1. Introduction
HIV infection disrupts the homeostasis of microbiota in the gut [
1,
2], and microbial translocation of bacterial products such as flagellin has been associated with HIV disease progression [
3,
4,
5]. Clinically, there are increased circulating levels of anti-flagellin antibodies in HIV-infected individuals compared to uninfected subjects [
6,
7,
8]. As a major immune cells of the host first line defense, monocytes and macrophages can be exposed to translocated bacterial flagellin during viral-bacterial co-infection, which can promotes HIV infection through the toll like receptor 5 (TLR5) and NF-κB signaling pathways, resulting in the induction of various inflammatory cytokines [
9,
10]. Therefore, monocytes/macrophages are the key contributors to the systemic inflammation and immune activation. Although it is known that flagellin affects the host immunity through its impact on different cell types in the context of viral infections [
11,
12,
13,
14], there is limited information about the direct effect of flagellin on HIV infection/replication in macrophages.
Although macrophages are vital for both innate and adaptive immunity against invading pathogens including HIV [
15,
16,
17,
18], they are the major target of HIV infection [
19]. Macrophages infected with HIV demonstrate increased resistance to apoptosis and decreased sensitivity to combination antiretroviral therapy. These features make macrophages the optimal HIV reservoirs and a key focus for therapeutic intervention [
15,
16,
20,
21,
22]. An early study [
22] reported that TLR5 activation by flagellin could activate NF-ĸB and latent HIV in CD4+ T cells in HIV-infected individuals. Schlaepfer et al. showed that flagellin treatment reinforced the nonpermissive state of polarized macrophage to HIV infection[
23]. However, despite of these findings, it is unclear about the mechanism(s) by which flagellin-TLR5 interactions interfere with HIV infection/replication. Given the important role of flagellin as a vaccine adjuvant in TLR5 activation-mediated immune regulation and in HIV infection of macrophages, we examined the impact of the flagellins from different bacteria on HIV infection of primary human macrophages and the mechanism associated with.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Reagents
Primary human macrophages were derived from purified peripheral blood monocytes which were acquired from the Human Immunology Core at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine. The Core has the Institutional Review Board approval for blood collection from healthy donors. The culture conditions for the monocytes’ differentiation into macrophages were described previously [
24,
25]. Monocytes were plated in 48-well plates (Corning CellBIND Surface) at the density of 2.5×10
5 cells/well in 0.5 ml complete Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM) with 20% fetal calf serum (FCS), 1% non-essential amino acid, 1% L-glutamine, and 1% penicillin–streptomycin solution at 37℃ with 5% CO
2. At day 7, monocytes differentiate into macrophages (MDMs). Flagellins from three different bacteria (BS: Bacillus Subtilis; ST: Salmonella Typhimurium; and PA: Pseudomonas Aeruginosa) were purchased from InvivoGen (San Diego, CA).
2.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
The cytotoxic effect of the flagellins of different bacteria on MDMs was evaluated by MTS (3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt) assay. Seven-day cultured MDMs in 96-well plate (10
5 cells/well) were treated with the flagellins at different concentrations (0 to 1000 ng/ml) for 72 h. The cells were then incubated with CellTiter 96® AQueous One Solution Reagent containing MTS and phenazine ethosulfate at 37℃ for 4 h. Absorbance exited at 490 nm was measured and recorded by a plate reader (SpectraMax i3, Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). As shown in
Supplementary Figure S1, flagellin had little effect on the cell viability even at the highest concentration 1000 ng/ml.
2.3. HIV Infection
HIV macrophage tropic R5 strain (Bal) was obtained from the AIDS Reagent Program, the National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD). MDMs (2.5 × 10
5 cells/well in 48-well plates) were treated with the flagellins (150 ng/ml) of different bacteria for 24h before HIV Bal (p24 protein 20 ng/10
6 cells) infection for 2 h. The cell cultures were then washed 3 times to remove the residue of the input viruses and the flagellins. The cells were not treated with flagellins after HIV infection. The culture supernatant was then collected at different time points after HIV infection and subjected to the real-time PCR for HIV GAG gene. HIV GAG standards with known copy numbers were used as the control for quantifying the GAG gene copy numbers. MDMs were incubated with hTLR5-Fc for 1 h followed by the flagellin treatment for 6 h. The cells were collected and subjected to RNA extraction for the real-time PCR. To investigate the blocking of HIV entry experiments by the flagellins, we used HIV NL4-3-ΔEnv-eGFP-Bal and HIV NL4-3-ΔEnv-eGFP-VSV-G. These viruses were constructed from the HIV Bal Env or VSV-G expression vector with plasmid pNL4-3-ΔEnv-eGFP and provided by Dr. Yun-Tao Wu (George Mason University) [
26,
27].
2.4. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
Total cellular RNA was isolated from MDMs using Tri-reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). In brief, the total cellular RNA was extracted by a single step, guanidium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. After centrifugation at 13,000 g for 15 min at 4℃, the RNA-containing aqueous phase was collected and precipitated in isopropanol. The RNA precipitates were then washed three times with 75% ethanol and resuspended in 20μl of RNase-free water. Total RNA (0.5 μg) was subjected to reverse transcription using the reverse transcription system (Promega, Madison, WI) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The cDNA was ready to serve as a template for PCR amplification qualification of the chemokines (MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and RANTES), and the receptors (CD4 and CCR5).
2.5. Chemokine Measurements-qRT-PCR for mRNA
Real-time PCR was performed with the SYBR Green Master Mix (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA). Thermal cycling conditions were designed as follows: initial denaturation at 50°C for 2 min and 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 s, and 60°C for 1 min. All values were normalized to GAPDH mRNA. The oligonucleotide primers were synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc. (Coralville, IA, USA), and sequences will be available upon request. Real-time PCR for the mRNA quantification was conducted as instructed by the manufacturer. The oligonucleotide primers were synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc. (Coralville, IA, USA) and sequences were shown in the Table below:
Table 1.
Primer sets for real-time PCR.
Table 1.
Primer sets for real-time PCR.
| Primer |
Accession No. |
Orientation |
Sequences |
| GAPDH |
NM_002046 |
Sense |
5′-GGTGGTCTCCTCTGACTTCAACA-3′ |
| MIP1-α |
NM_002983 |
Sense |
5′-GCTGACTACTTTGAGACGAGC-3′ |
| |
|
Antisense |
5′-CCAGTCCATAGAAGAGGTAGC-3′ |
| MIP1-β |
NM_002984 |
Sense |
5′-CCAAACCAAAAGAAGCAAGC-3′ |
| |
|
Antisense |
5′-AGAAACAGTGACAGTGGACC-3′ |
| RANTES |
NM_002985 |
Sense |
5′-CTGCATCTGCCTCCCCATA-5 |
| |
|
Antisense |
5′-GCGGGCAATGTAGGCAAA-3′ |
| CD4 |
NM_000616 |
Sense |
5′-GCACGACTCTGCAGAAGGAA-3′ |
| |
|
Antisense |
5′-CCTAAAAGGGACTCCCCGGT-3′ |
| CCR5 |
NM_000579 |
Sense |
5′-CAAGTGTCAAGTCCAATCTA-3 |
| |
|
Antisense |
5′-ACCAAAGATGAACACCAGTG-3′ |
2.6. Fluorescent Imaging and Flowcytometry
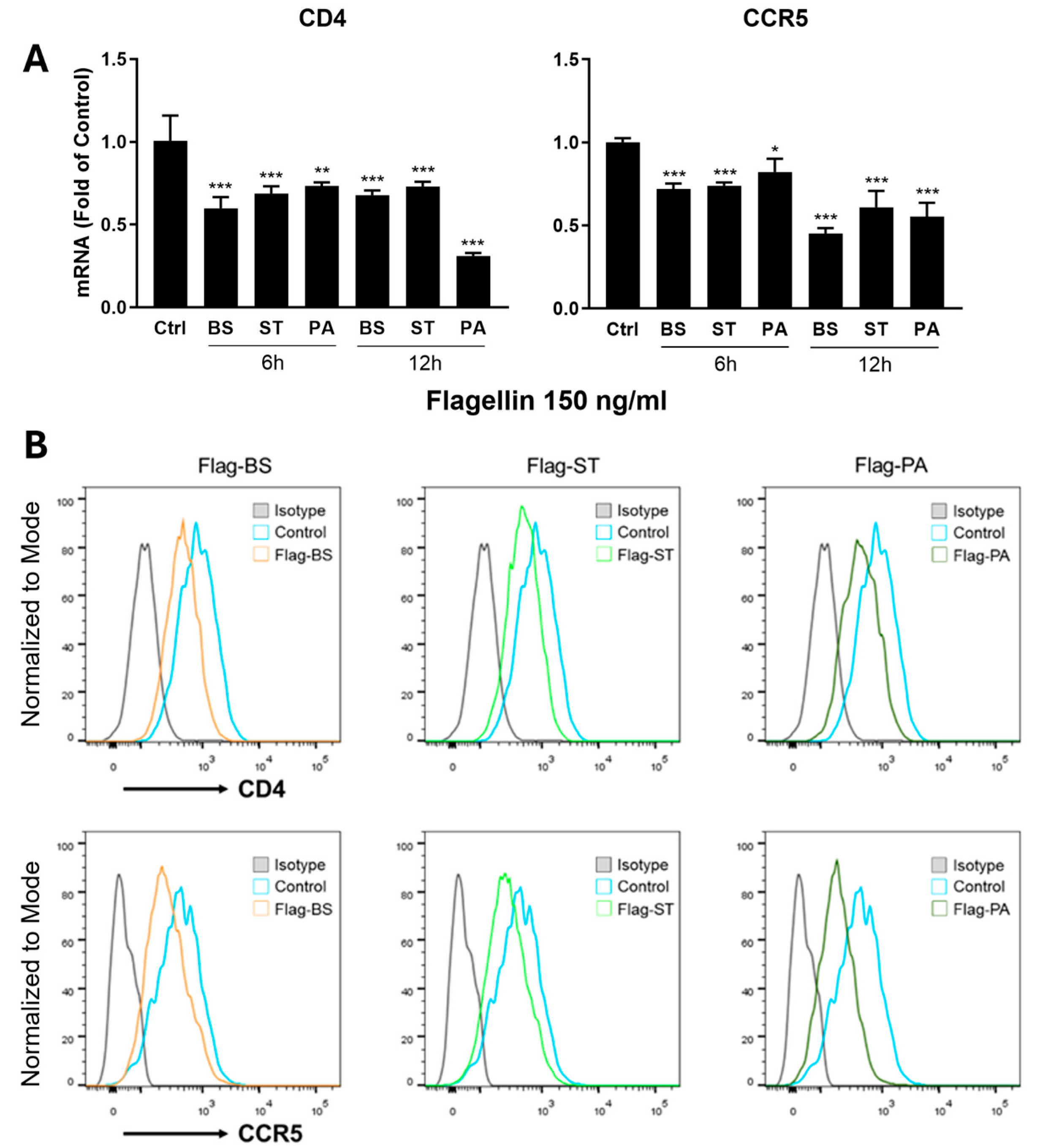
MDMs were pretreated with the flagellins (150 ng/ml) for 24 h and infected with VSV-G or Bal-Env pseudotyped HIV eGFP for 72 h. HIV particles in the macrophages were visualized with confocal fluorescent microscopy (Nikon A1R, Nikon, Japan) and processed using ImageJ software (NIH, USA). For flowcytometry, MDMs were pretreated with flagellins (BS, ST, PA, 150 ng/ml) for 24 h at 37°C and detached from the culture wells with Versene solution (0.48 mM EDTA). The harvested cells were washed cell staining buffer (BD Bioscience) containing 0.2% (w/v) bovine serum albumin (BSA) prior to immunostaining. To detect the cell surface markers expression, MDMs were stained with APC-conjugated CD14 (M5E2, BD Bioscience), FITC-conjugated CD4 (RPA-T4, BD Bioscience) and PE-conjugated CCR5 (3A9, BD Bioscience). Unstained and matched-isotype-stained cells were included as controls. Cells were acquired by FACSCanto II (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA), and data were analyzed using Flow-Jo software (Tree Star Inc, Ashland, OR).
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data were obtained from three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. The variance between two groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. Calculations were performed with GraphPad Prism 7.0 Statistical Software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA). Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05, P < 0.01 or P < 0.001.
3. Results and Discussion
Flagellin, a protein essential for bacterial motility, adherence, and virulence [
23,
28], is the only known agonist of TLR5, activation of which can induce the intracellular transcription factors including NF-κB, resulting in inflammatory and other immune responses [
29,
30,
31]. Importantly, the flagellin -TLR5 interaction is implicated in the systemic immune activation during HIV infection, as flagellin can leak into blood circulation through the gut-blood barrier and activate TLR5 on the surface of epithelial cells and the immune cells, particularly macrophages which are widely distributed in the body [
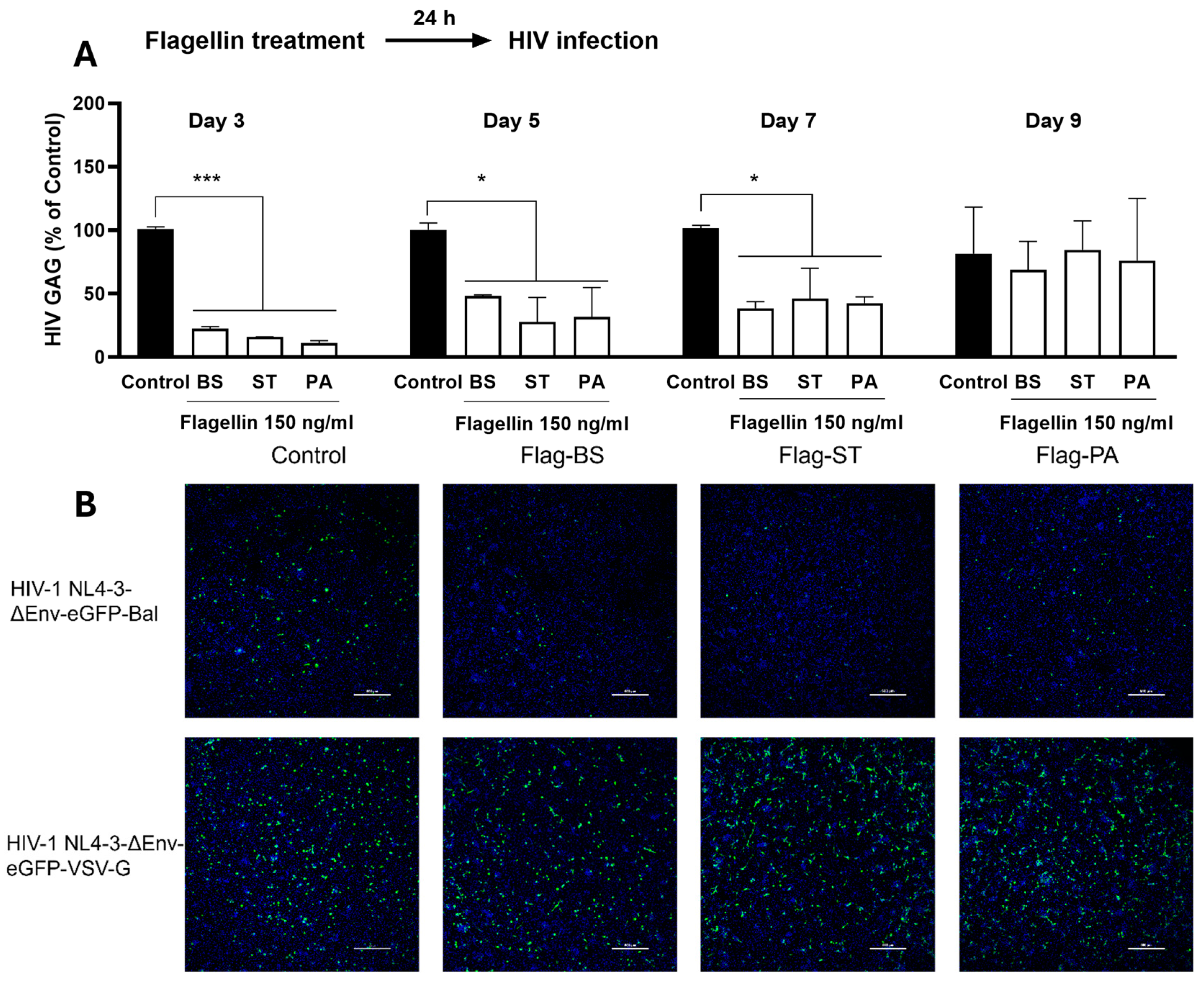
15]. Therefore, it is clinically important to examine the interplays between flagellin and macrophages in terms of HIV infection. We showed that the pretreatment of macrophages with flagellins from different bacteria could effectively inhibit HIV infection/replication (
Figure 1) without cytotoxicity (
Supplementary Figure S1). This finding supports an earlier study by Schlaepfer et al. who showed that flagellin treatment reinforced the nonpermissive state of polarized macrophage to HIV infection [
23]. Of note, the flagellin-TLR5 activation-mediated HIV inhibition was potent as MDMs were only treated once (24h before infection) with the flagellins at a relatively low dose (150ng/ml). The significant inhibitory effect of the flagellins on HIV last for seven days (
Figure 1A). At day 9 after HIV infection, the flagellins showed little effect on the viral replication (
Figure 1A), suggesting that the flagellin's blocking effect at the early stage of HIV infection.
To determine the mechanism(s) of flagellin-mediated HIV inhibition, we examined the impact of the flagellins on two pseudotyped viruses (HIV NL4-3-ΔEnv-eGFP-Bal and HIV NL4-3-ΔEnv-eGFP-VSV-G). Because HIV NL4-3-ΔEnv-eGFP-VSV-G can infect the MDMs without utilizing HIV entry receptors (CD4 and CCR5), the flagellins had little effect on HIV (
Figure 1B). In contrast, the flagellins could significantly block infection by HIV NL4-3-ΔEnv-eGFP-Bal (
Figure 1B), indicating that flagellin-mediated HIV inhibition occurs at the viral entry level. Our further investigation showed that the flagellin pretreatment of macrophages downregulated the HIV entry receptors (CD4 and CCR5) at both mRNA and protein levels (
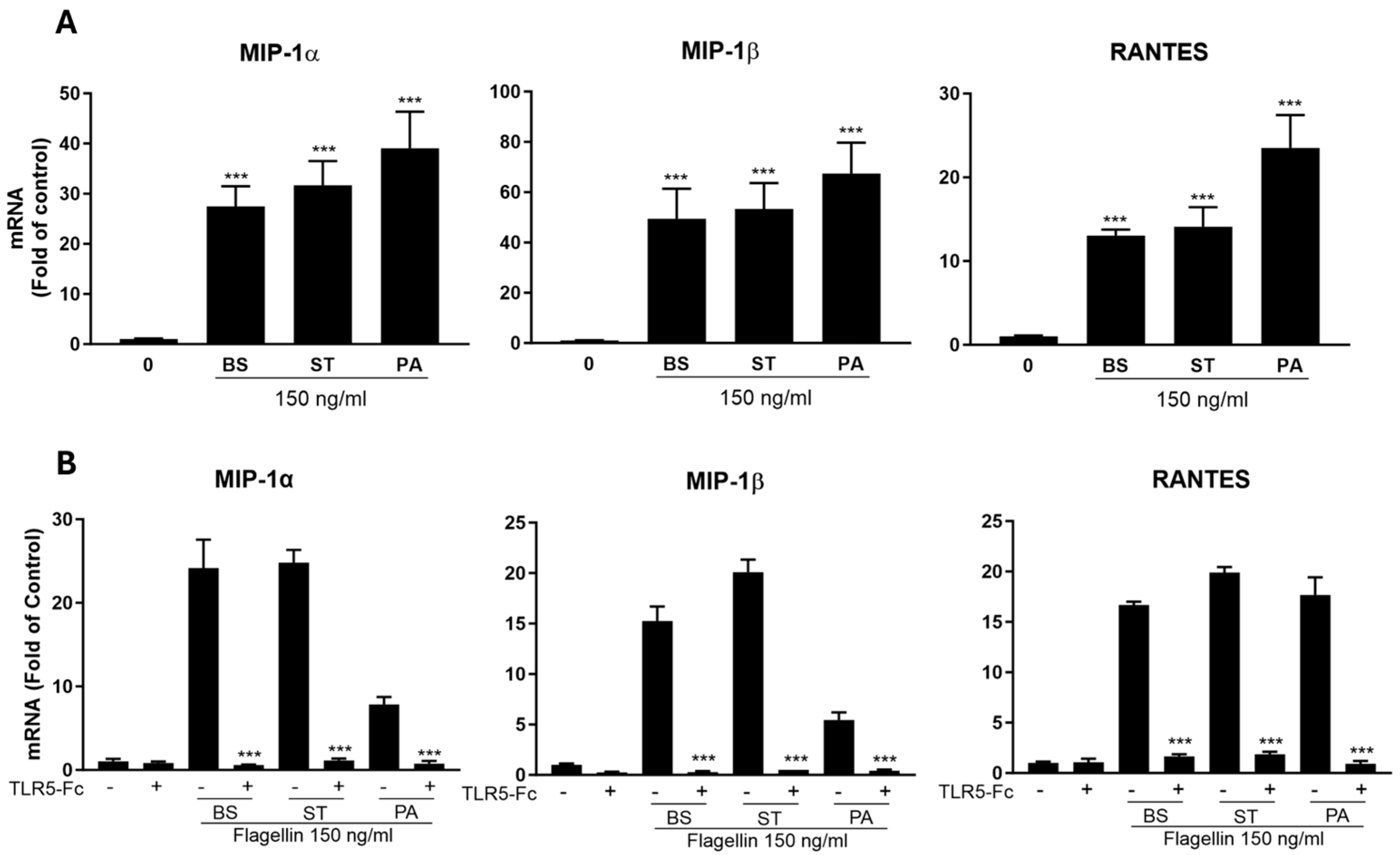
Figure 2) and upregulated the expression of the CC chemokines (MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and RANTES) (
Figure 3A), the ligands of CCR5. To determine whether flagellin-mediated CC chemokine induction is specifically through TLR5, we pretreated MDMs with hTLR5-Fc, a soluble antagonist of TLR5, prior to the flagellin treatment. As demonstrated in
Figure 3B, the pretreatment of MDMs with hTLR5-Fc could block the expression of the CC chemokines induced by the flagellins. Taken together, these findings provide the mechanistic evidence for flagellin’s blocking effect on HIV infection of macrophages.
Flagellin has been used as an adjuvant for the development of effective vaccines against various diseases, including HIV infection [
14,
32,
33,
34,
35]. The primary adjuvant effect of flagellin is to induce cytokines and chemokines. Although flagellin is a contributor to systemic inflammation/immune activation which facilitates HIV disease progression, it appears to be beneficial as an inducer of the macrophage's innate immunity against HIV infection. Studies by different groups have shown that flagellin is a monomer protein that can potentially induce both adaptive and innate immunity [
36,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42]. Therefore, using flagellin instead of bacteria in HIV research offers precise activation of specific immune pathways, controlled experimental conditions, and reduced biosafety risks. Our studies with the flagellins from different bacteria demonstrate that it is valuable to use flagellin for studies on TLR5-mediated immune responses in macrophages, which can provide not only the insights into host cell innate immunity but also evidence to support the development of targeted therapies with vaccine adjuvants against HIV.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: WZH. Performed the experiments: LZ and SK. Analyzed the data: LZ, XW and WZH. Wrote the paper: LZ and WZH.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants DA045568, and DA051893.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Brenchley, J.M.; Schacker, T.W.; Ruff, L.E.; Price, D.A.; Taylor, J.H.; Beilman, G.J.; Nguyen, P.L.; Khoruts, A.; Larson, M.; Haase, A.T.; et al. CD4+ T cell depletion during all stages of HIV disease occurs predominantly in the gastrointestinal tract. J Exp Med 2004, 200, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, C.L.; Ma, Z.M.; Mann, S.K.; Li, C.S.; Wu, J.; Knight, T.H.; Yotter, T.; Hayes, T.L.; Maniar, A.H.; Troia-Cancio, P.V.; et al. Molecular characterization of stool microbiota in HIV-infected subjects by panbacterial and order-level 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) quantification and correlations with immune activation. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2011, 57, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, N.G.; Douek, D.C. Microbial translocation in HIV infection: causes, consequences and treatment opportunities. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2012, 10, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Dunham, R.M.; Iwai, S.; Maher, M.C.; Albright, R.G.; Broadhurst, M.J.; Hernandez, R.D.; Lederman, M.M.; Huang, Y.; Somsouk, M.; et al. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota is associated with HIV disease progression and tryptophan catabolism. Sci Transl Med 2013, 5, 193ra191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Tincati, C.; Rizzardini, G.; Torti, C.; Quirino, T.; Haarman, M.; Ben Amor, K.; van Schaik, J.; Vriesema, A.; Knol, J.; et al. Early impairment of gut function and gut flora supporting a role for alteration of gastrointestinal mucosa in human immunodeficiency virus pathogenesis. J Clin Microbiol 2008, 46, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdurahman, S.; Barqasho, B.; Nowak, P.; Cuong do, D.; Amogne, W.; Larsson, M.; Lindquist, L.; Marrone, G.; Sonnerborg, A. Pattern of microbial translocation in patients living with HIV-1 from Vietnam, Ethiopia and Sweden. J Int AIDS Soc 2014, 17, 18841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, P.; Abdurahman, S.; Lindkvist, A.; Troseid, M.; Sonnerborg, A. Impact of HMGB1/TLR Ligand Complexes on HIV-1 Replication: Possible Role for Flagellin during HIV-1 Infection. Int J Microbiol 2012, 2012, 263836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesterbacka, J.; Nowak, P.; Barqasho, B.; Abdurahman, S.; Nystrom, J.; Nilsson, S.; Funaoka, H.; Kanda, T.; Andersson, L.M.; Gisslen, M.; et al. Kinetics of microbial translocation markers in patients on efavirenz or lopinavir/r based antiretroviral therapy. PLoS One 2013, 8, e55038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedikz, E.K.; Bailey, D.; Cook, C.N.L.; Gonçalves-Carneiro, D.; Buckner, M.M.C.; Blair, J.M.A.; Wells, T.J.; Fletcher, N.F.; Goodall, M.; Flores-Langarica, A.; et al. Bacterial flagellin promotes viral entry via an NF-kB and Toll Like Receptor 5 dependent pathway. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewirtz, A.T.; Simon, P.O., Jr.; Schmitt, C.K.; Taylor, L.J.; Hagedorn, C.H.; O'Brien, A.D.; Neish, A.S.; Madara, J.L. Salmonella typhimurium translocates flagellin across intestinal epithelia, inducing a proinflammatory response. J Clin Invest 2001, 107, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgel, A.F.; Cayet, D.; Pizzorno, A.; Rosa-Calatrava, M.; Paget, C.; Sencio, V.; Dubuisson, J.; Trottein, F.; Sirard, J.C.; Carnoy, C. Toll-like receptor 5 agonist flagellin reduces influenza A virus replication independently of type I interferon and interleukin 22 and improves antiviral efficacy of oseltamivir. Antiviral Res 2019, 168, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedikz, E.K. The effect of bacterial flagellin on virus infection. 2017.
- Brichacek, B.; Vanpouille, C.; Kiselyeva, Y.; Biancotto, A.; Merbah, M.; Hirsch, I.; Lisco, A.; Grivel, J.C.; Margolis, L. Contrasting roles for TLR ligands in HIV-1 pathogenesis. PLoS One 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porte, R.; Fougeron, D.; Muñoz-Wolf, N.; Tabareau, J.; Georgel, A.F.; Wallet, F.; Paget, C.; Trottein, F.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Carnoy, C.; et al. A Toll-Like Receptor 5 Agonist Improves the Efficacy of Antibiotics in Treatment of Primary and Influenza Virus-Associated Pneumococcal Mouse Infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015, 59, 6064–6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbein, G.; Varin, A. The macrophage in HIV-1 infection: From activation to deactivation? Retrovirology 2010, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Herbein, G. The macrophage: a therapeutic target in HIV-1 infection. Mol Cell Ther 2014, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M. The many faces of macrophage activation. J Leukoc Biol 2003, 73, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ye, L.; Hou, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Metzger, D.S.; Ho, W.Z. Cellular microRNA expression correlates with susceptibility of monocytes/macrophages to HIV-1 infection. Blood 2009, 113, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Ho, W.Z. Morphine Withdrawal Enhances HIV Infection of Macrophages. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.E.; Jaworowski, A.; Hearps, A.C. The HIV Reservoir in Monocytes and Macrophages. Frontiers in Immunology 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, W.; Tariq, M.; Iqbal, M.; Kumar, A.; Herbein, G. Eradication of HIV-1 from the macrophage reservoir: an uncertain goal? Viruses 2015, 7, 1578–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruize, Z.; Kootstra, N.A. The Role of Macrophages in HIV-1 Persistence and Pathogenesis. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, E.; Rochat, M.A.; Duo, L.; Speck, R.F. Triggering TLR2, -3, -4, -5, and -8 reinforces the restrictive nature of M1- and M2-polarized macrophages to HIV. J Virol 2014, 88, 9769–9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xu, X.Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, R.H.; Wang, X.; Li, J.L.; Liu, J.B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Ho, W.Z. Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Release Antiviral Factors That Inhibit HIV Infection of Macrophages. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Hu, Q.; Song, L.; Ye, L.; Zhou, D.; Ho, W. A critical function of toll-like receptor-3 in the induction of anti-human immunodeficiency virus activities in macrophages. Immunology 2010, 131, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.Z.; Liu, J.B.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Hu, W.H.; Hou, W.; Ho, W.Z. TLR7 Activation of Macrophages by Imiquimod Inhibits HIV Infection through Modulation of Viral Entry Cellular Factors. Biology (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.; Tang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Yu, D.; Wu, Y. Selective killing of HIV-1-positive macrophages and T cells by the Rev-dependent lentivirus carrying anthrolysin O from Bacillus anthracis. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Buckley, M.; Britton, B.; Mu, Y.; Warner, K.; Kumar, S.; Cory, T.J. Polarized macrophage subsets differentially express the drug efflux transporters MRP1 and BCRP, resulting in altered HIV production. Antivir Chem Chemother 2018, 26, 2040206617745168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr.; Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiko, J.; Westerlund-Wikström, B. The role of the bacterial flagellum in adhesion and virulence. Biology (Basel) 2013, 2, 1242–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.D.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Hayashi, F.; Strobe, K.; Bergman, M.A.; Barrett, S.L.; Cookson, B.T.; Aderem, A. Toll-like receptor 5 recognizes a conserved site on flagellin required for protofilament formation and bacterial motility. Nat Immunol 2003, 4, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnowski, C.; Kadzioch, N.; Damm, D.; Yan, H.; Temchura, V. Advantages and Limitations of Integrated Flagellin Adjuvants for HIV-Based Nanoparticle B-Cell Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen-Nissen, E.; Smith, K.D.; Strobe, K.L.; Barrett, S.L.; Cookson, B.T.; Logan, S.M.; Aderem, A. Evasion of Toll-like receptor 5 by flagellated bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 9247–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajamian, L.; Melnychuk, L.; Jean-Pierre, P.; Zaharatos, G.J. DNA Vaccine-Encoded Flagellin Can Be Used as an Adjuvant Scaffold to Augment HIV-1 gp41 Membrane Proximal External Region Immunogenicity. Viruses 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Swartz, J.R. Functional properties of flagellin as a stimulator of innate immunity. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 18379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciacci-Woolwine, F.; Blomfield, I.C.; Richardson, S.H.; Mizel, S.B. Salmonella flagellin induces tumor necrosis factor alpha in a human promonocytic cell line. Infect Immun 1998, 66, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuillet, V.; Medjane, S.; Mondor, I.; Demaria, O.; Pagni, P.P.; Galan, J.E.; Flavell, R.A.; Alexopoulou, L. Involvement of Toll-like receptor 5 in the recognition of flagellated bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 12487–12492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, F.; Means, T.K.; Luster, A.D. Toll-like receptors stimulate human neutrophil function. Blood 2003, 102, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, F.; Smith, K.D.; Ozinsky, A.; Hawn, T.R.; Yi, E.C.; Goodlett, D.R.; Eng, J.K.; Akira, S.; Underhill, D.M.; Aderem, A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 2001, 410, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, P.F.; Ciacci-Woolwine, F.; Snipes, J.A.; Mizel, S.B. High-affinity interaction between gram-negative flagellin and a cell surface polypeptide results in human monocyte activation. Infect Immun 2000, 68, 5525–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyant, T.L.; Tanner, M.K.; Sztein, M.B. Salmonella typhi flagella are potent inducers of proinflammatory cytokine secretion by human monocytes. Infect Immun 1999, 67, 3619–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhao, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Chassaing, B.; Gewirtz, A.T. Critical Role of Innate Immunity to Flagellin in the Absence of Adaptive Immunity. J Infect Dis 2021, 223, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).