Submitted:
22 May 2024
Posted:
23 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
The Clinical Challenges of Persistent Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia (SAB)
Treatment Approaches for Persistent SAB.
Small Colony Variant S. aureus Result in Reduced Antibiotic Efficacy and Infection Persistence
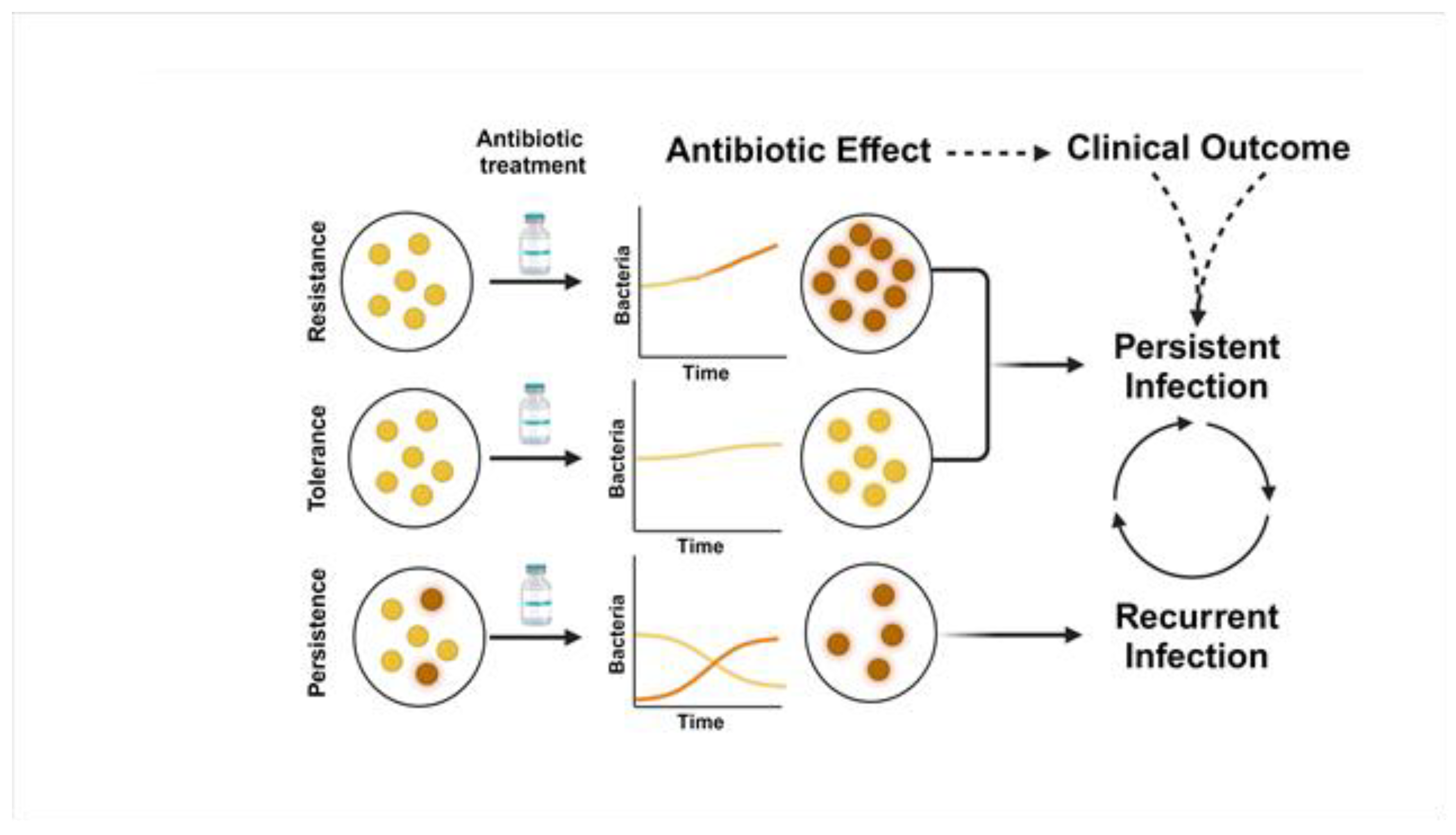
Antimicrobial Resistance, Tolerance, and Persistence in S. aureus Contribute to Persistent Bacteremia
Staphylococcus aureus Proclivity for Intracellularly Growth and Persistence
Intracellular S. aureus Reduce Immune Recognition and Activation
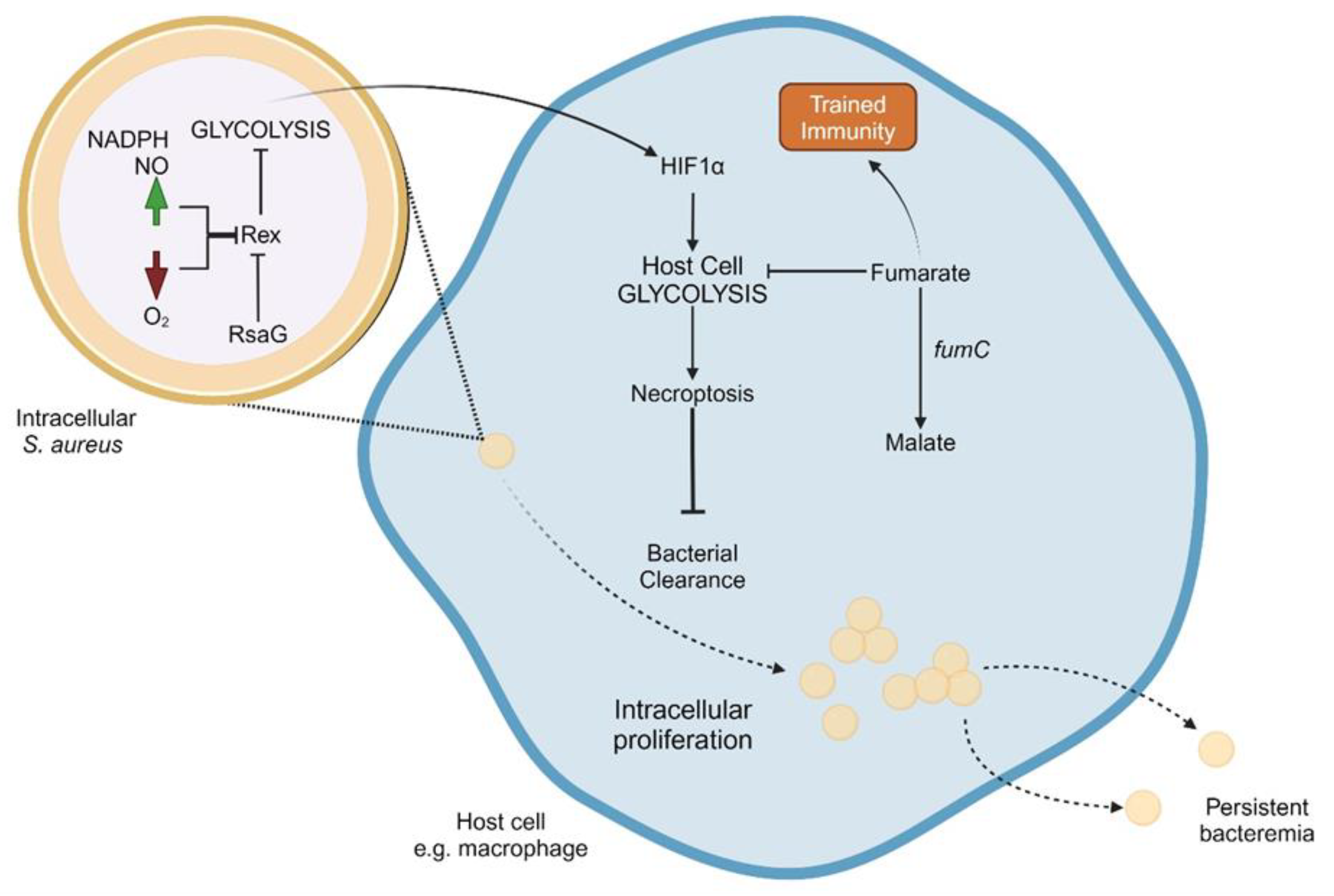
Anaerobic Metabolism of S. aureus Correlates to Intracellular Growth
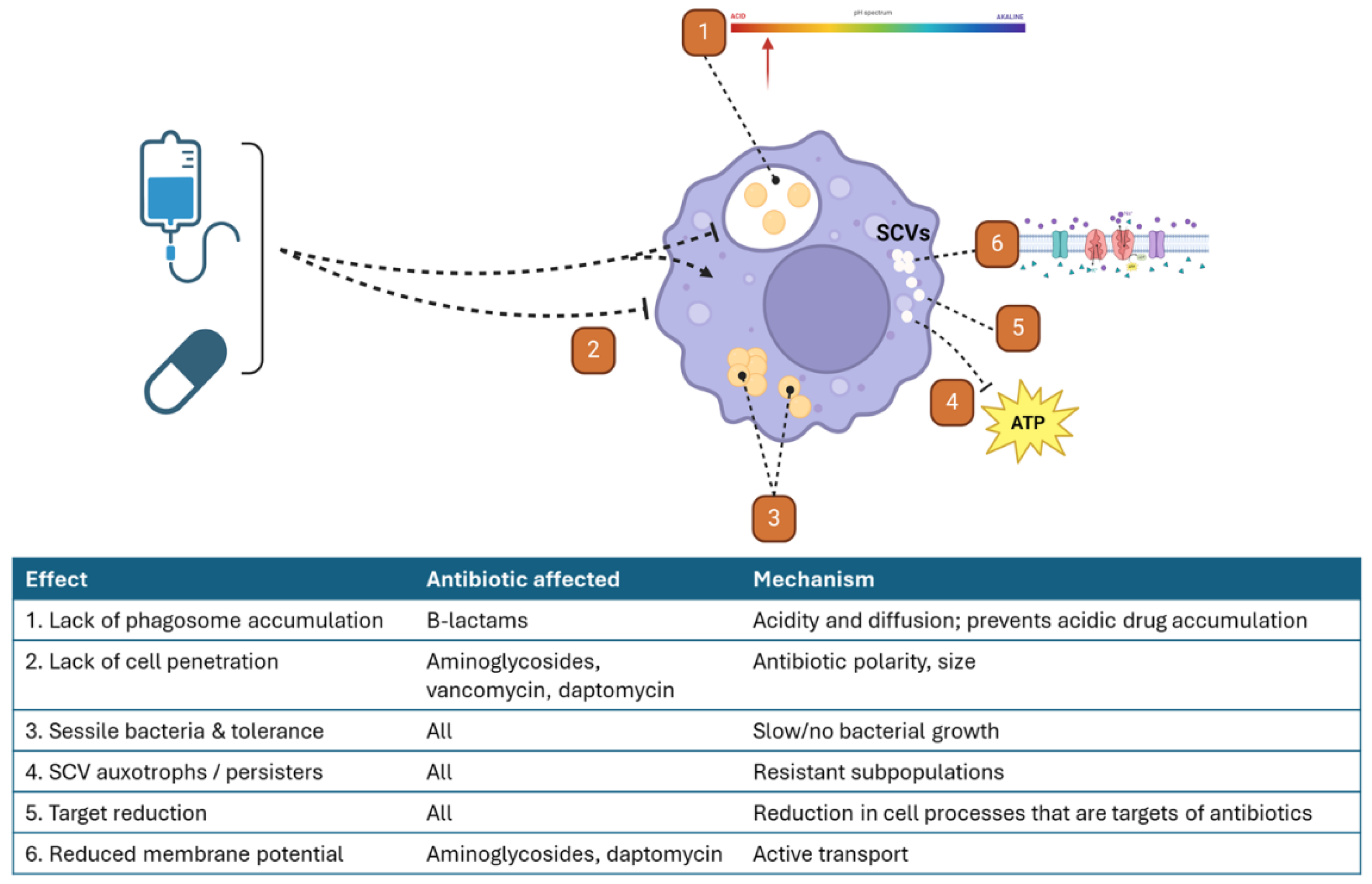
Intracellular S. aureus Are More Resistant to the Effects of Antibiotics through Multifaceted Mechanisms
Conclusions
References
- Rodvold, K.A.; McConeghy, K.W. , Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus therapy: Past, present, and future. Clin Infect Dis 2014, 58 (Suppl. S1), S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, T.L.; Bayer, A.S.; Fowler, V.G. , Persistent Methicilin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia: Resetting the Clock for Optimal Management. Clin Infect Dis 2022, 75, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullar, R.; Sakoulas, G.; Deresinski, S.; van Hal, S.J. , When sepsis persists: A review of MRSA bacteraemia salvage therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother 2016, 71, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, K.A.; Perez, K.K.; Forrest, G.N.; Goff, D.A. , Review of rapid diagnostic tests used by antimicrobial stewardship programs. Clin Infect Dis 2014, 59 (Suppl. S3), S134–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Fang, F.C. , Diagnostic Stewardship: Opportunity for a Laboratory–Infectious Diseases Partnership. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2018, 67, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, N.; Quinn, E.L.; Saravolatz, L.D. , Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole compared with vancomycin for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Ann Intern Med 1992, 117, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, D.P.; Fromm, B.S.; Reddy, B.R. , Slow response to vancomycin or vancomycin plus rifampin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Ann Intern Med 1991, 115, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, W.E.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Shukla, S.K.; Pantrangi, M.; Rooijakkers, S.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Nizet, V.; Sakoulas, G. , Elevated serum interleukin-10 at time of hospital admission is predictive of mortality in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. J Infect Dis 2012, 206, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullar, R.; McKinnell, J.A.; Sakoulas, G. , Avoiding the Perfect Storm: The Biologic and Clinical Case for Reevaluating the 7-Day Expectation for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Before Switching Therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2014, 59, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, W.E.; Shukla, S.K.; Berti, A.D.; Hayney, M.S.; Henriquez, K.M.; Ranzoni, A.; Cooper, M.A.; Proctor, R.A.; Nizet, V.; Sakoulas, G. , Increased Endovascular Staphylococcus aureus Inoculum Is the Link Between Elevated Serum Interleukin 10 Concentrations and Mortality in Patients With Bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis 2017, 64, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehl, R.; Morata, L.; Boeing, C.; Subirana, I.; Seifert, H.; Rieg, S.; Kern, W.V.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, E.S.; Liao, C.H.; Tilley, R.; Lopez-Cortes, L.E.; Llewelyn, M.J.; Fowler, V.G.; Thwaites, G.; Cisneros, J.M.; Scarborough, M.; Nsutebu, E.; Gurgui Ferrer, M.; Perez, J.L.; Barlow, G.; Hopkins, S.; Ternavasio-de la Vega, H.G.; Torok, M.E.; Wilson, P.; Kaasch, A.J.; Soriano, A.; International Staphylococcus aureus collaboration study, g. ; the Escmid Study Group for Bloodstream Infections, E.; Sepsis, Defining persistent Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: Secondary analysis of a prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 2020, 20, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, T.L.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Doernberg, S.B.; Jenkins, T.C.; Turner, N.A.; Boucher, H.W.; Pavlov, O.; Titov, I.; Kosulnykov, S.; Atanasov, B.; Poromanski, I.; Makhviladze, M.; Anderzhanova, A.; Stryjewski, M.E.; Assadi Gehr, M.; Engelhardt, M.; Hamed, K.; Ionescu, D.; Jones, M.; Saulay, M.; Smart, J.; Seifert, H.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Group, E.S. , Ceftobiprole for Treatment of Complicated Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. N Engl J Med 2023, 389, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakoulas, G.; Moise, P.A.; Casapao, A.M.; Nonejuie, P.; Olson, J.; Okumura, C.Y.; Rybak, M.J.; Kullar, R.; Dhand, A.; Rose, W.E.; Goff, D.A.; Bressler, A.M.; Lee, Y.; Pogliano, J.; Johns, S.; Kaatz, G.W.; Ebright, J.R.; Nizet, V. , Antimicrobial Salvage Therapy for Persistent Staphylococcal Bacteremia Using Daptomycin Plus Ceftaroline. Clin Ther 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, W.E.; Schulz, L.T.; Andes, D.; Striker, R.; Berti, A.D.; Hutson, P.R.; Shukla, S.K. , Addition of ceftaroline to daptomycin after emergence of daptomycin-nonsusceptible Staphylococcus aureus during therapy improves antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2012, 56, 5296–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.C.; Aung, G.; Thomas, A.; Jahng, M.; Johns, S.; Fierer, J. , The use of ceftaroline fosamil in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis and deep-seated MRSA infections: A retrospective case series of 10 patients. J Infect Chemother 2013, 19, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, W.; Fantl, M.; Geriak, M.; Nizet, V.; Sakoulas, G. , Current Paradigms of Combination Therapy in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Bacteremia: Does it Work, Which Combination, and For Which Patients? Clin Infect Dis 2021, 73, 2353–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.J.; Dotel, R.; Braddick, M.; Britton, P.N.; Eisen, D.P.; Francis, J.R.; Lynar, S.; McMullan, B.; Meagher, N.; Nelson, J.; O'Sullivan, M.V. N.; Price, D.J.; Robinson, J.O.; Whelan, A.; Tong, S.Y. C.; Bowen, A.C.; Davis, J.S. , Clindamycin adjunctive therapy for severe Staphylococcus aureus treatment evaluation (CASSETTE)-an open-labelled pilot randomized controlled trial. JAC Antimicrob Resist 2022, 4, dlac014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hal, S.J.; Jensen, S.O.; Vaska, V.L.; Espedido, B.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Gosbell, I.B. , Predictors of mortality in Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Clin Microbiol Rev 2012, 25, 362–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Boucher, H.W.; Corey, G.R.; Abrutyn, E.; Karchmer, A.W.; Rupp, M.E.; Levine, D.P.; Chambers, H.F.; Tally, F.P.; Vigliani, G.A.; Cabell, C.H.; Link, A.S.; DeMeyer, I.; Filler, S.G.; Zervos, M.; Cook, P.; Parsonnet, J.; Bernstein, J.M.; Price, C.S.; Forrest, G.N.; Fatkenheuer, G.; Gareca, M.; Rehm, S.J.; Brodt, H.R.; Tice, A.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Endocarditis, S. a.; Bacteremia Study, G. , Daptomycin versus standard therapy for bacteremia and endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus. N Engl J Med 2006, 355, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, M.; Miro, J.M.; Shaw, E.; Aguado, J.M.; San-Juan, R.; Puig-Asensio, M.; Pigrau, C.; Calbo, E.; Montejo, M.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Pais, M.J.; Pintado, V.; Escudero-Sanchez, R.; Lopez-Contreras, J.; Morata, L.; Montero, M.; Andres, M.; Pasquau, J.; Arenas, M.D.; Padilla, B.; Murillas, J.; Jover-Saenz, A.; Lopez-Cortes, L.E.; Garcia-Pardo, G.; Gasch, O.; Videla, S.; Hereu, P.; Tebe, C.; Pallares, N.; Sanllorente, M.; Dominguez, M.A.; Camara, J.; Ferrer, A.; Padulles, A.; Cuervo, G.; Carratala, J.; Investigators, M.B. T. , Daptomycin Plus Fosfomycin Versus Daptomycin Alone for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia and Endocarditis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin Infect Dis 2021, 72, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.S.; Sud, A.; O'Sullivan, M.V.; Robinson, J.O.; Ferguson, P.E.; Foo, H.; van Hal, S.J.; Ralph, A.P.; Howden, B.P.; Binks, P.M.; Kirby, A.; Tong, S.Y.; Combination Antibiotics for, M.R. S. a. s. g.; Australasian Society for Infectious Diseases Clinical Research, N. , Combination of Vancomycin and beta-Lactam Therapy for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia: A Pilot Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin Infect Dis 2016, 62, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Lye, D.C.; Yahav, D.; Sud, A.; Robinson, J.O.; Nelson, J.; Archuleta, S.; Roberts, M.A.; Cass, A.; Paterson, D.L.; Foo, H.; Paul, M.; Guy, S.D.; Tramontana, A.R.; Walls, G.B.; McBride, S.; Bak, N.; Ghosh, N.; Rogers, B.A.; Ralph, A.P.; Davies, J.; Ferguson, P.E.; Dotel, R.; McKew, G.L.; Gray, T.J.; Holmes, N.E.; Smith, S.; Warner, M.S.; Kalimuddin, S.; Young, B.E.; Runnegar, N.; Andresen, D.N.; Anagnostou, N.A.; Johnson, S.A.; Chatfield, M.D.; Cheng, A.C.; Fowler, V.G., Jr; Howden, B.P.; Meagher, N.; Price, D.J.; van Hal, S.J.; O’Sullivan, M.V. N.; Davis, J.S.; Network, f. t. A. S. f. I. D. C. R. , Effect of Vancomycin or Daptomycin With vs Without an Antistaphylococcal β-Lactam on Mortality, Bacteremia, Relapse, or Treatment Failure in Patients With MRSA Bacteremia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Miro, J.M.; Hoen, B.; Cabell, C.H.; Abrutyn, E.; Rubinstein, E.; Corey, G.R.; Spelman, D.; Bradley, S.F.; Barsic, B.; Pappas, P.A.; Anstrom, K.J.; Wray, D.; Fortes, C.Q.; Anguera, I.; Athan, E.; Jones, P.; van der Meer, J.T.; Elliott, T.S.; Levine, D.P.; Bayer, A.S.; Investigators, I.C. E. , Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis: A consequence of medical progress. JAMA 2005, 293, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.S.; Fowler, V.G.; Shukla, S.K.; Rose, W.E.; Proctor, R.A. , Development of a vaccine against Staphylococcus aureus invasive infections: Evidence based on human immunity, genetics and bacterial evasion mechanisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2020, 44, 123–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.K.; Rose, W.; Schrodi, S.J. , Complex host genetic susceptibility to Staphylococcus aureus infections. Trends Microbiol 2015, 23, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, J.; Stelzner, K.; Rudel, T.; Fraunholz, M. , Inside job: Staphylococcus aureus host-pathogen interactions. Int J Med Microbiol 2018, 308, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooijakkers, S.H.; van Kessel, K.P.; van Strijp, J.A. , Staphylococcal innate immune evasion. Trends Microbiol 2005, 13, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minejima, E.; Bensman, J.; She, R.C.; Mack, W.J.; Tuan Tran, M.; Ny, P.; Lou, M.; Yamaki, J.; Nieberg, P.; Ho, J.; Wong-Beringer, A. , A Dysregulated Balance of Proinflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Host Cytokine Response Early During Therapy Predicts Persistence and Mortality in Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Crit Care Med 2016, 44, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, C.F.; Burgdorf, S.; Edwardson, G.; Nizet, V.; Sakoulas, G.; Rose, W.E. , Interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-10 Host Responses in Patients With Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Determined by Antimicrobial Therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2020, 70, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, J.M.; Mills, R.H.; Olson, J.; Caldera, J.R.; Sepich-Poore, G.D.; Carrillo-Terrazas, M.; Tsai, C.M.; Vargas, F.; Knight, R.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Liu, G.Y.; Nizet, V.; Sakoulas, G.; Rose, W.; Gonzalez, D.J. , Mortality Risk Profiling of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia by Multi-omic Serum Analysis Reveals Early Predictive and Pathogenic Signatures. Cell 2020, 182, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, R.A.; Balwit, J.M.; Vesga, O. , Variant subpopulations of Staphylococcus aureus as cause of persistent and recurrent infections. Infect Agents Dis 1994, 3, 302–312. [Google Scholar]
- von Eiff, C. , Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants: A challenge to microbiologists and clinicians. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2008, 31, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, B.C.; Belling, G.; Becker, P.; Chatterjee, I.; Wardecki, K.; Hilgert, K.; Cheung, A.L.; Peters, G.; Herrmann, M. , Thymidine-dependent Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants are associated with extensive alterations in regulator and virulence gene expression profiles. Infect Immun 2005, 73, 4119–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolle, W.; Hetsch, H. , Die experimentelle Bakteriologie und die Infektionskrankheiten mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der Immunitätslehre. Urban und Schwarzenberg, Berlin, Germany 1911, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bigger, J.W.; Boland, C.R.; O'meara, R.A. Q. , Variant colonies of Staphylococcus aureus. The Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology 1927, 30, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youmans, G.P. , Production of Small-Colony Variants of Staphylococcus aureus. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 1937, 36, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, R.A.; von Eiff, C.; Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; McNamara, P.; Herrmann, M.; Peters, G. , Small colony variants: A pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2006, 4, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; Löffler, B. , Clinical Significance and Pathogenesis of Staphylococcal Small Colony Variants in Persistent Infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 2016, 29, 401–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maduka-Ezeh, A.N.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Karau, M.J.; Berbari, E.F.; Osmon, D.R.; Hanssen, A.D.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. , Antimicrobial susceptibility and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis small colony variants associated with prosthetic joint infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2012, 74, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.G.; Lemaire, S.; Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; Proctor, R.A.; Denis, O.; Tulkens, P.M.; Van Bambeke, F. , Antibiotic activity against small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus: Review of in vitro, animal and clinical data. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2013, 68, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltch, A.L.; Ritz, W.J.; Bopp, L.H.; Michelsen, P.; Smith, R.P. , Activities of daptomycin and comparative antimicrobials, singly and in combination, against extracellular and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus and its stable small-colony variant in human monocyte-derived macrophages and in broth. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2008, 52, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegeskorte, A.; Grubmuller, S.; Huber, C.; Kahl, B.C.; von Eiff, C.; Proctor, R.A.; Peters, G.; Eisenreich, W.; Becker, K. , Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants show common metabolic features in central metabolism irrespective of the underlying auxotrophism. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014, 4, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, N.N.; Bayer, A.S.; Weidenmaier, C.; Grau, T.; Wanner, S.; Stefani, S.; Cafiso, V.; Bertuccio, T.; Yeaman, M.R.; Nast, C.C.; Yang, S.J. , Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of daptomycin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains: Relative roles of mprF and dlt operons. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F.; Karlowsky, J.A. , Oritavancin: Mechanism of action. Clin Infect Dis 2012, 54 (Suppl. S3), S214–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouza, E.; Burillo, A. , Oritavancin: A novel lipoglycopeptide active against Gram-positive pathogens including multiresistant strains. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2010, 36, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamontagne Boulet, M.; Isabelle, C.; Guay, I.; Brouillette, E.; Langlois, J.P.; Jacques, P.E.; Rodrigue, S.; Brzezinski, R.; Beauregard, P.B.; Bouarab, K.; Boyapelly, K.; Boudreault, P.L.; Marsault, E.; Malouin, F. , Tomatidine Is a Lead Antibiotic Molecule That Targets Staphylococcus aureus ATP Synthase Subunit C. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, J.P.; Millette, G.; Guay, I.; Dube-Duquette, A.; Chamberland, S.; Jacques, P.E.; Rodrigue, S.; Bouarab, K.; Marsault, E.; Malouin, F. , Bactericidal Activity of the Bacterial ATP Synthase Inhibitor Tomatidine and the Combination of Tomatidine and Aminoglycoside Against Persistent and Virulent Forms of Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gefen, O.; Ronin, I.; Bar-Meir, M.; Balaban, N.Q. , Effect of tolerance on the evolution of antibiotic resistance under drug combinations. Science 2020, 367, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin-Reisman, I.; Ronin, I.; Gefen, O.; Braniss, I.; Shoresh, N.; Balaban, N.Q. , Antibiotic tolerance facilitates the evolution of resistance. Science 2017, 355, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.R.; Monk, J.M.; Szubin, R.; Berti, A.D. , Rapid resistance development to three antistaphylococcal therapies in antibiotic-tolerant staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.D.; Shukla, N.; Rottier, A.D.; McCrone, J.S.; Turner, H.M.; Monk, I.R.; Baines, S.L.; Howden, B.P.; Proctor, R.A.; Rose, W.E. , Daptomycin selects for genetic and phenotypic adaptations leading to antibiotic tolerance in MRSA. J Antimicrob Chemother 2018, 73, 2030–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauner, A.; Fridman, O.; Gefen, O.; Balaban, N.Q. , Distinguishing between resistance, tolerance and persistence to antibiotic treatment. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2016, 14, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, A.D.; Hirsch, E.B. , Tolerance to antibiotics affects response. Science 2020, 367, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, E.M.; Harven, L.T.; Berti, A.D. , Antimicrobial Efficacy against Antibiotic-Tolerant Staphylococcus aureus Depends on the Mechanism of Antibiotic Tolerance. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Peyrusson, F.; Varet, H.; Nguyen, T.K.; Legendre, R.; Sismeiro, O.; Coppee, J.Y.; Wolz, C.; Tenson, T.; Van Bambeke, F. , Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus persisters upon antibiotic exposure. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bojer, M.S.; George, S.E.; Wang, Z.; Jensen, P.R.; Wolz, C.; Ingmer, H. , Inactivation of TCA cycle enhances Staphylococcus aureus persister cell formation in stationary phase. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 10849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalis, E.A.; Nuxoll, A.S.; Manuse, S.; Clair, G.; Radlinski, L.C.; Conlon, B.P.; Adkins, J.; Lewis, K. , Stochastic Variation in Expression of the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Produces Persister Cells. mBio 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Loffler, B.; Proctor, R.A. , Persistence of Staphylococcus aureus: Multiple Metabolic Pathways Impact the Expression of Virulence Factors in Small-Colony Variants (SCVs). Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. , Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M.; Costerton, J.W. , Biofilms: Survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev 2002, 15, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. , The biofilm matrix. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raad, I.; Hanna, H.; Jiang, Y.; Dvorak, T.; Reitzel, R.; Chaiban, G.; Sherertz, R.; Hachem, R. , Comparative activities of daptomycin, linezolid, and tigecycline against catheter-related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus bacteremic isolates embedded in biofilm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2007, 51, 1656–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Ganesh, V.K.; Hook, M. , Adhesion, invasion and evasion: The many functions of the surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat Rev Microbiol 2014, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S. , Effect of antibacterials on biofilms. Am J Infect Control 2008, 36, S175–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, T.F.; O'Toole, G.A. , Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol 2001, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theis, T.J.; Daubert, T.A.; Kluthe, K.E.; Brodd, K.L.; Nuxoll, A.S. , Staphylococcus aureus persisters are associated with reduced clearance in a catheter-associated biofilm infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2023, 13, 1178526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safdar, A.; Rolston, K.V. , Vancomycin tolerance, a potential mechanism for refractory gram-positive bacteremia observational study in patients with cancer. Cancer 2006, 106, 1815–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzoni, C.; Kelley, W.L. , Staphylococcus aureus: New evidence for intracellular persistence. Trends Microbiol 2009, 17, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hu, G.; Luo, J.; Cheng, J.; Wu, D.; Cheng, L.; Huang, X.; Fu, S.; Liu, J. , Staphylococcus aureus induces mitophagy to promote its survival within bovine mammary epithelial cells. Vet Microbiol 2023, 280, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollin, G.; Tan, X.; Tros, F.; Dupuis, M.; Nassif, X.; Charbit, A.; Coureuil, M. , Intracellular Survival of Staphylococcus aureus in Endothelial Cells: A Matter of Growth or Persistence. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, K.; Patel, R. , Survival of Staphylococcus epidermidis in Fibroblasts and Osteoblasts. Infect Immun 2018, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Humaidan, A.H.; Elven, M.; Sonesson, A.; Garred, P.; Sorensen, O.E. , Persistent Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus in Keratinocytes Lead to Activation of the Complement System with Subsequent Reduction in the Intracellular Bacterial Load. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajsnar, T.K.; Serba, J.J.; Dekker, B.M.; Gibson, J.F.; Masud, S.; Fleming, A.; Johnston, S.A.; Renshaw, S.A.; Meijer, A.H. , The autophagic response to Staphylococcus aureus provides an intracellular niche in neutrophils. Autophagy 2021, 17, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, S.; Vaudaux, P.; Francois, P.; Schrenzel, J.; Huggler, E.; Kampf, S.; Chaponnier, C.; Lew, D.; Lacroix, J.S. , Evidence of an intracellular reservoir in the nasal mucosa of patients with recurrent Staphylococcus aureus rhinosinusitis. J Infect Dis 2005, 192, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Bassiouni, A.; Drilling, A.; Psaltis, A.J.; Vreugde, S.; Wormald, P.J. , The persistence of intracellular Staphylococcus aureus in the sinuses: A longitudinal study. Rhinology 2017, 55, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zautner, A.E.; Krause, M.; Stropahl, G.; Holtfreter, S.; Frickmann, H.; Maletzki, C.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Pau, H.W.; Podbielski, A. , Intracellular persisting Staphylococcus aureus is the major pathogen in recurrent tonsillitis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, J.K.; Harris, M.; Webb, L.; Smith, B.; Smith, T.; Tan, K.; Hudson, M. , Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. A mechanism for the indolence of osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2003, 85, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Wijenayaka, A.R.; Solomon, L.B.; Pederson, S.M.; Findlay, D.M.; Kidd, S.P.; Atkins, G.J. , Novel Insights into Staphylococcus aureus Deep Bone Infections: The Involvement of Osteocytes. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torlakovic, E.; Hibbs, J.R.; Miller, J.S.; Litz, C.E. , Intracellular bacteria in blood smears in patients with central venous catheters. Arch Intern Med 1995, 155, 1547–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmeier, M.; Tuchscherr, L.; Bruck, M.; Viemann, D.; Roth, J.; Willscher, E.; Becker, K.; Peters, G.; Loffler, B. , Staphylococcal strains vary greatly in their ability to induce an inflammatory response in endothelial cells. J Infect Dis 2010, 201, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, B.E.; Kourteva, I. , Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin induces apoptosis in endothelial cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2000, 29, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schnaith, A.; Kashkar, H.; Leggio, S.A.; Addicks, K.; Kronke, M.; Krut, O. , Staphylococcus aureus subvert autophagy for induction of caspase-independent host cell death. J Biol Chem 2007, 282, 2695–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soong, G.; Chun, J.; Parker, D.; Prince, A. , Staphylococcus aureus activation of caspase 1/calpain signaling mediates invasion through human keratinocytes. J Infect Dis 2012, 205, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Medina, E.; Hussain, M.; Volker, W.; Heitmann, V.; Niemann, S.; Holzinger, D.; Roth, J.; Proctor, R.A.; Becker, K.; Peters, G.; Loffler, B. , Staphylococcus aureus phenotype switching: An effective bacterial strategy to escape host immune response and establish a chronic infection. EMBO Mol Med 2011, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffler, B.; Tuchscherr, L.; Niemann, S.; Peters, G. , Staphylococcus aureus persistence in non-professional phagocytes. Int J Med Microbiol 2014, 304, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Loffler, B. , Staphylococcus aureus dynamically adapts global regulators and virulence factor expression in the course from acute to chronic infection. Curr Genet 2016, 62, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger-Loffler, B.; Kahl, B.C.; Grundmeier, M.; Strangfeld, K.; Wagner, B.; Fischer, U.; Cheung, A.L.; Peters, G.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Sinha, B. , Multiple virulence factors are required for Staphylococcus aureus-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells. Cell Microbiol 2005, 7, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.J.; Drilling, A.J.; Cooksley, C.; Bassiouni, A.; Kidd, S.P.; Psaltis, A.J.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. , Reduced Innate Immune Response to a Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variant Compared to Its Wild-Type Parent Strain. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2016, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, S.A.; Hoerr, V.; Beineke, A.; Kreis, C.; Tuchscherr, L.; Kalinka, J.; Lehne, S.; Schleicher, I.; Kohler, G.; Fuchs, T.; Raschke, M.J.; Rohde, M.; Peters, G.; Faber, C.; Loffler, B.; Medina, E. , A novel mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus chronic osteomyelitis that closely mimics the human infection: An integrated view of disease pathogenesis. Am J Pathol 2012, 181, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, K.; Solis, N.V.; Bayer, A.S.; Hady, W.A.; Ellison, S.; Klashman, M.C.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Filler, S.G. , Divergent responses of different endothelial cell types to infection with Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarry, T.M.; Cheung, A.L. , Staphylococcus aureus escapes more efficiently from the phagosome of a cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cell line than from its normal counterpart. Infect Immun 2006, 74, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, M.C.; Ramp, W.K.; Nicholson, N.C.; Williams, A.S.; Nousiainen, M.T. , Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by cultured osteoblasts. Microb Pathog 1995, 19, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinrick, B.; Dunman, P.M.; McAleese, F.; Murphy, E.; Projan, S.J.; Fang, Y.; Novick, R.P. , Effect of mild acid on gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 2004, 186, 8407–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubica, M.; Guzik, K.; Koziel, J.; Zarebski, M.; Richter, W.; Gajkowska, B.; Golda, A.; Maciag-Gudowska, A.; Brix, K.; Shaw, L.; Foster, T.; Potempa, J. , A potential new pathway for Staphylococcus aureus dissemination: The silent survival of S. aureus phagocytosed by human monocyte-derived macrophages. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.Y.; Schwartz, J.; Thoendel, M.; Ackermann, L.W.; Horswill, A.R.; Nauseef, W.M. , agr-Dependent interactions of Staphylococcus aureus USA300 with human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Innate Immun 2010, 2, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranchemontagne, Z.R.; Camire, R.B.; O'Donnell, V.J.; Baugh, J.; Burkholder, K.M. , Staphylococcus aureus Strain USA300 Perturbs Acquisition of Lysosomal Enzymes and Requires Phagosomal Acidification for Survival inside Macrophages. Infect Immun 2016, 84, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, K.E.; Unnikrishnan, M. , Evasion of host defenses by intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. Adv Appl Microbiol 2020, 112, 105–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lacoma, A.; Cano, V.; Moranta, D.; Regueiro, V.; Dominguez-Villanueva, D.; Laabei, M.; Gonzalez-Nicolau, M.; Ausina, V.; Prat, C.; Bengoechea, J.A. , Investigating intracellular persistence of Staphylococcus aureus within a murine alveolar macrophage cell line. Virulence 2017, 8, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschel, A.; Jack, R.W.; Otto, M.; Collins, L.V.; Staubitz, P.; Nicholson, G.; Kalbacher, H.; Nieuwenhuizen, W.F.; Jung, G.; Tarkowski, A.; van Kessel, K.P.; van Strijp, J.A. , Staphylococcus aureus resistance to human defensins and evasion of neutrophil killing via the novel virulence factor MprF is based on modification of membrane lipids with l-lysine. J Exp Med 2001, 193, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Kuiack, R.C.; McGavin, M.J.; Heinrichs, D.E. , Staphylococcus aureus Uses the GraXRS Regulatory System To Sense and Adapt to the Acidified Phagolysosome in Macrophages. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavolos, M.H.; Horsburgh, M.J.; Ingham, E.; Foster, S.J. , Role and regulation of the superoxide dismutases of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology (Reading) 2003, 149 Pt 10, 2749–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, K.; Coutts, G.; Jonsson, I.M.; Tarkowski, A.; Kokai-Kun, J.F.; Mond, J.J.; Foster, S.J. , Catalase (KatA) and alkyl hydroperoxide reductase (AhpC) have compensatory roles in peroxide stress resistance and are required for survival, persistence, and nasal colonization in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 2007, 189, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treffon, J.; Block, D.; Moche, M.; Reiss, S.; Fuchs, S.; Engelmann, S.; Becher, D.; Langhanki, L.; Mellmann, A.; Peters, G.; Kahl, B.C. , Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus to Airway Environments in Patients With Cystic Fibrosis by Upregulation of Superoxide Dismutase M and Iron-Scavenging Proteins. J Infect Dis 2018, 217, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treffon, J.; Chaves-Moreno, D.; Niemann, S.; Pieper, D.H.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J.; Kahl, B.C. , Importance of superoxide dismutases A and M for protection of Staphylococcus aureus in the oxidative stressful environment of cystic fibrosis airways. Cell Microbiol 2020, 22, e13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munzenmayer, L.; Geiger, T.; Daiber, E.; Schulte, B.; Autenrieth, S.E.; Fraunholz, M.; Wolz, C. , Influence of Sae-regulated and Agr-regulated factors on the escape of Staphylococcus aureus from human macrophages. Cell Microbiol 2016, 18, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarry, T.M.; Memmi, G.; Cheung, A.L. , The expression of alpha-haemolysin is required for Staphylococcus aureus phagosomal escape after internalization in CFT-1 cells. Cell Microbiol 2008, 10, 1801–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosz, M.; Kolter, J.; Paprotka, K.; Winkler, A.C.; Schafer, D.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Geiger, T.; Wolz, C.; Ohlsen, K.; Otto, M.; Rudel, T.; Sinha, B.; Fraunholz, M. , Cytoplasmic replication of Staphylococcus aureus upon phagosomal escape triggered by phenol-soluble modulin alpha. Cell Microbiol 2014, 16, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Braughton, K.R.; Kretschmer, D.; Bach, T.H.; Queck, S.Y.; Li, M.; Kennedy, A.D.; Dorward, D.W.; Klebanoff, S.J.; Peschel, A.; DeLeo, F.R.; Otto, M. , Identification of novel cytolytic peptides as key virulence determinants for community-associated MRSA. Nat Med 2007, 13, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queck, S.Y.; Jameson-Lee, M.; Villaruz, A.E.; Bach, T.H.; Khan, B.A.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Ricklefs, S.M.; Li, M.; Otto, M. , RNAIII-independent target gene control by the agr quorum-sensing system: Insight into the evolution of virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Cell 2008, 32, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, T.; Francois, P.; Liebeke, M.; Fraunholz, M.; Goerke, C.; Krismer, B.; Schrenzel, J.; Lalk, M.; Wolz, C. , The stringent response of Staphylococcus aureus and its impact on survival after phagocytosis through the induction of intracellular PSMs expression. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1003016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.S.; Joo, H.S.; Duong, A.C.; Dieringer, T.D.; Tan, V.Y.; Song, Y.; Fischer, E.R.; Cheung, G.Y.; Li, M.; Otto, M. , Essential Staphylococcus aureus toxin export system. Nat Med 2013, 19, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blattner, S.; Das, S.; Paprotka, K.; Eilers, U.; Krischke, M.; Kretschmer, D.; Remmele, C.W.; Dittrich, M.; Muller, T.; Schuelein-Voelk, C.; Hertlein, T.; Mueller, M.J.; Huettel, B.; Reinhardt, R.; Ohlsen, K.; Rudel, T.; Fraunholz, M.J. , Staphylococcus aureus Exploits a Non-ribosomal Cyclic Dipeptide to Modulate Survival within Epithelial Cells and Phagocytes. PLoS Pathog 2016, 12, e1005857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giese, B.; Glowinski, F.; Paprotka, K.; Dittmann, S.; Steiner, T.; Sinha, B.; Fraunholz, M.J. , Expression of delta-toxin by Staphylococcus aureus mediates escape from phago-endosomes of human epithelial and endothelial cells in the presence of beta-toxin. Cell Microbiol 2011, 13, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauditz, A.; Resch, A.; Wieland, K.P.; Peschel, A.; Gotz, F. , Staphyloxanthin plays a role in the fitness of Staphylococcus aureus and its ability to cope with oxidative stress. Infect Immun 2006, 74, 4950–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Heit, B.; Heinrichs, D.E. , Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Macrophages and the Immune Evasion Strategies of Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens 2015, 4, 826–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubrail, J.; Morris, P.; Bewley, M.A.; Stoneham, S.; Johnston, S.A.; Foster, S.J.; Peden, A.A.; Read, R.C.; Marriott, H.M.; Dockrell, D.H. , Inability to sustain intraphagolysosomal killing of Staphylococcus aureus predisposes to bacterial persistence in macrophages. Cell Microbiol 2016, 18, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Heit, B.; Heinrichs, D.E. , Intracellular replication of Staphylococcus aureus in mature phagolysosomes in macrophages precedes host cell death, and bacterial escape and dissemination. Cell Microbiol 2016, 18, 514–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehar, S.M.; Pillow, T.; Xu, M.; Staben, L.; Kajihara, K.K.; Vandlen, R.; DePalatis, L.; Raab, H.; Hazenbos, W.L.; Morisaki, J.H.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Darwish, M.; Lee, B.C.; Hernandez, H.; Loyet, K.M.; Lupardus, P.; Fong, R.; Yan, D.; Chalouni, C.; Luis, E.; Khalfin, Y.; Plise, E.; Cheong, J.; Lyssikatos, J.P.; Strandh, M.; Koefoed, K.; Andersen, P.S.; Flygare, J.A.; Wah Tan, M.; Brown, E.J.; Mariathasan, S. , Novel antibody-antibiotic conjugate eliminates intracellular S. aureus. Nature 2015, 527, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, A.; Afzal, M.A.; Tetzlaff, F.; Keinhorster, D.; Gratani, F.; Paprotka, K.; Westermann, M.; Nietzsche, S.; Wolz, C.; Fraunholz, M.; Hubner, C.A.; Loffler, B.; Tuchscherr, L. , Intracellular persistence of Staphylococcus aureus in endothelial cells is promoted by the absence of phenol-soluble modulins. Virulence 2021, 12, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgrail, M.M.; Chen, E.; Shaffer, M.G.; Srinivasa, V.; Griffith, M.P.; Mustapha, M.M.; Shields, R.K.; Van Tyne, D.; Culyba, M.J. , Convergent Evolution of Antibiotic Tolerance in Patients with Persistent Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. Infect Immun 2022, 90, e0000122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramulu, D.D.; Nimtz, M.; Romling, U. , Proteome analysis reveals adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the cystic fibrosis lung environment. Proteomics 2005, 5, 3712–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagels, M.; Fuchs, S.; Pane-Farre, J.; Kohler, C.; Menschner, L.; Hecker, M.; McNamarra, P.J.; Bauer, M.C.; von Wachenfeldt, C.; Liebeke, M.; Lalk, M.; Sander, G.; von Eiff, C.; Proctor, R.A.; Engelmann, S. , Redox sensing by a Rex-family repressor is involved in the regulation of anaerobic gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 2010, 76, 1142–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desgranges, E.; Barrientos, L.; Herrgott, L.; Marzi, S.; Toledo-Arana, A.; Moreau, K.; Vandenesch, F.; Romby, P.; Caldelari, I. , The 3'UTR-derived sRNA RsaG coordinates redox homeostasis and metabolism adaptation in response to glucose-6-phosphate uptake in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 2022, 117, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.D.; Chen, A.F. , Nitric oxide: A newly discovered function on wound healing. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005, 26, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, C.; Knight, D.; Burgess, S.; Franklin, P.; Horak, F.; Legg, J.; Moeller, A.; Stick, S. , Epithelial inducible nitric oxide synthase activity is the major determinant of nitric oxide concentration in exhaled breath. Thorax 2004, 59, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma Medina, L.M.; Becker, A.K.; Michalik, S.; Surmann, K.; Hildebrandt, P.; Gesell Salazar, M.; Mekonnen, S.A.; Kaderali, L.; Volker, U.; van Dijl, J.M. , Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus and Host Cells upon Infection of Bronchial Epithelium during Different Stages of Regeneration. ACS Infect Dis 2020, 6, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilde, A.D.; Snyder, D.J.; Putnam, N.E.; Valentino, M.D.; Hammer, N.D.; Lonergan, Z.R.; Hinger, S.A.; Aysanoa, E.E.; Blanchard, C.; Dunman, P.M.; Wasserman, G.A.; Chen, J.; Shopsin, B.; Gilmore, M.S.; Skaar, E.P.; Cassat, J.E. , Bacterial Hypoxic Responses Revealed as Critical Determinants of the Host-Pathogen Outcome by TnSeq Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Invasive Infection. PLoS Pathog 2015, 11, e1005341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Throup, J.P.; Zappacosta, F.; Lunsford, R.D.; Annan, R.S.; Carr, S.A.; Lonsdale, J.T.; Bryant, A.P.; McDevitt, D.; Rosenberg, M.; Burnham, M.K. , The srhSR gene pair from Staphylococcus aureus: Genomic and proteomic approaches to the identification and characterization of gene function. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 10392–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, T.; Han, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, T.; Francois, P.; Fischer, A.; Bai, L.; Gotz, F.; Qu, D. , Staphylococcus epidermidis SrrAB regulates bacterial growth and biofilm formation differently under oxic and microaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol 2015, 197, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Huseby, D.L.; Brandis, G.; Hughes, D. , Alternative Evolutionary Pathways for Drug-Resistant Small Colony Variant Mutants in Staphylococcus aureus. mBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickersham, M.; Wachtel, S.; Wong Fok Lung, T.; Soong, G.; Jacquet, R.; Richardson, A.; Parker, D.; Prince, A. , Metabolic Stress Drives Keratinocyte Defenses against Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Cell Rep 2017, 18, 2742–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong Fok Lung, T.; Monk, I.R.; Acker, K.P.; Mu, A.; Wang, N.; Riquelme, S.A.; Pires, S.; Noguera, L.P.; Dach, F.; Gabryszewski, S.J.; Howden, B.P.; Prince, A. , Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants impair host immunity by activating host cell glycolysis and inducing necroptosis. Nat Microbiol 2020, 5, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitur, K.; Wachtel, S.; Brown, A.; Wickersham, M.; Paulino, F.; Penaloza, H.F.; Soong, G.; Bueno, S.; Parker, D.; Prince, A. , Necroptosis Promotes Staphylococcus aureus Clearance by Inhibiting Excessive Inflammatory Signaling. Cell Rep 2016, 16, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kanev, L.; Woods, S.D.; Brenner, M.; Smith, B. , Managing hyperkalemia in high-risk patients in long-term care. Am J Manag Care 2017, 23, S27–S36. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.; Quintin, J.; Kerstens, H.H.; Rao, N.A.; Aghajanirefah, A.; Matarese, F.; Cheng, S.C.; Ratter, J.; Berentsen, K.; van der Ent, M.A.; Sharifi, N.; Janssen-Megens, E.M.; Ter Huurne, M.; Mandoli, A.; van Schaik, T.; Ng, A.; Burden, F.; Downes, K.; Frontini, M.; Kumar, V.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Ouwehand, W.H.; van der Meer, J.W.; Joosten, L.A.; Wijmenga, C.; Martens, J.H.; Xavier, R.J.; Logie, C.; Netea, M.G.; Stunnenberg, H.G. , Epigenetic programming of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and trained innate immunity. Science 2014, 345, 1251086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, R.J.; Novakovic, B.; Ter Horst, R.; Carvalho, A.; Bekkering, S.; Lachmandas, E.; Rodrigues, F.; Silvestre, R.; Cheng, S.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Habibi, E.; Goncalves, L.G.; Mesquita, I.; Cunha, C.; van Laarhoven, A.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Williams, D.L.; van der Meer, J.W.; Logie, C.; O'Neill, L.A.; Dinarello, C.A.; Riksen, N.P.; van Crevel, R.; Clish, C.; Notebaart, R.A.; Joosten, L.A.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Xavier, R.J.; Netea, M.G. , Glutaminolysis and Fumarate Accumulation Integrate Immunometabolic and Epigenetic Programs in Trained Immunity. Cell Metab 2016, 24, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornberg, M.D.; Bhargava, P.; Kim, P.M.; Putluri, V.; Snowman, A.M.; Putluri, N.; Calabresi, P.A.; Snyder, S.H. , Dimethyl fumarate targets GAPDH and aerobic glycolysis to modulate immunity. Science 2018, 360, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulkens, P.M. , Intracellular distribution and activity of antibiotics. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1991, 10, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, C.; Vanderhaeghe, H.J.; Claes, P.J.; Zenebergh, A.; Tulkens, P.M. , Influence of conversion of penicillin G into a basic derivative on its accumulation and subcellular localization in cultured macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1987, 31, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert-Tulkens, G.; Van Hoof, F.; Tulkens, P. , Gentamicin-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis in cultured rat fibroblasts. Quantitative ultrastructural and biochemical study. Lab Invest 1979, 40, 481–491. [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove, S.E.; Vigliani, G.A.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Abrutyn, E.; Corey, G.R.; Levine, D.P.; Rupp, M.E.; Chambers, H.F.; Karchmer, A.W.; Boucher, H.W. , Initial low-dose gentamicin for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis is nephrotoxic. Clin Infect Dis 2009, 48, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcia-Macay, M.; Seral, C.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.P.; Tulkens, P.M.; Van Bambeke, F. , Pharmacodynamic evaluation of the intracellular activities of antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus in a model of THP-1 macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006, 50, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, R.A.; Kahl, B.; von Eiff, C.; Vaudaux, P.E.; Lew, D.P.; Peters, G. , Staphylococcal small colony variants have novel mechanisms for antibiotic resistance. Clin Infect Dis 1998, 27 (Suppl. S1), S68–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, G.A.; Chaussee, M.S.; Morgan, C.I.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Dorward, D.W.; Reitzer, L.J.; Musser, J.M. , Staphylococcus aureus aconitase inactivation unexpectedly inhibits post-exponential-phase growth and enhances stationary-phase survival. Infect Immun 2002, 70, 6373–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, I.; Kriegeskorte, A.; Fischer, A.; Deiwick, S.; Theimann, N.; Proctor, R.A.; Peters, G.; Herrmann, M.; Kahl, B.C. , In vivo mutations of thymidylate synthase (encoded by thyA) are responsible for thymidine dependency in clinical small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 2008, 190, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, H.F.; Miller, M.H. , Emergence of resistance to cephalothin and gentamicin during combination therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in rabbits. J Infect Dis 1987, 155, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, B.P.; Rowe, S.E.; Gandt, A.B.; Nuxoll, A.S.; Donegan, N.P.; Zalis, E.A.; Clair, G.; Adkins, J.N.; Cheung, A.L.; Lewis, K. , Persister formation in Staphylococcus aureus is associated with ATP depletion. Nat Microbiol 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.; Gattuso, M.; Grondin, G.; Marsault, E.; Bouarab, K.; Malouin, F. , Tomatidine inhibits replication of Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2011, 55, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




