Introduction
Cryptorchidism is a common congenital anomaly in boys, affecting approximately 3% of male newborns [
1]. In almost 50% of cases, the undescended testis (UDT) descends spontaneously within the first year of life [
2]. Despite this high rate of spontaneous descent, orchidopexy remains one of the most frequently performed surgical interventions in childhood in Germany, with 12,000-18,000 procedures conducted annually [
3].
Orchidopexy is considered one of the most painful inguinal procedures due to the traction exerted on the testicle and the spermatic cord [
4]. Therefore, ensuring adequate analgesia is crucial, especially in outpatient surgery, to prevent unnecessary hospital readmissions.
Hence, in recent years, a combination of general anesthesia along with either a caudal block (CB) or inguinal block (IB) as regional anesthesia has gained acceptance for inguinal procedures.
In the late 1980s, Markham and Hannallah concluded that the safety and effectiveness of both CB and IB are comparable for postoperative pain relief, despite their specific advantages and disadvantages [
5,
6].Subsequent studies have also compared these regional techniques and often found them to be equivalent. However, it is important to note that in many of these studies, interventions other than orchidopexy were included in the assessment of inguinal procedures. In addition, the assessments primarily focused on the immediate postoperative outcome and did not consider the intraoperative course or the 24-hour course, which are crucial aspects of a potentially outpatient procedure [
7,
8,
9].
The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the effectiveness of CB and IB in orchidopexy, both intraoperatively and postoperatively. This is particularly relevant given the increasing trend of performing this procedure on an outpatient basis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
This prospective trial included 71 boys aged between 9 months and 4 years with ASA (American Society of Anaesthesiology) physical status I and II, who underwent elective unilateral orchidopexy at our department (a full member of ERN eUROGEN) in a one-day inpatient setting. Parental consent was obtained after explaining the procedure. Exclusion criteria for the study included bilateral orchidopexy, re-orchidopexy, intolerance or allergic reaction to any product used in the study, and inability to provide written informed consent.
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the University of Regensburg (No. 16-101-0115).
After obtaining written consent from the parents, the preoperative anaesthesiologist suggested the type of regional anaesthesia (RA). The patients were divided into two groups based on the type of RA used: the caudal block group (CB) and the inguinalis group (IB).
2.2. Study Intervention
General anesthesia was induced in all patients before performing RA. RA was typically performed under sterile conditions and with ultrasound guidance (LOGIQ ™ ℮, GE Healthcare, Wauwatosa, WI, USA). Patients in the CB group were positioned in the left lateral position with their knees and hips flexed at 90 degrees. This position causes a cranial shift of the dural sheath, minimizing the risk of dural perforation. The sacral hiatus was accessed using a 22 gauge caudal needle (Epican® Paed caudal needle, 45° Crawford type bevel for epidural anesthesia/analgesia, B.Braun ® Medical Inc., Melsungen, Germany) inserted at a 45-60° angle to the skin level. Once the ligamentum sacrococcygeum was passed, the needle was lowered to a 20-30° angle and advanced 3-5mm. An adrenaline test dose (1:200,000 ≙ 5 μg/ml) was then administered. Following a negative test with no pulse rise or T-wave elevation, 1.2 ml/kg bw of 0.2% ropivacaine with 2 μg/kg bw of clonidine was administered over 1 minute, with repeated aspiration, ECG monitoring and continuous sonographic demonstration of the ventral dura shift with cranial dissemination.
Patients in the IB group were maintained in a supine position. The Musculus obliquus externus, internus, and the Musculus transversus abdominis were then identified via ultrasound imaging. Between the latter two muscles, the nervus ilioinguinal and the nervus iliohypogastricus were identified. A 22-gauge Ultraplex® 360 needle (30°, 0.7 x 50 mm, B.Braun® Medical Inc., Melsungen, Germany) was inserted parallel to the ultrasound probe from the median to the anterior iliac spine. After confirming the target nerve and a negative aspiration test, 0.2ml/kg body weight of 0.2% ropivacaine was administered. The correct administration was confirmed by sonographic visualization of the internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis muscle drifting. All blocks were performed by an experienced anaesthesiologist, mainly by one of the authors (BK).
2.3. Preoperative Management
Depending on the patient's age, preoperative fasting times were 4 hours for milk and 6 hours for solid food, and 1 hour for clear fluids. All patients received oral premedication with Midazolam at a dose of 0.5mg/kg bw. An EMLA dressing was applied to both antecubital veins in all patients, and an IV catheter was inserted.
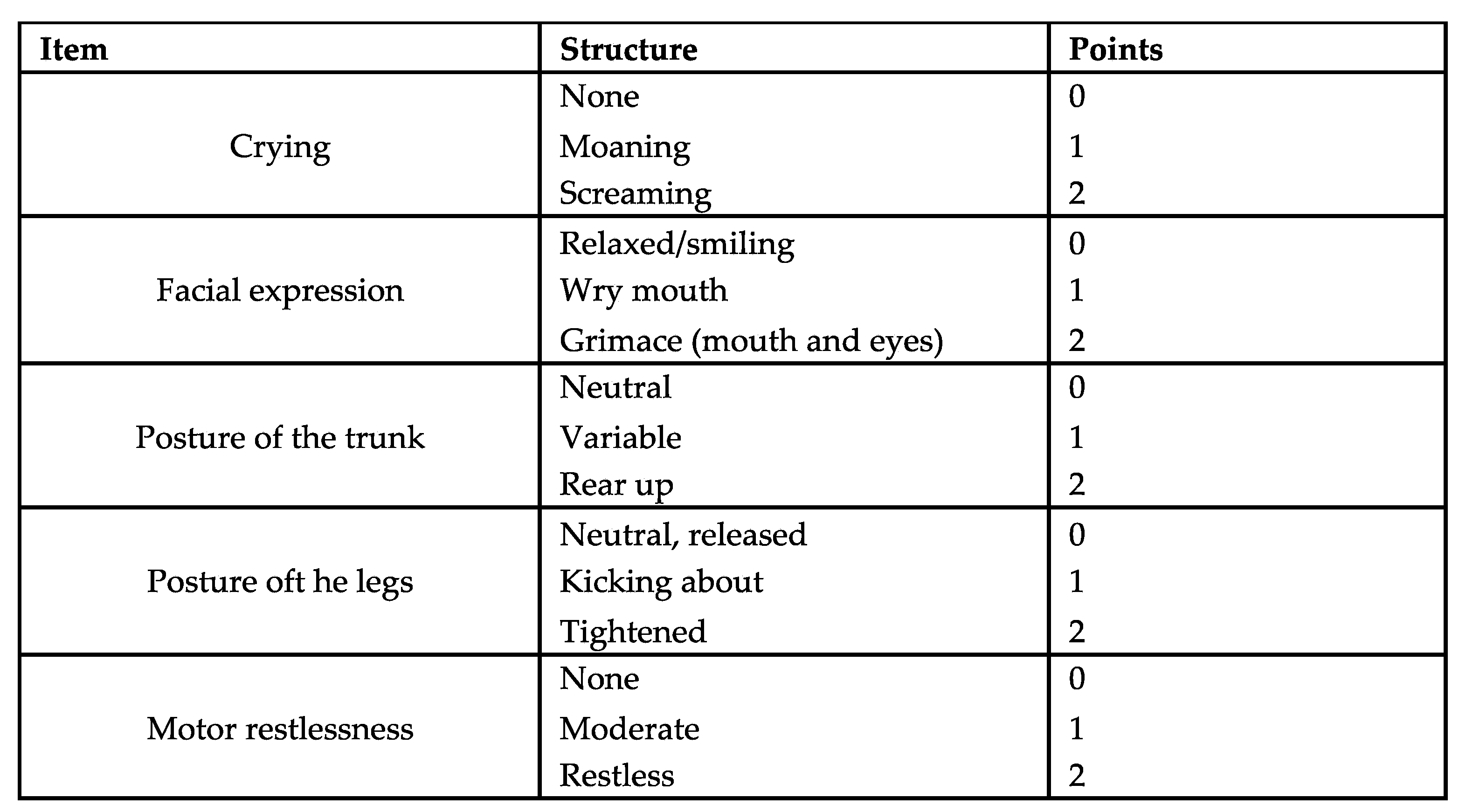
Figure 1.
Children´s and Infants Postoperative Pain Scale (CHIPPS).
Figure 1.
Children´s and Infants Postoperative Pain Scale (CHIPPS).
2.4. Anesthetic and Perioperative Management
The anaesthetic management was standardised for all patients. Standard monitoring techniques were employed. Adequate perioperative hydration was achieved by administering a balanced full electrolyte solution or a glucose 1% infusion at a rate of 10ml/kgbw/h via an infusion pump. Anaesthesia was induced via an IV line using propofol at a dose of 3-5mg/kg body weight and fentanyl at a dose of 2μg/kg body weight. Alternatively, in cases where an IV line was difficult to place, anaesthetic induction was performed using inhalation of sevoflurane at a concentration of 6-8Vol% in a nitrous oxide/oxygen mixture (50% N2O/50% O2). Subsequently, a laryngeal mask was inserted. The RA was performed using one of the described techniques under general anesthesia. Sevoflurane 2% end-tidal was used to maintain anesthesia, along with a fresh gas flow of 0.5-1 liter and a fraction of inspired oxygen of 0.3. If the patient's heart rate increased by more than 10% of baseline values during the operation, Remifentanil was intravenously administered at a dose of 1µg/kg bodyweight. The systolic and diastolic blood pressure, as well as the heart rate, were recorded at three different time points: at the beginning of the surgical procedure (t0), during manipulation of the spermatic cord (t1), and near the end of anesthesia at the time of skin suturing (t2). Anesthesia was stopped after the surgery was completed.
The anaesthesia induction time was recorded retrospectively using the operating theatre documentation.
2.5. Postoperative Management
Following surgery, patients were transferred to the post-anesthetic care unit (PACU) where their hemodynamics and respiratory parameters were continuously monitored. Pain assessment was conducted every 15 minutes using the Children's and Infants Postoperative Pain Scale (CHIPPS) in German language (
Figure 1). If the pain score exceeded 4, piritramide was intravenously administered at a dosage of 0.05-0.1 mg/kg body weight. Cardiac parameters were recorded before transferring patients to the general ward.
Patients were moved to the general ward once they achieved stable vital signs and a pain score below 4. Subsequent pain score assessments were conducted at four-hour intervals. If the pain score exceeded 4, metamizole was administered intravenously at a dosage of 15 mg/kg body weight (maximum dose 60 mg/kg body weight) as a short infusion. Patients were discharged from the hospital on the morning of the first postoperative day.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics 29. Baseline characteristics are presented as mean ± standard deviation or median (minimum - maximum), median (IQR), and as a number (percentage) for qualitative variables.
Normality was tested using frequency distribution (histogram). Unpaired or paired student's t-tests were used for normally distributed ordinal data. Mann-Whitney U test was used for non-normally distributed ordinal data. The study compared categorical data using either the χ2 test or Fisher's exact tests, as appropriate. Additionally, a binary linear regression analysis was conducted to evaluate the relationship between multiple independent variables and a dependent variable. Independent risk factors were identified based on data that had a p-value < 0.05. The threshold for statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
During the 16-month study period, 71 boys underwent unilateral orchiopexy, with 34 of them obtaining an IB and 37 receiving a CB.
Table 2 presents detailed demographic data.
The comparative analysis revealed no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of weight, duration of surgery and anaesthesia induction, and time spent in the PACU. However, a significant difference was observed in the age of the patients (p<0.05). No significant risk associated with the requirement for pain medication was identified in the context of binary linear regression, after adjusting for both the age and weight of the patients (
Table 3).
3.1. Intraoperative and PACU
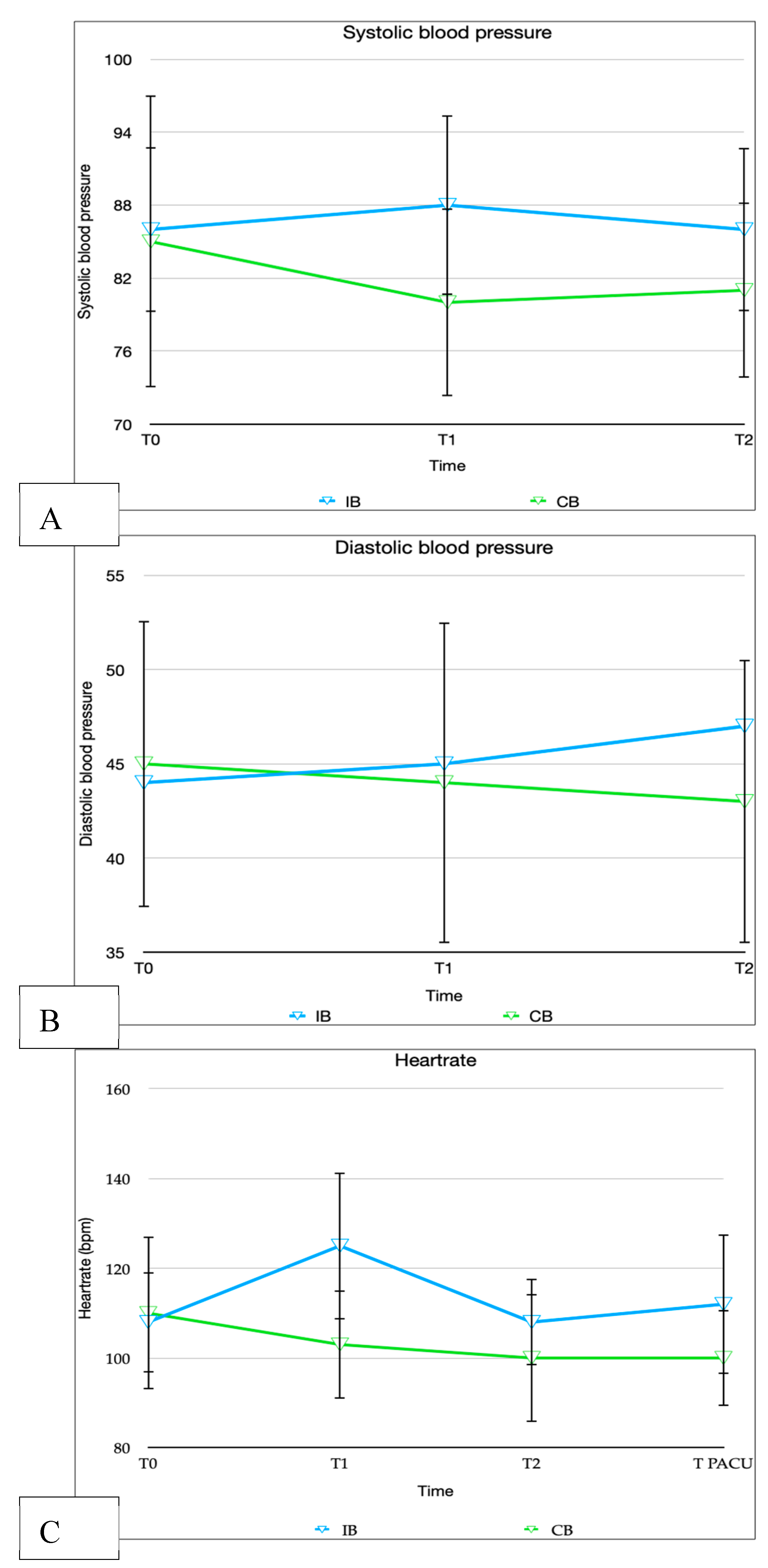
At the initial measurement point (T0), the baseline systolic and diastolic blood pressure, as well as the heart rate, were similar in both groups. However, the IB group showed a significant increase in systolic blood pressure (<0.001) and a significant increase in heart rate (<0.001) when compared to the baseline values. (Figure1)
Figure 2.
Mean arterial pressure and heart rate values in both groups.
Figure 2.
Mean arterial pressure and heart rate values in both groups.
In the CB group, none of the patients showed an increase in heart rate during the operation. However, in the IB group, 26 out of 34 patients (76.5%) experienced a heart rate increase of more than 10% (p< 0.001). As a result, the administration of Remifentanil was significantly higher in the IB group (p< 0.001). More than half of the patients in this group (53.8%) experienced multiple heart rate increases and required additional doses of Remifentanil.
In PACU, 8 out of 37 patients (21.6%) from CB group and 18 out of 34 patients (52.9%) from the IB group required the administration of piritramide. The results demonstrated no statistically significant difference in terms of the level of the CHIPPS score (p=0.533) or in the timing of piritramide administration (p=0.106). Detailed data are presented in
Table 4.
3.2. General Ward
For improved comparability of analgesic requirements on the ward, patients were stratified based on whether they received piritramide in the PACU. Piritramide, with a duration of action lasting 5-8 hours, was treated as a distinct variable owing to its potential influence on subsequent analgesic administration.
Patients who did not receive piritramide in the PACU did not exhibit a significant higher incidence of requiring metamizole on the ward (p=0.070) compared to those who had received piritramide earlier.
Among the 29 patients in the CB group who did not receive piritramide in the PACU, 25 individuals (86.2%) subsequently underwent metamizole administration. In contrast, within the IB group comprising 16 patients, 10 individuals (62.5%) received metamizole on the ward. However, no significant differences were observed between the two groups in terms of the onset of pain symptoms (p=0.619), the level of CHIPPS Score (p=0.439), or the 24-hour total dose of metamizole (p=0.986).
Furthermore, among the eight patients in the CB group who received piritramide in the PACU, five (62.5%) required additional metamizole on the ward. In the IB group, where 18 patients received piritramide in the PACU, 10 (55.6%) required metamizole on the ward. A significant difference in the onset of pain symptoms was demonstrated (p=0.030), whereas no significant differences were observed in the level of the CHIPPS Score (p=0.513) and the 24-hour total dose (p=0.310). Further detailed data is shown in
Table 5.
Regarding the occurrence of postoperative vomiting (PONV) the results demonstrated that in the group CB group, 5 (13.5%) and in the IB group, 9 (26.5%) patients suffered from PONV. No significant difference was found (p = 0.235).
All patients were able to be discharged on the morning of the following day without any complications. None of the patients exhibited urinary retention or prolonged motor blockades during the monitoring phase.
In the CB group, 5 patients (13.5%) and in the IB group, 2 patients (5.9%) demonstrated no need for analgesics; however, no statistically significant difference was observed between the groups (p=0.299). Consequently, 7 patients (9.9%) within the entire study population did not necessitate analgesic administration over the entire 24-hour duration of their hospital stay.
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
In our prospective study comparing the efficacy of caudal and inguinal blocks in the treatment of intraoperative and postoperative pain during orchidopexy, we demonstrated that caudal block is the superior procedure both intraoperatively and immediately postoperatively. Although the differences between the groups were not significant, there was a slightly higher metamizole consumption pattern in the CB group compared to the IB group in the 24-hour postoperative phase. A slightly lower incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) was observed in patients undergoing caudal anaesthesia, although this was not statistically significant. No significant complications were observed in either group.
4.2. Findings in the Context of Existing Evidence
The provision of adequate intra- and postoperative analgesia is a critical factor determining the success of any surgical procedure. It is evident that the incidence of pain, nausea and vomiting following orchidopexy is higher than that observed in other inguinal procedures [
10]. This is attributed to the manipulation of the spermatic cord during the procedure, which is a source of considerable discomfort for the patient undergoing this operation [
6]. Therefore, it is of paramount importance to ensure that adequate pain management is provided especially in an outpatient setting, as the most common rea- sons for unplanned hospital admission is pain [
11].
A number of studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of both regional anaesthesia techniques as methods for postoperative analgesia [
5,
6,
12,
13]. However, the literature on intraoperative efficacy is still relatively sparse. In order to obtain a more objective assessment of the pain stimulus, Somri et al. examined the effect of CB and IB by measuring intraoperative and postoperative catecholamine plasma levels. They found that catecholamine levels were reduced after application of regional anaesthesia in both procedures. Conversely, however, significantly higher catecholamine levels were observed in the IB group at the conclusion of the operation and in the recovery room [
4].
Our study did not include a measurement of catecholamine levels. However, during the intraoperative period, the IB group exhibited a significant increase in systolic blood pressure and heart rate, particularly at T1, which corresponded to the traction on the spermatic cord. Therefore, the administration of Remifentanil was significantly higher in the IB group. This leads to the conclusion that the CB block appears to be superior to the IB block in terms of intraoperative efficacy.
In recent years, various meta-analyses have been conducted to evaluate the postoperative effectiveness of caudal block with local regional anaesthesia in paediatric procedures in the groin region. Depending on the meta-analysis, the time to administration of rescue analgesia, the number of patients requiring rescue analgesia and the postoperative pain score were defined as outcome parameters [
14,
15,
16,
17].
In a recently published meta-analysis, Hung et al. found that in orchidopexy, CB was the only regional analgesia that prolonged the time to first rescue analgesia. In contrast, IB had a relatively small analgesic effect [
16]. A similar conclusion was reached by Shanthanna et al., who conducted a meta-analysis comparing caudal blocks with non-caudal blocks in inguinal procedures. The outcomes determined were efficacy based on analgesic requirement at 4 hours and at 4-24 hours. It was found that caudal anaesthesia was more effective than local regional procedures, especially in the later period [
17].
In contrast, Desai et al. found no difference between IB and CB in terms of the 0–2 hour postoperative pain score and the need for in-hospital rescue analgesia in their meta-analysis [
14].
In a meta-analysis from 2013, which included a total of 13 studies from monocentres with small case numbers, Baird et al. also found no significant differences in the pain score one hour postoperatively. Astonishingly, based on this balance, they postulated that in patients without additional indications for pain management, CB could be omitted for lower-risk and less time-consuming manoeuvres. However, clinical adverse effects were not investigated in this meta-analysis [
15].
In terms of clinical side effects, Shanthanna et al. found a higher risk of motor blockages and urinary retention [
17]. Desai and colleagues also reach a similar conclusion regarding urinary retention, although this is attributed to a single included publication by Markham and colleagues [
5,
14]. In his study, Markham used isobaric bupivacain 0.5% for caudal anaesthesia, which, in addition to its high concentration, has a higher tendency for motor blockade than the ropivacaine used in our study [
5].
In our study, the CB block was found to be neither more time-consuming than the IB block nor to result in any significant adverse effects, such as urinary retention or motor blockade.
Another crucial aspect, especially in outpatient surgery, is the potential for delayed discharge or unplanned hospital admission due to the occurrence of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), post-discharge nausea and vomiting, or opioid-induced nausea and vomiting. It is widely acknowledged that multimodal pain management, including perioperative regional and opioid-sparing analgesia, is an effective strategy for preventing nausea and vomiting [
11]. However, to the best of our knowledge, regarding groin surgery this has not yet been a focus of existing literature regarding. In our study, we observed a significant reduction in the need for opioids in the CB group compared to the IB group. Additionally, the incidence of PONV was lower in the CB group, although not to a statistically significant degree.
The available meta-analyses provide a clear illustration of the current inconsistency of the data situation. It is our conviction that the data of our study will serve to enhance the efficacy of pain management. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the study is not without limitations. Despite the prospective design, the study is subject to certain limitations. For example, no randomisation was conducted, which resulted in a difference in age between the two groups. Nevertheless, the influence of the measurement parameters was ruled out using a binary logistic regression analysis. Another limitation is the assessment of pain intensity using the CHIPPS score, despite this being a validated instrument for assessment. In addition to the age-related limitations in the ability to adequately verbalise pain, other factors such as the unfamiliar environment, hunger, thirst, and limited freedom of movement influence the ability to assess pain.
4.3. Implications for Clinical Practice
Both caudal block (CB) and inguinal block (IB) demonstrate safety and reliability in providing sufficient regional analgesia for orchidopexy. Intraoperatively and during early recovery, CB exhibits superiority, particularly in conjunction with supplementary opioid administration, potentially mitigating postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV). Conversely, IB may exhibit slight superiority in the late recovery phase. However, it is recognized that orchidopexy constitutes a procedure associated with considerable pain, often necessitating additional analgesia with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in the later postoperative phase. These considerations are particularly pertinent in the outpatient setting.
5. Conclusions
Our study has demonstrated that both the caudal block and inguinal block procedures represent safe and feasible methods. Despite the established status of both regional anesthesia techniques and the frequency of orchidopexy procedures, significant ambiguity and inconsistency persist in this domain. Therefore, a multicenter, randomized, prospective study would be desirable to gain further insights and establish clear guidelines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.K., G.B. and W.H.R.; methodology, B.K., G.B., W.H:R.; software, A.H., B.K., F.V., P.I.Z.; validation, A.H. B.K., G.B., W.H.R..; formal analysis, A.H., B.K..; investigation, A.H., B.K., F.V., G.B., W.H.R.; resources, A.H., B.K., F.V., P.I.Z.,G.B., W.H.R.; data curation, A.H., B.K., F.V., P.I.Z.; G.B., W.H.R.; writing—original draft preparation, A.H..; writing—review and editing, A.H.,B.K.,F.V.,G.B.,W.H.R.; visualization, A.H.,B.K..; supervision, G.B., W.H.R..; project administration, A.H., B.K., F.V.,P.I.Z; funding acquisition, W.H.R.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the KUNO–Foundation, Regensburg, Germany.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the University of Regensburg (No. 16-101-0115, 18.07.2016) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the parents or legal representatives of all study participants.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to all patients who participated in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Echeverría Sepúlveda, M.P.; Yankovic Barceló, F.; Lopez Egaña, P.J. The undescended testis in children and adolescents. Part 1: pathophysiology, classification, and fertility- and cancer-related controversies. Pediatr Surg Int 2022, 38, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, J.S. Surgical Management of the Undescended Testis: Recent Advances and Controversies. Eur J Pediatr Surg 2016, 26, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, M.; Ebert, A.K.; Baunacke, M.; Groeben, C.; Eisenmenger, N.; Thomas, C.; Huber, J. [Health care reality of selected pediatric urologic surgeries in Germany from 2006 to 2019]. Urologe A 2021, 60, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somri, M.; Gaitini, L.A.; Vaida, S.J.; Yanovski, B.; Sabo, E.; Levy, N.; Greenberg, A.; Liscinsky, S.; Zinder, O. Effect of ilioinguinal nerve block on the catecholamine plasma levels in orchidopexy: comparison with caudal epidural block. Paediatr Anaesth 2002, 12, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, S.J.; Tomlinson, J.; Hain, W.R. Ilioinguinal nerve block in children. A comparison with caudal block for intra and postoperative analgesia. Anaesthesia 1986, 41, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannallah, R.S.; Broadman, L.M.; Belman, A.B.; Abramowitz, M.D.; Epstein, B.S. Comparison of caudal and ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve blocks for control of post-orchiopexy pain in pediatric ambulatory surgery. Anesthesiology 1987, 66, 832–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, G.D.; Barrett, R.F. Comparison of two regional techniques for postoperative analgesia in children following herniotomy and orchidopexy. Anaesthesia 1987, 42, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatif, A.A. Ultrasound-guided ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve blocks versus caudal block for postoperative analgesia in children undergoing unilateral groin surgery. Saudi J Anaesth 2012, 6, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Splinter, W.M.; Bass, J.; Komocar, L. Regional anaesthesia for hernia repair in children: local vs caudal anaesthesia. Can J Anaesth 1995, 42, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.W.; Ragg, P.G.; Sheppard, S.; Chalkiadis, G.A. The severity and duration of postoperative pain and analgesia requirements in children after tonsillectomy, orchidopexy, or inguinal hernia repair. Paediatr Anaesth 2012, 22, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovac, A.L. Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting in Pediatric Patients. Pediatric Drugs 2021, 23, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyaz, S.G.; Tokgöz, O.; Tüfek, A. Caudal epidural block in children and infants: retrospective analysis of 2088 cases. Ann Saudi Med 2011, 31, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sujatha, C.; Zachariah, M.; Ranjan, R.V.; George, S.K.; Ramachandran, T.R.; Pillai, A.R. Transversus Abdominis Plane Block versus Ilioinguinal/Iliohypogastric Nerve Block with Wound Infiltration for Postoperative Analgesia in Inguinal Hernia Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesth Essays Res 2017, 11, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, N.; Chan, E.; El-Boghdadly, K.; Albrecht, E. Caudal analgesia versus abdominal wall blocks for pediatric genitourinary surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2020, 45, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, R.; Guilbault, M.P.; Tessier, R.; Ansermino, J.M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of caudal blockade versus alternative analgesic strategies for pediatric inguinal hernia repair. J Pediatr Surg 2013, 48, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.Y.; Bai, G.H.; Tsai, M.C.; Lin, Y.C. Analgesic Effects of Regional Analgesic Techniques in Pediatric Inguinal Surgeries: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Anesth Analg 2024, 138, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanthanna, H.; Singh, B.; Guyatt, G. A systematic review and meta-analysis of caudal block as compared to noncaudal regional techniques for inguinal surgeries in children. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014, 890626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).