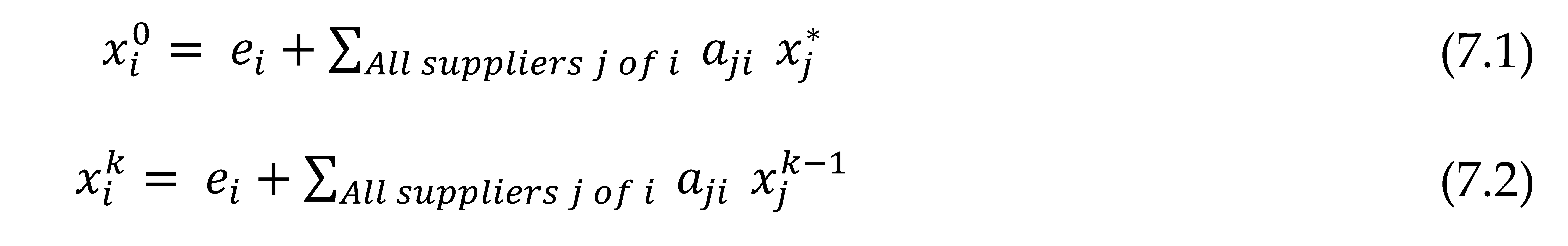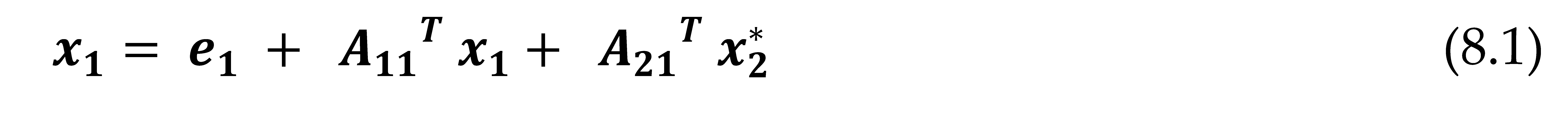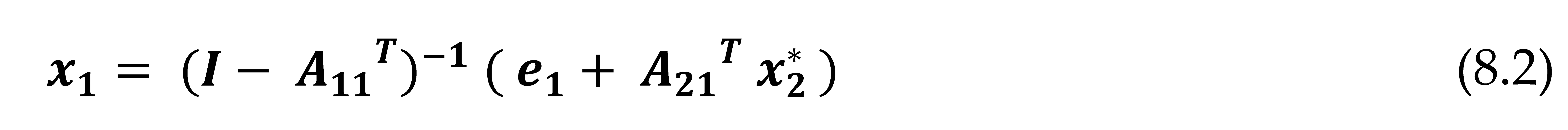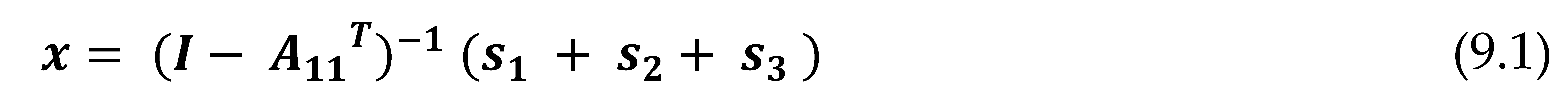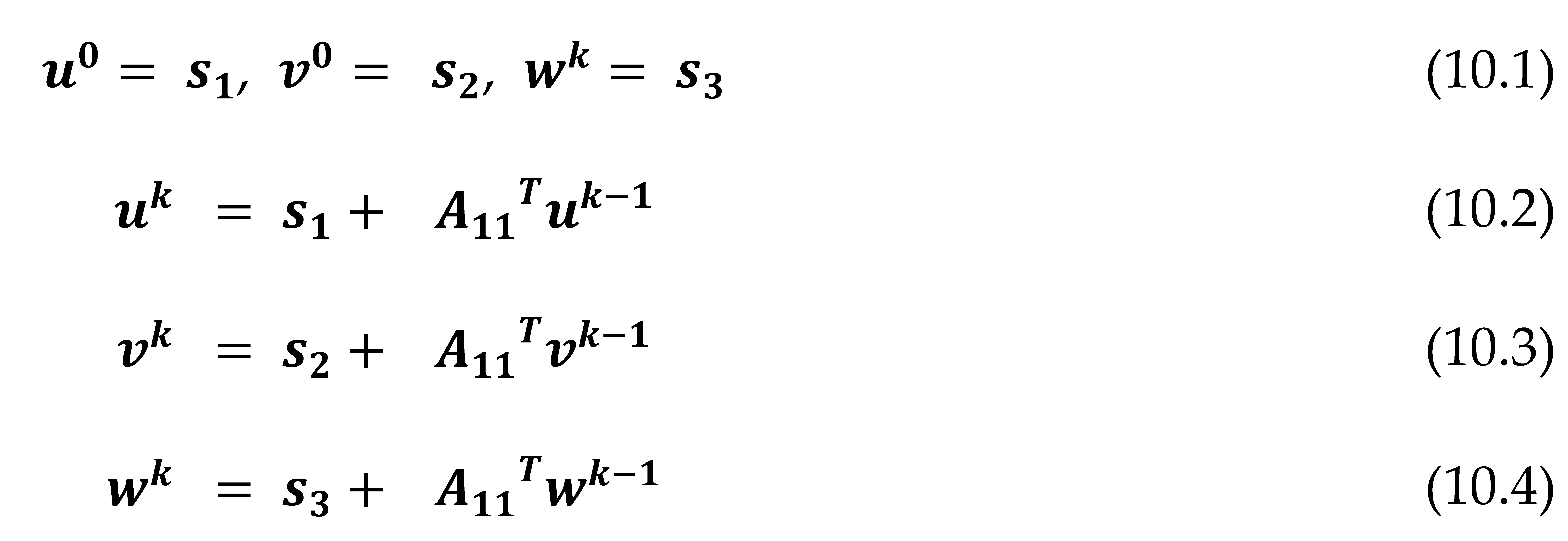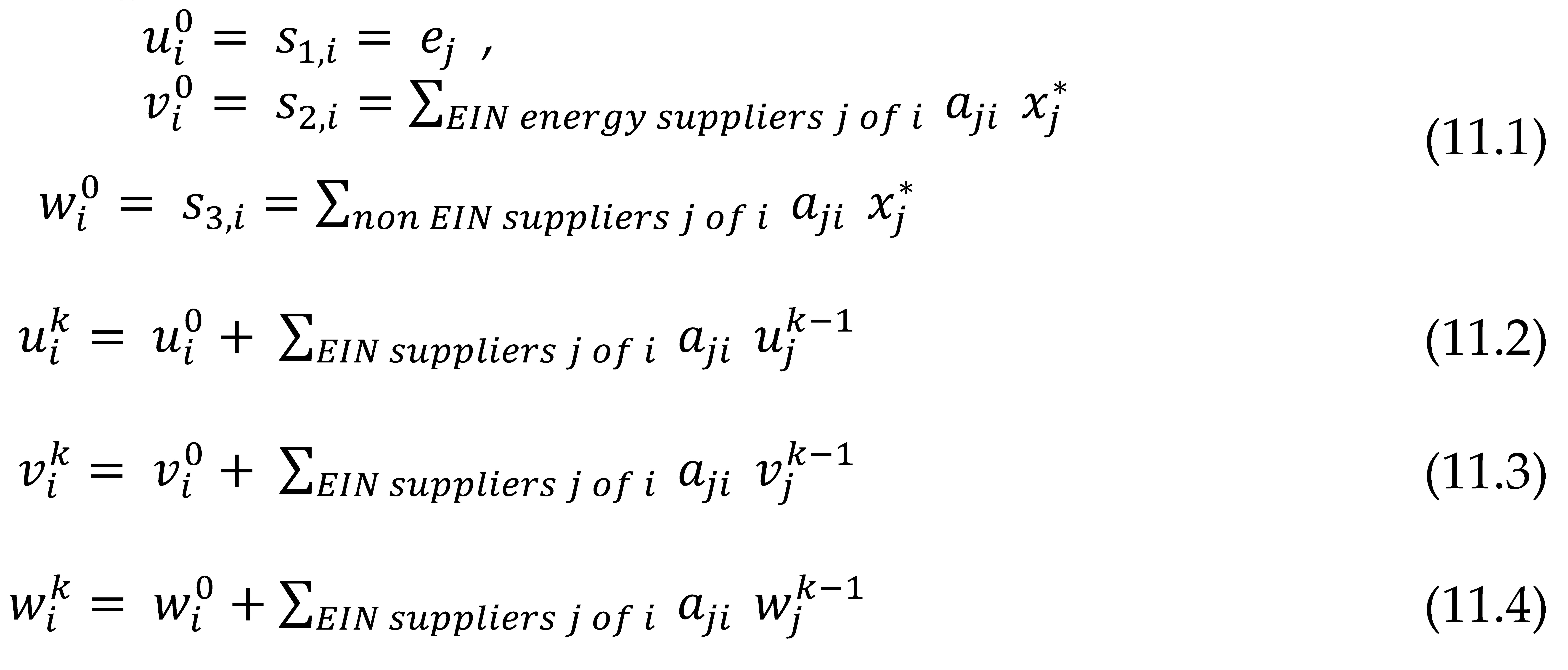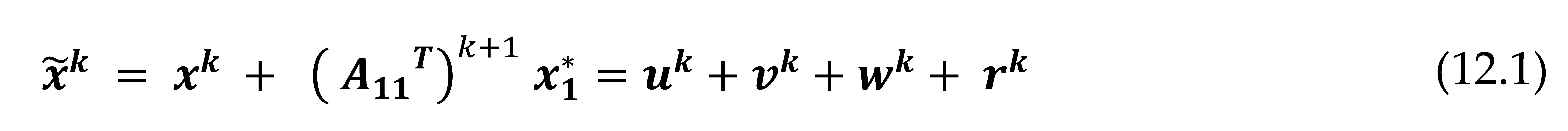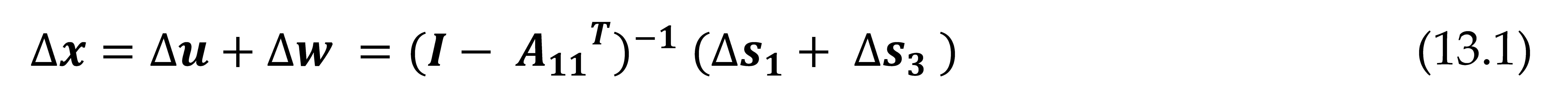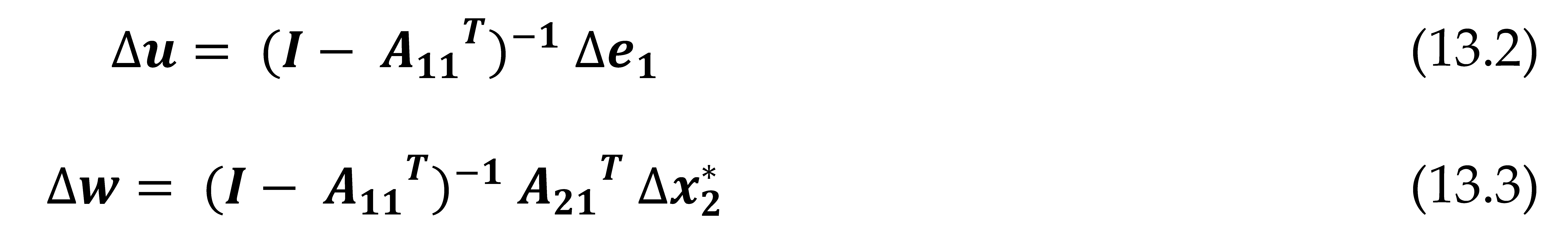1. Introduction
There is an increasing interest from governments, companies and NGO’s for mechanisms to inform purchasers about the carbon footprint of products and services, should the purchasers be company procurement decision makers or final consumers. The rationale is to help purchasers to minimize the climate impact of their purchasing decisions. So it is key to reduce the uncertainty of the figures provided to purchasers down to an acceptable level, to avoid erroneous decisions.
Conventional approaches of carbon footprinting still lack of precision, be it by using the GHG Protocol [
1,
2,
3] for estimating the scopes 1/2/3 of companies, or simply using average emissions factors (EF) provided by the Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) of products and services [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. For instance, the scope 3 reported by companies of the ICT sector seem to suffer from significant underestimation biases [
10,
11]. Using such carbon footprints estimates, a purchaser may be able to compare the carbon footprint of two products coming from two different supply chains belonging to different world regions with different carbon intensities of energy (e.g. Europe and Rest of World), but this will likely not be the case if the two supply chains belong to the same region (e.g. Europe).
To determine the level of precision that is required, one should estimate the biases and uncertainties of the production footprints of products (their emission factors). Let’s picture a purchaser that faces the choice between two suppliers of a product with the same price but different observed production footprints
x1 and
x2 >
x1 and let’s assume they are bias free and have equal standard deviation
σ. The common sense decision, based on the assumption the observed footprints are close estimators of the true footprints, is to choose the supplier with the lower observed footprint
x1. However the reliability of such a decision depends strongly on
σ. We illustrate two cases in
Figure 1 with two different values of
σ assuming gaussian probability distributions of the true footprint. When
σ is half the difference
x2 −
x1, probability distributions of the true footprints are well separated and there is around 8% probability for the purchaser to make a wrong decision; when
σ is equal to the full difference, such probability raises to 24%. And the situation obviously worsens in case of non-zero biases. In reality, the purchaser must not only look at the production footprint, he must include in his analysis the carbon footprint due to the use and disposal of the products (the downstream scope 3) but the rationale remains the same.
The purpose of this paper is to contribute to the research effort towards increasing the precision of carbon footprints, or more generally, of any environmental impact. More precisely, we look at improving the figures of the production footprints, defined as the sum of scope 1, scope 2 and upstream scope 3 footprints. We do not address the downsteam scope 3 footprints. To improve the production footprints, we propose to use the distributed computational model outlined in [
14], distributed ideally across all companies, or at least, to be pragmatic, involving a significant population of companies (e.g. a country or an economic sector) to obtain carbon footprints with increased reliability, from as much company-level direct emissions data as possible. The rationale is that for direct emissions, the bias is neglegible and the statistical uncertainty is small (in the order of 10%) while they are both significant for the emission factors of products and services, should they be obtained from Life Cycle Analyses (LCA) or from macroeconomic level Input Output (IO) analysis.
The computational model we propose in this paper also provides ways to estimate the level of precision, subject to hypotheses on the bias and statistical uncertainty of the input data at company-level, both for direct emissions and emission factors.
In
Section 2, we introduce the distributed computational model, that is derived from the classical IO model [
12]. It relies on a simple description of the economy as a network of economic players that operate both as suppliers and purchasers. The IO model can be seen as a genuine linear systemic model. For macroeconomic analyses, the number of players is small (e.g. 44 economic sectors in the ICIO database [
13]), but the IO model is by no means restricted to macroeconomic analyses. We propose to use it at the very dense microeconomic level of companies. A strong simplification at this stage is that we assume single-product firms (the multi-product case is discussed in Section VI). Dealing with companies requires to solve a linear system with very high dimensionality but in practice the matrix of the linear system is very sparse, because any given enterprise has a very low number of suppliers as compared to the total number of companies. Moreover, it was shown recently in [
14] that solving the linear system can be reformulated as calculating the limit of a sequence of approximated footprints converging towards the solution of the system. Because every company has a direct knowledge of its suppliers and the amounts bought from them, such sequential computation can be distributed throughout all the companies, so that the calculation finally consists of iterating sums of weighted inventories similar to the weighted inventories specified for the GHG protocol scope 3 calculations. In this paper, we review the model proposed in [
14] in the ideal case where all required information is available for all world ‘s companies, and we extend it into a more flexible and realistic model to take into account companies that do not take part in the distributed computational task.
In
Section 3, we look at the convergence rates. Satisfactory convergence is reached in no more than seven steps in the macroeconomic case we have studied (ICIO with 44 sectors and two world regions). However, the convergence rate depends on the mean length of the value chains. We hypothesize longer but reasonable convergence rates when working at the level of companies.
In
Section 4, using linear sensitivity analysis, we show how to estimate the bias of the calculated footprints, as a function of the biases of direct emissions (scope 1) and of average scope 2 and scope 3 emission factors derived from available databases. Such bias calculation can be built into the distributed computational task, for instance if we hypothesize three different biases for scope 1, scope 2 and scope 3 emissions factors. As for statistical uncertainty, even under the assumption that direct emissions and emissions factors are statistically independent, the calculation cannot be done in a distributed fashion, it has to be done by unfolding the tree of suppliers.
In
Section 5, we describe the actors involved in such a real world distributed process, and underline the necessity of a data exchange protocol. Finally, in
Section 6 we discuss the practical aspects for the process to work: dealing with multi-products firms, ensuring confidentiality of company data, integrating the mechanism in the accountancy processes and software, built-in heuristics for detecting faulty estimations, the need for auditing the estimations. We also discuss the use of physical units rather than monetary units, and we discuss the impact of the options how to take into account the carbon footprint of multi-year investments.
2. Applying the Input-Output Approach to the Calculation of Companies Production Footprints
2.1. Using the Standard Demand-Driven Model
Input-Output (IO) analysis is commonly used at a macroeconomic scale by national accounts to calculate the upstream footprint of final demand of households. Moreover, it is also suitable to calculate the upstream footprints of intermediate sectors, using the EIO-LCA approach [
15] and similar approaches [
16,
17]. Yet the underlying IO model is also theoretically relevant at the microeconomic level of companies, since it just relies on a simple description of the economy as a network of economic players that act both as suppliers and purchasers.
The economic activities are divided into
n economic players, typically
n = 44 ICIO economic sectors [
13] at the macroeconomic level, but reaching several millions players per country (23 milllions for the EU) when we go down to the microeconomic level of companies. The economic players buy one from another to enable their own productions. We refer to this as intermediate consumption, or intermediate demand. To the
n economic players correspond
n final demand markets, directly consuming their products for final use.
In the standard IO model, the natural system variables are an n dimension production vector P of all economic players, and an n dimension demand vector D of the final demand for their products and services. The economic exchanges between the economic actors are described by a matrix C, its Cij elements denoting in monetary units the sales of player i to economic player j.
The standard model is a demand driven model where the endogenous production variable P is related to the exogeneous final demand variable D by the linear system:
where Leontief matrix
A is the
C matrix normalized by the production values, on a column by column basis:
where [
P] denotes the diagonal matrix derived from the production vector
P.
The standard approach is used several ways. It is commonly used by national statistical offices to calculate the upstream footprint of final demand, on a global and sector level. More seldom is it used to calculate the production footprints of sectors [
10,
11,
12]. In this case final demand
D is no longer needed for the calculations, as the full information is contained in vector
P and matrix
A. Some care is needed in such calculations because of the interconnected nature of the economy, which induces cycling effects (e.g. cycling demand), that bring a significant overestimation bias at a macroeconomic scale [
17]. However working at a microeconomic level, we expect the cycling effect should be neglegible for a vast majority of companies.
2.2. Using Downstream Propagation Models
While the standard IO model using variables
P and
D disseminates the demand along the value chains in a upstream direction, from purchasers to suppliers (following a demand pull approach), we use a slightly different IO model with different variables: an
n dimension vector
e of direct emissions intensities of the economic players (monetary intensities) as the exogeneous variable, and an
n dimension vector
x of production footprint intensities as the endogeneous variable (Note that other notations conventions have been used, e.g. in [
18] denoting direct emissions intensities by
d and production footprint intensities by
e.).
It has been shown in [
14,
18] that they are related by the linear system:
where
AT denotes the transpose of the Leontief matrix
When working with absolute value footprints
X [
P]
x and direct emissions
E [
P]
e rather than intensity variables
x and
e, we obtain the formulation derived in [
17]:
with
B = [
P]
AT[
P]
−1.
Both formulations (3) and (4) propagate the carbon impact along the value chains downstream from suppliers to purchasers. They correspond to an impact propagation (a.k.a. impact inheritance) approach, in contrast to the demand pull approach of the standard method.
Like for endogenous variable
P of the standard approach, endogeneous variables
x and
X are subject to the cycling effect and need to be normalized by the diagonal elements of (
I −
AT)
−1 and (
I −
B)
−1 inverse matrices, that turn out to be identical values µ
i > 1, also equal to the diagonal element of the Leontief inverse (
I −
A)
−1. Thus, in theory, we should calculate footprints vectors net of cycling effect and
as
follows:
But as pointed out above, working at a microeconomic scale, we expext the cycling effect to be neglegible for the vast majority of companies. In other words, we expect µi ≈ 1 and x to be a very good estimation of . Therefore in the following we simply focus on calculating intensity vector x and its components, the intensity values xi.
2.3. Distributed Iterative Framework
At a macroeconomic level, matrix
C, production
P and final demand
D are provided by publicly available input-output tables (IOT) of yearly national accounts, in which countries report the productions, imports, exports, intermediate and final demands per industry, and on a world scale, by Multi-Region Input-Output (MRIO) tables (such as the ICIO [
13] or EXIOBASE [
19]), that further detail the international trade at a sector level. The information is centralized and the calculations are centralized in a single computer.
In the microeconomic approach developed in this paper, centralizing data collection and calculation become issues. The huge amount of data of matrix C is subject to confidentiality, and the linear system is of very large dimension, the order of magnitude being several millions vector components. With current ICT technology this is not impossible to do, but it is not practical. Thus we explore in the following a distributed approach whereby the C data remains at the nodes of the economic network, i.e. the companies, and part of the calculation is done by them.
The first step to obtain a distributed algorithm to solve equation (3) is to note that it can be solved iteratively as shown in [
14].
Instead of computing directly x = (I − AT)−1e, we compute the following sequence of vectors xk converging to x:
where vector x* is a first gross estimation (a “bootstrap”) of the companies production footprints. It is relevant to derive it from average emissions factors taken or derived from available LCA data, or in the absence of such data, or from average monetary emissions factors derived from IO analysis at a macro level. Yet, the choice of x* does not affect the convergence of the algorithm. In fact setting x* = 0 is acceptable and corresponds to the accumulation in xk of direct emissions along the value chains.
For the footprint intensity of a given company i, the iterative calculation of equation (6) can be expressed as :
where aij denote the usual “technical coefficients” of the high dimension Leontief matrix A of the companies network. In reality, A is a sparse matrix, because all companies i have a small number of suppliers compared to the total number of companies. Only few of the aji coefficients are non zero for the given enterprise i. Moreover they can be straightforwardly derived from the accountant’s book of suppliers of the enterprise, as the ratio of the purchases from every supplier j to the total sales of enterprise i. We see the summation parts of formulas (7) correspond to a converging sequence of weighted inventories of the same kind used in the GHG protocol. The summation for the first term xi0 is a classical GHG protocol estimation in terms of a monetary intensity.
2.4. Adapting the Distributed Framework to Real World Constraints
If such a distributed mechanism were to be deployed in real life, in what we may call an Environmental Impact Network (EIN), only a fraction of the companies would take part in the calculation, certainly for the first phases of the roll-out (on a given country or a given sector), and most realistically for a long time given that only a fraction of all countries may decide to implement such a system. We need to extend the model to take that fact into account.
To do this, we group the companies into two subsets, the subset of companies willing to enroll in the EIN system (the EIN subset), and the complementary subset of all other companies. For commodity, we arrange the numbering of the companies
i as follows: the companies of the EIN subset are numbered from 1 to
nEIN, and those of the complementary subset are numbered from
nEIN + 1 to
n. Transposed Leontief matrix
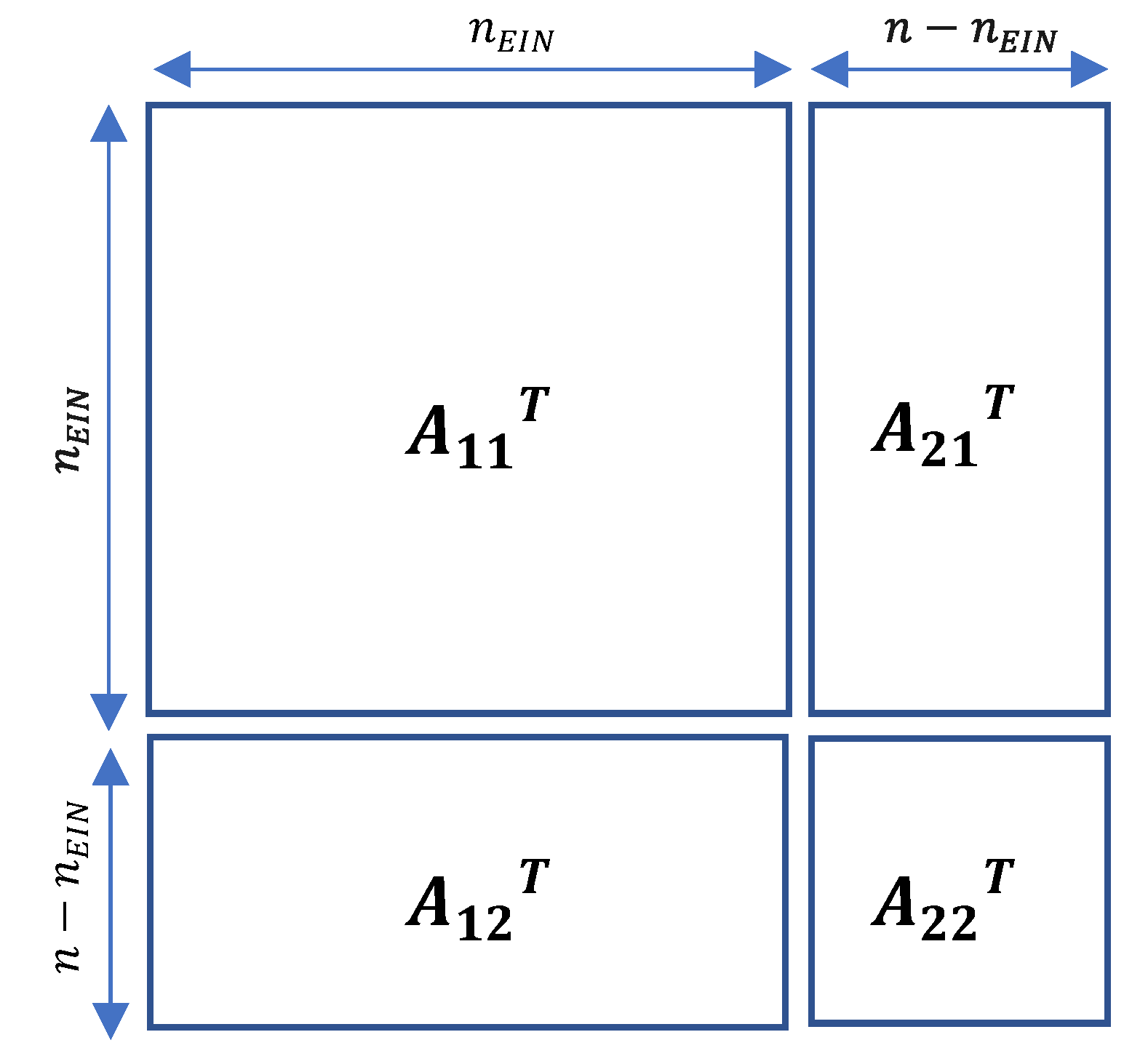
AT is partitioned, as shown in
Figure 2, into to four sub-matrices, two square matrices
A11T and
A22T resp. of dimensions
nDEIN and
n −
nEIN, and the two complementary rectangular matrices
A21T and
A12T. In the extended model, we take into account the
nEIN dimension vector of direct intensities
e1 of the EIN subset, while we use the
n −
nEIN dimension vector of approximated emissions factors
x2* of the complementary subset. The
nEIN dimension vector of estimated footprint intensities
x1 is the solutions of the following modified version of equation (3):
which we reformulate as :
Obviously, the x1 estimated intensities are different of the true intensities obtained by equations (3) or (6). The estimation error depends on the error made by replacing the true x2 intensity values of the companies outside the EIN subset by their approximated values x2*.
Note that Equation (8) only use the top two submatrices out of the four submatrices of
Figure 2.The term
A21T x2* is a constant
nEIN dimension vector containing the scope 2 and upstream scope 3 information of the complementary set, and playing a similar role to the direct intensities
e1.
Let’s reformulate equation (8.1), using notations x for x1 and s1 for e1 (the scope 1 intensity vector) and let’s split vector A21T x2* into two vectors s2 and s3 (resp. the scope 2 and upstream scope 3 intensity vectors):
We can compute a sequence of nEIN dimension vectors xk converging to x in a similar using (6) with s1 + s2 + s3 playing the role of e. Moreover, we can decompose x as the sum of three nEIN dimension vectors x = u + v + w such that:
that can be computed iteratively as three sequences of nEIN dimension vectors x = uk, vk, wk as follows:
Therefore, for a given company i, we can split its production footprint into three parts xi = ui, vi, wi with ui capturing the contribution of all known direct emissions intensities ej = s1,j of its EIN indirect suppliers, vi capturing the contribution of all scope 2 emissions factors s2,j of the energy suppliers of its indirect EIN suppliers (by convention energy suppliers are outside the EIN subset) and wi capturing the contribution of upstream scope 3 emissions factors s3,j of the non EIN suppliers of its indirect EIN suppliers. Such decomposition is interesting because the bias and uncertainty is fairly different between scope 1 and 2 emissions factors and scope 3 emissions factors.
The iteration equations (7) are replaced as follows:
In fact, taking the converging sequence xk = uk + vk + wk means starting with initial estimate x0 = e1 + A21T x2* but it does not contain an initial estimate x1* of the footprint of the EIN member. To do this we must add term A11T x1* to the initial term, which leads to a modified converging sequence with general term:
The residual term is obtained as:
It contains the dwindling contribution of EIN approximated emissions factors converging to zero. For a given company, it is computed as follows
The breakdown of the iterative footprints
into the four components
u,
v,
w,
r is illustrated in the convergence curves of
Figure 5(b).
Let’s note that the approach is flexible enough to handle finer grained divisions than breaking down the vector constants of (8.2) into three components s1, s2, s3, and therefore than the three corresponding accumulation variables u, v, w. Theoretically, it can support to any classification of emissions with respect to geographical origin, economic sector or even energy versus chemical process origin.
3. Convergence Rate
To simulate the behavior of the distributed model described in the previous section, we have used input output tables from the Inter-Country Input-Output (ICIO) database published by OECD [
13] for year 2018 and covering 44 economic sectors, and we have used the emissions data from EXIOBASE [
20].
Such simulation is done at macro level , so we need to anticipate what may happen at micro level. We have assimilated scope 2 to scope 1 since they follow a similar behavior in the iterative accumulation process and both exhibit low bias and uncertainty.
In
Figure 3 we illustrate convergence rates when all world economic players take part in the EIN system, thus all taking part to the calculation using formulas (7).
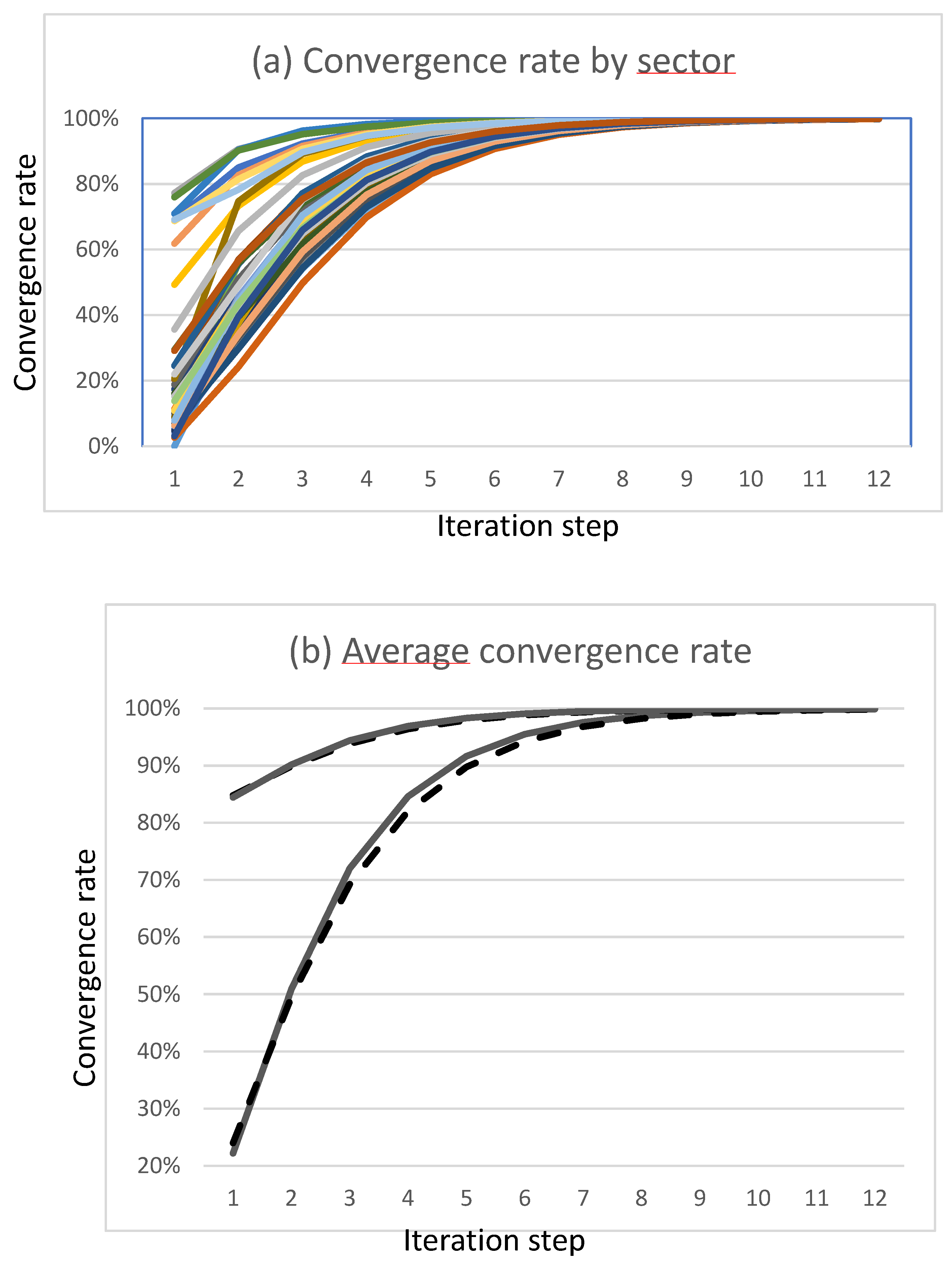
Figure 3(a) shows the convergence rate of the production intensities
xik for the 44 sectors aggregated at world level with zero initial values for emission factors. We observe significant dispersion of the convergence rates per sector. The heavy industry sectors start at higher value and converge faster than the service sectors that start at low values. For instance, one of the higher and faster converging curves corresponds to the sector of electricity, gas and steam production, while one of the lower and slower converging curves corresponds to the sector of IT services.
Figure 3(b) shows the average of convergence rates in two cases:
The areas under the lower curves of
Figure 3(b) correspond to the proportion of the
xik intensities corresponding to the intensity fractions
uik calculated from direct emissions, while the difference between lower and upper curves correspond to the proportion corresponding to the remaining intensity fractions
wik that have not been reduced to scope 1 or scope 2 intensities. As all players take part to the EIN system, the
xik values converge to the true values, and the fractions
wik tend to zero.
Taking a broad view, convergence is obtained in 4 to 7 steps which was observed by [
14] on a different dataset.
It is likely that the average length of value chains has a direct effect on convergence rate. At a micro level, the mean length of value chains are longer than at the macro level corresponding to these simulations. To evaluate the mean length of value chains, we would need realistic
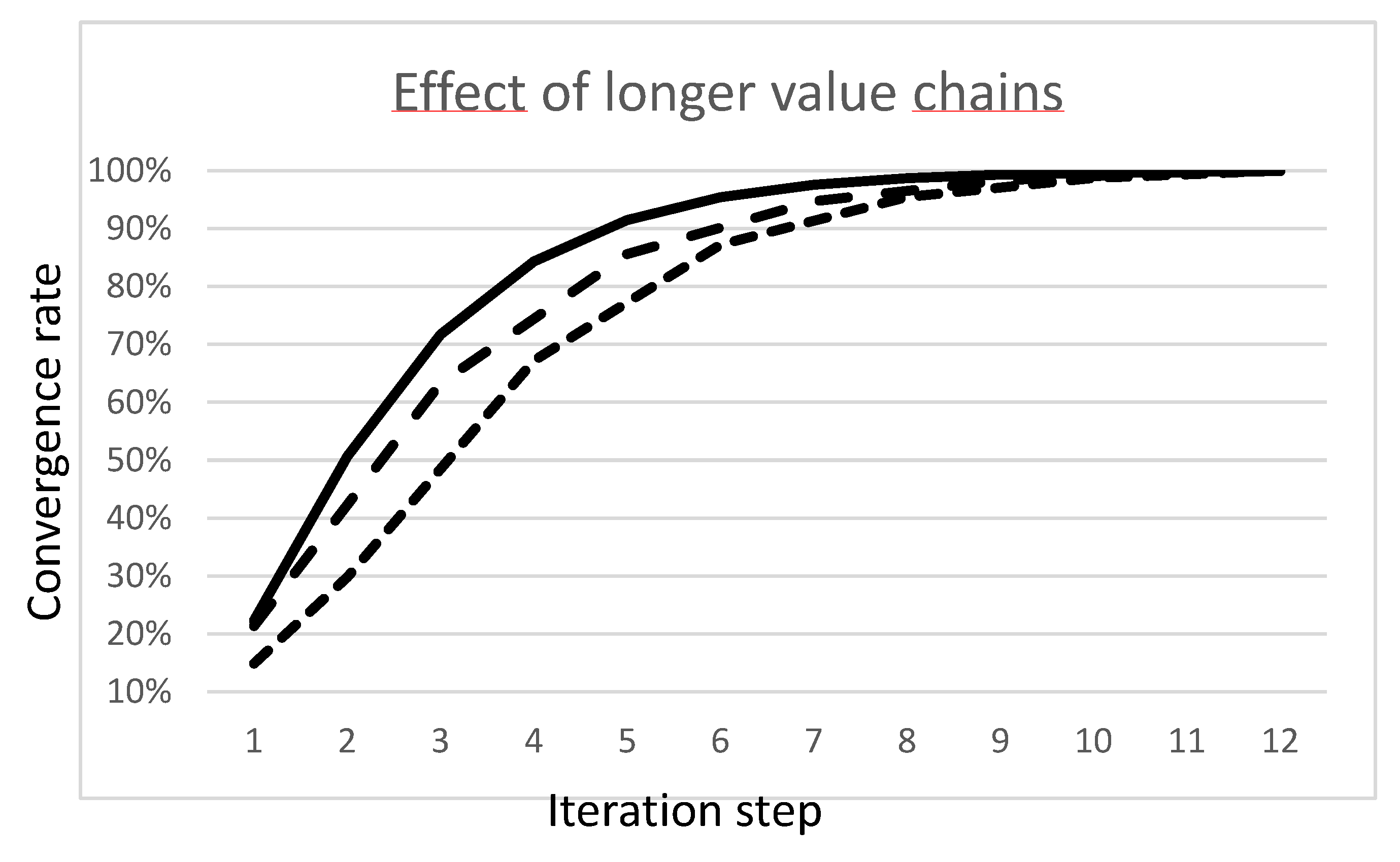
A data. For the time being we have illustrated the effect on the 44 sector ICIO data by splitting uniformly every sector into a production sub-sector and a distribution sub-sector. The theoretical effect is to double the value chains. In our simulation, we observe a significant slow down of the convergence rate for production sectors, in the order of one iteration step, and even more for distribution sectors (
Figure 4)
In Figure 5(a), using formulas (11), we illustrate convergence rates in the case of partial deployment of the distributed computational task, with two different EIN subsets, the EU and the “Rest of World”, and with the hypothesis the emission factors outside the EIN subsets are underestimated by 20%. When we take the EU as the EIN subset, the lower solid line shows the footprints that only converge to 93% of their true values, due to the Rest of World emissions factors being underestimated by 20%. The lower dashed line shows the convergence of the fraction
of the footprint calculated from direct emission data. The difference between the solid and dashed lines correspond to the fraction of footprint
that have not been reduced to scope 1 or scope 2 intensities. We see it no longer tends to zero as in
Figure 3(b). when the EIN domain encompassed the whole world. In the symmetrical situation where the Rest of World is taken as the EIN subset, the calculated footprints nearly attain their true values and the fraction of the footprint calculated from direct emission data accounts for most of them. Such different behavior between UE and Rest of World illustrates the strong dependency of UE on imports from Rest of World.
In
Figure 5(b), we show the more detailed breakdown of the iterative footprints into the four
u,
v,
w,
r components, in .the case when the EIN domain is the UE is further decomposed. While the three components
u,
v,
w,
r with their sum converging to same limit as
x and
, the residual
r decreases with the iterations and converges to zero, and its average value may serve as a convergence criterion of the whole distributed iterative system.
4. Bias and Standard Deviation
In this section we assume that coefficients aji, that are derived from companies accounts, are not subject to uncertainty, and we only explore uncertainty due to the exogeneous variables: direct emissions intensities e1 of the EIN players, and average emissions factors intensities x2* of the non-EIN players. As in the previous section, we have assimilated scope 2 emissions to scope 1 emissions since they follow a similar behavior in the iterative accumulation process and both exhibit low bias and uncertainty.
4.1. Bias Analysis
To look at the effect of the possible biases of e1 and x2* on the calculation of the production footprint x we use variation formulas derived from equations (8.2). Since the model is linear, the variations are expressed as:
We express the variations with respect to direct emissions e1 and emissions factors x2*:
In the following we explore the effect of EIN subset size on bias and uncertainty at a macroeconomic scale (economic players are economic sectors). We model the EIN subset as a world region of n = 44 ICIO sectors, with average economic structure, of variable size, and variable autonomy with respect to the rest of world. This means the sectors of the EIN region follow the same relative distribution as the sectors of the world economy, with same carbon intensities. It also means that we may vary the size of the EIN region and vary the preference of the EIN sectors for buying from EIN suppliers.
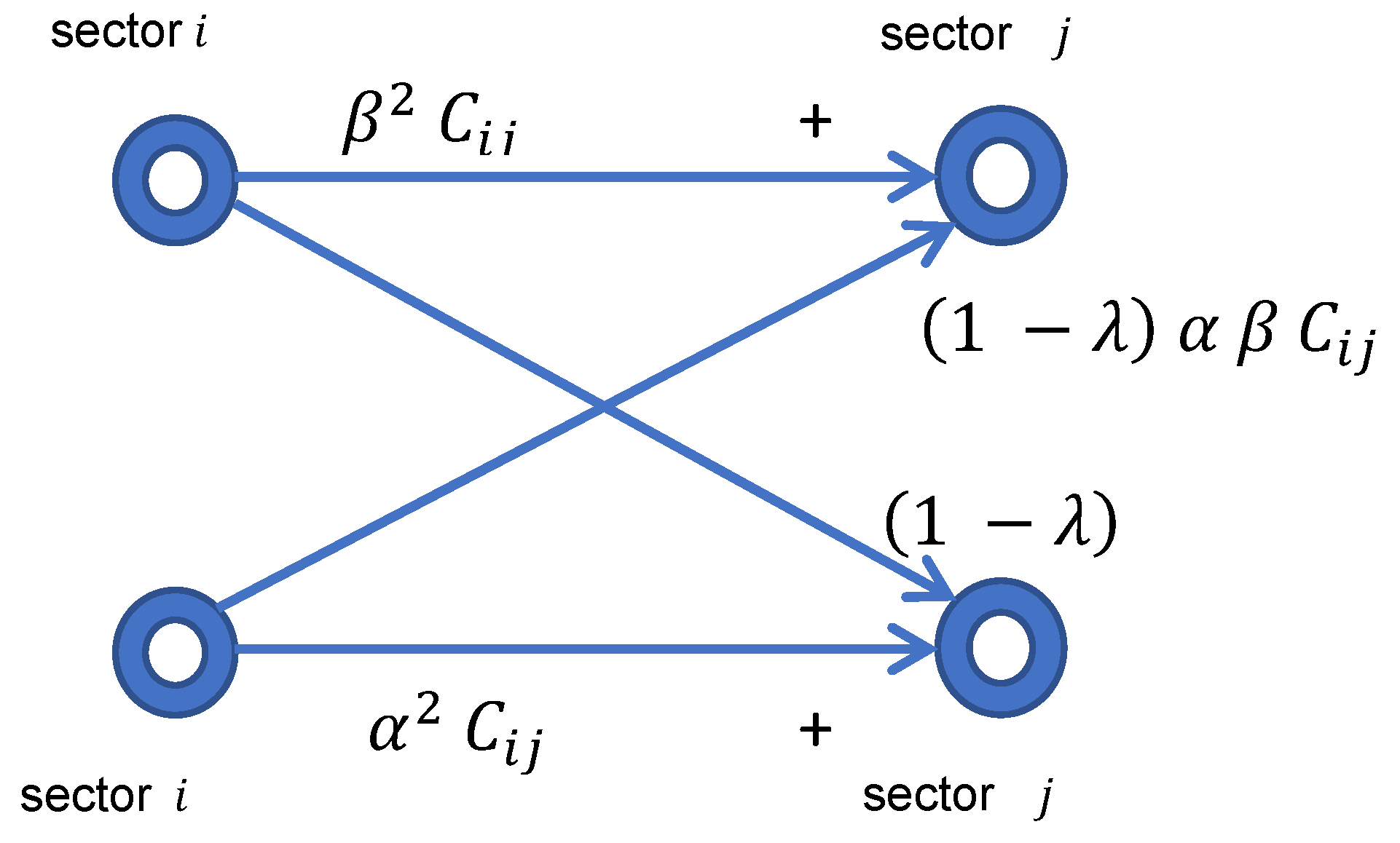
To do this we disaggregate the worldwide sectors into two regions , the EIN region itself, and the rest of world. The relative size of the EIN region is modeled by a weighting factor
β, with production vector
βP and the relative size of the rest of world by weighting factor
α = 1 −
β, with production vector
αP where
P is the world production. To derive the new table of intermediate consumptions, which now has a dimension 2
n = 88, we proceed as described in
Figure 6: we disaggregate each supply value
Cij appearing in the initial
C matrix into four values with respective weights
α2,
αβ,
αβ, and
β2, and we model the regional preference with a parameter
λ that reduces commercial exchanges between the region and the rest of the world. The Leontief matrix then results from formula (2).
Then, we use formulas (13) to compute the relative variations of the production footprints
x to 10% relative variations of direct emissions
e1 and 10% relative variation of emissions factors
x2*.
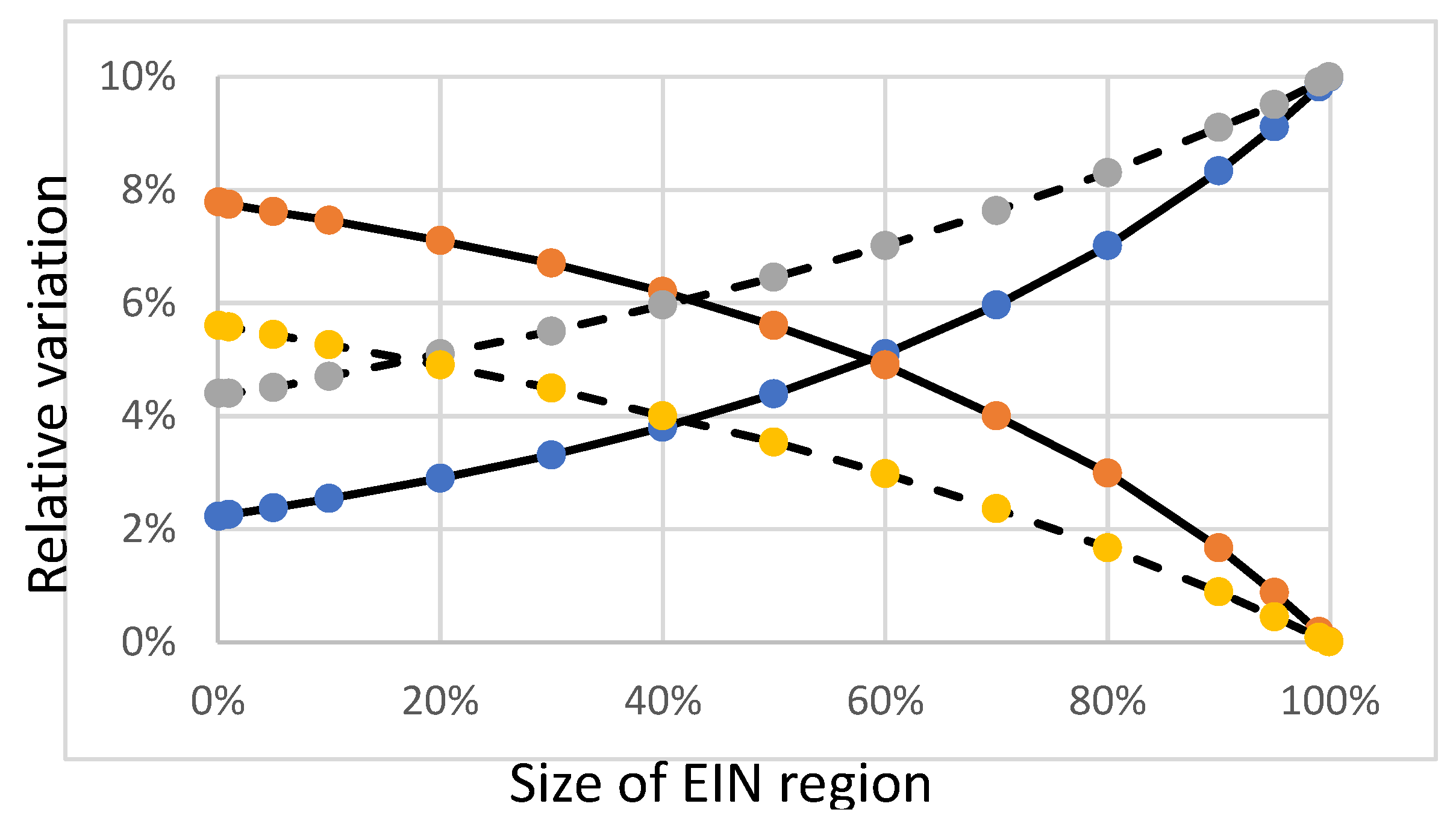
Figure 7 shows such relative variation curves as a function of region size in the case the EIN region has no autonomy
λ = 0 (solid lines) and in the case of significant autonomy with
λ = ½ (dashed lines). For very small size regions, the influence of imports are dominant, this can be seen in the high sensitivity to external emissions factors. Then as the size of the region increases, the sensitivity decreases and tends to zero as the region encompasses the whole world. Conversely, the contribution of the regions direct emissions is minimum for very small size regions, it increases with the size of the region and rends to the maximum 10% as the regions encompasses the whole world.
In reality, biases are expected to lower than 10% on EIN direct emissions and significantly higher on non-EIN emission factors, so that the rising curves in
Figure 7 are expected to be lower and the decreasing curves much higher, meaning the dominant bias is due to non EIN-emission factors.
4.2. Standard Deviation
We have used equations (8.2) to calculate the variances of the footprints assuming statistical independence of the components of the exogeneous data vectors
e1 and
x2*. Unfortunately the expression variances in not linear like (13) because of the quadratic nature of variance calculations. Calculating this for a given enterprise from the knowledge of its suppliers would require to develop the tree of its suppliers up to
k − 1 levels of indirection.
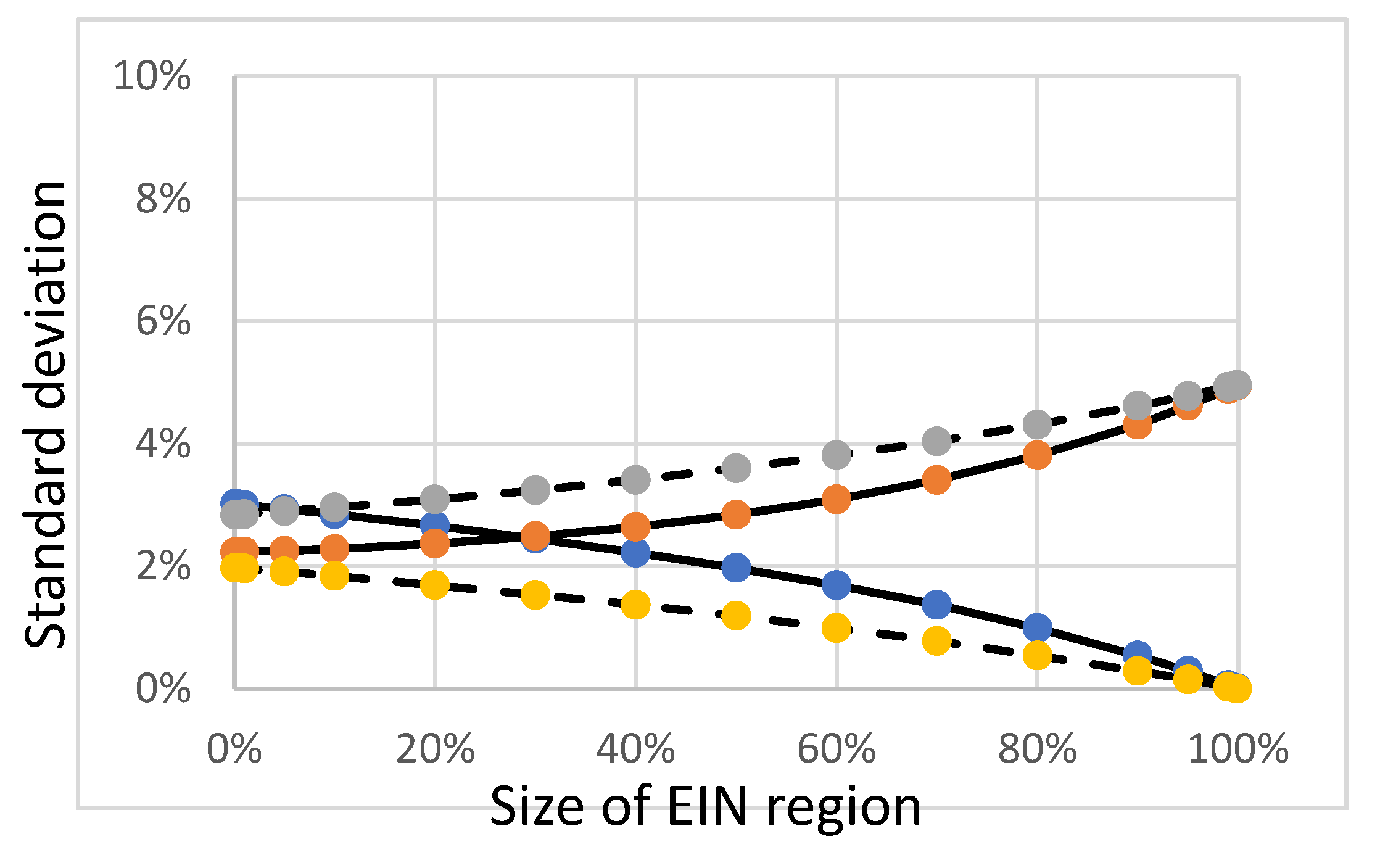
Figure 8 shows the relative standard deviations have smaller values than the relative variations of
Figure 7 and that their variations with respect to the size of the EIN region are flatter.
In reality, standard deviations are expected to range in the order 10% on EIN direct emissions, but much higher for non-EIN emission factors that rely on Life Cycle Analyses that estimate poorly uncertainty [
20]. As for biases, the dominant uncertainty due to standard deviations is expected to come from non EIN-emission factors.
5. Design of a Distributed Environmental Impact Process
In the previous section, we have simulated the results and behavior of a distributed Environment Impact Network (EIN) using ICIO data corresponding to a macroeconomic scale.
We now describe how the process may work at a microeconomic level for companies enrolled in such a EIN system.
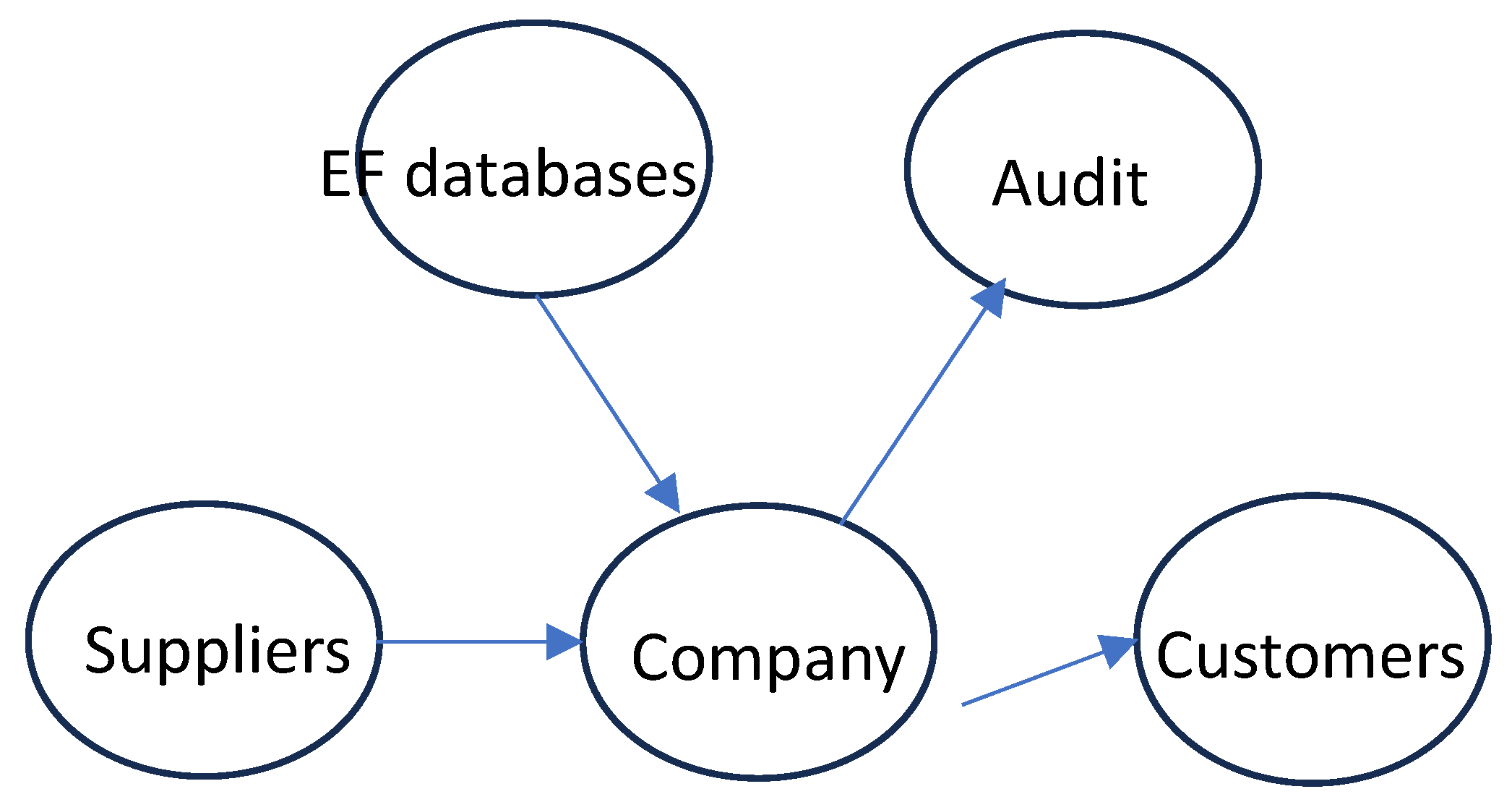
Figure 9 shows the information flows between the different parties involved in the process for any enrolled company.
The first requirement for the company is to calculate its direct emissions for the previous full year. Such estimations can be verified by auditing bodies, either systematically or on a sampling basis. Using its direct emissions intensity, the company calculates iteratively its footprint intensities and provides them to its direct customers. An updated value is provided to the customers after every iteration. In parallel, the company receives iteratively calculated footprint intensities from its suppliers also involved in the EIN process. For its suppliers outside the EIN process, the company estimates their footprint intensities from emissions factors (EF) from available databases. The calculated footprint intensities are subject to auditing, like the direct emissions.
An EIN application protocol is required for the exchange of information between suppliers and customers. The principle is very simple: send the updated values of the production footprint to the customers. A possible rule would be for the company to send an updated value only after having received the updated values from all its EIN direct suppliers. However, this may introduce delays in the process. A more flexible rule is to set a updating schedule, whereby all companies exchange their updates once every week. The protocol would include a “no change status” message to the customers.
There is a need also for a convergence criterion, for instance a threshold on the relative variation between two successive computed values. The protocol would include sending the “converged status” message to the customers. It is important to note that global convergence could be relatively fast, and would not require waiting long delay between updates. A fully converged status of the EIN calculations could be reached within a couple of months or a quarter, for the first year of operation (the “bootstrap year”). For following years (or more frequently if the accounting periods are more frequent), convergence would be much faster, since the initial values would no longer be taken from databases, but they would be the companies’ converged values of the previous year. Significant expansion of the EIN system, for instance, when the network would include new countries or new sectors, may slow down convergence, but not to the extent of the bootstrap year. Finally, the protocol must support permanent EIN boundary variations, to allow companies to join or leave the network. For instance, a company joining the EIN will be able, using the protocol, to discover the EIN members among its suppliers and customers.
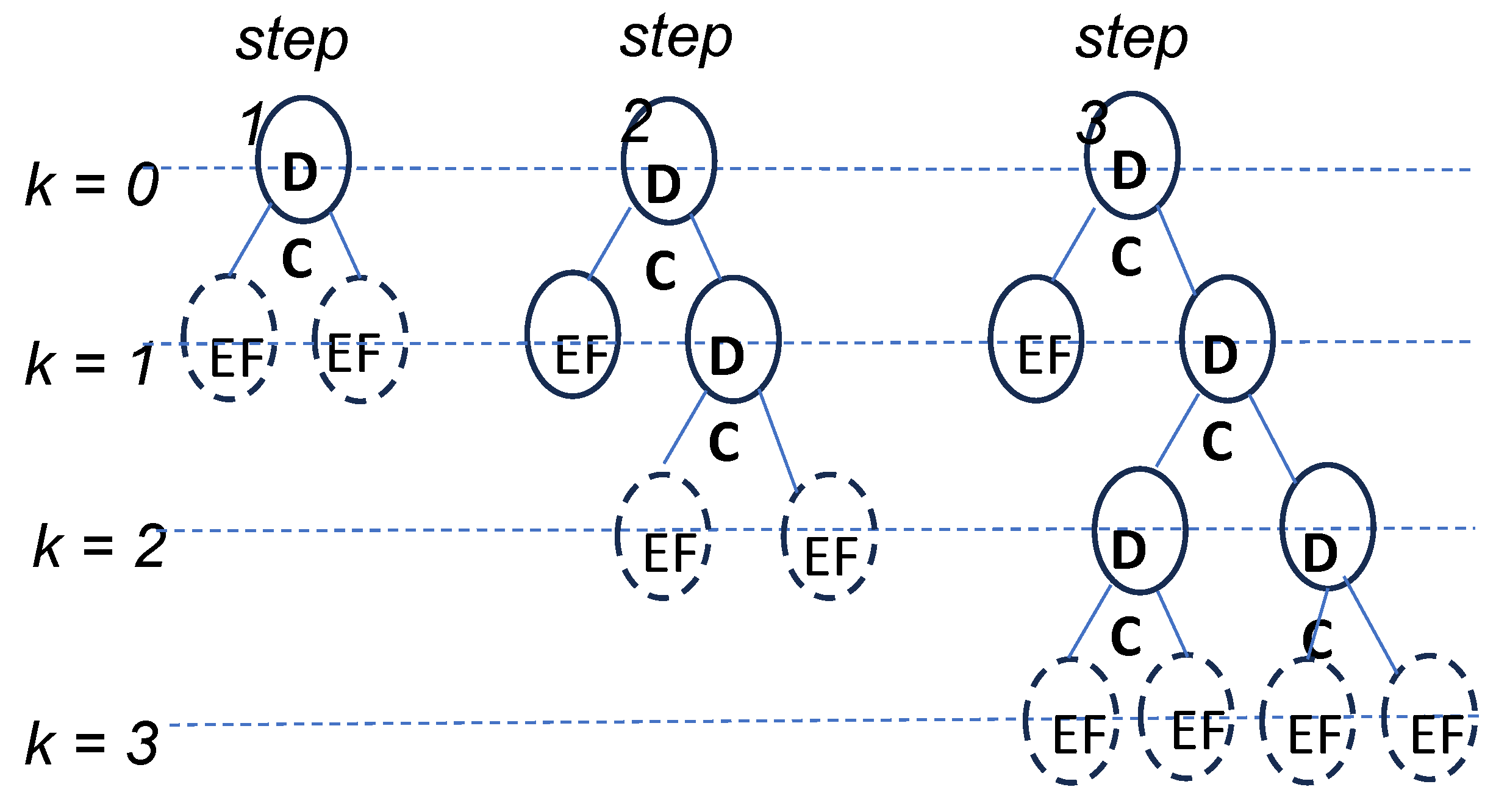
Figure 10 illustrates the iterative calculation of carbon footprints as a tree unfolding process, with
k denoting the level of indirection of the suppliers. Prior to any calculation the production footprint of the company can be estimated using average emissions factors from available databases. The first step of the calculation, illustrated on the left side of the figure, consists of adding the direct carbon emissions (DC) of the company to the emissions factors (EF) of its direct suppliers (supply level
k = 1). At this step, the emissions factors are temporary which is symbolized by dashed line circles. Consolidated data is symbolized by solid line circles. This first step actually corresponds to the GHG Protocol. At the second step, one of the direct suppliers is outside the DEIN, its emissions factor then gets consolidated, while another direct supplier belongs to the DEIN and provides him with its footprint calculated at its own first step. The process is iterated so that the tree of data contributing to the calculation unfolds as more and more data of the indirect suppliers is taken into account.
6. Discussion
In this paper, we have shown that with the simple linear framework of IO Analysis, it is theoretically possible to improve the current estimations of company level footprints, generally obtained by the current version of the GHG Protocol, using a distributed iterative system and a network that we have called a distributed Environmental Impact Network (EIN). This was suggested recently by [
14] with an EIN identical to the entire economy. We have shown that the approach is flexible enough to take into account companies that do not enroll in the EIN. The price to pay when the EIN does not encompass the whole economy is that we only obtain approximations of the true footprints, but the larger the EIN subset we can have, the better the approximations become. Such flexibility ensures that such a EIN system could be rolled out progressively throughout the economy. At the level of a given company, the process consists of replicating weighted inventory calculations of the same kind as the GHG Protocol using continuously improving emission factors produced by its suppliers, until a convergence criterion is met. We have also shown that a EIN system is capable of splitting the footprints into three components: a first component accumulating the scope 1 direct emissions of the upstream EIN companies, a second component accumulating the scope 2 indirect energy emissions of the upstream EIN companies, and a third part accumulating the upstream scope 3 emissions of the non-EIN companies selling to the upstream EIN companies. Such decomposition is interesting to analyze uncertainty, since the uncertainty is relatively low and well estimated for the two first components, while it is high and hard to estimate for the third component. We have shown that such a distributed approach can provide the adequate information for the estimation of biases. Assuming statistical independence of direct emissions on one hand, and of emission factors on the other hand, it is possible to estimate the standard deviations, but if to be done at a company level, this requires to develop the tree of the supply chain for each company up to a certain level.
More simulation work is needed including simulations on representative data of higher granularity than the 44 sector ICIO data we have used here. An important point is to check how this would slow down the convergence rate of the calculated footprint values to the “true” values.
But in the perspective of a real EIN deployable in the real economy, we also need to address several issues.
A first issue is the quality of the data produced at the level of the companies. The first answer to this is auditing by independent bodies, on a sampling or systematic basis. The provision of certified standard accountancy software to all companies also contributes to a correct application of the calculation rules. Such software should include heuristics to detect faulty data or faulty results. The detection of such outlayers could be done on the basis of existing emissions factors from databases.
Linked to the quality of data is the homogeneity of emission factors used from the databases. Given the various databases available, it seems useful to have a “one-stop shop” for retrieving emission factors. Such an entity would ensure the homogoneity and consistency of the emissions factors used by companies. This was proposed in [
14] as a “dissemination platform for GHG content data”.
A second issue is the need to calculate product footprints rather than company level footprints. In our paper we have assumed that all companies produce a single product. In reality we must handle the multi-product case. It is theoretically possible to desaggregate an enterprise into single product sub-companies. The accounting solution to this is cost accounting, whereby the procurement and expenses are attributed to specific products of the company, while general expenses are divided between all products using allocation rules. But only a few companies produce such cost accounting data. Another approach, although less precise, would be to share the total footprint of the company between its products based on the a priori knowledge contained in emissions factors from available databases.
Linked to the multi-product issue is the debate between using monetary factor of physical factors. In reality, the IO model is agnostic to that question, since a specific unit (monetary of physical) can be chosen for each economic player in the economy network. This is actually how it is implemented in Life Cycle Analysis software [
20]. In the usual vector and matrix equations, this means that every vector component may have its own unit. Using a monetary unit for all companies is easy because it corresponds to common accountants’ practice. However, the weakness of monetary units is due to price fluctuations.
A third issue is the confidentiality of the enterprise data. A distributed EIN system would partially address the problem by ensuring the accounting data (supplies, sales) stay within the limits of the company. However, the key principle is to share with the customers the production footprints, either at company level or at product level. We may expect companies to resist such an obligation because it would allow purchaser’s to make purchasing decisions not only on the basis of price, but also on the basis of carbon footprint. We believe solving that issue is the task of policy makers, on large economic scales, for at instance at the European level, hopefully at World level. It may be necessary to make sure that higher impact companies have a practical way to turn to lower impact production tools.
A last issue pertains to the exact definition of the production footprint, since there is a range of flexibility. Using macroeconomic IO analysis and data, the easy path is not to take into account the long term investment (so called “Fixed capital formation”). From an ownership perspective, this is relevant since the consumer owns the product or services he/she buys, but does not own the production infrastructure. On the other hand, from a physical perspective, it is relevant to take into account all the environmental impacts necessary to deliver the product, and this does include the production infrastructure. Some approaches were proposed to handle investments (capital expenses) as intermediate consumptions in the IO framework [
21,
22]. The difficulty is to compensate for the absence for investments IO tables in national or international accounts, in the similar form as those available for intermediate consumption (operational expenses). On the other hand, working at the company level in an EIN system, it is easier to include long term investment, by using the usual accountant’s multi-year amortization rules. However, it is important to check that the emission factors used in the system were obtained by including the footprint of infrastructure, since it seems to be an option of LCA software [
20].
Finally an opportunity of operating an EIN system would lie in the data collection at company level of direct emissions, product footprints, and even supply structure (the Leontief technical coefficients). Confidentiality is key at his stage, so it should be treated by trustworthy bodies tied by confidentiality obligations, and data could by anonymized and averaged so as to strengthen confidentiality. Such data would bring valuable new sources of data to the existing sources and in turn would help improving the robustness of the EIN system.
7. Conclusion
In this paper, we have presented a distributed iterative computational model for estimating the carbon and environmental footprints of companies, based on input-output (IO) analysis. Given the huge number of companies in the world, the direct and centralized approach remains far out of reach, but using both the iterative and the distributed feature of the model, a general footprint calculation for all companies, allowing comparability of footprints, appears a goal within reach, provided the practical hurdles discussed here above are overcome. The model is flexible enough to be able to work even though a large proportion of companies do not take part to the distributed iterative process.
Clearly ICT plays a key role since the system relies on a homogeneous computation model distributed across a large number of companies, that all interact permanently though a dedicated protocol to exchange intermediate calculations. Even though the system is highly decentralized, two functions need to be centralized to ensure homogeneity and comparability, a centralized database of emission factors and the auditing of the calculated footprints.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted for fruitful discussions to Jérôme Boutang, Bernardo Martins, Romain Bort and Niels Montanari from CITEPA, to Gilles Cormary and the other members of the Shifters working group on collaborative carbon accounting and to Jacques Combaz from Verimag, to Alexandre Bourgeois and Sylvain Larrieu from INSEE, to Joris Blain from La Société Nouvelle, and to members of the “Carbone sur Facture” initiative.
References
- World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), Greenhouse Gas Protocol - Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard, 2004.
- World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), Greenhouse Gas Protocol Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard, 2011.
- World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), GHG Protocol Scope 2 Guidance. An amendment to the GHG Protocol. Corporate Standard, 2015.
- Guinée, J.B. (Ed.) Handbook on Life Cycle Assessment-Operational Guide to the ISO Standards. Series: Eco-Efficiency in Industry and Science, Vol. 7. 2002.
-
ISO 14044:2006; Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. International Standardization Organisation (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- 6. European Commission - Joint Research Centre - Institute for Environment and Sustainability, International Reference Life Cycle Data System (ILCD) Handbook - General guide for Life Cycle Assessment - Detailed guidance. First edition March 2010.
- World Resources Institute (WRI), World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD): Product Life Cycle Accounting and Reporting Standard. Greenhouse Gas Protocol, 2011.
- Zampori, L.; Pant, R. “Suggestions for updating the Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) method”, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, 2019. [CrossRef]
- EU Commission, Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) and Organisation Environmental Footprint (EF), EU Commission Recommendation 2021/2279, Annex 1 and 2.
- Klassen, L.; Stoll, C. Harmonizing corporate carbon footprint. Nature Communications 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Freitag, Berners-Lee, Widdicks et al, The real climate and transformative impact of ICT: A critique of estimates, trends, and regulations. Patterns 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Suh (Ed.), Handbook of input-output economics in industrial ecology , Springer 2010.
- OECD Inter-Country Input-Output (ICIO) Tables - OECD.
- U. Von Kalckreuth, Pulling ourselves up by our bootstraps: the greenhouse gas value of products, enterprises and industries. Deutsche Bundesbank discussion paper 2022.
- Huang, Weber,Matthews, Categorization of Scope 3 Emissions for Streamlined Enterprise Carbon Footprinting, Environmental Science & Technology. 2009. [CrossRef]
- E.G. Hertwich, R. Wood, The growing importance of scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions from industry . Environ. Res. Let. 2018. [CrossRef]
- F. Charpentier, An Impact Inheritance Approach to the Estimation of the Carbon Footprints of Economic Activities, Proceedings of 8th Int. Conf. on ICT for Sustainability (ICT4S), 20 June 22.
- F. Meunier, Towards a generalized carbon accounting system - Tracing carbon at product level. Institut Messine. June 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Wood, K. Stadler, et al, Global sustainability accounting – developing EXIOBASE for multiregional footprint analysis, Sustainability, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Weidema, B. P. , Bauer, C., Hischier et al., Overview and methodology: Data quality guideline for the ecoinvent database version 3, Ecoinvent Report 1(v3), 2013.
- Södersten, C.-J.H.; Wood, R.; Hertwich, E.G. Endogenizing Capital in MRIO Models: The Implications for Consumption-Based Accounting. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13250–13259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanco, D.F. The role of services and capital in footprint modelling. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment 2020, 25, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
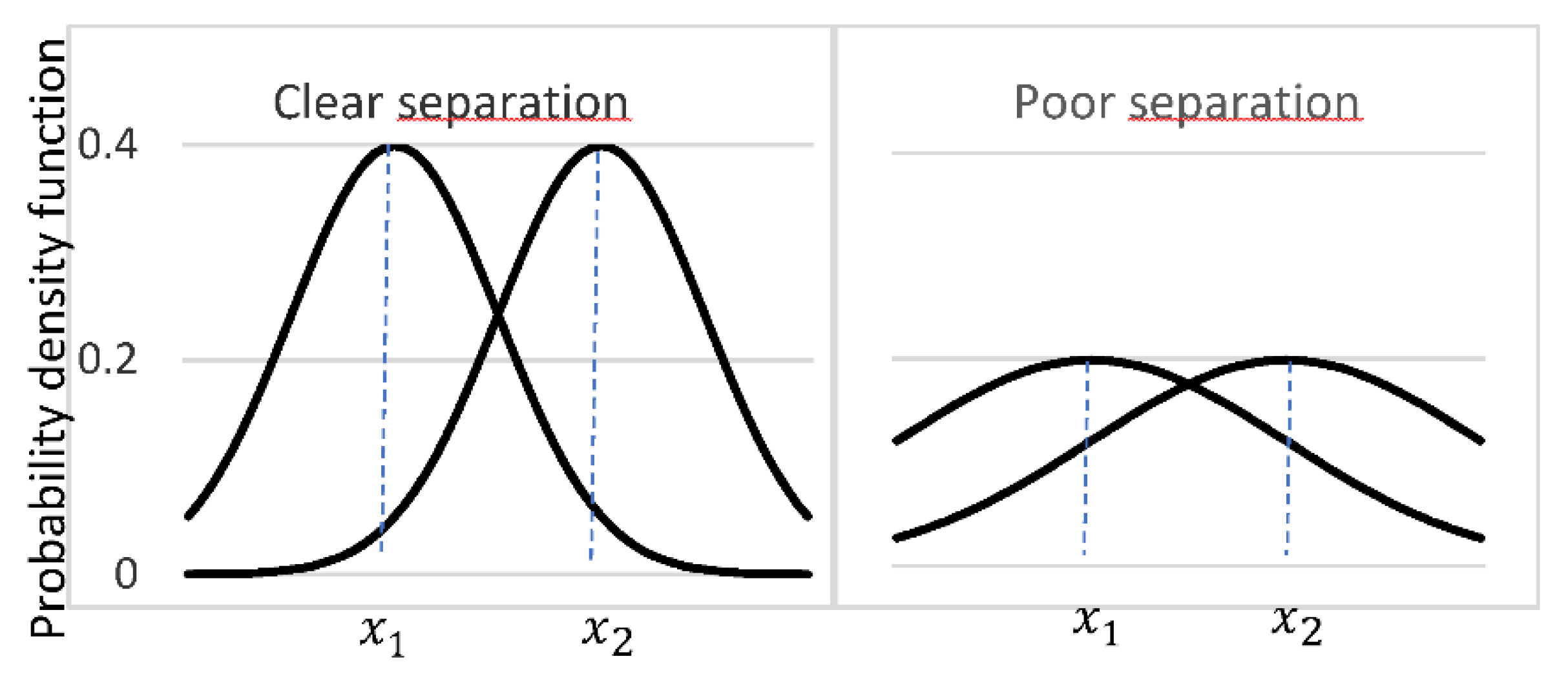
Two cases of statistical uncertainty leading to different risks of wrong decision when comparing two products’ emissions factors x1 and x2 > x1. In the “clear separation” case the standard deviation σ is half the difference x2 − x1, the probability of wrong decision being 8%, while in the “poor separation” case σ is equal to x2 − x1, the probability of wrong decision rises to 24%.
Figure 1.
Two cases of statistical uncertainty leading to different risks of wrong decision when comparing two products’ emissions factors x1 and x2 > x1. In the “clear separation” case the standard deviation σ is half the difference x2 − x1, the probability of wrong decision being 8%, while in the “poor separation” case σ is equal to x2 − x1, the probability of wrong decision rises to 24%.
Figure 2.
Partitioning of the Leontief matrix transpose corresponding to the grouping of companies into two subsets: the companies enrolled in the Environmental Impact Network (EIN), and all the others.
Figure 2.
Partitioning of the Leontief matrix transpose corresponding to the grouping of companies into two subsets: the companies enrolled in the Environmental Impact Network (EIN), and all the others.
Figure 3.
Convergence rate of the distributed iterative footprint algorithm with the ICIO data on 44 sectors and 2 regions (UE and RoW). (a) shows the individual convergence rate for all sectors, with initial emissions factors set to zero while (b) shows the convergence rate averaged across sectors for UE (dashed) and RoW (solid) in two cases: emission factors set to zero and set to 80% of their true value.
Figure 3.
Convergence rate of the distributed iterative footprint algorithm with the ICIO data on 44 sectors and 2 regions (UE and RoW). (a) shows the individual convergence rate for all sectors, with initial emissions factors set to zero while (b) shows the convergence rate averaged across sectors for UE (dashed) and RoW (solid) in two cases: emission factors set to zero and set to 80% of their true value.
Figure 4.
Convergence slowdown due to the lengthening the value chains in the ICIO data on 44 sectors for the world region with zero initial emission factors. The solid line shows the average convergence rate without lengthening. Dashed lines show the slower convergence rates when lengthening uniformally the value chains by breaking all sectors into production entities and distribution entities. The average convergence rates are shown separately for production entities (loosely dashed) and distribution entities (tightly dashed).
Figure 4.
Convergence slowdown due to the lengthening the value chains in the ICIO data on 44 sectors for the world region with zero initial emission factors. The solid line shows the average convergence rate without lengthening. Dashed lines show the slower convergence rates when lengthening uniformally the value chains by breaking all sectors into production entities and distribution entities. The average convergence rates are shown separately for production entities (loosely dashed) and distribution entities (tightly dashed).
Figure 5.
(a) Average convergence rate curves of footprints intensities (solid lines) with emissions factors set to 80% of their true value, and their fraction derived from direct emissions data (dashed lines), for two cases: RoW is the EIN subset (higher curves) and UE is the EIN subset (lower curves). (b) Breakdown of the average iterative footprints intensities (solid line) into the the four u, v, w, r. Components. The dotted-dashed line corresponds to the ccumulation of the S2 contributions v of the EIN players. The dashed line above corresponds to u + v, the addition to the previous line of the S1 contributions of the EIN players. The short dash line above corresponds to u + v + w, the addition to the previous line of the S3 contribution of the non-EIN players. The dotted line corresponds to the vanishing rcomponent containing the S3 contributions of EIN economic players. It serves as convergence criterion of the distributed iterative process. The emissions factors are set to 80% of their true value.
Figure 5.
(a) Average convergence rate curves of footprints intensities (solid lines) with emissions factors set to 80% of their true value, and their fraction derived from direct emissions data (dashed lines), for two cases: RoW is the EIN subset (higher curves) and UE is the EIN subset (lower curves). (b) Breakdown of the average iterative footprints intensities (solid line) into the the four u, v, w, r. Components. The dotted-dashed line corresponds to the ccumulation of the S2 contributions v of the EIN players. The dashed line above corresponds to u + v, the addition to the previous line of the S1 contributions of the EIN players. The short dash line above corresponds to u + v + w, the addition to the previous line of the S3 contribution of the non-EIN players. The dotted line corresponds to the vanishing rcomponent containing the S3 contributions of EIN economic players. It serves as convergence criterion of the distributed iterative process. The emissions factors are set to 80% of their true value.
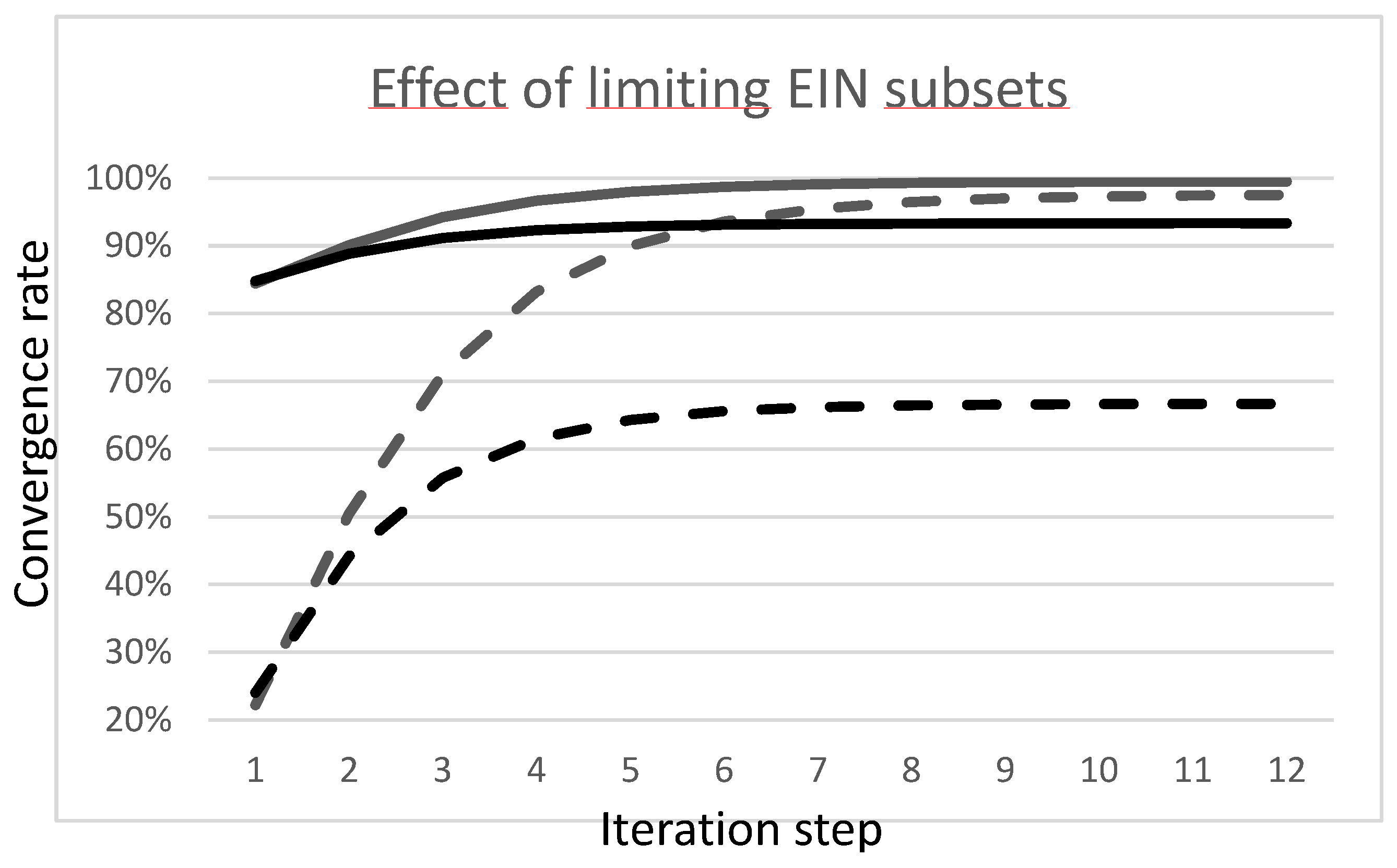
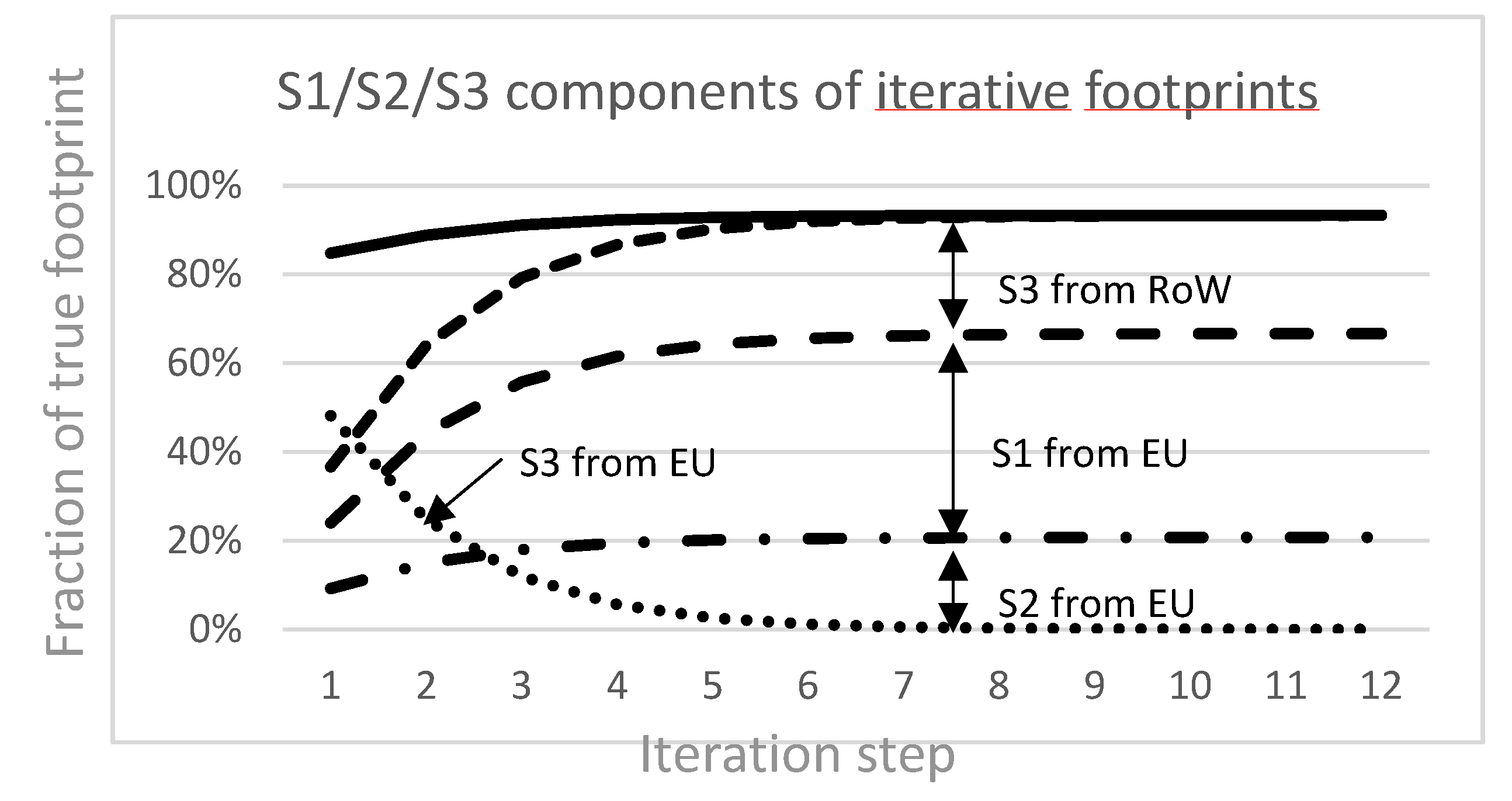
Figure 6.
Scheme to disaggregate the commercial exchanges between two sectors i and j to account for the disaggregation of the sectors into two subsectors each. The subsectors above are the sectors belonging to the EIN region and the subsectors below those belonging to the rest of the world. Parameter β is the weight of the EIN region, in the world economy. Parameter λ controls the preference towards suppliers of the same group, should it be the EIN region or “rest of the world”. In other terms, it models the degree of autonomy of each region.
Figure 6.
Scheme to disaggregate the commercial exchanges between two sectors i and j to account for the disaggregation of the sectors into two subsectors each. The subsectors above are the sectors belonging to the EIN region and the subsectors below those belonging to the rest of the world. Parameter β is the weight of the EIN region, in the world economy. Parameter λ controls the preference towards suppliers of the same group, should it be the EIN region or “rest of the world”. In other terms, it models the degree of autonomy of each region.
Figure 7.
Mean relative variation of the sector footprints of a variable size EIN region, as a function of its size. The increasing curves correspond to the variations due to 10% relative variation of the direct emissions intensities of the EIN region, while the decreasing curves correspond to the variations due to 10% relative variations of the emissions factors of the non EIN region. The solid lines correspond to the case of no autonomy (λ = 0) while the dashed lines correspond to a case of significant autonomy λ = ½.
Figure 7.
Mean relative variation of the sector footprints of a variable size EIN region, as a function of its size. The increasing curves correspond to the variations due to 10% relative variation of the direct emissions intensities of the EIN region, while the decreasing curves correspond to the variations due to 10% relative variations of the emissions factors of the non EIN region. The solid lines correspond to the case of no autonomy (λ = 0) while the dashed lines correspond to a case of significant autonomy λ = ½.
Figure 8.
Mean standard deviations of the sector footprints of a variable size EIN region, as a function of its size. The increasing curves correspond to to the standard deviations due to 10% standard deviation of the direct emissions intensities of the EIN region, while the decreasing curves correspond to the standard deviations due to 10% standard deviation of the emissions factors of the non-EIN region. The solid lines correspond to the case of no autonomy (λ = 0) while the dashed lines correspond to a case of significant autonomy λ = ½.
Figure 8.
Mean standard deviations of the sector footprints of a variable size EIN region, as a function of its size. The increasing curves correspond to to the standard deviations due to 10% standard deviation of the direct emissions intensities of the EIN region, while the decreasing curves correspond to the standard deviations due to 10% standard deviation of the emissions factors of the non-EIN region. The solid lines correspond to the case of no autonomy (λ = 0) while the dashed lines correspond to a case of significant autonomy λ = ½.
Figure 9.
The parties involved in a distributed environmental impact process around a given company belonging to the distributed environmental impact network (EIN). Suppliers provide their customers with iteratively calculated footprint intensities. The emissions factors needed to estimate missing data come from dedicated databases. The details of direct emissions and footprint calculations are audited by dedicated bodies.
Figure 9.
The parties involved in a distributed environmental impact process around a given company belonging to the distributed environmental impact network (EIN). Suppliers provide their customers with iteratively calculated footprint intensities. The emissions factors needed to estimate missing data come from dedicated databases. The details of direct emissions and footprint calculations are audited by dedicated bodies.
Figure 10.
The iterative steps of footprint calculations are schematized as the development of a data tree of the upstream chain of suppliers. Dashed line circles correspond to temporary emissions factors (EF) used in the calculations, Solid line circles correspond to consolidated data: direct carbon emissions (DC) of suppliers involved in the EIN, average emission factors (EF) for the others.
Figure 10.
The iterative steps of footprint calculations are schematized as the development of a data tree of the upstream chain of suppliers. Dashed line circles correspond to temporary emissions factors (EF) used in the calculations, Solid line circles correspond to consolidated data: direct carbon emissions (DC) of suppliers involved in the EIN, average emission factors (EF) for the others.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).