Submitted:
10 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Animals
Hepatic Non-Parenchymal Cell Isolation
Flow Cytometry Analysis
BMDM Isolation and LPS Stimulation
RNA and Protein Analyses
Mass Spectrometry-Based Analyses
Microbiota Analysis
Data Analysis
3. Results
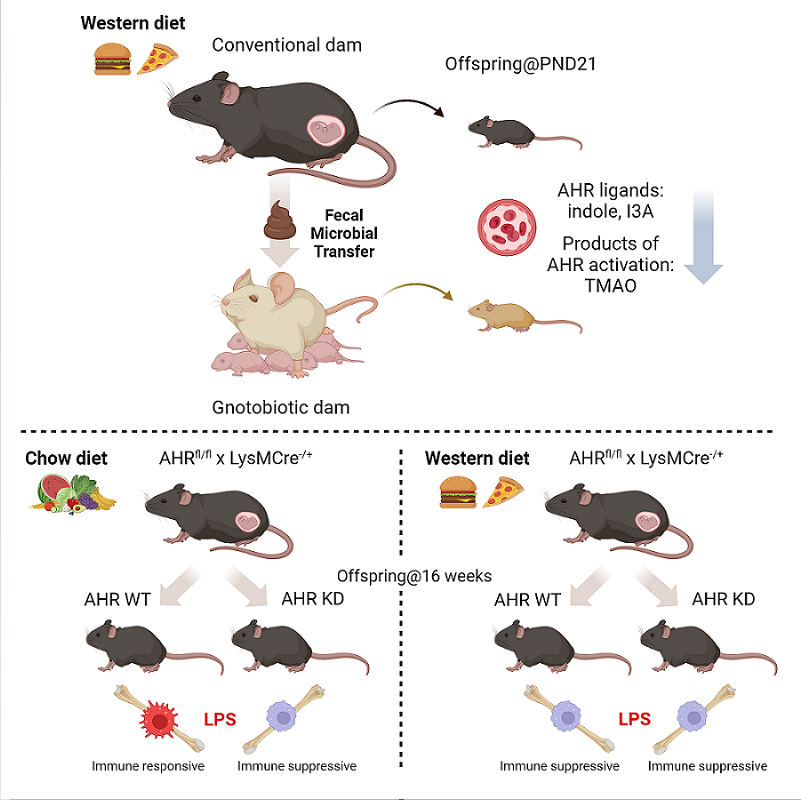
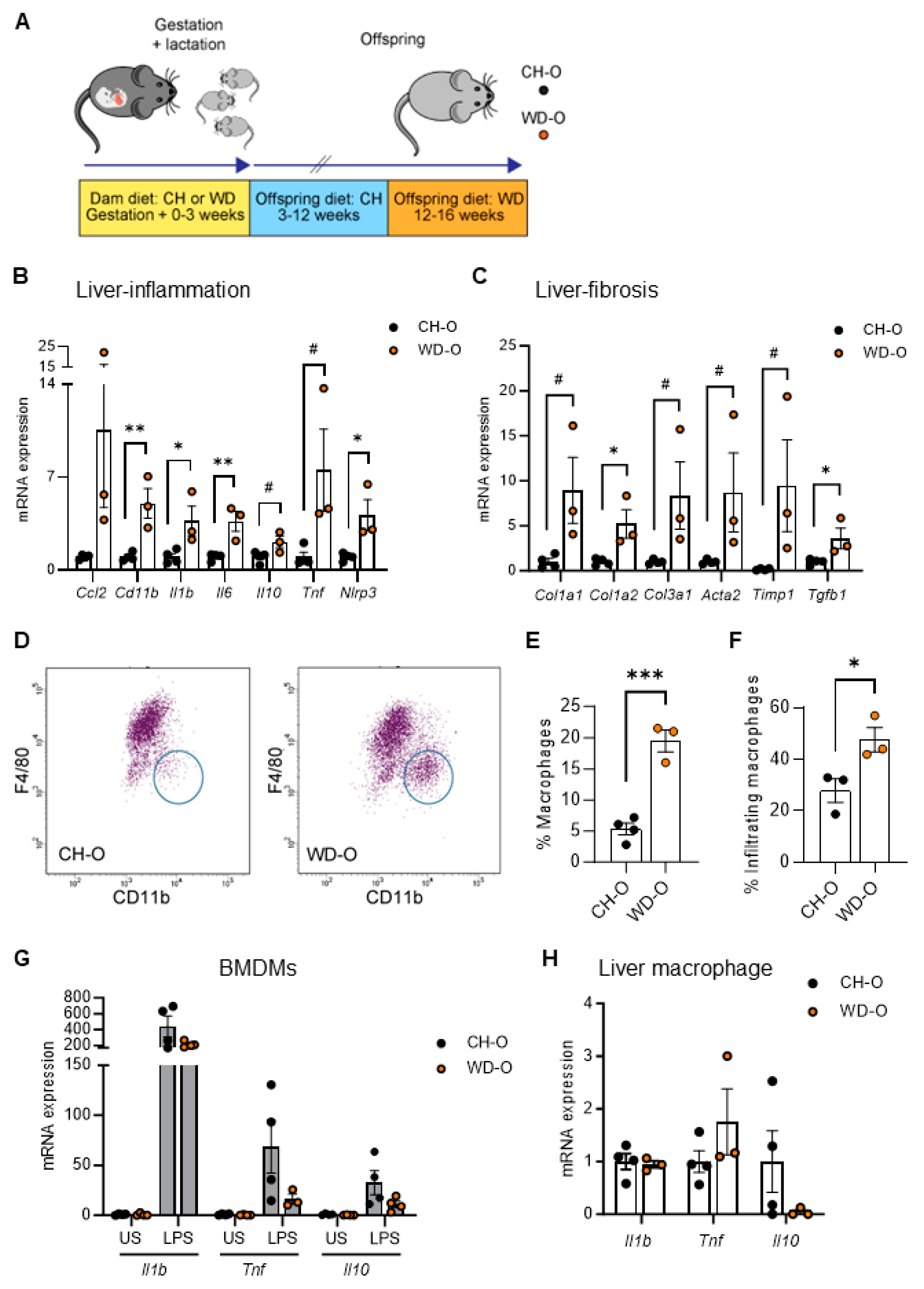
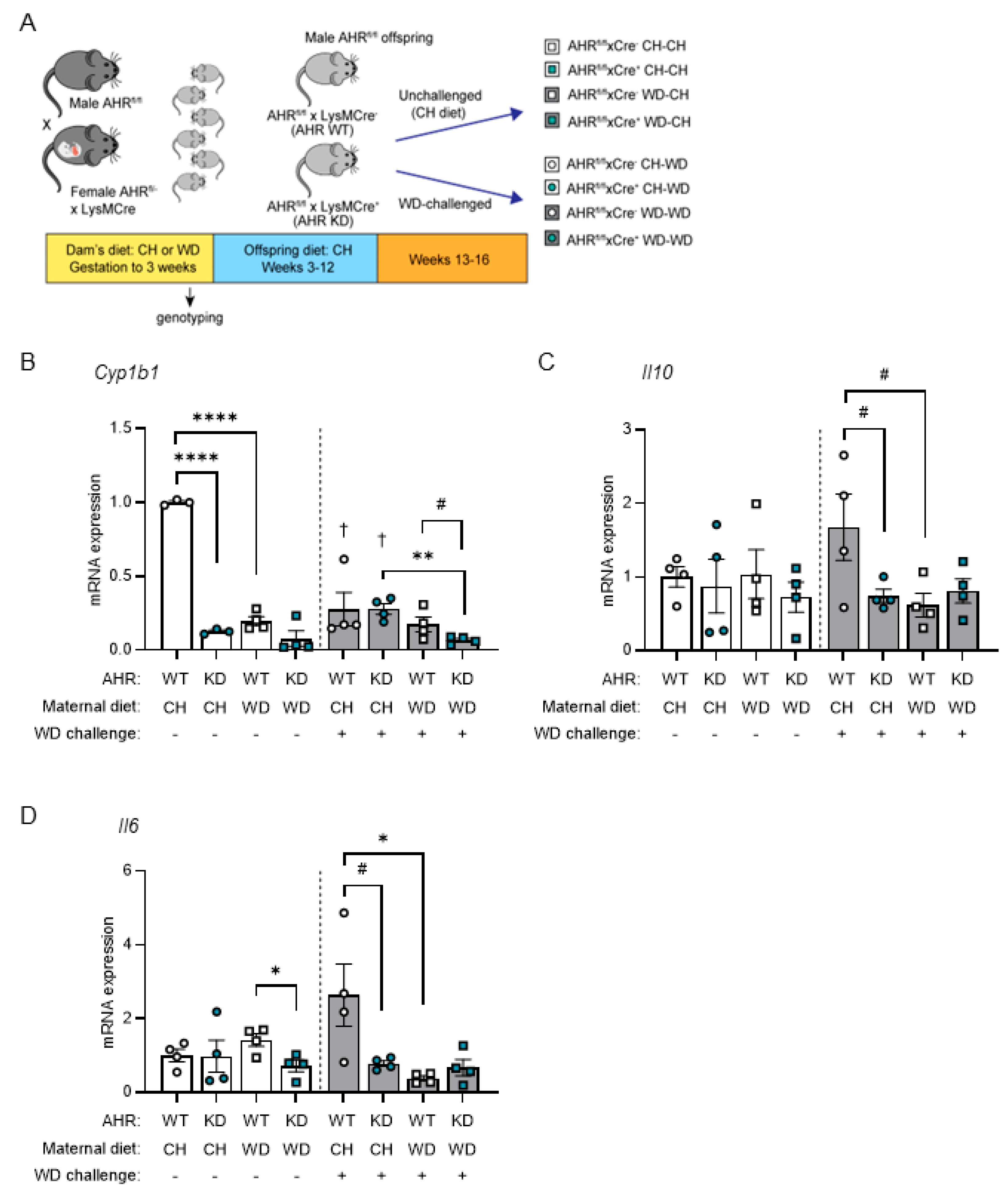
3.1. Maternal WD Induces Hepatic Macrophage Infiltration and Inflammation in WD-Challenged Adult Offspring
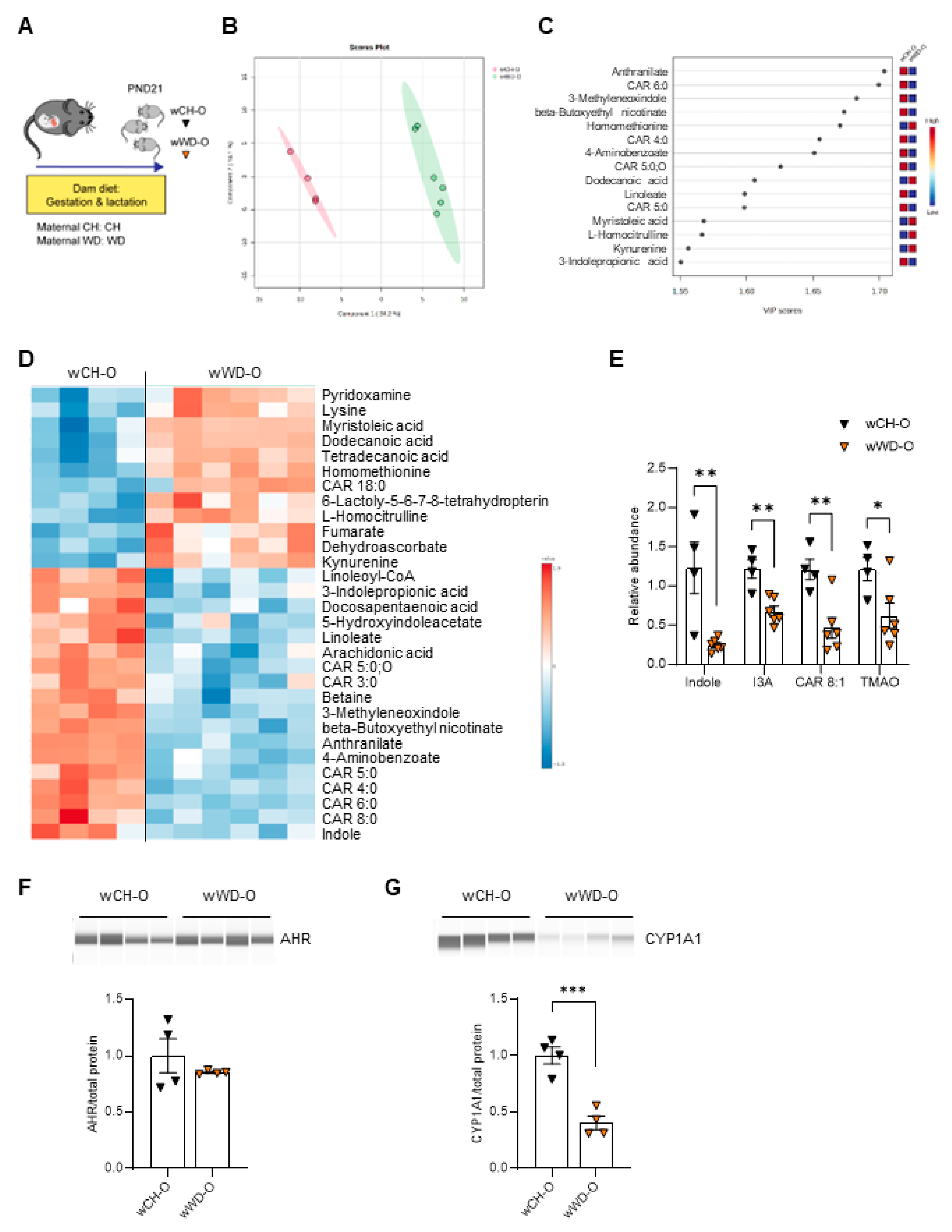
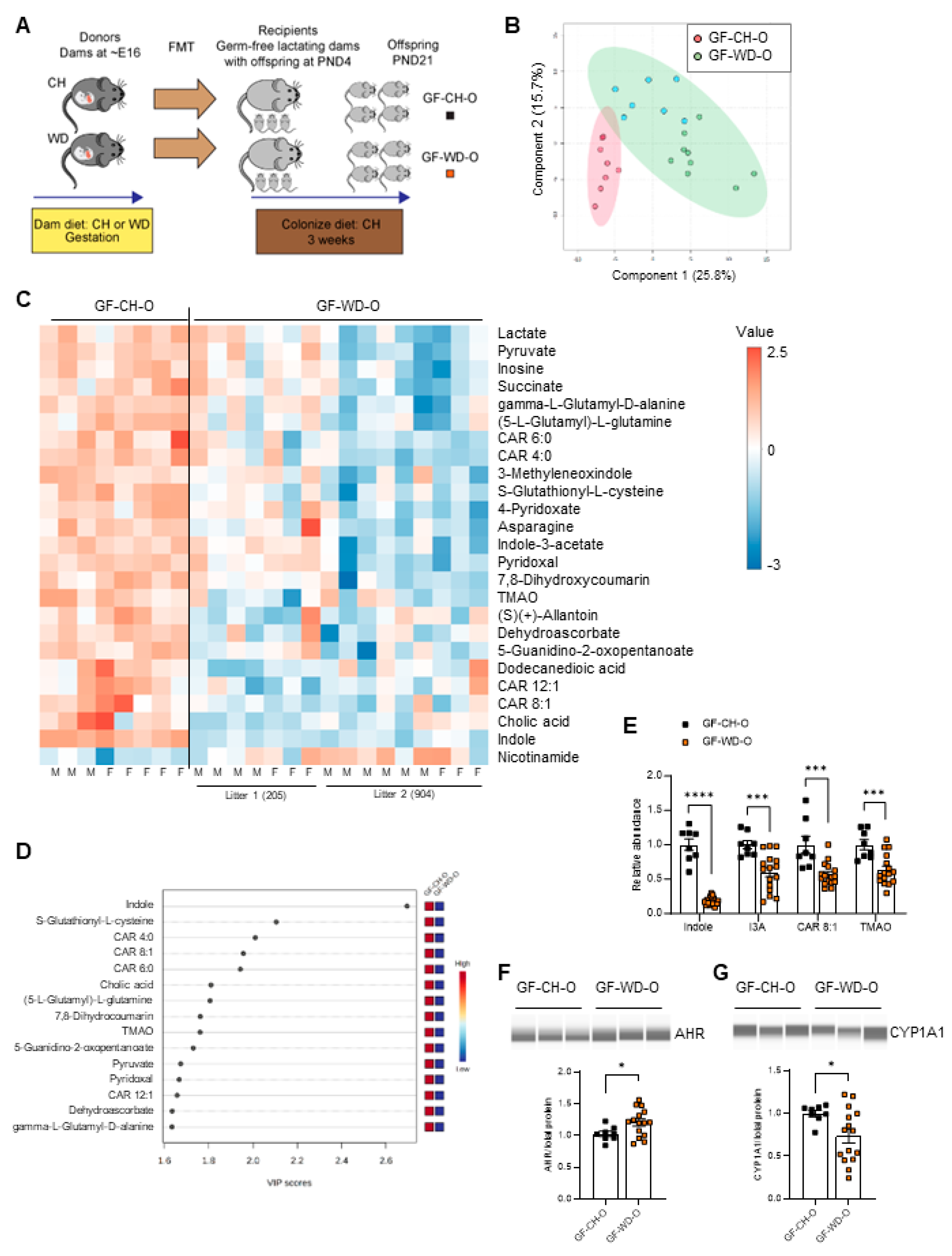
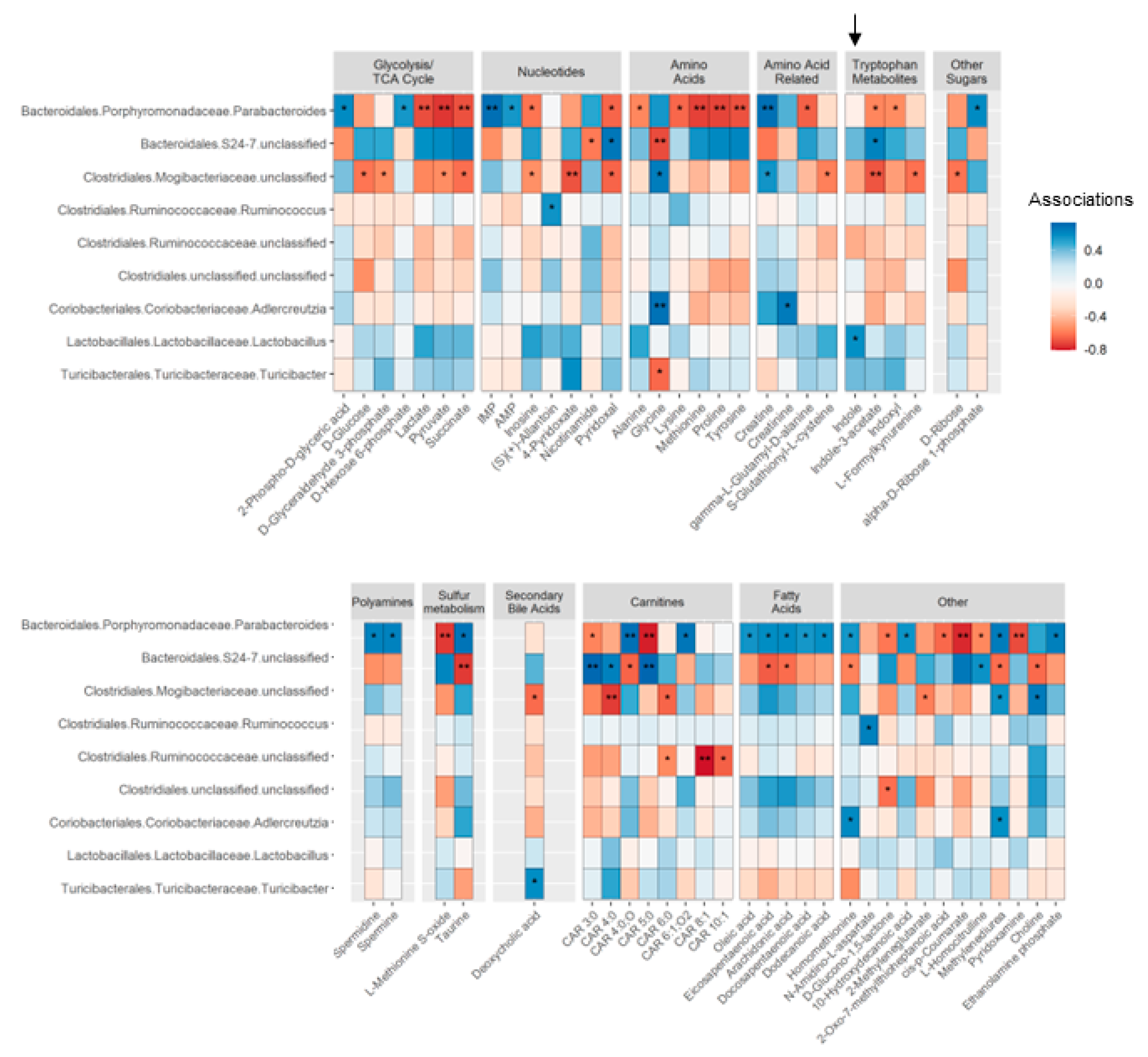
3.2. Circulating Bacteria-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites in Offspring Are Mediated by Maternal Gut Microbes
3.3. Lactobacillus Abundance Is Associated with Circulating Indole Levels
3.4. AHR Signaling in Myeloid Cells Is Impaired by Exposure to Maternal WD, with Tolerogenic Effects in BMDMs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cholankeril, G.; Perumpail, R.B.; Pham, E.A.; Ahmed, A.; Harrison, S.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: epidemiology, natural history, and diagnostic challenges. Hepatology 2016, 64, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.L.; Howe, L.D.; Jones, H.E.; Higgins, J.P.; Lawlor, D.A.; Fraser, A. The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0140908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, N.P.; Schwimmer, J.B. The progression and natural history of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayonrinde, O.T.; Oddy, W.H.; Adams, L.A.; Mori, T.A.; Beilin, L.J.; de Klerk, N.; Olynyk, J.K. Infant nutrition and maternal obesity influence the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellatorre, A.; Scherzinger, A.; Stamm, E.; Martinez, M.; Ringham, B.; Dabelea, D. Fetal overnutrition and adolescent hepatic fat fraction: the Exploring Perinatal Outcomes in Children Study. J. Pediatr. 2018, 192, 165–170.e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagström, H.; Simon, T.G.; Roelstraete, B.; Stephansson, O.; Söderling, J.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Maternal obesity increases the risk and severity of NAFLD in offspring. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, E.; Ibáñez, C.; Martínez-Samayoa, P.M.; Lomas-Soria, C.; Durand-Carbajal, M.; Rodríguez-González, G.L. Maternal obesity: lifelong metabolic outcomes for offspring from poor developmental trajectories during the perinatal period. Arch Med Res 2016, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Lawlor, D.A.; Callaway, M.; Macdonald-Wallis, C.; Sattar, N.; Fraser, A. Association of maternal diabetes/glycosuria and pre-pregnancy body mass index with offspring indicators of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Pediatr 2016, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, L.M.; Morrison, J.L.; Rattanatray, L.; Zhang, S.; Ozanne, S.E.; McMillen, I.C. The early origins of obesity and insulin resistance: timing, programming and mechanisms. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2016, 40, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouralidarane, A.; Soeda, J.; Visconti-Pugmire, C.; Samuelsson, A.M.; Pombo, J.; Maragkoudaki, X.; Butt, A.; Saraswati, R.; Novelli, M.; Fusai, G.; et al. Maternal obesity programs offspring nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by innate immune dysfunction in mice. Hepatology 2013, 58, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayol, S.A.; Simbi, B.H.; Fowkes, R.C.; Stickland, N.C. A maternal “junk food” diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rat offspring. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, K.D.; Cagampang, F.R.; Argenton, M.; Zhang, J.; Ethirajan, P.L.; Burdge, G.C.; Bateman, A.C.; Clough, G.F.; Poston, L.; Hanson, M.A.; et al. Maternal high-fat feeding primes steatohepatitis in adult mice offspring, involving mitochondrial dysfunction and altered lipogenesis gene expression. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorn, S.R.; Baquero, K.C.; Newsom, S.A.; El Kasmi, K.C.; Bergman, B.C.; Shulman, G.I.; Grove, K.L.; Friedman, J.E. Early life exposure to maternal insulin resistance has persistent effects on hepatic NAFLD in juvenile nonhuman primates. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2702–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Allen, J.; Hankey-Giblin, P.A. Ontogeny and polarization of macrophages in inflammation: blood monocytes versus tissue macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, H.; Lutaty, A.; Ariel, A. Macrophages, meta-inflammation, and immuno-metabolism. ScientificWorldJournal 2011, 11, 2509–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, A.; Günther, P.; Lauterbach, M.A.R.; Duewell, P.; Biswas, D.; Pelka, K.; Scholz, C.J.; Oosting, M.; Haendler, K.; Baßler, K.; et al. Western diet triggers NLRP3-dependent innate immune reprogramming. Cell 2018, 172, 162–175.e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Barreiro, L.B.; Chavakis, T.; Divangahi, M.; Fuchs, E.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Mhlanga, M.M.; Mulder, W.J.M.; et al. Defining trained immunity and its role in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2020, 20, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.L.; Hargreaves, D.C.; Medzhitov, R. Gene-specific control of inflammation by TLR-induced chromatin modifications. Nature 2007, 447, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, K.; You, C.; Kwon, G.; Kang, K. Two faces of macrophages: Training and tolerance. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.; Harmon, C.; O’Farrelly, C. Liver immunology and its role in inflammation and homeostasis. Cell Mol Immunol 2016, 13, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Lau, J.K.; Fu, K.; Lau, H.C.; Xu, W.; Chu, E.S.; Lan, H.; Yu, J. Bone marrow-derived macrophage contributes to fibrosing steatohepatitis through activating hepatic stellate cells. J Pathol 2019, 248, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luci, C.; Bourinet, M.; Leclère, P.S.; Anty, R.; Gual, P. Chronic inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 597648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, M.J.; Frank, D.N.; Friedman, J.E. Early microbes modify immune system development and metabolic homeostasis- the “Restaurant” hypothesis revisited. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2017, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, S.; Shen, N.; Wu, H.C.; Clemente, J.C. The microbiome in early life: implications for health outcomes. Nat Med 2016, 22, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubin, J.B.; Green, J.; Maddux, S.; Denu, L.; Duranova, T.; Lanza, M.; Wynosky-Dolfi, M.; Flores, J.N.; Grimes, L.P.; Brodsky, I.E.; et al. Arresting microbiome development limits immune system maturation and resistance to infection in mice. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 554–570.e557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.E.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Alfonso-Garcia, A.; Fast, A.; Janssen, R.C.; Soderborg, T.K.; Anderson, A.L.; Reisz, J.A.; D’Alessandro, A.; Frank, D.N.; et al. Pyrroloquinoline quinone prevents developmental programming of microbial dysbiosis and macrophage polarization to attenuate liver fibrosis in offspring of obese mice. Hepatol Commun 2018, 2, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankhade, U.D.; Zhong, Y.; Kang, P.; Alfaro, M.; Chintapalli, S.V.; Thakali, K.M.; Shankar, K. Enhanced offspring predisposition to steatohepatitis with maternal high-fat diet is associated with epigenetic and microbiome alterations. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0175675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, I.A.; Fontecilla, N.M.; Janelsins, B.M.; Vithayathil, P.J.; Segre, J.A.; Datta, S.K. Parental dietary fat intake alters offspring microbiome and immunity. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3200–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, A.; Clément, K.; Sokol, H. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as central regulators in metabolic disorders. Gut 2021, 70, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips-Farfán, B.; Gómez-Chávez, F.; Medina-Torres, E.A.; Vargas-Villavicencio, J.A.; Carvajal-Aguilera, K.; Camacho, L. Microbiota signals during the neonatal period forge life-long immune responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carambia, A.; Schuran, F.A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in liver inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 2021, 43, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natividad, J.M.; Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Lamas, B.; Jarry, A.C.; Martin, R.; Michel, M.L.; Chong-Nguyen, C.; Roussel, R.; Straube, M.; et al. Impaired aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand production by the gut microbiota is a key factor in metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab 2018, 28, 737–749.e734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, N.Y.; Friedman, J.E.; Joshi, A.D. Role of hepatic aryl hydrocarbon receptor in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Receptors (Basel) 2023, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walisser, J.A.; Glover, E.; Pande, K.; Liss, A.L.; Bradfield, C.A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent liver development and hepatotoxicity are mediated by different cell types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005, 102, 17858–17863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubbrey, A.L.; Allison, K.C.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Jakubzick, C.V.; Janssen, W.J. Promoter specificity and efficacy in conditional and inducible transgenic targeting of lung macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, B.E.; Burkhardt, C.; Reith, W.; Renkawitz, R.; Forster, I. Conditional gene targeting in macrophages and granulocytes using LysMcre mice. Transgenic Res 1999, 8, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.P.; Cheng, L.; Ju, C. Identification and characterization of infiltrating macrophages in acetaminophen-induced liver injury. J Leukoc Biol 2008, 84, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kasmi, K.C.; Anderson, A.L.; Devereaux, M.W.; Vue, P.M.; Zhang, W.; Setchell, K.D.; Karpen, S.J.; Sokol, R.J. Phytosterols promote liver injury and Kupffer cell activation in parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. Sci Transl Med 2013, 5, 206ra137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerwagen, M.J.; Stewart, M.S.; de la Houssaye, B.A.; Janssen, R.C.; Friedman, J.E. Transgenic increase in n-3/n-6 fatty acid ratio reduces maternal obesity-associated inflammation and limits adverse developmental programming in mice. PLoS One 2013, 8, e67791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemkov, T.; Reisz, J.A.; Gehrke, S.; Hansen, K.C.; D’Alessandro, A. High-throughput metabolomics: Isocratic and gradient mass spectrometry-based methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1978, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.; Rice, S.; Stefanoni, D.; Wilkerson, R.B.; Nemkov, T.; Reisz, J.A.; Hansen, K.C.; Lucas, A.; Cabrales, P.; Drew, K.; et al. Red blood cell metabolic responses to Torpor and Arousal in the hibernator arctic ground squirrel. J Proteome Res 2019, 18, 1827–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemas, D.J.; Young, B.E.; Baker, P.R., 2nd; Tomczik, A.C.; Soderborg, T.K.; Hernandez, T.L.; de la Houssaye, B.A.; Robertson, C.E.; Rudolph, M.C.; Ir, D.; et al. Alterations in human milk leptin and insulin are associated with early changes in the infant intestinal microbiome. Am J Clin Nutr 2016, 103, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, K.Y.; Mandala, A.; Janssen, R.C.; Gurung, S.; Trammell, M.; Day, M.W.; Brush, R.S.; Papin, J.F.; Dyer, D.W.; Agbaga, M.-P.; et al. Western diet-induced shifts in the maternal microbiome are associated with altered microRNA expression in baboon placenta and fetal liver. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc 2022, 3, 945768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package, 2.6-2; 2022.
- Gloor, G.B.; Macklaim, J.M.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J. Microbiome datasets are compositional: And this is not optional. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J R Statist Soc 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Dongiovanni, P.; Corey, K.E.; Wang, X.; Shmarakov, I.O.; Zheng, Z.; Kasikara, C.; Davra, V.; Meroni, M.; Chung, R.T.; et al. Macrophage MerTK promotes liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cell Metab 2020, 31, 406–421.e407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenkel, O.; Tacke, F. Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2017, 17, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, M.J.; Bouladoux, N.; Belkaid, Y. Intestinal microbiota: shaping local and systemic immune responses. Semin Immunol 2012, 24, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Wu, E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Mu, A.; Wallace, M.; Gengatharan, J.M.; Furst, A.J.; Bode, L.; Metallo, C.M.; Ayres, J.S. Microbiota control of maternal behavior regulates early postnatal growth of offspring. Sci Adv 2021, 7, eabe6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Anfora, A.T.; Liu, J.; Schultz, P.G.; Lesley, S.A.; Peters, E.C.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 3698–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frericks, M.; Meissner, M.; Esser, C. Microarray analysis of the AHR system: tissue-specific flexibility in signal and target genes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 220, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennis, M.; Cavanaugh, C.R.; Leo, G.C.; Mabus, J.R.; Lenhard, J.; Hornby, P.J. Microbiota-derived tryptophan indoles increase after gastric bypass surgery and reduce intestinal permeability in vitro and in vivo. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambrova, M.; Makrecka-Kuka, M.; Kuka, J.; Vilskersts, R.; Nordberg, D.; Attwood, M.M.; Smesny, S.; Sen, Z.D.; Guo, A.C.; Oler, E.; et al. Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, biomarkers, therapeutic potential, drug targets, and clinical trials. Pharmacol Rev 2022, 74, 506–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koves, T.R.; Ussher, J.R.; Noland, R.C.; Slentz, D.; Mosedale, M.; Ilkayeva, O.; Bain, J.; Stevens, R.; Dyck, J.R.; Newgard, C.B.; et al. Mitochondrial overload and incomplete fatty acid oxidation contribute to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Cell Metab 2008, 7, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyeth, F.J. The effects of acids, alkalies, and sugars on the growth and indole formation of Bacillus coli: A report to the Medical Research Committee. Biochem J 1919, 13, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, C.; Candal-Uslu, C.; Özhanlı, H.; Arslan-Tontul, S.; Erbas, M. Modulating of food glycemic response by lactic acid bacteria. Food Bioscience 2022, 47, 101685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, Z.; Poulíková, K.; Mani, S. Indole scaffolds as a promising class of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands. Eur J Med Chem 2021, 215, 113231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.E.; Sun, L. Targeting the IDO1/TDO2-KYN-AhR pathway for cancer immunotherapy - challenges and ppportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2018, 39, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, H.H.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Byun, H.M.; Cantoral, A.; Just, A.C.; Pantic, I.; Solano-Gonzalez, M.; Svensson, K.; Tamayo y Ortiz, M.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Offspring DNA methylation of the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor repressor gene is associated with maternal BMI, gestational age, and birth weight. Epigenetics 2015, 10, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, N.N.; Abd-Elwahab, G.T.; Tawfiq, A.A.; Abdelgawad, H.M. Potential role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling in childhood obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 2020, 1865, 158714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez de Agüero, M.; Ganal-Vonarburg, S.C.; Fuhrer, T.; Rupp, S.; Uchimura, Y.; Li, H.; Steinert, A.; Heikenwalder, M.; Hapfelmeier, S.; Sauer, U.; et al. The maternal microbiota drives early postnatal innate immune development. Science 2016, 351, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, M.; Caligiuri, A.; Raggi, C.; Navari, N.; Piombanti, B.; Di Maira, G.; Rovida, E.; Piccinni, M.P.; Lombardelli, L.; Logiodice, F.; et al. Macrophage MerTK promotes profibrogenic cross-talk with hepatic stellate cells via soluble mediators. JHEP Rep 2022, 4, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, E.H.; Wang, X.; Balaji, S.; Butte, M.J.; Bollyky, P.L.; Keswani, S.G. The role of the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 in tissue fibrosis. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2020, 9, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensollen, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Blumberg, R.S. How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes the immune system. Science 2016, 352, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nabhani, Z.; Eberl, G. Imprinting of the immune system by the microbiota early in life. Mucosal Immunol 2020, 13, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszak, T.; An, D.; Zeissig, S.; Vera, M.P.; Richter, J.; Franke, A.; Glickman, J.N.; Siebert, R.; Baron, R.M.; Kasper, D.L.; et al. Microbial exposure during early life has persistent effects on natural killer T cell function. Science 2012, 336, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nabhani, Z.; Dulauroy, S.; Marques, R.; Cousu, C.; Al Bounny, S.; Déjardin, F.; Sparwasser, T.; Bérard, M.; Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Eberl, G. A weaning reaction to microbiota is required for resistance to immunopathologies in the adult. Immunity 2019, 50, 1276–1288.e1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoop, K.A.; Gustafsson, J.K.; McDonald, K.G.; Kulkarni, D.H.; Coughlin, P.E.; McCrate, S.; Kim, D.; Hsieh, C.S.; Hogan, S.P.; Elson, C.O.; et al. Microbial antigen encounter during a preweaning interval is critical for tolerance to gut bacteria. Sci Immunol 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, H.; Goulet, P.O.; Mashiko, S.; Desjardins, J.; Pérez, G.; Koenig, M.; Senécal, J.L.; Constante, M.; Santos, M.M.; Sarfati, M. Early-life antibiotic exposure causes intestinal dysbiosis and exacerbates skin and lung pathology in experimental systemic sclerosis. J Invest Dermatol 2017, 137, 2316–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, R. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites maintain gut and systemic homeostasis. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalowo, O.E.; Adegoye, G.A.; Obuotor, T.M. Microbial-based bioactive compounds to alleviate inflammation in obesity. Curr Issues Mol Biol 2024, 46, 1810–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J. The dynamic effects of maternal high-calorie diet on glycolipid metabolism and gut microbiota from weaning to adulthood in offspring mice. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 941969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Jia, Y.; Shi, J.; Tong, Z.; Fang, D.; Yang, B.; Su, C.; Li, R.; Xiao, X.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in high-fat-diet-fed mice are associated with antibiotic tolerance. Nat Microbiol 2021, 6, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Ding, Y.; Saedi, N.; Choi, M.; Sridharan, G.V.; Sherr, D.H.; Yarmush, M.L.; Alaniz, R.C.; Jayaraman, A.; Lee, K. Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites modulate inflammatory response in hepatocytes and macrophages. Cell Rep 2018, 23, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yanagi, K.; Yang, F.; Callaway, E.; Cheng, C.; Hensel, M.E.; Menon, R.; Alaniz, R.C.; Lee, K.; Jayaraman, A. Oral supplementation of gut microbial metabolite indole-3-acetate alleviates diet-induced steatosis and inflammation in mice. Elife 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malany, K.; Li, X.; Vogel, C.F.A.; Ehrlich, A.K. Mechanisms underlying aryl hydrocarbon receptor-driven divergent macrophage function. Toxicol Sci 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezaveh, K.; Shinde, R.S.; Klötgen, A.; Halaby, M.J.; Lamorte, S.; Ciudad, M.T.; Quevedo, R.; Neufeld, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Jin, R.; et al. Tryptophan-derived microbial metabolites activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in tumor-associated macrophages to suppress anti-tumor immunity. Immunity 2022, 55, 324–340.e328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamah, W.H.; Busbee, P.B.; Alghetaa, H.; Abdulla, O.A.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P. AhR activation leads to alterations in the gut microbiome with consequent effect on induction of myeloid derived suppressor cells in a CXCR2-dependent manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celius, T.; Roblin, S.; Harper, P.A.; Matthews, J.; Boutros, P.C.; Pohjanvirta, R.; Okey, A.B. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent induction of flavin-containing monooxygenase mRNAs in mouse liver. Drug Metab Dispos 2008, 36, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconi, E.; Palma, G.; De Biase, D.; Luciano, A.; Barbieri, M.; de Nigris, F.; Bruzzese, F. Microbiota effect on trimethylamine N-oxide production: From cancer to fitness-a practical preventing recommendation and therapies. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Henderson, A.; Petriello, M.C.; Romano, K.A.; Gearing, M.; Miao, J.; Schell, M.; Sandoval-Espinola, W.J.; Tao, J.; Sha, B.; et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide binds and activates PERK to promote metabolic dysfunction. Cell Metab 2019, 30, 1141–1151.e1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, I.A.; Nichols, R.G.; Zhang, L.; Patterson, A.D.; Perdew, G.H. Expression of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor contributes to the establishment of intestinal microbial community structure in mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korecka, A.; Dona, A.; Lahiri, S.; Tett, A.J.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Braniste, V.; D’Arienzo, R.; Abbaspour, A.; Reichardt, N.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y.; et al. Bidirectional communication between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and the microbiome tunes host metabolism. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2016, 2, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, W.; Osborn, L.J.; Banerjee, R.; Horak, A.; Fung, K.K.; Orabi, D.; Chan, E.R.; Sangwan, N.; Wang, Z.; Brown, J.M. Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3) is critical for dioxin-induced reorganization of the gut microbiome and host insulin sensitivity. Metabolites 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakhamaneshi, M.S.; Abdolahi, A.; Vahabzadeh, Z.; Abdi, M.; Andalibi, P. Toll-like receptor 4: A macrophage cell surface receptor is activated by trimethylamine-N-oxide. Cell J 2021, 23, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino-Jonapa, L.A.; Espinoza-Palacios, Y.; Escalona-Montaño, A.R.; Hernández-Ruiz, P.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Amedei, A.; Aguirre-García, M.M. Contribution of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) to chronic inflammatory and degenerative diseases. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GF dams | GF weanlings | Conventional weanlings | ||||||||||
| FC | Log2(FC) | Raw p value | Log10(p) | FC | Log2(FC) | Raw p value | Log10(p) | FC | Log2(FC) | Raw p value | Log10(p) | |
| Indole | 0.13 | -2.90 | 0.0143 | 1.84 | 0.18 | -2.48 | 7E-12 | 11.18 | 0.20 | -2.32 | 0.0022 | 2.66 |
| I3A | 0.54 | -0.89 | 0.0929 | 1.03 | 0.60 | -0.74 | 0.0055 | 2.26 | 0.55 | -0.85 | 0.0042 | 2.38 |
| TMAO | 0.34 | -1.56 | 0.0704 | 1.15 | 0.64 | -0.66 | 0.0014 | 2.86 | 0.51 | -0.97 | 0.0373 | 1.43 |
| CAR 8:1 | 0.59 | -0.77 | 0.0008 | 3.07 | 0.57 | -0.82 | 0.0002 | 3.64 | 0.38 | -1.38 | 0.0104 | 1.98 |
| Nicotinamide | 1.80 | 0.85 | 0.0217 | 1.66 | 2.68 | 1.42 | 0.0040 | 2.40 | 2.34 | 1.23 | 0.0170 | 1.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





