Submitted:
02 May 2024
Posted:
07 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
3-chymotrypsin-Like Protease: A Validated Molecular Target
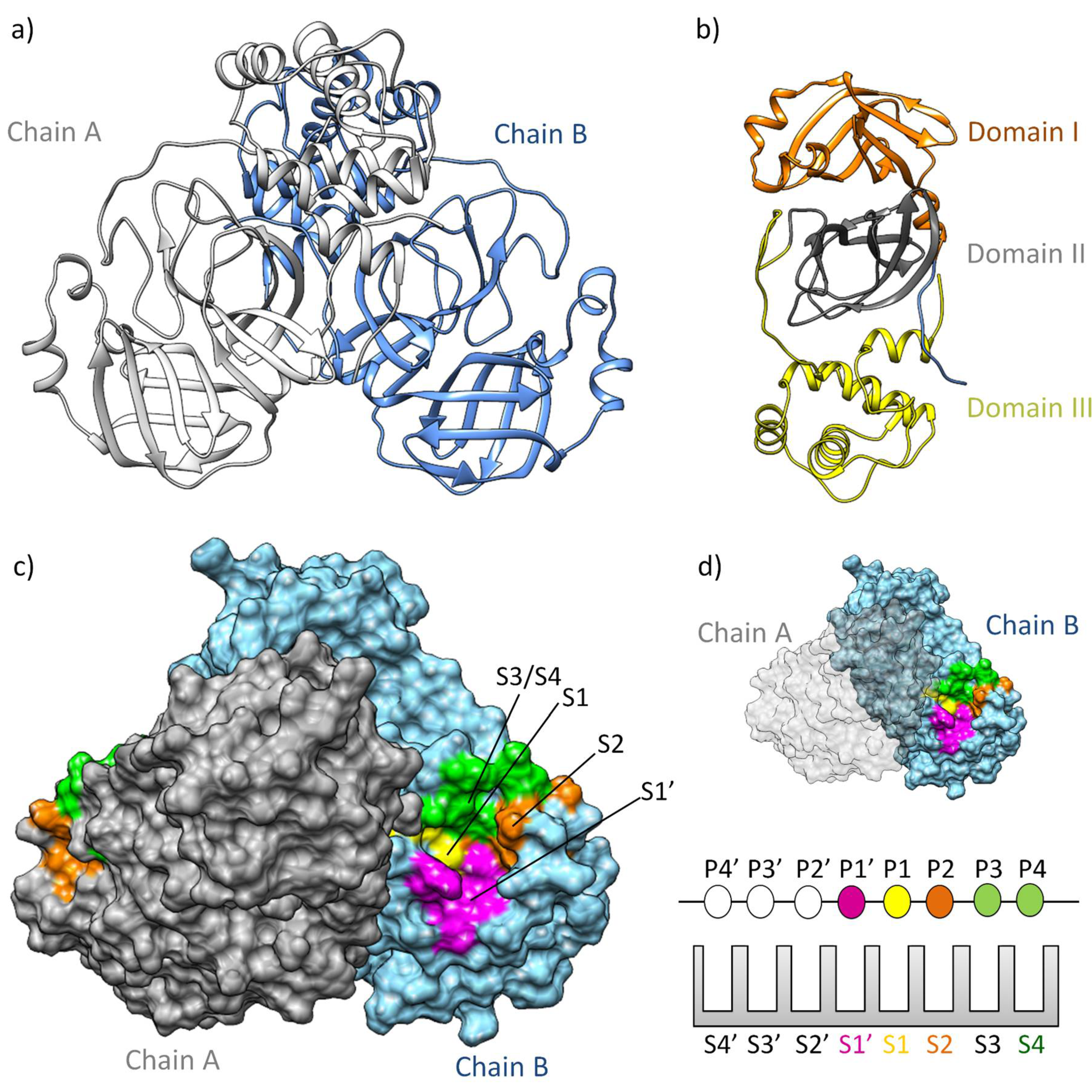
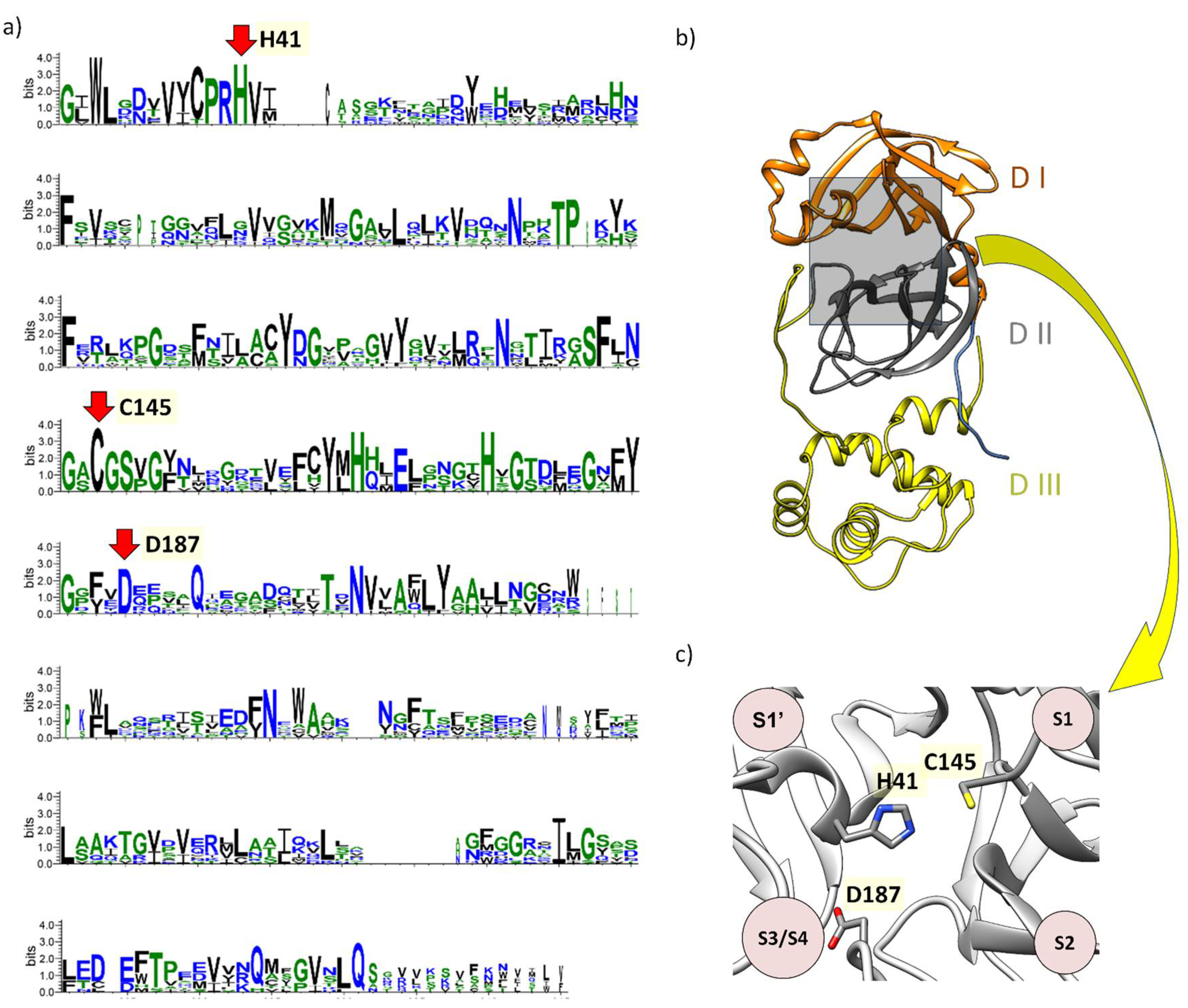
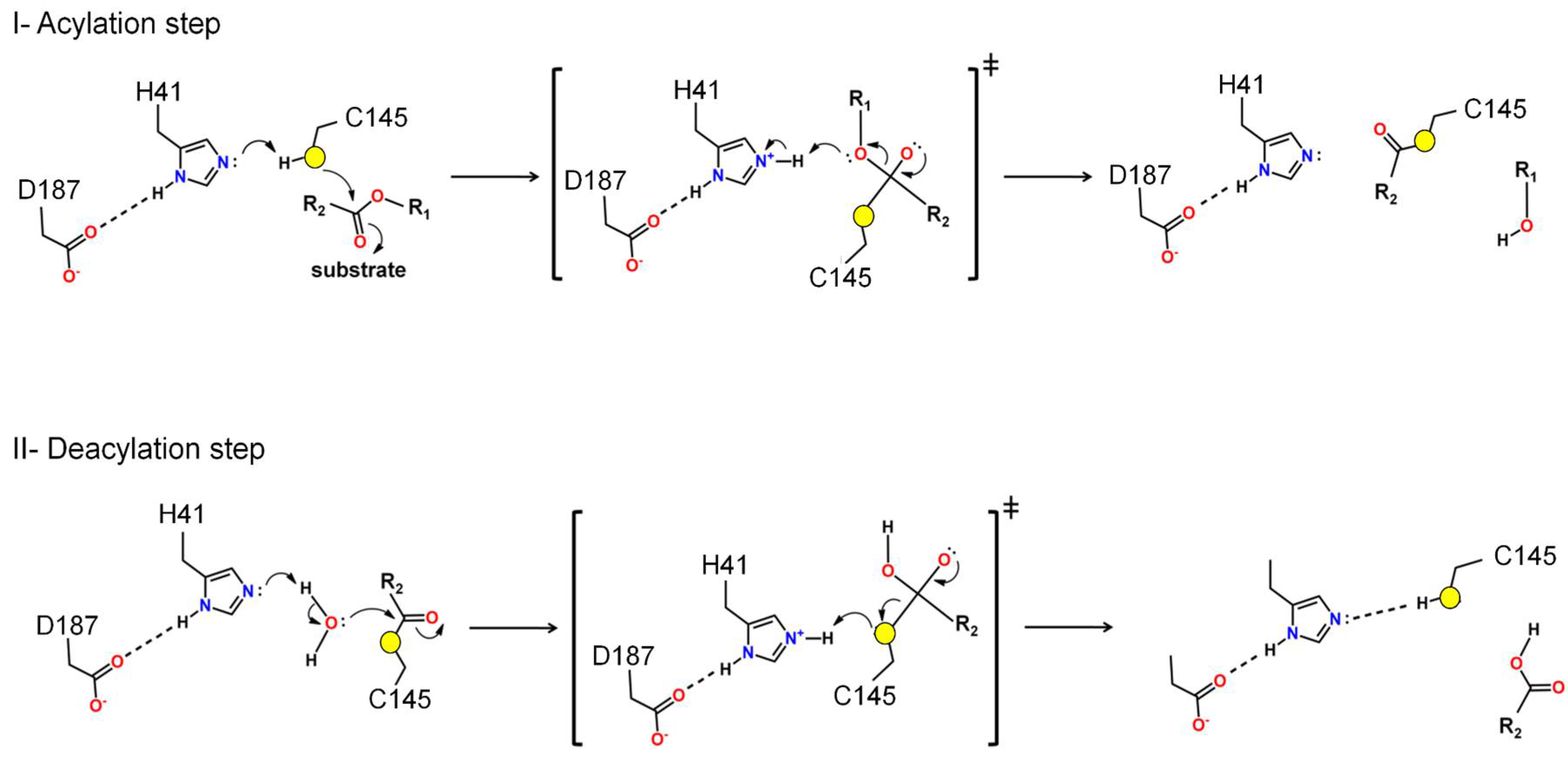
Structure and Function of Mpro: A Novel Proposal for the Mechanism of Polyprotein Processing
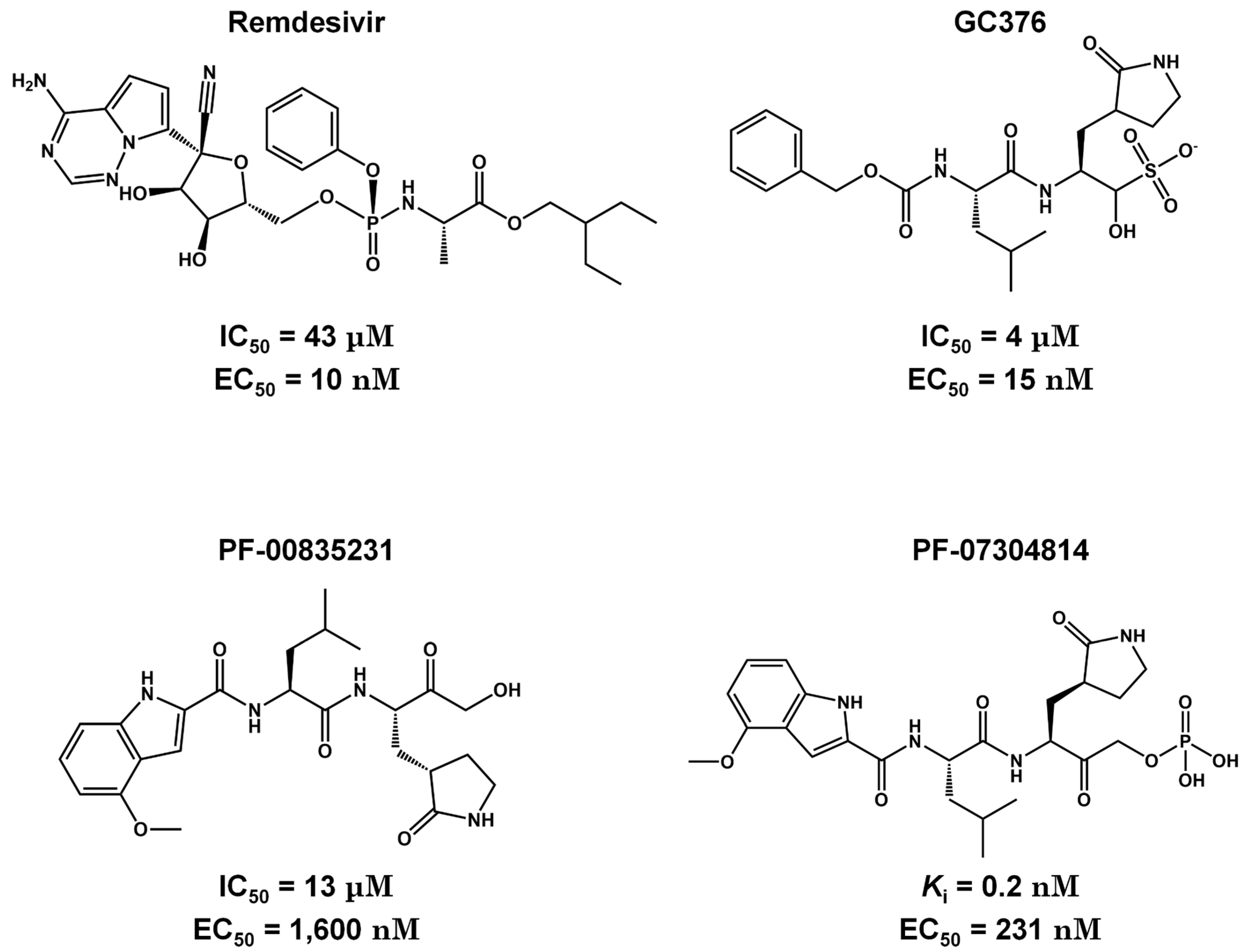
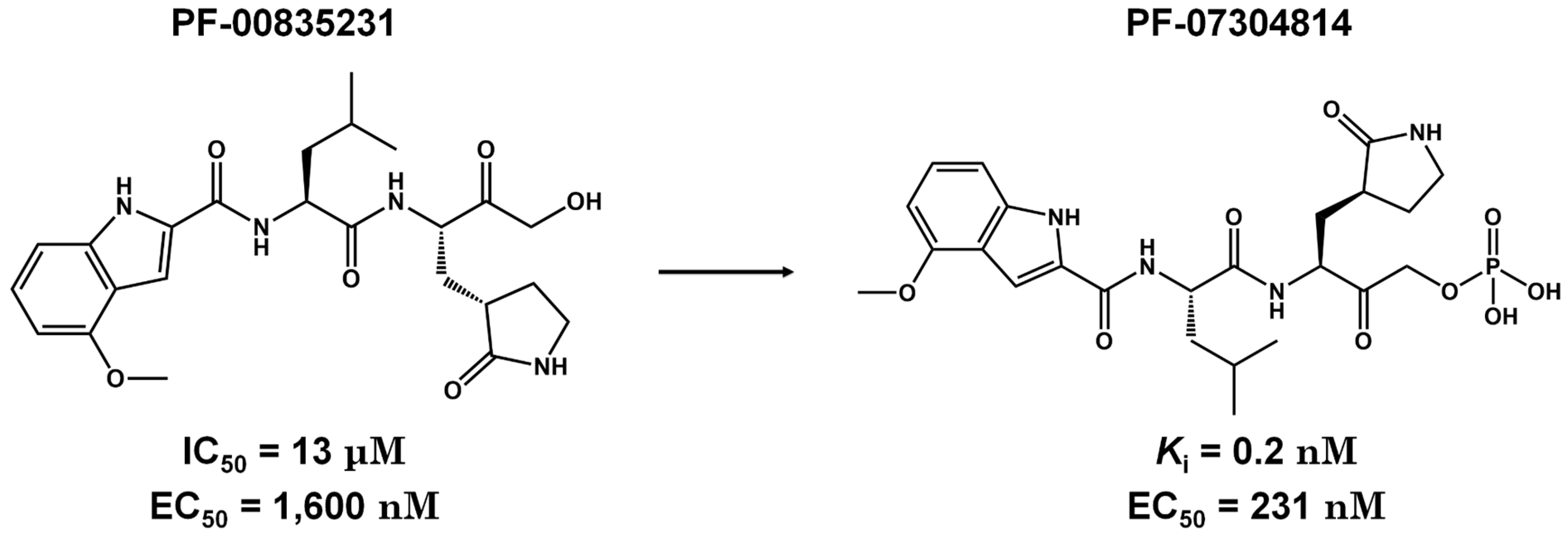
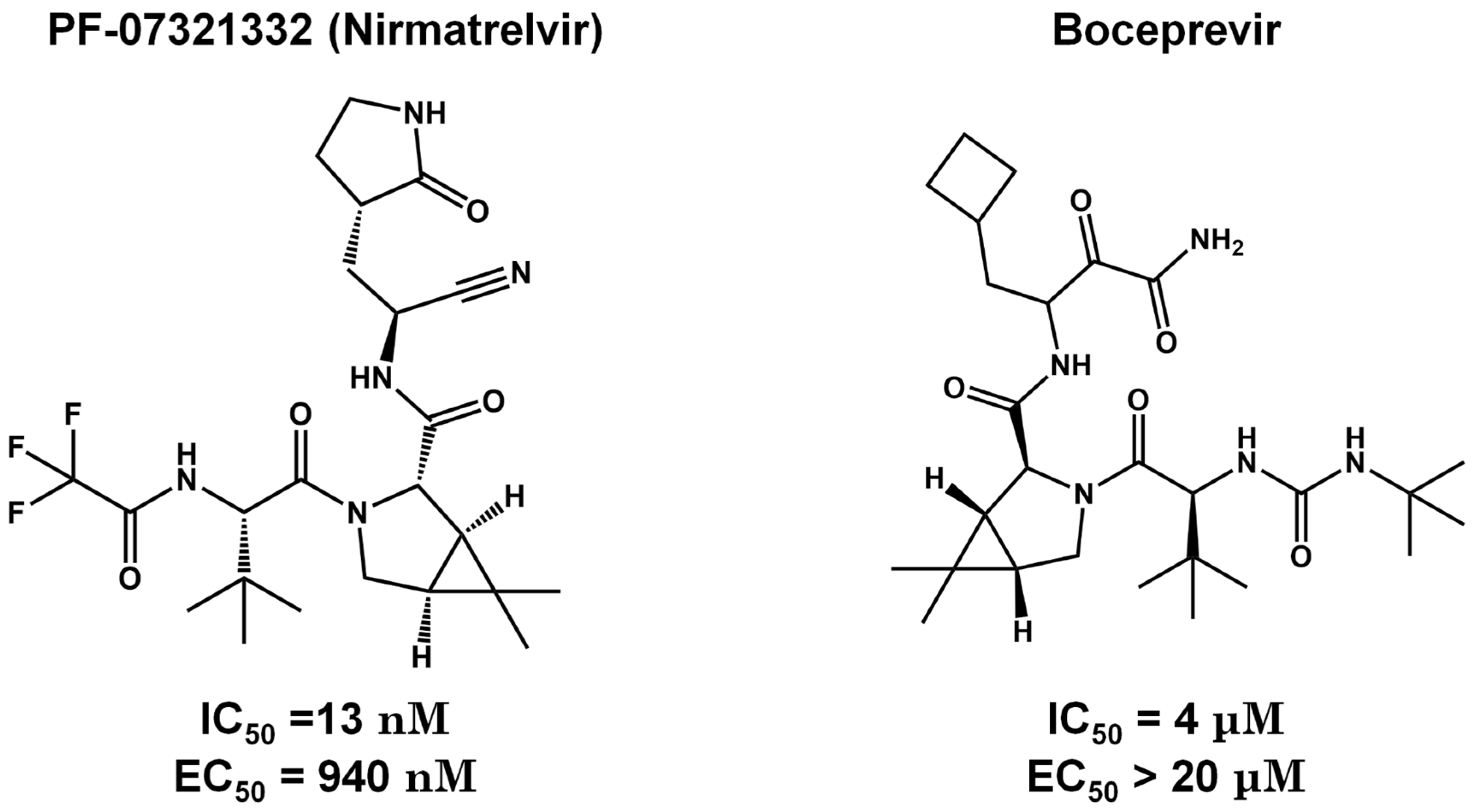
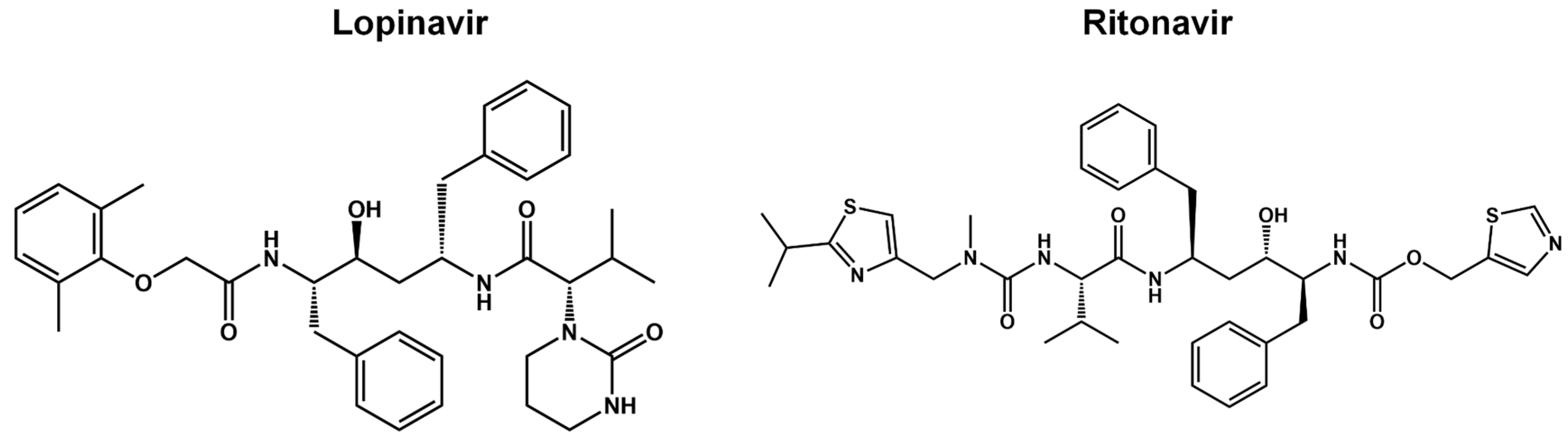
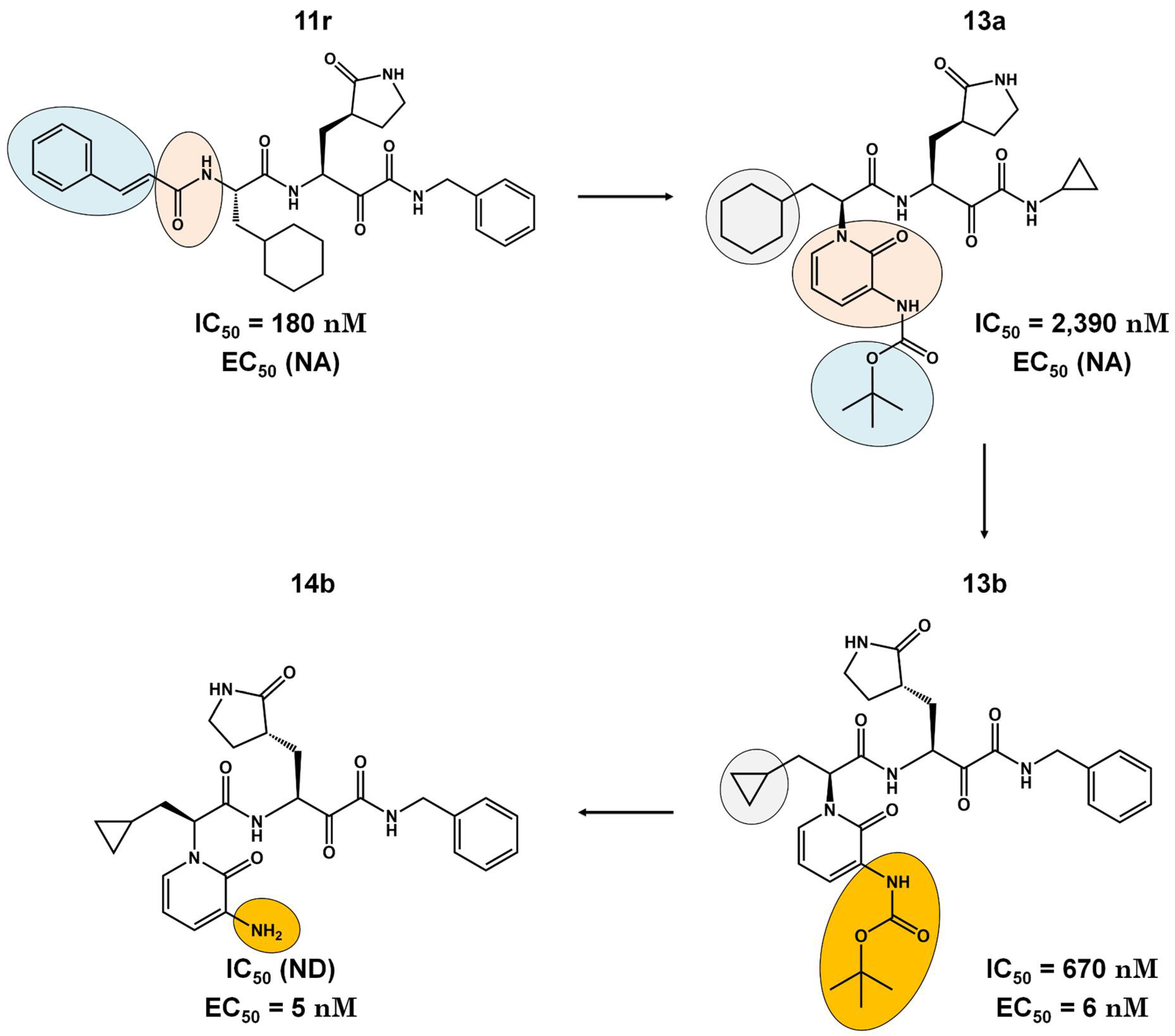
Pre-Clinical and Clinical Trials of Reversible and Irreversible 3CLpro Inhibitors Against SARS-CoV-2
| Drug | Company | Delivery | State | IC50 (nM) | EC50 (μM) | ID (clinical trials) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nirmatrelvir (PF-07321332) | Pfizer | Oral | Phase II | 10-100 | 0.07-0.3 | NCT05011513 |
| Lopinavir and Ritonavir | Abbvie | Oral | Discontinued | 12000.0# | 26.6* | NCT04381936 |
| Paxlovid™ (Nirmatrelvir and Ritonavir) | Pfizer | Oral | Phase II/III | 3.1 | 0.075 | NCT04960202 258 |
| Boceprevir | Merck | Oral | Preclinical | 1.6 | 2-10& | ND |
| GC376 | Kansas State University | Oral | Preclinical | 26.4 | 2.6 ± 0.2**/ 1.1 ± 0.2*** | ND |
| Lufotrelvir (PF-07304814) | Pfizer | IV | Phase I | 0.27 | 760 | NCT05050682 |
| Xiannuoxin™:Simnotrelvir (SIM0417) and Ritonavir (SSD8432) | Simcere | Oral | Phase II/III | 9 | 34 | NCT05373433 [103] |
Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kar, S.; Ganguly, M.; Sen, S. Lifting Scheme-Based Wavelet Transform Method for Improved Genomic Classification and Sequence Analysis of Coronavirus. Innovation and Emerging Technologies 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, J.F.D.; M. , V.; Drosten, C. Ecology, Evolution and Classification of Bat Coronaviruses in the Aftermath of SARS. Antiviral Res. 2014, 101, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.A.; Sheikh, F.N.; Jamal, S.; Ezeh, J.K.; Akhtar, A. Coronavirus (COVID-19): A Review of Clinical Features, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Cureus 2020, 12, e7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wei, L.; Niu, P. The Novel Coronavirus Outbreak in Wuhan, China. Global Health Research and Policy 2020, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, A.S.; de Freitas Amorim, V.M.; Guardia, G.D.A.; Dos Santos, F.F.; Ulrich, H.; Galante, P.A.F.; de Souza, R.F.; Guzzo, C.R. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Variants of Concern: A Perspective for Emerging More Transmissible and Vaccine-Resistant Strains. Viruses 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-Time Tracking of Pathogen Evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.S.; Amorim, V.M. de F.; de Souza, R.F.; Guzzo, C.R. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Spike Trimeric Ectodomain of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: Structural Relationships with Infectivity, Evasion to Immune System and Transmissibility. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 1–18.
- de Souza, A.S.; de Souza, R.F.; Guzzo, C.R. Cooperative and Structural Relationships of the Trimeric Spike with Infectivity and Antibody Escape of the Strains Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (BA.2, BA.5, and BQ.1). J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2023, 37, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva de Souza, A.; Rivera, J.D.; Almeida, V.M.; Ge, P.; de Souza, R.F.; Farah, C.S.; Ulrich, H.; Marana, S.R.; Salinas, R.K.; Guzzo, C.R. Molecular Dynamics Reveals Complex Compensatory Effects of Ionic Strength on the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike/Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Interaction. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 10446–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V’kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus Biology and Replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses Post-SARS: Update on Replication and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, Y.; Mizrahi, O.; Nachshon, A.; Weingarten-Gabbay, S.; Morgenstern, D.; Yahalom-Ronen, Y.; Tamir, H.; Achdout, H.; Stein, D.; Israeli, O.; et al. The Coding Capacity of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 589, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Nyodu, R.; Maurya, V.K.; Saxena, S.K. Morphology, Genome Organization, Replication, and Pathogenesis of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), 2020; 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cannalire, R.; Cerchia, C.; Beccari, A.R.; Di Leva, F.S.; Summa, V. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteases and Polymerase for COVID-19 Treatment: State of the Art and Future Opportunities. J. Med. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.; Ruggiero, A.; Squeglia, F.; Maga, G.; Berisio, R. A Structural View of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Replication Machinery: RNA Synthesis, Proofreading and Final Capping. Cells 2020, 9, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.V. Overview of Targets and Potential Drugs of SARS-CoV-2 According to the Viral Replication. J. Proteome Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzikov, M.; Costanzi, E.; Reinshagen, J.; Esposito, F.; Vangeel, L.; Wolf, M.; Ellinger, B.; Claussen, C.; Geisslinger, G.; Corona, A.; et al. Identification of Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3CL-Pro Enzymatic Activity Using a Small Molecule in Vitro Repurposing Screen. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci 2021, 4, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, S.; Nitsche, C. The SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease as Drug Target. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, T.; Zhang, F.; Haider, S.; Kraut, D.; Huang, Z. An Integrated Computational and Experimental Approach to Identifying Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 3CL Protease. Front Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 661424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaab, E.; Manoharan, G.B.; Abankwa, D. Pharmacophore Model for SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Small-Molecule Inhibitors and in Vitro Experimental Validation of Computationally Screened Inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Ma, X.; Shen, W.; Rao, Q.; Yang, S. Discovery of 3CLpro Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Future Sci OA 2023, 9, FSO853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.S.; de Souza, R.F.; Guzzo, C.R. Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Reveal Drug Repurposing Candidates as Potent SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schake, P.; Dishnica, K.; Kaiser, F.; Leberecht, C.; Haupt, V.J.; Schroeder, M. An Interaction-Based Drug Discovery Screen Explains Known SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors and Predicts New Compound Scaffolds. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, V.; Ho, J.; Wills, S.; Mawri, A.; Lawson, L.; Ebert, M.C.C.J.C.; Fortin, G.M.; Rayalam, S.; Taval, S. Identification of 3-Chymotrypsin like Protease (3CLPro) Inhibitors as Potential Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents. Commun Biol 2021, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luttens, A.; Gullberg, H.; Abdurakhmanov, E.; Vo, D.D.; Akaberi, D.; Talibov, V.O.; Nekhotiaeva, N.; Vangeel, L.; De Jonghe, S.; Jochmans, D.; et al. Ultralarge Virtual Screening Identifies SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors with Broad-Spectrum Activity against Coronaviruses. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2905–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.C.; Freitas, H.F.; Campos, J.M.; Kimani, N.M.; Silva, C.H.T.P.; Borges, R.S.; Pita, S.S.R.; Santos, C.B.R. Natural Products-Based Drug Design against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro 3CLpro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharkar, O.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Tsurkan, M.V. Natural Products from Marine Actinomycete Genus Salinispora Might Inhibit 3CLpro and PLpro Proteins of SARS-CoV-2: An in Silico Evidence. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1907–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gautam, A.; Chandel, S.; Ghosh, A.; Dey, D.; Roy, S.; Ravichandiran, V.; Ghosh, D. Protease Inhibitory Effect of Natural Polyphenolic Compounds on SARS-CoV-2: An In Silico Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.-M.; Su, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, X.; Jin, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, F.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Antiviral Drug Candidates Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Science 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, L. Dali Server: Structural Unification of Protein Families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W210–W215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, L.; Laiho, A.; Törönen, P.; Salgado, M. DALI Shines a Light on Remote Homologs: One Hundred Discoveries. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Shuai, L.; Zhang, L.; Xie, X.; Tang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tan, Q.; Zhong, G.; et al. Development of Highly Potent Noncovalent Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro. ACS Cent Sci 2023, 9, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xie, W.; Xue, X.; Yang, K.; Ma, J.; Liang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Pei, D.; Ziebuhr, J.; et al. Design of Wide-Spectrum Inhibitors Targeting Coronavirus Main Proteases. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e324. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez, D.; Díaz, N. SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monica, G.; Bono, A.; Lauria, A.; Martorana, A. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease for Treatment of COVID-19: Covalent Inhibitors Structure–Activity Relationship Insights and Evolution Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Amorim, V.M.; de Souza, R.F.; Guzzo, C.R.; de Souza, A.S. Molecular Dynamics Simulations Suggest SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Mutations in Beta and Omicron Variants Do Not Alter Binding Affinities for Cleavage Sites of Non-Structural Proteins. COVID 2023, 3, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-C.; Chang, G.-G.; Chou, C.-Y. Mutation of Glu-166 Blocks the Substrate-Induced Dimerization of SARS Coronavirus Main Protease. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, N.; Zhang, S.; Zou, P.; Chen, J.; Kang, X.; Li, Z.; Liang, C.; Jin, C.; Xia, B. Without Its N-Finger, the Main Protease of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Can Form a Novel Dimer through Its C-Terminal Domain. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4227–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-P.; Chou, C.-Y.; Chang, G.-G. Reversible Unfolding of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Main Protease in Guanidinium Chloride. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świderek, K.; Moliner, V. Revealing the Molecular Mechanisms of Proteolysis of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro by QM/MM Computational Methods. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10626–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, H. Structural Biology of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro and Drug Discovery. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2023, 82, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, H.S.; Akkus, E.; Yildiz, M.; Kocak, A. Computational Analysis of Substrate Recognition of Sars-Cov-2 Mpro Main Protease. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2023, 107, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Ma, S.; Wang, H.; Shang, L.; Zhu, C.; Ye, S. Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 3CLPro Peptidomimetic Inhibitors through the Catalytic Dyad Histidine-Specific Protein–Ligand Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Sun, X.; Curth, U.; Drosten, C.; Sauerhering, L.; Becker, S.; Rox, K.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Provides a Basis for Design of Improved α-Ketoamide Inhibitors. Science 2020, 368, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumskiy, R.S.; Tumskaia, A.V.; Klochkova, I.N.; Richardson, R.J. SARS-CoV-2 Proteases Mpro and PLpro: Design of Inhibitors with Predicted High Potency and Low Mammalian Toxicity Using Artificial Neural Networks, Ligand-Protein Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulations, and ADMET Calculations. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 153, 106449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miczi, M.; Golda, M.; Kunkli, B.; Nagy, T.; Tőzsér, J.; Mótyán, J.A. Identification of Host Cellular Protein Substrates of SARS-COV-2 Main Protease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rut, W.; Groborz, K.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Zmudzinski, M.; Pawlik, B.; Młynarski, W.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Drag, M. Substrate Specificity Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Enables Design of Activity-Based Probes for Patient-Sample Imaging. bioRxiv, 9819; 2020.03.07.981928. [Google Scholar]
- Henry Chan, H.T.; Moesser, M.A.; Walters, R.K.; Malla, T.R.; Twidale, R.M.; John, T.; Deeks, H.M.; Johnston-Wood, T.; Mikhailov, V.; Sessions, R.B.; et al. Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Peptide Inhibitors from Modelling Substrate and Ligand Binding. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 13686–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Jin, Z.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Feng, L.; Du, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Structural Basis for Replicase Polyprotein Cleavage and Substrate Specificity of Main Protease from SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2022, 119, e2117142119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paasche, A.; Zipper, A.; Schäfer, S.; Ziebuhr, J.; Schirmeister, T.; Engels, B. Evidence for Substrate Binding-Induced Zwitterion Formation in the Catalytic Cys-His Dyad of the SARS-CoV Main Protease. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Guzmán, C.A.; Javier Ruiz-Pernía, J.; Tuñón, I. Unraveling the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Mechanism Using Multiscale Methods. ACS Catal. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świderek, K.; Moliner, V. Revealing the Molecular Mechanisms of Proteolysis of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro by QM/MM Computational Methods. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10626–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudáky, P.; Perczel, A. A Self-Stabilized Model of the Chymotrypsin Catalytic Pocket. The Energy Profile of the Overall Catalytic Cycle. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinf. 2006, 62, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, S.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tung, N.T.; Mai, B.K. Insights into the Binding and Covalent Inhibition Mechanism of PF-07321332 to SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 3729–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M.; Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. MMseqs Software Suite for Fast and Deep Clustering and Searching of Large Protein Sequence Sets. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HMMER HMMER Available online:. Available online: http://hmmer.org/ (accessed on 27 April 2024).
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The Protein Families Database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deorowicz, S.; Debudaj-Grabysz, A.; Gudyś, A. FAMSA: Fast and Accurate Multiple Sequence Alignment of Huge Protein Families. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.D.; Stephens, R.M. Sequence Logos: A New Way to Display Consensus Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6097–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.-M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A Sequence Logo Generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Adem, K.; Ferreira, J.C.; Fadl, S.; Mustafa, M.; Rabeh, W.M. Key Allosteric and Active Site Residues of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Promising Drug Targets. Biochem. J 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, D. The Role of Hydrogen Bond in Catalytic Triad of Serine Proteases †. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 34, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinces, T.C.; de Souza, A.S.; Carvalho, C.F.; Visnardi, A.B.; Teixeira, R.D.; Llontop, E.E.; Bismara, B.A.P.; Vicente, E.J.; Pereira, J.O.; de Souza, R.F.; et al. Monomeric Esterase: Insights into Cooperative Behavior, Hysteresis/Allokairy. Biochemistry 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinen, L.S.; Hansell, E.; Cheng, J.; Roush, W.R.; McKerrow, J.H.; Fletterick, R.J. A Target within the Target: Probing Cruzain’s P1' Site to Define Structural Determinants for the Chagas' Disease Protease. Structure 2000, 8, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.S.; de Oliveira, M.T.; Andricopulo, A.D. Development of a Pharmacophore for Cruzain Using Oxadiazoles as Virtual Molecular Probes: Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Studies. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2017, 31, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, E.; Vukoti, K.; Miyagi, M.; Lodowski, D.T. Conformational Flexibility in the Catalytic Triad Revealed by the High-Resolution Crystal Structure of Streptomyces Erythraeus Trypsin in an Unliganded State. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljuhani, A.; Ahmed, H.E.A.; Ihmaid, S.K.; Omar, A.M.; Althagfan, S.S.; Alahmadi, Y.M.; Ahmad, I.; Patel, H.; Ahmed, S.; Almikhlafi, M.A.; et al. In Vitro and Computational Investigations of Novel Synthetic Carboxamide-Linked Pyridopyrrolopyrimidines with Potent Activity as SARS-CoV-2-MPro Inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 26895–26907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.M.A.; da Silva, K.P.A.; de Oliveira, L.P.M.; Costa, E.V.; Koolen, H.H.F.; Pinheiro, M.L.B.; de Souza, A.Q.L.; de Souza, A.D.L. Flavonoid Glycosides and Their Putative Human Metabolites as Potential Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro) and RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2020, 115, e200207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lin, X.; Xing, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Xue, W. Structure-Based Discovery of Novel Nonpeptide Inhibitors Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.; Feys, J.R. SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitors: Achieved Diversity, Developing Resistance and Future Strategies. Future Pharmacology 2023, 3, 80–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Nikam, A.N.; Shreya, A.B.; Mutalik, S.P.; Gopalan, D.; Kulkarni, S.; Padya, B.S.; Fernandes, G.; Mutalik, S.; Prassl, R. Potential Therapeutic Targets for Combating SARS-CoV-2: Drug Repurposing, Clinical Trials and Recent Advancements. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, Y.; Wen, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, G.; Ruan, L.; Song, B.; Cai, Y.; Wei, M.; et al. A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Boland, S.; Scholle, M.D.; Bardiot, D.; Marchand, A.; Chaltin, P.; Blatt, L.M.; Beigelman, L.; Symons, J.A.; Raboisson, P.; et al. Dual Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 and Human Rhinovirus with Protease Inhibitors in Clinical Development. Antiviral Res. 2021, 187, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharma, C. Cocrystal Pharma Selects Lead Compound for Further Development Against Coronaviruses . Available online: https://www.cocrystalpharma.com/news/press-releases/detail/105/cocrystal-pharma-selects-lead-compound-for-further (accessed on 28 April 2024).
- Nakayama, T.; Lee, I.T.; Jiang, S.; Matter, M.S.; Yan, C.H.; Overdevest, J.B.; Wu, C.T.; Goltsev, Y.; Shih, L.C.; Liao, C.K.; et al. Determinants of SARS-CoV-2 Entry and Replication in Airway Mucosal Tissue and Susceptibility in Smokers. Cell Reports Medicine 2021, 2, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalligeros, M.; Tashima, K.T.; Mylona, E.K.; Rybak, N.; Flanigan, T.P.; Farmakiotis, D.; Beckwith, C.G.; Sanchez, M.; Neill, M.; Johnson, J.E.; et al. Remdesivir Use Compared With Supportive Care in Hospitalized Patients With Severe COVID-19: A Single-Center Experience. Open Forum Infect Dis 2020, 7, ofaa319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandyck, K.D.J. Considerations for the Discovery and Development of 3-Chymotrypsin-like Cysteine Protease Inhibitors Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 49, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boras, B.; Jones, R.M.; Anson, B.J.; Arenson, D.; Aschenbrenner, L.; Bakowski, M.A.; Beutler, N.; Binder, J.; Chen, E.; Eng, H.; et al. Discovery of a Novel Inhibitor of Coronavirus 3CL Protease for the Potential Treatment of COVID-19. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajouhesh, H.; Lenz, G.R. Medicinal Chemical Properties of Successful Central Nervous System Drugs. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Trials ID NCT04535167 History of Changes for Study: NCT04535167. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/history/NCT04535167?V_9=View (accessed on 28 April 2024).
- Owen, D.R.; Allerton, C.M.N.; Anderson, A.S.; Aschenbrenner, L.; Avery, M.; Berritt, S.; Boras, B.; Cardin, R.D.; Carlo, A.; Coffman, K.J.; et al. An Oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Inhibitor Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of COVID-19. Science 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnabi, R.; Foo, C.S.; Jochmans, D.; Vangeel, L.; De Jonghe, S.; Augustijns, P.; Mols, R.; Weynand, B.; Wattanakul, T.; Hoglund, R.M.; et al. The Oral Protease Inhibitor (PF-07321332) Protects Syrian Hamsters against Infection with SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lin, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, F.; Zeng, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Fan, X.; McCormick, P.J.; et al. Structural Basis of the Main Proteases of Coronavirus Bound to Drug Candidate PF-07321332. J. Virol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noske, G.D.; de Souza Silva, E.; de Godoy, M.O.; Dolci, I.; Fernandes, R.S.; Guido, R.V.C.; Sjö, P.; Oliva, G.; As. , G. Structural Basis of Nirmatrelvir and Ensitrelvir Activity against Naturally Occurring Polymorphisms of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 103004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, J.; Iglesias, C. [Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir (Paxlovid) a potent SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro protease inhibitor combination]. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2022, 35, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelson, A.S.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Phan, T. An Explanation for SARS-CoV-2 Rebound after Paxlovid Treatment. medRxiv, 2023; 2023.05.30.23290747. [Google Scholar]
- Khalilieh, S.; Feng, H.-P.; Hulskotte, E.G.J.; Wenning, L.A.; Butterton, J.R. Clinical Pharmacology Profile of Boceprevir, a Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease Inhibitor: Focus on Drug-Drug Interactions. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 54, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutho, B.; Mahalapbutr, P.; Hengphasatporn, K.; Pattaranggoon, N.C.; Simanon, N.; Shigeta, Y.; Hannongbua, S.; Rungrotmongkol, T. Why Are Lopinavir and Ritonavir Effective against the Newly Emerged Coronavirus 2019? Atomistic Insights into the Inhibitory Mechanisms. Biochemistry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvetkovic, R.S.; Goa, K.L. Lopinavir/Ritonavir. Drugs 2012, 63, 769–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoergenhofer, C.; Jilma, B.; Stimpfl, T.; Karolyi, M.; Zoufaly, A. Pharmacokinetics of Lopinavir and Ritonavir in Patients Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Ann. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, H.; Dantonio, A.L.; Kadar, E.P.; Obach, R.S.; Di, L.; Lin, J.; Patel, N.C.; Boras, B.; Walker, G.S.; Novak, J.J.; et al. Disposition of Nirmatrelvir, an Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3C-Like Protease, across Animals and Humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2022, 50, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denissen, J.F.; Grabowski, B.A.; Johnson, M.K.; Buko, A.M.; Kempf, D.J.; Thomas, S.B.; Surber, B.W. Metabolism and Disposition of the HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Ritonavir (ABT-538) in Rats, Dogs, and Humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1997, 25, 489–501. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Liang, B.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Xing, D. Advances and Challenges in Using Nirmatrelvir and Its Derivatives against SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J Pharm Anal 2023, 13, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Kusov, Y.; Nian, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; von Brunn, A.; Leyssen, P.; Lanko, K.; Neyts, J.; et al. α-Ketoamides as Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors of Coronavirus and Enterovirus Replication: Structure-Based Design, Synthesis, and Activity Assessment. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4562–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.L.; Cui, H.; Beck, P.; Dubiella, C.; Voss, C.; Krüger, A.; Schmidt, B.; Groll, M. Systematic Comparison of Peptidic Proteasome Inhibitors Highlights the α-Ketoamide Electrophile as an Auspicious Reversible Lead Motif. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 2014, 53, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Guzmán, C.A.; Javier Ruiz-Pernía, J.; Tuñón, I. Inhibition Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease with Ketone-Based Inhibitors Unveiled by Multiscale Simulations: Insights for Improved Designs**. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 25933–25941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Jochmans, D.; Xie, H.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Chang, D.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Zhu, L.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Peptidomimetic Aldehydes as Broad-Spectrum Inhibitors against Enterovirus and SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, K.S.; Geng, Z.Z.; Alugubelli, Y.R.; Shaabani, N.; Vatansever, E.C.; Ma, X.R.; Cho, C.C.; Khatua, K.; Xiao, J.; et al. A Multi-Pronged Evaluation of Aldehyde-Based Tripeptidyl Main Protease Inhibitors as SARS-CoV-2 Antivirals. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 240, 114570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chenna, B.C.; Yang, K.S.; Cole, T.R.; Goodall, Z.T.; Giardini, M.; Moghadamchargari, Z.; Hernandez, E.A.; Gomez, J.; Calvet, C.M.; et al. Self-Masked Aldehyde Inhibitors: A Novel Strategy for Inhibiting Cysteine Proteases. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 11267–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Su, H.; Shang, W.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, H.; Jiang, L.; Nie, T.; et al. Structure-Based Development and Preclinical Evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 3C-like Protease Inhibitor Simnotrelvir. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandwal, S.; Fayne, D. Genetic Conservation across SARS-CoV-2 Non-Structural Proteins – Insights into Possible Targets for Treatment of Future Viral Outbreaks. Virology 2023, 581, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Sen Gupta, P.S.; Panda, S.K.; Biswal, S.; Bhattacharya, U.; Rana, M.K. Repurposing of FDA-Approved Drugs as Potential Inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: Molecular Insights into Improved Therapeutic Discovery. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 142, 105183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lewandowski, E.M.; Tan, H.; Zhang, X.; Morgan, R.T.; Zhang, X.; Jacobs, L.M.C.; Butler, S.G.; Gongora, M.V.; Choy, J.; et al. Naturally Occurring Mutations of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Confer Drug Resistance to Nirmatrelvir. ACS Central Science 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





