Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus type 2 (T2DM) is a metabolic disease where pancreatic beta cells cannot sustain increased demand for insulin; thus, deficiency results progressively. The common feature in Type 2 Diabetes is relative insulin deficiency, so there is an insufficient reduction in the resistance to insulin action. Management of diabetes is aimed at improving hyperglycemia symptoms and minimizing the long-term microvascular and macrovascular complications such as diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular effects. Compared to the general population, individuals with type 2 diabetes have a significantly greater risk of both fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events. The complications often contribute to low quality of life among patients and increased rate of mortality due to various factors [
1] but mainly due to cardiovascular events [
2]. The treatment modalities range from dietary and lifestyle management to oral antidiabetics and injectable therapies. The risk of macro-vascular problems is increased by the substantial correlation observed between the severity of hyperglycemia, metabolic alterations resulting from type 2 diabetes, and vascular damage. The discovery of medications that regulate hyperglycemia and affect other metabolic risk variables to enhance cardiovascular outcomes is in high demand. Obesity, aging, and genetic vulnerability are factors in the rising prevalence of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Insulin resistance, the functional failure of pancreatic beta cells, and excessive or incorrect glucagon output are the leading contributors to the development of type 2 diabetes. Currently, T2DM is considered a systemic illness in which hyperglycemia is caused by a malfunction in several organs and tissues [
3]. Diabetes is a chronic condition that impacts the patient's day-to-day activities and thus requires a sustained change in lifestyle activities, including dietary choices. Educating the patient is critical to achieving and maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing the disease. Each patient's management should be individualized, considering comorbidities and personal and cultural beliefs [
4]. Diabetes type 2 is a long-term comorbidity brought on by decreased insulin production and actions due to peripheral tissue insulin resistance, mainly in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Combined with β-cell malfunction in addition to causing microangiopathy, homeostatic hyperglycemia increases the risk of microangiopathy, leading to cardiovascular diseases. Economic disadvantages, a decline in healthy life expectancy, and a decline in patient quality of life are all caused by complications from these vascular conditions. Furthermore, obese patients with type 2 diabetes need more rigorous glycemic control and weight management because obesity is linked to the pathophysiology of the disease and is a risk factor for macroangiopathy [
5,
6]. Medication and lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise can help with treatment. However, for people with chronic diabetes, proper medication is crucial.
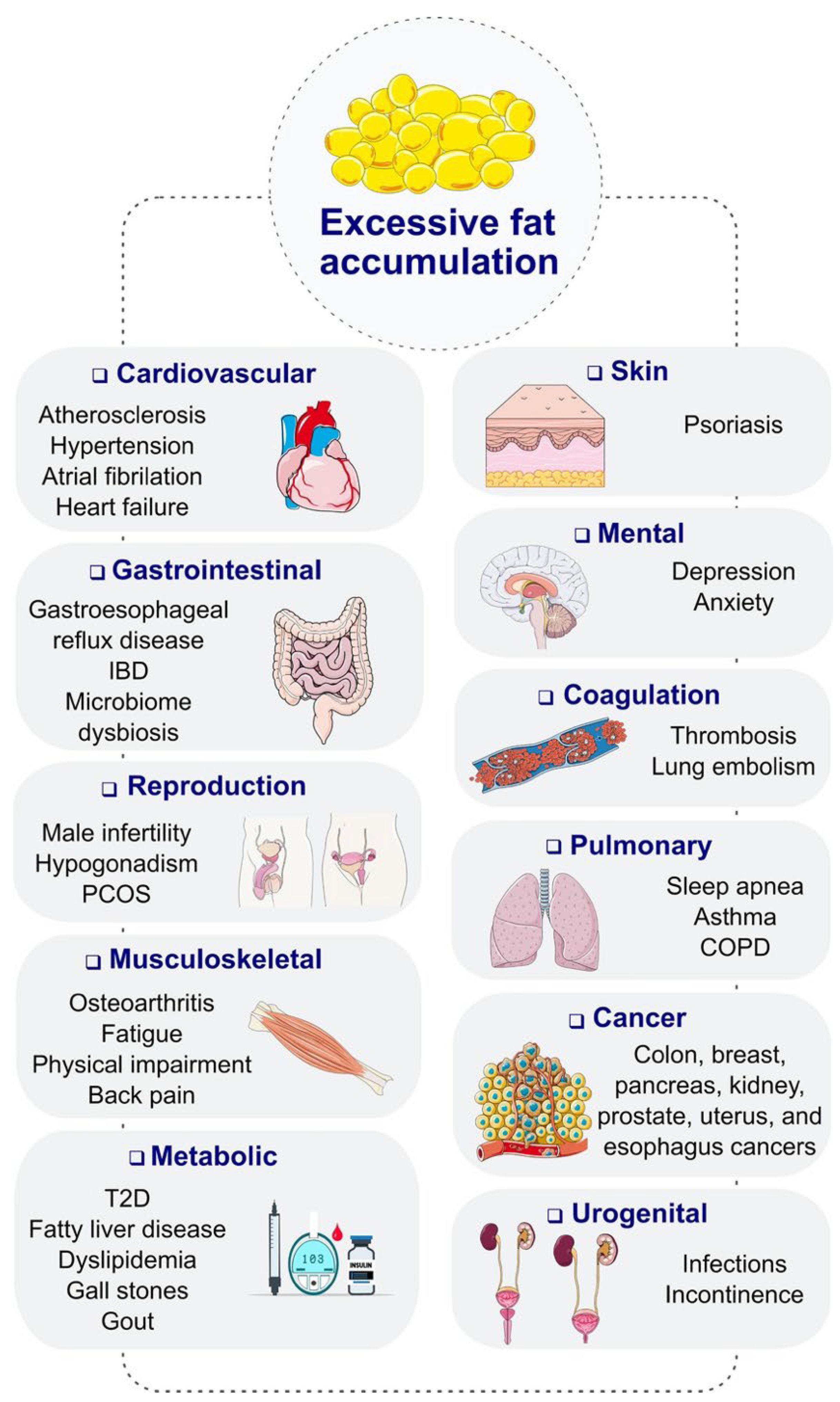
Obesity is a major factor that contributes to the development and complications of diabetes mellitus. Patients who are obese are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes due to the increased resistance to insulin. Obesity can cause dysfunction in the production and utilization of insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Furthermore, obesity can exacerbate the complications of diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and neuropathy. These complications can significantly impact the quality of life of patients and increase the risk of mortality. Moreover, obesity complicates the management of diabetes as it can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels through diet and medication alone. Patients who are obese may require higher doses of insulin or other medications to achieve optimal glycemic control. Additionally, obesity can also lead to other comorbidities, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia, which further increase the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes (
Figure 1). Therefore, effective strategies for managing obesity in diabetic patients are essential to prevent and mitigate the complications associated with this chronic condition [
7,
8].
The majority of Type 2 diabetes treatment drugs that target various pathways have been linked to adverse effects, including edema, obesity, hypoglycemia, and diminished insulin sensitivity. However, recently, treatments that target incretin hormones have come to light as potentially safe options for the management of type 2 diabetes. The incretin pathway regulates the human body's daily blood glucose level. Most of the total insulin secreted by β-cells in response to oral glucose consumption is accounted for by it [
9]. Together with lifestyle changes and lowering cardiovascular risk, metformin is still the drug of choice for type 2 diabetes and is advised among those agents for first-line treatment. The American Diabetes Association's guidance encourages the adoption of a patient-centered strategy to direct further therapy, considering factors like cost, side effects, weight fluctuations, hypoglycemia risk, and efficacy with additional medication. Add-on therapy for metformin includes thiazolidinediones, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, insulin, sodium-glucose co-transporter two inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, luminal glucosidase inhibitors, diet, and sulfonylureas [
6,
10,
11].
Incretin Hormones
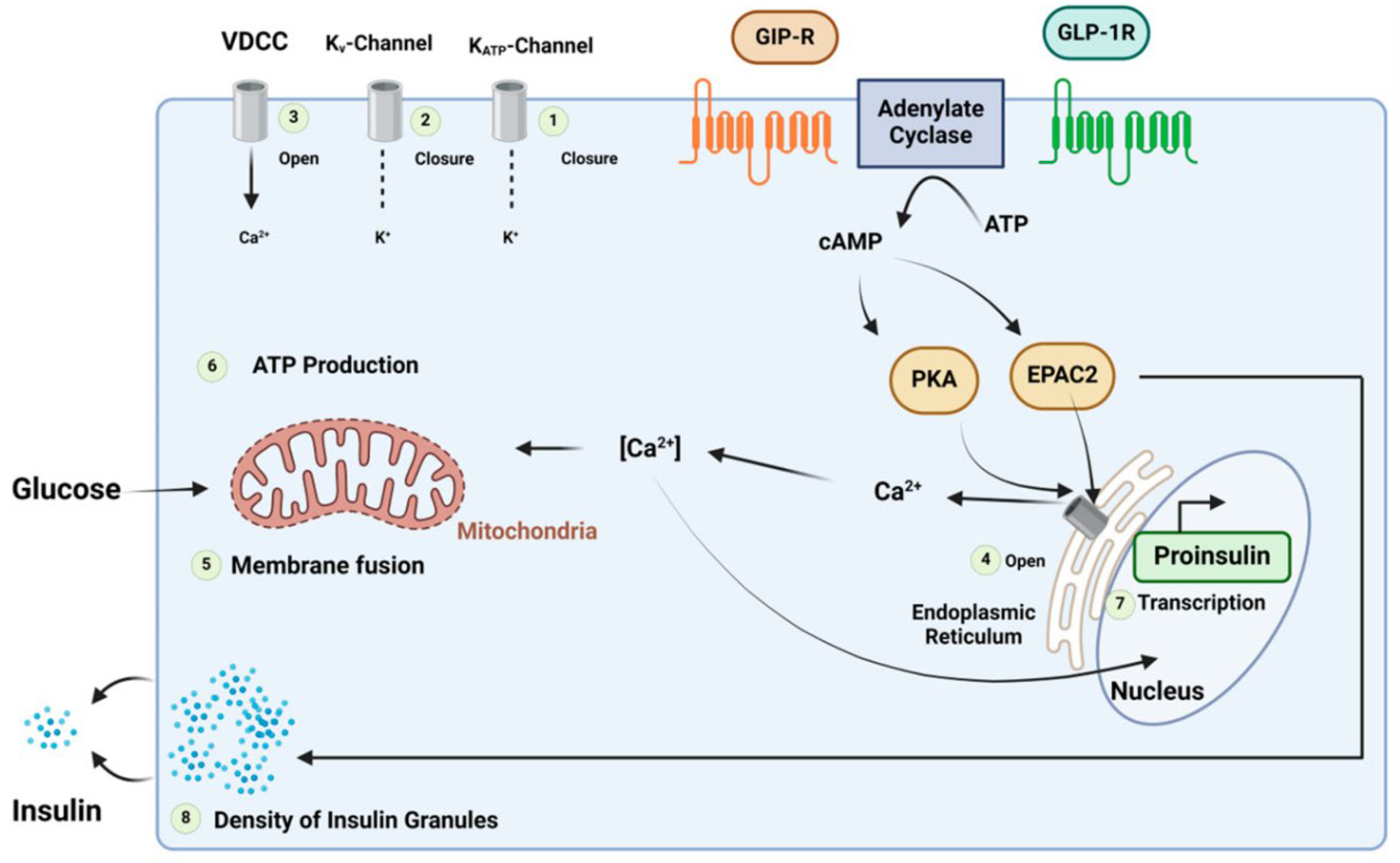
Incretin hormones include glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and Gastric inhibitory peptide, also known as a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), facilitating insulin hormone release from pancreatic beta cells [
12]. The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme rapidly breaks down the incretin hormones. The incretin effect entails the increased insulin production response when a glucose stimulus is given orally rather than intravenously. The incretin effect is markedly diminished in patients with diabetes [
13]. This has led to the development of two major incretin-based therapeutic approaches. This is caused by a decreased GIP capacity to induce insulin release. This may be linked to a general dysfunction of beta cells or particular abnormalities in the GIP signaling pathway. Deterioration of glycemic regulation may be related to a decreased incretin action, which affects post-prandial glycemic excursions. On the other hand, GLP-1's insulinotropic efficacy is significantly less compromised. This indicates that exogenous GLP-1 can increase insulin secretion, decrease glucagon secretion, and lower plasma glucose levels throughout fasting and post-prandial periods (
Figure 2). This has prompted the creation of drugs that lower blood sugar based on incretin actions [
14].
The incretin hormones released from the gastrointestinal tract's epithelium significantly influence normal glucose tolerance. They prevent an excessive rise in post-prandial glucose levels by promoting insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. The incretin action is dose-dependent, meaning that even as the meal's carbohydrate content increases, similar post-prandial glucose elevations are generated [
15]. The insulin responses of oral and intravenous glucose treatments that produce comparable glucose excursions are typically compared to quantify the incretin effect. The incretin effect may be accountable for up to five times spikes in post-prandial glucose clearance, as indicated by contrasts of the amounts of glucose that must be infused intravenously to resemble the concentrations induced by the oral administration [
13].
The oral glucose delivery causes the two gut incretin hormones, GIP and GLP-1, to be released more. This, in turn, enhances insulin secretion, leading to an increase in glucose disposal. This explains why the incretin effect relies on the quantity of carbohydrates consumed [
15]. The proportion of carbohydrates consumed affects the incretin secretion and the insulin response. The incretin effect accounts for up to 70% of the insulin released in response to glucose intake in normal healthy individuals. Endocrine L-cells, primarily found in the mucosa of the distal section of the small intestine and colon, metabolize proglucagon to produce glucagon-like peptide-1, a 30-amino acid polypeptide. On the other hand, glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide is produced from the endocrine K-cells located in the mucosa of the duodenum and upper jejunum. It is a 42-amino acid polypeptide. Glucagon-like peptide is rapidly broken down by the ubiquitous enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase 4, with a brief half-life of about 1.5 minutes. In contrast, glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide typically has a longer half-life of approximately 7 minutes. The hormones have no risk of causing hypoglycemia despite enhancing insulin secretion from the beginning of a meal intake [
16] because these hormones have no insulinotropic activity at lower glucose concentrations. Insulin gene expression and synthesis are both improved by glucagon-like peptide-1. Moreover, it has trophic and protective properties on beta cells and, in a glucose-dependent way, potently suppresses pancreatic glucagon release. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, on the other hand, has been demonstrated to increase glucagon secretion. The pancreatic beta-cells G-protein coupled receptors allow the hormones to exert their insulinotropic action [
14].
These two incretin hormones have various other roles besides influencing the endocrine pancreas. Several brain regions have glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors. These receptors are thought to stimulate the perception of satiety, especially when combined with the glucagon-like peptide-1-induced slowing of gastrointestinal motility mediated by the vagus nerve, decrease food consumption, and control body weight. The glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone is responsible for the delay in gastric emptying, which helps reduce post-meal glucose elevations. On the other hand, GIP has no role in gastric emptying delay. Therefore, the effect of delayed gastric emptying is only noted with the GLP-1 analogs. However, a reduction in delayed gastric emptying to the successive doses of the glucagon-like peptide-1 mimetics may be emphasized [
16].
The 463 amino acid GLP-1 receptor has eight hydrophobic domains. The N-terminal extracellular hydrophobic domain homologs expressed in several tissues and organs, including the heart, kidney, gut, pancreatic islets, stomach, and lung, are highly retained. After GLP-1R is activated, intracellular calcium and cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP) levels rise quickly, and subsequent insulin release is glucose-dependent. With a half-life of only 1-2 minutes, the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) quickly inactivates the GLP-1 hormone. Amino acid changes at specific locations in the C-terminus and in the N-terminus also play a direct role in receptor engagement and resistance to DPP-4 inhibition, extending the half-life and impact of the receptor [
2]. Only a small percentage of the various forms of GLP-1 in circulation are physiologically active. GLP-1 amide, a significant secretory product, is the active form of GLP-1. After entering the bloodstream, GLP-1 amide has a half-life of less than two minutes because the DPP-4 enzyme quickly cleaves it between positions 8 and 9 to produce the N-terminally truncated metabolite GLP-1 amide, which is physiologically inert and does not bind to the GLP-1 receptor. When delivered therapeutically, metabolites may have advantageous glucose-regulatory and cardio-protective effects, such as lowering oxidative stress in vascular tissues, protecting beta cells, and preventing gluconeogenesis and oxidative stress in hepatocytes. Vasodilation and cardiomyocyte viability are directly impacted by GLP-1 amide and its metabolites, which also improve cardiac function. For instance, while GLP-1[
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36] amide acts through a GLP-1R-independent mechanism, GLP-1[
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36] amide acts through a GLP-1R-dependent pathway to affect the cardiovascular system. Since targeting GLP-1R activation or GLP-1 degradation may have various cardiovascular implications, these metabolites have a wide range of therapeutic potential [
13].
The heart contains glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors, and most research indicates that glucagon-like peptide-1 protects the myocardium. Moreover, it has been discovered that GLP-1 lowers human concentrations of free fatty acids and minimizes the post-prandial rise in triglycerides. It also has diuretic and natriuretic effects by modifying renal Na+/H+ exchange, which helps lower blood pressure [
14]. Other roles of glucagon-like peptide-1 include the facilitation of increased glucose uptake within the muscles, decreased rate of glucose production from the liver, and neuroprotection. Patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes have a significantly diminished incretin effect. The characteristic in concern is likely the main cause of these patients' incapacity to release enough insulin to prevent hyperglycemia after oral glucose [
2]. The diminished incretin impact in patients with type 2 diabetes appears to be caused by diminished post-prandial production, decreased insulinotropic potency, and diminished insulinotropic effect of glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide.
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1RAs)
Incretin Mimetics are hormone-like agents that can be used in addition to metformin and or sulfonylurea drugs in the management of Type 2 diabetes. In some cases, the GLP-1 analogs have been used to manage obesity. These agents act like incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1. They stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin by binding to the GLP-1 receptors. These drugs include liraglutide, albiglutide, lixisenatide, exenatide, semaglutide, and dulaglutide. Although they can be taken in place of or in addition to insulin, incretin mimetics are not meant to be used in place of anti-diabetic medications. GLP-1 receptor agonists should be utilized selectively following metformin failure in patients with known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or in individuals without established cardiovascular disease but with high-risk signs, according to the current American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) consensus protocol. A pre-filled pen is used to administer these medications beneath the skin due to poor oral bioavailability [
15].
The amount that GLP-1 receptor agonists reduce plasma glucose in fasting and post-prandial states varies according to the formulation. Long-acting GLP-1 agonists such as dulaglutide, Liraglutide, albiglutide, and exenatide extended-release lower blood glucose by increasing insulin secretion and decreasing glucagon. Short-acting GLP-1 mimetics such as exenatide short-acting and lixisenatide primarily lower post-prandial plasma glucose by delaying stomach emptying [
17]. The role of incretin mimetics in promoting weight loss and a comparatively reduced risk of hypoglycemia compared to other anti-hyperglycemic medications are the main advantages of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists are structurally similar to the incretin hormone GLP-1. The incretin mimetics have distinctions in potency and chemical makeup; these therapies also vary significantly in how long they take to act. The mimetics are modified to resist breakdown by the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 enzyme. The components are not orally active due to rapid gastrointestinal inactivation and thus have to be administered via subcutaneous injections [
18]. The incretin-based mimetics are considered in patients with contraindications or intolerance to the first-line agent, metformin. It can also be used in patients who do not achieve their glycated hemoglobin target within three months of therapy and, particularly, in patients with atherosclerosis, chronic renal disease, and heart failure. Some of the GLP-1 analogs, such as semaglutide and Liraglutide, have been approved for obesity management and in overweight patients with comorbidities. The major barriers to prescribing these drugs are higher costs and tolerability [
18].
The incretin mimetic agents have also been demonstrated to reduce total cholesterol and systolic and diastolic blood pressure and to encourage weight loss. The benefit of weight loss is facilitated by directly acting on the hypothalamus to cause an increased satiety, thus reducing caloric intake. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus frequently develop atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, which is also a leading cause of mortality in this population. Research has shown that in individuals with type 2 diabetes, reducing cardiovascular risk factors can help avoid atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. GLP-1 agonists have significant cardiovascular benefits, including improving the overall cardiac output, reducing infarction size, and decreasing the general risk for cardiovascular events. They additionally enhance left ventricular ejection fraction, myocardial contractility, coronary blood flow, and endothelial function [
19].
The primary adverse effect is mild to moderate nausea that typically subsides after a few weeks. Hypoglycemia, a well-known adverse effect of several pre-existing antidiabetic therapy options, is rare and mostly happens when sulfonylurea is used in concert with incretin mimetics. Insulin and incretin mimetics should not be used concurrently [
20]. The other primary adverse reactions of Glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists are vomiting and diarrhea, which can cause acute kidney injury through volume reduction. Side effects may also include headaches, infections, moderate tachycardia, dyspepsia, and dizziness.
Patients who use this class of medication should be counseled that eating when feeling full may cause temporary, moderate nausea. If nausea is experienced, the dosage of these drugs should be increased cautiously [
18]. Erythema and pruritus at the injection site are other frequent side effects, particularly with the longer-acting drugs in this group of agents. Antibodies may develop against specific GLP-1 analogs and may impair the effectiveness of these agents, especially exenatide. This immunogenicity could result in Anaphylaxis or responses at the injection site [
15]. Antibody formation has been reported more frequently with the weekly administration of exenatide than with the twice-daily dosing. Due to statistically negligible glycemic improvement and exacerbated hypoglycemia effects, combination therapy with GLP-1 agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors is not currently advocated.
Reactive oxygen species partially oxidize low-density lipoproteins (LDL) cholesterol when it traverses through the intima layer of arterial blood arteries, producing oxidized LDL molecules and may contribute to the formation of atheromas. By producing adhesion molecules such as vascular cell adhesion protein 1 and E-selectin, the interaction between monocytes and macrophages with oxidized LDL and free radicals stimulates additional infiltration of monocytes. When oxidized LDL stimulates monocytes, they develop into macrophages. Pro-inflammatory cytokines macrophages. Through phagocytosis, macrophages absorb lipid particles and inhibit the production of Krüppel-like factor 2 that inhibits endothelial nitric oxide synthase, resulting in decreased Nitric oxide (NO) production and inhibiting vasodilation via NO-mediated vascular smooth muscle relaxation [
21]. Macrophages become foam cells in a condition where reactive oxygen species and oxidized LDL predominate. These cells can undergo apoptosis and discharge their lipid content into the lipid core of developing atherosclerotic plaques. The thick fibrous cap covering stable plaques, primarily made of collagen, serves as a barrier against rupture. When atherogenesis advances, the fibrous cap is broken down by matrix metalloproteinase through proteolysis, endothelial cells then undergo apoptosis, and more necrotic regions emerge. Plaque rupture, thrombus development, and bleeding into areas of necrotic plaque are the outcomes of this.
The expression of GLP-1 receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells, monocytes, endothelial cells, and macrophages can have a variety of consequences that may impede the development or rupture of atherosclerotic plaques. First, GLP-1, exenatide, liraglutide, and semaglutide lower the generation of ROS. GLP-1 receptor stimulation, such as that provided by GLP-1, exenatide, dulaglutide, and Liraglutide, effectively reduces the activation of adhesion molecules and monocytes and macrophages caused by oxidized LDL and its subsequent activation [
20]. For instance, exenatide reduces the buildup of monocytes in the vascular wall. Endothelial cells result in vascular smooth muscle relaxation and endothelium-derived vasodilation by suppressing endothelin synthesis, producing more nitric oxide, and expressing more nitric oxide synthase. Lixisenatide, Liraglutide, and dulaglutide are examples of drugs that preferentially produce M2 macrophages from monocytes. This leads to an increase in the otherwise repressed development of KLF-2. Following GLP-1 receptor stimulation, there is a decrease in reactive oxygen species exposure, which hinders the process of foam cell formation, reduces caspase-mediated foam cell apoptosis, and limits the development of necrosis in the core of atherosclerotic plaques [
19].
Moreover, GLP-1 receptor activation decreases the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle and its potential migration into plaques. Exenatide stabilizes endothelial cell integrity. Semaglutide decreases the amount of plaque hemorrhage. Metalloproteinase expression is downregulated, keeping fibrous caps intact and inhibiting plaque rupture. Plaque stabilization and a slowdown of plaque progression are the overall outcomes [
20]. GLP-1 receptor agonists significantly decrease atherosclerotic plaques' creation, extent, and vulnerability. Renal benefits have been reported following the use of incretin mimetics. GLP-1 receptor agonists decrease albumin excretion in the urine, prevent new-onset macroalbuminuria, or delay the rate at which the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) declines over time. Most of the processes underlying these kidney benefits are unclear [
18]. Although significant decreases in renal composite outcomes have been reported, these reports mostly depended on prevailing effects that prevented new-onset chronic macro-albuminuria.
Some of the high-risk variables are the presence of albuminuria, eGFR < 60 ml/min, left ventricular hypertrophy, coronary artery stenosis >50%, and individuals who are ≥ 55 years of age. Additionally, it is possible to avoid hypoglycemia and weight gain by using incretin mimetics. Going one step further, the ESC guidelines suggest using GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT-2 inhibitors as first-line treatment for patients at high or very high risk or with existing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Extremely high-risk variables include diabetes for a length of more than ten years without target organ damage, three or more main risk factors, and any additional risk factors [
14]. Approximately 30 to 60 percent of individuals with type 2 diabetes would be eligible for a GLP-1 RA based on these guidelines. However, in actual clinical practice, the proportion of patients on incretin mimetics medication is very low. The apparent discrepancy between clinical practice and guidelines has several causes. First, the expense of treating with GLP-1 receptor agonists is similar to that of an intensified insulin treatment regimen, including glucose monitoring expenses, but significantly more than that of most oral glucose-lowering medications. While several cost-effectiveness assessments have indicated that the overall benefits of GLP-1 RA therapy far exceed the direct treatment costs, the cost of the GLP-1 receptor agonists currently on the market continues to be a significant barrier in most nations. In addition, certain patients may be reluctant to begin incretin mimetics due to the requirement for daily or weekly injections. Third, patients who have a history of pancreatitis, diabetic retinopathy, or medullary thyroid cancer may not be able to take GLP-1 RAs due to contraindications [
18].
Increased glucagon secretion contributes to the underlying cause of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes. The use of incretin as a medication for type 2 diabetes has been actively explored as it both increases insulin secretion and inhibits the production of glucagon. Nonetheless, because type 2 diabetes reduces the responsiveness of GIP in β-cells, research into GLP-1-related medications has resulted in the usage of GLP-1 receptor agonists in managing the condition [
20].
Conclusions
In conclusion, the management of diabetes is aimed at improving hyperglycemia symptoms and minimizing long-term microvascular and macrovascular complications such as diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular effects. The discovery of medications that regulate hyperglycemia and affect other metabolic risk variables to enhance cardiovascular outcomes is in high demand. Obesity, aging, genetic vulnerability, and diversity are factors in the rising prevalence of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Insulin resistance, the functional failure of pancreatic beta cells, and excessive or incorrect glucagon output are the main causes of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes type 2 is a long-term comorbidity brought on by decreased insulin production as a result of peripheral tissue insulin resistance and β-cell malfunction. In addition to causing microangiopathy, homeostatic hyperglycemia increases the risk of macroangiopathy, leading to cardiovascular diseases. Economic disadvantages, a decline in healthy life expectancy, and a decline in patient quality of life are all caused by complications from these vascular conditions. Furthermore, obese patients with type 2 diabetes need more rigorous glycemic control and weight management strategies because obesity is linked to the pathophysiology of the disease and is a risk factor for macroangiopathy [
7]. Medication and lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise can help with effective treatment for obesity and Type 2 diabetes. In addition, simultaneous administration of a low dose of a luminal α-glucosidase inhibitor agent with the GLP-1 agent with or without insulin may help to reduce the potential side effects of both agents and further improve the clinical efficacy of the therapeutic regimen. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are a valuable therapy alternative for people with type 2 diabetes since they target several of the disease's pathophysiology problems. GLP-1 RAs lower glucagon secretion slows the pace of gastric emptying and enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Additionally, they are linked to decreased hunger, which results in weight loss. These drugs have been linked to dose-limiting adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Efforts have been made to increase tolerability and efficacy by looking into dose-escalation regimens that enable larger doses linked to better efficacy while minimizing undesirable effects. Glucagon-like receptor agonists have both central and peripheral effects. These agents have been shown to minimize food intake and reduce appetite. This eventually contributes to weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and improvements in beta-pancreatic cell function. Administration of incretin mimetics enhances insulin release, inhibits glucagon production, and consequently slows gastric emptying. It results in better glycemic control, as shown by reduced glycated hemoglobin and decreased fasting glucose and post-prandial glucose levels. The most common adverse effects of GLP-1 agonists are vomiting, diarrhea, and nausea, which can cause acute kidney injury by volume contraction. There may also be headaches, infections, moderate tachycardia, dyspepsia, and dizziness.
Patients who use this class of medication should be cautioned that eating when feeling full may cause temporary, moderate nausea. If nausea is experienced, the dosage of these drugs should be increased gradually. Erythema and pruritus at the injection site are other frequent side effects, particularly with the longer-acting drugs in this class of medications. There is a minimal chance of having a minor hypoglycemic episode, although as of yet, no significant hypoglycemic episodes have been reported in the available research. Antibodies that patients may develop against specific GLP-1 analogs may impair the effectiveness of these drugs, especially exenatide. Anaphylaxis or responses at the injection site could result from this immunogenicity. Pregnancy and hypersensitivity are two conditions that make GLP-1 agonist use contraindicated and prevent the prescription of this family of drugs. For women of reproductive age, the recommended course of action when using GLP-1 agonists following conception is unclear since controlled studies of the safety of incretin use during pregnancy are lacking. Individuals with serious gastrointestinal conditions such as Gastroparesis and inflammatory bowel disease should also avoid GLP-1 analogs. Very recently, it has been reported that monotherapy with GLP-1 is associated with a risk of new-onset nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, Diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic macular edema [
56,
57].
In summary, the increasing use of incretin mimetics therapy during T2DM and associated comorbidities, including obesity and overweight and glucose-intolerant conditions, shows a promising future, whether used as mono- or combination therapy [
58,
59,
60], or when combined with nutraceuticals, lifestyle, or dietary factors that may augment the physiologic responses [
61].