Submitted:
14 May 2024
Posted:
14 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
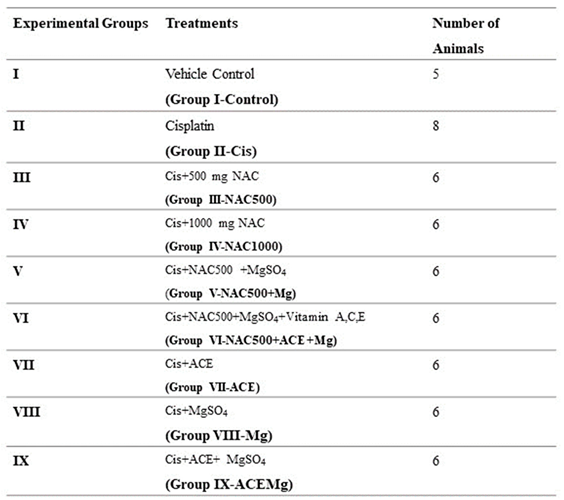
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Induction of Ototoxicity by Cisplatin and Otoprotection Treatment Groups
2.3. Auditory Brainstem Response Recordings (ABRs)
2.4. Cochlear Fixation and Processing for Histology
2.5. Immunohistochemistry on “In Toto” Cochlear Surface Preparations for Outer Hair Cell Quantification
2.6. Immunohistochemistry for 3- Nitrotyrosine in Cochlear Sections
2.7. OHC Counts
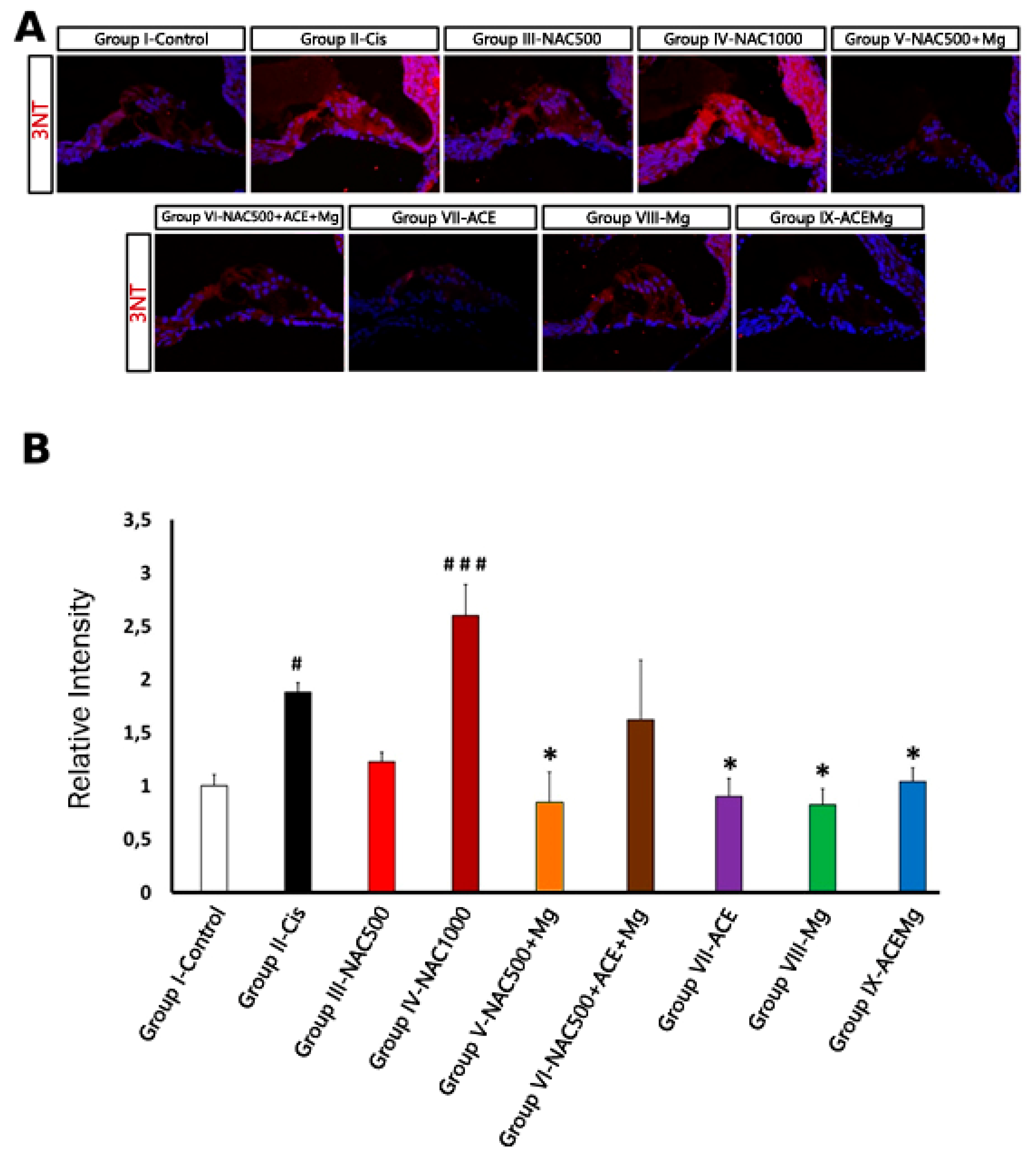
2.8. Semiquantitative Measurement of Fluorescent Signal Intensity for 3-Nitrotyrosine
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
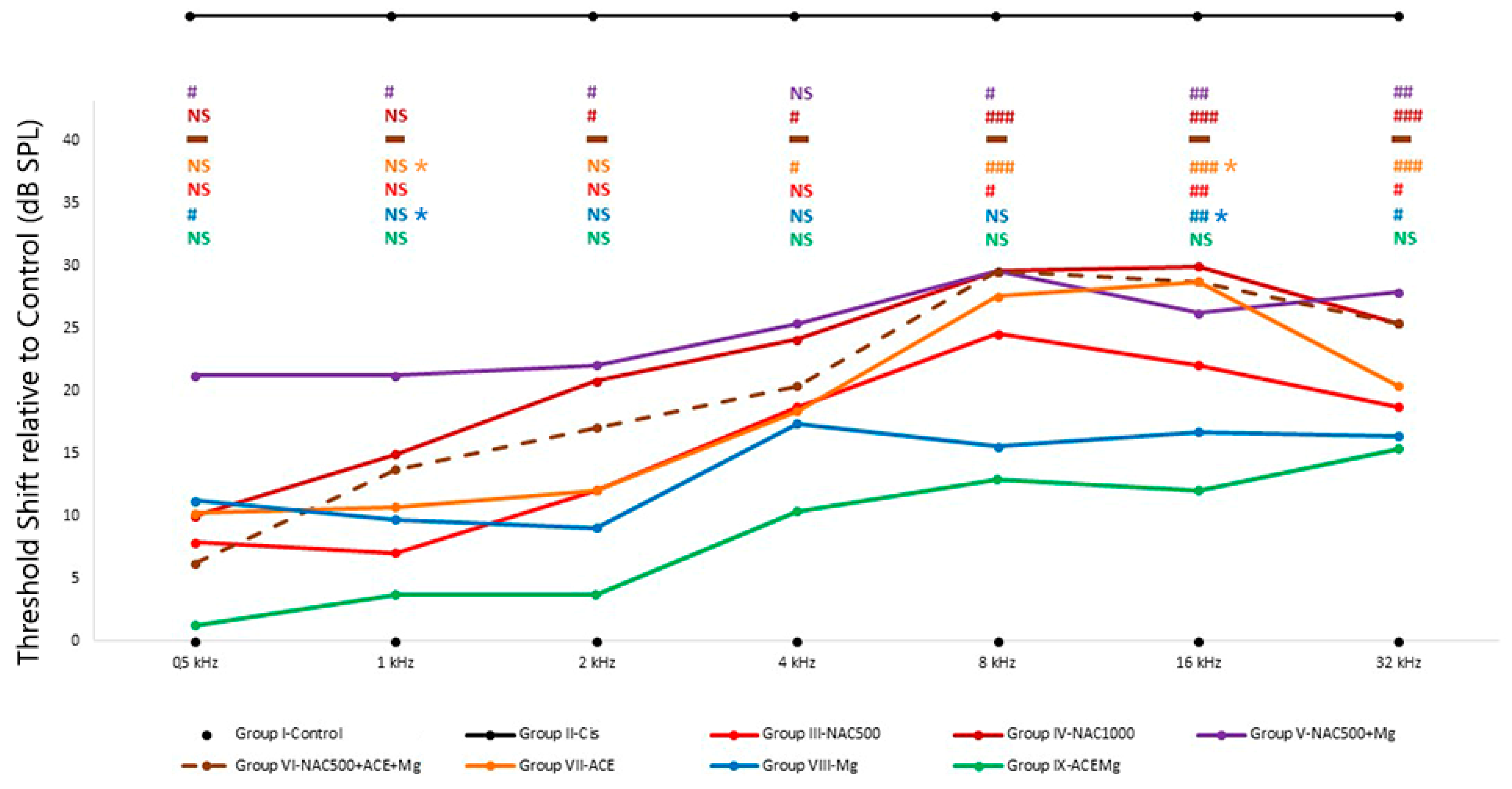
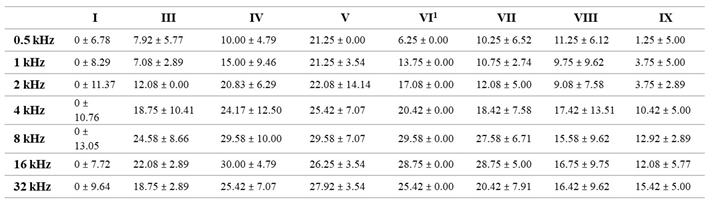
3.1. Auditory Threshold Shifts after Different Antioxidant Treatments
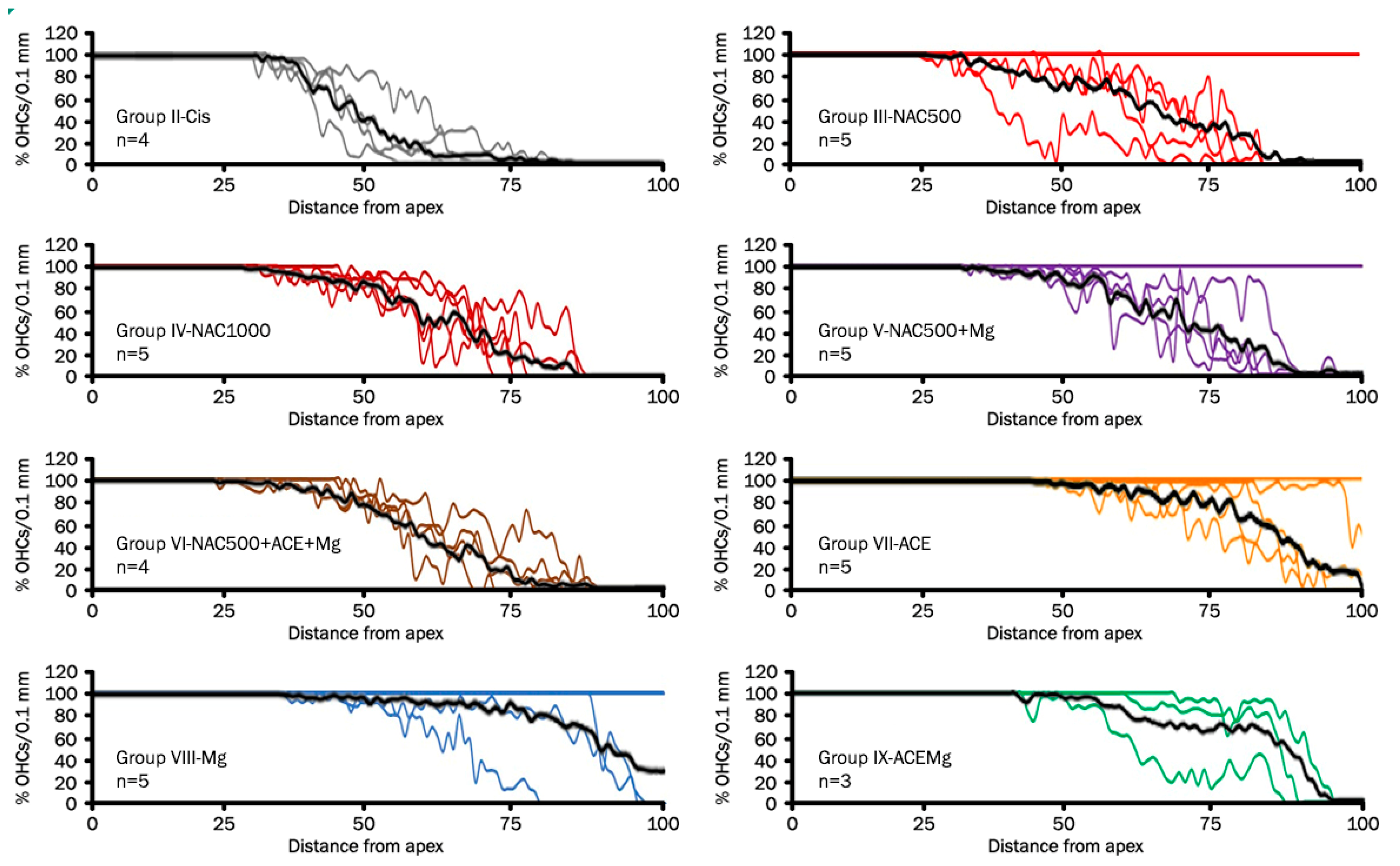
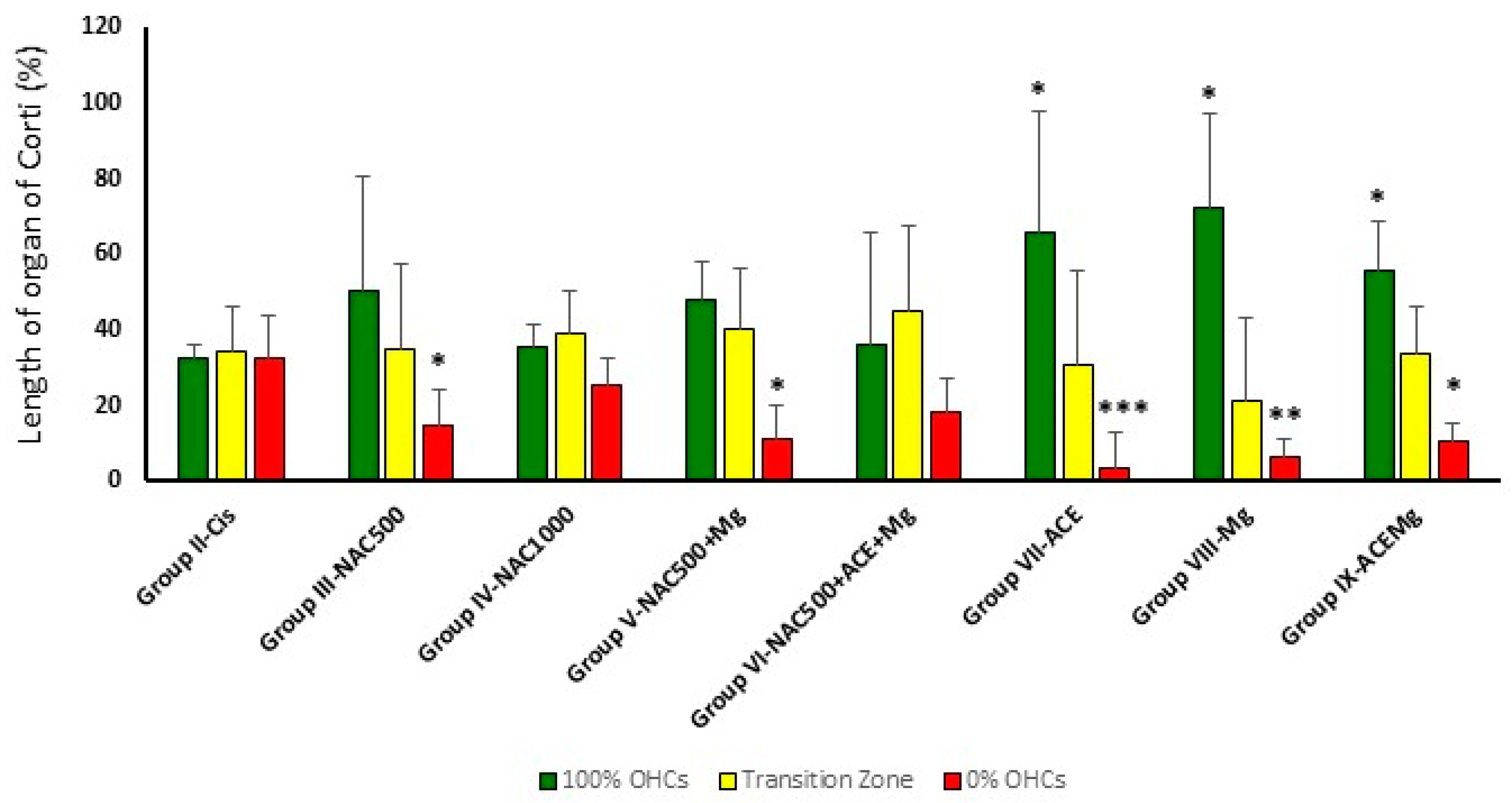
3.2. Outer Hair Cell Counts
4. Discussion
4.1. Hearing Loss and Cochlear Damage after Cisplatin Ototoxicity in the Rat Model
4.2. Antioxidants and Antioxidant Combinations in Otoprotection against Cisplatin Ototoxicity
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The First Metal Based Anticancer Drug. Bioorg Chem 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauman R et Dulon D Ototoxicilté Médicamenteuse. Encycl Méd Chir 1995, 20-184-B-10,1995,10p.
- Callejo, A.; Sedó-Cabezón, L.; Domènech Juan, I.; Llorens, J. Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Effects, Mechanisms and Protection Strategies. Toxics 2015, 3, 268–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paken, J.; Govender, C.D.; Pillay, M.; Sewram, V. A Review of Cisplatin-Associated Ototoxicity. Semin Hear 2019, 40, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.P. Cis-Platinum Associated Hearing Loss. J Laryngol Otol 1981, 95, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Kapteijn, T.S.; Hart, A.A.; Pinedo, H.M. Ototoxicity of Cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum (II): Influence of Dose, Schedule and Mode of Administration. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 1983, 19, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böheim, K.; Bichler, E. Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Audiometric Findings and Experimental Cochlear Pathology. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 1985, 242, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekborn, A.; Laurell, G.; Andersson, A.; Wallin, I.; Eksborg, S.; Ehrsson, H. Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss: Influence of the Mode of Drug Administration in the Guinea Pig. Hearing Research 2000, 140, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroso, M.J.; Blair, R.L. A Review of Cis-Platinum Ototoxicity. J Otolaryngol 1983, 12, 365–369. [Google Scholar]
- Freyer, D.R.; Brock, P.R.; Chang, K.W.; Dupuis, L.L.; Epelman, S.; Knight, K.; Mills, D.; Phillips, R.; Potter, E.; Risby, D.; et al. Prevention of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Children and Adolescents with Cancer: A Clinical Practice Guideline. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 2020, 4, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kros, C.J.; Steyger, P.S. Aminoglycoside- and Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Mechanisms and Otoprotective Strategies. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2019, 9, a033548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Eur J Pharmacol 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Mi, Y.; Liu, L.; Dong, M.; Chen, Y.; Zou, Z. Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Updates on Molecular Mechanisms and Otoprotective Strategies. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2021, 163, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, L.P. Mechanisms of Cisplatin Ototoxicity and Progress in Otoprotection. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2007, 15, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacht, J.; Talaska, A.E.; Rybak, L.P. Cisplatin and Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: Hearing Loss and Its Prevention. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2012, 295, 1837–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.S.; Silveira, A.F.; Teixeira, A.R.; Hyppolito, M.A. Mechanisms of Cisplatin Ototoxicity: Theoretical Review. J Laryngol Otol 2013, 127, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breglio, A.M.; Rusheen, A.E.; Shide, E.D.; Fernandez, K.A.; Spielbauer, K.K.; McLachlin, K.M.; Hall, M.D.; Amable, L.; Cunningham, L.L. Cisplatin Is Retained in the Cochlea Indefinitely Following Chemotherapy. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjea, D.; Jajoo, S.; Sheehan, K.; Kaur, T.; Sheth, S.; Bunch, J.; Perro, C.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. NOX3 NADPH Oxidase Couples Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 to Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 1-Mediated Inflammation and Hearing Loss. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, S.; Mukherjea, D.; Rybak, L.P.; Ramkumar, V. Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity and Otoprotection. Front Cell Neurosci 2017, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, L.P.; Husain, K.; Morris, C.; Whitworth, C.; Somani, S. Effect of Protective Agents against Cisplatin Ototoxicity. Am J Otol 2000, 21, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Shin, B.; Choo, O.-S.; Lee, J.J.; Choung, Y.-H. Connexin 43 Acts as a Proapoptotic Modulator in Cisplatin-Induced Auditory Cell Death. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Sunose, H.; Takasaka, T. Effects of Free Radicals on the Intracellular Calcium Concentration in the Isolated Outer Hair Cell of the Guinea Pig Cochlea. Acta Otolaryngol. 1993, 113, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohri, H.; Ninoyu, Y.; Sakaguchi, H.; Hirano, S.; Saito, N.; Ueyama, T. Nox3-Derived Superoxide in Cochleae Induces Sensorineural Hearing Loss. J Neurosci 2021, 41, 4716–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marullo, R.; Werner, E.; Degtyareva, N.; Moore, B.; Altavilla, G.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Doetsch, P.W. Cisplatin Induces a Mitochondrial-ROS Response That Contributes to Cytotoxicity Depending on Mitochondrial Redox Status and Bioenergetic Functions. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e81162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, R.; Ong, K. Antioxidants in the Prevention of Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asian Journal of Oncology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto-Urata, M.; Urata, S.; Fujimoto, C.; Yamasoba, T. Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Acquired Inner Ear Disorders. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, W.C.; Brown, R.D.; Gage-White, L.; Kupetz, S.; Anniko, M.; Penny, J.E.; Henley, C.M. Effects of Cisplatin and Thiosulfate upon Auditory Brainstem Responses of Guinea Pigs. Hear Res 1988, 35, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y. Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: From Signaling Network to Therapeutic Targets. Biomed Pharmacother 2023, 157, 114045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.C.; Rybak, L.P.; Meech, R.P.; Hughes, L. D-Methionine Provides Excellent Protection from Cisplatin Ototoxicity in the Rat. Hear. Res. 1996, 102, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.C.M.; Meech, R.P.; Klemens, J.J.; Gerberi, M.T.; Dyrstad, S.S.W.; Larsen, D.L.; Mitchell, D.L.; El-Azizi, M.; Verhulst, S.J.; Hughes, L.F. Prevention of Noise- and Drug-Induced Hearing Loss with D-Methionine. Hear Res 2007, 226, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, L.P.; Whitworth, C.; Somani, S. Application of Antioxidants and Other Agents to Prevent Cisplatin Ototoxicity. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, W.-T.; Chinosornvatana, N.; Chang, K.W. Prevention of Cisplatin Ototoxicity Using Transtympanic N-Acetylcysteine and Lactate. Otol. Neurotol. 2004, 25, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas Dickey, D.; Muldoon, L.L.; Kraemer, D.F.; Neuwelt, E.A. Protection against Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity by N-Acetylcysteine in a Rat Model. Hear. Res. 2004, 193, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Pisani, A.; Rolesi, R.; Paciello, F.; Viziano, A.; Moleti, A.; Sisto, R.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G.; Grassi, C. Early Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Accelerates Presbycusis Altering Aging Processes in the Cochlea. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 803973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammill, T.L.; Campbell, K.C. Protection for Medication-Induced Hearing Loss: The State of the Science. Int J Audiol 2018, 57, S67–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Juiz, J.M. Antioxidants and Vasodilators for the Treatment of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Are They Really Effective? Front Cell Neurosci 2020, 14, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Prell Free Radical Scavengers, Vitamins A, C, and E, plus Magnesium Reduces Noise Trauma. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1950331/ (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Le Prell Assessment of Nutrient Supplement to Reduce Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24590390/ (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Scheper, V.; Schmidtheisler, M.; Lasch, F.; von der Leyen, H.; Koch, A.; Schwieger, J.; Büchner, A.; Lesinski-Schiedat, A.; Lenarz, T. Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Investigating the Effect of Antioxidants and a Vasodilator on Overall Safety and Residual Hearing Preservation in Cochlear Implant Patients. Trials 2020, 21, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Gabaldón-Ull, M.C.; Juiz, J.M. An Oral Combination of Vitamins A, C, E, and Mg++ Improves Auditory Thresholds in Age-Related Hearing Loss. Front Neurosci 2018, 12, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scasso, F.; Sprio, A.E.; Canobbio, L.; Scanarotti, C.; Manini, G.; Berta, G.N.; Bassi, A.M. Dietary Supplementation of Coenzyme Q10 plus Multivitamins to Hamper the ROS Mediated Cisplatin Ototoxicity in Humans: A Pilot Study. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lloyd Faulconbridge, R.V.; Fetoni, A.; Guitton, M.J.; Pujol, R.; Puel, J.L. Local Application of Sodium Thiosulfate Prevents Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss in the Guinea Pig. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeriņa, D.; Takano, Y.; Hanaoka, K.; Urano, Y.; Dick, T.P. N-Acetyl Cysteine Functions as a Fast-Acting Antioxidant by Triggering Intracellular H2S and Sulfane Sulfur Production. Cell Chem Biol 2018, 25, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Timmins, K.; Jalali, Z. Cisplatin-Induced Renal Toxicity: Possible Reversal by N-Acetylcysteine Treatment. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1997, 8, 1640–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, J.H.; Beijnen, J.H.; Balm, A.J.M.; Schellens, J.H.M. Future Opportunities in Preventing Cisplatin Induced Ototoxicity. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2006, 32, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Smyth, B.J.; Namin, A.; Phillips, G.; Gratton, M.A. Targeted Amelioration of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Guinea Pigs. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2014, 151, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theneshkumar, S.; Lorito, G.; Giordano, P.; Petruccelli, J.; Martini, A.; Hatzopoulos, S. Effect of Noise Conditioning on Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: A Pilot Study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, BR173–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tropitzsch, A.; Arnold, H.; Bassiouni, M.; Müller, A.; Eckhard, A.; Müller, M.; Löwenheim, H. Assessing Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity and Otoprotection in Whole Organ Culture of the Mouse Inner Ear in Simulated Microgravity. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 227, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, W.; Sies, H. Lycopene: A Biologically Important Carotenoid for Humans? Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 1996, 336, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Nelson, K.C.; Wu, M.; Sternberg, P.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Damage and Protection of the RPE. Prog Retin Eye Res 2000, 19, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán-Fidalgo, A.; Martín Saldaña, S.; Trinidad, A.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Rodríguez-Valiente, A.; García-Berrocal, J.R.; Ramírez-Camacho, R. In Vitro and in Vivo Effects of Lutein against Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 68, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundelin, S.P.; Nilsson, S.E. Lipofuscin-Formation in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Is Reduced by Antioxidants. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciçek, M.T.; Kalcioğlu, T.M.; Bayindir, T.; Toplu, Y.; Iraz, M. The Effect of Lycopene on the Ototoxicity Induced by Cisplatin. Turk J Med Sci 2014, 44, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkırış, M.; Kapusuz, Z.; Karaçavuş, S.; Saydam, L. The Effects of Lycopene on Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2013, 270, 3027–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kınal, M.E.; Tatlıpınar, A.; Uzun, S.; Keskin, S.; Tekdemir, E.; Özbeyli, D.; Akakın, D. Investigación Del Efecto de La Astaxantina Sobre La Ototoxicidad Del Cisplatino En Ratas Mediante El Uso de La Emisión Otoacústica, La Capacidad Antioxidante Total y Métodos Histopatológicos. Ear Nose Throat J 2021, 100, NP198–NP205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.W. Antioxidant Action of Carotenoids. J. Nutr. 1989, 119, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.W.; Joyce, A.; Ingold, K.U. Is Vitamin E the Only Lipid-Soluble, Chain-Breaking Antioxidant in Human Blood Plasma and Erythrocyte Membranes? Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1983, 221, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, C.K.; Ibrahim, W.; Wei, Z.; Chan, A.C. Vitamin E Regulates Mitochondrial Hydrogen Peroxide Generation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryor Vitamin E and Heart Disease: Basic Science to Clinical Intervention Trials - PubMed . Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10656300/ (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Teranishi, M.; Nakashima, T.; Wakabayashi, T. Effects of Alpha-Tocopherol on Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Guinea Pigs. Hear. Res. 2001, 151, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Sergi, B.; Ferraresi, A.; Paludetti, G.; Troiani, D. Protective Effects of Alpha-Tocopherol and Tiopronin against Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004, 124, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokgöz, S.A.; Vuralkan, E.; Sonbay, N.D.; Çalişkan, M.; Saka, C.; Beşalti, Ö.; Akin, İ. Protective Effects of Vitamins E, B and C and L-Carnitine in the Prevention of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Rats. J Laryngol Otol 2012, 126, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teranishi, M.; Nakashima, T. Effects of Trolox, Locally Applied on Round Windows, on Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity in Guinea Pigs. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2003, 67, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebi, S.; Gurdal, M.M.; Ozkul, M.H.; Yasar, H.; Balikci, H.H. The Effect of Intratympanic Vitamin C Administration on Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2013, 270, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.C.; Meech, R.P.; Rybak, L.P.; Hughes, L.F. D-Methionine Protects against Cisplatin Damage to the Stria Vascularis. Hear. Res. 1999, 138, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibaja, A.; Alvarado, J.C.; Scheper, V.; Carles, L.; Juiz, J.M. Kanamycin and Cisplatin Ototoxicity: Differences in Patterns of Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant Enzyme Expression and Hair Cell Loss in the Cochlea. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadır, A.; Ceyhan, A.; Öz Gergin, Ö.; Yalçın, B.; Ülger, M.; Özyazgan, T.M.; Yay, A. Protective Effects of Curcumin and Beta-Carotene on Cisplatin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: An Experimental Rat Model. Anatol J Cardiol 2018, 19, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Cao, L.; Chi, Z. Ascorbic Acid Ameliorates Seizures and Brain Damage in Rats through Inhibiting Autophagy. Brain Res 2013, 1535, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Cho, S.; Park, S.; Han, S. Magnesium Sulfate Does Not Protect Spinal Cord against Ischemic Injury. J Invest Surg 2011, 24, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somdaş, M.A.; Güntürk, İ.; Balcıoğlu, E.; Avcı, D.; Yazıcı, C.; Özdamar, S. Protective Effect of N-Acetylcysteine against Cisplatin Ototoxicity in Rats: A Study with Hearing Tests and Scanning Electron Microscopy. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology 2020, 86, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, M.; Wada, M.; Ikeda, R.; Fuchigami, Y.; Koyama, H.; Ohkawara, S.; Kawakami, S.; Kuroda, N.; Nakashima, K. Quantitative and Antioxidative Behavior of Trolox in Rats’ Blood and Brain by HPLC-UV and SMFIA-CL Methods. Luminescence 2016, 31, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Gabaldón-Ull, M.C.; Blanco, J.L.; Juiz, J.M. Wistar Rats: A Forgotten Model of Age-Related Hearing Loss. Front Aging Neurosci 2014, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Jareño-Flores, T.; Blanco, J.L.; Juiz, J.M. Normal Variations in the Morphology of Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Waveforms: A Study in Wistar Rats. Neuroscience Research 2012, 73, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Gabaldón-Ull, M.C.; Jareño-Flores, T.; Miller, J.M.; Juiz, J.M. Noise-Induced “Toughening” Effect in Wistar Rats: Enhanced Auditory Brainstem Responses Are Related to Calretinin and Nitric Oxide Synthase Upregulation. Front Neuroanat 2016, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.M.; de Haan, J.B. Combating Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Complications with Nrf2 Activators: How Much Is Too Much? Redox Rep 2014, 19, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, S.H.; Taylor, R.; Forge, A.; Schacht, J. Differential Vulnerability of Basal and Apical Hair Cells Is Based on Intrinsic Susceptibility to Free Radicals. Hear. Res. 2001, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astolfi, L.; Simoni, E.; Valente, F.; Ghiselli, S.; Hatzopoulos, S.; Chicca, M.; Martini, A. Coenzyme Q10 plus Multivitamin Treatment Prevents Cisplatin Ototoxicity in Rats. PLoS One 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petremann, M.; Tran Van Ba, C.; Broussy, A.; Romanet, C.; Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J. Oral Administration of Clinical Stage Drug Candidate SENS-401 Effectively Reduces Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss in Rats. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M. Frequency Representation in the Rat Cochlea. Hear Res 1991, 51, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, R.; Somani, S.M.; Rybak, L.P. Mechanism of Cisplatin Ototoxicity: Antioxidant System. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 76, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Z.; Ye, F.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Hearing Loss: Oxidative Stress, Autophagy and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Cell Dev Biol 2023, 11, 1119773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirrier, A.L.; Pincemail, J.; Van Den Ackerveken, P.; Lefebvre, P.P.; Malgrange, B. Oxidative Stress in the Cochlea: An Update. Curr Med Chem 2010, 17, 3591–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.J.T.; Song, L. Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Hear Res 2023, 434, 108783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares, C.; Ramírez-Camacho, R.; Trinidad, A.; Roldán, A.; Jorge, E.; García-Berrocal, J.R. Reactive Oxygen Species in Apoptosis Induced by Cisplatin: Review of Physiopathological Mechanisms in Animal Models. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2012, 269, 2455–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, H. Hair Cell Protection from Ototoxic Drugs. Neural Plast 2021, 2021, 4909237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.; Boikess, R.S.; Schwartz, R.A.; Cohen, P.J. Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO): A Solvent That May Solve Selected Cutaneous Clinical Challenges. Arch Dermatol Res 2023, 315, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Yamashita, D.; Minami, S.B.; Yamasoba, T.; Miller, J.M. Mechanisms of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Indicate Multiple Methods of Prevention. Hear Res 2007, 226, 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Hughes, L.F.; Miller, J.M. Free Radical Scavengers Vitamins A, C, and E plus Magnesium Reduce Noise Trauma. Free Radic Biol Med 2007, 42, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendowski Magnesium and Hearing Loss - Magnesium in the Central Nervous System - NCBI Bookshelf. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507266/ (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Sahin, A.A.; Oysu, C.; Yilmaz, H.B.; Topak, M.; Kulekci, M.; Okar, I. Effect of Oral Magnesium Supplementation on Cisplatin Ototoxicity. J Otolaryngol 2006, 35, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevette, M.J.; Drew, D.; Webb, T.M.; Marion, M.S. Cisplatin Ototoxicity, Increased DPOAE Amplitudes, and Magnesium Deficiency. Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions. J Am Acad Audiol 2000, 11, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaner, W.S.; Shmarakov, I.O.; Traber, M.G. Vitamin A and Vitamin E: Will the Real Antioxidant Please Stand Up? Annu Rev Nutr 2021, 41, 105–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, M.G.; Stevens, J.F. Vitamins C and E: Beneficial Effects from a Mechanistic Perspective. Free Radic Biol Med 2011, 51, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Gagnon, P.M.; Bennett, D.C.; Ohlemiller, K.K. Nutrient-Enhanced Diet Reduces Noise-Induced Damage to the Inner Ear and Hearing Loss. Transl Res 2011, 158, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, D.G.; Kurabi, A.; Ryan, A.F. Screening Antioxidants for the Protection of Cochlear Sensory Cells. Neural Regen Res 2018, 13, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, M.-E.; Théorêt, Y.; Saliba, I. The Role of Intratympanic Lactate Injection in the Prevention of Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, H. 3-Nitrotyrosine: A Biomarker of Nitrogen Free Radical Species Modified Proteins in Systemic Autoimmunogenic Conditions. Hum Immunol 2013, 74, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





