Submitted:
23 May 2024
Posted:
23 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Patients
Cell Lines
Multiparametric Spectral Cytometry Immunophenotypic Studies
Cytotoxicity and Proliferation Assay
Data Analysis
Statistical Analysis
Results
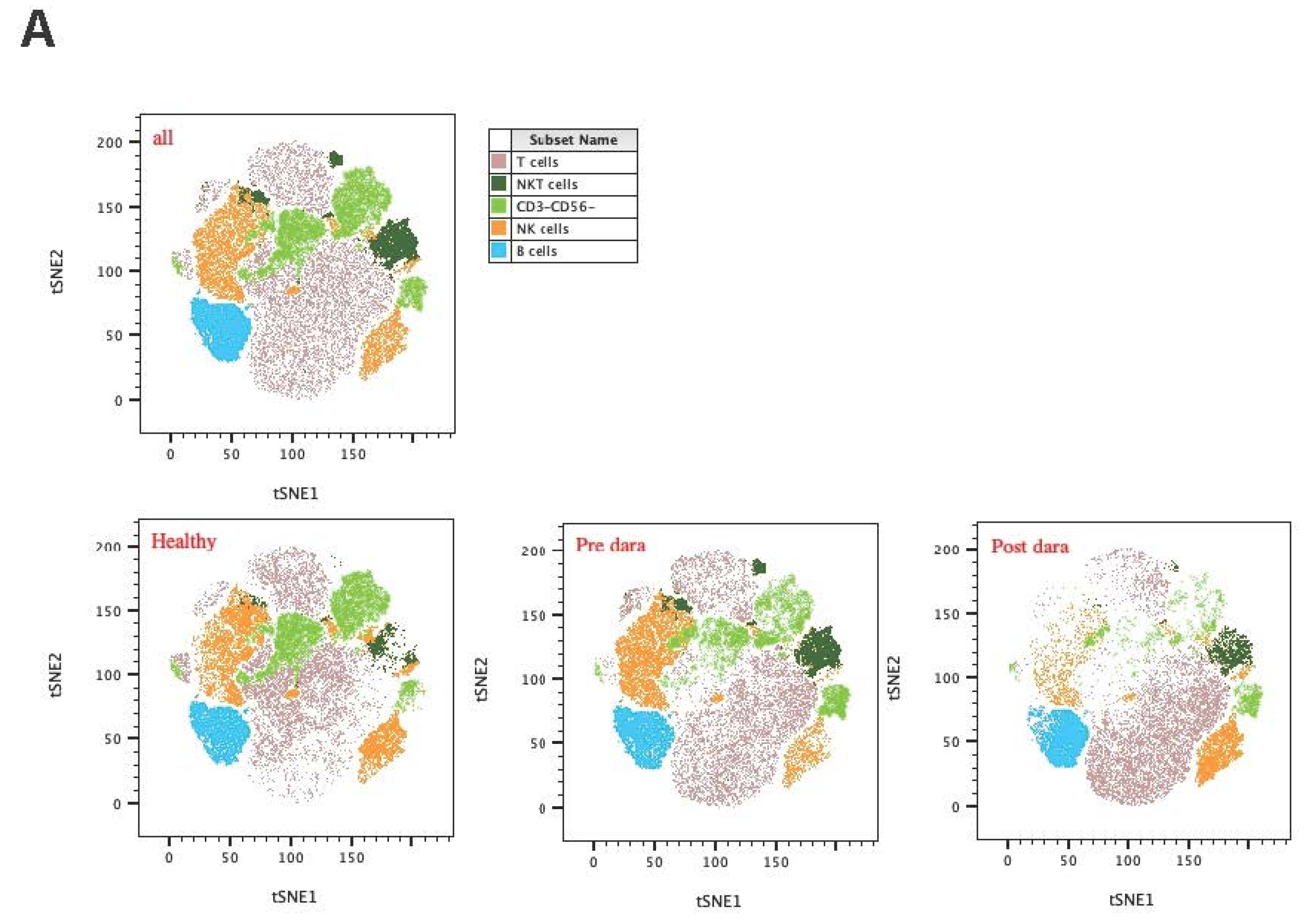
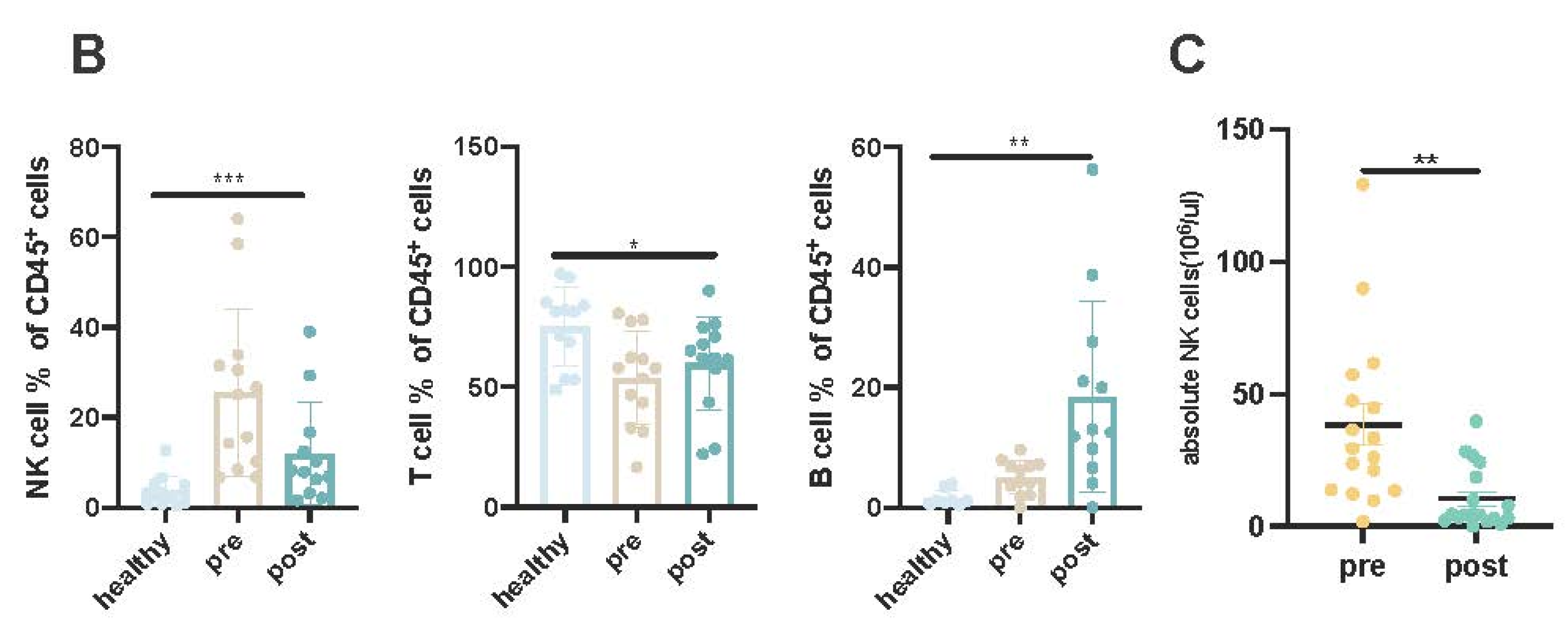
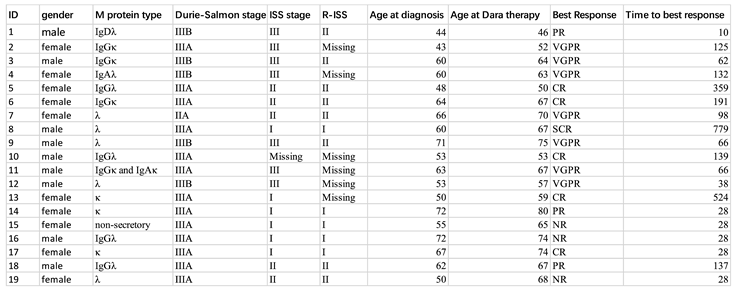
Cohort Characteristics
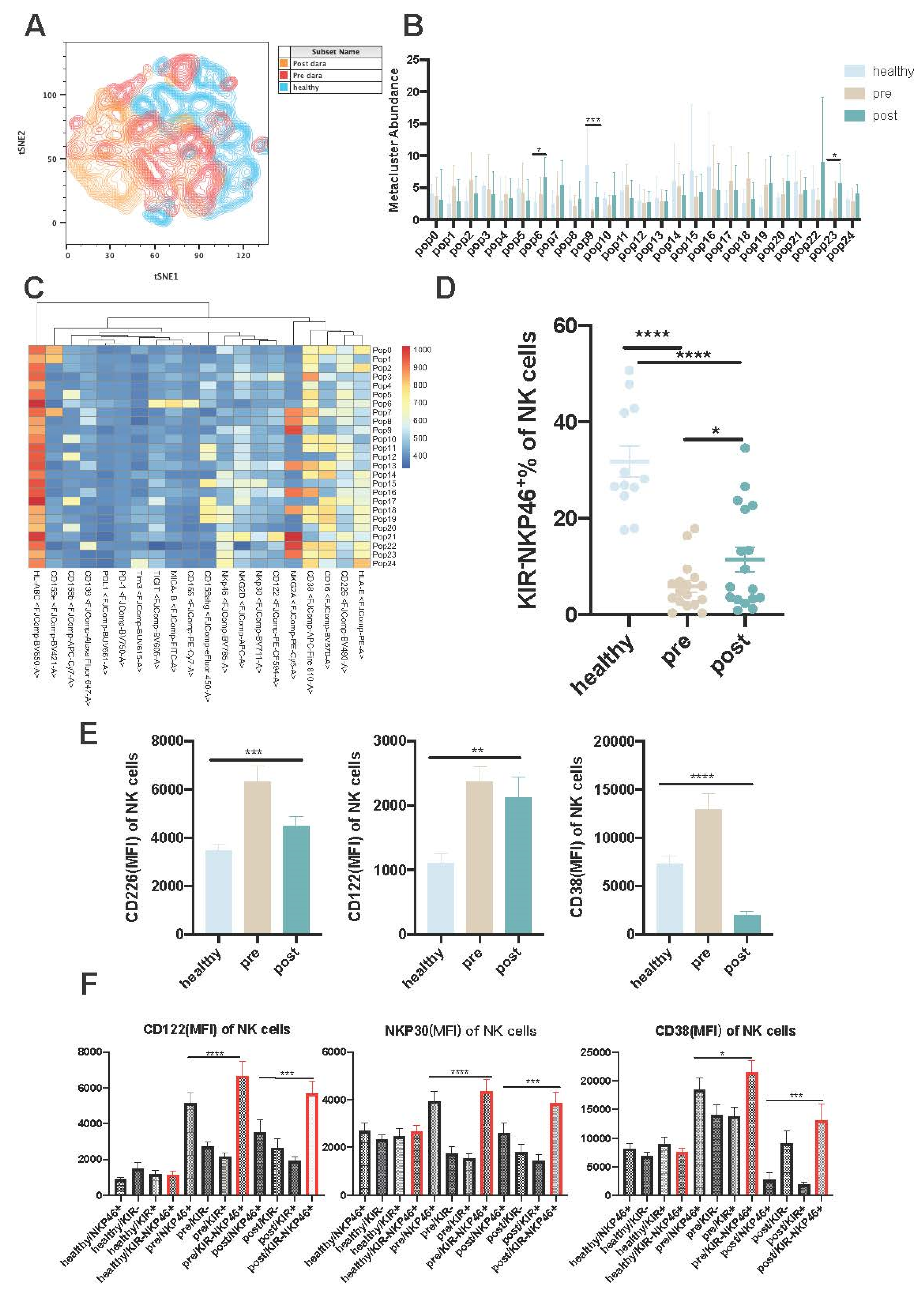
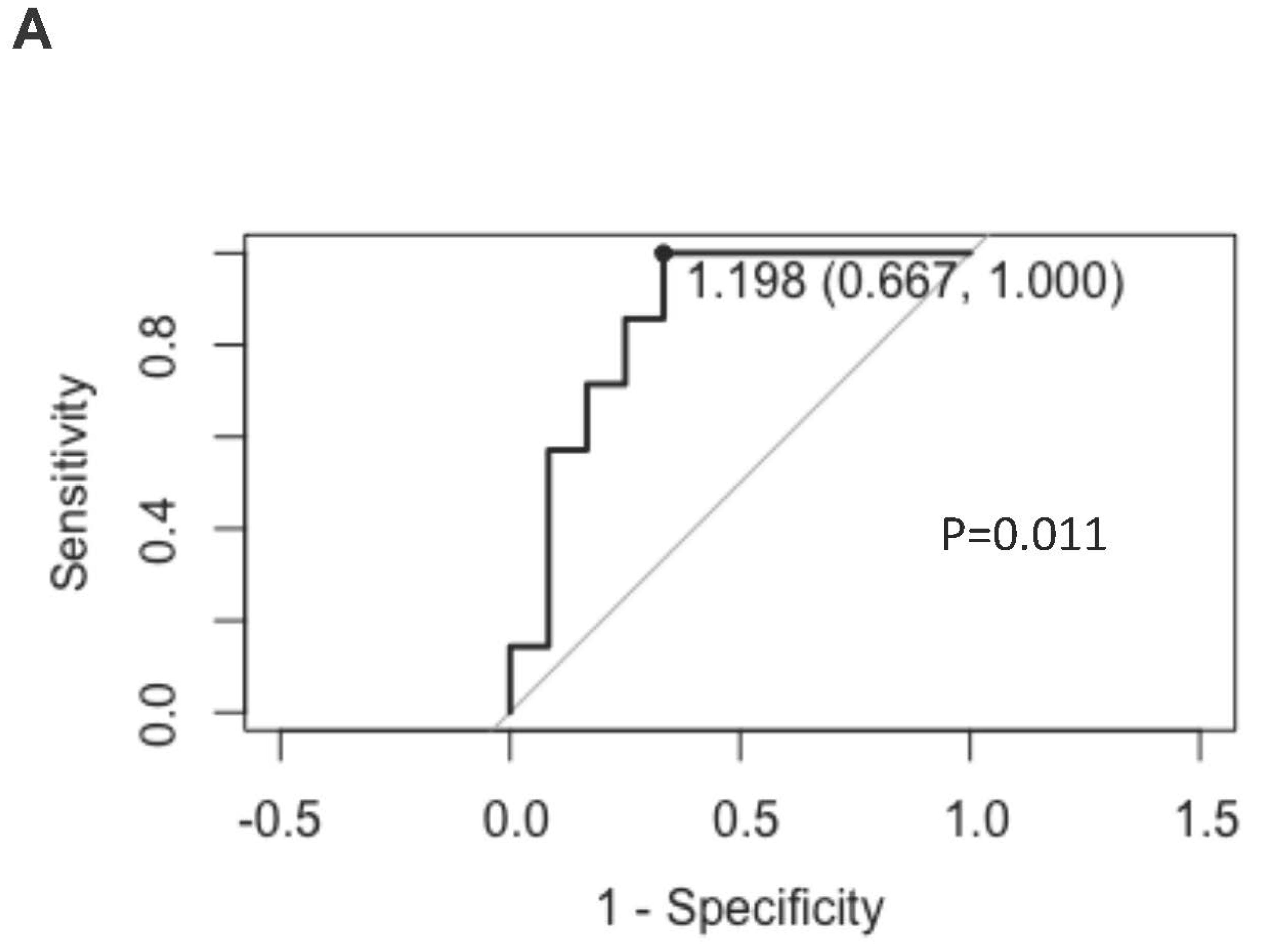
Increased Activated KIR-NKP46+ NK Cells Post Daratumumab Treatment
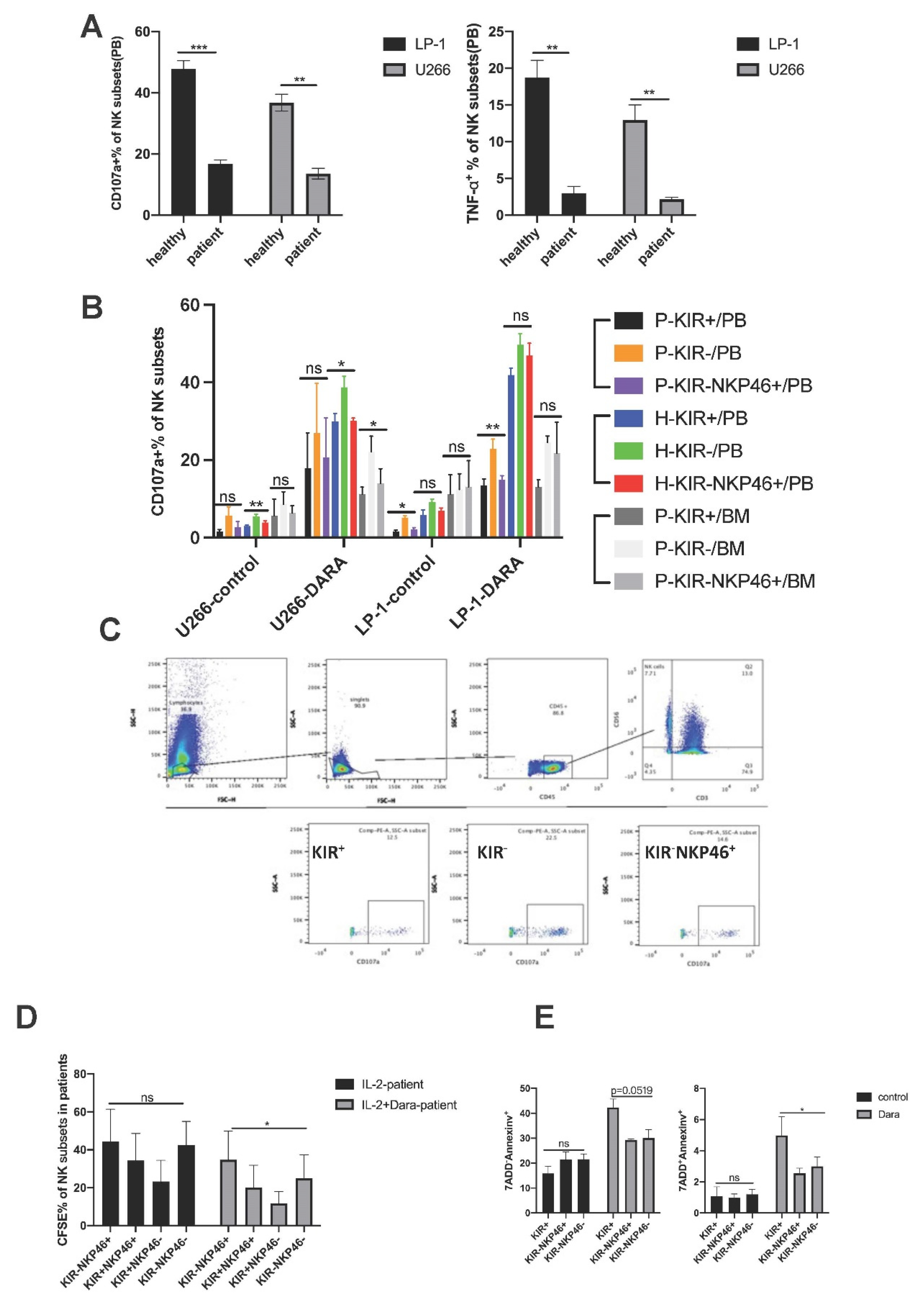
KIR-NKP46+ Subpopulations Are Resistant to Dara-Induced NK Cell Fratricide and Exert Sustainable Anti-MM Effects
Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgment
Declaration of interests
References
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, V.; Kyle, R.A.; et al. Multiple myeloma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017, 3, 17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.Z.; Weiss, B.M.; Plesner, T.; Bahlis, N.J.; Belch, A.; Lonial, S.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Voorhees, P.M.; Richardson, P.G.; Chari, A.; et al. Clinical efficacy of daratumumab monotherapy in patients with heavily pretreated relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2016, 128, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, V.; Gormley, N.J.; Luo, L.; et al. FDA approval summary: Daratumumab for treat- ment of multiple myeloma after one prior therapy. Oncologist. 2017, 22, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Oriol, A.; Nahi, H.; et al. ; POLLUX Investigators. Daratumumab, lenali- domide, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2016, 375, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Van De Donk, N.W.C.J.; Janmaat, M.L.; Mutis, T.; Lammerts Van Bueren, J.J.; Ahmadi, T.; Sasser, A.K.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Parren, P.W.H.I. Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD 38 in hematological malignancies and beyond. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 270, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejcik, J.; Casneuf, T.; Nijhof, I.S.; et al. Daratumumab depletes CD38 immune regulatory cells, promotes T-cell expansion, and skews T-cell repertoire in multiple mye- loma. Blood. 2016, 128, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigley A B, Spade S, Agha N H. ; et al.FcεRIγ-negative NK cells persist in vivo and enhance efficacy of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies in multiple myeloma. Blood advances 2021, 5, 3021–3031.
- Sivori, S.; Pende, D.; Bottino, C.; Marcenaro, E.; Pessino, A.; Biassoni, R.; Moretta, L.; Moretta, A. NKp46 is the major triggering receptor involved in the natural cytotoxicity of fresh or cultured human NK cells. Correlation between surface density of NKp46 and natural cytotoxicity against autologous, allogeneic or xenogeneic target cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahi, H.; Chrobok, M.; Gran, C.; Lund, J.; Gruber, A.; Gahrton, G.; Ljungman, P.; Wagner, A.K.; Alici, E. Infectious complications and NK cell depletion following daratumumab treatment of Multiple Myeloma. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0211927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kararoudi, M.N.; Nagai, Y.; Elmas, E.; Pereira, M.d.S.F.; Ali, S.A.; Imus, P.H.; Wethington, D.; Borrello, I.M.; Lee, D.A.; Ghiaur, G. CD38 deletion of human primary NK cells eliminates daratumumab-induced fratricide and boosts their effector activity. Blood The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2020, 136, 2416–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clara, J.A.; Levy, E.R.; Reger, R.; Barisic, S.; Chen, L.; Cherkasova, E.; Chakraborty, M.; Allan, D.S.J.; Childs, R. High-affinity CD16 integration into a CRISPR/Cas9-edited CD38 locus augments CD38-directed antitumor activity of primary human natural killer cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Phan, M.-T.T.; Kweon, S.; Yu, H.; Park, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Hwang, I.; Han, S.; Kwon, M.-J.; Cho, D. A Flow Cytometry-Based Whole Blood Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity Assay Using Overnight Cytokine Activation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, C.; Keam, S.P.; Yeang, H.X.A.; Neeson, M.; Richardson, K.; Hsu, A.K.; Canfield, R.; Bezman, N.; Robbins, M.; Quach, H.; et al. Myeloma natural killer cells are exhausted and have impaired regulation of activation. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2522–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfossi, N.; André, P.; Guia, S.; Falk, C.S.; Roetynck, S.; Stewart, C.A.; Breso, V.; Frassati, C.; Reviron, D.; Middleton, D.; et al. Human NK Cell Education by Inhibitory Receptors for MHC Class I. Immunity 2006, 25, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahlne, G.; Becker, S.; Brodin, P.; Johansson, M.H. IFN-γ Production and Degranulation are Differentially Regulated in Response to Stimulation in Murine Natural Killer Cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 2007, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazina, T.; MacFarlane, I.V. ; A. W.; Bernabei, L.; et al.Alterations of NK cell phenotype in the disease course of multiple myeloma. Cancers 2021, 13, 226. [Google Scholar]
- Romagne, F.; Andre, P.; Spee, P.; Zahn, S.; Anfossi, N.; Gauthier, L.; et al. Preclinical characterization of 1-7F9, a novel human anti-KIR receptor therapeutic antibody that augments natural killer-mediated killing of tumor cells. Blood 2009, 114, 2667–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.M.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Padmanabhan, S.; Suvannasankha, A.; Jagannath, S.; Abonour, R.; et al. A phase 1 trial of the anti-KIR antibody IPH2101 in patients with relapsed / refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 4324–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, N.; Carlsten, M.; Lee, M.-J.; Minter, A.; Tan, E.; Kwok, M.; Manasanch, E.; Bhutani, M.; Tageja, N.; Roschewski, M.; et al. A phase II trial of pan-KIR2D blockade with IPH2101 in smoldering multiple myeloma. Haematologica 2014, 99, e81–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.M.; Cohen, A.D.; Jagannath, S.; Munshi, N.C.; Spitzer, G.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Efebera, Y.A.; Andre, P.; Zerbib, R.; Caligiuri, M.A. A Phase I Trial of the Anti-KIR Antibody IPH2101 and Lenalidomide in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4055–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohrt, H.E.; Thielens, A.; Marabelle, A.; Sagiv-Barfi, I.; Sola, C.; Chanuc, F.; Fuseri, N.; Bonnafous, C.; Czerwinski, D.; Rajapaksa, A.; et al. Anti-KIR antibody enhancement of anti-lymphoma activity of natural killer cells as monotherapy and in combination with anti-CD20 antibodies. Blood 2014, 123, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewen, E.M.; Pahl, J.H.; Miller, M.; et al. KIR downregulation by IL-12/15/18 unleashes human NK cells from KIR/HLA-I inhibition and enhances killing of tumor cells. European journal of immunology 2018, 48, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





