1. Introduction
Plastic films are a commonly utilized material that has substantially assisted human growth [
1,
2,
3]. The popularity of these films has grown in lockstep with scientific and technical developments and the beginning of industrialization. Despite their widespread usage, these films constitute a severe concern since they degrade over hundreds of years and generate “white pollution” that harms the ecology [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Biodegradable films, which undergo decomposition by bacteria and enzymes, might provide a solution to this problem.
Poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) is a noteworthy example of a biodegradable vinyl polymer; it has been observed to degrade by 75% in as little as 46 days [
10]. It is translucent, nontoxic, and has a great affinity for water. However, because it negatively affects its mechanical and barrier qualities in the wet state, its hydrophilicity restricts the applications that may be made of it [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. Several studies have been conducted to improve PVA’s mechanical strength and water resistance. These studies have explored a wide range of approaches, including the use of crosslinked networks, silane-coupling agents, clay, graphene nanocomposites and blends of polymers [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Mechanical stability of PVA may be improved by establishing a three-dimensional network, as well as its water resistance. One approach is to combine multifunctional chemicals, such as silane coupling agents or clay, with the hydroxyl groups in each PVA repeating unit [
22,
23]
However, the most significant challenge is avoiding aggregation, which may be overcome by PVA-based organic-inorganic hybrid films produced by reinforcing PVA with silane-functionalized nanomaterials. The interaction of organic and inorganic phases of these hybrid films impacts the quality of these films. By fostering strong interfacial adhesion between the two phases, hybrid materials can achieve a stable homogenous nanophase and improved material properties [
24,
25,
26,
27].
Graphene oxide (GO) is a nanomaterial possessing oxygenated surfaces on both the basal planes (epoxy and hydroxyl) and the edges (carboxylic acids) [
28], This property of GO allows it to be readily functionalized, making it extremely desired. Furthermore, GO is biocompatible, amphiphilic, and may be readily exfoliated via sonication [
29] Because of these qualities, it is the perfect choice to improve the mechanical and barrier properties of polymers, potentially contributing to a variety of applications.
Utilizing an organic-inorganic hybrid methodology, we have produced hybrid NCFs, wherein the organic constituent is PVA and the inorganic precursor is VTES functionalized graphene oxide (VTESFGO). A three-dimensional network has formed in NCFs as a result of the establishment of covalent connection between PVA and VTESFGO. It is anticipated that this three-dimensional network would produce NCFs with remarkable characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 99.9%), sodium nitrate (NaNO3, >99.5%), graphite, vinyltriethoxysilane (VTES, 98%), triethylamine (TEA, 99.5%), hydrochloric acid (HCl, 98 %), N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF, 99%) and poly (vinyl alcohol) with an average molecular weight in the range of 146,000-186,000 were also purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, USA.
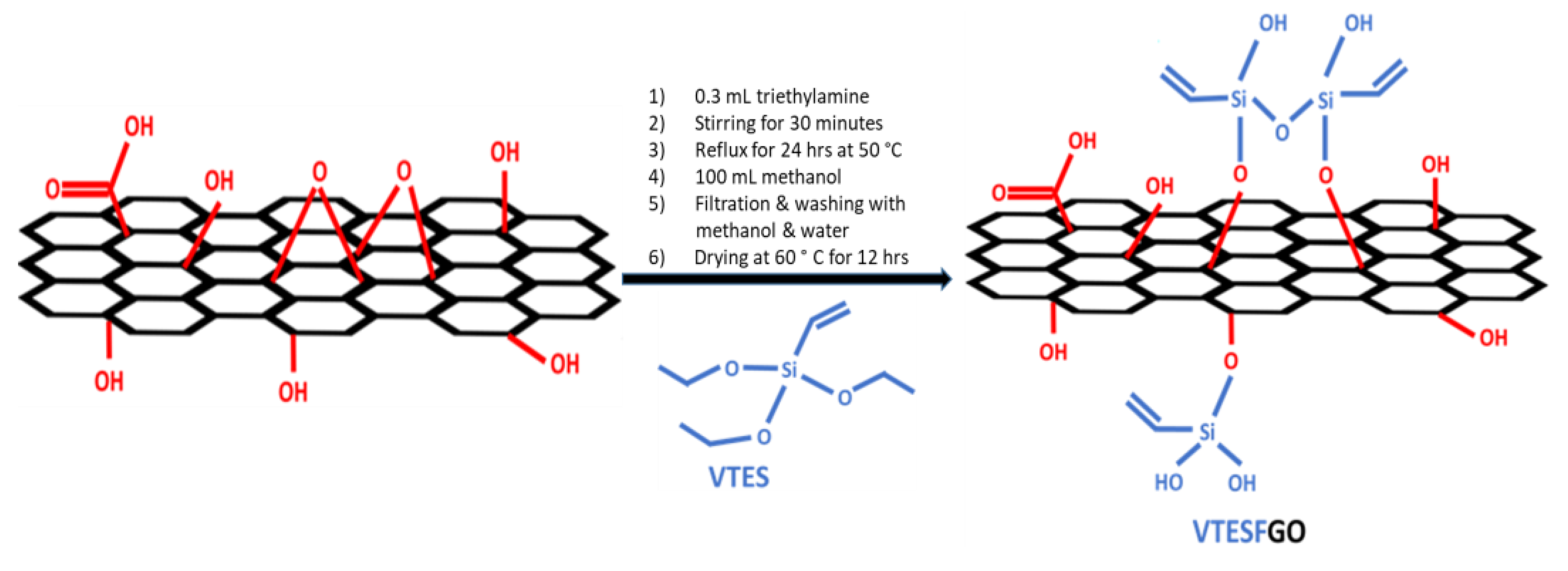
2.1. Synthesis of VTESFGO
Graphene oxide (GO) was synthesized by following the Hummer’s method. 0.3 mL of triethylamine (TEA) and 1.2 g of vinyltriethoxysilane (VTES) were added to this GO dispersion in DMF and it was then stirred for 30 minutes. This mixture was then refluxed at 70°C for 24 hours under a controlled, inert atmosphere. It was then treated with 100 mL of methanol to remove residual silane. The solid product obtained after filtration was washed sequentially with methanol and water repeatedly, later it was dried for 12 hours at 60°C [
30] showed in
Scheme 1.
2.2. Synthesis of NCFs
Dispersions containing varying amounts of VTESFGO in DMF (0.2 to 3.0 wt%) were added separately to a 1 wt% aqueous PVA solution. 1.0 mL of HCl was added to this mixture, which was stirred and sonicated for 3 hours. It was then transferred to a petri plate and heated at 50°C to enable the formation of VTESFGO/PVA NCFs with varying VTESFGO concentrations. After carefully removing the NCFs from the petri plate, they were dried at 80°C for 24 hours. The whole process is presented in
Scheme 2.
2.3. Material Characterization
XPS spectra were obtained using a VG Scientific ESCA Lab 2201-XL. The X-ray diffractograms were generated using a Rigaku D/A X-ray diffractometer with a scanning rate of 2o min-1. A Nicolet Avatar 320 FT-IR spectrometer with a spectral resolution of 4 cm-1 was used to acquire FTIR spectra in the 500-4000 cm-1 range. The scanning electron micrographs (SEM) were taken using a LEO 1530 VP field emission scanning electron microscope. The tensile properties of the NCFs were determined using the Instron 5565 electronic universal tensile strength tester. Five specimens for each sample were evaluated and average tensile characteristics were determined.
Additionally, using TA 2000 (TA Instruments, Inc., USA), NCF thermal stability was examined in a nitrogen atmosphere at a heating rate of 10 oC/min, throughout a temperature range of 25 to 600 oC.
The rate of oxygen transmission was measured using an oxygen permeability tester (OTR 8001) at 25 °C in a dry environment.
The water resistance pressure was measured by adding water drop by drop to a thin graduated tube, one end of which was sealed with NCF. Because of the continuous water permeability, there was variations in the height of the water column in the tube, and these variations were noted from these variations water resistance pressure was calculated [
31].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization VTESFGO
3.1.1. XPS analysis of VTESFGO
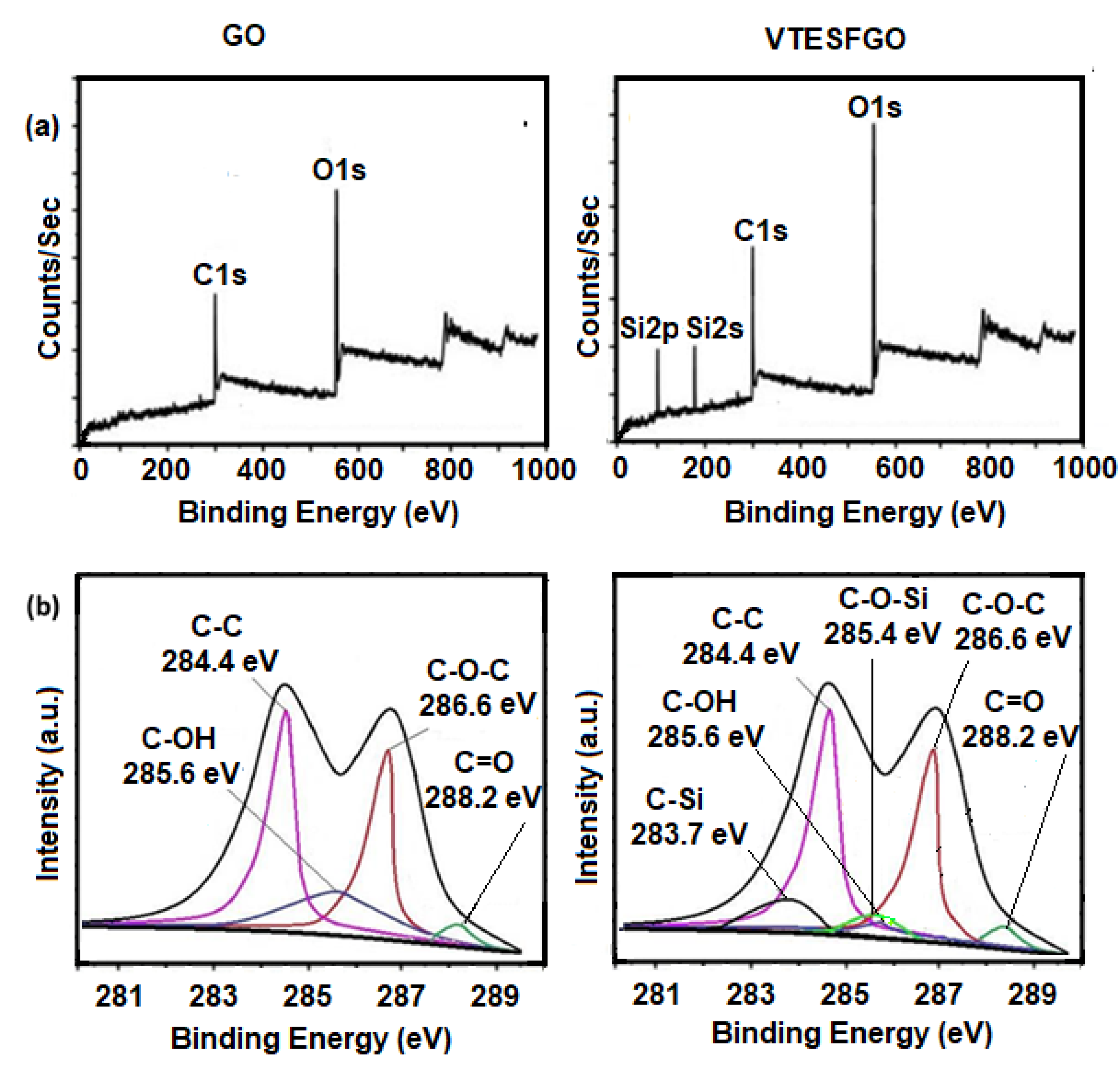
To confirm the presence of VTES on the GO surface, the XPS survey scan of pure GO was compared with that of VTESFGO in
Figure 1a. The appearance of two new peaks, Si2s and Si2p, in the VTESFGO survey scan supports VTES’s existence on the GO surface [
32,
33]. Comparing the C1s spectra of GO and VTESFGO in
Figure 1b compares the C1s spectrum of GO with VTESFGO, to explore the functionalization reveals the functionalization process that results in the creation of VTESFGO. The magnitude of the OH peak at 285.6 eV in the C1s spectra of VTESFGO is reduced, and two new peaks appear at 283.7 eV and 285.4 eV, indicating the formation of C-Si and C-O-Si bonds.
3.1.2. XRD Analysis of VTESFGO
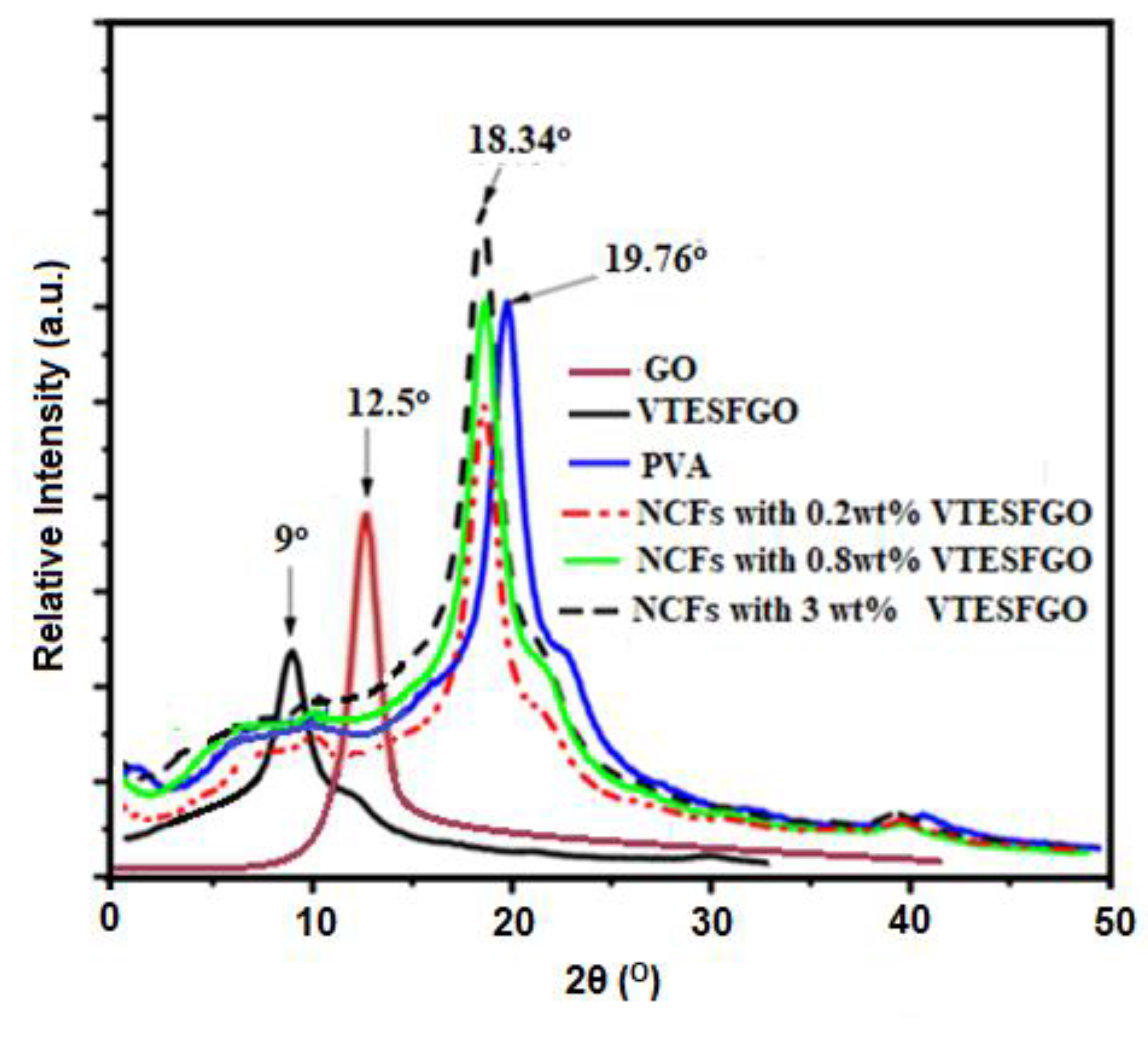
XRD analysis was used to validate GO functionalization with VTES and the findings are displayed in
Figure 2, along with the XRD analysis of NCFs. Functionalization with VTES reduced GO’s diffraction angle (2θ) from 12.5
o to 9.0
o and increased interlayer spacing, perhaps due to VTES on the surface. Diffractogram of VTESFGO shows no peak at 2θ = 9.0
o, indicating effective GO functionalization with VTES [
34,
35].
3.1.3. FT-IR Analysis of VTESFGO
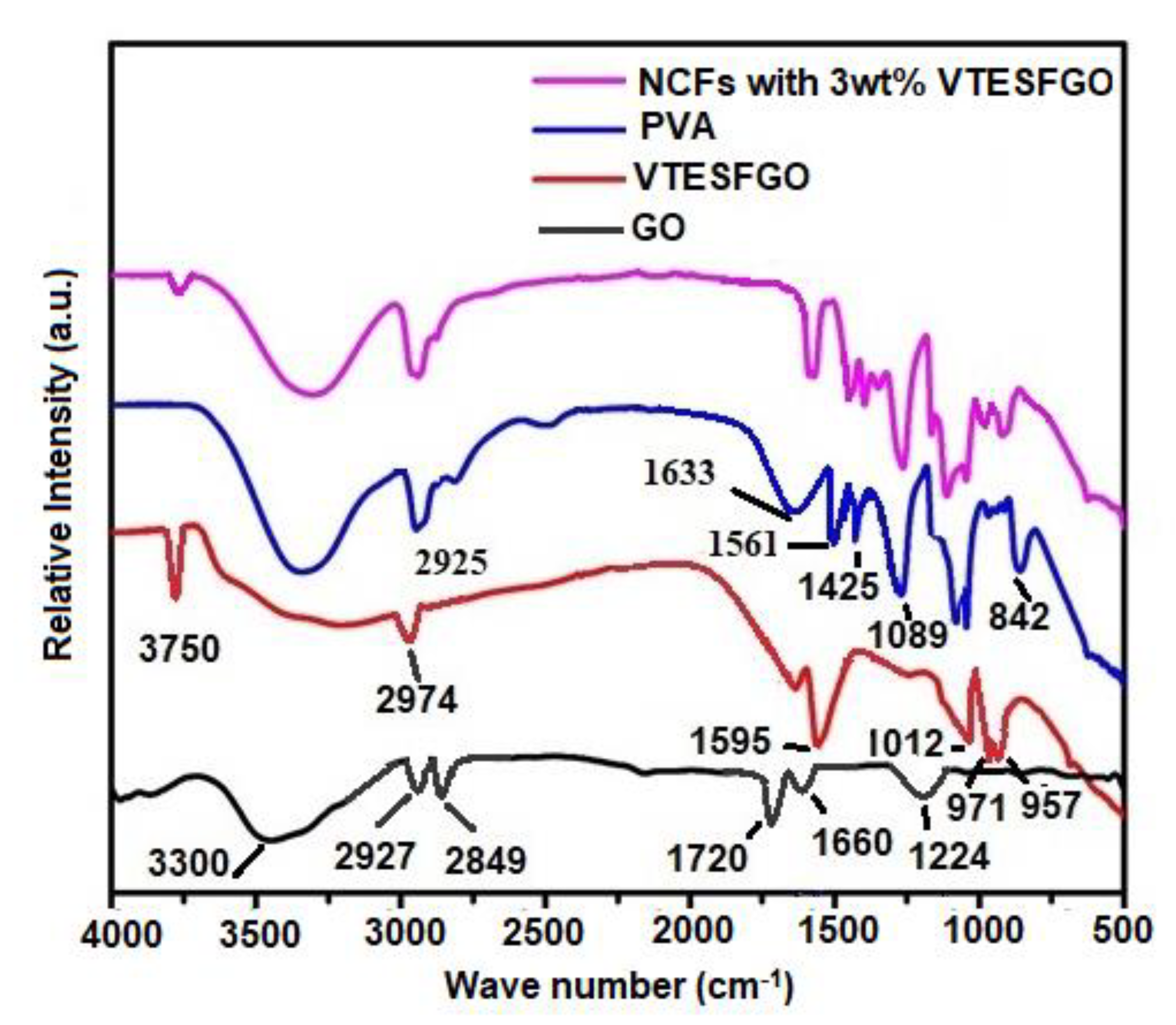
The chemical composition of the VTESFGO was evaluated by comparing its FTIR spectrum with those of GO as shown in
Figure 3 along with spectra of PVA and NCFs. The FTIR spectrum of VTESFGO shows peaks owing to the wagging of the -CH
2 group of Si-CH=CH2 at 957 cm
-1, stretching of Si-O-C at 971 cm
-1, Si-O-Si network construction at 1,012 cm
-1, Si-OH termination of this network at 3750 cm
-1, C=C group of VTES at 1,595 cm
-1, and vinyl’s CH stretching at 2,974 cm
-1, respectively [
36,
37,
38]. FTIR Spectrum shows peaks owing to C-OH stretching at 1224 cm
-1, C=C stretching at 1660 cm
-1, C=O stretching at 1720 cm
-1, asymmetric and symmetric stretching of CH
2 at 2849 and 2827 cm
-1 respectively. Band at 3300 cm
-1 is due to presence of OH groups on the surface of GO. The intensity of this band decreases when GO is functionalized with VTES indicating the involvement of OH group of GO in attachment of VTES on the surface of GO. These findings are in accordance with the results of XPS presented in
Figure 1.
3.2. Characterization of Nanocomposite Films (NCFs)
3.2.1. XRD Analysis of NCFs
The XRD results for the pure PVA, VTESFGO and NCFs are all presented in
Figure 2. The peak at 2θ = 9° represents the VTESFGO, as discussed previously. PVA, due to its semi-crystalline nature, shows its peak at 2θ = 19.76°. The peak at 2θ = 18.34° represents the VTESFGO/PVA nanocomposites, and its intensity shows a continuous rise with the increase in the concentration of VTESFGO. The NCFs show the individual characteristic peaks neither for the VTESFGO (2θ = 9°) nor for the pure PVA (2θ = 19.76°), indicating the homogenous distribution of VTESFGO in the PVA matrix during the fabrication of VTESFGO/PVA nanocomposite.
3.2.2. FT-IR Analysis of NCFs
The chemical composition of NCFs was verified by comparing its FTIR spectrum with those of PVA and VTESFGO, as shown in
Figure 3. The FTIR spectrum of pure PVA film exhibits peaks representing C–C stretching vibration at 842 cm
-1, C–O stretching at 1089 cm
-1, O–H bending at 1425 cm
-1, C=C stretching at 1561 and 1633 cm
-1, asymmetric –CH
2 group stretching vibration at 2925 cm
-1, and stretching vibration of the hydroxyl group by a band at 3300 cm
-1. On the other hand, the FTIR of NCFs with 3 wt% VTESFGO shows peaks corresponding to both VTESFGO and PVA. The intensity of the band at 3300 cm
-1 and the peak at 3750 cm
-1 decreases in the case of NCFs with 3wt% VTESFGO, indicating the formation of a bond between the Si-OH group of VTESFGO and the C–OH group of PVA. This bond between the nanofiller (VTESFGO) and the matrix (PVA) leads to strong interfacial adhesion, which results in extraordinary properties of the NCFs.
3.2.3. Mechanical Analysis of NCFs
The results of a mechanical examination of NCFs with various VTESFGO compositions are displayed in
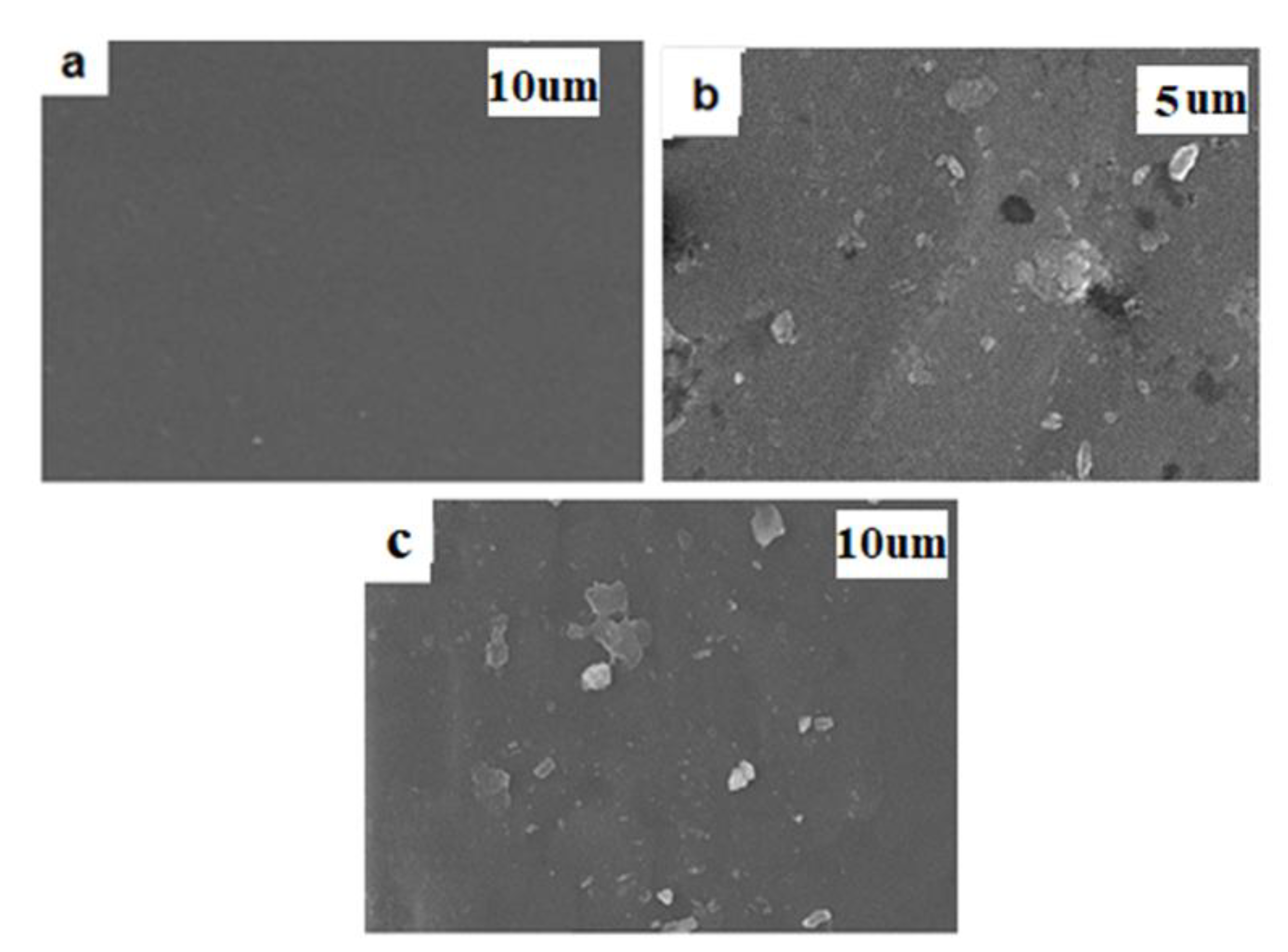
Table 1. This table shows that when VTESFGO quantities are increased to 0.8 weight percent, tensile strength and Young’s modulus first increase (88.26% and 93.64%, respectively) in relation to PVA before dropping. Elongation at break rises with the addition of 0.2 weight percent VTESFGO and then falls. Particulate matter might be the cause of the decrease in mechanical property values at high filler content, as can be observed in the SEM pictures in
Figure 4b,c.
3.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopic Analysis of NCFs
Scanning electron microscopic analysis as used to study the surface morphology of NCFS. For this purpose SEM image of NCFs was compared with SEM image of PVA. The SEM image of pure PVA in
Figure 4a shows a smooth and homogeneous surface, but the SEM images of the cracked surfaces of NCFs containing 3 weight percent VTESFGO in
Figure 4b,c shows some particulates which might be the consequence of silanol condensation on its own.
3.2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of NCFs
TGA was used to evaluate the thermal stability of NCFs, and the results are shown in
Figure 5, revealing that NCFs outperform PVA in terms of thermal stability, which increases with increasing VTESFGO concentration. The temperatures required to achieve 5% weight loss of NCFs with 0.2, 0.8, and 3.0% VTESFGO are 30.5, 75.0, and 105.5 oC higher than pure PVA, respectively. It also seems from this figure that the residual weight percentage at 600
oC increases with the increase in the VTESFGO levels and for NCF with 3.0% VTESFGO residual weight percentage is 47.5% greater compared to pure PVA, indicating a slower rate of breakdown and hence increased thermal stability, which might be related to the presence of VTESFGO, which slows the segmental movements of polymer chains by creating a network in the matrix [
39].
3.2.6. Oxygen Transmission Rate Analysis of NCFs
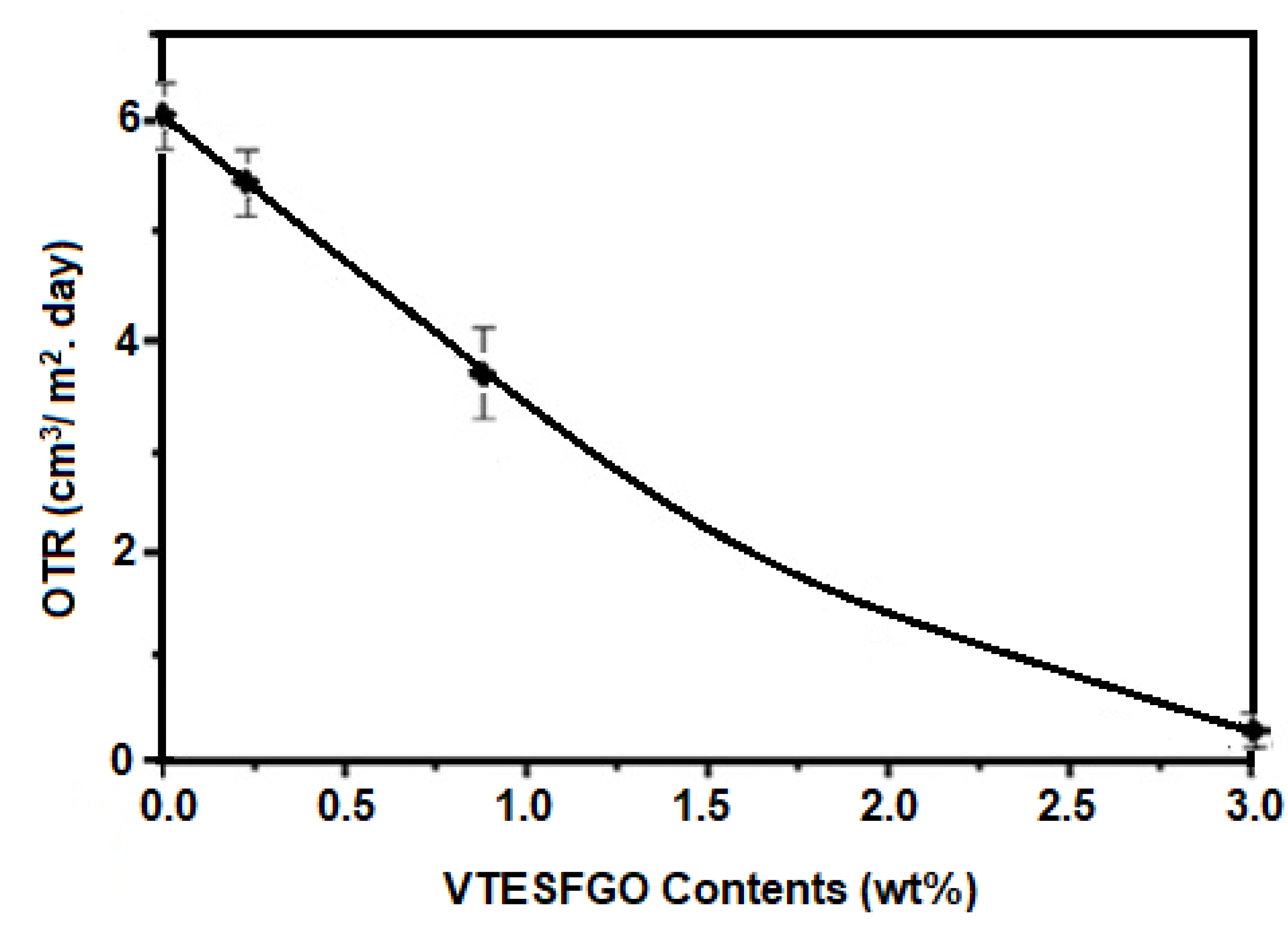
The oxygen transmission rate (OTR) of pure PVA and NCFs with varying VTESFGO concentrations was examined, and the findings are shown in
Figure 6, indicating that the addition of VTESFGO significantly lowers the permeance of oxygen for NCFs when compared to pure PVA. The OTR for NCFs with 0.2 wt.% VTESFGO is 5.4 cm3/m2 per day, which decreases to 0.3 cm3/m2 per day for 3 wt.% VTESFGO, compared to 6.12 cm3/m2 per day for pure PVA. This decrease in OTR may be related to the existence of a Si-O-Si network in NCFs [
40].
3.2.7. Water Resistance Pressure (WRP) Analysis of NCFs
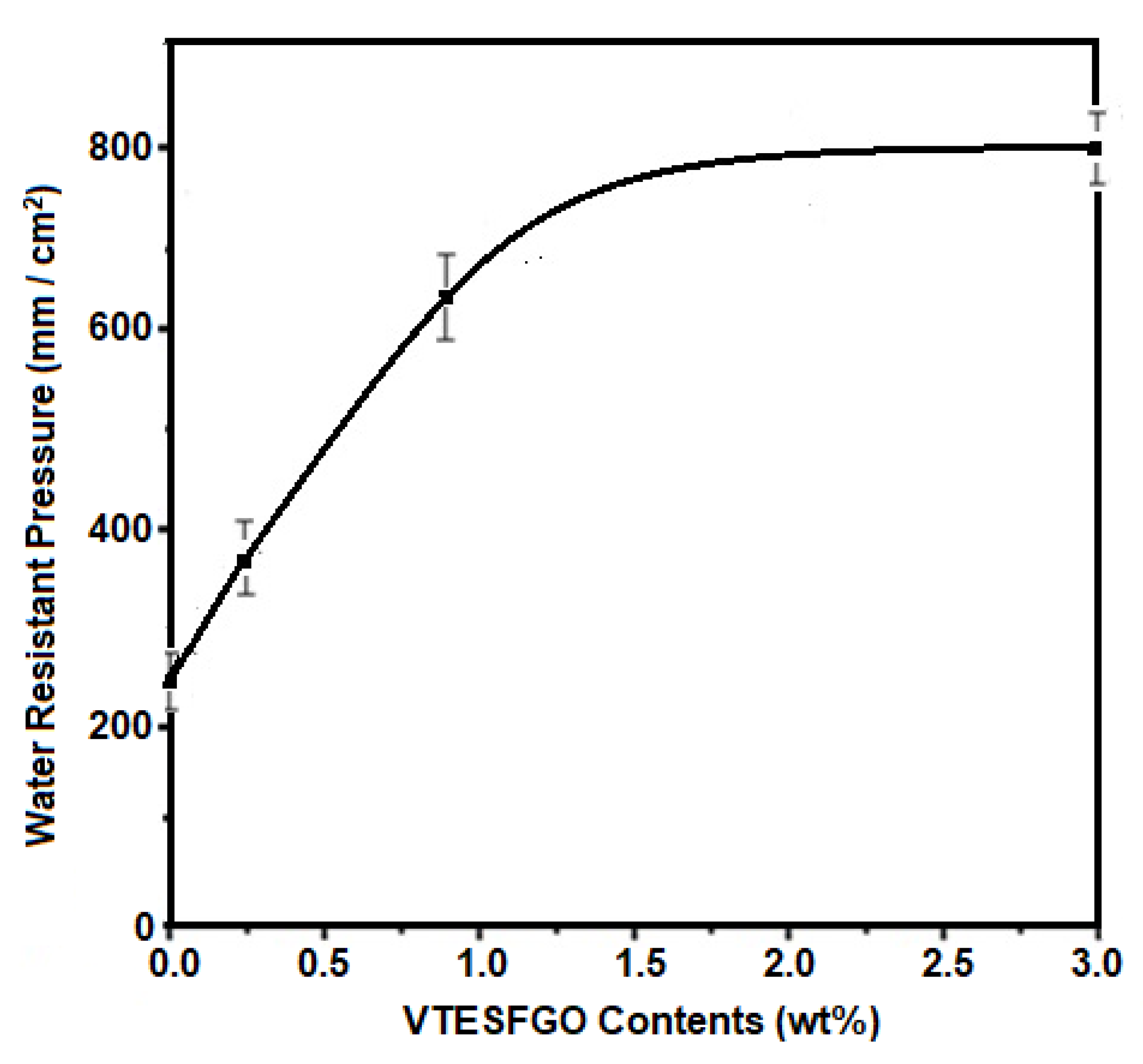
Water resistance pressure (WRP) for NCFs was measured, and the findings are shown in
Figure 7, indicating that adding VTESFGO increases water resistance pressure. NCFs with 3.0 weight percent VTESFGO improves by 212%, with a value of 780 mm/cm2, perhaps due to the creation of a Si-O-Si network in NCFs, which improves the structural integrity and morphology of NCFs.
5. Conclusions
The present study reports successful functionalization of GO with VTES. Varying concentrations (0.2 to 3 wt. %) of VTES functionalized graphene oxide (VTESFGO) were utilized to reinforce PVA for enhanced oxygen transmission resistance and water pressure resistance. The study revealed that the nanocomposite films (NCFs) developed a three-dimensional Si-O-Si network through the interactions between the hydroxyl groups of PVA and the hydroxyl groups of silanols present in VTESFGO, which resulted in a homogeneous and dense composite system. Moreover, the thermal stability of these NCFs improved significantly, with a residual amount of 47.5 wt. % remaining for NCF with 3.0 wt. % VTESFGO. The NCF reinforced with 3.0 wt. % VTESFGO exhibited a remarkable 96.73% increase in oxygen transmission rate and a 212% improvement in water resistance pressure compared to pure PVA film, making these NCFs a promising candidate for various coatings, films, and packaging applications.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R628), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for supporting this research.
References
- Muller, C.; Neves, L.E.; Gomes, L.; Guimarães, M.; Ghesti, G. Processes for alcohol-free beer production: A review. Food Science and Technology 2019, 40, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cornish, K.; Vodovotz, Y. Narrowing the gap for bioplastic use in food packaging: an update. Environmental science & technology 2020, 54, 4712–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K. , Jiang, Z., Zhao, F., Wang, W., Jäkle, F., Wang, N., Tang, X., Yin, X., Chen, P. Triarylboron-Doped Acenethiophenes as Organic Sonosensitizers for Highly Efficient Sonodynamic Therapy with Low Phototoxicity. Advanced Materials 2022, 34, 2206594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y. , Shen, Z., Long, X., Chen, C., Qi, L.,... Chao, X. Gaussian filtering method of evaluating the elastic/elasto-plastic properties of sintered nanocomposites with quasi-continuous volume distribution. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2023, 872, 145001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.K.; Arnott, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plastic degradation and its environmental implications with special reference to poly (ethylene terephthalate). Polymers 2012, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Park, H.-M.; Ha, C.-S. Bio-nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Progress in polymer science 2013, 38, 1629–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. , Sun, P., Ye, L., Xu, D. Progress of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor in Municipal Wastewater Treatment. Science of Advanced Materials 2023, 15, 1277–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. , Xu, Y., Zhai, W., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Cheng, S., Zhang, H. In-situ growth of robust superlubricated nano-skin on electrospun nanofibers for post-operative adhesion prevention. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jridi, M.; Hajji, S.; Ayed, H.B.; Lassoued, I.; Mbarek, A.; Kammoun, M.; Souissi, N.; Nasri, M. Physical, structural, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of gelatin–chitosan composite edible films. International journal of biological macromolecules 2014, 67, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C. , Awasthi, A.P., Sung, J., Geubelle, P.H., Sottos, N.R. Multi-scale model of effects of roughness on the cohesive strength of self-assembled monolayers. International Journal of Fracture 2017, 208, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selke, S.E.; Culter, J.D.; Auras, R.A.; Rabnawaz, M. Plastics packaging: properties, processing, applications, and regulations; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH Co KG: 2021.
- Zhang, C. , Awasthi, A.P., Geubelle, P.H., Grady, M.E., Sottos, N.R. Effects of interface roughness on cohesive strength of self-assembled monolayers. Applied Surface Science 2017, 397, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.W.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhu, A.M. Pervaporation dehydration of water/ethanol/ethyl acetate mixtures using poly (vinyl alcohol)–silica hybrid membranes. Journal of applied polymer science 2012, 126, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, I.; Daştan, H.; Altaş, A.; Yayli, A.; Atakol, O.; Aksu, M. Preparation and Characterization of PVA/Boron Polymer Produced by an Electrospinning Technique. e-Polymers 2007, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapalidis, A.; Katsaros, F.; Steriotis, T.A.; Kanellopoulos, N. Properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)—Bentonite clay nanocomposite films in relation to polymer–clay interactions. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2012, 123, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, F.; Dong, S.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y. Thermal, mechanical and chemical properties of hydrophilic poly (vinyl alcohol) film improved by hydrophobic poly (propylene glycol). Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering 2013, 52, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; De Sarkar, M.; Bhowmick, A. Poly (vinyl alcohol)/silica hybrid nanocomposites by sol-gel technique: Synthesis and properties. Journal of materials science 2005, 40, 5233–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.; Kim, D.; Seo, J.; Han, H. Preparation and properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)/vinyltrimethoxysilane (PVA/VTMS) hybrid films with enhanced thermal stability and oxygen barrier properties. Macromolecular Research 2014, 22, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapalidis, A.; Katsaros, F.; Steriotis, T.A.; Kanellopoulos, N. Properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)—Bentonite clay nanocomposite films in relation to polymer–clay interactions. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2012, 123, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, M.; Shang, X. Preparation of graphene/poly (vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical properties and water resistance. Polymer International 2011, 60, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W. Preparation and barrier property of poly (vinyl alcohol)/SiO 2 hybrid coating films. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering 2008, 25, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumova, M.; Lopez, D.; Benavente, R.; Mijangos, C.; Perena, J. Effect of crosslinking on the mechanical and thermal properties of poly (vinyl alcohol). polymer 2000, 41, 9265–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Shao, C.L.; Lee, D.R.; Park, S.J.; Kwag, G.B.; Choi, K.J. Preparation and characterization of a nanoscale poly (vinyl alcohol) fiber aggregate produced by an electrospinning method. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics 2002, 40, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.; Takahashi, R.; Terauchi, A. Phase structure and mechanical and adhesion properties of epoxy/silica hybrids. Polymer 2001, 42, 5151–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.H.; Dong, J.H.; Qiu, K.Y.; Wei, Y. Preparation of poly (methyl acrylate-co-itaconic anhydride)/SiO2 hybrid materials via the sol–gel process—The effect of the coupling agent, inorganic content, and nature of the catalyst. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry 2000, 38, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Dong, J.H.; Qiu, K.Y.; Wei, Y. Effect of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane on properties of poly (butyl acrylate-co-maleic anhydride)/silica hybrid materials. Journal of applied polymer science 1999, 73, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-L.; Ma, C.-C.M. Synthesis, characterization and thermal properties of novel epoxy containing silicon and phosphorus nanocomposites by sol–gel method. European polymer journal 2002, 38, 2219–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luceño-Sánchez, J.A.; Maties, G.; Gonzalez-Arellano, C.; Diez-Pascual, A.M. Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide derivatives via functionalization reaction with hexamethylene diisocyanate. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Ruan, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, J.; Wo, Y.; Guo, S.; Cui, D. Biocompatibility of graphene oxide. Nanoscale Res Lett 2011, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Liu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xie, Y.; Cai, Z.; Xu, B. UV-cured organic-inorganic hybrid networks for durable antifogging coating. Progress in Organic Coatings 2024, 186, 108012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Xiang, Y.; Cai, E.; Ge, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Shen, J. Inorganic–organic hybrid nanomaterials for photothermal antibacterial therapy. Coordination Chemistry Reviews 2023, 496, 215426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.-S.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.-S. Improving the thermal and mechanical properties of silicone polymer by incorporating functionalized graphene oxide. Journal of Materials Science 2013, 48, 5287–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G. Properties of polyurethane-poly (2, 2, 3, 3-tetrafluoropropyl acrylate) triblock copolymer aqueous dispersion and its film cast from the dispersion. Fibers and Polymers 2007, 8, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, F.; Shan, C.; Han, D.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, L.; Ivaska, A. Covalent functionalization of chemically converted graphene sheets via silane and its reinforcement. Journal of Materials Chemistry 2009, 19, 4632–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrin, H.; Higgins, D.; Jun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fowler, M. Functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposite membrane for low humidity and high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2011, 115, 20774–20781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, T.; Chen, Y. Molecular-level dispersion of graphene into poly (vinyl alcohol) and effective reinforcement of their nanocomposites. Advanced Functional Materials 2009, 19, 2297–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Fang, J.; Xu, H.; Yin, J. Graphene oxide/polybenzimidazole composites fabricated by a solvent-exchange method. Carbon 2011, 49, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Q.L.; Shi, F.F.; Xiong, Y. Structure and permeation of organic–inorganic hybrid membranes composed of poly (vinyl alcohol) and polysilisesquioxane. Journal of Materials Chemistry 2008, 18, 4646–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagar, M.; Majeed, S.A.; Selvaganapathi, A.; Gnanasundaram, P. Studies on thermal, thermal ageing and morphological characteristics of EPDM-g-VTES/LLDPE. European polymer journal 2006, 42, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Q.L.; Meng, X.J.; Broadwell, I. Structure and pervaporation performance of novel quaternized poly (vinyl alcohol)/γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane hybrid membranes. Journal of applied polymer science 2010, 118, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawhecker, K.; Manias, E. Structure and properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)/Na+ montmorillonite nanocomposites. Chemistry of materials 2000, 12, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coclite, A.M.; Milella, A.; d’Agostino, R.; Palumbo, F. On the relationship between the structure and the barrier performance of plasma deposited silicon dioxide-like films. Surface and Coatings Technology 2010, 204, 4012–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).