Submitted:
16 May 2024
Posted:
16 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- A novel model has been proposed for the summarization of scientific articles consisting of SciBERT trained on a large corpus of scientific text and a graph trans former that benefits from the relational structures of the knowledge graph without linearization or hierarchical constraints.
2. Related Work
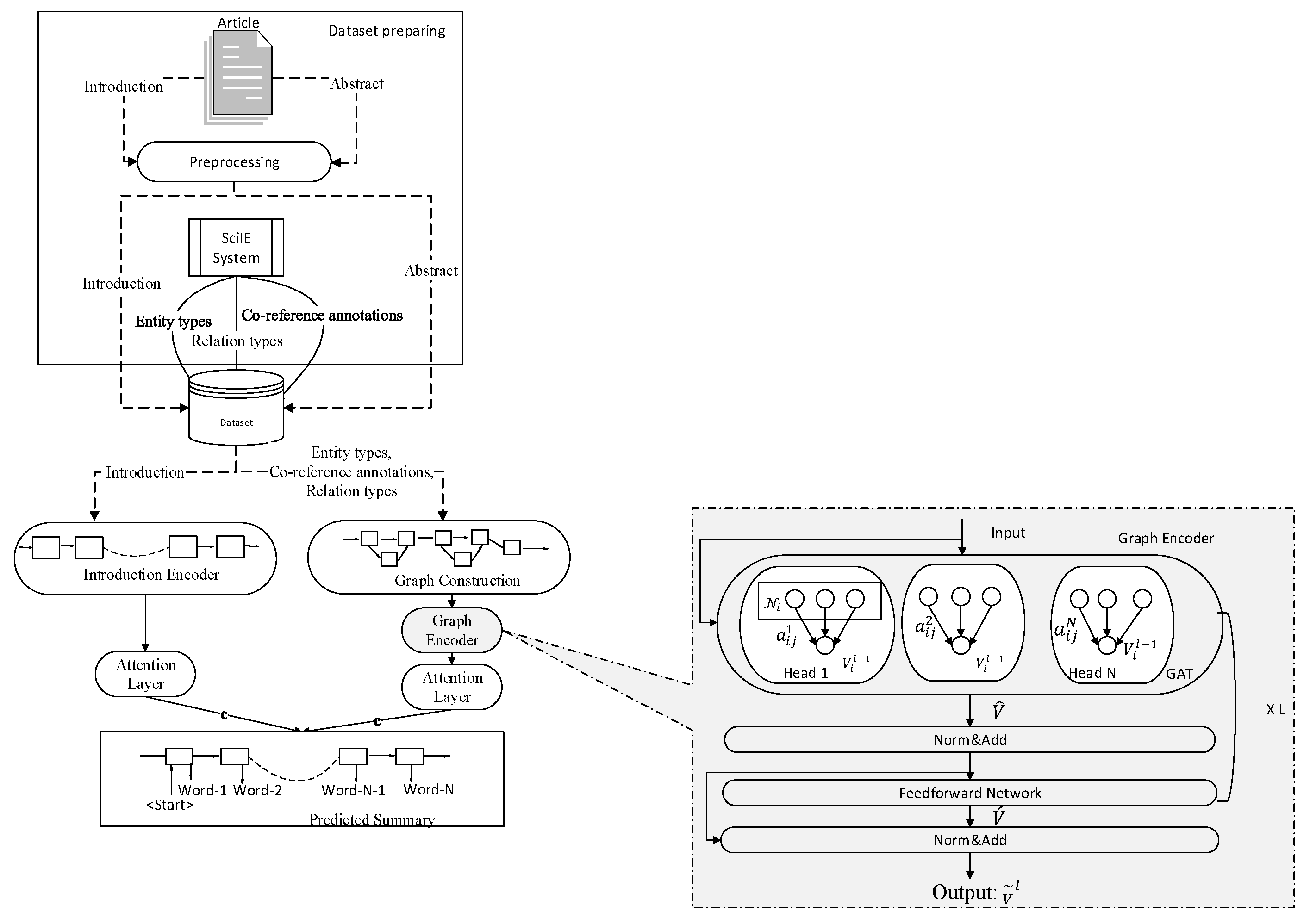
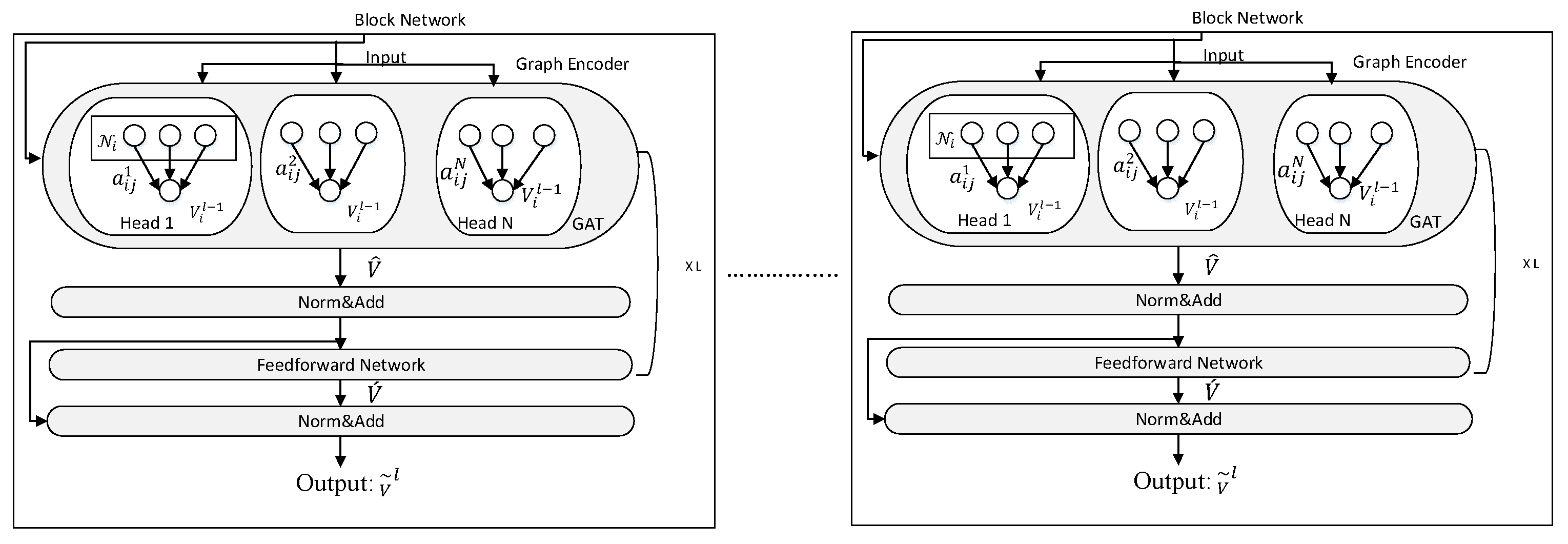
3. Proposed Model
3.1. Dataset
3.2. The Graph-Based Abstractive Summarization Model: (GBAS)
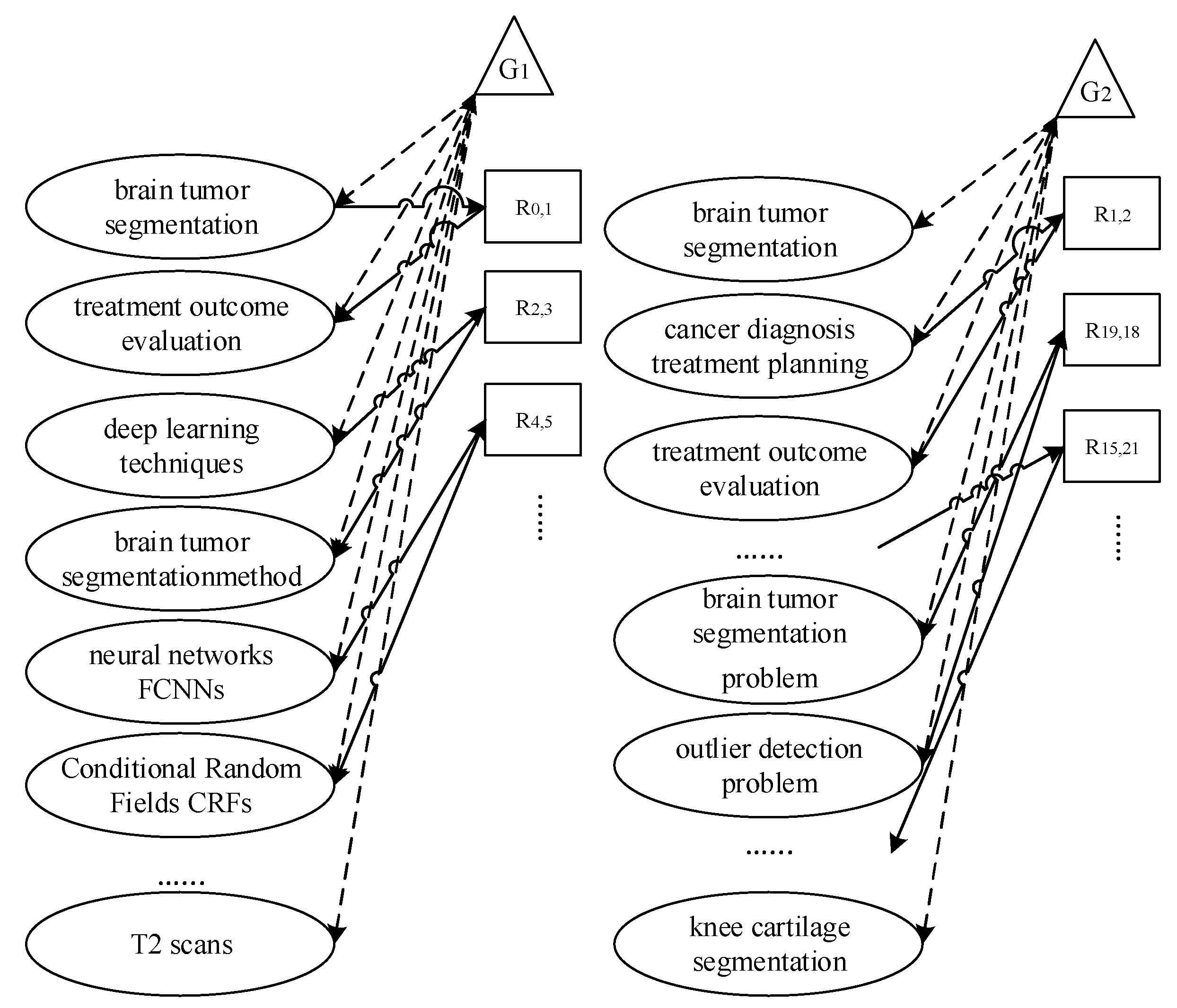
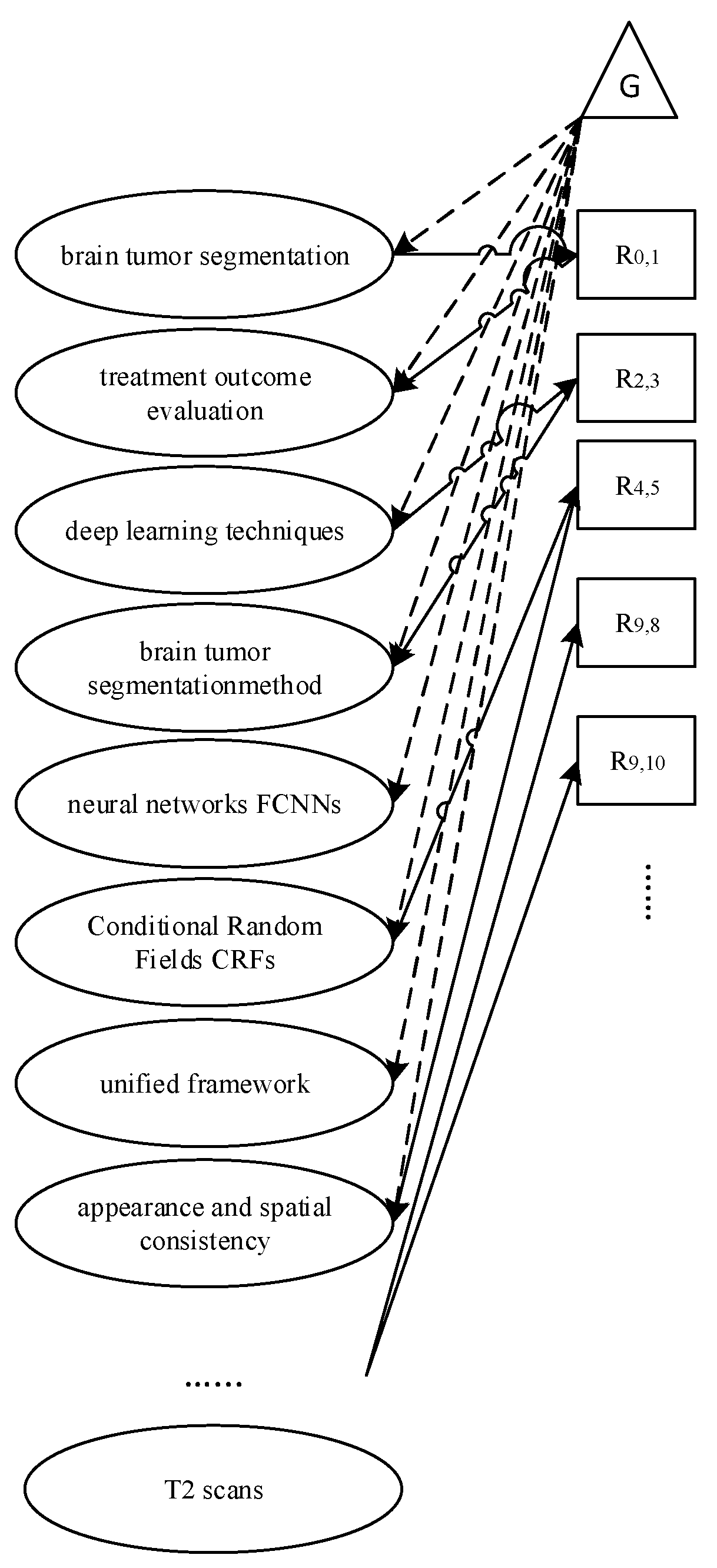
- The "abstract-relations" and "document-relations" arrays are rebuilt according to the "relations types", "abstract-entities", and "document-entities" indexes.
- For instance, the "abstract-relations" array is converted to "0 1 1", according to the example of "brain tumor segmentation – CONJUNCTION – treatment outcome evaluation", so that the index of brain tumor segmentation is "0", the index of CONJUNCTION is "1" and the index of treatment outcome evaluation is "1".
- For instance, the "abstract-relations" array is converted to "2 0 3", according to the example of "Deep learning techniques – USED-FOR – brain tumor segmentation-method", so that the index of deep learning techniques is "2", the index of USED-FOR is "0" and the index of brain tumor segmentation method is "3".
- Entity names that could not be extracted because of spelling errors were excluded from the novel array. Accordingly, the "abstract-relations" array is [0 1 1; 2 0 3; 4 1 5; 9 0 8; 9 1 10; 10 0 8; 12 0 8; 10 0 8; 13 0 81; 9 0 17; 21 0 17; 23 0 22; 28 0 22 ; 28 1 29 ; 29 0 22].
- The same transformation was performed in the introduction section.
- The array of "document-relations" is [1 1 2; 19 0 18; 15 0 21; 25 0 26; 25 1 2; 28 0 26; 25 0 30; 31 0 5; 34 0 5; 34 0 36; 37 6 36; 39 6 36; 40 0 41; 49 1 50 ; 54 0 53 ; 55 6 54 ; 60 0 52 ; 63 0 66 ; 66 0 67 ; 34 0 75].
- As a result, a comprehensive graph was constructed by combining the new transformation array of "abstract-relations" and "document relations"
4. Experiments
4.1. Evaluation Metric
4.2. Baseline Methods
- TextRank [38] is a graph-based method applied to ex tractive methods. The number of similar words between two sentences is calculated as similarity.
- LexRank [39] is a graph-based method that calculates based on cosine similarity.
- LSA [40] is an algebraic method for extractive methods. This model is performed in three stages: input matrix creation, singular value decomposition (SVD), and sentence selection.
- The performance of the proposed model was compared with a fine-tuned T5 model pretrained on 4515 English news articles 1.
- Billsum [41] is a T5-based fine-tuned model on the Billsum dataset which consists of scientific articles.
- GraphWriter [8] is a graph-based tool that generates a summary from the title for abstractive methods.
5. Discussion
5.1. Human Evaluation
6. Conclusions
| 1 | |
| 2 |
References
- Alomari, A. ; Idris, Sabri A.Q.M.; Alsmadi, I. Deep reinforcement and transfer learning for abstractive text summarization A review. Computer Speech & Language, 2022; 71, 101276. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, M.; Liu, P.; Wang, D.; Qiu, X.; Huang, X. Searching for effective neural extractive summarization: What works and what’s next, arXiv preprint. arXiv:19031907.03491, 2019.
- Mojrian, M.; Mirroshandel, S.A. A novel extractive multi-document text summarization system using quantum-inspired genetic algorithm: Mtsqiga, Expert systems with applications, 2021; Volume 171, 114555.
- Cai, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, D.; Liu, T. Covidsum: A linguistically enriched scibert-based summarization model for covid19 scientific papers., Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2022; Volume 127, 103999.
- Du, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, Q.T. Ugdas: Unsupervised graph-network based denoiser for abstractive summarization in biomedical domain, Methods,2022; Volume 203, pp. 160–166.
- Beltagy, I.; Lo, K.; Cohan, A. a: A pretrained language model for scientific text, Available; arXiv:1903.10676, 2019.
- Luan, Y.; He, L.; Ostendorf, M.; Hajishirzi, H. Multi-task identification of entities, relations, and co-reference for scientific knowledge graph construction, arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.09602, 2018. arXiv:1808.09602, 2018.
- Koncel-Kedziorski, R.; Bekal, D.; Luan, Y.; Lapata, M.; Hajishirzi, H. Text generation from knowledge graphs with graph transformers, arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.02342, 2019. arXiv:1904.02342, 2019.
- Fan,A.; Grangier, D.; Auli, M. Controllable abstractive summarization, arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05217. 2017.
- Liang, Z.; Du, J.; Li, C. Abstractive social media text summarization using selective reinforced seq2seq attention model, Neurocomputing , 2020; Volume 410, pp. 432–440.
- El-Kassas, W.S.; Salama, C.R.; Rafea, A.A.; Mohamed, H.K. Edgesumm: Graphbased framework for automatic text summarization, Information Processing & Management,2020; Volume 57, 102264.
- Cagliero, L.; La Quatra, M. Extracting highlights of scientific articles: A supervised summarization approach, Expert Systems with Applications, 2020; Volume 160, 102264.
- Yasunag, M.; Kasai, R.; Zhang, J.; Fabbri, A.R.; Li, I.; Friedman, D.; Radev, D.R. Scisummnet: A large annotated corpus and content-impact models for scientific paper summarization with citation networks, arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.01716, 2019.
- Ju, J.; Liu, M.; Gao, L.; Pan, S. Scisummpip: An unsupervised scientific paper summarization pipeline, arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.09190, 2020. arXiv:2010.09190.
- Zhou, Q.; Wei, F.; Zhou, M. At which level should we extract? an empirical analysis on extractive document summarization, arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.02664, 2020. arXiv:2004.02664.
- Cachola, I.; Lo, K.; Cohan, A.; Weld, D.S. Tldr: Extreme summarization of scientific documents, arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.15011, 2020. arXiv:2004.15011.
- Suleiman, D.; Awajan, A. Multilayer encoder and single-layer decoder for abstractive arabic text summarization, Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022; Volume 237, 107791.
- Moirangthem, D.S.; Lee, M. Abstractive summarization of long texts by representing multiple compositionalities with temporal hierarchical pointer generator network, Neural Networks, 2020, Volume 124, pp.1-11.
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training,2018, Available online: https://www.mikecaptain.com/resources/pdf/GPT-1.pdf (accessed on 16.05.2024).
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding, arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805. arXiv:1810.04805.
- Liu, Y.; Lapata, M. Text summarization with pretrained encoders, arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.08345, 2019. arXiv:1908.08345.
- Dou, Z.Y.; Liu, P.; Hayashi, H.; Jiang, Z.; Neubig, G. Gsum: A general framework for guided neural abstractive summarization, arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.08014, 2020; arXiv:2010.08014. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to text transformer, arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.10683, 2020. arXiv:1910.10683.
- Liu, Y.; Dou, Z.Y.; Liu, P. Refsum: Refactoring neural summarization,arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.07210, 2021. arXiv:2104.07210.
- Yun, S.; Jeong, M.; Kim, R.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.J. Graph transformer networks. advances in neural information processing systems, arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.06455, 2019. arXiv preprint arXiv:, arXiv:1911.06455.
- Zheng, B.; Wen, H.; Liang, Y.; Duan, N.; Che, W.; Jiang, D.; Liu, T. Document modeling with graph attention networks for multi-grained machine reading comprehension, arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.05806, 2020. arXiv:2005.05806.
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Han, T.; Chen, T. Automatic source code summarization with graph attention networks, Journal of Systems and Software,2022; Volume 188, 111257.
- Chen, H.; Hong, P.; Han, W.; Majumder, N.; Poria, S. Dialogue relation extraction with document-level heterogeneous graph attention networks, arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.05092, 2020. arXiv:2009.05092.
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Cao, R.; Zhu, S.; Yu, K. Line graph enhanced AMRto-text generation with mix-order graph attention networks, In Proceedings of the 58rd Annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, 2020, pp. 732–741.
- Veliˇckovi´c, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks, arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10903, 2017. arXiv:1710.10903.
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Zettlemoyer, L. Bart: Denoising sequence-to-sequence pre-training for natural language generation, translation, and comprehension, arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.13461, 2019. arXiv:1910.13461.
- Xie, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, K. Extractive text-image summarization with relationenhanced graph attention network, Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 2022; Volume 61, pp.1-17.
- Kumar, Y.; Kaur, K.; Kaur, S. Study of automatic text summarization approaches in different languages Artificial Intelligence Review, 2021; Volume 54, pp. 5897–5929.
- Augenstein, I.; Das, M.; Riedel, S.; Vikraman,L.; McCallum,A. Semeval2017 task 10: Scienceie-extracting keyphrases and relations from scientific publications ,arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.02853, 2017.
- Beck, D.; Haffari, G.; Cohn, T. Graph-to-sequence learning using gated graph neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.09835, 2018. arXiv:1806.09835.
- See, A.; Liu, P.J.; Manning, C.D. Get to the point: Summarization with pointer-generator networks, arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04368, 2017. arXiv:1704.04368.
- Lin, C.Y. Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries, In Text Summarization Branches Out, 2014; pp.74-81.
- Mihalcea, T.R. Textrank: Bringing order into text., Conference on empirical methods in natural language processing, 2004; pp. 404-411.
- Erkan, G.; Radev, D.R. Lexrank: Graph-based lexical centrality as salience in text summarization, Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2004, Volume 22, 457–479.
- Gong, Y.; Liu, X. Generic text summarization using relevance measure and latent semantic analysis. In Proceedings of the 24th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval; 2001; pp. 679–688. [Google Scholar]
- Kornilova and V. Eidelman, Billsum: A corpus for automatic summarization of us legislation, arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.00523, 2019.
| Ref. | Target | Methodology | Dataset | Metric | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [3] | Extractive | Modified quantum-inspired genetic algorithm | DUC 2005 DUC 2007 |
Rouge | DUC 2005: R1:47.67, R2:12.87, RSU4: 18.85 DUC 2007: R1:41.06, R2:08.98, RSU4: 14.72 |
| [11] | Extractive | Graph structure, statistical-based, semantic-based, and centrality-based methods | DUC 2001 DUC 2002 |
Rouge | DUC 2001: R1:51.37, R2:27.16, RL:47.36, RSU4: 25.65 DUC 2002: R1:53.37, R2:28.58, RL:49.79, RSU4: 27.65 |
| [12] | Extractive | Word2vec, Decision Tree, Random Forest, Multi-Layer Perceptron, Gradient Boosting | CSPubSum AlPubSum BioPubSumm |
Rouge | CSPubSumm: RL:31.6 AlPubSum: RL:28.00 BioPubSumm: RL:28.90 |
| [13] | Extractive | The graph-based multi-document summarization, Reference paper, Graph Convolutional Network | CL-SciSumm SciSummNet |
Rouge, Human Evaluation |
SciSummNet: R2:29.30 R3:24.65 RSU4:18.56CL-SciSumm: R2:18.46, R3 12.77 RSU4:12.21 |
| [14] | Extractive Abstractive |
SciBERT, PageRank | LongSumm | Rouge, Human Evaluation |
R1:40.90, R2:9.52, RL:15.47 |
| [16] | Extractive Abstractive |
BART, Shuffled Data | SciTLDR | Rouge, Human Evaluation |
R1:43.8, R2:21.3, RL:35.5 R1:31.7, R2:11.1 RL: 25.0 |
| [5] | Abstractive | Graph network, auto-regressive generator, knowledge domain | CORD-19 PubMed |
Rouge | CORD-19: R1:33.68, R2:22.56, RL:32.84 PubMed: R1:33.03 R2:13.51 RL:29.30 |
| [17] | Abstractive | Seq2seq model, AraVec based word2vec | CNN/Daily Mail, Specific dataset |
Rouge, Human Evaluation |
R1:38.6, R1-Noorder:46.5, R1-stem: 52.6, R1-context:58.1 |
| [4] | Abstractive | Graph Attention Networks, BioBERT, SciBERT | CORD-19 | Rouge, Human Evaluation |
R1:44.56, R2:18.89, RL: 36.53 |
| [18] | Abstractive | Multiple timescales gated recurrent unit (MTGRU), The pointer-generator-coverage network | CNN/Daily Mail, Specific dataset |
Rouge | CNN/Daily Mail: R1:40.94, R2:18.14, RL:38.57 Specific dataset: R1:56.91, R2:37.48, RL:54.02 |
| Dataset | Doc. Size | Target Avg. Word | Source Avg. Word | Avg. Entities | Avg. Relation |
| SciSummNet | 710 | 132.90 | 338.18 | 13.35 | 6.36 |
| SciTLDR | 1548 | 166.63 | 3036.71 | 15.29 | 10.20 |
| ArxivComp | 16.807 | 158.24 | 549.06 | 16.14 | 5.92 |
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| "relations types:" | ["USED-FOR", "CONJUNCTION", "FEATURE OF", "PART OF", "COMPARE", "EVALUATE FOR", "HYPONYM-OF" ] |
| "abstract entities": | "entities": [ "brain tumor segmentation", "treatment outcome evaluation", "deep learning techniques", "brain tumor segmentation method", "neural networks FCNNs", "Conditional Random Fields CRFs", "unified frame work", "appearance and spatial consistency",..., "T2 scans"] |
| "abstract relations": | "relations": [ "brain tumor segmentation– CONJUNCTION– treatment outcome evaluation", "deep learning techniques– USED-FOR– brain tumor segmenta tion method", "neural networks FCNNs– CONJUNC TION– Conditional Random Fields CRFs", "2D image patches– USED-FOR– deep learning based segmentation model", "2D image patches– CONJUNCTION image slices",..., "T2 scans– USED-FOR– those" ] |
| "document entities": "document relations": |
[ "brain tumor segmentation", "cancer diagnosis treat ment planning", "treatment outcome evaluation", "manual segmentation of brain tumors", "semiautomatic or automatic brain tumor segmentation methods", "brain tumor segmentation studies", "gliomas", "magnetic resonance imaging mri", "segmentation of gliomas", "appearance", "gliosis", "mri data gliomas", "fuzzy bound aries",...,"knee cartilage segmentation"][ "cancer diagnosis treatment planning– CONJUNC TION– treatment outcome evaluation", "manual segmentation– USED-FOR– manual segmentation of brain tumors", "mri data– USED-FOR– segmentation of gliomas", "discriminative model based methods CONJUNCTION–discriminative model","probabilistic image atlases– USED-FOR– brain tumor segmentation problem", "outlier detection problem– USED-FOR– brain tumor segmentation problem", "discriminative model based methods– USED-FOR– tumor sementation problem",..., "back propagation algorithms– CON JUNCTION–mrfs crfs"] |
| Model | Rouge-1 | Rouge-2 | Rouge-L |
| TextRank | 28.52 | 9.20 | 25.67 |
| LexRank | 36.63 | 10.94 | 33.18 |
| LSA | 30.18 | 8.02 | 27.90 |
| BART(fine-tuned) | 24.39 | 9.52 | 23.17 |
| T5 (fine-tuned) | 20.38 | 2.28 | 12.62 |
| Billsum | 30.96 | 22.87 | 28.86 |
| GraphWriter | 43.63 | 18.63 | 36.31 |
| GBAS(proposed) | 45.05 | 19.35 | 37.1 |
| Model | Rouge-1 | Rouge-2 | Rouge-L |
| TextRank | 33.77 | 18.39 | 31.99 |
| LexRank | 34.22 | 18.18 | 32.39 |
| LSA | 34.25 | 18.13 | 32.30 |
| BART(fine-tuned) | 42.37 | 18.49 | 41.37 |
| T5 (fine-tuned) | 40.98 | 12.49 | 34.42 |
| Billsum | 43.27 | 35.79 | 39.65 |
| GraphWriter | 43.64 | 15.11 | 36.94 |
| GBAS(proposed) | 45.05 | 15.11 | 38.36 |
| Model | Rouge-1 | Rouge-2 | Rouge-L |
| TextRank | 16.11 | 4.34 | 13.67 |
| LexRank | 16.68 | 4.50 | 14.07 |
| LSA | 18.22 | 4.93 | 15.26 |
| BART(fine-tuned) | 25.24 | 4.41 | 25.25 |
| T5 (fine-tuned) | 14.85 | 8.48 | 7.51 |
| Billsum | 16.11 | 10.11 | 9.15 |
| GraphWriter | 42.19 | 15.46 | 34.62 |
| GBAS(proposed) | 42.93 | 14.90 | 34.96 |
| Dataset | Con | In. | Coh. | R. | G. |
| Mean/Var. | 3.11(0.57) | 4.06(0.61) | 4.03(0.56) | 3.92(0.51) | 3.15(0.56) |
| Fleiss kappa | 0.671 | 0.611 | 0.534 | 0.603 | 0.613 |
| Summary Type | Summary |
| Gold | "This work presents a self-supervised method to learn dense semantically rich visual concept embeddings for images inspired by methods for learning word embed dings in NLP. Our method improves on prior work by generating more expressive embeddings and by being applicable for high-resolution images. Viewing the generation of natural images as a stochastic process where a set of latent visual concepts give rise to observable pixel appearances, our method is ..." |
| Gen | "Masked language models are an efficient tool used across NLP. It is considered task to implement many self supervised learning in the complexity-based view sampling. In this paper, we explore effective stochastic process and apply it to derive regional contextual masking such as dense semantically rich visual concept embed dings. We demonstrate how to train better complexity based view sampling when training data can achieve state-of-the-art performance on multiple NLP." |
| Gold | “Sentence embedding methods offer a powerful approach for working with short textual constructs or sequences of words. By representing sentences as dense numerical vectors, many natural language processing (NLP) ap plications have improved their performance. However, relatively little is understood about the latent structure of sentence embeddings. Specifically, research has not addressed whether the length and structure of sentences impact the sentence embedding space and topology. This paper reports research on a set of comprehensive clus tering and network analyses targeting sentence and sub sentence embedding spaces...” |
| Gen | "In this paper, we demonstrate how sentence embedding models can be used to improve the performance of natural language processing NLP applications. We perform topology by means that sentence embedding models such as network analyses require more relevant to sentence and sub-sentence embedding spaces and topology can achieve the same sentence embedding models performance is compared to short textual constructs". |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





