1. Introduction
Gene expression in medulloblastoma (MB) has been studied in terms of major histopathological types as well as molecular subgroups (1). These studies have generated large publicly available datasets that can be used to mine information on genes that potentially can be targeted for therapeutic purposes. In 2012, a consensus study from a number of laboratories identified four major molecular subgroups of MB: Group 3, Group 4, SHH, and WNT (2). In 2017, Cavalli et al. published a landmark study (3) which confirmed the four major molecular subgroups of MB, and defined subtypes within each subgroup. In 2019, Weishaupt et al. integrated and normalized 23 transcriptome datasets which allowed for the comparison of the gene expression values in MB subgroups to the values from a non-tumor group (4).
Several chromosomal aberrations have been related to MB. Thompson et al. (2006) (1) noted that downregulated genes on chromosome 6 were over-represented among all downregulated genes in MB and predicted a loss of a copy of chromosome 6 in the WNT group of MB. These findings were further confirmed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis (1) and replicated by subsequent studies (5, 6). Cavalli et al. (2017) reported monosomy of chromosome 6 in 48 of the 49 subjects from the WNTα subtype (3).
Thompson et al (2006) also detected deletions of chromosome 17p in one of their MB groups, in the context of isochromosome 17 for most of the cases (1). Previous studies have also reported isochromosome 17, in MB Groups 3 and 4 (2, 3, 7). Other chromosomal aberrations in MB include deletions of chromosomes 9 and 10, in the SHH group (2), isolated deletions of 17p (8), and copy number gains of 17p in MB cell lines (9). These chromosomal aberrations have been noted in various reports on MB subgroups including the report of Cavalli et al. (3).
The report of Cavalli et al. (3) included survival curves for each of the MB subgroups and subtypes. Zhu et al. (10), on the other hand, identified a 12 gene-signature, independent of MB subgroups and subtypes, to predict survival.
Herein we examined the publicly available MB gene expression data to identify genes significantly associated with overall survival, using the Cox proportional hazards regression model. We find that the survival related genes (SRGs) are over-represented on chromosomes 6 and 17. Secondly, we provide detailed gene expression profiles of these SRGs on these two chromosomes and relate them to the MB subgroups and subtypes described by Cavalli et al. (2017) (3), where possible. Furthermore, we relate the transcriptome findings to the literature on monosomy 6 and isochromosome 17 in MB (1, 11, 12). Finally, we provide information on the major biological pathways represented by the SRGs on these chromosomes and suggest several potential therapeutic targets. This is the first comprehensive analysis of SRGs on chromosomes 6 and 17.
2. METHODS
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
2.1. Data Sources
The Cavalli dataset: The gene expression dataset for 763 MB samples by Cavalli et al (2017) (3) was downloaded from the R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform (
https://hgserver1.amc.nl). The gene expression profile for each primary MB tumor sample was generated from the Affymetrix Human Gene 1.1 ST Array. Clinical data, such as age, overall survival status, and survival years, were also included in the downloaded file.
The Swartling dataset: For some of the survival related genes (see below), we also presented their gene expression levels by the MB molecular subgroups using the data from Weishaupt et al. (2019) (i.e. the Swartling dataset in the R2 Genomics) (4). This dataset contains normalized gene expression profiles from 1,641 samples, including 1,350 primary MB samples and 291 normal brain samples (cerebellum), from 23 transcription datasets (4). The normal cerebellar tissues served as controls in this meta-analysis.
2.2. Data Analyses
With the Cavalli dataset, the Cox proportional hazards regression model was used for the relationships between the overall survival status (alive vs. not alive) and gene expression for each gene with age as the covariate. Survival year was used as the time variable. The function coxph from the R statistical package Survival was applied for this model. A gene was considered statistically significant at the Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p value <0.05.
After identifying the survival related genes (SRGs), the genes were grouped by their chromosome and cytogenetic band. The chromosomal location was determined with the gene symbol checker of the Human Genome Nomenclature Committee (HGNC). Since the total number of protein coding genes differs by chromosome, we expressed the data as a proportion of the number of SRGs to the total number of protein coding genes for each chromosome. Using the two-sample z-test for the equality of two observed proportions, we tested if chromosomes 6 and 17 contained significantly more SRGs compared to the other chromosomes.
The cox proportional hazards regression model was also used to determine SRGs after the removal of individuals with known somatic copy number alterations (SCNAs) in chromosome 6 and chromosome 17.
2.3. Kaplan Meier and pathway analysis of SRGs.
Subsequently, we presented heatmaps of gene expression profiles of the SRGs located on chromosomes 6 and 17 by molecular subgroup and subtype, using the R2 Genomics Analysis and Visualization Platform. For the most significant SRGs, Kaplan Meier curves were presented using the platform’s KaplanScan, which separates the individuals into high vs. low gene expression groups based on an optimum survival cut-off for a gene. Finally, pathway analyses were conducted for all SRGs and for those on chromosomes 6 and 17 using Cytoscape 3.8.2, with the ClueGO plug-in (13). Our list of SRGs were scanned for oncogenes using the list at
https://www.oncokb.org/cancer-genes and
https://ongene.bioinfo-minzhao.org/ongene_human.txt.
3. RESULTS
Of the 763 samples from the MB dataset by Cavalli et al. (3), 467 were labeled as alive, 165 as not alive, and 131 with missing survival information.
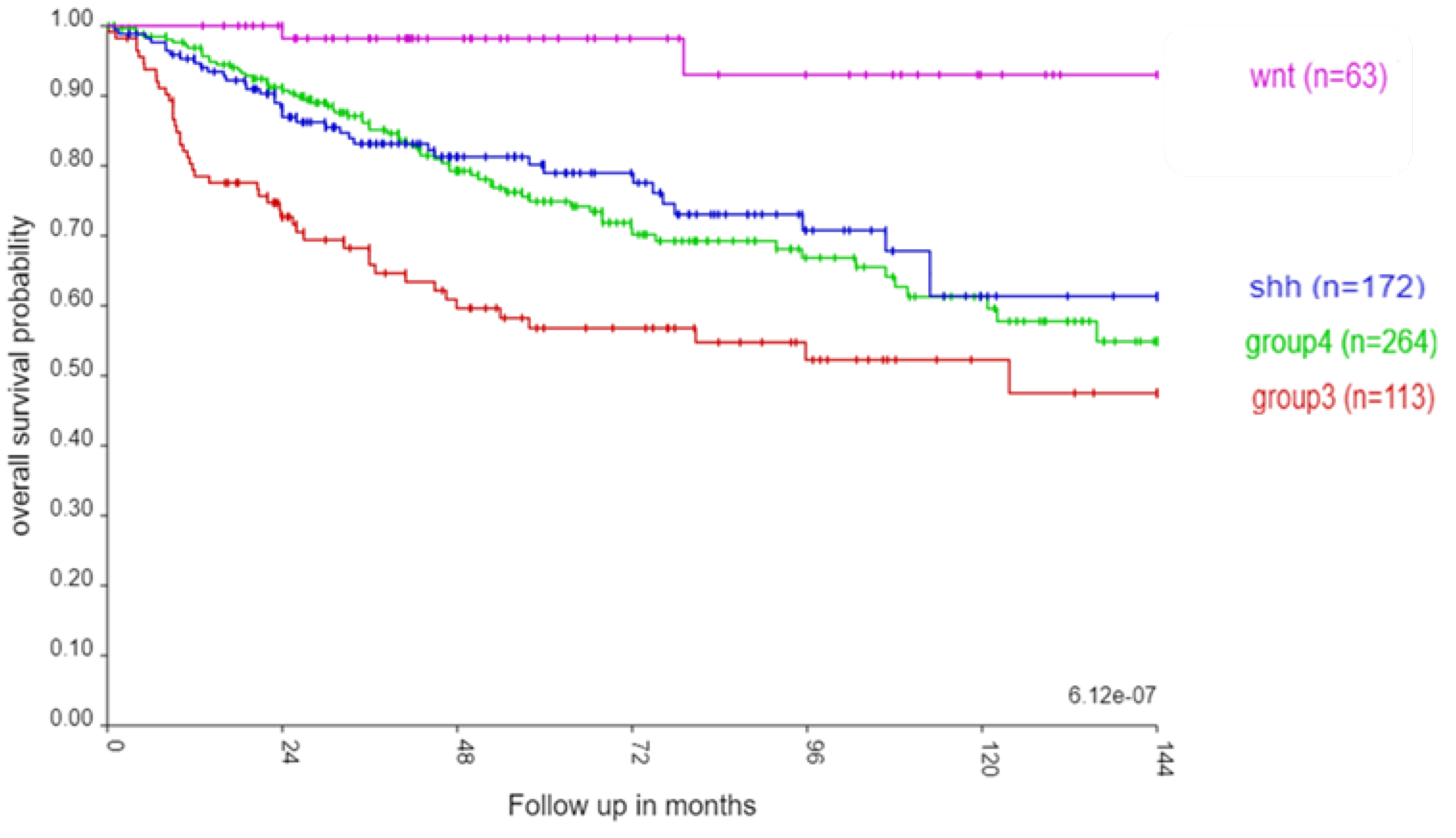
Figure 1 illustrates the well known pattern of survival in the four consensus MB subgroups (2, 14). Individuals from the WNT subgroup had the best survival rate, while those from Group 3 had the worse survival, with intermediate survival rates in Group 4 and the SHH group. Within each subgroup, the survival outcomes were also different among the 12 MB subtypes, but statistically not as significant as the differences in survival rates between the four MB subgroups (Suppl. FigureS1).
A total of 967 SRGs were identified with the Benjamini-Hochberg p value <0.05, after adjusting for age.
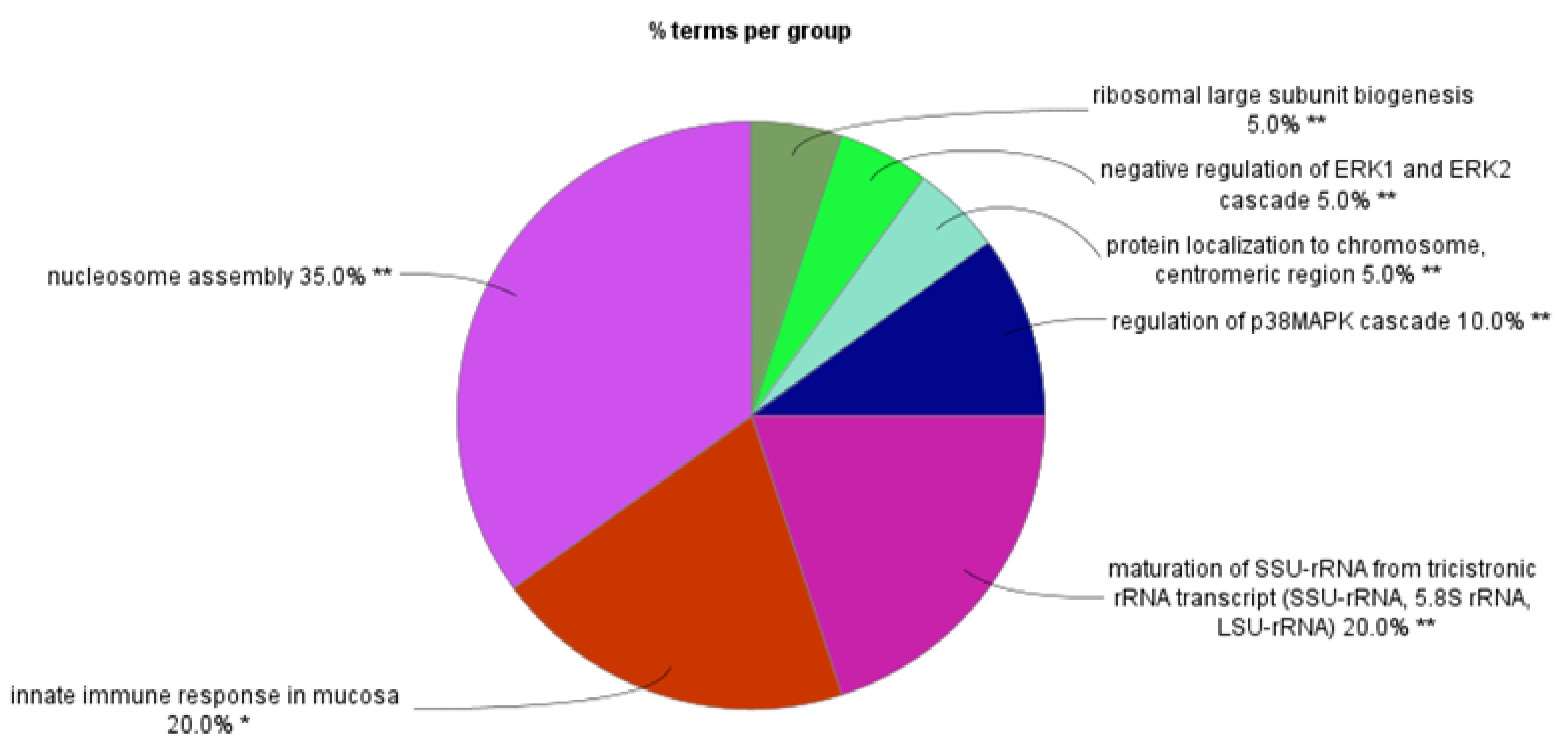
Supplementary Table S1 lists the survival analysis of the SRGs by chromosome using the Cavalli dataset. Pathway analysis showed that a total of 96 Gene Ontology (GO) terms in 16 GO groups were statistically associated (p < 0.01) with our list of SRGs (Suppl.
Table S2). The percentage of GO terms per group for all SRGs is shown in Suppl.
Figure S2. The highest percentage of GO terms per group were in the GO group “regulation of chromosome organization”. The SRGs contributing to this GO group in the Cavalli dataset included five genes coding for proteins making up the TCP1 ring complex (TCP1, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT8) in each of the 19 GO terms of the group. The GO terms comprising this group were related to regulation of the telomere and telomerase RNA localization to the Cajal body (Suppl.
Table S1). The next most significant GO group represented in the list of SRGs was mitotic cell cycle process. Of the 967 SRGs, 51 were on the Ongene list of human oncogenes.
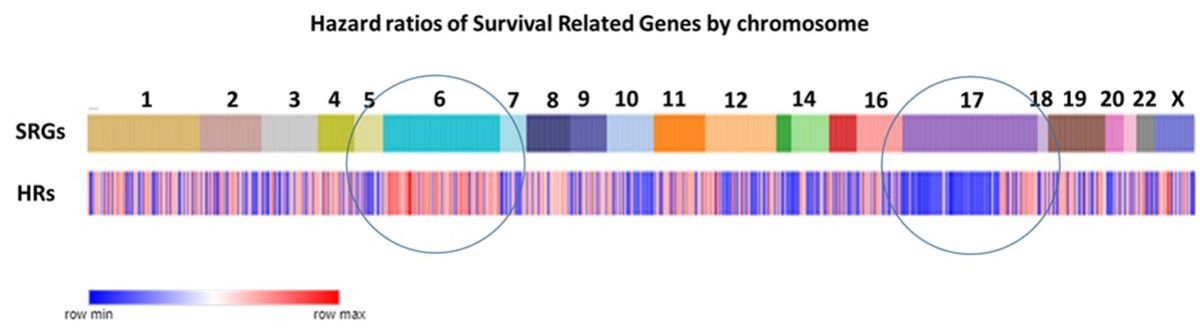
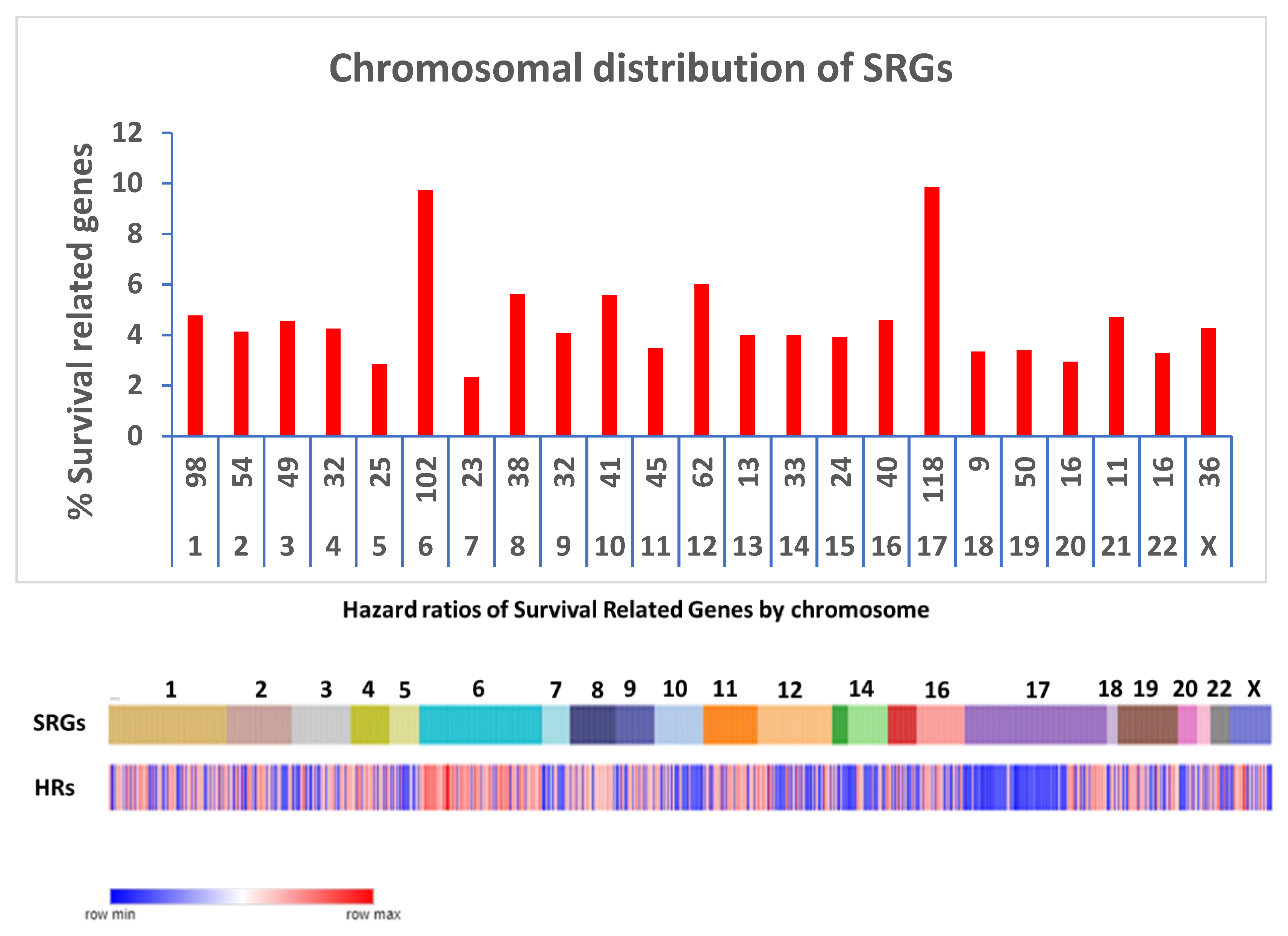
Compared to other chromosomes, SRGs on chromosomes 6 and 17 were significantly over-represented among the 967 SRGs, with 9.73% and 9.86% on chromosomes 6 and 17 respectively versus an average of 5.89% on the other chromosomes (p<0.0001) (
Figure 2A). Our analysis focuses on the SRGs located on these two chromosomes. SRB hazard ratios by chromosome are shown in
Figure 2B.
3.1. SRGs on CHROMOSOME 6.
We observed decreased expression of many SRGs on chromosome 6 in the WNTα subtype, due to the loss of gene expression of SRGs on chromosome 6. However, we also observed some major unexpected findings of SRGs on chromosomes 6.
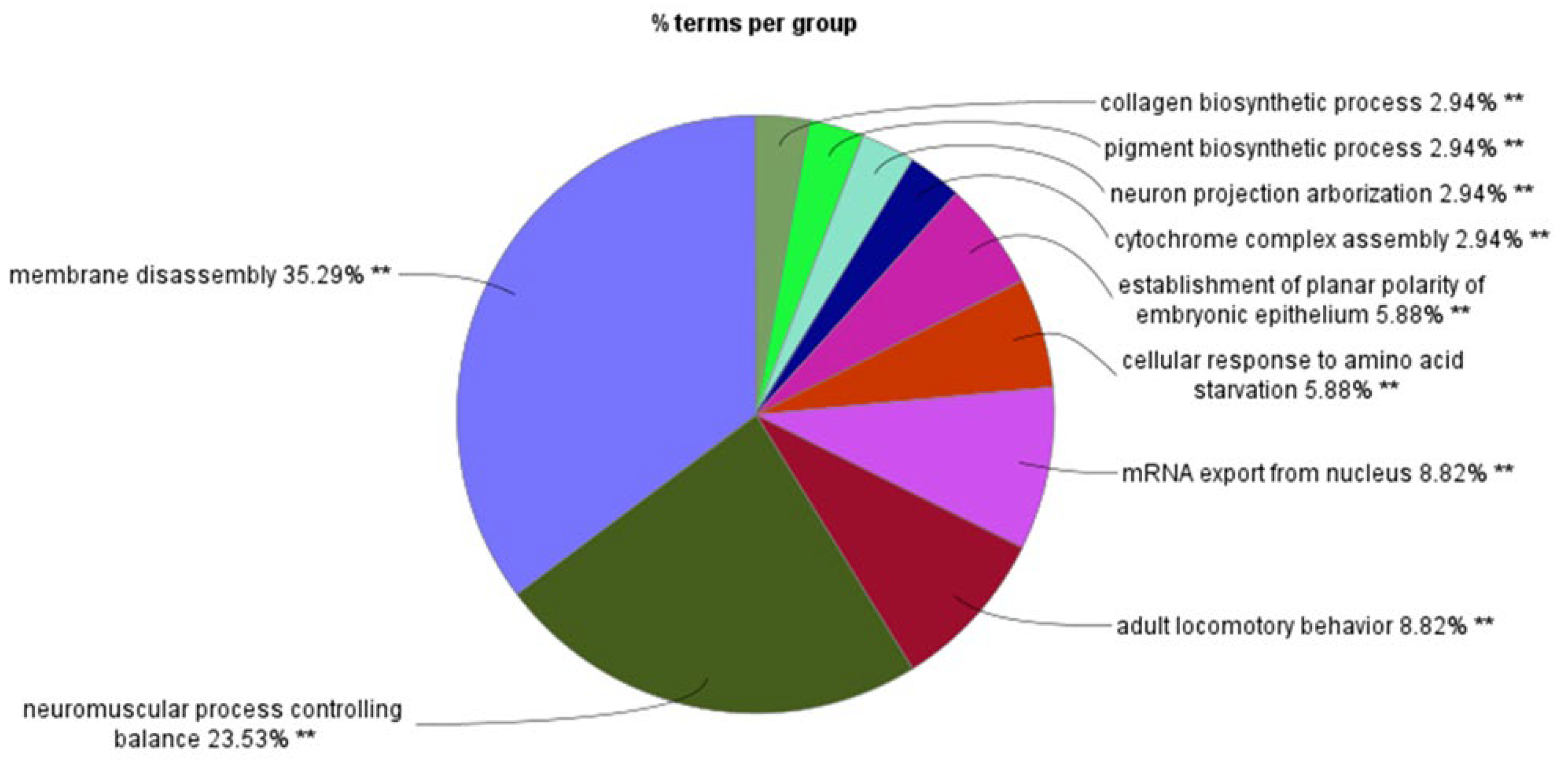
Figure 3 shows the GO pathways associated with SRGs on chromosome 6. The greatest number of GO terms were associated with nucleosome assembly. Below, we present the findings separately for the short and the long arm of chromosomes 6 (6p and 6q).
3.2. Chromosome 6p and expression of survival related genes
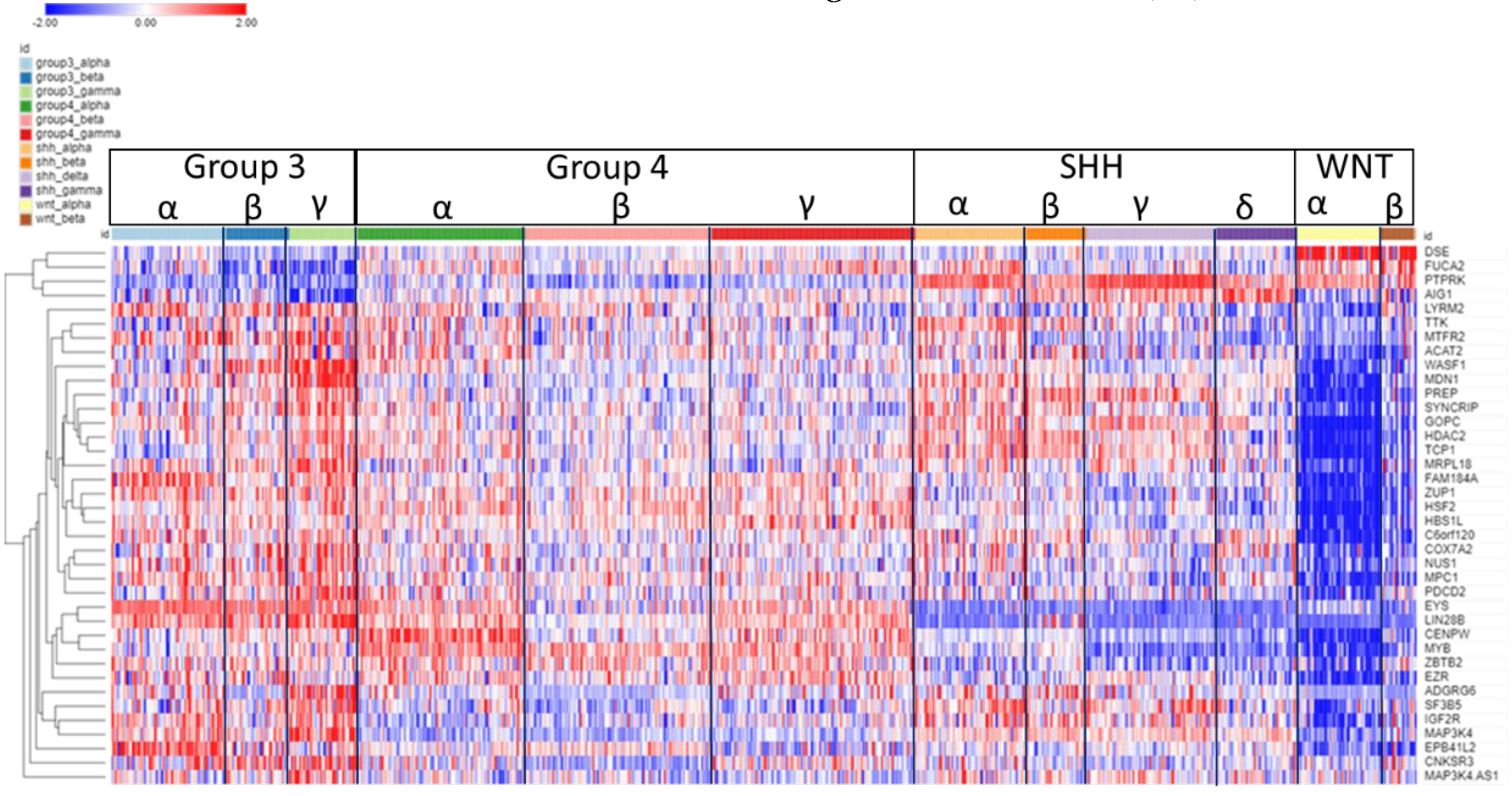
The expression of SRGs on chromosome 6p are presented in the heatmap of
Figure 4. Sixty-four of the 102 SRGs on chromosome 6 are located on its short arm (6p). For 61 of the 64 SRGs on 6p, high expression were associated with worse survival (HR>1). For the majority of these genes, high expression (including higher expression than the NT group in the Swartling dataset) was found in the Group 3γ subjects, the subtype with the worst prognosis, while low expression were noted in many of the WNTα subjects (
Figure 4), the subtype with monosomy 6 and the best prognosis. However, several genes located to the histone cluster at 6p22.1-22.2 showed high expression (
Figure 4) in the WNT group (including higher than the NT group in the Swartling dataset) with poor prognosis (HR>1).
As noted, pathway analysis of chromosome 6 SRGs showed enrichment of the genes involved in nucleosome assembly (Fig 3). The SRGs were BRD2, CENPW, DAXX , H1-2, H2BC11, H2BC15, H2BC17, H2BC4, H2BC5, H2BC8, H3C2, and HMGA1. These genes, with the exception of CENPW, are located on 6p.
The group of nucleosome related genes consisted of four SRGs coding core nucleosomal histone components (H2BC11, H2BC17, H2BC5, H3C2) and H1.2, which encodes a histone linker; these genes are all located in the histone cluster at 6p22.1 and 6p22.2 (15) and cluster together in the heatmap of 6p (
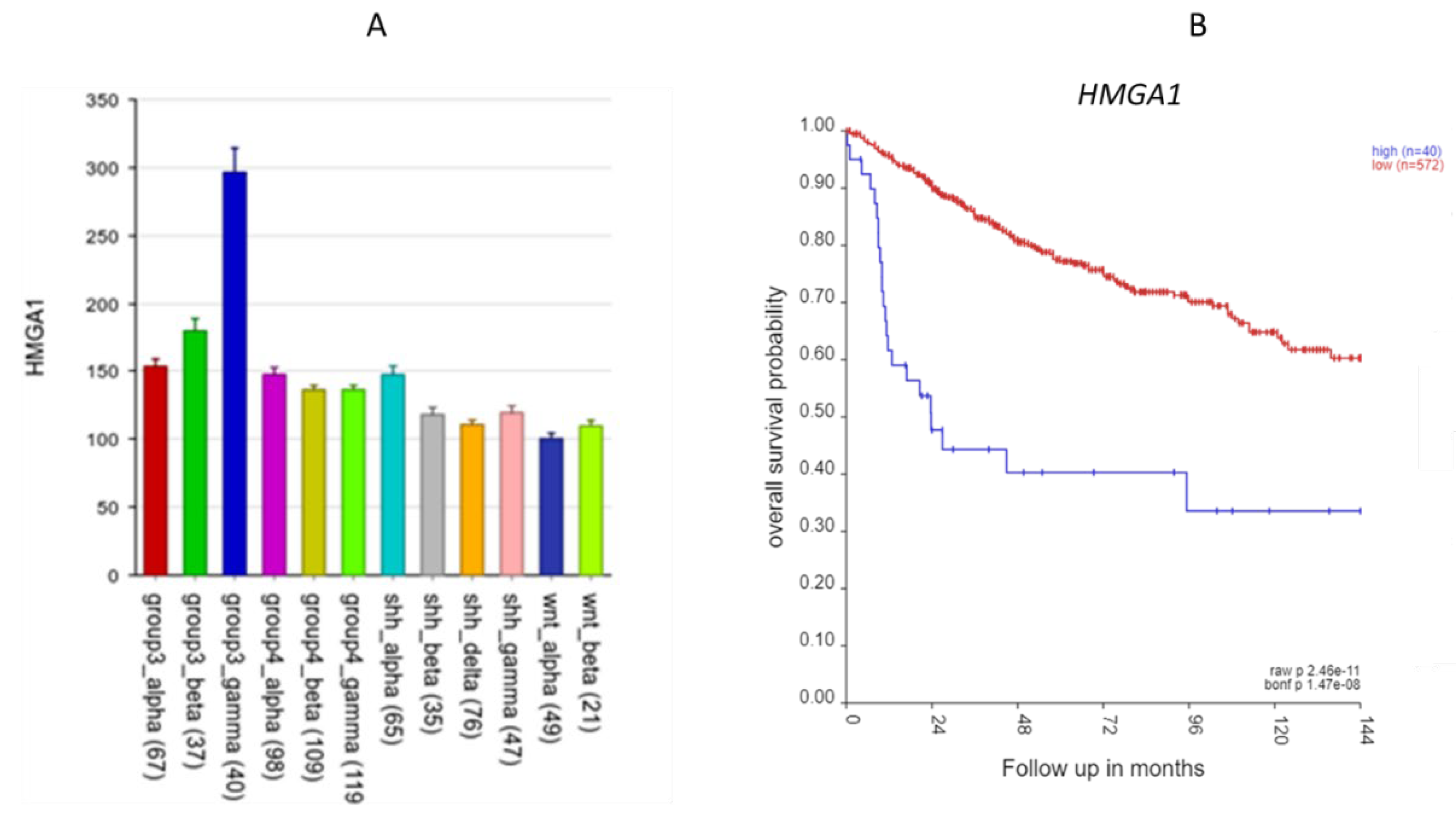
Figure 4). Additional 6p SRGs related to nucleosomes include DAXX which codes for a histone linker, BRD2, which encodes a histone transcription regulator and HMGA1, a histone H1 competitor (16). The latter three genes are located at 6p21.31, 6p21.32, and 6p21.32 respectively. Expression of HMGA1 was specifically elevated in Group 3γ MB in the Cavalli dataset.
Furthermore, HMGA1 was the most significant SRG of all the 967 SRGs (HR = 1.68, p = 8.36 x 10-13). HMGA1, located at 6p21.31, encodes the high-mobility group AT-Hook protein I. In the Weishaupt et al. (2019) (4) dataset, the expression of HMGA1 was significantly higher in the Group 3 subjects than in the subjects from the other groups, including the non-tumor group. The HMGA1 expression was specifically elevated in the Group 3γ subjects, 2-fold greater than its expression in the subjects from the other subtypes (
Figure 5A). The Group 3γ subtype (n = 40) had poor survival.
Cox analysis of the individuals in the Cavalli dataset in which individuals with known SCNAs of chromosome 6 had been removed showed that expression of the 6p survival related genes H2BC11, H2BC4, H2BC8, and HMGA1 were not associated with monosomy 6 or any other known SCNA. .
3.3. Chromosome 6q survival related genes
Figure 6 shows the heatmap of the gene expression of the 38 SRGs on chromosome 6q in the Cavalli et al. dataset. For 33 of the 38 SRGs on chromosome 6q, high gene expression was associated with poor survival (HR>1). High expression for most of the 6q SRGs was noted in Group 3, while lower expression of most of the 6q SRGs was found in the WNTα subtype (
Figure 6). SRGs with high expression in Group 3γ (and worse survival) included ADGRG6 (GPR126), NUS1, MDN1, SYNCRIP, WASF1, and LIN28B. SYNCRIP is on the list of driver genes of Northcott (17).
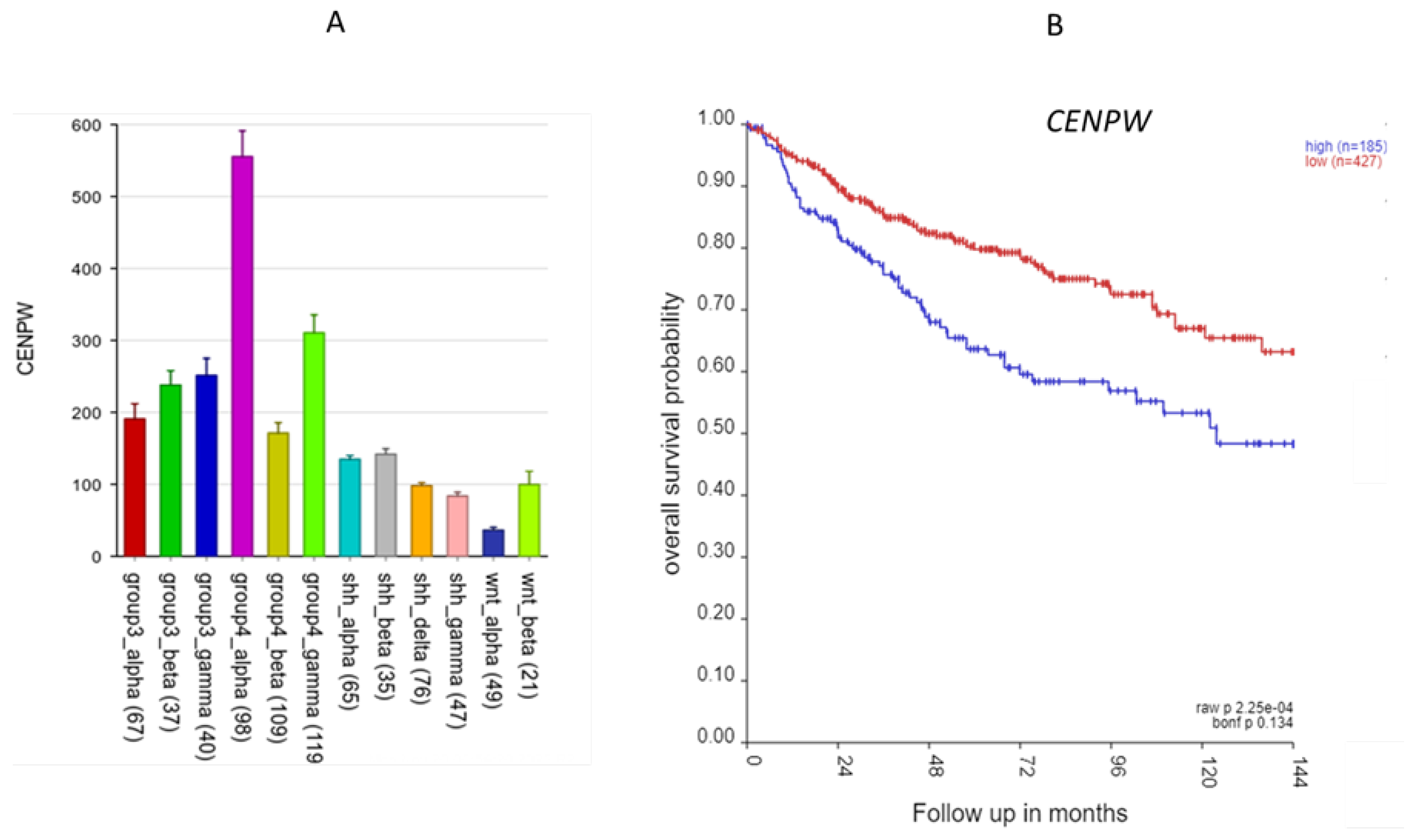
CENPW, located on 6q, was shown to contribute to the nucleosome assembly pathway, along with several SRGs of 6p (see above). CENPW codes for a protein that binds to nucleosomes at the centromere. CENPW expression was highest in Group 4α (
Figure 7) Worse survival was associated with high expression of CENPW (
Figure 7).
Chromosome 6q also contributed two genes, TCP1 and MAP3K4, to the most significant pathway over-represented in all 963 SRGs, regulation of chromosome organization. TCP1 (aka CCT1) encodes a component of the TCP1 ring complex, a structure which assists in protein folding in cells. MAP3K4 encodes a protein kinase. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that high expression of TCP1 was associated with poor survival (p = 5.19 x 10-10).
3.4. SRGs on CHROMOSOME 17
Figure 8 shows the GO pathways associated with SRGs on chromosome 17. The greatest number of GO terms were associated with membrane disassembly. When individuals with SCNAs were removed from the cox proportional hazards regression analysis there were no longer any significant chromosome 17 SRGs. This would suggest the probability that SRGs on chromosome 17 are related to copy number variations, including isochromosome 17. Here we present the findings separately for the short and the long arm of chromosomes 17 (17p and 17q). According to the supplemental data of Cavalli et al. (3). SCNAs of 17p and 17q were found in 403 out of 763 individuals in the study, mostly in MB Groups 3 and 4.
3.5. Chromosome 17p survival related genes
Seventy-two of 74 SRGs on 17p showed that low gene expression was associated with poor survival, and high expression was associated with survival protection (HR<1).
Figure 9 illustrates the heatmap of the gene expression levels for the 17p SRGs by MB subtype. The most significant SRGs had low expression in Group 4β (
Figure 9). Cavalli et al. (2017) found that 87 of the 109 subjects (80%) in this subtype Group 4β had isochromosome 17 (3). In their supplementary table of SCNAs (Cavalli et al. (2017) supplemental Table1), however, we find that 93% of Group 4β had a deletion of 17p. Two of the most significant 17p SRGs are SCO1 (HR = 0.73, p = 2.21 x 10-05) and TTC19 (HR = 0.68, p = 4.52 x 10-07). Low expression of SCO1 and TTC19 in Group 4β and significantly worse survival with low expression was noted, compared to the other MB subtypes.
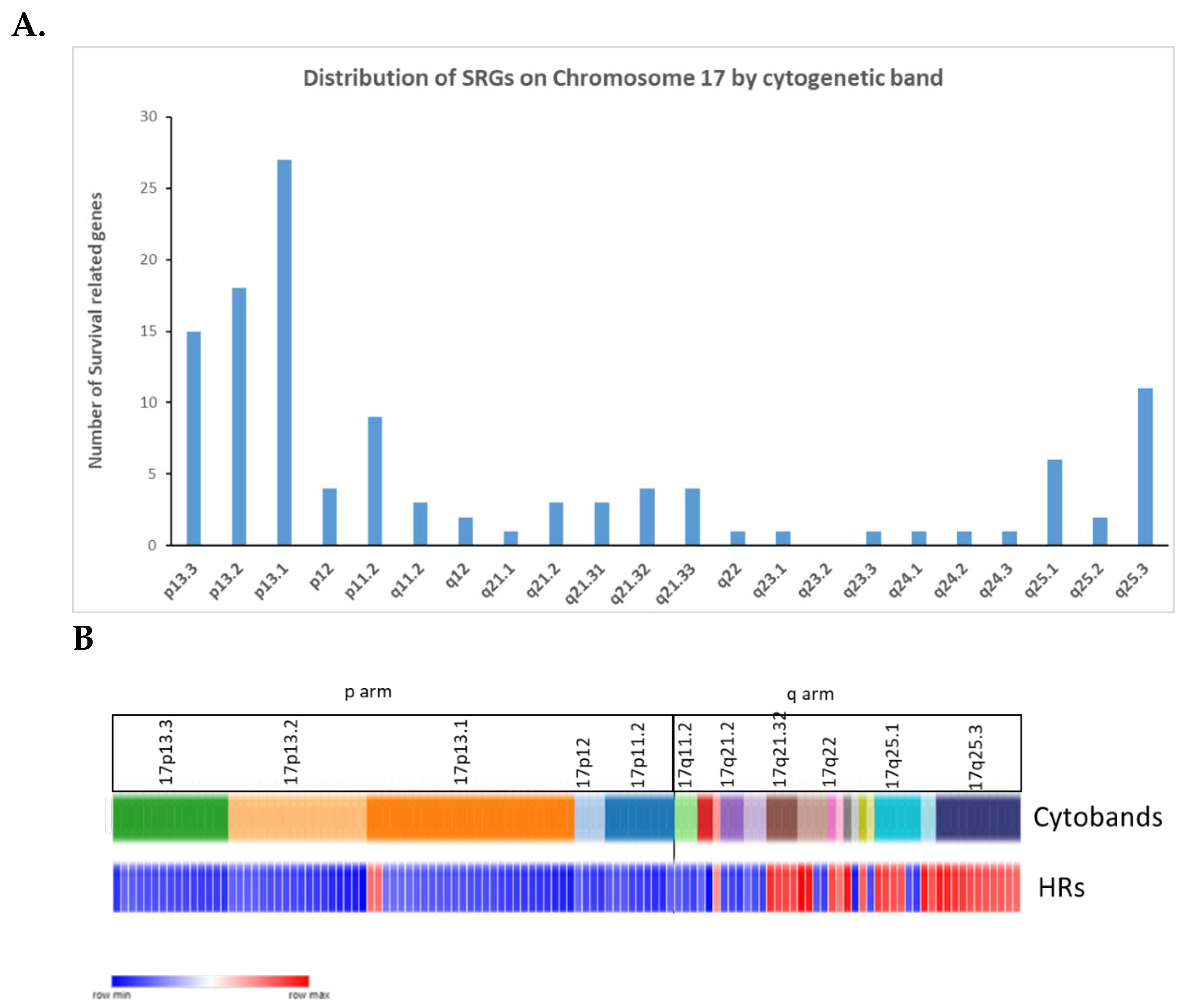
3.6. Chromosome 17p and telomere genes
In our analysis of the SRGs on chromosome 17, the most frequently represented cytogenetic band on chromosome 17p was 17p13.1, with 27 SRGs (
Figure 10A). Three of the17p SRGs contribute to telomere regulation, SMG6 (at 17p13.3), RPA1 (also at 17p13.3), and CTC1 (at 17p13.1).
3.7. Pathway analysis of chromosome 17p SRGs
The pathway analysis of 17p SRGs is shown in
Table 1. Pathway analysis of these SRGs showed that CTDNEP1, a driver gene (17) along with the SRGs NDEL1, and PAFAH1B1, contributed to the most significant GO terms nuclear membrane disassembly (
Table 1). The SRGs, SCO1 and TTC19, contributed to the GO pathway of cytochrome complex assembly.
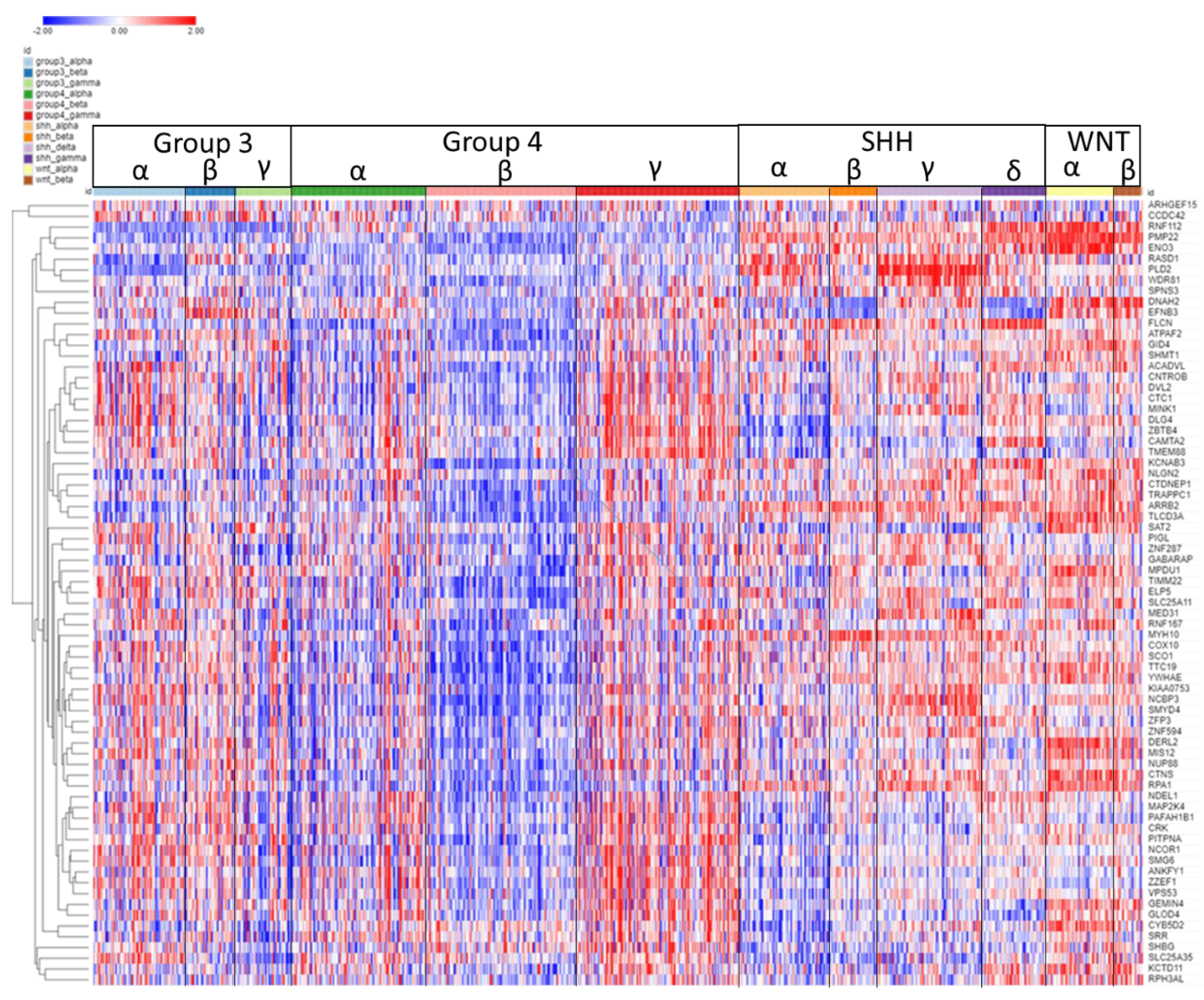
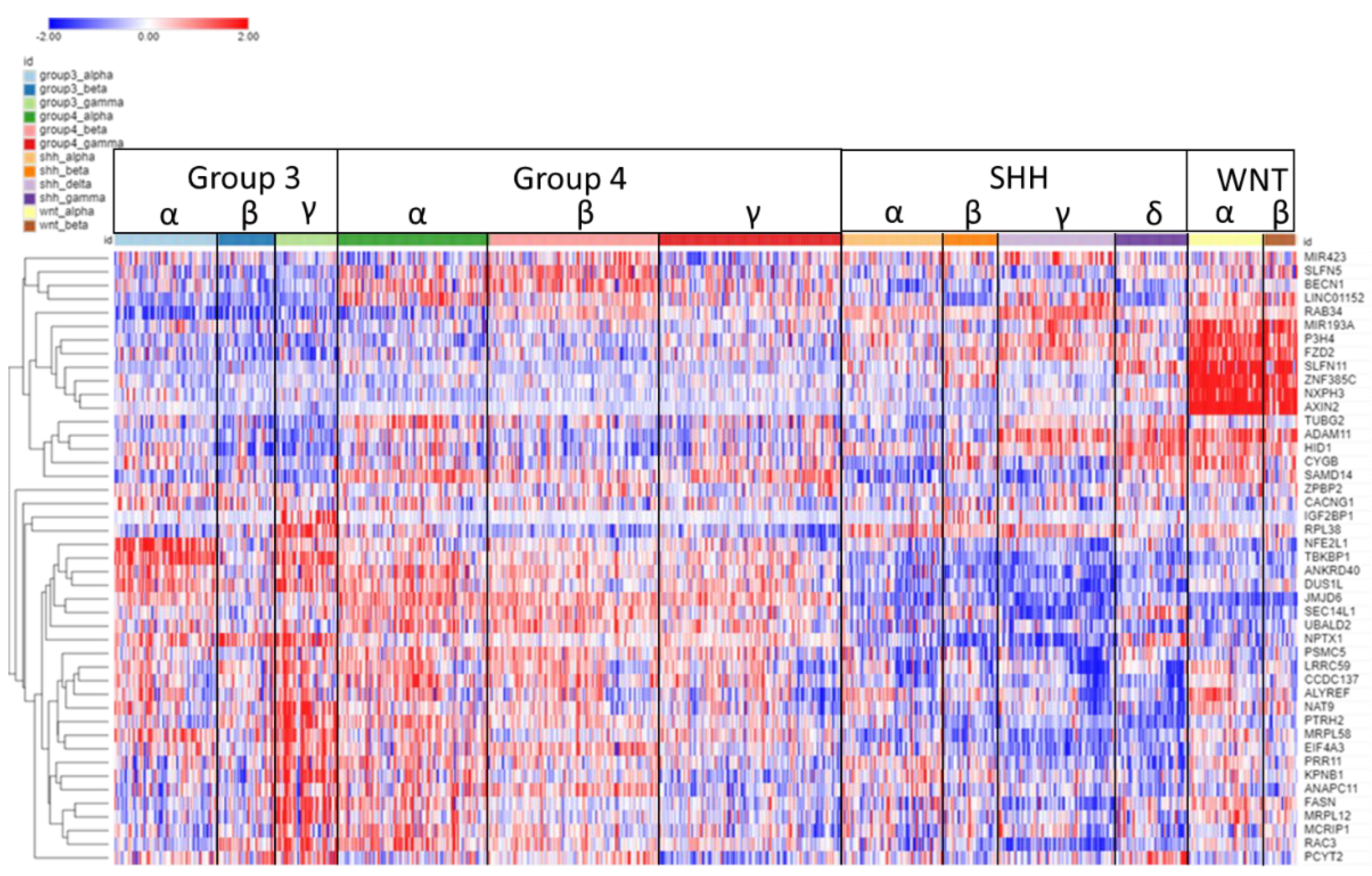
3.8. Chromosome 17q
The expression of the 17q SRGs by subgroup and subtype is illustrated in the heatmap of Fig 11. As shown in the heatmap, a group of seven of these SRGs, MIR183A, P3H4, FZD2, SLFN11, ZNF385C, NXPH3, AXIN2 were over-expressed in the WNT subgroup. High expression was associated with survival protection (HR<1).
On the other hand, for 28 out of the 45 SRGs on chromosome 17q, high expression was associated with worse survival (HR>1) (Figure11). All of the twelve SRGs at 17q25.3 (SEC14L1, FASN, DUS1L, MRPL12, PCYT2, NPTX1, ANAPC11, EIF4A3, RAC3, MCRIP1, ALYREF, CCDC137) showed high expression related to worse survival (HR > 1,
Figure 10B). Relatively higher expression of these genes was noted primarily in MB Groups 3 and 4 (
Figure 11).
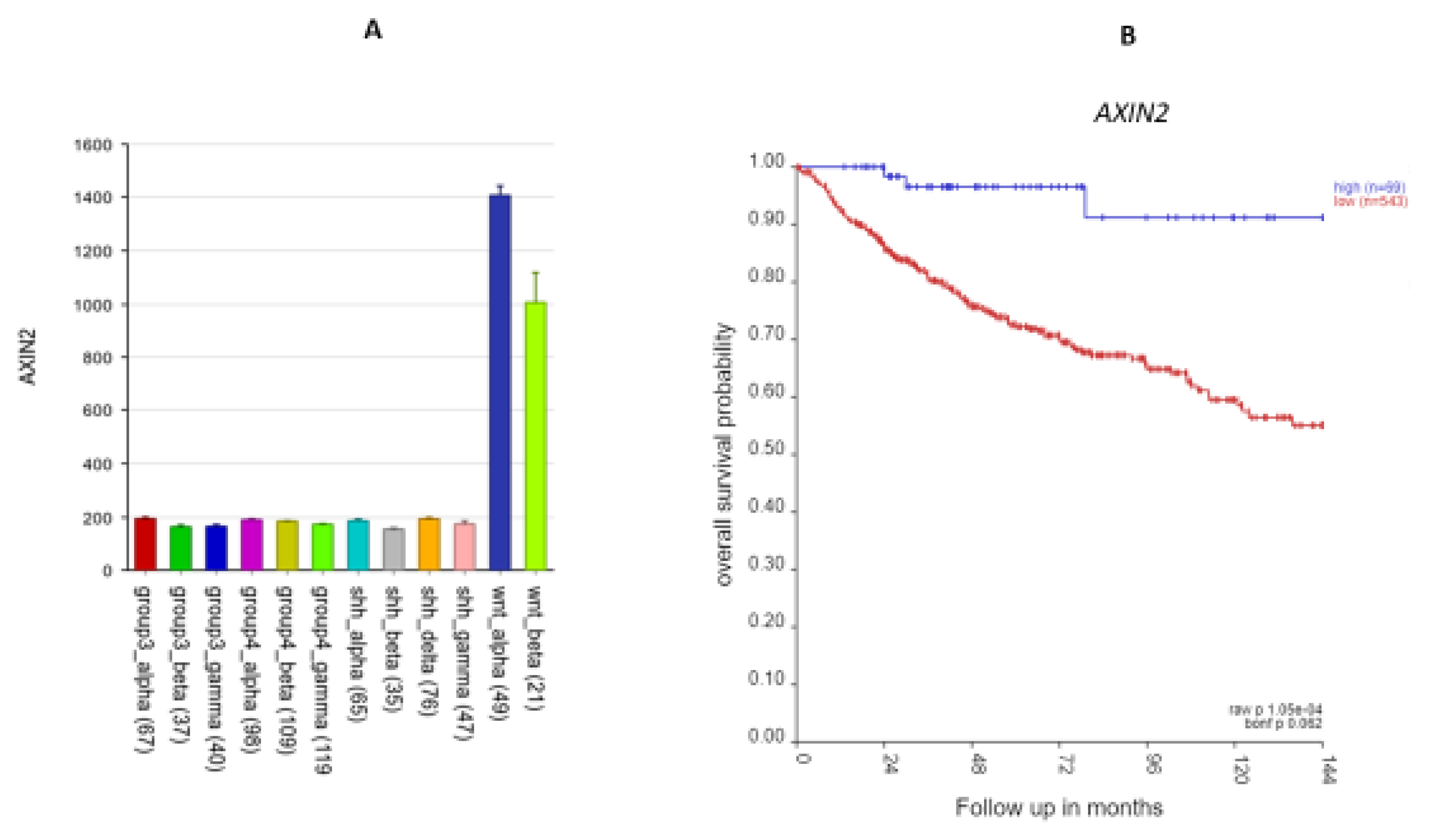
The most significant differentially expressed SRG on 17q in the Cavalli dataset was AXIN2 (
Figure 11).
Figure 12A shows that the expression of AXIN2 was higher in the WNT subtypes than in all the other subtypes (F = 577.14, p < 1.0 x 10-300). Its expression was also higher than non-tumor samples in the Swartling dataset (p = 8.62 x 10-127). For AXIN2, high expression was associated with better survival (
Figure 12B). Its hazard ratio was 0.64 (low 0.50, high 0.83, p = 6.09 x 10-05); elevated expression was associated with survival protection (
Figure 12B). All of the individuals (N = 49) in the WNTα subtype had elevated AXIN2 expression, while 15/21 in the WNTβ had elevated AXIN2 expression.
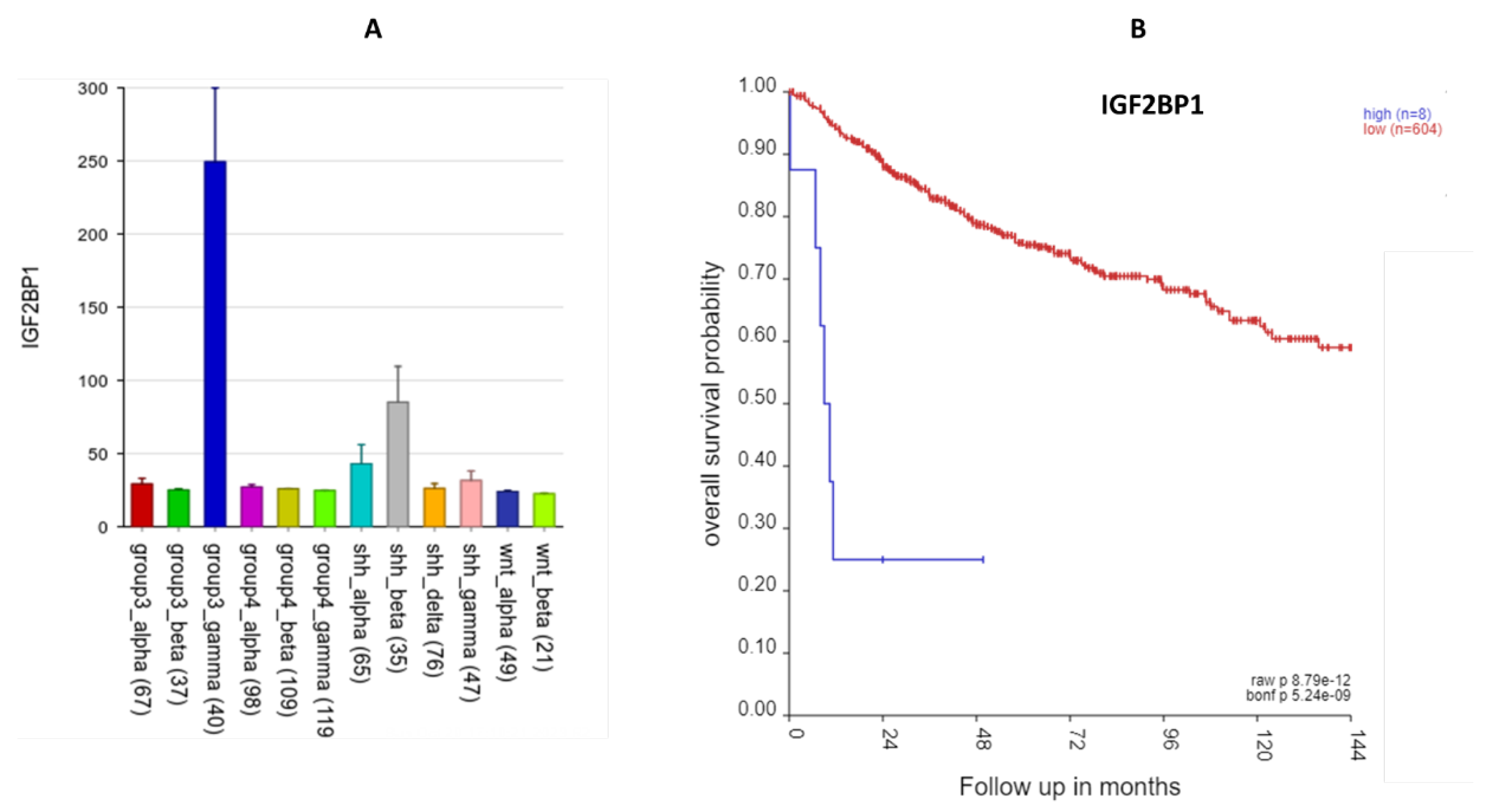
The most significant SRG on 17q was IGF2BP1 (HR = 1.34 p = 2.88 X 10-08). IGF2BP1 is over-expressed in the Group 3γ MB samples and that high expression was associated with worse prognosis (
Figure 13). In the Swartling meta-analysis (4), IGF2BP1 was also over-expressed compared to that of non-tumor samples. Our pathway analysis of 17q SRGs (Table 3) showed that IGF2BP1 expression was associated with the significant GO terms mRNA transport and RNA localization.
Another 17q SRG associated with significant GO terms (
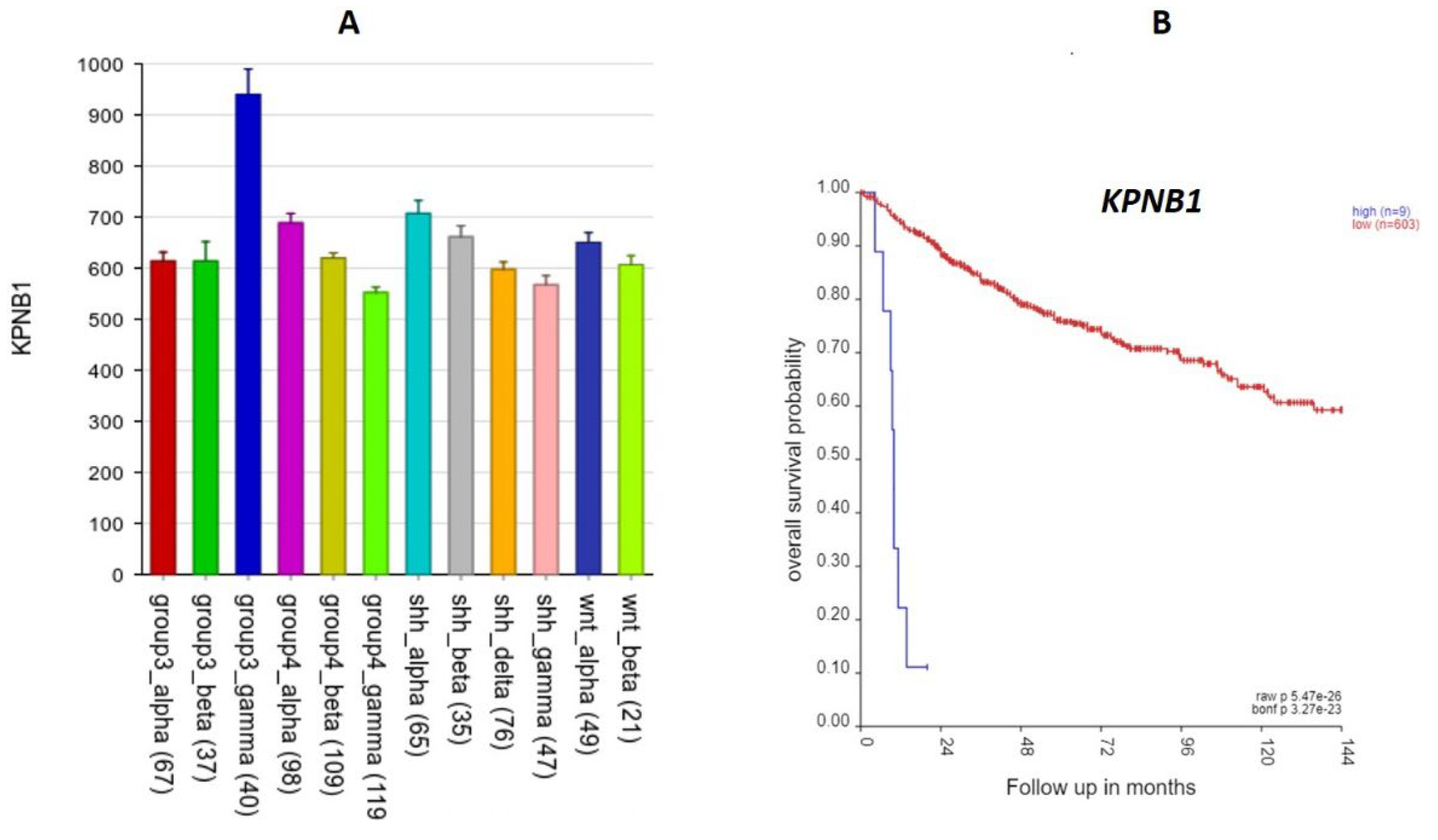
Table 2) was KPNB1 (Karyopherin). High expression was associated with worse survival (
Figure 14) (HR = 1.40, p = 2.92 x 10-05). KPNB1 expression was also specifically over-expressed in Group 3γ (
Figure 14) in the Cavalli dataset , and in Group 3 in the Swartling dataset. The KPNB1 protein is involved in nuclear import of proteins and also plays a role in mitosis (18, 19).
4. DISCUSSION
Although the SRGs were distributed on all chromosomes, our analysis showed over-representation of SRGs on chromosomes 6 and 17. Aberrations of chromosomes 6 and 17 in MB are well documented: monosomy 6 was found in 48 of the 49 WNTα subtype subjects in the Cavalli dataset; isochromosome 17 was reported in MB groups 3 and 4 in the Cavalli report (3), with the greatest frequency in the Group 4β subtype (87 of the 109 subjects). Our analysis identifies SRGs whose expression are associated with these aberrations as well as some that are not. Results from the cox proportional hazards regression analysis showed that 27 chromosome 6 SRGs remained after removal of individuals with known SCNAs wheras no significant number of chromosome 17 SRGs remained after removal of individuals with known SCNAs. We conclude that chromosome 6 contributes major SRGs unrelated to SCNAs such as monosomy 6, but that chromosome 17 SRGs are primarily related to known SCNAs, primarily isochromosome 17. Because of the samples size we cannot rule out the possibility that some chromosome 17 SRGs are unrelated to chromosome 17 SCNAs.
The SRGs we identify have some overlap with the Northcott driver genes (17) and 49 SRGs overlap with the top 1% of genes supporting the major molecular subgroups in the Cavalli study. However, we also identified SRGs on chromosomes 6 and 17 that are not on the Northcott list of driver genes (17) and not on the top 1% of genes supporting the 4 major molecular subgroups in the Cavalli report. The four molecular subgroups and subtypes reported, having been defined by unsupervised cluster analysis, do not necessarily correspond to the primary clinical outcomes, overall survival. Zhu et al. (10) reported a twelve gene signature as a prognostic tool to predict overall survival in MB. Two of the SRGs we identified on chromosomes 6 and 17, SYNCRIP and EIF4A3, overlapped with the twelve gene signature reported by Zhu et al. (10) using the Cavalli dataset (referred to in their report as the Florence [sic] dataset). Different from the methods used by Zhu et al. (10), our multivariate survival analysis model adjusted for age but not for MB subgroup, thus, is more likely to identify SRGs which were expressed differentially by MB subgroups and subtypes. Here, we discuss the most significant age-adjusted SRGs, located on chromosomes 6 and 17, and the biological pathways associated with these genes. The SRG data allow us to identify genes encoding proteins that should be further examined as potential therapeutic targets in selected subgroups or subtypes of MB.
The data suggest that the expression of SRGs is partially explained by chromosomal aberrations. Monosomy of chromosome 6 is associated with reduced gene expression, in the WNT group, of many genes, including SRGs. Copy number aberrations of chromosome 6q has been used by Pfister et al. (20) in MB survival prediction. Gain of 6q contributed to poor outcome while 6q deletion was associated with better survival (20). Aberrations of chromosome 17, including isochromosome 17, isodicentric 17, and loss of 17p have also been used as prognostic factors in MB. Variations in expression of some of the SRGs would be expected to reflect these chromosomal aberrations.
4.1. Chromosome 6 survival related genes (SRGs)
While monosomy of chromosome 6, in one of the WNT subtypes, is the major chromosomal aberration reported for this chromosome, here we discuss SRGs on 6p and 6q separately to facilitate identification of biological pathways and individual genes that are statistically associated with overall survival.
4.2. Chromosome 6p SRGs
Of all the 967 SRGs identified by the survival analysis, the most significant SRG was HMGA1, located at chromosome 6p21.31; it codes for a non-histone chromatin protein for many cellular processes including cancer metastasis. As shown in
Figure 5 high expression of this gene in Group 3γ MB was associated with poor survival. HMGA1 is a histone H1 competitor (21); as such it plays a role in epigenetic regulation of gene expression.
Sumter et al. (22) has reviewed the role of HMGA1 as an oncogene for various tumors, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, and lung cancer, when overexpressed. Pathway analysis of chromosome 6 p SRGS identifies HMGA1 as associated with the GO terms nucleosome organization and nucleosome assembly; this is consistent with its role as a histone H1 competitor. There are several additional MB SRGs in the nucleosome organization pathway. These include 5 genes in the histone cluster of genes located at 6p 22.1-22.2, expressed during S-phase of the cell cycle (23), DAXX, which encodes a histone linker, and BRD2, which encodes a histone transcription regulator. These data further support a key role for the nucleosome in Group 3γ MBs. Also included in the SRGs in the nucleosome assembly GO term was CENPW, a gene located on chromosome 6q. It binds to nucleosomes at the centromere (24).The data suggest the hypothesis that dysregulation of nucleosome components plays a role in MB survival related to gene expression of chromosome 6p. Our analysis highlights HMGA1 and genes coding for nucleosome components as of major significance in Group 3γ MB survival and of potential therapeutic targets in Group 3γ MBs. HMGA1 and DAXX are both included in the ONGene database of oncogenes (25). CENPW has been reported as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma and a potential target for gene therapy in this cancer (24). The current analysis suggests that CENPW is a marker for Group 4α MB and should be examined further as a potential therapeutic target for this MB subtype.
Other chromosome 6p SRGs whose expression was also elevated in Group 3γ include SNRPC, (required for formation of the spliceosome), XPO5 (involved in transport of small RNAs from nucleus to cytoplasm), FANCE (which encodes a protein that contributes to DNA cross link repair), and H2BC8 (a gene located on the histone cluster of chromosome 6). These SRGs, as well as HMGA1, are on our list of chromosome 6 SRGs that remain after removal of individuals with known CNVs. From the point of view of statistical survival, HMGA1 was most significant.
Chromosome 6p amplification has been associated with various cancers by comparative genomic hybridization or FISH (26) leading to the hypothesis that these cancers are caused by increased expression of one or more oncogenes on chromosome 6. While Cavalli et al. (3) showed some cases with chromosome 6p gain in Group 3γ, their report indicates that this is not a statistically significant gain compared to the other subgroups in Group 3 (see their
Figure 5E). To the best of our knowledge, significant 6p amplification has not been reported for MB. An alternative explanation for selective increased SRG expression in Group 3γ is that it may represent an epigenetic phenomenon.
4.3 Chromosome 6q survival related genes
SYNCRIP (aka HnRNP-Q), an 6q SRG with a high HR, is included in the list of ‘driver genes’ by Northcott et al. (17) as well as in a 12 gene signature for MB prognosis reported by Zhu et al. (10). For several 6q SRGs with HR>1, including SYNCRIP, expression was upregulated in Group 3 or Group 3γ (
Figure 6). Since SYNCRIP expression was elevated in Group 3 MB compared to the non-tumor group at a high level of significance in the Swartling dataset (p = 2.01e-19), overall the dataset show that, in addition to being on the Northcott list of driver genes (17), SYNCRIP is significantly related to survival of Group 3 MBs. SYNCRIP encodes a splicing protein (27) and modulates mRNA translation (28) and transport (29).
TCP1 (aka CCT1), another 6q SRG with a HR>1, is located on 6q25.3. It encodes the one of the proteins of the TCP1 ring complex, a molecular structure that folds proteins. Several SRGs coded for proteins that contribute to the TCP1 ring structure. These SRGs TCP1 (Chr 6), CCT2 (Chr 12), CCT3 (Chr 1), CCT4 (Chr 2), CCT8 (Chr 21), were found, in the overall pathway analysis (p < 0.01)of SRGs (Supplemental
Table 1), to contribute to a highly significant group of GO terms related to the telomeric region of chromosomes and to the Cajal body, including regulation of telomerase RNA localization to the Cajal body. Meier analysis showed that high levels of TCP1 (Chr 6) , CCT2 (Chr 12), CCT3 (Chr 1), CCT4 (Chr 2), CCT8 (Chr 21) were associated with worse survival. Our analysis of the data suggests that dysregulation of the TCP1 ring complex is a significant factor contributing to survival of MB.
4.4. Chromosome 17 survival related genes
Isochromosome 17, with loss of a copy of 17p and gain of 17q, is found in both Group 3 and Group 4 MB (3, 30). The isochromosome 17 aberration has been reported to be a prognostic factor in infant MB (31). It has been suggested that isochromosome 17q may be a marker for uncontrolled cell proliferation in MB (32). From our analysis, we conclude that a number of chromosome 17 SRGs are related to known CNVs, primarily isochromosome 17.
Here, we discuss the most significant SRGs on 17p and 17q in MB separately.
4.5. Chromosome 17p survival related genes
The heatmap and cluster analysis of 17p SRGs illustrate that low expression is found in most of the Group 4β subjects (
Figure 9). Worse survival with low expression of the genes in
Figure 9 suggests the possibility of one or more tumor suppressor genes in the list of SRGs on chromosome 17p. Our analysis suggests the interpretation that worse survival in Group 4β is due to a reduced expression of one or more SRGs due to loss of a copy of 17p, whether or not associated with the isochromosome 17 aberration. McCabe and colleagues reported that 17p loss predicated a poor prognosis (33) in pediatric MB. Cogen and McDonald (34) reviewed the reports of tumor suppressor genes on 17p in MB. They pointed out that the most common location for 17p loss was in the 17p13.1 cytogenetic band; we identified the 17p13.1-p13.3 region as the most frequently represented cytogenetic bands of the SRGs on chromosome 17. Our analysis supports the hypothesis of one or more tumor suppressor genes among our list of 17p SRGs are specific for MB subtype Group 4β. While the tumor suppressor gene TP53 is located on 17p13.1, this gene was not found in our list of 17p SRGs.
The most significant 17p SRG in our model was CYB5D2 (Cytochromes B5 domain containing 2). Low expression of this gene was associated with worse survival prognosis. CYB5D2 was included in a 13-gene list of MB prognosis predictors (35). Other cytochrome complex related SRGs included COX10 (Cytochrome C Oxidase Assembly Factor Heme), SCO1 (Synthesis of Cytochrome C Oxidase) and TTC19 (Tetratricopeptide Repeat Domain 19) (
Table 1). Low expression of these three genes was associated with poorer survival. Lowest expression of these genes was noted in Group 4β. These data suggest a deficiency in the cytochrome oxidase C contributes to worse prognosis in Group 4β.
One of the 17p SRGs, CTDNEP1 (CTD Nuclear envelope phosphatase 1), was listed as an MB ‘driver’ gene by Northcott (17) and an oncogene by Luo et al.(36). This gene is located at 17p13.1. High expression of this gene was associated with survival protection (HR = 0.72), while reduced expression of this gene in Group 4β was associated with worse survival. Pathway analysis of 17p SRGs showed that CTDNEP1 contributed to one of the major GO biological pathways, nuclear membrane disassembly (
Table 1). Reduced expression of CTDNEP1 would be expected in cases with loss of 17p, whether or not part of the isochromosome 17 aberration.
The finding that several 17p SRGs located at 17p13.1 and 17p13.3 contributed to the GO molecular pathway of telomeric DNA binding in the pathway analysis of SRGs needs further elaboration. These genes include SMG6 and RPA1 (Replication Protein A 1) located at 17p13.3, and CTC1 (CST Telomere Replication Maintenance Complex Component 1) located at 17p13.1. SMG6 codes for a protein that is a part of the telomerase ribonucleotide complex and has a role in telomere regulation (37-39). RPA1 protein contributes to DNA replication, DNA damage response (40), and telomere maintenance (41, 42). CTC1 (aka C17orf68) encodes a protein that inhibits telomere degradation and contributes to DNA damage repair (43, 44). Telomerase activation occurs in many cancers (45) and has been reported in childhood MB (46). The telomerase inhibitor Imetelstat has been used in clinical trials for selective blood cancers (47). It has also been used to inhibit the growth of MB cells injected into mice (48). We suggest it be investigated further in Group 3 MBs, particularly in those of the Group 3γ subtype.
Using the GO pathway of Regulation of telomere maintenance, we queried all our identified SRGs using the R2 genomics platform and found eight that were significantly different between the four MB subgroups (TCP1, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT8, SMG1, SMG6, and MAP3K4). One of the eight SRGs related to telomere maintenance, SMG6, is located on chromosome 17p. By Kaplan-Meier analysis SMG6 was associated with an HR below 1 (HR = 0.73 with 95% CI 0.62. to 0.86). High levels of this gene therefore were associated with protection whereas low expression levels were associated with worse survival. SMG6, a telomerase subunit, has been reported to bind to telomere DNA and to contribute to telomere regulation (38, 39). Our analysis of the data suggest that dysregulation of the TCP1 ring complex and telomerase activity are major factors in determination of survival in MB.
The pathway analysis of 17p SRGs (
Table 1) lists some pathways that do not seem to be related to cancer, including the GO pathway of adult locomotory behavior. However, a search of the literature shows that a number of the genes associated with this pathway are in fact related to various cancers as well. ARRB2 (β-arrestin 2) expression has been shown to modulate growth of colorectal cancer (49), glioblastoma (50), lung cancer (51), ovarian cancer (52), and prostate cancer (53). In the Cavalli dataset, high expression of ARRB2 and of PAFAH1B1 was protective (HR = 0.70, p = 1.38 x 10-05 and HR = 0.72, p = 4.90 x 10-05).
4.6. Chromosome 17q survival related genes
A gain in copy number of chromosome 17q has been reported to be associated with poor prognosis (14, 20). The heatmap of 17q SRGs (
Figure 11) suggests that some of these genes were over-expressed in the Group 3γ subtype, and some in the WNT group. For a number of SRGs on chromosome 17q, high expression was associated with MB groups 3 and 4. The high expression is consistent with isochromosome 17 aberration. Targeting the proteins encoding by these SRGs could be a way of overcoming the negative effects of overexpression of these genes due to isochromosome 17.
AXIN2 up-regulation (at 17q24.1) was associated with survival protection (
Figure 12) in the WNT subgroup. The AXIN2 protein is an inhibitor of the WNT signaling pathway (54), and a part of the destruction complex regulating β-catenin (55, 56) which is an immunohistochemical marker for WNT tumors (11). The AXIN2 protein also acts as a negative feedback signal limiting activation of the WNT pathway (54, 57). Mutations of AXIN2 have been reported to activate the WNT pathway (58). Our analysis shows that AXIN2 over-expression, perhaps as part of 17q gain, is associated with better survival in the WNT group than in the other 3 MB groups. Over-expression of AXIN2,as part of the feedback loop, may contribute to survival protection by limiting the WNT pathway signaling.
Two 17q SRGs significantly over-expressed in Group3γ were IGF2BP1 and KPBN1 (
Figure 13 and
Figure 14). For both, over-expression was associated with poor survival and a significant HR greater than one. To the best of our knowledge, there are no other reports linking these two genes to MB. However, IGF2BP1 promotes tumor growth in various cancers (59). IGF2BP1 enhances tumor growth by stabilizing mRNAs that code for cell cycle regulators (59, 60). The potential use of IGF2BP1 inhibitors in cancer therapy has been suggested by Huang et al. based on data showing that IGF2BP1 is over-expressed in various cancers (61). Our analysis suggests that the use of IGF2BP1 inhibitors may be more useful in Group 3γ MBs than in the other subtypes.
KPNB1 has been shown to stimulate proliferation of cancer cells in various cancers including breast cancer (62), prostate cancer (63), gastric cancer (64), colon cancer (65) and ovarian cancer (66). KPNB1 inhibitors have been reported to be effective in inhibiting proliferation of cancer cells (19). KPBN1 is involved in the transport of proteins and RNA to the nucleus (19, 67). Our pathway analysis of 17q SRGs identified KPNB1 as one of the genes associated with the mRNA transport pathway (Table 3). We suggest that KPNB1 inhibitors be tested in Group 3γ cells as a step in determining its therapeutic potential in this subtype of MB. KPNB1 has been identified as an oncogene in ovarian cancer (68). Our analysis supports the hypothesis that KPNB1 is a 17q oncogene that stimulates proliferation in Group 3γ MBs. In summary, various reports suggest that KPBN1 may be a potential therapeutic target (18) in cancers. Our analysis suggests KPBN1 may be a potential therapeutic target in Group 3γ MBs. Our list of 17q SRGs may contain one or more oncogenes that are likely MB subtype specific. It appears that, at least statistically, KPNB1 fits the category. Its importance in MB is enhanced by the statistical evidence relating it to survival.
5. Summary
We have identified chromosomes 6 and 17 as the location of over-representation of SRGs in the Cavalli dataset. We conclude that genes on chromosome 6 makes a major contribution to survival risk, a contribution, at least partially unrelated to monosomy 6, while chromosome 17 SRGs are related to SCNAs, primarily isochromosome 17. The most significant biological pathways associated with these genes were mitotic cell cycle process and regulation of chromosome organization at the telomeric region.
Statistically, the most significant SRG was HGMA1 on chromosome 6p. As an histone competitor it functions as an important transcription factor and regulator of the nucleosome. High expression of this gene is found in MB Group 3γ, which has the worst survival prognosis compared to the other MB subtypes. The most significant SRG on chromosome 6q was SYNCRIP, a gene previously described as an MB driver gene. Thus, high expression of selected chromosome 6 SRGs are markers of poor prognosis in the MB Group 3γ tumors and potential therapeutic targets for this MB subtype.
Eight SRG genes (TCP1, CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT8, SMG1, SMG6, and MAP3K4) contributed to the GO term regulation of telomere maintenance, including TCPI and MAP3K4 located on chromosome 6q and SMG6 on chromosome 17p. Five of these genes encoded components of the TCP1 complex, a structure in which protein folding occurs. The TCP1 complex has been shown to play a role in regulation of telomerase (69). The data provide a rationale for clinical testing of the telomerase inhibitor Imetelstat in Group 3 MBs.
Our analysis supports the hypothesis of one or more tumor suppressor genes among our list of 17p SRGs. Included in the 17p SRGs is CTDNEP1, another gene on the Northcott list of driver genes. Decreased expression of this gene was associated with worse survival. Decreased expression of CTDNEPI was found in the MB Group 4β compared to all the 12 subgroups in the Cavalli dataset. CTDNEP1 has recently been reported as a tumor suppressor in aggressive MB (36).
High expression of AXIN2, an SRG on 17q, was associated with survival protection in the WNTα subgroup. High hazard ratios were found for several SRGs at the telomere end of 17q. Overexpression of SRGs on 17q appears to be related to isochromosome 17 and poor prognosis. KPBN1, a 17q SRG and oncogene, overexpressed in Group 3γ MBs, encodes for a protein over-expressed in various cancers. Several KPBN1 inhibitors are available (19) that could be used to determine their effectiveness as therapeutic agents in Group 3γ MBs.
Our analysis shows that the top genes supporting four molecular groups in MB are not necessarily the genes most associated with survival. The SRGs identified in this study, however, provide information on potentially therapeutic targets, some of which are MB subgroup or subtype specific.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
References
- Thompson, M.C.; Fuller, C.; Hogg, T.L.; Dalton, J.; Finkelstein, D.; Lau, C.C.; Chintagumpala, M.; Adesina, A.; Ashley, D.M.; Kellie, S.J.; et al. Genomics Identifies Medulloblastoma Subgroups That Are Enriched for Specific Genetic Alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Cho, Y.-J.; Clifford, S.C.; Eberhart, C.G.; Parsons, D.W.; Rutkowski, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 123, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.M.G.; Remke, M.; Rampasek, L.; Peacock, J.; Shih, D.J.H.; Luu, B.; Garzia, L.; Torchia, J.; Nor, C.; Morrissy, A.S.; et al. Intertumoral Heterogeneity within Medulloblastoma Subgroups. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaupt, H.; Johansson, P.; Sundström, A.; Lubovac-Pilav, Z.; Olsson, B.; Nelander, S.; Swartling, F.J. Batch-normalization of cerebellar and medulloblastoma gene expression datasets utilizing empirically defined negative control genes. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goschzik, T.; Mühlen, A.Z.; Kristiansen, G.; Haberler, C.; Stefanits, H.; Friedrich, C.; von Hoff, K.; Rutkowski, S.; Pfister, S.M.; Pietsch, T. Molecular stratification of medulloblastoma: comparison of histological and genetic methods to detect Wnt activated tumours. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2015, 41, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, D.J.; Northcott, P.A.; Remke, M.; Korshunov, A.; Ramaswamy, V.; Kool, M.; Luu, B.; Yao, Y.; Wang, X.; Dubuc, A.M.; et al. Cytogenetic Prognostication Within Medulloblastoma Subgroups. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Witt, H.; Hielscher, T.; Eberhart, C.G.; Mack, S.; Bouffet, E.; Clifford, S.C.; Hawkins, C.E.; French, P.; et al. Medulloblastoma Comprises Four Distinct Molecular Variants. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, N.; Rasheed, B.K.A.; McLendon, R.E.; Friedman, H.S.; Bigner, D.D.; Bigner, S.H. Characterization of chromosome 17 abnormalities in medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2000, 99, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Yu, D.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Lin, N.; Huang, H.; Xu, L. Clinical findings and genetic analysis of patients with copy number variants involving 17p13.3 using a single nucleotide polymorphism array: a single-center experience. BMC Med Genom. 2022, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lin, F.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Identification of a Twelve-Gene Signature and Establishment of a Prognostic Nomogram Predicting Overall Survival for Medulloblastoma. Front. Genet. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford SC, Lusher ME, Lindsey JC, Langdon JA, Gilbertson RJ, Straughton D, et al. Wnt/Wingless pathway activation and chromosome 6 loss characterize a distinct molecular sub-group of medulloblastomas associated with a favorable prognosis. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(22):2666-70.
- A Northcott, P.; Dubuc, A.M.; Pfister, S.; Taylor, M.D. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2012, 12, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.-H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Cheong, H.; Ramaswamy, V.; Park, S.-H.; Kool, M.; Phi, J.H.; Choi, S.A.; Cavalli, F.; Taylor, M.D.; et al. Subgroup-specific prognostic signaling and metabolic pathways in pediatric medulloblastoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seal, R.L.; Denny, P.; Bruford, E.A.; Gribkova, A.K.; Landsman, D.; Marzluff, W.F.; McAndrews, M.; Panchenko, A.R.; Shaytan, A.K.; Talbert, P.B. A standardized nomenclature for mammalian histone genes. Epigenetics Chromatin 2022, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senigagliesi, B.; Penzo, C.; Severino, L.U.; Maraspini, R.; Petrosino, S.; Morales-Navarrete, H.; Pobega, E.; Ambrosetti, E.; Parisse, P.; Pegoraro, S.; et al. The High Mobility Group A1 (HMGA1) Chromatin Architectural Factor Modulates Nuclear Stiffness in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcott, P.A.; Buchhalter, I.; Morrissy, A.S.; Hovestadt, V.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Ehrenberger, T.; Gröbner, S.; Segura-Wang, M.; Zichner, T.; Rudneva, V.A.; et al. The whole-genome landscape of medulloblastoma subtypes. Nature 2017, 547, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.-C.; Liu, J.-W.; Li, K.; Zheng, J.; Xiong, Z.-Q. KPNB1 inhibition disrupts proteostasis and triggers unfolded protein response-mediated apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2936–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Lin, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, S.; Lang, K.; Yang, Z.; Sun, X. KPNB1-mediated nuclear import in cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 955, 175925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, S.; Remke, M.; Benner, A.; Mendrzyk, F.; Toedt, G.; Felsberg, J.; Wittmann, A.; Devens, F.; Gerber, N.U.; Joos, S.; et al. Outcome Prediction in Pediatric Medulloblastoma Based on DNA Copy-Number Aberrations of Chromosomes 6q and 17q and the MYC and MYCN Loci. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikov, Y.V.; Bustin, M. Functional interplay between histone H1 and HMG proteins in chromatin. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumter, T.; Xian, L.; Huso, T.; Koo, M.; Chang, Y.-T.; Almasri, T.; Chia, L.; Inglis, C.; Reid, D.; Resar, L. The High Mobility Group A1 (HMGA1) Transcriptome in Cancer and Development. Curr. Mol. Med. 2016, 16, 353–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Q.; Huang, J.; Chen, W.; Tang, J.; Xu, C.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, L.; Yu, X.; Li, S. Regulation of DNA replication-coupled histone gene expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95005–95022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Z.; He, S.; Chen, S. Histone-fold centromere protein W (CENP-W) is associated with the biological behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhao, M. ONGene: A literature-based database for human oncogenes. J. Genet. Genom. 2017, 44, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, G.C.; Zielenska, M.; Prasad, M.; A Squire, J. Chromosome 6p amplification and cancer progression. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuck C, Williamson JR, Wuthrich K, Serrano P. The acidic domain is a unique structural feature of the splicing factor SYNCRIP. Protein Sci. 2016;25(8):1545-50.
- Geuens, T.; Bouhy, D.; Timmerman, V. The hnRNP family: insights into their role in health and disease. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duning, K.; Buck, F.; Barnekow, A.; Kremerskothen, J. SYNCRIP, a component of dendritically localized mRNPs, binds to the translation regulator BC200 RNA. J. Neurochem. 2007, 105, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sursal, T.; Ronecker, J.S.; Dicpinigaitis, A.J.; Mohan, A.L.; Tobias, M.E.; Gandhi, C.D.; Jhanwar-Uniyal, M. Molecular Stratification of Medulloblastoma: Clinical Outcomes and Therapeutic Interventions. Anticancer. Res. 2022, 42, 2225–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, E.; Pellarin, M.; Holmes, E.; Smirnov, I.; Misra, A.; Eberhart, C.G.; Burger, P.C.; Biegel, J.A.; Feuerstein, B.G. Isochromosome 17q Is a Negative Prognostic Factor in Poor-Risk Childhood Medulloblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4733–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeChiara, C.; Borghese, A.; Fiorillo, A.; Genesio, R.; Conti, A.; D'Amore, R.; Pettinato, G.; Varone, A.; Maggi, G. Cytogenetic evaluation of isochromosome 17q in posterior fossa tumors of children and correlation with clinical outcome in medulloblastoma. Child's Nerv. Syst. 2002, 18, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.G.; Bäcklund, L.M.; Leong, H.S.; Ichimura, K.; Collins, V.P. Chromosome 17 alterations identify good-risk and poor-risk tumors independently of clinical factors in medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogen, P.H.; McDonald, J.D. Tumor suppressor genes and medulloblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncology 1996, 29, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zou, H.; Xiong, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Miyagishima, D.F.; Wanggou, S.; Li, X. Construction and Validation of a 13-Gene Signature for Prognosis Prediction in Medulloblastoma. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Xin, D.; Liao, Y.; Berry, K.; Ogurek, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Rao, R.; Dong, X.; et al. Loss of phosphatase CTDNEP1 potentiates aggressive medulloblastoma by triggering MYC amplification and genomic instability. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venteicher, A.S.; Abreu, E.B.; Meng, Z.; McCann, K.E.; Terns, R.M.; Veenstra, T.D.; Terns, M.P.; Artandi, S.E. A Human Telomerase Holoenzyme Protein Required for Cajal Body Localization and Telomere Synthesis. Science 2009, 323, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichenbach, P.; Höss, M.; Azzalin, C.M.; Nabholz, M.; Bucher, P.; Lingner, J. A Human Homolog of Yeast Est1 Associates with Telomerase and Uncaps Chromosome Ends When Overexpressed. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, B.E.; Erdmann, N.; Cruickshank, J.; Goldman, H.; Gill, R.; Robinson, M.O.; Harrington, L. Functional Conservation of the Telomerase Protein Est1p in Humans. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Shivji, M.K.K.; Chen, C.; Kolodner, R.; Wood, R.D.; Dutta, A. The Evolutionarily Conserved Zinc Finger Motif in the Largest Subunit of Human Replication Protein A Is Required for DNA Replication and Mismatch Repair but Not for Nucleotide Excision Repair. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudic, A.; Jul-Larsen. ; Haring, S.J.; Wold, M.S.; Lønning, P.E.; Bjerkvig, R.; Bøe, S.O. Replication protein A prevents accumulation of single-stranded telomeric DNA in cells that use alternative lengthening of telomeres. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7267–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sahoo, S.S.; Honda, M.; Granger, S.L.; Goodings, C.; Sanchez, L.; Kunstner, A.; Busch, H.; Beier, F.; Pruett-Miller, S.M.; et al. Gain-of-function mutations in RPA1 cause a syndrome with short telomeres and somatic genetic rescue. Blood 2021, 139, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Nabetani, A.; Shimamura, S.; Tamura, M.; Yonehara, S.; Saito, M.; Ishikawa, F. RPA-like Mammalian Ctc1-Stn1-Ten1 Complex Binds to Single-Stranded DNA and Protects Telomeres Independently of the Pot1 Pathway. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Stewart, J.; Price, C.M. Human CST abundance determines recovery from diverse forms of DNA damage and replication stress. [CrossRef]
- Barthel, F.P.; Wei, W.; Tang, M.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Hu, X.; Amin, S.B.; Akdemir, K.C.; Seth, S.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; et al. Systematic analysis of telomere length and somatic alterations in 31 cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasi, S.; Baldi, C.; Pietsch, T.; Donofrio, V.; Pollo, B.; Antonelli, M.; Massimino, M.; Giangaspero, F.; Buttarelli, F.R. Telomere elongation via alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) and telomerase activation in primary metastatic medulloblastoma of childhood. J. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 142, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olschok, K.; Altenburg, B.; de Toledo, M.A.S.; Maurer, A.; Abels, A.; Beier, F.; Gezer, D.; Isfort, S.; Paeschke, K.; Brümmendorf, T.H.; et al. The telomerase inhibitor imetelstat differentially targets JAK2V617F versus CALR mutant myeloproliferative neoplasm cells and inhibits JAK-STAT signaling. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1277453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, S.; Kumar, S.S.; Bondra, K.; Sobo, M.; Mo, X.; Drissi, R. Limitations of radiosensitization by direct telomerase inhibition to treat high-risk medulloblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Lin, Z.; Ye, Y.; Luo, R.; Zeng, L. ARRB2 promotes colorectal cancer growth through triggering WTAP. Acta Biochim. et Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae WY, Choi JS, Nam S, Jeong JW. beta-arrestin 2 stimulates degradation of HIF-1alpha and modulates tumor progression of glioblastoma. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(11):3092-104.
- Kim JY, Shin JH, Kim MJ, Kang Y, Lee JS, Son J, et al. beta-arrestin 2 negatively regulates lung cancer progression by inhibiting the TRAF6 signaling axis for NF-kappaB activation and autophagy induced by TLR3 and TLR4. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(7):422.
- Czogalla B, Partenheimer A, Jeschke U, von Schonfeldt V, Mayr D, Mahner S, et al. beta-arrestin 2 Is a Prognostic Factor for Survival of Ovarian Cancer Patients Upregulating Cell Proliferation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:554733.
- Zhou, B.; Song, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qi, W. The Comprehensive Analysis of Hub Gene ARRB2 in Prostate Cancer. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund JN, Costantini F. Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(4):1172-83.
- Stamos JL, Weis WI. The beta-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(1):a007898.
- Schaefer, K.N.; Peifer, M. Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling Regulation and a Role for Biomolecular Condensates. Dev. Cell 2019, 48, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung JY, Kolligs FT, Wu R, Zhai Y, Kuick R, Hanash S, et al. Activation of AXIN2 expression by beta-catenin-T cell factor. A feedback repressor pathway regulating Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(24):21657-65.
- Koch, A.; Hrychyk, A.; Hartmann, W.; Waha, A.; Mikeska, T.; Waha, A.; Schüller, U.; Sörensen, N.; Berthold, F.; Goodyer, C.G.; et al. Mutations of the Wnt antagonist AXIN2 (Conductin) result in TCF-dependent transcription in medulloblastomas. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Bley, N.; Busch, B.; Gla, M.; Lederer, M.; Misiak, C.; Fuchs, T.; Wedler, A.; Haase, J.; Bertoldo, J.B.; et al. The oncofetal RNA-binding protein IGF2BP1 is a druggable, post-transcriptional super-enhancer of E2F-driven gene expression in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 8576–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaß, M.; Misiak, D.; Bley, N.; Müller, S.; Hagemann, S.; Busch, B.; Rausch, A.; Hüttelmaier, S. IGF2BP1, a Conserved Regulator of RNA Turnover in Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang X, Zhang H, Guo X, Zhu Z, Cai H, Kong X. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):88.
- Sheng C, Qiu J, He Z, Wang H, Wang Q, Guo Z, et al. Suppression of Kpnbeta1 expression inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation by abrogating nuclear transport of Her2. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(2):554-64.
- Grupp, K.; Habermann, M.; Sirma, H.; Simon, R.; Steurer, S.; Hube-Magg, C.; Prien, K.; Burkhardt, L.; Jedrzejewska, K.; Salomon, G.; et al. High nuclear karyopherin α 2 expression is a strong and independent predictor of biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer patients treated by radical prostatectomy. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, B.; Yokobori, T.; Mochiki, E.; Ohno, T.; Ogata, K.; Ogawa, A.; Yanai, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Luvsandagva, B.; Asao, T.; et al. Nuclear karyopherin-α2 expression in primary lesions and metastatic lymph nodes was associated with poor prognosis and progression in gastric cancer. Carcinog. 2013, 34, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Li KF. Karyopherin beta1 deletion suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer (CRC) by reducing MET expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;120:109127.
- Huang, L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Li, J.-D.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, R.-Z.; Yun, J.-P.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.-H.; Zheng, M. KPNA2 promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity in epithelial ovarian carcinoma through upregulation of c-Myc and downregulation of FOXO3a. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e745–e745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakielny, S.; Dreyfuss, G. Transport of Proteins and RNAs in and out of the Nucleus. Cell 1999, 99, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, M.; Kodama, T.; Newberg, J.Y.; Katayama, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Hanash, S.M.; Yoshihara, K.; Wei, Z.; Tien, J.C.; Rangel, R.; et al. In vivo loss-of-function screens identify KPNB1 as a new druggable oncogene in epithelial ovarian cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, E7301–E7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund A, Zhong FL, Venteicher AS, Meng Z, Veenstra TD, Frydman J, et al. Proteostatic control of telomerase function through TRiC-mediated folding of TCABCell. 2014;159(6):1389-403.
Figure 1.
Kaplan Meier curves for the four consensus MB subgroups in the Cavalli et al. (2017) dataset up to 144 months (χ2 = 31.68, p = 6.12 x 10-07). Sample sizes by MB subgroup: Group3 (red) n = 113; Group 4 (green) n = 264; SHH (blue) n = 172; WNT (purple) n = 63.
Figure 1.
Kaplan Meier curves for the four consensus MB subgroups in the Cavalli et al. (2017) dataset up to 144 months (χ2 = 31.68, p = 6.12 x 10-07). Sample sizes by MB subgroup: Group3 (red) n = 113; Group 4 (green) n = 264; SHH (blue) n = 172; WNT (purple) n = 63.
Figure 2.
Chromosomal distribution of SRGs. A. Distribution of the proportions of the number of SRGs to the total number of genes on each chromosome. For the x-axis legends, the top row shows the number of the SRGs, the bottom row shows the chromosome number. The number of SRG genes for each chromosome was divided by the total number of protein coding genes for each chromosome and expressed as a percentage in the y-axis legend. The highest proportions of the SRGs were noted on chromosomes 6 and 17 (both p values < 0.0001), compared to the SRG proportions for the other chromosomes. B. Chromosomal distribution of hazard ratios of SRGs. For chromosome 6, most of the hazard ratios for SRGs were >1 (red, i.e, high gene expression poor survival). For chromosome 17, most of the hazard ratios for the p arm SRGs were <1 (blue; i.e. high gene expression better survival), while most of the hazard ratios for the q arm SRGs were >1 (red; i.e. high gene expression poor survival).
Figure 2.
Chromosomal distribution of SRGs. A. Distribution of the proportions of the number of SRGs to the total number of genes on each chromosome. For the x-axis legends, the top row shows the number of the SRGs, the bottom row shows the chromosome number. The number of SRG genes for each chromosome was divided by the total number of protein coding genes for each chromosome and expressed as a percentage in the y-axis legend. The highest proportions of the SRGs were noted on chromosomes 6 and 17 (both p values < 0.0001), compared to the SRG proportions for the other chromosomes. B. Chromosomal distribution of hazard ratios of SRGs. For chromosome 6, most of the hazard ratios for SRGs were >1 (red, i.e, high gene expression poor survival). For chromosome 17, most of the hazard ratios for the p arm SRGs were <1 (blue; i.e. high gene expression better survival), while most of the hazard ratios for the q arm SRGs were >1 (red; i.e. high gene expression poor survival).
Figure 3.
Pathway analysis of SRPs on chromosome 6. Percentage of GO terms per group.
Figure 3.
Pathway analysis of SRPs on chromosome 6. Percentage of GO terms per group.
Figure 4.
Heatmap and cluster analysis of the SRGs on chromosome 6p. Each column is an individual, each row is an SRG, and the colour shows the low (blue) to high (red) gene expression levels. The individuals were grouped by the MB molecular subgroups and subtypes. Increased gene expression with worse survival (HR>1) is shown for 61/64 SRGs. Increased expression of the 6p SRGs (red) was found primarily in the Group 3γ subtype, while decreased expression (blue) primarily in the WNTα subtype.
Figure 4.
Heatmap and cluster analysis of the SRGs on chromosome 6p. Each column is an individual, each row is an SRG, and the colour shows the low (blue) to high (red) gene expression levels. The individuals were grouped by the MB molecular subgroups and subtypes. Increased gene expression with worse survival (HR>1) is shown for 61/64 SRGs. Increased expression of the 6p SRGs (red) was found primarily in the Group 3γ subtype, while decreased expression (blue) primarily in the WNTα subtype.
Figure 5.
The HMGA1 gene. A. HMGA1expression by subtype. It was most elevated in Group 3 gamma subtype (p < 0.0001). B. Kaplan-Meier curves for the high (blue) vs. low (red) expression groups for HMGA1 up to 144 months using the Cavalli dataset (p = 2.46 x 10-11, high n = 40, low n = 572).
Figure 5.
The HMGA1 gene. A. HMGA1expression by subtype. It was most elevated in Group 3 gamma subtype (p < 0.0001). B. Kaplan-Meier curves for the high (blue) vs. low (red) expression groups for HMGA1 up to 144 months using the Cavalli dataset (p = 2.46 x 10-11, high n = 40, low n = 572).
Figure 6.
Heatmap and cluster analysis of the SRGs on chromosome 6q. Each column is an individual, each row is a SRG, and the colour shows the low (blue) to high (red) gene expression levels. The individuals were grouped by the MB molecular subtypes and subgroups, and the genes were clustered by rows (gene expression).
Figure 6.
Heatmap and cluster analysis of the SRGs on chromosome 6q. Each column is an individual, each row is a SRG, and the colour shows the low (blue) to high (red) gene expression levels. The individuals were grouped by the MB molecular subtypes and subgroups, and the genes were clustered by rows (gene expression).
Figure 7.
The CENPW gene. A. Gene expression of CENPW by MB subtypes (p < 0.0001); B. Kaplan-Meier curves (p = 2.25 x 10-04).
Figure 7.
The CENPW gene. A. Gene expression of CENPW by MB subtypes (p < 0.0001); B. Kaplan-Meier curves (p = 2.25 x 10-04).
Figure 8.
Pathway analysis of SRGs on chromosome 17. Percentage of GO terms per group.
Figure 8.
Pathway analysis of SRGs on chromosome 17. Percentage of GO terms per group.
Figure 9.
Heatmap and cluster analysis of the SRGs on chromosome 17p. Each column is an individual, each row is an SRG, and the colour shows the low (blue) to high (red) gene expression levels. Genes expression was ordered by the cluster analysis. The individuals were grouped by the MB molecular subtypes and subgroups. Group 4β shows relatively decreased expression of SRGs. Genes were ordered by cluster analysis of expression.
Figure 9.
Heatmap and cluster analysis of the SRGs on chromosome 17p. Each column is an individual, each row is an SRG, and the colour shows the low (blue) to high (red) gene expression levels. Genes expression was ordered by the cluster analysis. The individuals were grouped by the MB molecular subtypes and subgroups. Group 4β shows relatively decreased expression of SRGs. Genes were ordered by cluster analysis of expression.
Figure 10.
A. The distribution of the SRGs on the p and q arms of chromosome 17 by cytogenetic band. The X axis legend indicates the cytogenetic band and the total number of genes on each cytogenetic band. B. Distribution of the SRG hazard ratios on chromosome 17 by cytogenetic band. Blue bars indicate HRs of less than one for an SRG, while red bars indicate HRs of greater than one. P arm has more SRGs than q arm. High hazard ratios are noted for SRGs at the telomere end of 17q,.
Figure 10.
A. The distribution of the SRGs on the p and q arms of chromosome 17 by cytogenetic band. The X axis legend indicates the cytogenetic band and the total number of genes on each cytogenetic band. B. Distribution of the SRG hazard ratios on chromosome 17 by cytogenetic band. Blue bars indicate HRs of less than one for an SRG, while red bars indicate HRs of greater than one. P arm has more SRGs than q arm. High hazard ratios are noted for SRGs at the telomere end of 17q,.
Figure 11.
Heatmap and cluster analysis of the SRGs for MB on chromosome 17q. Each column is an individual, each row is a SRG, and the colour shows the low (blue) to high (red) gene expression levels. The individuals were grouped by the MB molecular subtypes and subgroups. Genes were grouped by cluster analysis of expression.
Figure 11.
Heatmap and cluster analysis of the SRGs for MB on chromosome 17q. Each column is an individual, each row is a SRG, and the colour shows the low (blue) to high (red) gene expression levels. The individuals were grouped by the MB molecular subtypes and subgroups. Genes were grouped by cluster analysis of expression.
Figure 12.
AXIN2 on 17q. A. AXIN2 gene expression by MB subtype: higher expression in the WNT subgroup (F = 577.14, p < 1.0 x 10-300) B. Kaplan-Meier curves: elevated expression of AXIN2 is associated with better survival (p = 1.05 x 10-04).
Figure 12.
AXIN2 on 17q. A. AXIN2 gene expression by MB subtype: higher expression in the WNT subgroup (F = 577.14, p < 1.0 x 10-300) B. Kaplan-Meier curves: elevated expression of AXIN2 is associated with better survival (p = 1.05 x 10-04).
Figure 13.
IGF2BP1 expression elevated in Group3γ. A High expression of this gene in Group 3γ. By analysis of variance, F = 23.59, p = 6.81 x 10-42; B. Kaplan Meier survival curves (p = 8.9 x 10-12).
Figure 13.
IGF2BP1 expression elevated in Group3γ. A High expression of this gene in Group 3γ. By analysis of variance, F = 23.59, p = 6.81 x 10-42; B. Kaplan Meier survival curves (p = 8.9 x 10-12).
Figure 14.
The KPNB1 gene A.KPNB1 expression elevated in Group3γ. By analysis of variance, F = 20.27, p = 4.26 x 10-36. B. High expression of this gene was associated with poor survival. Kaplan Meier survival curves (p = 5.47 x 10-26).
Figure 14.
The KPNB1 gene A.KPNB1 expression elevated in Group3γ. By analysis of variance, F = 20.27, p = 4.26 x 10-36. B. High expression of this gene was associated with poor survival. Kaplan Meier survival curves (p = 5.47 x 10-26).
Table 1.
Pathway analysis of chromosome 17p SRGs.
Table 1.
Pathway analysis of chromosome 17p SRGs.
| Gene Ontology analysis of chromosome 17p |
|---|
| Gene Ontology Term |
GO Term p value |
SRGs |
| Nuclear membrane disassembly |
6.53 x 10-06
|
CTDNEP1, NDEL1, PAFAH1B1 |
| Adult locomotory (walking) behavior |
1.37 x 10-05
|
ARRB2, CTNS, EFNB3, NLGN2, PAFAH1B1 |
| Cytochrome complex assembly |
3.12 x 10-04
|
COX10, SCO1, TTC19 |
| Neuromuscular process controlling balance |
1.03 x 10-03
|
DLG4, NGLN2, PAFAH1B1 |
Table 2.
Pathway analysis of chromosome 17q SRGs.
Table 2.
Pathway analysis of chromosome 17q SRGs.
| Gene Ontology Term |
GO term p value |
SRGs |
| nuclear chromosome segregation |
3.72 x 10-06
|
ANAPC11, AXIN2, BECN1, HID1, KPNB1, P3H4, TUBG2 |
| RNA transport |
4.56 x 10-04
|
ALYREF, EIF4A3, IGF2BP1, KPNB1 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).