Submitted:
14 May 2024
Posted:
14 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Method
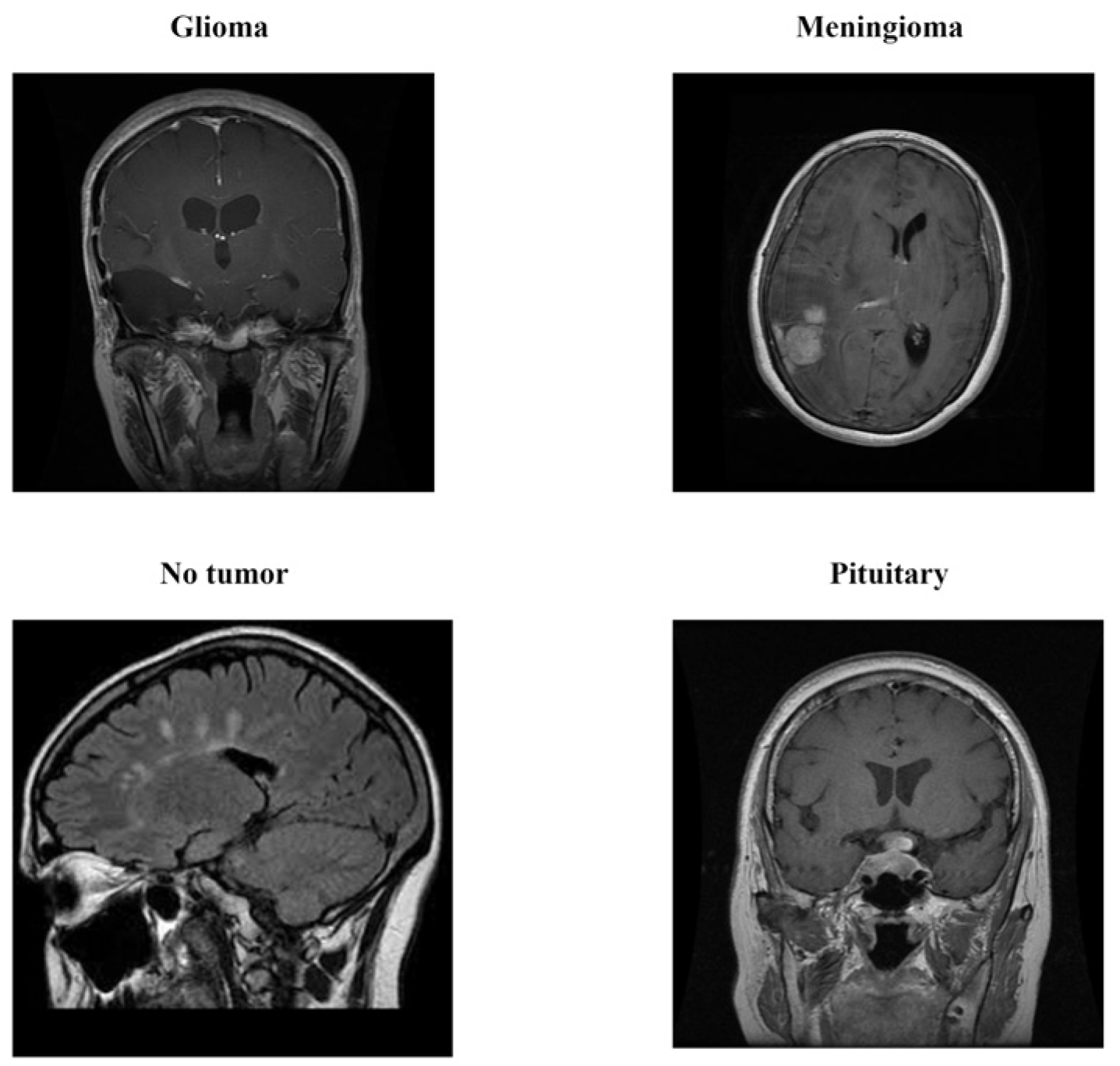
2.1. Dataset
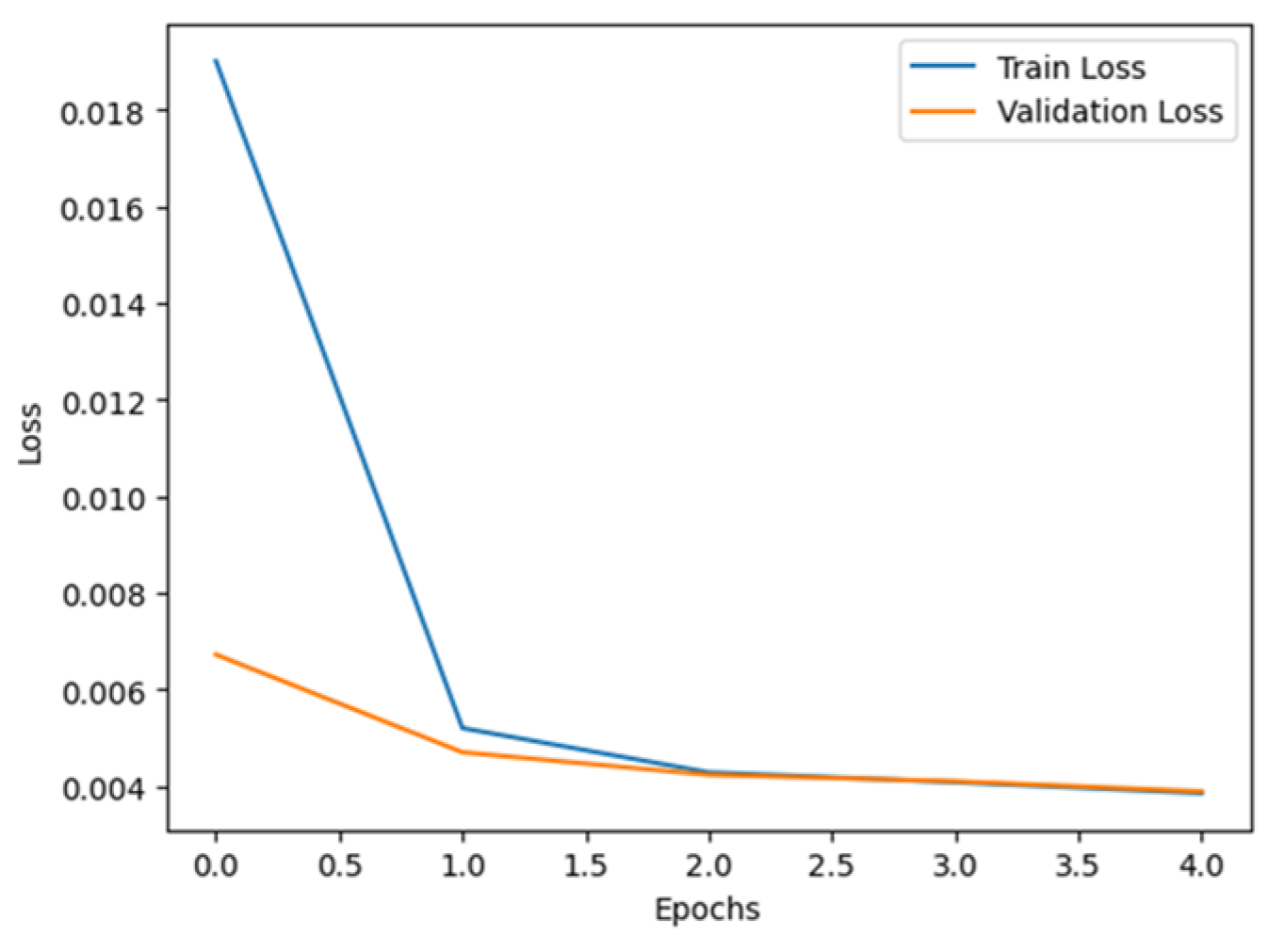
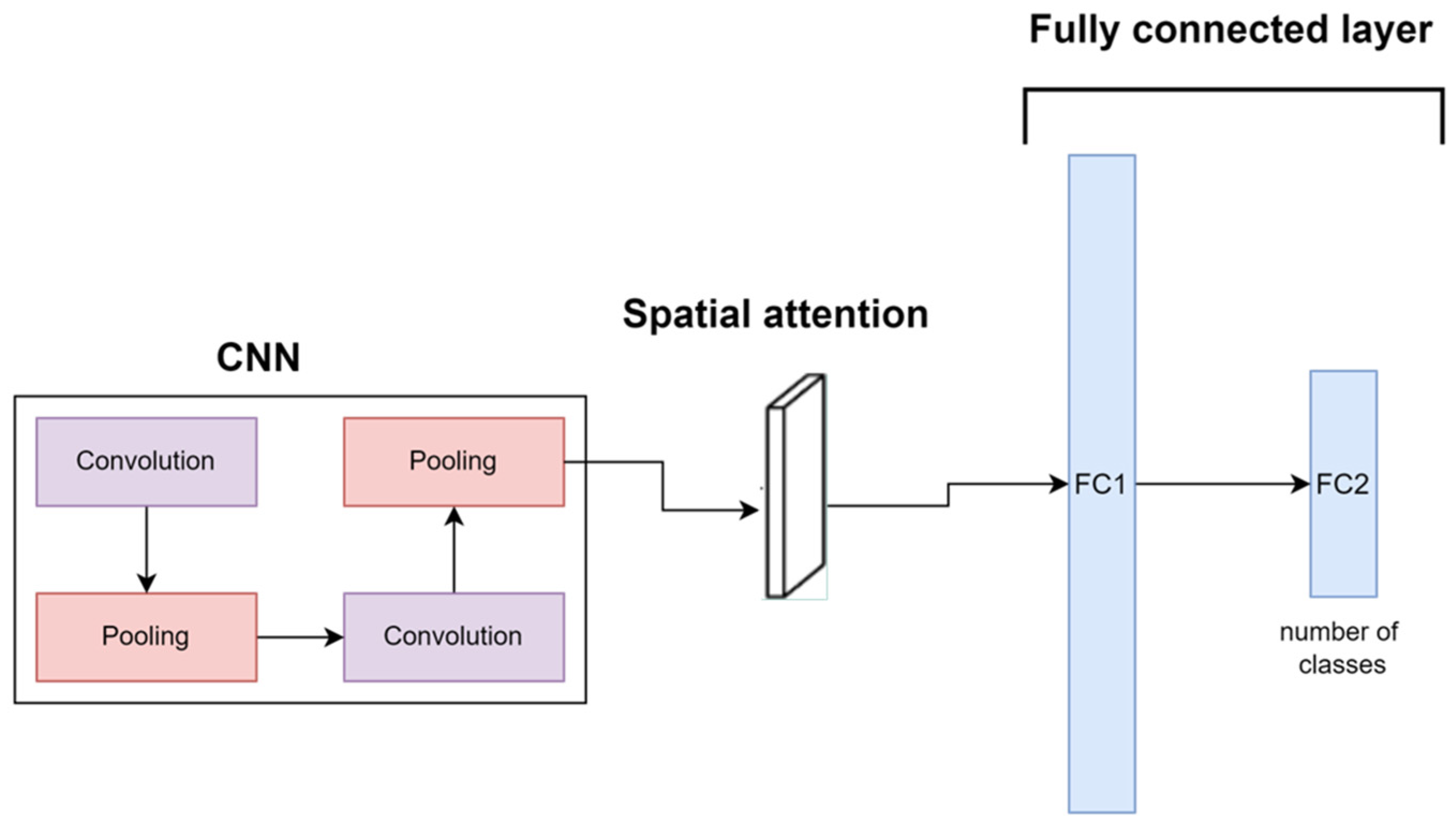
2.2. Implementation of Pre-Trained Models for Comparison
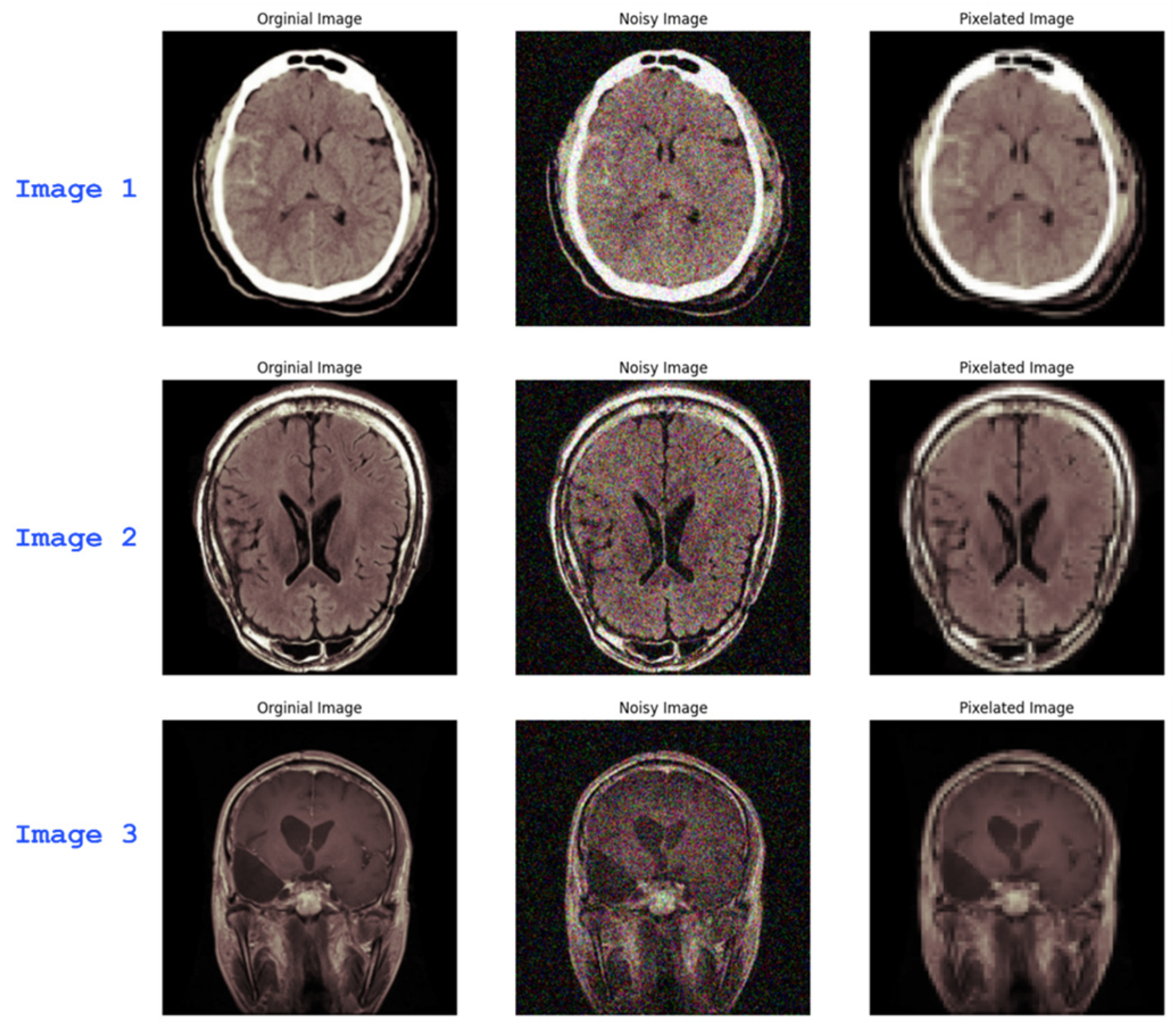
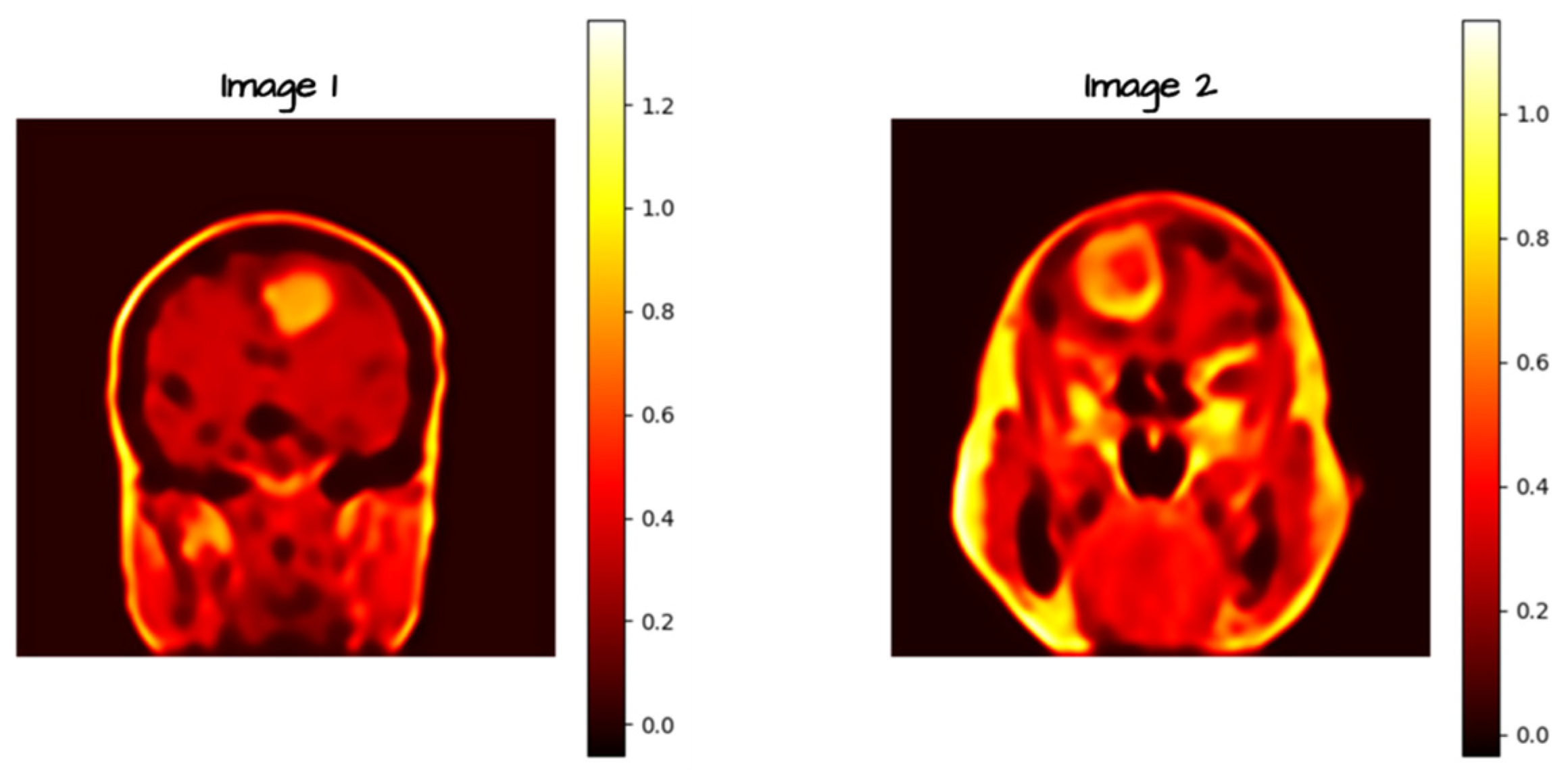
2.3. Noise and Blur Introduction
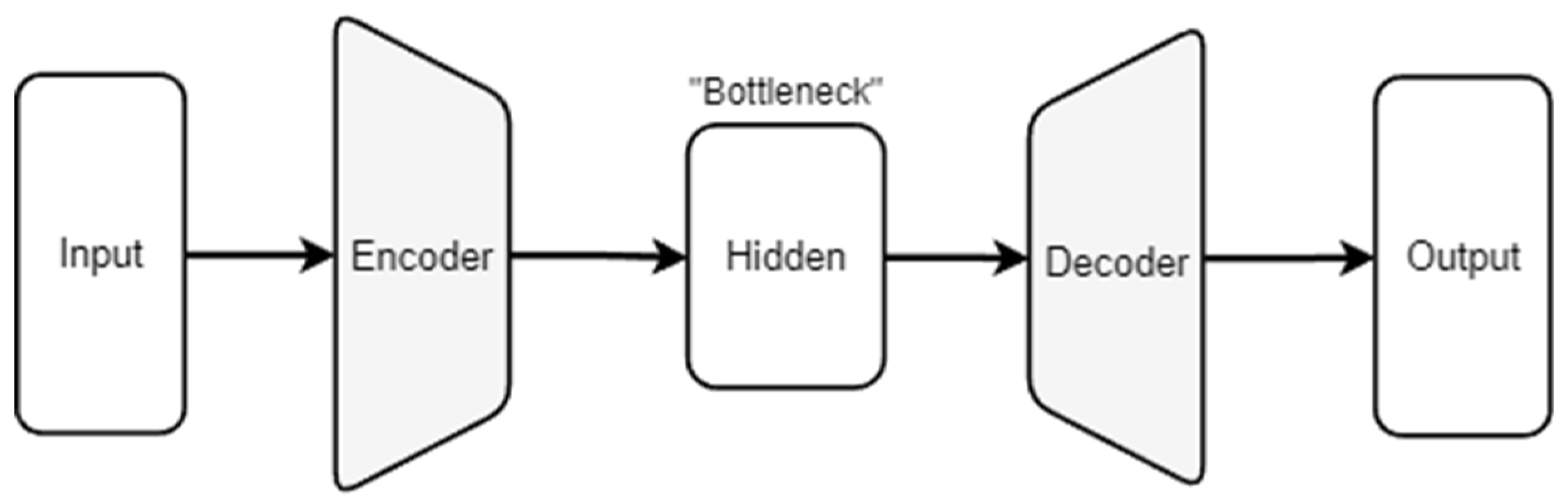
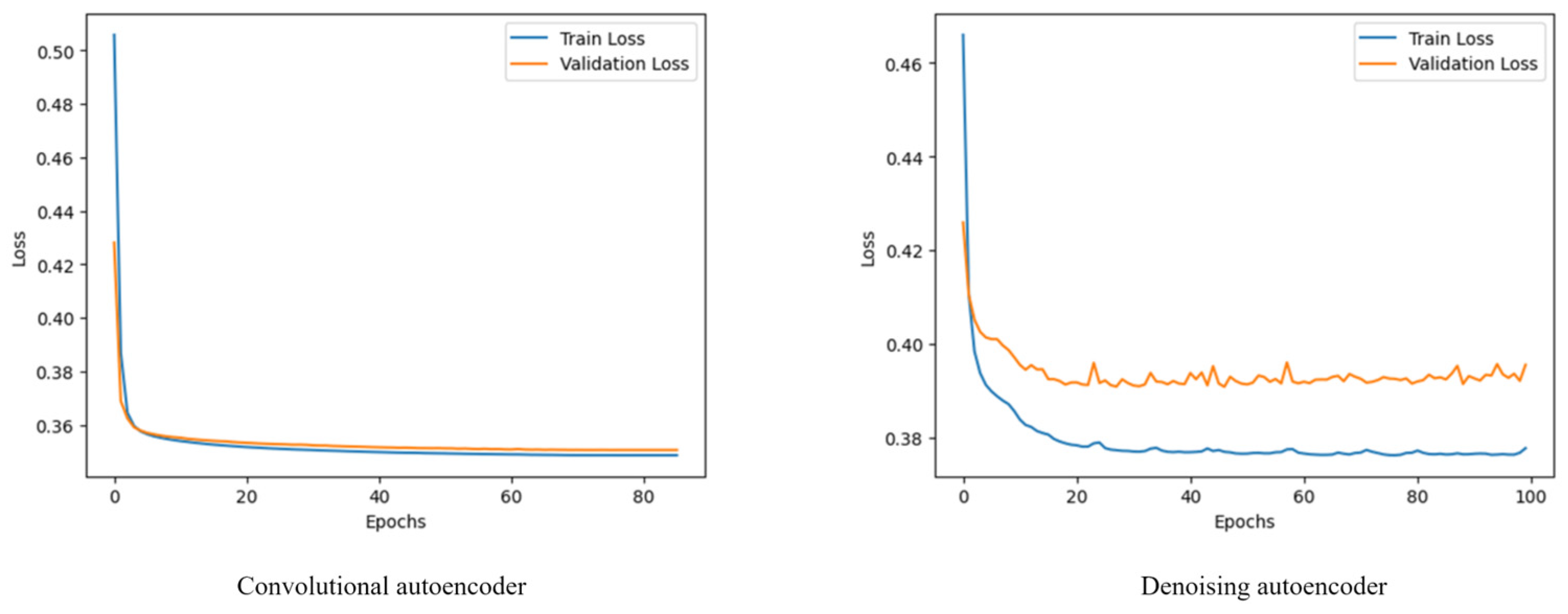
2.3. Autoencoders for Noise and Blur Mitigation
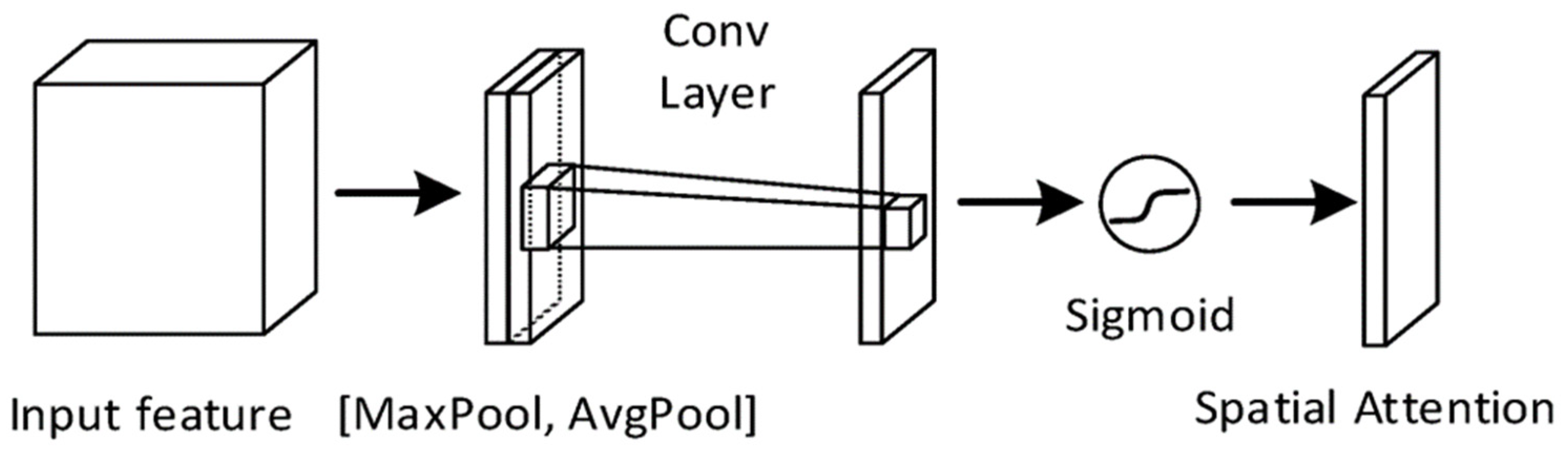
2.3. Noise Ablation Study
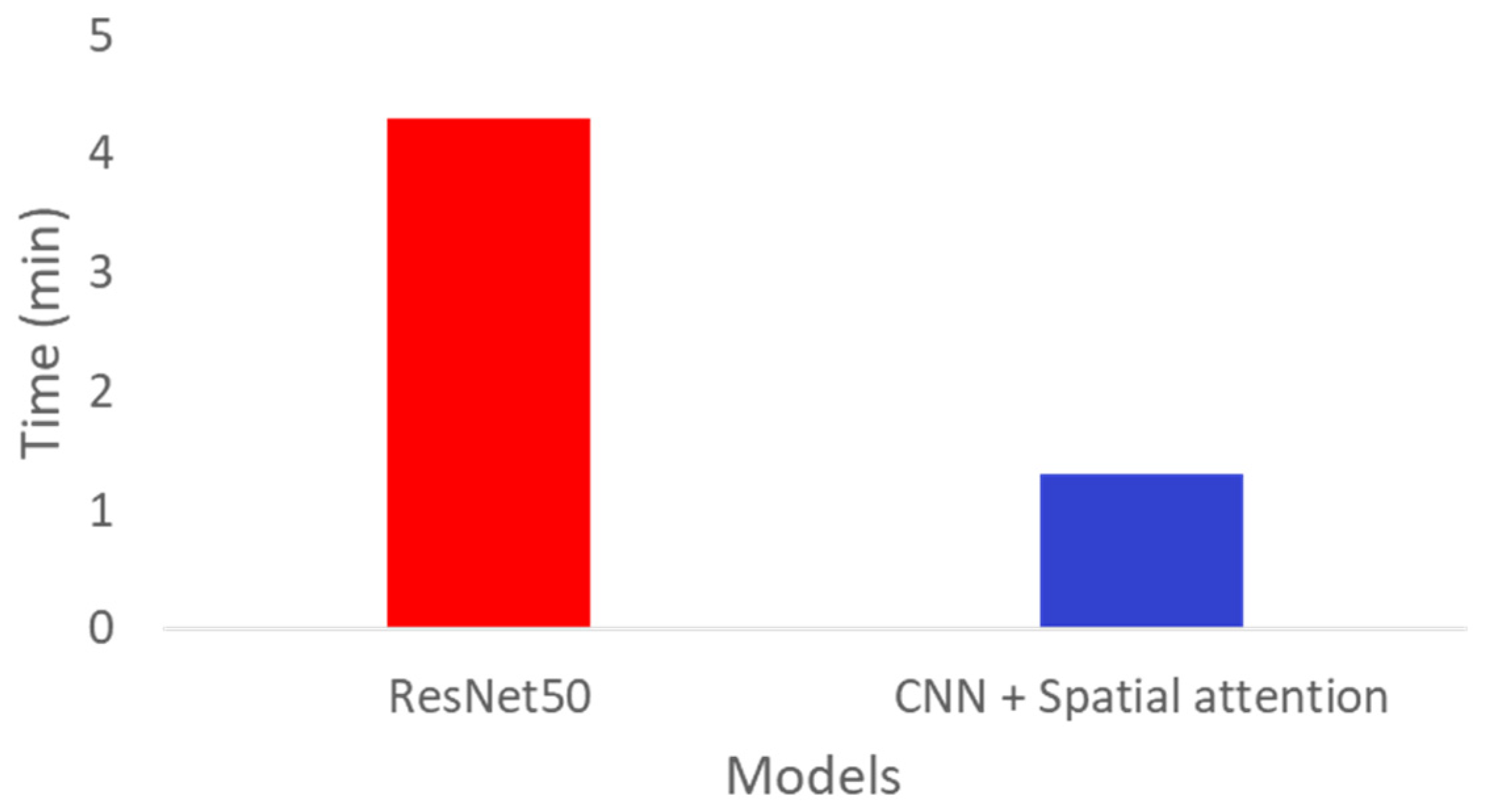
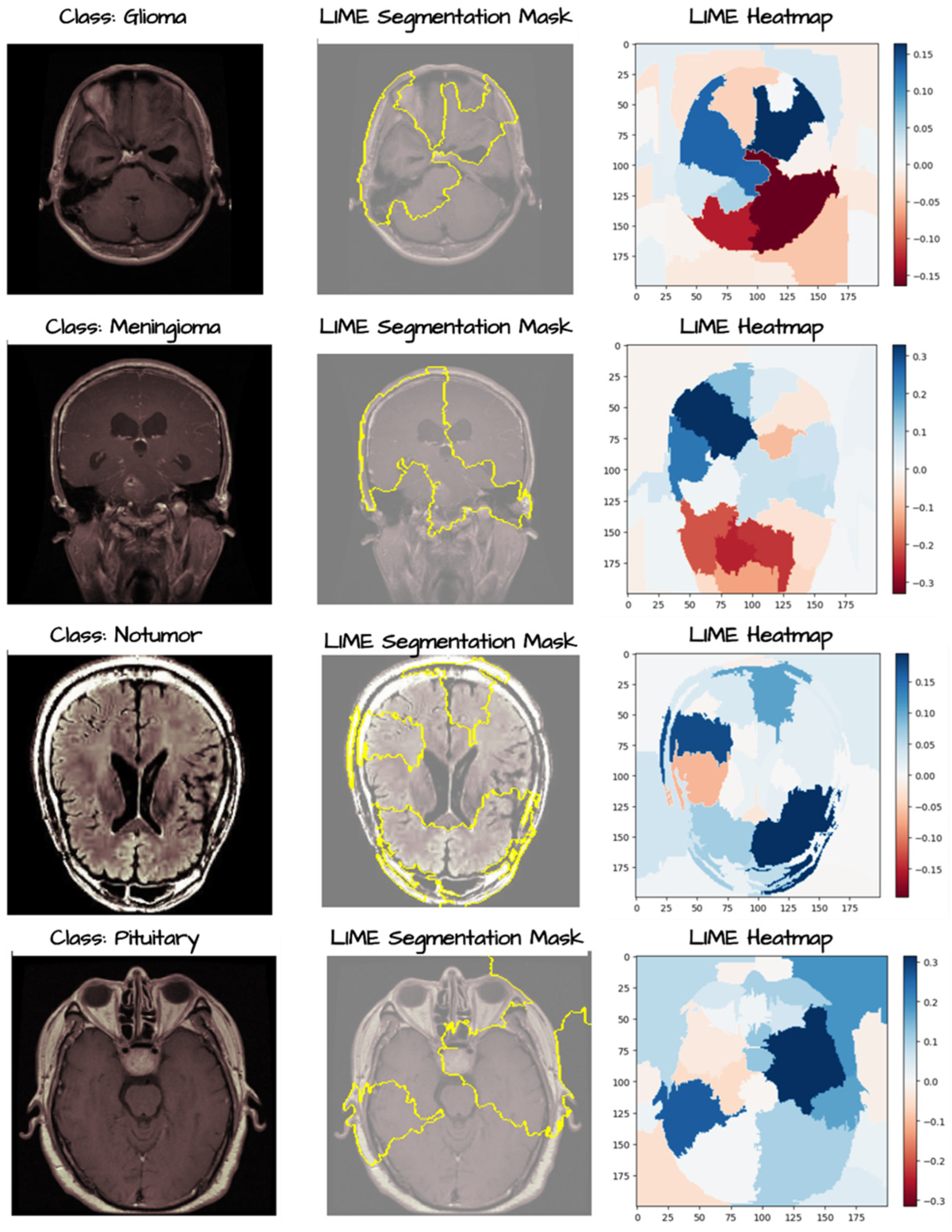
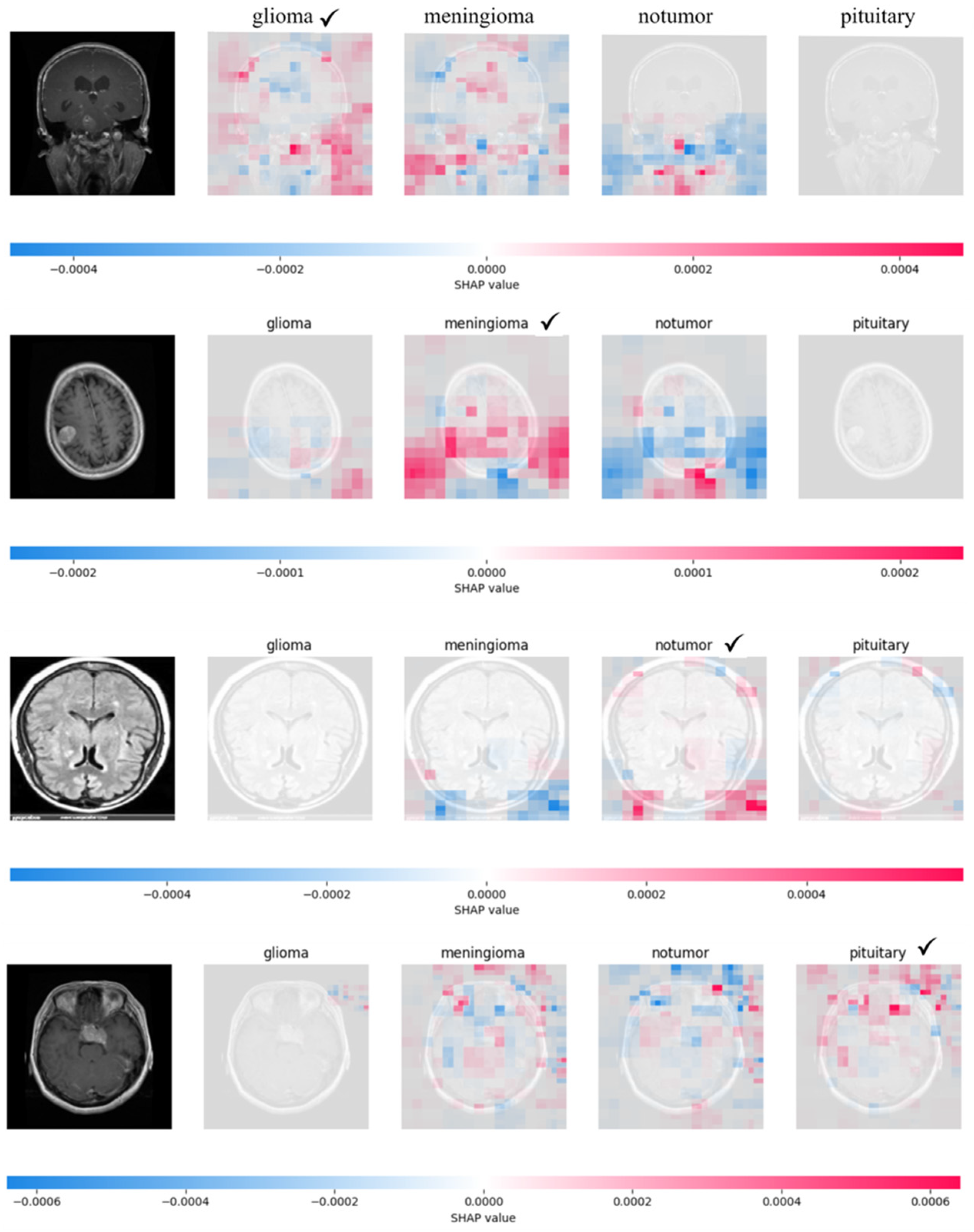
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nanyue, W. et al. Comparative study of pulse-diagnosis signals between 2 kinds of liver disease patients based on the combination of unsupervised learning and supervised learning. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine 2013, pp. 260-262. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. K., Yoo, T. K., Oh, E., & Kim, D. W. Osteoporosis risk prediction using machine learning and conventional methods. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society 2013, pp. 188-191. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Seixas, J. L., Barbon, S., & Mantovani, R. G. Pattern Recognition of Lower Member Skin Ulcers in Medical Images with Machine Learning Algorithms. 2015 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems 2015, pp. 50-53. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- van Tulder, G. & de Bruijne, M. Combining Generative and Discriminative Representation Learning for Lung CT Analysis With Convolutional Restricted Boltzmann Machines. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2016, 35(5), pp. 1262-1272. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Gerazov, B. & Conceicao, R. C. Deep learning for tumour classification in homogeneous breast tissue in medical microwave imaging. IEEE EUROCON 2017 - 17th International Conference on Smart Technologies 2017, pp. 564-569. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A., Mehra, R., & Saxena, A. Interactive Thyroid Disease Prediction System Using Machine Learning Technique. 2018 Fifth International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Grid Computing (PDGC) 2018, pp. 689-693. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, A., Pitoglou, S., Androutsou, T., Kostalas, E., Matsopoulos, G., & Koutsouris, D. MODELHealth: An Innovative Software Platform for Machine Learning in Healthcare Leveraging Indoor Localization Services. 2019 20th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM) 2019, pp. 443-446. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Tsarapatsani, K. et al. Machine Learning Models for Cardiovascular Disease Events Prediction. 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC) 2022, pp. 1066-1069. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.W., Khan, Z., Saad, N.M., Khan, D.M., Al-Khasawneh, M.A., Perveen, K., Qayyum, A., & Ali, S.S. Azhar. Segmentation of Liver Tumor in CT Scan Using ResU-Net. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 8650. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X., Fang, C., Fan, D.-J., Lin, X., Gao, F., & Li, G. Cross-Level Contrastive Learning and Consistency Constraint for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation. 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2022, pp. 1-5. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., Fan, Y., Zheng, H., Gao, J., Wei, X., & Yu, M. Balanced And Discriminative Contrastive Learning For Class-Imbalanced Medical Images. ICASSP 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) 2024, pp. 3735-3739. [Online. [CrossRef]
- Workman, T. E. et al. Explainable Deep Learning Applied to Understanding Opioid Use Disorder and Its Risk Factors. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) 2019, pp. 4883-4888. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M. S., Muhammad, G., & Guizani, N. Explainable AI and Mass Surveillance System-Based Healthcare Framework to Combat COVID-19 Like Pandemics. IEEE Network 2020, 34(4), pp. 126-132, July/August. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Marvin, G. & Alam, M. G. R. Explainable Feature Learning for Predicting Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) Admissions. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Computer and Information Technology for Health 2021, pp. 69-74. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Ammar, N. et al. SPACES: Explainable Multimodal AI for Active Surveillance, Diagnosis, and Management of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs). 2021 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) 2021, pp. 5843-5847. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- She, W. J. et al. Investigation of a Web-Based Explainable AI Screening for Prolonged Grief Disorder. IEEE Access 2022, 10, pp. 41164-41185. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A. & Alam, M. G. Rabiul. Explainable AI-based Maternal Health Risk Prediction using Machine Learning and Deep Learning. 2023 IEEE World AI IoT Congress (AIIoT) 2023, pp. 0013-0018. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Palkar, A., Dias, C. C., Chadaga, K., & Sampathila, N. Empowering Glioma Prognosis With Transparent Machine Learning and Interpretative Insights Using Explainable AI. IEEE Access 2024, 12, pp. 31697-31718. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Shinde, G., Mohapatra, R., Krishan, P., Garg, H., Prabhu, S., Das, S., Masum, M., & Sengupta, S. The State of Lithium-Ion Battery Health Prognostics in the CPS Era. to be submitted.
- Chen, D., Hong, W., & Zhou, X. Transformer Network for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries. IEEE Access 2022, 10, pp. 19621-19628. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J., Shen, Y., Liu, N., & Pan, Q. Frequency-Enhanced Channel-Spatial Attention Module for Grain Pests Classification. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2046. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., & Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier 2016. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1602.04938.
- Lundberg, S. & Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions 2017. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1705.07874.
- Radford, A. & Narasimhan, K. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training 2018.
- Touvron, H., Lavril, T., Izacard, G., Martinet, X., Lachaux, M.-A., Lacroix, T., Rozière, B., Goyal, N., Hambro, E., Azhar, F., Rodriguez, A., Joulin, A., Grave, E., & Lample, G. LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models 2023. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2302.13971.
- Singhal, K., Azizi, S., Tu, T. et al. Large language models encode clinical knowledge. Nature 620, 172–180 2023. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P., Perez, E., Piktus, A., Petroni, F., Karpukhin, V., Goyal, N., Küttler, H., Lewis, M., Yih, W.-t., Rocktäschel, T., Riedel, S., & Kiela, D. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks 2021. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2005.11401.
- Chen, Y., Zhang, M., Li, J., & Kuang, X. Adversarial Attacks and Defenses in Image Classification: A Practical Perspective. 2022 7th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC) 2022, pp. 424-430. [Online]. [CrossRef]

| Test accuracy (%) | ||
| Noise level (%) | ResNet-50 | Autoencoder + Resnet-50 |
| 15% | 88.94% | 94.51% |
| 20% | 81.69% | 83.60% |
| 30% | 73.07% | 77.96% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




