time According to Experiments). Laupp,Tübingen, Germany: 1868.
- Rammsayer, T.; Ulrich, R. No evidence for qualitative differences in the processing of short and long temporal intervals. Acta Psychol. (Amst.) 2005, 120, 141–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellotti, S.; D’agostino, O.; Biondi, A.; Pignatiello, L.; Del Viva, M. Influence of motor and cognitive tasks on time estimation. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macar, F.; Grondin, S.; Casini, L. Controlled attention sharing influences time estimation. Mem. Cognit. 1994, 22, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, A.P.; Gardner, H.; Chaabene, H.; Talpey, S.; Alizadeh, S.; Behm, D.G. Maximal and Submaximal Intensity Isometric Knee Extensions Induce an Underestimation of Time Estimates with Both Younger And Older Adults: A Randomized Crossover Trial. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2023, 22, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.M.; McCormick, A. Time Perception, Pacing and Exercise Intensity: Maximal Exercise Distorts the Perception of Time. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 180, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allman, M.; Meck, W. Pathophysiological distortions in time perception and timed performance. Brain 2012, 135, 656–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allman, M.; Teki, S.; Griffiths, T.; Meck, W. Properties of the internal clock: first- and second-order principles of subjective time. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2014, 65, 743–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grondin, S. Timing and time perception: a review of recent behavioral and neuroscience findings and theoretical directions. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2010, 72, 561–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oprisan, S.A.; Novo, D.; Buhusi, M.; Buhusi, C.V. Resource Allocation in the Noise-Free Striatal Beat Frequency Model of Interval Timing. Timing Time Percept. 2023, 11, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, H.; Harrington, D.; Meck, W. Neural Basis of the perception and estimation of time. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 36, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meck, W. Neuropsychology of time and time perception. Brain Cogn. 2005, 58, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matell, M.; Meck, W. Cortico-striatal circuits and interval timing: coincidence detection of oscillatory processes. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 2004, 21(2), 139–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, B.; Jacobs, I. Onset of blood lactate accumulation and marathon running performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 1981, 2, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, H.; Mader, A.; Hess, G.; Mucke, S.; Muller, R.; Hollmann, W. Justification of the 4 mmol/l lactate threshold. Int. J. Sports Med. 1985, 6, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco, M.; Di Corrado, D.; Calogero, R.A.; Perciavalle, Va.; Maci, T.; Perciavalle, V. Attentional processes and blood lactate levels. Brain Res. 2009, 1302, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coco, M.; Alagona, G.; Rapisarda, G.; Costanzo, E.; Calogero, R.A.; Perciavalle, Va.; Perciavalle, V. Elevated blood lactate is associated with increased motor cortex excitability. Somatosens Mot Res, 2010; 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.M.; Polman, R.C. Pacing and awareness: brain regulation of physical activity. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stergiou, M.; Robles-Pérez, JJ.; Rey-Mota, J.; Tornero-Aguilera, JF.; Clemente-Suárez, VJ. Psychophysiological Responses in Soldiers during Close Combat: Implications for Occupational Health and Fitness in Tactical Populations. Healthcare (Basel) 2023, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Malley, C.A.; Fullerton, C.L.; Mauger, A.R. Analysing experienced and inexperienced cyclists' attentional focus and self-regulatory strategies during varying intensities of fixed perceived effort cycling: A mixed method study. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2024, 70, 102544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, S.; Droit-Volet, S. Emotional Time Distortions: The Fundamental Role of Arousal. Cogn. Emot. 2012, 26, 847–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).