Submitted:
23 March 2023
Posted:
27 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
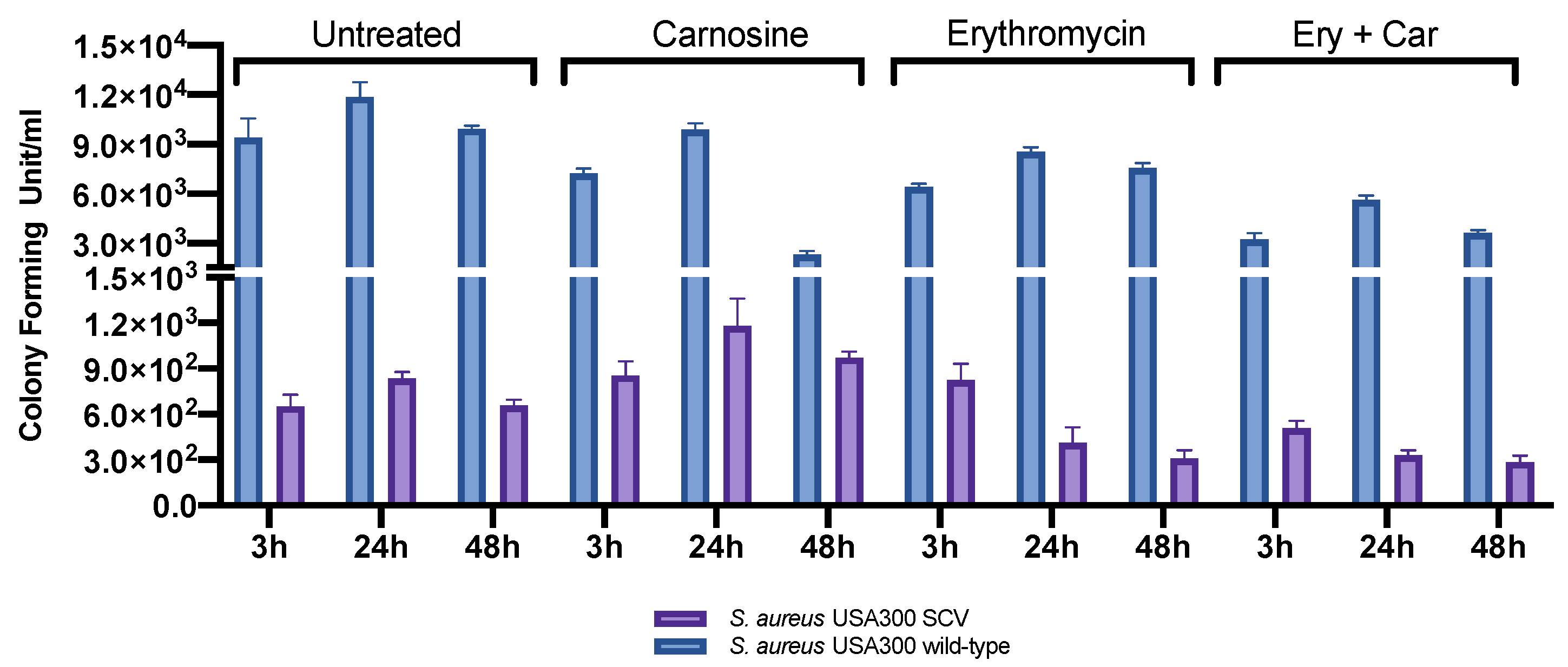
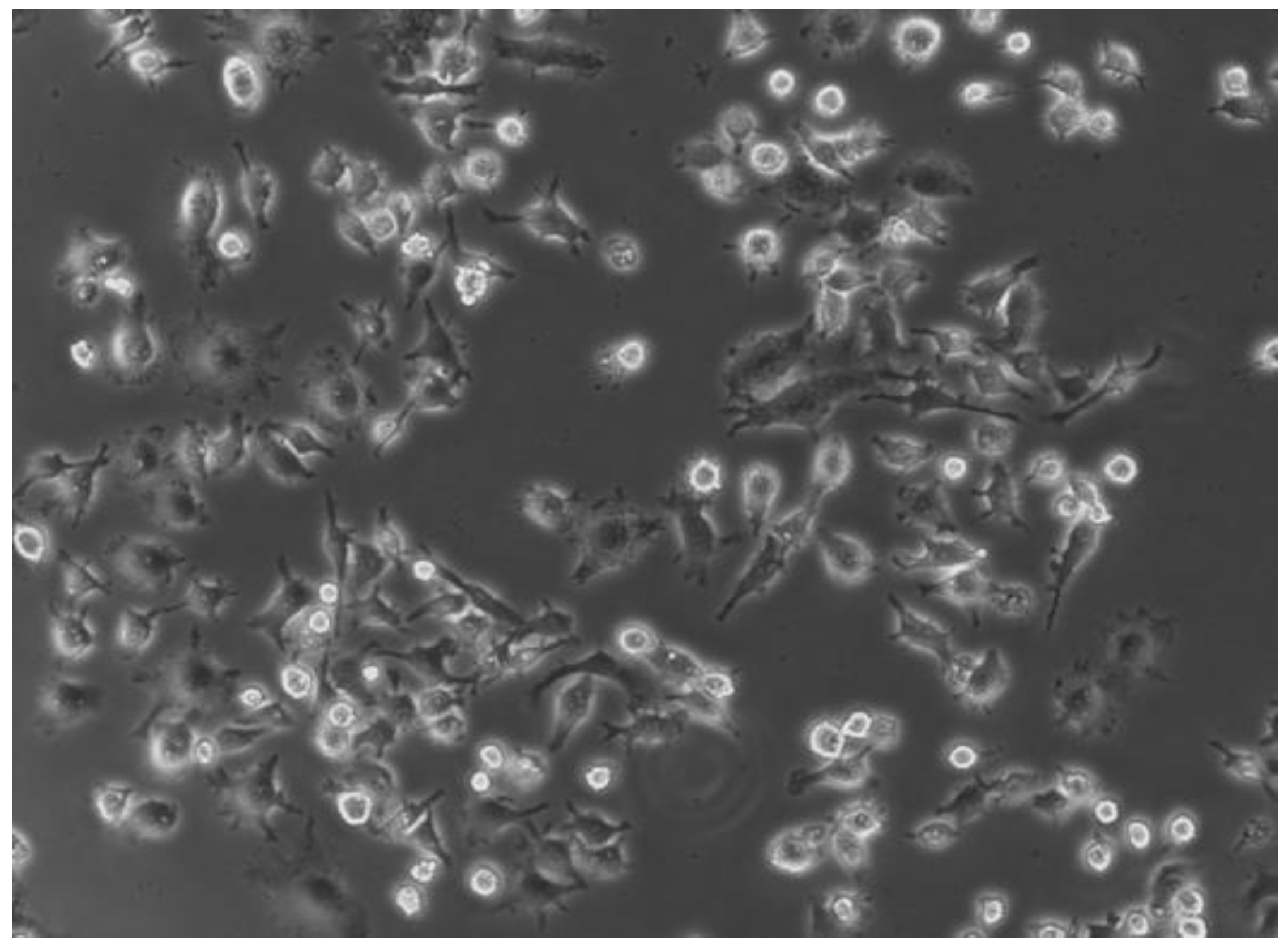
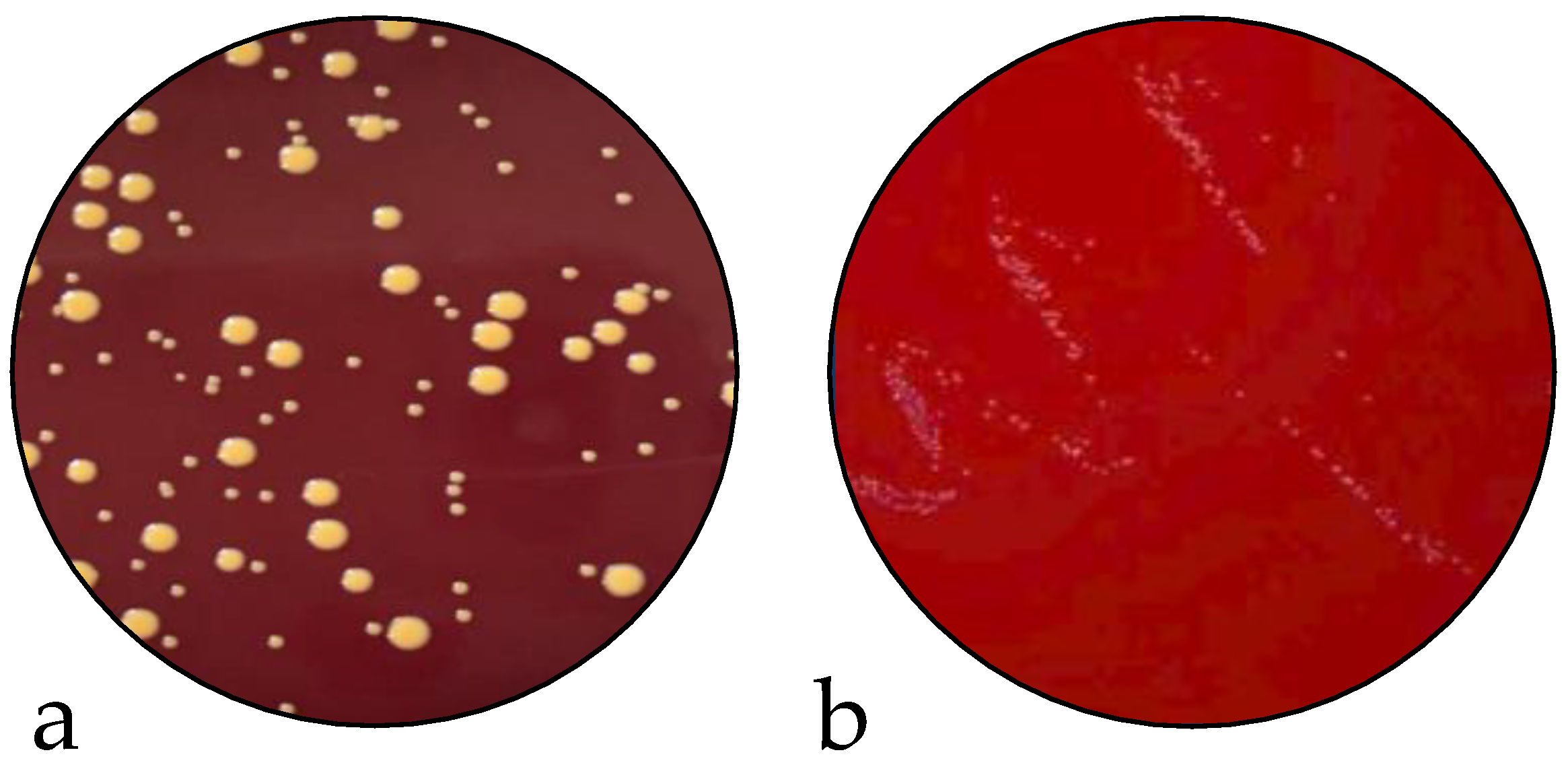
2.2. Infection Assay and Evaluation of SCV Stability
2.3. Genomic Analysis
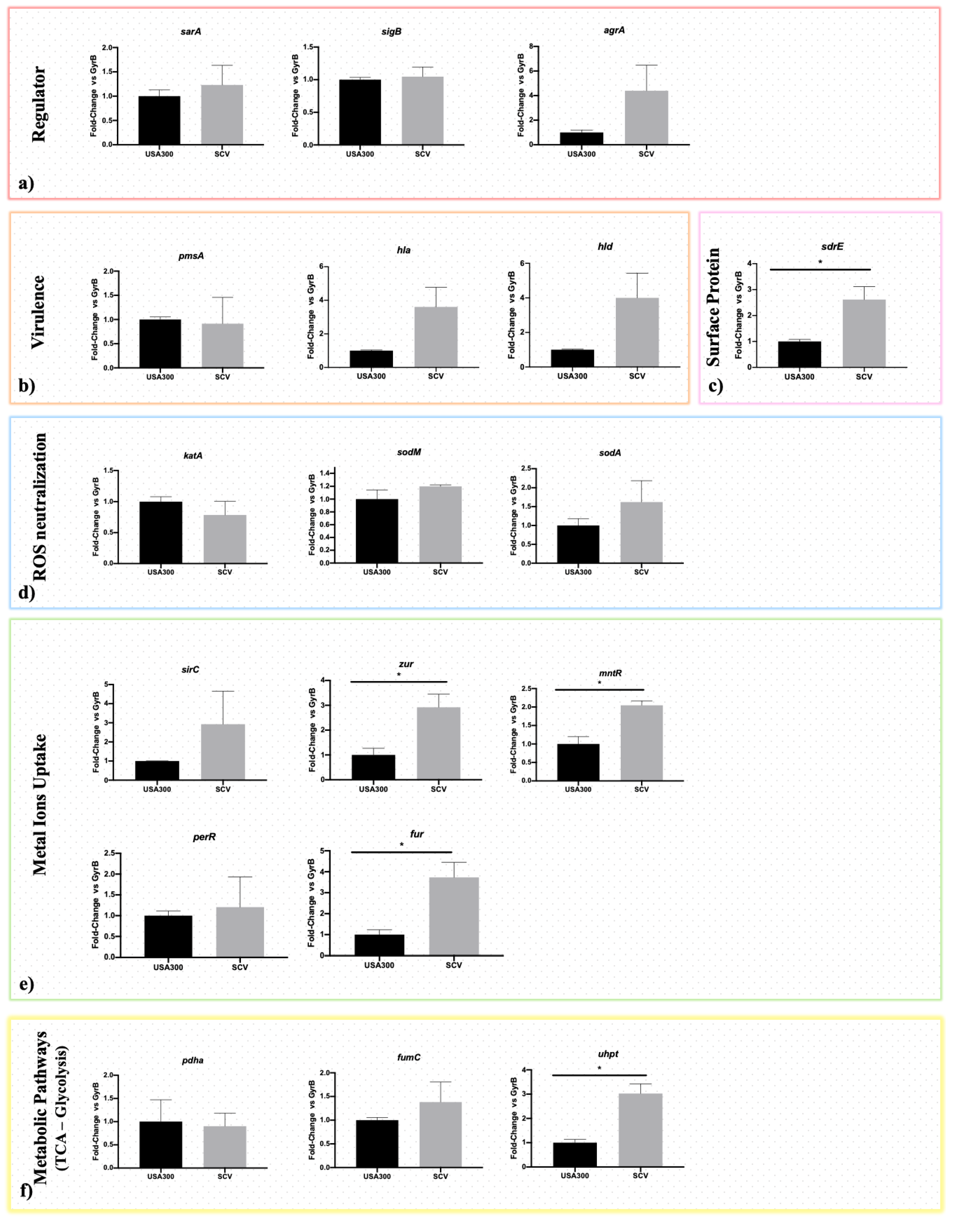
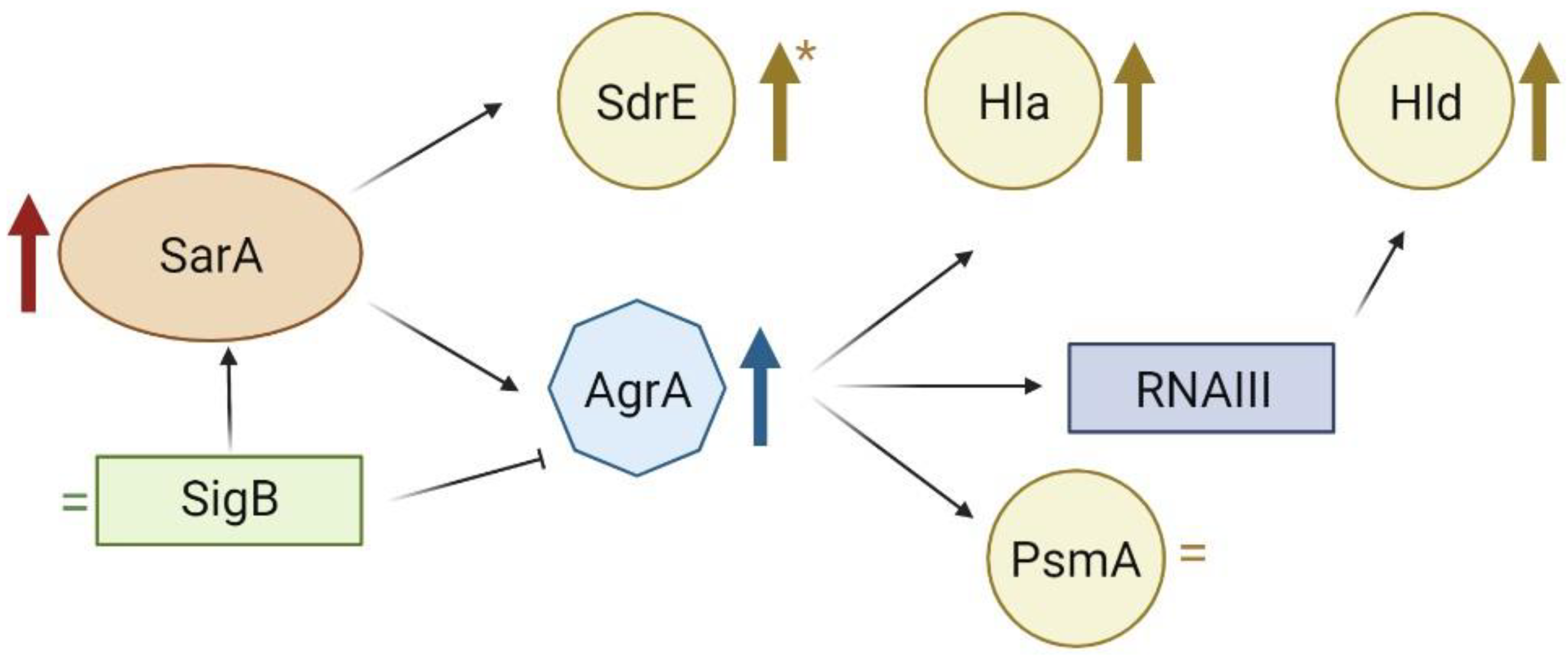
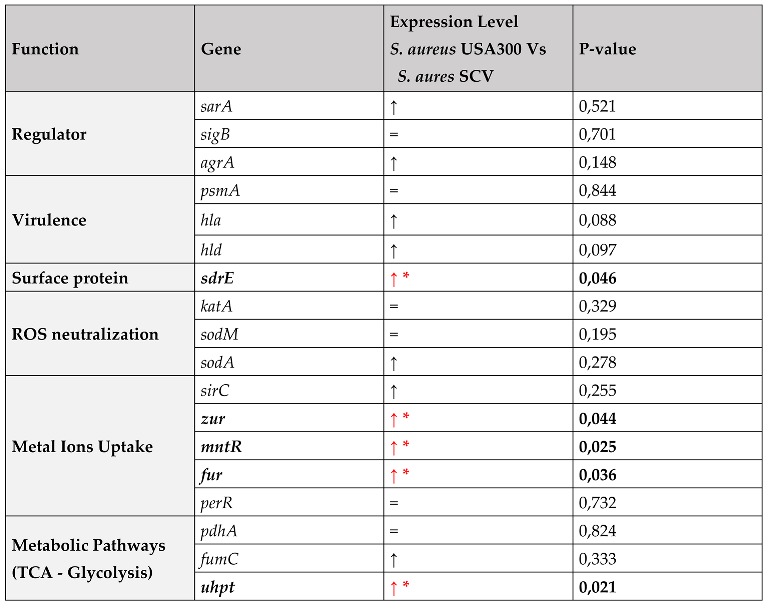
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Description
4.2. Broth Microdilution
4.3. Infection Assay
4.3.1. Eukaryotic Cell Culture Preparation
4.3.2. Infection of RAW 264.7 cells
4.3.3. Evaluation of SCV Stability
4.4. Genomic Analysis
4.4.1. DNA Extraction
4.4.2. Whole Genome Sequencing
4.4.3. Data Analysis
4.4.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.4.5. Data Availability Statement
4.5. Expression Study
4.5.1. RNA Extraction
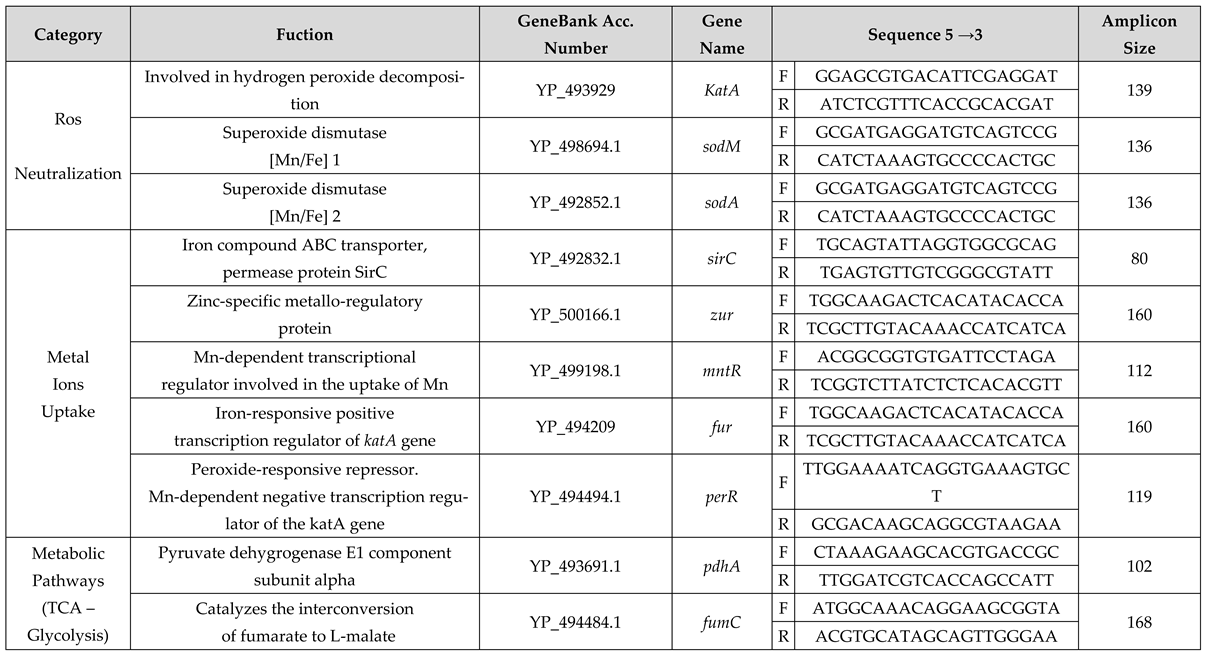
4.5.2. Primer Design
4.5.3. RT-qPCR
4.5.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Lencastre, H.; Oliveira, D.; Tomasz, A. Antibiotic Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: A Paradigm of Adaptive Power. Curr Opin Microbiol 2007, 10, 428–435. [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Corey, G.R. Epidemiology of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Clin Infect Dis 2008, 46 Suppl 5, S344-349. [CrossRef]
- Filippova, E.V.; Zemaitaitis, B.; Aung, T.; Wolfe, A.J.; Anderson, W.F. Structural Basis for DNA Recognition by the Two-Component Response Regulator RcsB. mBio 2018, 9, e01993-17. [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Staphylococcus Aureus Infections: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Management. Clin Microbiol Rev 2015, 28, 603–661. [CrossRef]
- Lakhundi, S.; Zhang, K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Molecular Characterization, Evolution, and Epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 2018, 31, e00020-18. [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Medina, E.; Hussain, M.; Völker, W.; Heitmann, V.; Niemann, S.; Holzinger, D.; Roth, J.; Proctor, R.A.; Becker, K.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Phenotype Switching: An Effective Bacterial Strategy to Escape Host Immune Response and Establish a Chronic Infection. EMBO Mol Med 2011, 3, 129–141. [CrossRef]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Heit, B.; Heinrichs, D.E. Intracellular Replication of Staphylococcus Aureus in Mature Phagolysosomes in Macrophages Precedes Host Cell Death, and Bacterial Escape and Dissemination. Cell Microbiol 2016, 18, 514–535. [CrossRef]
- Fraunholz, M.; Sinha, B. Intracellular Staphylococcus Aureus: Live-in and Let Die. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2012, 2, 43. [CrossRef]
- Horn, J.; Stelzner, K.; Rudel, T.; Fraunholz, M. Inside Job: Staphylococcus Aureus Host-Pathogen Interactions. Int J Med Microbiol 2018, 308, 607–624. [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, D.; Musso, N.; Lazzaro, L.M.; Mongelli, G.; Stefani, S.; Campanile, F. Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Persistence in Osteoblasts Using Imaging Flow Cytometry. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1017. [CrossRef]
- Stracquadanio, S.; Musso, N.; Costantino, A.; Lazzaro, L.M.; Stefani, S.; Bongiorno, D. Staphylococcus Aureus Internalization in Osteoblast Cells: Mechanisms, Interactions and Biochemical Processes. What Did We Learn from Experimental Models? Pathogens 2021, 10, 239. [CrossRef]
- Kubica, M.; Guzik, K.; Koziel, J.; Zarebski, M.; Richter, W.; Gajkowska, B.; Golda, A.; Maciag-Gudowska, A.; Brix, K.; Shaw, L.; et al. A Potential New Pathway for Staphylococcus Aureus Dissemination: The Silent Survival of S. Aureus Phagocytosed by Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. PLoS One 2008, 3, e1409. [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Tirado, F.H.; Onken, M.D.; Cooper, J.A.; Klein, R.S.; Doering, T.L. Trojan Horse Transit Contributes to Blood-Brain Barrier Crossing of a Eukaryotic Pathogen. mBio 2017, 8, e02183-16. [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Tirado, F.H.; Doering, T.L. False Friends: Phagocytes as Trojan Horses in Microbial Brain Infections. PLoS Pathog 2017, 13, e1006680. [CrossRef]
- Cafruny, W.A.; Bradley, S.E. Trojan Horse Macrophages: Studies with the Murine Lactate Dehydrogenase-Elevating Virus and Implications for Sexually Transmitted Virus Infection. J Gen Virol 1996, 77 ( Pt 12), 3005–3012. [CrossRef]
- Percivalle, E.; Sammartino, J.C.; Cassaniti, I.; Arbustini, E.; Urtis, M.; Smirnova, A.; Concardi, M.; Belgiovine, C.; Ferrari, A.; Lilleri, D.; et al. Macrophages and Monocytes: “Trojan Horses” in COVID-19. Viruses 2021, 13, 2178. [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, D.; Musso, N.; Caruso, G.; Lazzaro, L.M.; Caraci, F.; Stefani, S.; Campanile, F. Staphylococcus Aureus ST228 and ST239 as Models for Expression Studies of Diverse Markers during Osteoblast Infection and Persistence. Microbiologyopen 2021, 10, e1178. [CrossRef]
- Pidwill, G.R.; Gibson, J.F.; Cole, J.; Renshaw, S.A.; Foster, S.J. The Role of Macrophages in Staphylococcus Aureus Infection. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Hipkiss, A.R.; Preston, J.E.; Himsworth, D.T.; Worthington, V.C.; Keown, M.; Michaelis, J.; Lawrence, J.; Mateen, A.; Allende, L.; Eagles, P.A.; et al. Pluripotent Protective Effects of Carnosine, a Naturally Occurring Dipeptide. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1998, 854, 37–53. [CrossRef]
- Gariballa, S.E.; Sinclair, A.J. Carnosine: Physiological Properties and Therapeutic Potential. Age Ageing 2000, 29, 207–210. [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.; Harris, R.C.; Kim, H.J.; Harris, B.D.; Sale, C.; Boobis, L.H.; Kim, C.K.; Wise, J.A. Influence of Beta-Alanine Supplementation on Skeletal Muscle Carnosine Concentrations and High Intensity Cycling Capacity. Amino Acids 2007, 32, 225–233. [CrossRef]
- Kalyankar, G.D.; Meister, A. Enzymatic Synthesis of Carnosine and Related Beta-Alanyl and Gamma-Aminobutyryl Peptides. J Biol Chem 1959, 234, 3210–3218. [CrossRef]
- Aldini, G.; Piccoli, A.; Beretta, G.; Morazzoni, P.; Riva, A.; Marinello, C.; Maffei Facino, R. Antioxidant Activity of Polyphenols from Solid Olive Residues of c.v. Coratina. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 121–128. [CrossRef]
- Rokicki, J.; Li, L.; Imabayashi, E.; Kaneko, J.; Hisatsune, T.; Matsuda, H. Daily Carnosine and Anserine Supplementation Alters Verbal Episodic Memory and Resting State Network Connectivity in Healthy Elderly Adults. Front Aging Neurosci 2015, 7, 219. [CrossRef]
- Proctor, R.A.; von Eiff, C.; Kahl, B.C.; Becker, K.; McNamara, P.; Herrmann, M.; Peters, G. Small Colony Variants: A Pathogenic Form of Bacteria That Facilitates Persistent and Recurrent Infections. Nat Rev Microbiol 2006, 4, 295–305. [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.A.; Olsen, R.J.; Long, S.W.; Rosato, A.E.; Musser, J.M. Identification of Point Mutations in Clinical Staphylococcus Aureus Strains That Produce Small-Colony Variants Auxotrophic for Menadione. Infect Immun 2014, 82, 1600–1605. [CrossRef]
- Besier, S.; Ludwig, A.; Ohlsen, K.; Brade, V.; Wichelhaus, T.A. Molecular Analysis of the Thymidine-Auxotrophic Small Colony Variant Phenotype of Staphylococcus Aureus. Int J Med Microbiol 2007, 297, 217–225. [CrossRef]
- Guérillot, R.; Kostoulias, X.; Donovan, L.; Li, L.; Carter, G.P.; Hachani, A.; Vandelannoote, K.; Giulieri, S.; Monk, I.R.; Kunimoto, M.; et al. Unstable Chromosome Rearrangements in Staphylococcus Aureus Cause Phenotype Switching Associated with Persistent Infections. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2019, 116, 20135–20140. [CrossRef]
- Wong Fok Lung, T.; Monk, I.R.; Acker, K.P.; Mu, A.; Wang, N.; Riquelme, S.A.; Pires, S.; Noguera, L.P.; Dach, F.; Gabryszewski, S.J.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Small Colony Variants Impair Host Immunity by Activating Host Cell Glycolysis and Inducing Necroptosis. Nat Microbiol 2020, 5, 141–153. [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, A.; Fraunholz, M.J. In or out: Phagosomal Escape of Staphylococcus Aureus. Cell Microbiol 2019, 21, e12997. [CrossRef]
- Tuchscherr, L.; Bischoff, M.; Lattar, S.M.; Noto Llana, M.; Pförtner, H.; Niemann, S.; Geraci, J.; Van de Vyver, H.; Fraunholz, M.J.; Cheung, A.L.; et al. Sigma Factor SigB Is Crucial to Mediate Staphylococcus Aureus Adaptation during Chronic Infections. PLoS Pathog 2015, 11, e1004870. [CrossRef]
- Horsburgh, M.J.; Clements, M.O.; Crossley, H.; Ingham, E.; Foster, S.J. PerR Controls Oxidative Stress Resistance and Iron Storage Proteins and Is Required for Virulence in Staphylococcus Aureus. Infect Immun 2001, 69, 3744–3754. [CrossRef]
- Horsburgh, M.J.; Ingham, E.; Foster, S.J. In Staphylococcus Aureus, Fur Is an Interactive Regulator with PerR, Contributes to Virulence, and Is Necessary for Oxidative Stress Resistance through Positive Regulation of Catalase and Iron Homeostasis. J Bacteriol 2001, 183, 468–475. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, A.; Singh, V.K.; Cabrera, G.; Jayaswal, R.K. Molecular Characterization of the Ferric-Uptake Regulator, Fur, from Staphylococcus Aureus. Microbiology (Reading) 2000, 146 ( Pt 3), 659–668. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N. Metal Ion Transporters and Homeostasis. EMBO J 1999, 18, 4361–4371. [CrossRef]
- Agranoff, D.D.; Krishna, S. Metal Ion Homeostasis and Intracellular Parasitism. Mol Microbiol 1998, 28, 403–412. [CrossRef]
- Kriegeskorte, A.; König, S.; Sander, G.; Pirkl, A.; Mahabir, E.; Proctor, R.A.; von Eiff, C.; Peters, G.; Becker, K. Small Colony Variants of Staphylococcus Aureus Reveal Distinct Protein Profiles. Proteomics 2011, 11, 2476–2490. [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Conly, J.; McClure, J.-A.; Kurwa, H.A.; Zhang, K. Arginine Catabolic Mobile Element in Evolution and Pathogenicity of the Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Strain USA300. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 275. [CrossRef]
- M100Ed32 | Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 32nd Edition Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- EUCAST: Clinical Breakpoints and Dosing of Antibiotics Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- MiSeq System Denature and Dilute Libraries Guide (15039740). 15.
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet.journal 2011, 17, 10–12. [CrossRef]
- Krueger, F. Trim Galore 2022.
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving Bacterial Genome Assemblies from Short and Long Sequencing Reads. PLOS Computational Biology 2017, 13, e1005595. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [CrossRef]
- Li, H. A Statistical Framework for SNP Calling, Mutation Discovery, Association Mapping and Population Genetical Parameter Estimation from Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; et al. Twelve Years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet 2000, 16, 276–277. [CrossRef]
- Fresta, C.G.; Fidilio, A.; Lazzarino, G.; Musso, N.; Grasso, M.; Merlo, S.; Amorini, A.M.; Bucolo, C.; Tavazzi, B.; Lazzarino, G.; et al. Modulation of Pro-Oxidant and Pro-Inflammatory Activities of M1 Macrophages by the Natural Dipeptide Carnosine. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 776. [CrossRef]
- Cafiso, V.; Bertuccio, T.; Purrello, S.; Campanile, F.; Mammina, C.; Sartor, A.; Raglio, A.; Stefani, S. DltA Overexpression: A Strain-Independent Keystone of Daptomycin Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2014, 43, 26–31. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shopsin, B.; Zhao, Y.; Smyth, D.; Wasserman, G.A.; Fang, C.; Liu, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N. Real-Time Nucleic Acid Sequence-Based Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection and Quantification of Agr Functionality in Clinical Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates. J Clin Microbiol 2012, 50, 657–661. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





