Submitted:
21 May 2024
Posted:
23 May 2024
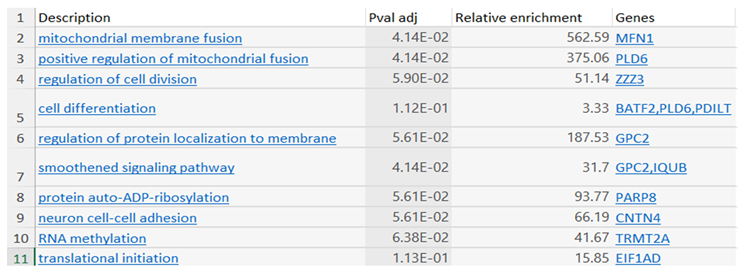
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Results
| Ligand | Binding Affinity |
| GPC2 + Ursolic acid | 8.7 |
| PDILT + Ursolic acid | 8.6 |
| MFN1 + Ursolic acid | 8.2 |
| ZZZ3 + Ursolic acid | 7.1 |

Discussion
Conclusion
References
- Sun, Y. S., Zhao, Z., Yang, Z. N., Xu, F., Lu, H. J., Zhu, Z. Y., ... & Zhu, H. P. (2017). Risk factors and preventions of breast cancer. International journal of biological sciences, 13(11), 1387.
- Stewart BW, and Wild CP. World Cancer Report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press; 2014.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, and Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017; 67: 7-30.
- Polyak K. Breast cancer: origins and evolution. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117: 3155-3163. [CrossRef]
- . Valenti G, Quinn HM, Heynen G, et al. Cancer Stem Cells Regulate Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts via Activation of Hedgehog Signalling in Mammary Gland Tumors. Cancer Res. 2017; 77: 2134-2147. [CrossRef]
- Eisemann N, Waldmann A, Geller AC, Weinstock MA, Volkmer B, Greinert R, Breitbart EW and Katalinic A: Non-melanoma skin cancer incidence and impact of skin cancer screening on incidence. J Invest Dermatol 134: 43-50, 2014.
- Muzic JG, Schmitt AR, Wright AC, Alniemi DT, Zubair AS, Olazagasti Lourido JM, Sosa Seda IM, Weaver AL and Baum CL: Breast cancer: A population-based study in olmsted county, minnesota, 2000 to 2010. Mayo Clin Proc 92: 890-898, 2017.
- Burton KA, Ashack KA and Khachemoune breast cancer: A review of high-risk and metastatic disease. Am J Clin Dermatol 17: 491-508, 2016.
- Diepgen T, Fartasch M, Drexler H and Schmitt J: Occupational breast cancer induced by ultraviolet radiation and its prevention. Br J Dermatol 167 (Suppl 2): S76-S84, 2012.
- Boeckx C, Baay M, Wouters A, Specenier P, Vermorken JB, Peeters M and Lardon F: Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Focus on potential molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. Oncologist 18: 850-864, 2013.
- Moosavinasab S, Patterson J, Strouse R, Rastegar-Mojarad M, Regan K, Payne PR, Huang Y and Lin SM: ‘RE:fine drugs’: An interactive dashboard to access drug repurposing opportunities. Database (Oxford) 2016: pii: baw083, 2016.
- Andronis C, Sharma A, Virvilis V, Deftereos S and Persidis A: Literature mining, ontologies and information visualization for drug repurposing. Brief Bioinform 12: 357-368, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Liu H, Beck TN, Golemis EA and Serebriiskii IG: Integrating in silico resources to map a signaling network. Methods Mol Biol 1101: 197-245, 2014.
- Baran J, Gerner M, Haeussler M, Nenadic G and Bergman CM: pubmed2ensembl: A resource for mining the biological literature on genes. PLoS One 6: e24716, 2011.
- Carmona-Saez P, Chagoyen M, Tirado F, Carazo JM and Pascual-Montano A: GENECODIS: A web-based tool for finding significant concurrent annotations in gene lists. Genome Biol 8: R3, 2007.
- Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-CepasJ, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos A, Tsafou KP, et al.: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43: D447-D452, 2015.
- Harbeck N, Beckmann MW, Rody A, Schneeweiss A, Müller V, Fehm T, Marschner N, Gluz O, Schrader I, Heinrich G, et al.: HER2 dimerization inhibitor pertuzumab-mode of action and clinical data in breast cancer. Breast Care (Basel) 8: 49-55, 2013. ttps://doi.org/10.1159/000346837.
- Balduzzi S, Mantarro S, Guarneri V, Tagliabue L, Pistotti V, Moja L and D’Amico R: Trastuzumab-containing regimens for metastatic breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD006242, 2014.
- Jacob, R. B., Andersen, T., & McDougal, O. M. (2012). Accessible high-throughput virtual screening molecular docking software for students and educators. PLoS computational biology, 8(5), e1002499. [CrossRef]
- Kondapuram, S. K., Sarvagalla, S., & Coumar, M. S. (2021). Docking-based virtual screening using PyRx Tool: autophagy target Vps34 as a case study. In Molecular Docking for Computer-Aided Drug Design (pp. 463-477). Academic Press.
- Majewska, A., Wolska, E., Śliwińska, E., Furmanowa, M., Urbańska, N., Pietrosiuk, A., ... & Kuraś, M. (2003). Antimitotic effect, G2/M accumulation, chromosomal and ultrastructure changes in meristematic cells of Allium cepa L. root tips treated with the extract from Rhodiola rosea roots. Caryologia, 56(3), 337-351.
- Van de Bovenkamp, M., Groothuis, G. M. M., Meijer, D. K. F., & Olinga, P. (2007). Liver fibrosis in vitro: cell culture models and precision-cut liver slices. Toxicology in vitro, 21(4), 545-557. [CrossRef]
- Naik, R. S., Mujumdar, A. M., & Ghaskadbi, S. (2004). Protection of liver cells from ethanol cytotoxicity by curcumin in liver slice culture in vitro. Journal of ethnopharmacology, 95(1), 31-37. [CrossRef]
- Wood JP, Smith AJ, Bowman KJ, Thomas AL and Jones GD: Comet assay measures of DNA damage as biomarkers of irino- tecan response in colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Med 4: 1309-1321, 2015.
- Cogle CR, Scott BL, Boyd T and Garcia-Manero G: Oral azaciti- dine (CC-486) for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Oncologist 20: 1404-1412, 2015.
- Su G, Morris JH, Demchak B and Bader GD: Biological network exploration with Cytoscape 3. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 47: 8.13.1-24, 2014.
- Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al.: Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBio- Portal. Sci Signal 6: pl1, 2013.
- Wagner AH, Coffman AC, Ainscough BJ, Spies NC, Skidmore ZL, Campbell KM, Krysiak K, Pan D, McMichael JF, Eldred JM, et al.: DGIdb 2.0: Mining clinically relevant drug-gene interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 44: D1036-D1044, 2016.
- Ribas A and Flaherty KT: BRAF targeted therapy changes the treatment paradigm in melanoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8: 426-433, 2011.
- UniProt Consortium. (2019). UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic acids research, 47(D1), D506-D515. [CrossRef]
- Karsch-Mizrachi I., Takagi T., Cochrane G.International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration The international nucleotide sequence database collaboration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; 46:D48–D51.
- Giraldo-Calderón G.I., Emrich S.J., MacCallum R.M., Maslen G., Dialynas E., Topalis P., Ho N., Gesing S.VectorBase ConsortiumVectorBase ConsortiumMadey G.et al. VectorBase: an updated bioinformatics resource for invertebrate vectors and other organisms related with human diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; 43:D707–D713. [CrossRef]
- Zerbino D.R., Achuthan P., Akanni W., Amode M.R., Barrell D., Bhai J., Billis K., Cummins C., Gall A., Girón C.G.et al. Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; 46:D754–D761. [CrossRef]
- Chen C., Natale D.A., Finn R.D., Huang H., Zhang J., Wu C.H., Mazumder R. Representative proteomes: a stable, scalable and unbiased proteome set for sequence analysis and functional annotation. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e18910.
- Chen C., Huang H., Mazumder R., Natale D.A., McGarvey P.B., Zhang J., Polson S.W., Wang Y., Wu C.H., Consortium UniProt Computational clustering for viral reference proteomes. Bioinformatics. 2016; 32:2041–2043.
- Mitchell A.L., Scheremetjew M., Denise H., Potter S., Tarkowska A., Qureshi M., Salazar G.A., Pesseat S., Boland M.A., Hunter F.M.I.et al. EBI Metagenomics in 2017: enriching the analysis of microbial communities, from sequence reads to assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; 46:D726–D735.
- Gene Ontology Consortium The Gene Ontology project in 2008. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008; 36:D440–D444.
- Hastings J., Owen G., Dekker A., Ennis M., Kale N., Muthukrishnan V., Turner S., Swainston N., Mendes P., Steinbeck C. ChEBI in 2016: Improved services and an expanding collection of metabolites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016; 44:D1214–D1219. [CrossRef]
- Poux S., Arighi C.N., Magrane M., Bateman A., Wei C.-H., Lu Z., Boutet E., Bye-A-Jee H., Famiglietti M.L., Roechert B.et al. On expert curation and scalability: UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot as a case study. Bioinformatics. 2017; 33:3454–3460.
- Orchard S., Kerrien S., Abbani S., Aranda B., Bhate J., Bidwell S., Bridge A., Briganti L., Brinkman F.S.L., Cesareni G.et al. Protein interaction data curation: the International Molecular Exchange (IMEx) consortium. Nat. Methods. 2012; 9:345–350. [CrossRef]
- Rao, V. S., Srinivas, K., Sujini, G. N., & Kumar, G. N. (2014). Protein-protein interaction detection: methods and analysis. International journal of proteomics, 2014.
- Pillutla, R. C., Fisher, P. B., Blume, A. J., & Goldstein, N. I. (2002). Target validation and drug discovery using genomic and protein–protein interaction technologies. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets, 6(4), 517-531. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y., Wang, Q., & Wang, T. (2017). Drug target protein-protein interaction networks: a systematic perspective. BioMed research international, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Archakov, A. I., Govorun, V. M., Dubanov, A. V., Ivanov, Y. D., Veselovsky, A. V., Lewi, P., & Janssen, P. (2003). Protein-protein interactions as a target for drugs in proteomics. Proteomics, 3(4), 380-391. [CrossRef]
- Scott, D. E., Bayly, A. R., Abell, C., & Skidmore, J. (2016). Small molecules, big targets: drug discovery faces the protein–protein interaction challenge. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 15(8), 533-550.
- Wang R, Lai L, Wang S (2002) Further development and validation of empirical scoring functions for structure-based binding affinity prediction. J Comput-Aided Mol Des 16: 11–26.
- Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (1990) Automated docking of substrates to proteins by simulated annealing. Proteins 8: 195–202.
- Ounthaisong, U., & Tangyuenyongwatana, P. (2017). Cross-docking study of flavonoids against tyrosinase enzymes using PyRx 0.8 virtual screening tool. TJPS, 41(2017).
- Morris G, Goodsell D, Halliday R, Huey R, Hart W (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical free energy function. J Comput Chem 19: 1639–1662.
- Kavitha, M., Srinivasan, P. T., Renuga, G., & Jayakumar, L. V. (2014). Evaluation of Antimitotic Activity of Mukia maderaspatana L. Leaf Extract in Allium cepa Root Model. International Journal of Pharmacy Research & Technology (IJPRT), 4(2), 1-4.
- Aşkin Çelik, T., & Aslantürk, Ö. S. (2006). Anti-mitotic and anti-genotoxic effects of Plantago lanceolata aqueous extract on Allium cepa root tip meristem cells. Biologia, 61, 693-697. [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, A., Nagalakshmi, A., & Rao, U. M. (2011). Study of cytotoxic and antimitotic activities of Solanum nigrum by using Allium cepa root tip assay and cancer chemopreventive activity using MCF-7-human mammary gland breast adenocarcinoma cell lines. Int J Sci Technol, 1(2), 26-48.
- Nordmann R, Ribièrea C, Rouach H. Implication of free radical mechanisms in ethanol-induced cellular injury. Free Radic Biol Med 1992;12:3219-40. [CrossRef]
- Artee GE. Oxidants and antioxidants in alcohol-induced liver disease. Gastroenterol 2003;124:778-90.
- Wu D, Cederbaum AI. Alcohol, oxidative stress, and free radical damage. Alcohol Res Health 2003;27:274-84.
- Kurose I, Higuchi H, Kato S, Miura S, Ishii H. Ethanol-induced oxidative stress in the liver. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 1996;20:77-85. [CrossRef]
- Kumaran A, Karunakaran RJ. In vitro antioxidant activities of methanol extracts of five Phyllanthus species from India. Food Sci Technol-LEB 2007;40:344-52. [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D., Franceschini, A., Wyder, S., Forslund, K., Heller, D., Huerta-Cepas, J., ... & Von Mering, C. (2015). STRING v10: protein–protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic acids research, 43(D1), D447-D452.
- Safari-Alighiarloo, N., Taghizadeh, M., Rezaei-Tavirani, M., Goliaei, B., & Peyvandi, A. A. (2014). Protein-protein interaction networks (PPI) and complex diseases. Gastroenterology and Hepatology from bed to bench, 7(1), 17.
- Saito, R., Smoot, M. E., Ono, K., Ruscheinski, J., Wang, P. L., Lotia, S., ... & Ideker, T. (2012). A travel guide to Cytoscape plugins. Nature methods, 9(11), 1069-1076. [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J. T., Ramage, D., ... & Ideker, T. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome research, 13(11), 2498-2504. [CrossRef]
- Smoot, M. E., Ono, K., Ruscheinski, J., Wang, P. L., & Ideker, T. (2011). Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics, 27(3), 431-432. [CrossRef]
- Noor, F., Tahir ul Qamar, M., Ashfaq, U. A., Albutti, A., Alwashmi, A. S., & Aljasir, M. A. (2022). Network pharmacology approach for medicinal plants: review and assessment. Pharmaceuticals, 15(5), 572. [CrossRef]
- S Azmi, A. (2013). Adopting network pharmacology for cancer drug discovery. Current drug discovery technologies, 10(2), 95-105.
- Pei, C., Yang, K., Chen, Y., Dong, Y., Meng, X., & Song, N. (2024). Mechanisms of action of Qinghao in treating breast cancer and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity based on network pharmacology and molecular docking.
- Hopkins, A. L. (2008). Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nature chemical biology, 4(11), 682-690. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z., Han, P., You, Z. H., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Yu, H., ... & Chen, X. (2017). In silico prediction of drug-target interaction networks based on drug chemical structure and protein sequences. Scientific reports, 7(1), 11174. [CrossRef]
- Irwin JJ, Shoichet BK (2004) ZINC – A free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J Chem Inf Model 45: 177–182.
- Collignon B, Schulz R, Smith JC, Baudry J (2011) Task-parallel message passing interface implementation of Autodock4 for docking of very large databases of compounds using high-performance super-computers. J Comp Chem 32: 1202–1209.
- Aşkin Çelik, T., & Aslantürk, Ö. S. (2006). Anti-mitotic and anti-genotoxic effects of Plantago lanceolata aqueous extract on Allium cepa root tip meristem cells. Biologia, 61, 693-697. [CrossRef]
- Palamanda JR, Kehre JP. Inhibition of protein carbonyl formation and lipid peroxidation by glutathione in rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys 1992;293:103-9.
- Baraya, Y. U. S. A. B., Wong, K. K., & Yaacob, N. S. (2017). The immunomodulatory potential of selected bioactive plant-based compounds in breast cancer: a review. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents), 17(6), 770-783. [CrossRef]
- Kapinova, A., Stefanicka, P., Kubatka, P., Zubor, P., Uramova, S., Kello, M., ... & Kruzliak, P. (2017). Are plant-based functional foods better choice against cancer than single phytochemicals? A critical review of current breast cancer research. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 96, 1465-1477. [CrossRef]
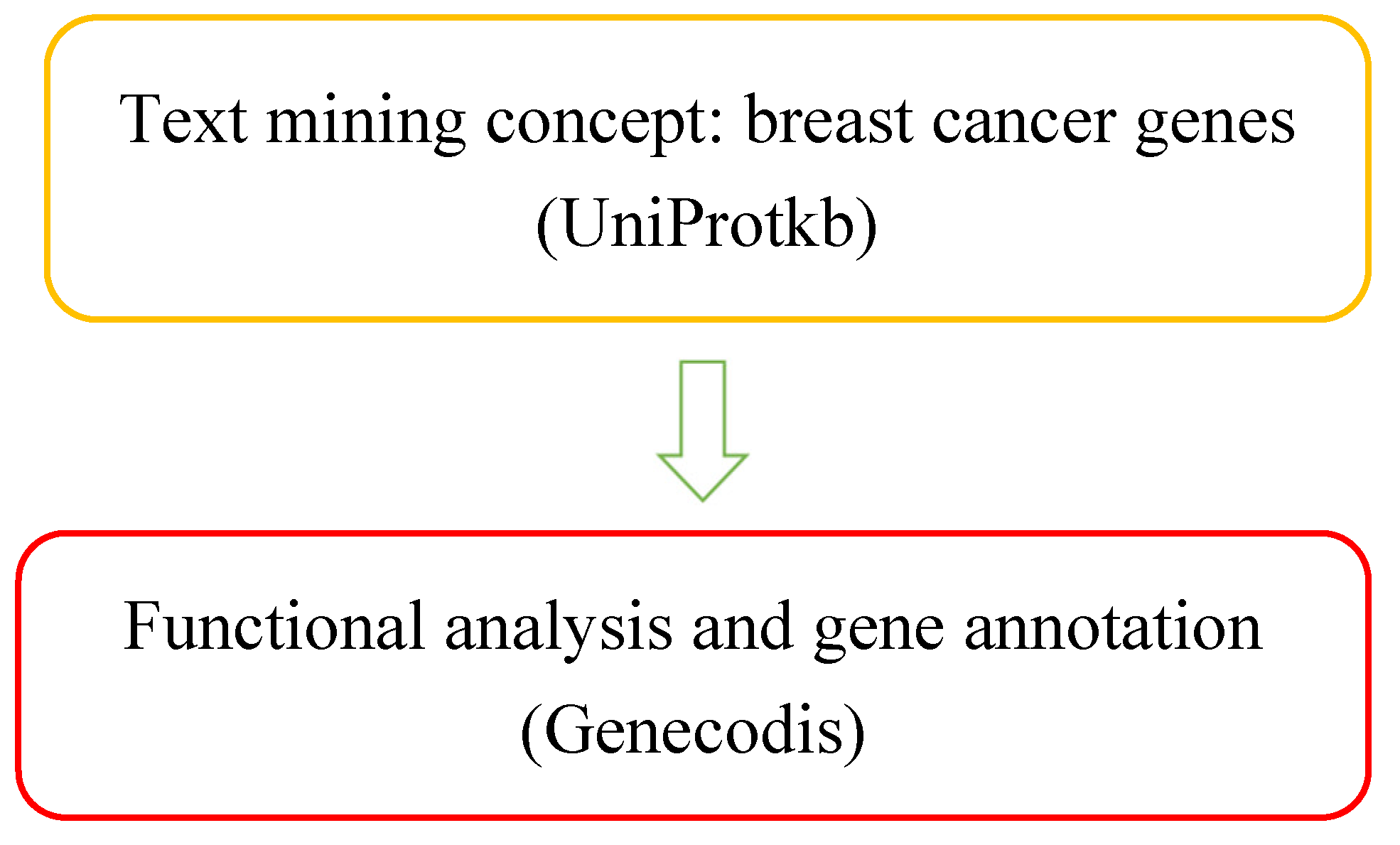
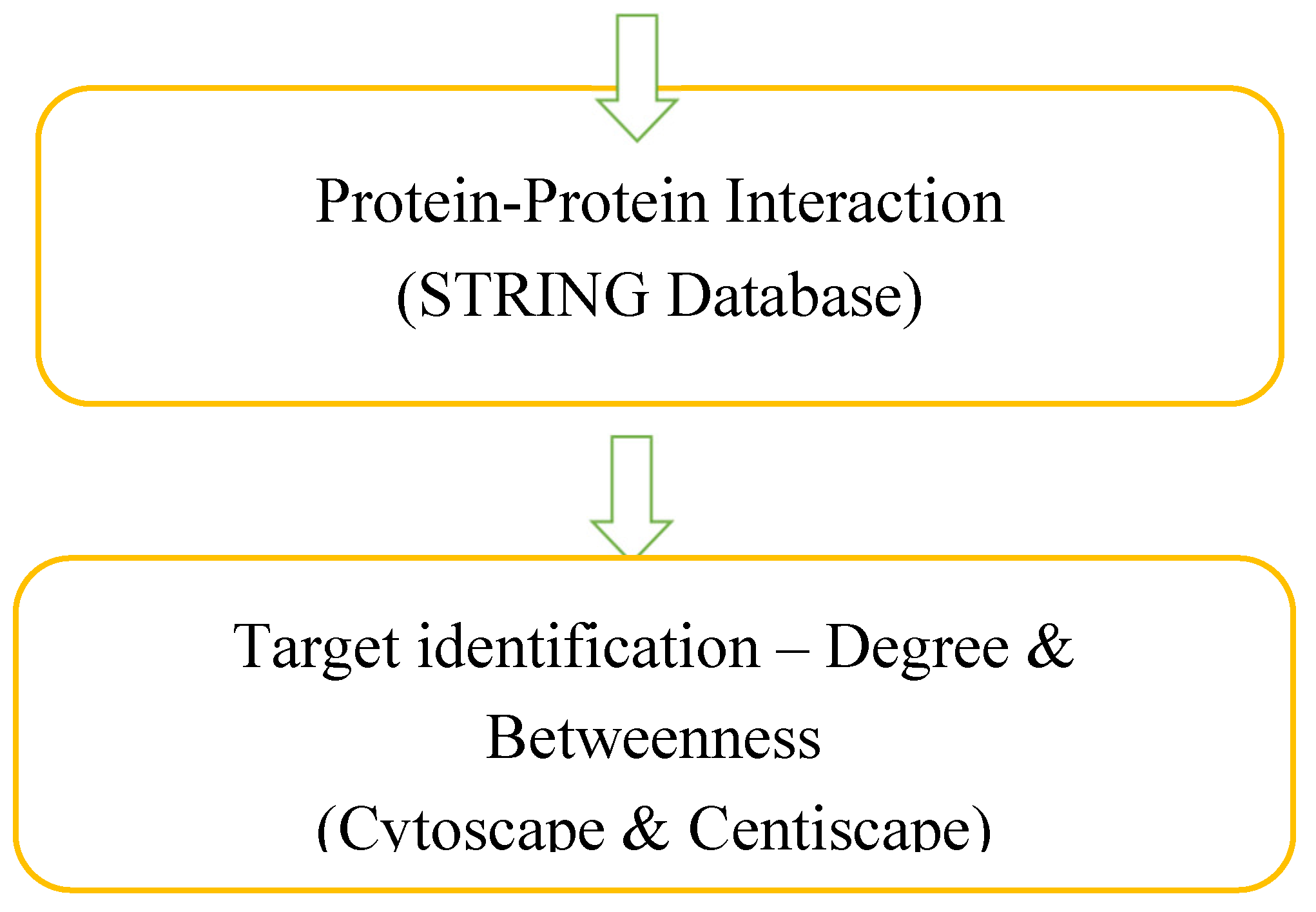
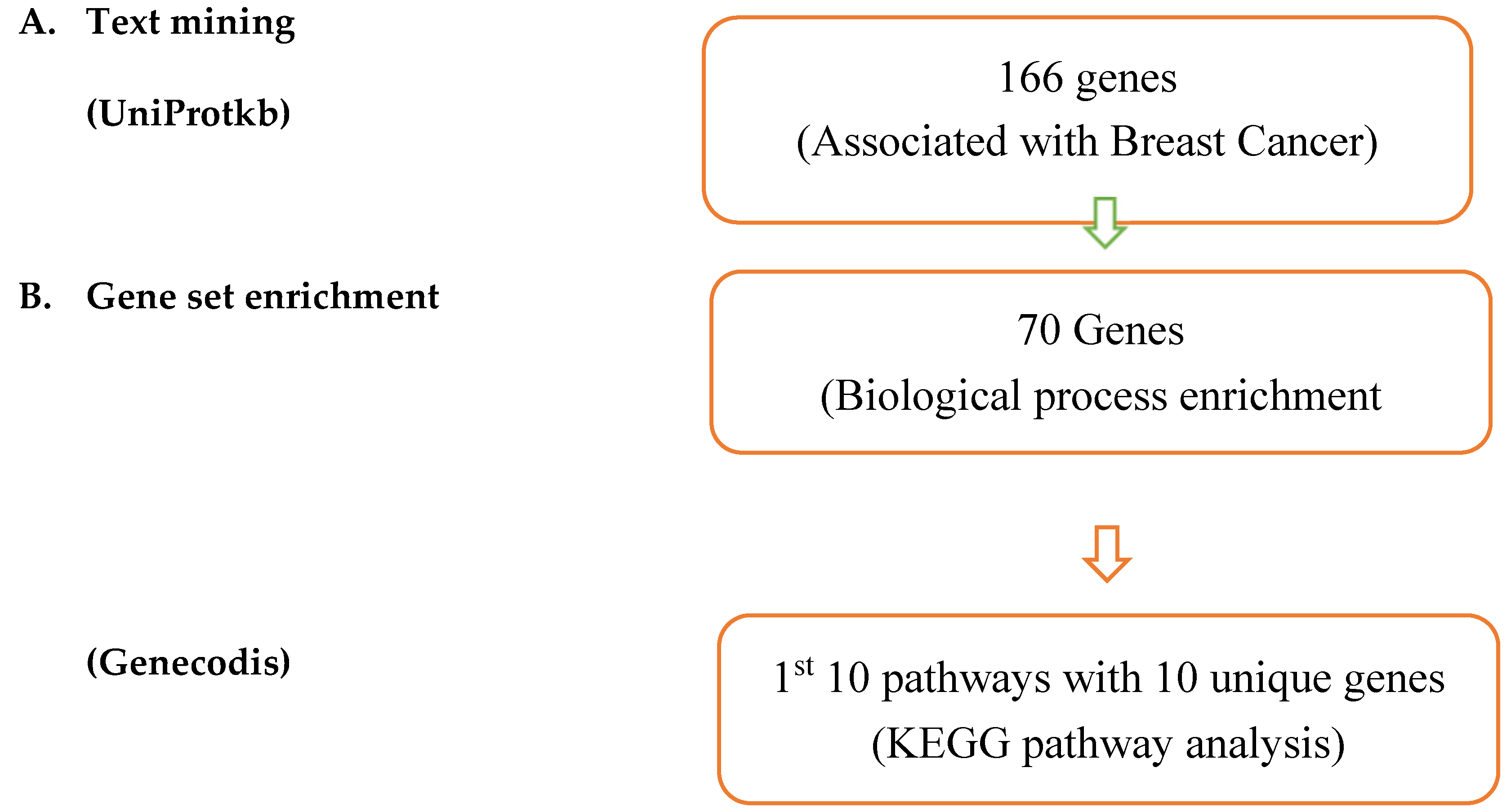
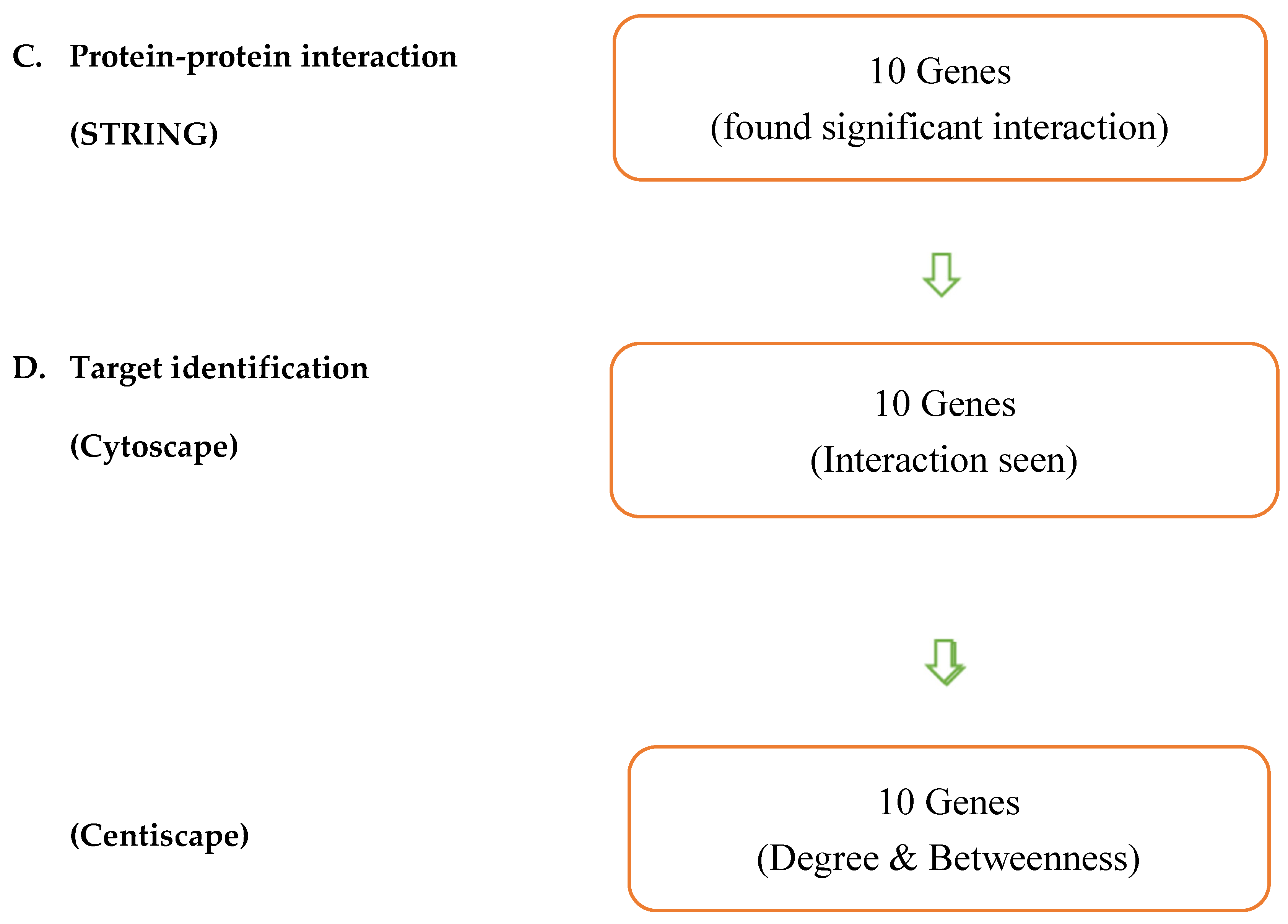

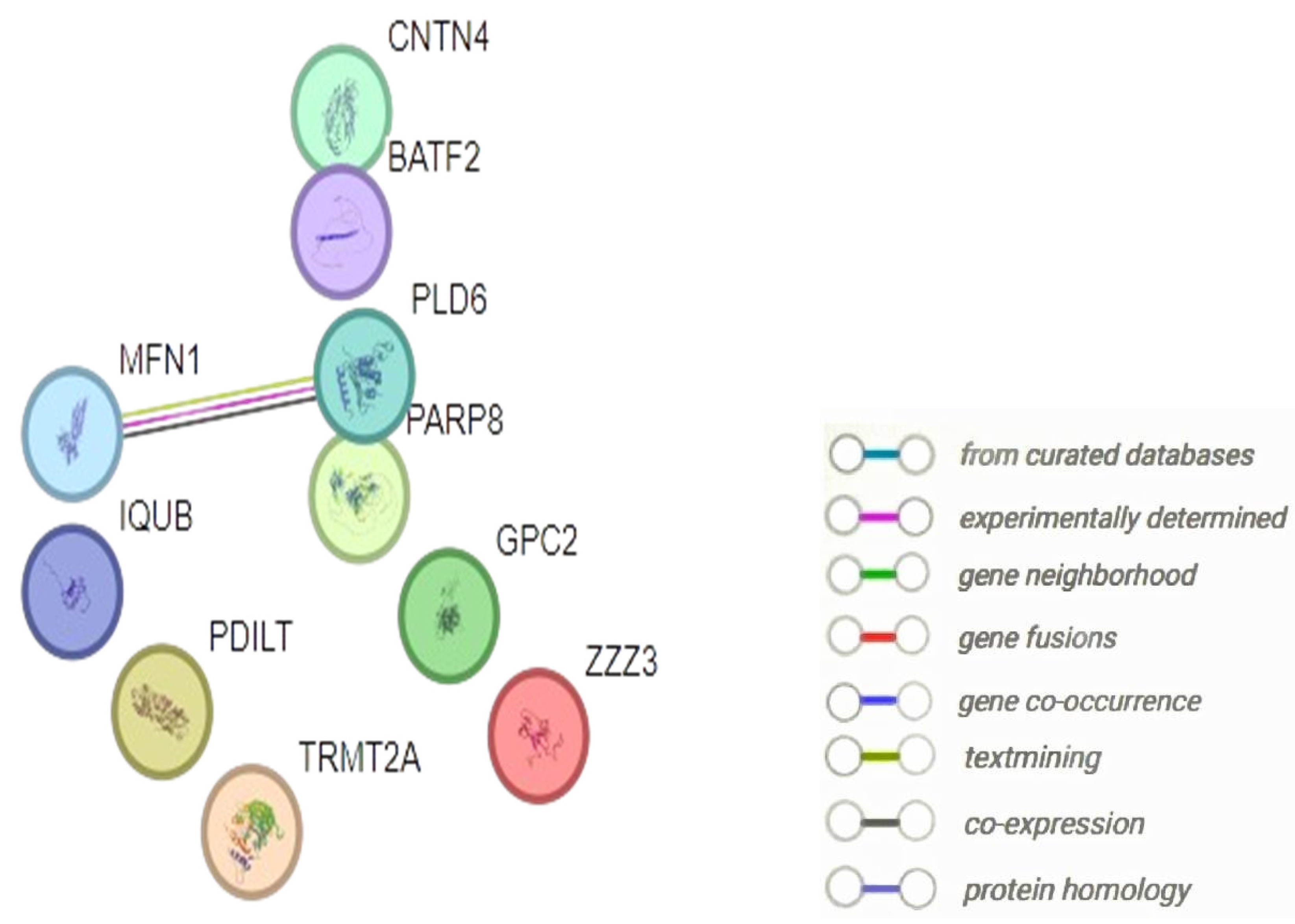
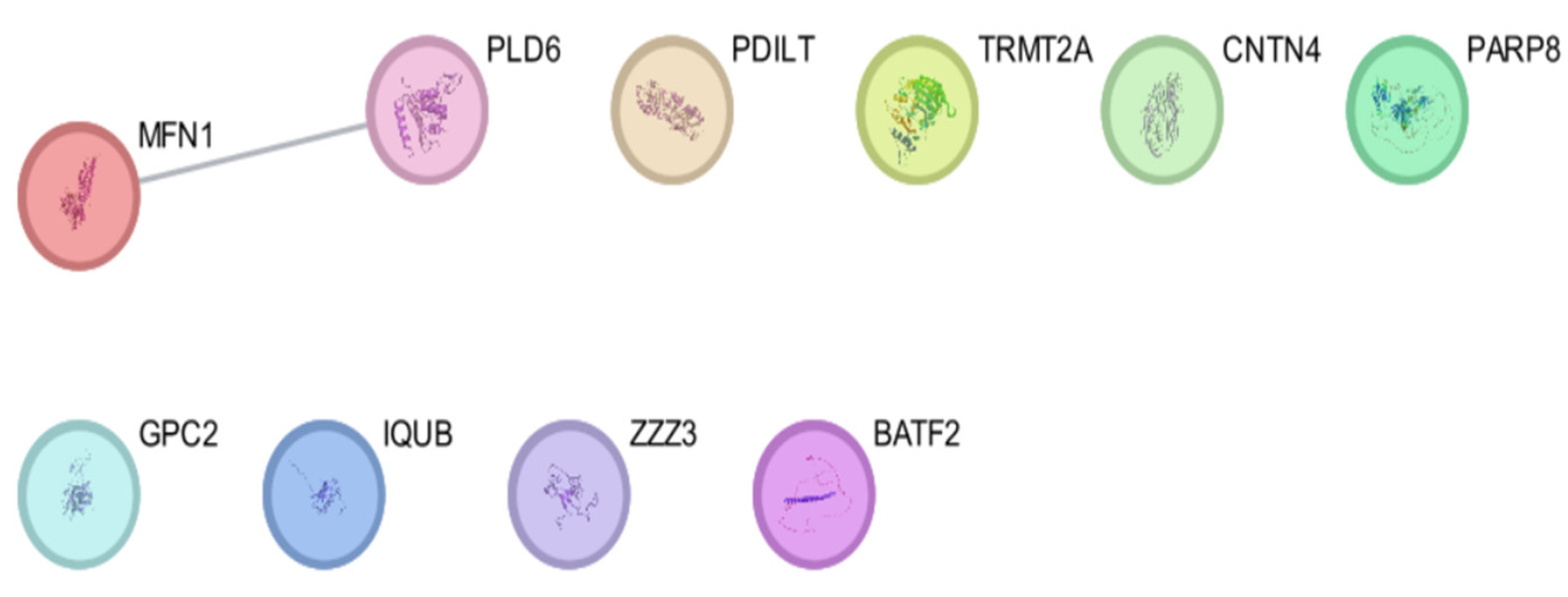
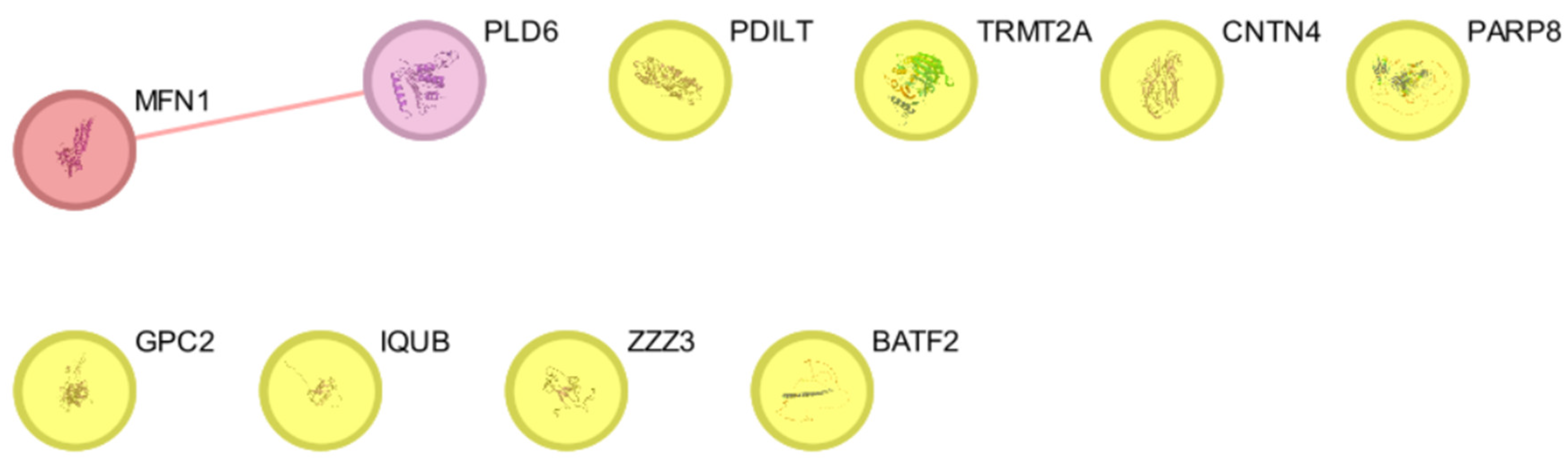
| Entry | Gene Names | Organism | Length |
| Q8IV36 | HID1 C17orf28 DMC1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 788 |
| Q8IV76 | PASD1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 773 |
| Q8IVG5 | SAMD9L C7orf6 DRIF2 KIAA2005 UEF | Homo sapiens (Human) | 1584 |
| Q8IVH2 | FOXP4 FKHLA | Homo sapiens (Human) | 680 |
| Q8IVL5 | P3H2 LEPREL1 MLAT4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 708 |
| Q8IVL8 | CPO | Homo sapiens (Human) | 374 |
| Q8IVM8 | SLC22A9 hOAT4 OAT7 UST3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 553 |
| Q8IVT5 | KSR1 KSR | Homo sapiens (Human) | 923 |
| Q8IW00 | VSTM4 C10orf72 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 320 |
| Q8IWA4 | MFN1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 741 |
| Q8IWU5 | SULF2 KIAA1247 UNQ559/PRO1120 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 870 |
| Q8IWU6 | SULF1 KIAA1077 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 871 |
| Q8IWV2 | CNTN4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 1026 |
| Q8IWW8 | ADHFE1 HMFT2263 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 467 |
| Q8IWX7 | UNC45B CMYA4 UNC45 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 931 |
| Q8IX03 | WWC1 KIAA0869 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 1113 |
| Q8IX12 | CCAR1 CARP1 DIS | Homo sapiens (Human) | 1150 |
| Q8IXB3 | TRARG1 IFITMD3 LOST1 TUSC5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 177 |
| Q8IXJ6 | SIRT2 SIR2L SIR2L2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 389 |
| Q8IY92 | SLX4 BTBD12 KIAA1784 KIAA1987 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 1834 |
| Q8IYB4 | PEX5L PEX5R PXR2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 626 |
| Q8IYF1 | ELOA2 TCEB3B TCEB3L | Homo sapiens (Human) | 753 |
| Q8IYH5 | ZZZ3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 903 |
| Q8IYK4 | COLGALT2 C1orf17 GLT25D2 KIAA0584 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 626 |
| Q8IYT3 | CCDC170 C6orf97 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 715 |
| Q8IZ41 | RASEF RAB45 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 740 |
| Q8IZ69 | TRMT2A | Homo sapiens (Human) | 625 |
| Q8IZF3 | ADGRF4 GPR115 PGR18 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 695 |
| Q8IZJ1 | UNC5B P53RDL1 UNC5H2 UNQ1883/PRO4326 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 945 |
| Q8IZL8 | PELP1 HMX3 MNAR | Homo sapiens (Human) | 1130 |
| Q8IZW8 | TNS4 CTEN PP14434 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 715 |
| Q8N0W4 | NLGN4X KIAA1260 NLGN4 UNQ365/PRO701 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 816 |
| Q8N104 | DEFB106A BD6 DEFB106 DEFB6; DEFB106B | Homo sapiens (Human) | 65 |
| Q8N108 | MIER1 KIAA1610 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 512 |
| Q8N136 | DAW1 ODA16 WDR69 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 415 |
| Q8N158 | GPC2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 579 |
| Q8N163 | CCAR2 DBC1 KIAA1967 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 923 |
| Q8N1B3 | CCNQ FAM58A | Homo sapiens (Human) | 248 |
| Q8N1L9 | BATF2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 274 |
| Q8N2A8 | PLD6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 252 |
| Q8N2M8 | CLASRP SFRS16 SWAP2 UNQ2428/PRO4988 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 674 |
| Q8N2U9 | SLC66A2 PQLC1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 271 |
| Q8N371 | KDM8 JMJD5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 416 |
| Q8N3A8 | PARP8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 854 |
| Q8N3F8 | MICALL1 KIAA1668 MIRAB13 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 863 |
| Q8N427 | NME8 SPTRX2 TXNDC3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 588 |
| Q8N474 | SFRP1 FRP FRP1 SARP2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 314 |
| Q8N488 | RYBP DEDAF YEAF1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 228 |
| Q8N4F0 | BPIFB2 BPIL1 C20orf184 LPLUNC2 UNQ2489/PRO5776 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 458 |
| Q8N554 | ZNF276 CENP-Z ZFP276 ZNF477 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 614 |
| Q8N556 | AFAP1 AFAP | Homo sapiens (Human) | 730 |
| Q8N5H7 | SH2D3C NSP3 UNQ272/PRO309/PRO34088 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 860 |
| Q8N695 | SLC5A8 AIT SMCT SMCT1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 610 |
| Q8N6D2 | RNF182 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 247 |
| Q8N752 | CSNK1A1L | Homo sapiens (Human) | 337 |
| Q8N7J2 | AMER2 FAM123A | Homo sapiens (Human) | 671 |
| Q8N7W2 | BEND7 C10orf30 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 519 |
| Q8N807 | PDILT | Homo sapiens (Human) | 584 |
| Q8N8S7 | ENAH MENA | Homo sapiens (Human) | 591 |
| Q8N9N5 | BANP BEND1 SMAR1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 519 |
| Q8N9N8 | EIF1AD | Homo sapiens (Human) | 165 |
| Q8NA54 | IQUB | Homo sapiens (Human) | 791 |
| Q8NAP8 | ZBTB8B | Homo sapiens (Human) | 495 |
| Q8NAX2 | KDF1 C1orf172 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 398 |
| Q8NB49 | ATP11C ATPIG ATPIQ | Homo sapiens (Human) | 1132 |
| Q8NBU5 | ATAD1 FNP001 | Homo sapiens (Human) | 361 |
| Genes/Proteins | Betweenness | Degree |
| MFN1 | 0 | 1 |
| PDILT | 0 | 0 |
| TRMT2A | 0 | 0 |
| CNTN4 | 0 | 0 |
| PARP8 | 0 | 0 |
| GPC2 | 0 | 0 |
| IQUB | 0 | 0 |
| ZZZ3 | 0 | 0 |
| BAFT2 | 0 | 0 |
| PLD6 | 0 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





