Submitted:
18 May 2024
Posted:
20 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Diagnosis
3. Demographics and Cost
4. Mechanisms and Treatments
4.1. PAH-Specific Drugs and Vasoconstrictor-Vasodilator Imbalances
4.2. Hypoxia and Oxygen Therapies
4.3. Genetics and Signaling Pathways
4.4. Inflammation
4.5. General Therapies
4.6. Autonomic Nervous System Imbalance, Therapies, and Neurostimulation
4.6.1. Multiple Pharmacological Therapies Have Been Tested to Assess the Role of the Autonomic System in the Pathogenesis of PH
4.6.2. Non-Pharmacological Therapies: Sympathetic Activity Modulation and Stimulation of Vagal Nerve or Somatosensory Nerves
| Reference | Model | Technique | Findings Relevant to PH |
|---|---|---|---|
| [189] | Pre-clinical Hypoxic-induced PH |
EA | mPAP ↓, RV size ↓ Pathological pulmonary remodeling ↓ Serum/lung eNOS ↑, serum/lung ET-1 ↓ |
| [190,246] | Pre-clinical Hypertension |
EA Non-EA |
Sympathetic activity (e.g. via NOS pathways) ↓ Serum norepinephrine ↓ Serum interleukins/C-reactive protein ↓ Serum ET-1 ↓, myocardial eNOS ↑ |
| [193,194] | Clinical Hypertension |
Non-EA + EECP | Serum NO ↑, serum ET-1 ↓ |
| [195,196,197,198,199,200,201] | Clinical COPD (i.e. Group 3) |
EA Non-EA |
Oxygen utilization/efficiency ↑, dyspnea ↓, exercise capacity ↑ |
| [203,248–252,261,264] | Pre-clinical Systemic inflammation |
EA Non-EA |
Serum/lung TNF-α, interleukins ↓ Parasympathetic (vagus) outflow ↑ Ejection fraction ↑ |
| [204] | Pre-clinical Heart failure (i.e. Group 2) |
EA | Sympathetic outflow ↓ Heart function ↑ (i.e. left ventricle ejection fraction ↑, left ventricle size ↓ |
| [216–218,220,221,227–230,240,241,243] | Pre-clinical Sympathetically stressed |
EA | Sympathetic outflow ↓ (i.e. via central opioid, CRH pathways) Serum CRH, cortisol, norepinephrine, adrenaline |
| [257] | Clinical Post-surgery secondary to lung cancer |
EA | PaO2/FiO2 ↑ SOD activity ↑ Length of hospital stay ↓ |
| [247] | Clinical Systemic sclerosis (i.e. Group 5) |
EA | Plasma ET-1 ↓ |
| [258,262,263] | Pre-clinical Lung injury |
EA | Lung SOD activity ↑ Serum/lung cytokines ↓ PaO2 ↑ Lung injury score ↓ |
| [260,267] | Pre-clinical COPD |
EA | Pathological pulmonary remodeling ↓ Lung cytokines ↓ Lung function (i.e. expiratory volume) ↑ |
| PH = pulmonary hypertension; EA = electroacupuncture; ET-1 = endothelin-1, NO = nitric oxide, eNOS = endothelial nitric oxide synthase; EECP = enhanced external counterpulsation; COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CRH = corticotropin-releasing hormone; PaO2/FiO2 = arterial oxygen pressure/fraction of inspired oxygen; SOD = superoxide dismutase | |||
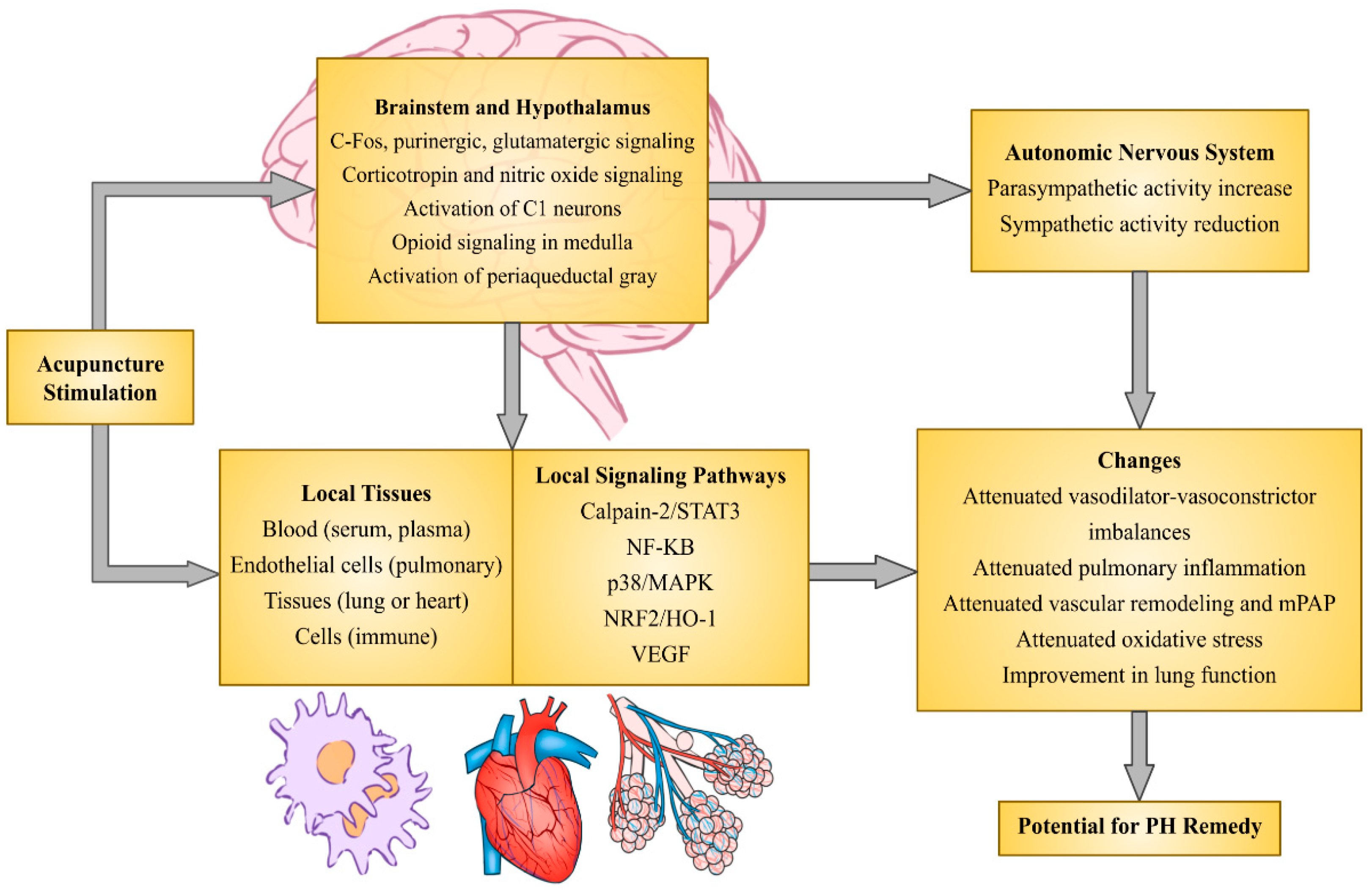
5. Conclusion
Funding
References
- Humbert, M., Kovacs, G., Hoeper, M. M., Badagliacca, R., Berger, R. M. F., Brida, M., Carlsen, J., Coats, A. J. S., Escribano-Subias, P., Ferrari, P., Ferreira, D. S., Ghofrani, H. A., Giannakoulas, G., Kiely, D. G., Mayer, E., Meszaros, G., Nagavci, B., Olsson, K. M., Pepke-Zaba, J., Quint, J. K., … ESC/ERS Scientific Document Group (2022). 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. European heart journal, 43(38), 3618–3731. [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G., Montani, D., Celermajer, D. S., Denton, C. P., Gatzoulis, M. A., Krowka, M., Williams, P. G., & Souza, R. (2019). Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. The European respiratory journal, 53(1), 1801913.
- Hoeper, M. M., Ghofrani, H. A., Grünig, E., Klose, H., Olschewski, H., & Rosenkranz, S. (2017). Pulmonary Hypertension. Deutsches Arzteblatt international, 114(5), 73–84. [CrossRef]
- Barst, R. J., Chung, L., Zamanian, R. T., Turner, M., & McGoon, M. D. (2013). Functional class improvement and 3-year survival outcomes in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension in the REVEAL Registry. Chest, 144(1), 160–168. [CrossRef]
- Sitbon, O., Humbert, M., Nunes, H., Parent, F., Garcia, G., Hervé, P., Rainisio, M., & Simonneau, G. (2002). Long-term intravenous epoprostenol infusion in primary pulmonary hypertension: prognostic factors and survival. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 40(4), 780–788. [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, H. A., Galiè, N., Grimminger, F., Grünig, E., Humbert, M., Jing, Z. C., Keogh, A. M., Langleben, D., Kilama, M. O., Fritsch, A., Neuser, D., Rubin, L. J., & PATENT-1 Study Group (2013). Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 369(4), 330–340. [CrossRef]
- Montani, D., Günther, S., Dorfmüller, P., Perros, F., Girerd, B., Garcia, G., Jaïs, X., Savale, L., Artaud-Macari, E., Price, L. C., Humbert, M., Simonneau, G., & Sitbon, O. (2013). Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Orphanet journal of rare diseases, 8, 97. [CrossRef]
- Rich, S., Dantzker, D. R., Ayres, S. M., Bergofsky, E. H., Brundage, B. H., Detre, K. M., Fishman, A. P., Goldring, R. M., Groves, B. M., & Koerner, S. K. (1987). Primary pulmonary hypertension. A national prospective study. Annals of internal medicine, 107(2), 216–223. [CrossRef]
- Henkens, I. R., Mouchaers, K. T., Vonk-Noordegraaf, A., Boonstra, A., Swenne, C. A., Maan, A. C., Man, S. C., Twisk, J. W., van der Wall, E. E., Schalij, M. J., & Vliegen, H. W. (2008). Improved ECG detection of presence and severity of right ventricular pressure load validated with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 294(5), H2150–H2157. [CrossRef]
- Diller, G. P., & Gatzoulis, M. A. (2007). Pulmonary vascular disease in adults with congenital heart disease. Circulation, 115(8), 1039–1050. [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, V. V., Archer, S. L., Badesch, D. B., Barst, R. J., Farber, H. W., Lindner, J. R., Mathier, M. A., McGoon, M. D., Park, M. H., Rosenson, R. S., Rubin, L. J., Tapson, V. F., Varga, J., American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents, American Heart Association, American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, Inc, & Pulmonary Hypertension Association (2009). ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 53(17), 1573–1619. [CrossRef]
- Pfeuffer, E., Krannich, H., Halank, M., Wilkens, H., Kolb, P., Jany, B., & Held, M. (2017). Anxiety, Depression, and Health-Related QOL in Patients Diagnosed with PAH or CTEPH. Lung, 195(6), 759–768. [CrossRef]
- Harzheim, D., Klose, H., Pinado, F. P., Ehlken, N., Nagel, C., Fischer, C., Ghofrani, A., Rosenkranz, S., Seyfarth, H. J., Halank, M., Mayer, E., Grünig, E., & Guth, S. (2013). Anxiety and depression disorders in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Respiratory research, 14(1), 104. [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M. M., Humbert, M., Souza, R., Idrees, M., Kawut, S. M., Sliwa-Hahnle, K., Jing, Z. C., & Gibbs, J. S. (2016). A global view of pulmonary hypertension. The Lancet. Respiratory medicine, 4(4), 306–322. [CrossRef]
- Zlotnick, D. M., Ouellette, M. L., Malenka, D. J., DeSimone, J. P., Leavitt, B. J., Helm, R. E., Olmstead, E. M., Costa, S. P., DiScipio, A. W., Likosky, D. S., Schmoker, J. D., Quinn, R. D., Sisto, D., Klemperer, J. D., Sardella, G. L., Baribeau, Y. R., Frumiento, C., Brown, J. R., O'Rourke, D. J., & Northern New England Cardiovascular Disease Study Group (2013). Effect of preoperative pulmonary hypertension on outcomes in patients with severe aortic stenosis following surgical aortic valve replacement. The American journal of cardiology, 112(10), 1635–1640. [CrossRef]
- Tichelbäcker, T., Dumitrescu, D., Gerhardt, F., Stern, D., Wissmüller, M., Adam, M., Schmidt, T., Frerker, C., Pfister, R., Halbach, M., Baldus, S., & Rosenkranz, S. (2019). Pulmonary hypertension and valvular heart disease. Pulmonale Hypertonie und Herzklappenerkrankungen. Herz, 44(6), 491–501. [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, A., Potekhina, A., Belyavskiy, E., & Ageev, F. (2022). Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Pulmonary Hypertension: Focus on Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland), 15(8), 1024. [CrossRef]
- Mocumbi, A., Humbert, M., Saxena, A., Jing, Z. C., Sliwa, K., Thienemann, F., Archer, S. L., & Stewart, S. (2024). Pulmonary hypertension. Nature reviews. Disease primers, 10(1), 1. [CrossRef]
- Thienemann, F., Dzudie, A., Mocumbi, A. O., Blauwet, L., Sani, M. U., Karaye, K. M., Ogah, O. S., Mbanze, I., Mbakwem, A., Udo, P., Tibazarwa, K., Damasceno, A., Keates, A. K., Stewart, S., & Sliwa, K. (2016). The causes, treatment, and outcome of pulmonary hypertension in Africa: Insights from the Pan African Pulmonary Hypertension Cohort (PAPUCO) Registry. International journal of cardiology, 221, 205–211. [CrossRef]
- Katoto, P. D. M. C., Mukasa, S. L., Sani, M. U., Karaye, K. M., Mbanze, I., Damasceno, A., Mocumbi, A. O., Dzudie, A., Sliwa, K., & Thienemann, F. (2023). HIV status and survival of patients with pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease: the Pan African Pulmonary Hypertension Cohort. Scientific reports, 13(1), 9790. [CrossRef]
- Schikowski, E. M., Swabe, G., Chan, S. Y., & Magnani, J. W. (2022). Association between income and likelihood of right heart catheterization in individuals with pulmonary hypertension: A US claims database analysis. Pulmonary circulation, 12(3), e12132. [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, S., Mani, A., G, S., M, A., Menon, J., G, R., Kumar, R. K., Koshy, A. G., Attacheril, T. V., George, R., Punnose, E., Ashraf, S. M., Sr, A., Cholakkal, M., Jeemon, P., Joseph, S., Govindan, U., Joseph, J., Eapen, K., Sreedharan, M., … Venugopal, K. (2022). Pulmonary Hypertension Registry of Kerala, India (PRO-KERALA): One-year outcomes. Indian heart journal, 74(1), 34–39. [CrossRef]
- Talwar, A., Sahni, S., Talwar, A., Kohn, N., & Klinger, J. R. (2016). Socioeconomic status affects pulmonary hypertension disease severity at time of first evaluation. Pulmonary circulation, 6(2), 191–195. [CrossRef]
- Caravita, S., Baratto, C., Di Marco, F., Calabrese, A., Balestrieri, G., Russo, F., Faini, A., Soranna, D., Perego, G. B., Badano, L. P., Grazioli, L., Lorini, F. L., Parati, G., & Senni, M. (2020). Haemodynamic characteristics of COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome requiring mechanical ventilation. An invasive assessment using right heart catheterization. European journal of heart failure, 22(12), 2228–2237. [CrossRef]
- Pagnesi, M., Baldetti, L., Beneduce, A., Calvo, F., Gramegna, M., Pazzanese, V., Ingallina, G., Napolano, A., Finazzi, R., Ruggeri, A., Ajello, S., Melisurgo, G., Camici, P. G., Scarpellini, P., Tresoldi, M., Landoni, G., Ciceri, F., Scandroglio, A. M., Agricola, E., & Cappelletti, A. M. (2020). Pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular involvement in hospitalised patients with COVID-19. Heart (British Cardiac Society), 106(17), 1324–1331. [CrossRef]
- Charif, F., Dakroub, F., Bou Akl, I., Kularatne, M., & Montani, D. (2023). Pulmonary arterial hypertension and COVID-19: Piecing the puzzle. Respiratory medicine and research, 84, 101053. [CrossRef]
- Tudoran, C., Tudoran, M., Lazureanu, V. E., Marinescu, A. R., Pop, G. N., Pescariu, A. S., Enache, A., & Cut, T. G. (2021). Evidence of Pulmonary Hypertension after SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Subjects without Previous Significant Cardiovascular Pathology. Journal of clinical medicine, 10(2), 199. [CrossRef]
- Khan, A. W., Ullah, I., Khan, K. S., Tahir, M. J., Masyeni, S., & Harapan, H. (2021). Pulmonary arterial hypertension post COVID-19: A sequala of SARS-CoV-2 infection?. Respiratory medicine case reports, 33, 101429. [CrossRef]
- Zozaya, N., Abdalla, F., Casado Moreno, I., Crespo-Diz, C., Ramírez Gallardo, A. M., Rueda Soriano, J., Alcalá Galán, M., & Hidalgo-Vega, Á. (2022). The economic burden of pulmonary arterial hypertension in Spain. BMC pulmonary medicine, 22(1), 105. [CrossRef]
- Burger, C. D., Ghandour, M., Padmanabhan Menon, D., Helmi, H., & Benza, R. L. (2017). Early intervention in the management of pulmonary arterial hypertension: clinical and economic outcomes. ClinicoEconomics and outcomes research : CEOR, 9, 731–739. [CrossRef]
- Bergot, E., De Leotoing, L., Bendjenana, H., Tournier, C., Vainchtock, A., Nachbaur, G., & Humbert, M. (2019). Hospital burden of pulmonary arterial hypertension in France. PloS one, 14(9), e0221211. [CrossRef]
- Selexipag (Uptravi) for pulmonary arterial hypertension. (2016). The Medical letter on drugs and therapeutics, 58(1488), 21–23.
- Sikirica, M., Iorga, S. R., Bancroft, T., & Potash, J. (2014). The economic burden of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in the US on payers and patients. BMC health services research, 14, 676. [CrossRef]
- Ogbomo, A., Tsang, Y., Mallampati, R., & Panjabi, S. (2022). The direct and indirect health care costs associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension among commercially insured patients in the United States. Journal of managed care & specialty pharmacy, 28(6), 608–616. [CrossRef]
- Sherif, A. A., Gilvaz, V. J., Abraham, S., Saji, A. M., Mathew, D., Isath, A., Rajendran, A., Contreras, J., Lanier, G. M., & Reginato, A. M. (2024). Systemic sclerosis is associated with increased in-patient mortality in patients hospitalized for heart failure. ESC heart failure, 10.1002/ehf2.14457. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Said, Q., Martin, B. C., Joish, V. N., Kreilick, C., & Mathai, S. C. (2012). The cost to managed care of managing pulmonary hypertension. Journal of medical economics, 15(3), 500–508. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, T., Near, A. M., Zhao, X., Ramey, D. R., Banerji, T., Xie, H., & Nathan, S. D. (2023). Healthcare resource utilization in patients with pulmonary hypertension associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (PH-COPD): a real-world data analysis. BMC pulmonary medicine, 23(1), 455. [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M., & Howard, L. (2015). Pulmonary arterial hypertension: the burden of disease and impact on quality of life. European respiratory review : an official journal of the European Respiratory Society, 24(138), 621–629. [CrossRef]
- Fuge, J., Park, D. H., von Lengerke, T., Richter, M. J., Gall, H., Ghofrani, H. A., Kamp, J. C., Hoeper, M. M., & Olsson, K. M. (2022). Impact of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension on Employment, Work Productivity, and Quality of Life - Results of a Cross-Sectional Multi-Center Study. Frontiers in psychiatry, 12, 781532. [CrossRef]
- Runheim, H., Kjellström, B., Beaudet, A., Ivarsson, B., Husberg, M., Pillai, N., Levin, L. Å., & Bernfort, L. (2023). Societal costs associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A study utilizing linked national registries. Pulmonary circulation, 13(1), e12190. [CrossRef]
- Kjellström, B., Runheim, H., Beaudet, A., Husberg, M., Ivarsson, B., Pillai, N., Levin, L. Å., & Bernfort, L. (2023). Societal costs associated to chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A study utilizing linked national registries. Pulmonary circulation, 13(2), e12254. [CrossRef]
- Tuder, R. M., Abman, S. H., Braun, T., Capron, F., Stevens, T., Thistlethwaite, P. A., & Haworth, S. G. (2009). Development and pathology of pulmonary hypertension. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 54(1 Suppl), S3–S9. [CrossRef]
- Stenmark, K. R., Gerasimovskaya, E., Nemenoff, R. A., & Das, M. (2002). Hypoxic activation of adventitial fibroblasts: role in vascular remodeling. Chest, 122(6 Suppl), 326S–334S. [CrossRef]
- Davie, N. J., Crossno, J. T., Jr, Frid, M. G., Hofmeister, S. E., Reeves, J. T., Hyde, D. M., Carpenter, T. C., Brunetti, J. A., McNiece, I. K., & Stenmark, K. R. (2004). Hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery adventitial remodeling and neovascularization: contribution of progenitor cells. American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology, 286(4), L668–L678. [CrossRef]
- Stacher, E., Graham, B. B., Hunt, J. M., Gandjeva, A., Groshong, S. D., McLaughlin, V. V., Jessup, M., Grizzle, W. E., Aldred, M. A., Cool, C. D., & Tuder, R. M. (2012). Modern age pathology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 186(3), 261–272. [CrossRef]
- Chazova, I., Loyd, J. E., Zhdanov, V. S., Newman, J. H., Belenkov, Y., & Meyrick, B. (1995). Pulmonary artery adventitial changes and venous involvement in primary pulmonary hypertension. The American journal of pathology, 146(2), 389–397.
- Tuder R. M. (2017). Pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension. Cell and tissue research, 367(3), 643–649. [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M., Torbicki, A., Gopalan, D., Sitbon, O., Klok, F. A., Lang, I., Jenkins, D., Kim, N. H., Humbert, M., Jais, X., Vonk Noordegraaf, A., Pepke-Zaba, J., Brénot, P., Dorfmuller, P., Fadel, E., Ghofrani, H. A., Hoeper, M. M., Jansa, P., Madani, M., Matsubara, H., … Simonneau, G. (2021). ERS statement on chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. The European respiratory journal, 57(6), 2002828. [CrossRef]
- Giaid, A., Yanagisawa, M., Langleben, D., Michel, R. P., Levy, R., Shennib, H., Kimura, S., Masaki, T., Duguid, W. P., & Stewart, D. J. (1993). Expression of endothelin-1 in the lungs of patients with pulmonary hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 328(24), 1732–1739. [CrossRef]
- Reesink, H. J., Meijer, R. C., Lutter, R., Boomsma, F., Jansen, H. M., Kloek, J. J., & Bresser, P. (2006). Hemodynamic and clinical correlates of endothelin-1 in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation journal : official journal of the Japanese Circulation Society, 70(8), 1058–1063. [CrossRef]
- Goerre, S., Wenk, M., Bärtsch, P., Lüscher, T. F., Niroomand, F., Hohenhaus, E., Oelz, O., & Reinhart, W. H. (1995). Endothelin-1 in pulmonary hypertension associated with high-altitude exposure. Circulation, 91(2), 359–364.
- Cacoub, P., Dorent, R., Nataf, P., Carayon, A., Riquet, M., Noe, E., Piette, J. C., Godeau, P., & Gandjbakhch, I. (1997). Endothelin-1 in the lungs of patients with pulmonary hypertension. Cardiovascular research, 33(1), 196–200. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R., Yuan, T., Wang, R., Gong, D., Wang, S., Du, G., & Fang, L. (2023). Insights into Endothelin Receptors in Pulmonary Hypertension. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(12), 10206. [CrossRef]
- Brewster, L. M., Garcia, V. P., Levy, M. V., Stockelman, K. A., Goulding, A., DeSouza, N. M., Greiner, J. J., Hijmans, J. G., & DeSouza, C. A. (2020). Endothelin-1-induced endothelial microvesicles impair endothelial cell function. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 128(6), 1497–1505. [CrossRef]
- Marsden, P. A., Danthuluri, N. R., Brenner, B. M., Ballermann, B. J., & Brock, T. A. (1989). Endothelin action on vascular smooth muscle involves inositol trisphosphate and calcium mobilization. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 158(1), 86–93. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. M., Wang, K. Q., Zhou, G. M., Zuo, J., & Ge, J. B. (2003). Endothelin-1 promoted proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell through pathway of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and cyclin D1. Acta pharmacologica Sinica, 24(6), 563–568.
- Douglas, S. A., & Ohlstein, E. H. (1997). Signal transduction mechanisms mediating the vascular actions of endothelin. Journal of vascular research, 34(3), 152–164. [CrossRef]
- Simonson, M. S., Wann, S., Mené, P., Dubyak, G. R., Kester, M., Nakazato, Y., Sedor, J. R., & Dunn, M. J. (1989). Endothelin stimulates phospholipase C, Na+/H+ exchange, c-fos expression, and mitogenesis in rat mesangial cells. The Journal of clinical investigation, 83(2), 708–712. [CrossRef]
- Rubin, L. J., Badesch, D. B., Barst, R. J., Galie, N., Black, C. M., Keogh, A., Pulido, T., Frost, A., Roux, S., Leconte, I., Landzberg, M., & Simonneau, G. (2002). Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 346(12), 896–903. [CrossRef]
- Galiè, N., Rubin, L.j, Hoeper, M., Jansa, P., Al-Hiti, H., Meyer, G., Chiossi, E., Kusic-Pajic, A., & Simonneau, G. (2008). Treatment of patients with mildly symptomatic pulmonary arterial hypertension with bosentan (EARLY study): a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England), 371(9630), 2093–2100. [CrossRef]
- Pulido, T., Adzerikho, I., Channick, R. N., Delcroix, M., Galiè, N., Ghofrani, H. A., Jansa, P., Jing, Z. C., Le Brun, F. O., Mehta, S., Mittelholzer, C. M., Perchenet, L., Sastry, B. K., Sitbon, O., Souza, R., Torbicki, A., Zeng, X., Rubin, L. J., Simonneau, G., & SERAPHIN Investigators (2013). Macitentan and morbidity and mortality in pulmonary arterial hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 369(9), 809–818. [CrossRef]
- Galiè, N., Olschewski, H., Oudiz, R. J., Torres, F., Frost, A., Ghofrani, H. A., Badesch, D. B., McGoon, M. D., McLaughlin, V. V., Roecker, E. B., Gerber, M. J., Dufton, C., Wiens, B. L., Rubin, L. J., & Ambrisentan in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter, Efficacy Studies (ARIES) Group (2008). Ambrisentan for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: results of the ambrisentan in pulmonary arterial hypertension, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, efficacy (ARIES) study 1 and 2. Circulation, 117(23), 3010–3019. [CrossRef]
- Koller, B., Steringer-Mascherbauer, R., Ebner, C. H., Weber, T., Ammer, M., Eichinger, J., Pretsch, I., Herold, M., Schwaiger, J., Ulmer, H., & Grander, W. (2017). Pilot Study of Endothelin Receptor Blockade in Heart Failure with Diastolic Dysfunction and Pulmonary Hypertension (BADDHY-Trial). Heart, lung & circulation, 26(5), 433–441. [CrossRef]
- Vachiéry, J. L., Delcroix, M., Al-Hiti, H., Efficace, M., Hutyra, M., Lack, G., Papadakis, K., & Rubin, L. J. (2018). Macitentan in pulmonary hypertension due to left ventricular dysfunction. The European respiratory journal, 51(2), 1701886. [CrossRef]
- Packer, M., McMurray, J. J. V., Krum, H., Kiowski, W., Massie, B. M., Caspi, A., Pratt, C. M., Petrie, M. C., DeMets, D., Kobrin, I., Roux, S., Swedberg, K., & ENABLE Investigators and Committees (2017). Long-Term Effect of Endothelin Receptor Antagonism With Bosentan on the Morbidity and Mortality of Patients With Severe Chronic Heart Failure: Primary Results of the ENABLE Trials. JACC. Heart failure, 5(5), 317–326. [CrossRef]
- Park, J., Song, J. H., Park, D. A., Lee, J. S., Lee, S. D., & Oh, Y. M. (2013). Systematic review and meta-analysis of pulmonary hypertension specific therapy for exercise capacity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of Korean medical science, 28(8), 1200–1206. [CrossRef]
- Giaid, A., & Saleh, D. (1995). Reduced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the lungs of patients with pulmonary hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 333(4), 214–221. [CrossRef]
- Nagendran, J., Archer, S. L., Soliman, D., Gurtu, V., Moudgil, R., Haromy, A., St Aubin, C., Webster, L., Rebeyka, I. M., Ross, D. B., Light, P. E., Dyck, J. R., & Michelakis, E. D. (2007). Phosphodiesterase type 5 is highly expressed in the hypertrophied human right ventricle, and acute inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 5 improves contractility. Circulation, 116(3), 238–248. [CrossRef]
- Wharton, J., Strange, J. W., Møller, G. M., Growcott, E. J., Ren, X., Franklyn, A. P., Phillips, S. C., & Wilkins, M. R. (2005). Antiproliferative effects of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition in human pulmonary artery cells. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 172(1), 105–113. [CrossRef]
- Galiè, N., Ghofrani, H. A., Torbicki, A., Barst, R. J., Rubin, L. J., Badesch, D., Fleming, T., Parpia, T., Burgess, G., Branzi, A., Grimminger, F., Kurzyna, M., Simonneau, G., & Sildenafil Use in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (SUPER) Study Group (2005). Sildenafil citrate therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 353(20), 2148–2157. [CrossRef]
- Galiè, N., Brundage, B. H., Ghofrani, H. A., Oudiz, R. J., Simonneau, G., Safdar, Z., Shapiro, S., White, R. J., Chan, M., Beardsworth, A., Frumkin, L., Barst, R. J., & Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Response to Tadalafil (PHIRST) Study Group (2009). Tadalafil therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation, 119(22), 2894–2903. [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, H. A., D'Armini, A. M., Grimminger, F., Hoeper, M. M., Jansa, P., Kim, N. H., Mayer, E., Simonneau, G., Wilkins, M. R., Fritsch, A., Neuser, D., Weimann, G., Wang, C., & CHEST-1 Study Group (2013). Riociguat for the treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 369(4), 319–329. [CrossRef]
- Tuder, R. M., Cool, C. D., Geraci, M. W., Wang, J., Abman, S. H., Wright, L., Badesch, D., & Voelkel, N. F. (1999). Prostacyclin synthase expression is decreased in lungs from patients with severe pulmonary hypertension. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 159(6), 1925–1932. [CrossRef]
- Barst, R. J., Rubin, L. J., Long, W. A., McGoon, M. D., Rich, S., Badesch, D. B., Groves, B. M., Tapson, V. F., Bourge, R. C., Brundage, B. H., Koerner, S. K., Langleben, D., Keller, C. A., Murali, S., Uretsky, B. F., Clayton, L. M., Jöbsis, M. M., Blackburn, S. D., Shortino, D., Crow, J. W., … Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group (1996). A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 334(5), 296–301. [CrossRef]
- Badesch, D. B., Tapson, V. F., McGoon, M. D., Brundage, B. H., Rubin, L. J., Wigley, F. M., Rich, S., Barst, R. J., Barrett, P. S., Kral, K. M., Jöbsis, M. M., Loyd, J. E., Murali, S., Frost, A., Girgis, R., Bourge, R. C., Ralph, D. D., Elliott, C. G., Hill, N. S., Langleben, D., … Medsger, T. A., Jr (2000). Continuous intravenous epoprostenol for pulmonary hypertension due to the scleroderma spectrum of disease. A randomized, controlled trial. Annals of internal medicine, 132(6), 425–434. [CrossRef]
- Tjen-A-Looi, S., Ekman, R., Lippton, H., Cary, J., & Keith, I. (1992). CGRP and somatostatin modulate chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. The American journal of physiology, 263(3 Pt 2), H681–H690. [CrossRef]
- Keith, I. M., & Ekman, R. (1992). Dynamic aspects of regulatory lung peptides in chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Experimental lung research, 18(2), 205–224. [CrossRef]
- Champion, H. C., Bivalacqua, T. J., Lambert, D. G., McNamara, D. B., & Kadowitz, P. J. (1999). The influence of candesartan and PD123319 on responses to angiotensin II in the hindquarters vascular bed of the rat. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN, 10 Suppl 11, S95–S97.
- Yan, X., Huang, J., Zeng, Y., Zhong, X., Fu, Y., Xiao, H., Wang, X., Lian, H., Luo, H., Li, D., & Guo, R. (2024). CGRP attenuates pulmonary vascular remodeling by inhibiting the cGAS-STING-NFκB pathway in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Biochemical pharmacology, 222, 116093. [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, J. T., Shimoda, L. A., Aaronson, P. I., & Ward, J. P. (2012). Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Physiological reviews, 92(1), 367–520. [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M., Lakshminrusimha, S., & Vento, M. (2022). Pulmonary hypertension and oxidative stress: Where is the link?. Seminars in fetal & neonatal medicine, 27(4), 101347. [CrossRef]
- Tjen-A-Looi, S.C., Fu, LW., Nguyen, A.T., Gong, Y., Malik, S. (2022). Autonomic Function and Electroacupuncture. In: Xia, Y. (eds) Advanced Acupuncture Research: From Bench to Bedside. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Tjen-A-Looi, S., Kraiczi, H., Ekman, R., & Keith, I. M. (1998). Sensory CGRP depletion by capsaicin exacerbates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Regulatory peptides, 74(1), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D. E., & Georgieff, M. K. (1989). Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells. Their secretory products and their potential roles in health and chronic lung disease in infancy. The American review of respiratory disease, 140(6), 1807–1812. [CrossRef]
- Heath, D., Yacoub, M., Gosney, J. R., Madden, B., Caslin, A. W., & Smith, P. (1990). Pulmonary endocrine cells in hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease. Histopathology, 16(1), 21–28. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X. W., Nurse, C. A., Wong, V., & Cutz, E. (2002). Hypoxia-induced secretion of serotonin from intact pulmonary neuroepithelial bodies in neonatal rabbit. The Journal of physiology, 539(Pt 2), 503–510. [CrossRef]
- Eddahibi, S., Raffestin, B., Hamon, M., & Adnot, S. (2002). Is the serotonin transporter involved in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension?. The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine, 139(4), 194–201. [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C. D., Hernandez-Diaz, S., Van Marter, L. J., Werler, M. M., Louik, C., Jones, K. L., & Mitchell, A. A. (2006). Selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors and risk of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. The New England journal of medicine, 354(6), 579–587. [CrossRef]
- McQuillan, L. P., Leung, G. K., Marsden, P. A., Kostyk, S. K., & Kourembanas, S. (1994). Hypoxia inhibits expression of eNOS via transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms. The American journal of physiology, 267(5 Pt 2), H1921–H1927. [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, L., Janaszak-Jasiecka, A., Siekierzycka, A., Bartoszewska, S., Woźniak, M., Lejnowski, D., Collawn, J. F., & Bartoszewski, R. (2016). Posttranscriptional and transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase during hypoxia: the role of microRNAs. Cellular & molecular biology letters, 21, 16. [CrossRef]
- Xu, W., Kaneko, F. T., Zheng, S., Comhair, S. A., Janocha, A. J., Goggans, T., Thunnissen, F. B., Farver, C., Hazen, S. L., Jennings, C., Dweik, R. A., Arroliga, A. C., & Erzurum, S. C. (2004). Increased arginase II and decreased NO synthesis in endothelial cells of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 18(14), 1746–1748. [CrossRef]
- Jaitovich, A., & Jourd'heuil, D. (2017). A Brief Overview of Nitric Oxide and Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling in Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, 967, 71–81. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Y., Zhao, Y. D., Mirza, M. K., Huang, J. H., Potula, H. H., Vogel, S. M., Brovkovych, V., Yuan, J. X., Wharton, J., & Malik, A. B. (2009). Persistent eNOS activation secondary to caveolin-1 deficiency induces pulmonary hypertension in mice and humans through PKG nitration. The Journal of clinical investigation, 119(7), 2009–2018. [CrossRef]
- Block, E. R., Herrera, H., & Couch, M. (1995). Hypoxia inhibits L-arginine uptake by pulmonary artery endothelial cells. The American journal of physiology, 269(5 Pt 1), L574–L580. [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K., Discher, D. J., Hu, J., Bishopric, N. H., & Webster, K. A. (2001). Molecular regulation of the endothelin-1 gene by hypoxia. Contributions of hypoxia-inducible factor-1, activator protein-1, GATA-2, AND p300/CBP. The Journal of biological chemistry, 276(16), 12645–12653. [CrossRef]
- Tuder, R. M., Chacon, M., Alger, L., Wang, J., Taraseviciene-Stewart, L., Kasahara, Y., Cool, C. D., Bishop, A. E., Geraci, M., Semenza, G. L., Yacoub, M., Polak, J. M., & Voelkel, N. F. (2001). Expression of angiogenesis-related molecules in plexiform lesions in severe pulmonary hypertension: evidence for a process of disordered angiogenesis. The Journal of pathology, 195(3), 367–374. [CrossRef]
- Alba, G. A., Samokhin, A. O., Wang, R. S., Zhang, Y. Y., Wertheim, B. M., Arons, E., Greenfield, E. A., Lundberg Slingsby, M. H., Ceglowski, J. R., Haley, K. J., Bowman, F. P., Yu, Y. R., Haney, J. C., Eng, G., Mitchell, R. N., Sheets, A., Vargas, S. O., Seo, S., Channick, R. N., Leary, P. J., … Maron, B. A. (2021). NEDD9 Is a Novel and Modifiable Mediator of Platelet-Endothelial Adhesion in the Pulmonary Circulation. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 203(12), 1533–1545. [CrossRef]
- Chai, X., Sun, D., Han, Q., Yi, L., Wu, Y., & Liu, X. (2018). Hypoxia induces pulmonary arterial fibroblast proliferation, migration, differentiation and vascular remodeling via the PI3K/Akt/p70S6K signaling pathway. International journal of molecular medicine, 41(5), 2461–2472. [CrossRef]
- Ryanto, G. R. T., Ikeda, K., Miyagawa, K., Tu, L., Guignabert, C., Humbert, M., Fujiyama, T., Yanagisawa, M., Hirata, K. I., & Emoto, N. (2021). An endothelial activin A-bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 link is overdriven in pulmonary hypertension. Nature communications, 12(1), 1720. [CrossRef]
- Merfeld-Clauss, S., Lu, H., Wu, X., March, K. L., & Traktuev, D. O. (2018). Hypoxia-induced activin A diminishes endothelial cell vasculogenic activity. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 22(1), 173–184. [CrossRef]
- Macias, D., Moore, S., Crosby, A., Southwood, M., Du, X., Tan, H., Xie, S., Vassallo, A., Wood, A. J. T., Wallace, E. M., & Cowburn, A. S. (2021). Targeting HIF2α-ARNT hetero-dimerisation as a novel therapeutic strategy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. The European respiratory journal, 57(3), 1902061. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z., Zhu, M. M., Peng, Y., Machireddy, N., Evans, C. E., Machado, R., Zhang, X., & Zhao, Y. Y. (2018). Therapeutic Targeting of Vascular Remodeling and Right Heart Failure in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension with a HIF-2α Inhibitor. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 198(11), 1423–1434. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T., Zhou, Q., Tang, H., Bozkanat, M., Yuan, J. X., Raj, J. U., & Zhou, G. (2016). miR-17/20 Controls Prolyl Hydroxylase 2 (PHD2)/Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 (HIF1) to Regulate Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation. Journal of the American Heart Association, 5(12), e004510. [CrossRef]
- Docherty, C. K., Nilsen, M., & MacLean, M. R. (2019). Influence of 2-Methoxyestradiol and Sex on Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1-α. Journal of the American Heart Association, 8(5), e011628. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y., Zhou, Y., Peng, G., Liu, N., Tian, H., Pan, D., Liu, L., Yang, X., Li, C., Li, W., Chen, L., Ran, P., & Dai, A. (2018). Topotecan prevents hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension and inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and TRPC channels. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 104, 161–170. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C. C., Chi, P. L., Shen, M. C., Shu, C. W., Wann, S. R., Liu, C. P., Tseng, C. J., & Huang, W. C. (2019). Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Rescues Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension through the Inhibition of AKT/ERK-Dependent PDGF/HIF-1α In Vitro and In Vivo. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(6), 1468. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y., Teng, X., Zhang, L., Chen, J., Liu, Z., Chen, X., Zhao, S., Yang, S., Feng, J., & Yan, X. (2019). CD146-HIF-1α hypoxic reprogramming drives vascular remodeling and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nature communications, 10(1), 3551. [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, J., Aguirre, J. S., Pulido, T., Martinez-Guerra, M. L., Santos, E., Alvarado, P., Rosas, M., & Bautista, E. (2001). Nocturnal oxygen therapy in patients with the Eisenmenger syndrome. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 164(9), 1682–1687. [CrossRef]
- Green, S., & Stuart, D. (2021). Oxygen and pulmonary arterial hypertension: effects, mechanisms, and therapeutic benefits. European journal of preventive cardiology, 28(1), 127–136. [CrossRef]
- Din, S., Sarathchandra, P., Yacoub, M. H., & Chester, A. H. (2009). Interaction between bone morphogenetic proteins and endothelin-1 in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle. Vascular pharmacology, 51(5-6), 344–349. [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H., Dewachter, C., Belhaj, A., Rondelet, B., Sakai, S., Remmelink, M., Vachiery, J. L., Naeije, R., & Dewachter, L. (2015). Endothelin-Bone morphogenetic protein type 2 receptor interaction induces pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell hyperplasia in pulmonary arterial hypertension. The Journal of heart and lung transplantation : the official publication of the International Society for Heart Transplantation, 34(3), 468–478. [CrossRef]
- Soon, E., Crosby, A., Southwood, M., Yang, P., Tajsic, T., Toshner, M., Appleby, S., Shanahan, C. M., Bloch, K. D., Pepke-Zaba, J., Upton, P., & Morrell, N. W. (2015). Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II deficiency and increased inflammatory cytokine production. A gateway to pulmonary arterial hypertension. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 192(7), 859–872. [CrossRef]
- Talati, M., West, J., Zaynagetdinov, R., Hong, C. C., Han, W., Blackwell, T., Robinson, L., Blackwell, T. S., & Lane, K. (2014). BMP pathway regulation of and by macrophages. PloS one, 9(4), e94119. [CrossRef]
- Kim, C. W., Song, H., Kumar, S., Nam, D., Kwon, H. S., Chang, K. H., Son, D. J., Kang, D. W., Brodie, S. A., Weiss, D., Vega, J. D., Alberts-Grill, N., Griendling, K., Taylor, W. R., & Jo, H. (2013). Anti-inflammatory and antiatherogenic role of BMP receptor II in endothelial cells. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 33(6), 1350–1359. [CrossRef]
- Diebold, I., Hennigs, J. K., Miyagawa, K., Li, C. G., Nickel, N. P., Kaschwich, M., Cao, A., Wang, L., Reddy, S., Chen, P. I., Nakahira, K., Alcazar, M. A., Hopper, R. K., Ji, L., Feldman, B. J., & Rabinovitch, M. (2015). BMPR2 preserves mitochondrial function and DNA during reoxygenation to promote endothelial cell survival and reverse pulmonary hypertension. Cell metabolism, 21(4), 596–608. [CrossRef]
- Sutendra, G., & Michelakis, E. D. (2014). The metabolic basis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Cell metabolism, 19(4), 558–573. [CrossRef]
- Palakeel, J. J., Ali, M., Chaduvula, P., Chhabra, S., Lamsal Lamichhane, S., Ramesh, V., Opara, C. O., Khan, F. Y., Kabiraj, G., Kauser, H., & Mostafa, J. A. (2022). An Outlook on the Etiopathogenesis of Pulmonary Hypertension in HIV. Cureus, 14(7), e27390. [CrossRef]
- Ryanto, G. R. T., Musthafa, A., Hara, T., & Emoto, N. (2023). Inactivating the Uninhibited: The Tale of Activins and Inhibins in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. International journal of molecular sciences, 24(4), 3332. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, O. E., Sankar, M., Elsaadi, S., Hella, H., Buene, G., Darvekar, S. R., Misund, K., Katagiri, T., Knaus, P., & Holien, T. (2018). BMPR2 inhibits activin and BMP signaling via wild-type ALK2. Journal of cell science, 131(11), jcs213512. [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M., McLaughlin, V., Gibbs, J. S. R., Gomberg-Maitland, M., Hoeper, M. M., Preston, I. R., Souza, R., Waxman, A., Escribano Subias, P., Feldman, J., Meyer, G., Montani, D., Olsson, K. M., Manimaran, S., Barnes, J., Linde, P. G., de Oliveira Pena, J., Badesch, D. B., & PULSAR Trial Investigators (2021). Sotatercept for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 384(13), 1204–1215. [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M. M., Badesch, D. B., Ghofrani, H. A., Gibbs, J. S. R., Gomberg-Maitland, M., McLaughlin, V. V., Preston, I. R., Souza, R., Waxman, A. B., Grünig, E., Kopeć, G., Meyer, G., Olsson, K. M., Rosenkranz, S., Xu, Y., Miller, B., Fowler, M., Butler, J., Koglin, J., de Oliveira Pena, J., … STELLAR Trial Investigators (2023). Phase 3 Trial of Sotatercept for Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. The New England journal of medicine, 388(16), 1478–1490. [CrossRef]
- Soon, E., Holmes, A. M., Treacy, C. M., Doughty, N. J., Southgate, L., Machado, R. D., Trembath, R. C., Jennings, S., Barker, L., Nicklin, P., Walker, C., Budd, D. C., Pepke-Zaba, J., & Morrell, N. W. (2010). Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines predict survival in idiopathic and familial pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation, 122(9), 920–927. [CrossRef]
- Hurst, L. A., Dunmore, B. J., Long, L., Crosby, A., Al-Lamki, R., Deighton, J., Southwood, M., Yang, X., Nikolic, M. Z., Herrera, B., Inman, G. J., Bradley, J. R., Rana, A. A., Upton, P. D., & Morrell, N. W. (2017). TNFα drives pulmonary arterial hypertension by suppressing the BMP type-II receptor and altering NOTCH signaling. Nature communications, 8, 14079. [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, J. M., Pereira, M., Wen, S., Dooner, M. S., Del Tatto, M., Papa, E., Goldberg, L. R., Baird, G. L., Ventetuolo, C. E., Quesenberry, P. J., & Klinger, J. R. (2016). Exosomes induce and reverse monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Cardiovascular research, 110(3), 319–330. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y., Goncharov, D. A., Pena, A., Baust, J., Chavez Barragan, A., Ray, A., Rode, A., Bachman, T. N., Chang, B., Jiang, L., Dieffenbach, P., Fredenburgh, L. E., Rojas, M., DeLisser, H., Mora, A. L., Kudryashova, T. V., & Goncharova, E. A. (2022). Cross-talk between TSC2 and the extracellular matrix controls pulmonary vascular proliferation and pulmonary hypertension. Science signaling, 15(763), eabn2743. [CrossRef]
- Tuder, R. M., Marecki, J. C., Richter, A., Fijalkowska, I., & Flores, S. (2007). Pathology of pulmonary hypertension. Clinics in chest medicine, 28(1), 23–vii. [CrossRef]
- Heath, D., & Yacoub, M. (1991). Lung mast cells in plexogenic pulmonary arteriopathy. Journal of clinical pathology, 44(12), 1003–1006. [CrossRef]
- Perros, F., Dorfmüller, P., Souza, R., Durand-Gasselin, I., Mussot, S., Mazmanian, M., Hervé, P., Emilie, D., Simonneau, G., & Humbert, M. (2007). Dendritic cell recruitment in lesions of human and experimental pulmonary hypertension. The European respiratory journal, 29(3), 462–468. [CrossRef]
- Tuder, R. M., Groves, B., Badesch, D. B., & Voelkel, N. F. (1994). Exuberant endothelial cell growth and elements of inflammation are present in plexiform lesions of pulmonary hypertension. The American journal of pathology, 144(2), 275–285.
- Humbert, M., Monti, G., Brenot, F., Sitbon, O., Portier, A., Grangeot-Keros, L., Duroux, P., Galanaud, P., Simonneau, G., & Emilie, D. (1995). Increased interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 serum concentrations in severe primary pulmonary hypertension. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 151(5), 1628–1631. [CrossRef]
- Smolders, V. F. E. D., Lodder, K., Rodríguez, C., Tura-Ceide, O., Barberà, J. A., Jukema, J. W., Quax, P. H. A., Goumans, M. J., & Kurakula, K. (2021). The Inflammatory Profile of CTEPH-Derived Endothelial Cells Is a Possible Driver of Disease Progression. Cells, 10(4), 737. [CrossRef]
- Parpaleix, A., Amsellem, V., Houssaini, A., Abid, S., Breau, M., Marcos, E., Sawaki, D., Delcroix, M., Quarck, R., Maillard, A., Couillin, I., Ryffel, B., & Adnot, S. (2016). Role of interleukin-1 receptor 1/MyD88 signalling in the development and progression of pulmonary hypertension. The European respiratory journal, 48(2), 470–483. [CrossRef]
- Brock, M., Trenkmann, M., Gay, R. E., Michel, B. A., Gay, S., Fischler, M., Ulrich, S., Speich, R., & Huber, L. C. (2009). Interleukin-6 modulates the expression of the bone morphogenic protein receptor type II through a novel STAT3-microRNA cluster 17/92 pathway. Circulation research, 104(10), 1184–1191. [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M. K., Syrkina, O. L., Kolliputi, N., Mark, E. J., Hales, C. A., & Waxman, A. B. (2009). Interleukin-6 overexpression induces pulmonary hypertension. Circulation research, 104(2), 236–244. [CrossRef]
- Coll-Bonfill, N., Musri, M. M., Ivo, V., Barberà, J. A., & Tura-Ceide, O. (2015). Transdifferentiation of endothelial cells to smooth muscle cells play an important role in vascular remodelling. American journal of stem cells, 4(1), 13–21.
- Selimovic, N., Bergh, C. H., Andersson, B., Sakiniene, E., Carlsten, H., & Rundqvist, B. (2009). Growth factors and interleukin-6 across the lung circulation in pulmonary hypertension. The European respiratory journal, 34(3), 662–668. [CrossRef]
- Li, A., Varney, M. L., Valasek, J., Godfrey, M., Dave, B. J., & Singh, R. K. (2005). Autocrine role of interleukin-8 in induction of endothelial cell proliferation, survival, migration and MMP-2 production and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis, 8(1), 63–71. [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, N., King, N. E., Laporte, J., Yang, M., Mishra, A., Pope, S. M., Muntel, E. E., Witte, D. P., Pegg, A. A., Foster, P. S., Hamid, Q., & Rothenberg, M. E. (2003). Dissection of experimental asthma with DNA microarray analysis identifies arginase in asthma pathogenesis. The Journal of clinical investigation, 111(12), 1863–1874. [CrossRef]
- Tamosiuniene, R., Tian, W., Dhillon, G., Wang, L., Sung, Y. K., Gera, L., Patterson, A. J., Agrawal, R., Rabinovitch, M., Ambler, K., Long, C. S., Voelkel, N. F., & Nicolls, M. R. (2011). Regulatory T cells limit vascular endothelial injury and prevent pulmonary hypertension. Circulation research, 109(8), 867–879. [CrossRef]
- Huertas, A., Tu, L., Gambaryan, N., Girerd, B., Perros, F., Montani, D., Fabre, D., Fadel, E., Eddahibi, S., Cohen-Kaminsky, S., Guignabert, C., & Humbert, M. (2012). Leptin and regulatory T-lymphocytes in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. The European respiratory journal, 40(4), 895–904. [CrossRef]
- Becker, M. O., Kill, A., Kutsche, M., Guenther, J., Rose, A., Tabeling, C., Witzenrath, M., Kühl, A. A., Heidecke, H., Ghofrani, H. A., Tiede, H., Schermuly, R. T., Nickel, N., Hoeper, M. M., Lukitsch, I., Gollasch, M., Kuebler, W. M., Bock, S., Burmester, G. R., Dragun, D., … Riemekasten, G. (2014). Vascular receptor autoantibodies in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with systemic sclerosis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 190(7), 808–817. [CrossRef]
- Isern, R. A., Yaneva, M., Weiner, E., Parke, A., Rothfield, N., Dantzker, D., Rich, S., & Arnett, F. C. (1992). Autoantibodies in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension: association with anti-Ku. The American journal of medicine, 93(3), 307–312. [CrossRef]
- Zaid, Y., Puhm, F., Allaeys, I., Naya, A., Oudghiri, M., Khalki, L., Limami, Y., Zaid, N., Sadki, K., Ben El Haj, R., Mahir, W., Belayachi, L., Belefquih, B., Benouda, A., Cheikh, A., Langlois, M. A., Cherrah, Y., Flamand, L., Guessous, F., & Boilard, E. (2020). Platelets Can Associate with SARS-Cov-2 RNA and Are Hyperactivated in COVID-19. Circulation research, 127(11), 1404–1418. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Connors, J. M., & Levy, J. H. (2020). COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation. Blood, 135(23), 2033–2040. [CrossRef]
- Voelkel, N. F., Tamosiuniene, R., & Nicolls, M. R. (2016). Challenges and opportunities in treating inflammation associated with pulmonary hypertension. Expert review of cardiovascular therapy, 14(8), 939–951. [CrossRef]
- Meloche, J., Renard, S., Provencher, S., & Bonnet, S. (2013). Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents in PAH. Handbook of experimental pharmacology, 218, 437–476. [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, R. T., Badesch, D., Chung, L., Domsic, R. T., Medsger, T., Pinckney, A., Keyes-Elstein, L., D'Aveta, C., Spychala, M., White, R. J., Hassoun, P. M., Torres, F., Sweatt, A. J., Molitor, J. A., Khanna, D., Maecker, H., Welch, B., Goldmuntz, E., & Nicolls, M. R. (2021). Safety and Efficacy of B-Cell Depletion with Rituximab for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis-associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 204(2), 209–221. [CrossRef]
- Trankle, C. R., Canada, J. M., Kadariya, D., Markley, R., De Chazal, H. M., Pinson, J., Fox, A., Van Tassell, B. W., Abbate, A., & Grinnan, D. (2019). IL-1 Blockade Reduces Inflammation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Right Ventricular Failure: A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase IB/II Pilot Study. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 199(3), 381–384. [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, H. A., Simonneau, G., D'Armini, A. M., Fedullo, P., Howard, L. S., Jaïs, X., Jenkins, D. P., Jing, Z. C., Madani, M. M., Martin, N., Mayer, E., Papadakis, K., Richard, D., Kim, N. H., & MERIT study investigators (2024). Macitentan for the treatment of inoperable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (MERIT-1): results from the multicentre, phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. The Lancet. Respiratory medicine, 12(4), e21–e30. [CrossRef]
- Ordi-Ros, J., Sáez-Comet, L., Pérez-Conesa, M., Vidal, X., Riera-Mestre, A., Castro-Salomó, A., Cuquet-Pedragosa, J., Ortiz-Santamaria, V., Mauri-Plana, M., Solé, C., & Cortés-Hernández, J. (2019). Rivaroxaban Versus Vitamin K Antagonist in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Randomized Noninferiority Trial. Annals of internal medicine, 171(10), 685–694. [CrossRef]
- Frank, H., Mlczoch, J., Huber, K., Schuster, E., Gurtner, H. P., & Kneussl, M. (1997). The effect of anticoagulant therapy in primary and anorectic drug-induced pulmonary hypertension. Chest, 112(3), 714–721. [CrossRef]
- Preston, I. R., Roberts, K. E., Miller, D. P., Sen, G. P., Selej, M., Benton, W. W., Hill, N. S., & Farber, H. W. (2015). Effect of Warfarin Treatment on Survival of Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) in the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-Term PAH Disease Management (REVEAL). Circulation, 132(25), 2403–2411. [CrossRef]
- Ehlken, N., Lichtblau, M., Klose, H., Weidenhammer, J., Fischer, C., Nechwatal, R., Uiker, S., Halank, M., Olsson, K., Seeger, W., Gall, H., Rosenkranz, S., Wilkens, H., Mertens, D., Seyfarth, H. J., Opitz, C., Ulrich, S., Egenlauf, B., & Grünig, E. (2016). Exercise training improves peak oxygen consumption and haemodynamics in patients with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension and inoperable chronic thrombo-embolic pulmonary hypertension: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. European heart journal, 37(1), 35–44. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A., Garg, S., Khunger, M., Garg, S., Kumbhani, D. J., Chin, K. M., & Berry, J. D. (2015). Efficacy and Safety of Exercise Training in Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circulation. Heart failure, 8(6), 1032–1043. [CrossRef]
- Velez-Roa, S., Ciarka, A., Najem, B., Vachiery, J. L., Naeije, R., & van de Borne, P. (2004). Increased sympathetic nerve activity in pulmonary artery hypertension. Circulation, 110(10), 1308–1312. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Gonçalves Bós, D., Van Der Bruggen, C. E. E., Kurakula, K., Sun, X. Q., Casali, K. R., Casali, A. G., Rol, N., Szulcek, R., Dos Remedios, C., Guignabert, C., Tu, L., Dorfmüller, P., Humbert, M., Wijnker, P. J. M., Kuster, D. W. D., van der Velden, J., Goumans, M. J., Bogaard, H. J., Vonk-Noordegraaf, A., de Man, F. S., … Handoko, M. L. (2018). Contribution of Impaired Parasympathetic Activity to Right Ventricular Dysfunction and Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circulation, 137(9), 910–924. [CrossRef]
- Bristow, M. R., Ginsburg, R., Umans, V., Fowler, M., Minobe, W., Rasmussen, R., Zera, P., Menlove, R., Shah, P., & Jamieson, S. (1986). Beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic-receptor subpopulations in nonfailing and failing human ventricular myocardium: coupling of both receptor subtypes to muscle contraction and selective beta 1-receptor down-regulation in heart failure. Circulation research, 59(3), 297–309. [CrossRef]
- Patel, M. K., Chan, P., Betteridge, L. J., Schachter, M., & Sever, P. S. (1995). Inhibition of human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by the novel multiple-action antihypertensive agent carvedilol. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology, 25(4), 652–657. [CrossRef]
- Farha, S., Saygin, D., Park, M. M., Cheong, H. I., Asosingh, K., Comhair, S. A., Stephens, O. R., Roach, E. C., Sharp, J., Highland, K. B., DiFilippo, F. P., Neumann, D. R., Tang, W. H. W., & Erzurum, S. C. (2017). Pulmonary arterial hypertension treatment with carvedilol for heart failure: a randomized controlled trial. JCI insight, 2(16), e95240. [CrossRef]
- Bogaard, H. J., Natarajan, R., Mizuno, S., Abbate, A., Chang, P. J., Chau, V. Q., Hoke, N. N., Kraskauskas, D., Kasper, M., Salloum, F. N., & Voelkel, N. F. (2010). Adrenergic receptor blockade reverses right heart remodeling and dysfunction in pulmonary hypertensive rats. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 182(5), 652–660. [CrossRef]
- Perros, F., Ranchoux, B., Izikki, M., Bentebbal, S., Happé, C., Antigny, F., Jourdon, P., Dorfmüller, P., Lecerf, F., Fadel, E., Simonneau, G., Humbert, M., Bogaard, H. J., & Eddahibi, S. (2015). Nebivolol for improving endothelial dysfunction, pulmonary vascular remodeling, and right heart function in pulmonary hypertension. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 65(7), 668–680. [CrossRef]
- Kamp, O., Metra, M., Bugatti, S., Bettari, L., Dei Cas, A., Petrini, N., & Dei Cas, L. (2010). Nebivolol: haemodynamic effects and clinical significance of combined beta-blockade and nitric oxide release. Drugs, 70(1), 41–56. [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M., Sato, N., Asai, K., Takano, T., & Mizuno, K. (2009). Effects of a pure alpha/beta-adrenergic receptor blocker on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension with right ventricular hypertrophy in rats. Circulation journal : official journal of the Japanese Circulation Society, 73(12), 2337–2341. [CrossRef]
- de Man, F. S., Handoko, M. L., van Ballegoij, J. J., Schalij, I., Bogaards, S. J., Postmus, P. E., van der Velden, J., Westerhof, N., Paulus, W. J., & Vonk-Noordegraaf, A. (2012). Bisoprolol delays progression towards right heart failure in experimental pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. Heart failure, 5(1), 97–105. [CrossRef]
- van Campen, J. S., de Boer, K., van de Veerdonk, M. C., van der Bruggen, C. E., Allaart, C. P., Raijmakers, P. G., Heymans, M. W., Marcus, J. T., Harms, H. J., Handoko, M. L., de Man, F. S., Vonk Noordegraaf, A., & Bogaard, H. J. (2016). Bisoprolol in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: an explorative study. The European respiratory journal, 48(3), 787–796. [CrossRef]
- Moretti, C., Grosso Marra, W., D'Ascenzo, F., Omedè, P., Cannillo, M., Libertucci, D., Fusaro, E., Meynet, I., Giordana, F., Salera, D., Annone, U., Chen, S. L., Marra, S., & Gaita, F. (2015). Beta blocker for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A single center experience. International journal of cardiology, 184, 528–532. [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S., Herve, P., Jais, X., Lebrec, D., Humbert, M., Simonneau, G., & Sitbon, O. (2006). Deleterious effects of beta-blockers on exercise capacity and hemodynamics in patients with portopulmonary hypertension. Gastroenterology, 130(1), 120–126. [CrossRef]
- So, P. P., Davies, R. A., Chandy, G., Stewart, D., Beanlands, R. S., Haddad, H., Pugliese, C., & Mielniczuk, L. M. (2012). Usefulness of beta-blocker therapy and outcomes in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. The American journal of cardiology, 109(10), 1504–1509. [CrossRef]
- Martyniuk, T. V., Konosova, I. D., & Chazova, I. E. (2012). Terapevticheskii arkhiv, 84(12), 49–53.
- Karpov, A. A., Vachrushev, N. S., Shilenko, L. A., Smirnov, S. S., Bunenkov, N. S., Butskih, M. G., Chervaev, A. A., Vaulina, D. D., Ivkin, D. Y., Moiseeva, O. M., & Galagudza, M. M. (2023). Sympathetic Denervation and Pharmacological Stimulation of Parasympathetic Nervous System Prevent Pulmonary Vascular Bed Remodeling in Rat Model of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of cardiovascular development and disease, 10(2), 40. [CrossRef]
- Xu, W., Wang, D. Y., Chen, Z. Y., Gao, Q., Zou, Y. L., Sun, D. H., Zhang, S., Zhao, X. B., Gong, Y. T., Zhang, Y., Zhang, D. X., & Li, Y. (2023). Noninvasive Stereotactic Radiotherapy for PADN in an Acute Canine Model of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. JACC. Basic to translational science, 9(2), 244–256. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. L., Zhang, F. F., Xu, J., Xie, D. J., Zhou, L., Nguyen, T., & Stone, G. W. (2013). Pulmonary artery denervation to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension: the single-center, prospective, first-in-man PADN-1 study (first-in-man pulmonary artery denervation for treatment of pulmonary artery hypertension). Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 62(12), 1092–1100. [CrossRef]
- Rothman, A. M. K., Vachiery, J. L., Howard, L. S., Mikhail, G. W., Lang, I. M., Jonas, M., Kiely, D. G., Shav, D., Shabtay, O., Avriel, A., Lewis, G. D., Rosenzweig, E. B., Kirtane, A. J., Kim, N. H., Mahmud, E., McLaughlain, V. V., Chetcuti, S., Leon, M. B., Ben-Yehuda, O., & Rubin, L. J. (2020). Intravascular Ultrasound Pulmonary Artery Denervation to Treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (TROPHY1): Multicenter, Early Feasibility Study. JACC. Cardiovascular interventions, 13(8), 989–999. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., Jiang, X. M., Zhang, J., Li, B., Li, J., Xie, D. J., & Hu, Z. Y. (2016). Pulmonary artery denervation improves pulmonary arterial hypertension induced right ventricular dysfunction by modulating the local renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. BMC cardiovascular disorders, 16(1), 192. [CrossRef]
- Na, S., Kim, O. S., Ryoo, S., Kweon, T. D., Choi, Y. S., Shim, H. S., & Oh, Y. J. (2014). Cervical ganglion block attenuates the progression of pulmonary hypertension via nitric oxide and arginase pathways. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex. : 1979), 63(2), 309–315. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L., Zhang, J., Jiang, X. M., Xie, D. J., Wang, J. S., Li, L., Li, B., Wang, Z. M., Rothman, A. M. K., Lawrie, A., & Chen, S. L. (2015). Pulmonary Artery Denervation Attenuates Pulmonary Arterial Remodeling in Dogs with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Induced by Dehydrogenized Monocrotaline. JACC. Cardiovascular interventions, 8(15), 2013–2023. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. L., Zhang, Y. J., Zhou, L., Xie, D. J., Zhang, F. F., Jia, H. B., Wong, S. S., & Kwan, T. W. (2013). Percutaneous pulmonary artery denervation completely abolishes experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension in vivo. EuroIntervention : journal of EuroPCR in collaboration with the Working Group on Interventional Cardiology of the European Society of Cardiology, 9(2), 269–276. [CrossRef]
- Rothman, A. M., Arnold, N. D., Chang, W., Watson, O., Swift, A. J., Condliffe, R., Elliot, C. A., Kiely, D. G., Suvarna, S. K., Gunn, J., & Lawrie, A. (2015). Pulmonary artery denervation reduces pulmonary artery pressure and induces histological changes in an acute porcine model of pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. Cardiovascular interventions, 8(11), e002569. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Gonçalves Bos, D., Happé, C., Schalij, I., Pijacka, W., Paton, J. F. R., Guignabert, C., Tu, L., Thuillet, R., Bogaard, H. J., van Rossum, A. C., Vonk-Noordegraaf, A., de Man, F. S., & Handoko, M. L. (2017). Renal Denervation Reduces Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling and Right Ventricular Diastolic Stiffness in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension. JACC. Basic to translational science, 2(1), 22–35. [CrossRef]
- Qingyan, Z., Xuejun, J., Yanhong, T., Zixuan, D., Xiaozhan, W., Xule, W., Zongwen, G., Wei, H., Shengbo, Y., & Congxin, H. (2015). Beneficial Effects of Renal Denervation on Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling in Experimental Pulmonary Artery Hypertension. Revista espanola de cardiologia (English ed.), 68(7), 562–570. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., Liu, Y. W., Pan, H. Z., Zhang, X. L., Li, J., Xiang, L., Meng, J., Wang, P. H., Yang, J., Jing, Z. C., & Zhang, H. (2019). Transthoracic Pulmonary Artery Denervation for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 39(4), 704–718. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. L., Zhang, H., Xie, D. J., Zhang, J., Zhou, L., Rothman, A. M., & Stone, G. W. (2015). Hemodynamic, functional, and clinical responses to pulmonary artery denervation in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension of different causes: phase II results from the Pulmonary Artery Denervation-1 study. Circulation. Cardiovascular interventions, 8(11), e002837. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., Wei, Y., Zhang, C., Yang, Z., Kan, J., Gu, H., Fan, F., Gu, H., Wang, Q., Xie, D., Zhang, G., Guo, X., Yin, Y., Jin, B., Zhou, H., Yang, Z., Wang, Z., Xin, Y., Zhang, C., Meng, L., … Chen, S. L. (2022). Pulmonary Artery Denervation for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Sham-Controlled Randomized PADN-CFDA Trial. JACC. Cardiovascular interventions, 15(23), 2412–2423. [CrossRef]
- Rothman, A. M. K., Vachiery, J. L., Howard, L. S., Mikhail, G. W., Lang, I. M., Jonas, M., Kiely, D. G., Shav, D., Shabtay, O., Avriel, A., Lewis, G. D., Rosenzweig, E. B., Kirtane, A. J., Kim, N. H., Mahmud, E., McLaughlain, V. V., Chetcuti, S., Leon, M. B., Ben-Yehuda, O., & Rubin, L. J. (2020). Intravascular Ultrasound Pulmonary Artery Denervation to Treat Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (TROPHY1): Multicenter, Early Feasibility Study. JACC. Cardiovascular interventions, 13(8), 989–999. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., Zhang, J., Chen, M., Xie, D. J., Kan, J., Yu, W., Li, X. B., Xu, T., Gu, Y., Dong, J., Gu, H., Han, Y., & Chen, S. L. (2019). Pulmonary Artery Denervation Significantly Increases 6-Min Walk Distance for Patients With Combined Pre- and Post-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Left Heart Failure: The PADN-5 Study. JACC. Cardiovascular interventions, 12(3), 274–284. [CrossRef]
- Romanov, A., Cherniavskiy, A., Novikova, N., Edemskiy, A., Ponomarev, D., Shabanov, V., Losik, D., Elesin, D., Stenin, I., Mikheenko, I., Zhizhov, R., Kretov, E., Pokushalov, E., Po, S. S., Martynyuk, T. V., & Steinberg, J. S. (2020). Pulmonary Artery Denervation for Patients With Residual Pulmonary Hypertension After Pulmonary Endarterectomy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 76(8), 916–926. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K., Saku, K., Kamada, K., Abe, K., Tanaka-Ishikawa, M., Tohyama, T., Nishikawa, T., Kishi, T., Sunagawa, K., & Tsutsui, H. (2018). Electrical Vagal Nerve Stimulation Ameliorates Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling and Improves Survival in Rats With Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. JACC. Basic to translational science, 3(5), 657–671. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K., Saku, K., Jan Bogaard, H., Abe, K., Sunagawa, K., & Tsutsui, H. (2022). Vagal nerve stimulation preserves right ventricular function in a rat model of right ventricular pressure overload. Pulmonary circulation, 12(4), e12154. [CrossRef]
- Pan, P., Zhang, X., Qian, H., Shi, W., Wang, J., Bo, Y., & Li, W. (2010). Effects of electro-acupuncture on endothelium-derived endothelin-1 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase of rats with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.), 235(5), 642–648. [CrossRef]
- Xin, J. J., Gao, J. H., Liu, Q., Zhao, Y. X., Zhou, C., & Yu, X. C. (2022). Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 42(6), 647–653. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. R., Yi, W., Qiao, Y., Zhuo, S. Y., Zhang, Q., Yang, X. J., Liang, T., & Ling, X. (2023). Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 43(8), 937–943. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y., Liang, Y., Zhuo, S., Yang, X., Liang, T., Ling, X., Zhang, Q., Shi, Y., & Yi, W. (2024). Effect and mechanism of acupuncture on airway smooth muscle relaxation during acute asthma attack in rats. 针刺松弛哮喘急性发作大鼠气道平滑肌的作用机制. Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 44(3), 295–302. [CrossRef]
- Lin, M., Wang, X., Ye, B., Zhang, J., Lin, S., Xu, Y., Zhou, J., Liu, S., Zhou, S., Guan, X., Jin, Y., & Wang, L. (2023). External counterpulsation stimulation combined with acupuncture for vascular endothelial function in patients with hypertension: A randomized pilot trial. Clinical and experimental hypertension (New York, N.Y. : 1993), 45(1), 2181355. [CrossRef]
- Jiang X. (2003). Effects of magnetic needle acupuncture on blood pressure and plasma ET-1 level in the patient of hypertension. Journal of traditional Chinese medicine = Chung i tsa chih ying wen pan, 23(4), 290–291.
- Maekura, T., Miki, K., Miki, M., Kitada, S., & Maekura, R. (2019). Clinical Effects Of Acupuncture On The Pathophysiological Mechanism Of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease During Exercise. International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, 14, 2787–2798. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.i, Ouyang, B. S., Sun, G., Fan, C., Wu, Y. J., & Ji, L. L. (2011). Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 31(10), 893–897.
- Ge, Y., Yao, H., Tong, J., He, Y., Li, G., & Kong, X. (2017). Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 37(4), 366–371. [CrossRef]
- Feng, J., Wang, X., Li, X., Zhao, D., & Xu, J. (2016). Acupuncture for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A multicenter, randomized, sham-controlled trial. Medicine, 95(40), e4879. [CrossRef]
- Tong, J., Guo, Y. M., He, Y., Li, G. Y., Chen, F., & Yao, H. (2014). Zhongguo zhen jiu = Chinese acupuncture & moxibustion, 34(9), 846–850.
- Suzuki, M., Muro, S., Ando, Y., Omori, T., Shiota, T., Endo, K., Sato, S., Aihara, K., Matsumoto, M., Suzuki, S., Itotani, R., Ishitoko, M., Hara, Y., Takemura, M., Ueda, T., Kagioka, H., Hirabayashi, M., Fukui, M., & Mishima, M. (2012). A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of acupuncture in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): the COPD-acupuncture trial (CAT). Archives of internal medicine, 172(11), 878–886. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M., Namura, K., Ohno, Y., Tanaka, H., Egawa, M., Yokoyama, Y., Akao, S., Fujiwara, H., & Yano, T. (2008). The effect of acupuncture in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of alternative and complementary medicine (New York, N.Y.), 14(9), 1097–1105. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C., Wu, M. Z., Liu, Q., Xin, J. J., Wu, S., Zhao, Y. X., Zhang, W. X., Yu, X. C., & Gao, J. H. (2022). Synergistic and Attenuating Effect of Electroacupuncture on Aconitine in Improving Heart Failure and Its Calcium Regulation Mechanism. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2022, 4940745. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z., Xia, Y., Wang, C., Lu, W., Zuo, H., Wu, D., Li, Y., Guo, R., Lu, J., & Zhang, L. (2023). Electroacupuncture at Neiguan (PC6) attenuates cardiac dysfunction caused by cecal ligation and puncture via the vagus nerve. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 162, 114600. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L., Cui, B., Shao, Y., Ni, B., Zhang, W., Luo, Y., & Zhang, S. (2014). Electroacupuncture improves cardiac function and remodeling by inhibition of sympathoexcitation in chronic heart failure rats. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 306(10), H1464–H1471. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H., Kim, T. H., & Leem, J. (2016). Acupuncture for heart failure: A systematic review of clinical studies. International journal of cardiology, 222, 321–331. [CrossRef]
- Pullamsetti, S. S., Mamazhakypov, A., Weissmann, N., Seeger, W., & Savai, R. (2020). Hypoxia-inducible factor signaling in pulmonary hypertension. The Journal of clinical investigation, 130(11), 5638–5651. [CrossRef]
- Hewes J.L., Lee J.Y., Fagan K.A., Bauer N.N. (2020). The changing face of pulmonary hypertension diagnosis: a historical perspective on the influence of diagnostics and biomarkers. Pulmonary Circulation 10:2045894019892801.
- Szidon, J. P., & Flint, J. F. (1977). Significance of sympathetic innervation of pulmonary vessels in response to acute hypoxia. Journal of applied physiology: respiratory, environmental and exercise physiology, 43(1), 65–71. [CrossRef]
- Kummer W. (2011). Pulmonary vascular innervation and its role in responses to hypoxia: size matters!. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society, 8(6), 471–476. [CrossRef]
- Iturriaga, R., & Castillo-Galán, S. (2019). Potential Contribution of Carotid Body-Induced Sympathetic and Renin-Angiotensin System Overflow to Pulmonary Hypertension in Intermittent Hypoxia. Current hypertension reports, 21(11), 89. [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, R., Andrade, D. C., Lucero, C., Arias, P., & Iturriaga, R. (2016). Carotid Body Ablation Abrogates Hypertension and Autonomic Alterations Induced by Intermittent Hypoxia in Rats. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex. : 1979), 68(2), 436–445. [CrossRef]
- Iturriaga R. (2018). Carotid Body Ablation: a New Target to Address Central Autonomic Dysfunction. Current hypertension reports, 20(6), 53. [CrossRef]
- Marina, N., Tang, F., Figueiredo, M., Mastitskaya, S., Kasimov, V., Mohamed-Ali, V., Roloff, E., Teschemacher, A. G., Gourine, A. V., & Kasparov, S. (2013). Purinergic signalling in the rostral ventro-lateral medulla controls sympathetic drive and contributes to the progression of heart failure following myocardial infarction in rats. Basic research in cardiology, 108(1), 317. [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, J. H., Zoccal, D. B., & Machado, B. H. (2012). Chronic intermittent hypoxia alters glutamatergic control of sympathetic and respiratory activities in the commissural NTS of rats. American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology, 302(6), R785–R793. [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, A. L., Calderon, A. S., Andrade, M. A., Cunningham, J. T., Mifflin, S. W., & Toney, G. M. (2013). Chronic intermittent hypoxia increases sympathetic control of blood pressure: role of neuronal activity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 305(12), H1772–H1780. [CrossRef]
- Chao, D. M., Shen, L. L., Tjen-A-Looi, S., Pitsillides, K. F., Li, P., & Longhurst, J. C. (1999). Naloxone reverses inhibitory effect of electroacupuncture on sympathetic cardiovascular reflex responses. The American journal of physiology, 276(6), H2127–H2134. [CrossRef]
- Li, P., Pitsillides, K. F., Rendig, S. V., Pan, H. L., & Longhurst, J. C. (1998). Reversal of reflex-induced myocardial ischemia by median nerve stimulation: a feline model of electroacupuncture. Circulation, 97(12), 1186–1194. [CrossRef]
- Li, P., Tjen-A-Looi, S. C., & Longhurst, J. C. (2006). Excitatory projections from arcuate nucleus to ventrolateral periaqueductal gray in electroacupuncture inhibition of cardiovascular reflexes. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 290(6), H2535–H2542. [CrossRef]
- Li, P., Tjen-A-Looi, S., & Longhurst, J. C. (2001). Rostral ventrolateral medullary opioid receptor subtypes in the inhibitory effect of electroacupuncture on reflex autonomic response in cats. Autonomic neuroscience : basic & clinical, 89(1-2), 38–47. [CrossRef]
- Tjen-A-Looi, S. C., Fu, L. W., Zhou, W., Syuu, Z., & Longhurst, J. C. (2005). Role of unmyelinated fibers in electroacupuncture cardiovascular responses. Autonomic neuroscience : basic & clinical, 118(1-2), 43–50. [CrossRef]
- Tjen-A-Looi, S. C., Li, P., & Longhurst, J. C. (2003). Prolonged inhibition of rostral ventral lateral medullary premotor sympathetic neurons by electroacupuncture in cats. Autonomic neuroscience : basic & clinical, 106(2), 119–131. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z. L., & Longhurst, J. C. (2010). Activation of reciprocal pathways between arcuate nucleus and ventrolateral periaqueductal gray during electroacupuncture: involvement of VGLUT3. Brain research, 1360, 77–88. [CrossRef]
- Kakall, Z. M., Pilowsky, P. M., & Farnham, M. M. J. (2018). PACAP-(6-38) or kynurenate microinjections in the RVLM prevent the development of sympathetic long-term facilitation after acute intermittent hypoxia. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 314(3), H563–H572. [CrossRef]
- Farnham, M. M. J., Tallapragada, V. J., O'Connor, E. T., Nedoboy, P. E., Dempsey, B., Mohammed, S., Fong, A. Y., Lung, M. S. Y., Derakhshan, F., Wilson, R. J. A., & Pilowsky, P. M. (2019). PACAP-PAC1 Receptor Activation Is Necessary for the Sympathetic Response to Acute Intermittent Hypoxia. Frontiers in neuroscience, 13, 881. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W., Fu, L. W., Tjen-A-Looi, S. C., Guo, Z. L., & Longhurst, J. C. (2006). Role of glutamate in a visceral sympathoexcitatory reflex in rostral ventrolateral medulla of cats. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 291(3), H1309–H1318. [CrossRef]
- Silva, A. Q., & Schreihofer, A. M. (2011). Altered sympathetic reflexes and vascular reactivity in rats after exposure to chronic intermittent hypoxia. The Journal of physiology, 589(Pt 6), 1463–1476. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W., Fu, L. W., Guo, Z. L., & Longhurst, J. C. (2007). Role of glutamate in the rostral ventrolateral medulla in acupuncture-related modulation of visceral reflex sympathoexcitation. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 292(4), H1868–H1875. [CrossRef]
- Tjen-A-Looi, S. C., Li, P., & Longhurst, J. C. (2009). Processing cardiovascular information in the vlPAG during electroacupuncture in rats: roles of endocannabinoids and GABA. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 106(6), 1793–1799. [CrossRef]
- Fu, L. W., & Longhurst, J. C. (2009). Electroacupuncture modulates vlPAG release of GABA through presynaptic cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 106(6), 1800–1809. [CrossRef]
- Li, P., Tjen-A-Looi, S. C., Guo, Z. L., Fu, L. W., & Longhurst, J. C. (2009). Long-loop pathways in cardiovascular electroacupuncture responses. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 106(2), 620–630. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A. C., Karas, M. M., Alves, M., He, J., de Kloet, A. D., Krause, E. G., Richards, E. M., Bryant, A. J., & Raizada, M. K. (2023). ACE2 overexpression in corticotropin-releasing-hormone cells offers protection against pulmonary hypertension. Frontiers in neuroscience, 17, 1223733. [CrossRef]
- Goncharuk, V. D., Van Heerikhuize, J., Swaab, D. F., & Buijs, R. M. (2002). Paraventricular nucleus of the human hypothalamus in primary hypertension: activation of corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons. The Journal of comparative neurology, 443(4), 321–331. [CrossRef]
- Dampney, R. A., Michelini, L. C., Li, D. P., & Pan, H. L. (2018). Regulation of sympathetic vasomotor activity by the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in normotensive and hypertensive states. American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology, 315(5), H1200–H1214. [CrossRef]
- Li, D. P., Zhou, J. J., Zhang, J., & Pan, H. L. (2017). CaMKII Regulates Synaptic NMDA Receptor Activity of Hypothalamic Presympathetic Neurons and Sympathetic Outflow in Hypertension. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 37(44), 10690–10699. [CrossRef]
- Ruyle, B. C., Martinez, D., Heesch, C. M., Kline, D. D., & Hasser, E. M. (2019). The PVN enhances cardiorespiratory responses to acute hypoxia via input to the nTS. American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology, 317(6), R818–R833. [CrossRef]
- King, T. L., Heesch, C. M., Clark, C. G., Kline, D. D., & Hasser, E. M. (2012). Hypoxia activates nucleus tractus solitarii neurons projecting to the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology, 302(10), R1219–R1232. [CrossRef]
- Silva, T. M., Takakura, A. C., & Moreira, T. S. (2016). Acute hypoxia activates hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus-projecting catecholaminergic neurons in the C1 region. Experimental neurology, 285(Pt A), 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. A., Nguyen, D. H., & Mifflin, S. W. (2019). Corticotropin-releasing hormone projections from the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus to the nucleus of the solitary tract increase blood pressure. Journal of neurophysiology, 121(2), 602–608. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. A., Nguyen, D. H., & Mifflin, S. W. (2018). CRHR2 (Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor 2) in the Nucleus of the Solitary Tract Contributes to Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Hypertension. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex. : 1979), 72(4), 994–1001. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L., Ye, Z., Zhang, M., Xu, W., Wang, R., Wu, S., & Gao, H. (2023). Electroacupuncture intervention on stress-induced cardiac autonomic imbalance in rats involves corticotropin-releasing hormone system activity. Neuroreport, 34(7), 401–410. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z., Zhu, L., Li, X. J., Gao, H. Y., Wang, J., Wu, S. B., Wu, Z. J., & Gao, H. R. (2023). PC6 electroacupuncture reduces stress-induced autonomic and neuroendocrine responses in rats. Heliyon, 9(4), e15291. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., Sun, J., Wang, Y., & Tian, Z. (2021). Secretagogin Mediates the Regulatory Effect of Electroacupuncture on Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Dysfunction in Surgical Trauma. Neural plasticity, 2021, 8881136. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q. Z., Peng, X. H., Wu, Q. F., Yu, S. G., Wei, J. L., Xu, H. Y., Wang, W., & Yin, H. Y. (2008). Zhen ci yan jiu = Acupuncture research, 33(6), 372–376.
- Huang, J., Tamisier, R., Ji, E., Tong, J., & Weiss, W. J. (2007). Chronic intermittent hypoxia modulates nNOS mRNA and protein expression in the rat hypothalamus. Respiratory physiology & neurobiology, 158(1), 30–38. [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, T., Tsutsui, M., Kido, T., Sakanashi, M., Naito, K., Oda, K., Ishimoto, H., Yamada, S., Wang, K. Y., Toyohira, Y., Izumi, H., Masuzaki, H., Shimokawa, H., Yanagihara, N., Yatera, K., & Mukae, H. (2018). Protective Role of Myelocytic Nitric Oxide Synthases against Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension in Mice. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 198(2), 232–244. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. I., Kim, Y. S., Kang, S. K., Kim, C., Park, C., Lee, M. S., & Huh, Y. (2008). Electroacupuncture decreases nitric oxide synthesis in the hypothalamus of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuroscience letters, 446(2-3), 78–82. [CrossRef]
- Maeda, M., Kachi, H., Ichihashi, N., Oyama, Z., & Kitajima, Y. (1998). The effect of electrical acupuncture-stimulation therapy using thermography and plasma endothelin (ET-1) levels in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis (PSS). Journal of dermatological science, 17(2), 151–155. [CrossRef]
- Lim, H. D., Kim, M. H., Lee, C. Y., & Namgung, U. (2016). Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Acupuncture Stimulation via the Vagus Nerve. PloS one, 11(3), e0151882. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., Wang, Z., Su, Y., Qi, L., Yang, W., Fu, M., Jing, X., Wang, Y., & Ma, Q. (2021). A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal-adrenal axis. Nature, 598(7882), 641–645. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., Wang, Z. F., Su, Y. S., Ray, R. S., Jing, X. H., Wang, Y. Q., & Ma, Q. (2020). Somatotopic Organization and Intensity Dependence in Driving Distinct NPY-Expressing Sympathetic Pathways by Electroacupuncture. Neuron, 108(3), 436–450.e7. [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rosas, R., Yehia, G., Peña, G., Mishra, P., del Rocio Thompson-Bonilla, M., Moreno-Eutimio, M. A., Arriaga-Pizano, L. A., Isibasi, A., & Ulloa, L. (2014). Dopamine mediates vagal modulation of the immune system by electroacupuncture. Nature medicine, 20(3), 291–295. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. X., He, W., Jing, X. H., Liu, J. L., Rong, P. J., Ben, H., Liu, K., & Zhu, B. (2012). Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation protects endotoxemic rat from lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2012, 627023. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Wu, Z., Zhou, J., Lu, S., Wang, C., Xia, Y., Ren, H., Tong, Z., Ke, L., & Li, W. (2021). Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Acute Pancreatitis: A Role for the Vagus Nerve-Mediated Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway. Frontiers in molecular biosciences, 8, 647647. [CrossRef]
- Abe, C., Inoue, T., Inglis, M. A., Viar, K. E., Huang, L., Ye, H., Rosin, D. L., Stornetta, R. L., Okusa, M. D., & Guyenet, P. G. (2017). C1 neurons mediate a stress-induced anti-inflammatory reflex in mice. Nature neuroscience, 20(5), 700–707. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. K., Kim, J., Woo, H. S., Jeong, H., Lee, H., Min, B. I., Nam, S., & Bae, H. (2010). Electroacupuncture induces Fos expression in the nucleus tractus solitarius via cholecystokinin A receptor signaling in rats. Neurological research, 32 Suppl 1, 116–119. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M. H., Park, Y. C., & Namgung, U. (2012). Acupuncture-stimulated activation of sensory neurons. Journal of acupuncture and meridian studies, 5(4), 148–155. [CrossRef]
- Ju, S., Liu, M., Wang, B., Yu, D., Zhang, H., Zhang, M., & Li, J. (2023). Transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation improves pulmonary function by regulating oxidative stress during one-lung ventilation in patients with lung cancer undergoing thoracoscopic surgery: a randomized controlled trial. BMC complementary medicine and therapies, 23(1), 463. [CrossRef]
- Ma, W., Li, Z., Lu, Z., Tan, W., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Yang, Z., Zhou, J., Tang, H., & Cui, H. (2017). Protective Effects of Acupuncture in Cardiopulmonary Bypass-Induced Lung Injury in Rats. Inflammation, 40(4), 1275–1284. [CrossRef]
- Tang, W., Dong, M., Teng, F., Cui, J., Zhu, X., Wang, W., Wuniqiemu, T., Qin, J., Yi, L., Wang, S., Dong, J., & Wei, Y. (2021). TMT-based quantitative proteomics reveals suppression of SLC3A2 and ATP1A3 expression contributes to the inhibitory role of acupuncture on airway inflammation in an OVA-induced mouse asthma model. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie, 134, 111001. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Tian, Y., Zhao, P., Jin, F., Miao, Y., Liu, Y., & Li, J. (2022). Electroacupuncture attenuates pulmonary vascular remodeling in a rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via the VEGF/PI3K/Akt pathway. Acupuncture in medicine : journal of the British Medical Acupuncture Society, 40(4), 389–400. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., Wang, L., Ying, X., Zheng, Y., Tan, Q., Yu, X., Gong, J., Li, M., Deng, X., Yang, G., Li, S., & Jiang, S. (2022). Electroacupuncture pre-treatment alleviates sepsis-induced cardiac inflammation and dysfunction by inhibiting the calpain-2/STAT3 pathway. Frontiers in physiology, 13, 961909. [CrossRef]
- Gong, L. R., Kan, Y. X., Lian, Y., Dong, S. A., Zhao, D. H., Shi, J., & Yu, J. B. (2020). Electroacupuncture Attenuates Limb Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Lung Injury Via p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Nuclear Factor Erythroid-2-Related Factor-2/Heme Oxygenase Pathway. The Journal of surgical research, 246, 170–181. [CrossRef]
- Luo, J., Yan, R., Ding, L., Ning, J., Chen, M., Guo, Y., Liu, J., Chen, Z., & Zhou, R. (2024). Electroacupuncture Attenuates Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury by Modulating the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. The Journal of surgical research, 295, 811–819. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T., Xiong, Y., Long, M., Zheng, D., Ke, H., Xie, J., Yin, N., & Chen, Z. (2019). Electro-acupuncture Pretreatment at Zusanli (ST36) Acupoint Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Rats by Inhibiting Ca2+ Influx Associated with Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors. Inflammation, 42(1), 211–220. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Zhang, H., Yang, J., Zhan, M., Hu, X., Liu, Y., Yu, L., Yan, X., Liang, S., Zhang, R., Lu, Y., Li, B., Liu, C., & Li, M. (2021). P2Y12 receptor as a new target for electroacupuncture relieving comorbidity of visceral pain and depression of inflammatory bowel disease. Chinese medicine, 16(1), 139. [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y. S., Lee, S. W., Park, J. H., Seo, H. B., Choi, B. T., & Shin, H. K. (2016). Electroacupuncture preconditioning reduces ROS generation with NOX4 down-regulation and ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke. Journal of biomedical science, 23, 32. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J., Xie, J. J., Xiang, S. Y., Li, Y., Cong, W. J., Lin, X. G., & Liu, Z. B. (2018). Zhen ci yan jiu = Acupuncture research, 43(12), 759–766. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. F., Zhu, J., Geng, W. Y., Zhao, S. J., Jiang, C. W., Cai, S. R., Cheng, M., Zhou, C. Y., & Liu, Z. B. (2014). Electroacupuncture at Feishu (BL13) and Zusanli (ST36) down-regulates the expression of orexins and their receptors in rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of integrative medicine, 12(5), 417–424. [CrossRef]
- Tjen-A-Looi, S., Ekman, R., Lippton, H., Cary, J., & Keith, I. (1992). CGRP and somatostatin modulate chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. The American journal of physiology, 263(3 Pt 2), H681–H690. [CrossRef]
- Tjen-A-Looi, S., Kraiczi, H., Ekman, R., & Keith, I. M. (1998). Sensory CGRP depletion by capsaicin exacerbates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Regulatory peptides, 74(1), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Champion, H. C., Bivalacqua, T. J., Toyoda, K., Heistad, D. D., Hyman, A. L., & Kadowitz, P. J. (2000). In vivo gene transfer of prepro-calcitonin gene-related peptide to the lung attenuates chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in the mouse. Circulation, 101(8), 923–930. [CrossRef]
- Li, W. J., Li, S. M., Ding, Y., He, B., Keegan, J., Dong, H., Ruan, J. W., & Zeng, Y. S. (2012). Electro-acupuncture upregulates CGRP expression after rat spinal cord transection. Neurochemistry international, 61(8), 1397–1403. [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, K., Itoh, K., & Okada, K. (2008). Experimental model of trigger points using eccentric exercise. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain, 16(1-2), 29-35.
- Vickers, A. J., Vertosick, E. A., Lewith, G., MacPherson, H., Foster, N. E., Sherman, K. J., Irnich, D., Witt, C. M., Linde, K., & Acupuncture Trialists' Collaboration (2018). Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Update of an Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. The journal of pain, 19(5), 455–474. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C. X., Wang, X., Yu, Z., Lian, X. Y., & Xu, B. (2024). Electroacupuncture improves peripheral neuropathy by up-regulating Sirt1/PGC-1α/TFAM pathway in type 2 diabetes rats with peripheral neuropathy. 基于Sirt1/PGC-1α/TFAM通路探讨电针治疗2型糖尿病周围神经病变的机制. Zhen ci yan jiu = Acupuncture research, 49(4), 349–357. [CrossRef]
- Hoerder, S., Habermann, I. V., Hahn, K., Meyer-Hamme, G., Ortiz, M., Grabowska, W., Roll, S., Willich, S. N., Schroeder, S., Brinkhaus, B., & Dietzel, J. (2023). Acupuncture in diabetic peripheral neuropathy-neurological outcomes of the randomized acupuncture in diabetic peripheral neuropathy trial. World journal of diabetes, 14(12), 1813–1823. [CrossRef]
- Yang, N. N., Lin, L. L., Li, Y. J., Li, H. P., Cao, Y., Tan, C. X., Hao, X. W., Ma, S. M., Wang, L., & Liu, C. Z. (2022). Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Effectiveness of Acupuncture in Depression. Current neuropharmacology, 20(4), 738–750. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S., Li, J., Yan, L., Zhang, X., Huang, J., & Zhou, P. (2024). Electroacupuncture alleviates the symptom of depression in mice by regulating the cGAS-STING-NLRP3 signaling. Aging, 16(8), 6731–6744. [CrossRef]
Group 1: Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
|
| HIV = human immunodeficiency virus; PCH = pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis; PVOD = pulmonary veno-occlusive disease |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





