1. Introduction
Galectins are a family of beta-galactoside-binding proteins that are characterised by their carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD) [
1]. The family includes galectin-3, the only member of the chimeric sub-family, that is able to undergo oligomerisation to form lattice structures that play a pleiotropic role in the development of fibrosis and cancer [
2,
3,
4]. This occurs via binding of the CRDs to glycans on cell surface receptors, disrupting or exacerbating a number of different mechanisms [
5]. In addition, galectin-1 is a member of the prototypical galectin sub-family that can also bind glycans but as a monomer or dimer resulting in modulation of immune response and pro-oncogenic pathways [
6,
7].
As a result of their pro-fibrotic and pro-tumorigenic effects, galectin-3 and galectin-1 have been investigated as potential therapeutic targets, with small and large molecule inhibitors in development [
6]. The generation of simple and robust functional
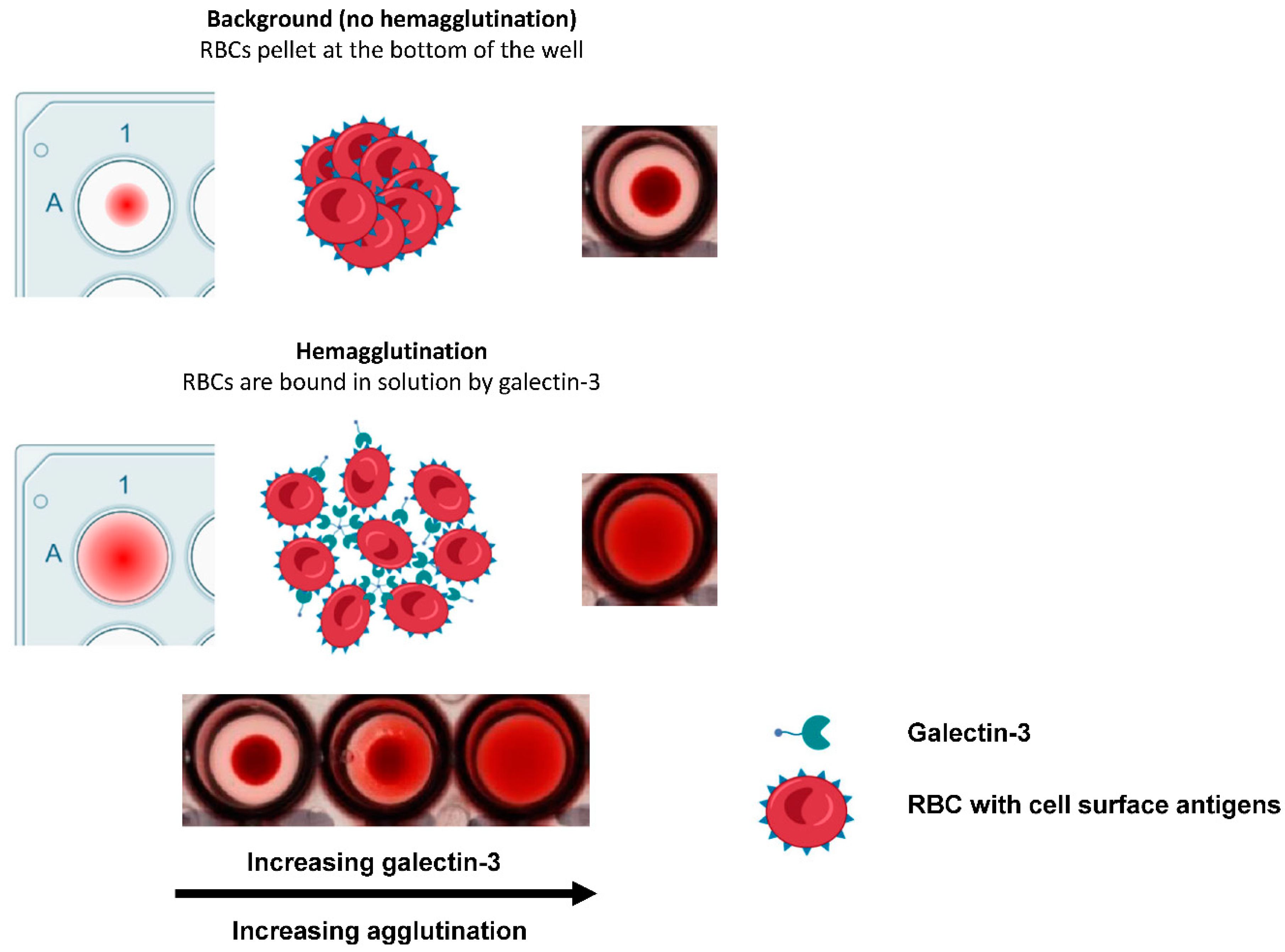
in vitro assays for measuring the effects of galectins, and inhibitors thereof, can be a challenge. However, one of the methods that has been used is galectin-induced hemagglutination of red blood cells (RBCs) [
8,
9,
10] as summarised in
Figure 1. These assays offer a simple, fast and relatively high throughput approach to demonstrating functional activities of different protein batches and constructs of galectins across species in a binary fashion, though they have yet to be used for showing efficacy and selectivity of glycomimetic inhibitors. Historically the main drawback of using RBC hemagglutination has been the lack of quantitative and accurate readouts, where analysis has been confined to visual observations [
8,
9,
10].
The aim of this study was to develop quantitative RBC agglutination assays for galectin-1 and-3 whereby sensitive readouts would allow more insight into the effects of these proteins on different blood groups in addition to allowing the analysis of concentration response effects of small molecule glycomimetic inhibitors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Unless otherwise stated all small molecule galectin inhibitors were synthesized by the Medicinal Chemistry Department at Galecto Biotech AB (Gothenburg, Sweden). The following galectin inhibitors were tested: GB0139 (dual human galectin-1/3 inhibitor) [
11,
12,
13], GB1211 (human galectin-3 inhibitor) [
14,
15], GB1908 (human galectin-1 inhibitor) [
16] and OTX008 (allosteric galectin-1 inhibitor, also known as Calixarene 0118, was purchased from MedChemExpress (NJ, USA)) [
17]. All compound stocks were made up in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at 30 mM except for OTX008 which due to poor solubility in DMSO was made up to 10 mM in 100% ethanol, then tested at a final DMSO or ethanol final assay concentration of 0.1%. Galectin-1 monomer and concatemer were generated as previously described [
10,
18]. Galectin-3 monomer was generated as previously described [
19]. All reagents and plasticware were purchased from ThermoFisher Scientific (MA, USA), unless otherwise stated.
2.2. Red Blood Cell Preparation
Whole blood from groups A, B and O were obtained from NHS Blood and Transplant with approval granted by the South Central (Hampshire B) Research Ethics Committee (REC) under REC reference 21/SC/0238. Whole blood was diluted to 20% in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), washed 4x in PBS (each centrifugation step at 600 g for 20 minutes at room temperature) then resuspended to between 2.5% and 10% in Alsever’s. Red blood cell (RBC) counts were completed using a Neubauer cell counter before washing, and then again prior to final resuspension in Alsever’s, to negate loss of RBCs during wash steps and resuspension.
2.3. Hemagglutination Assay
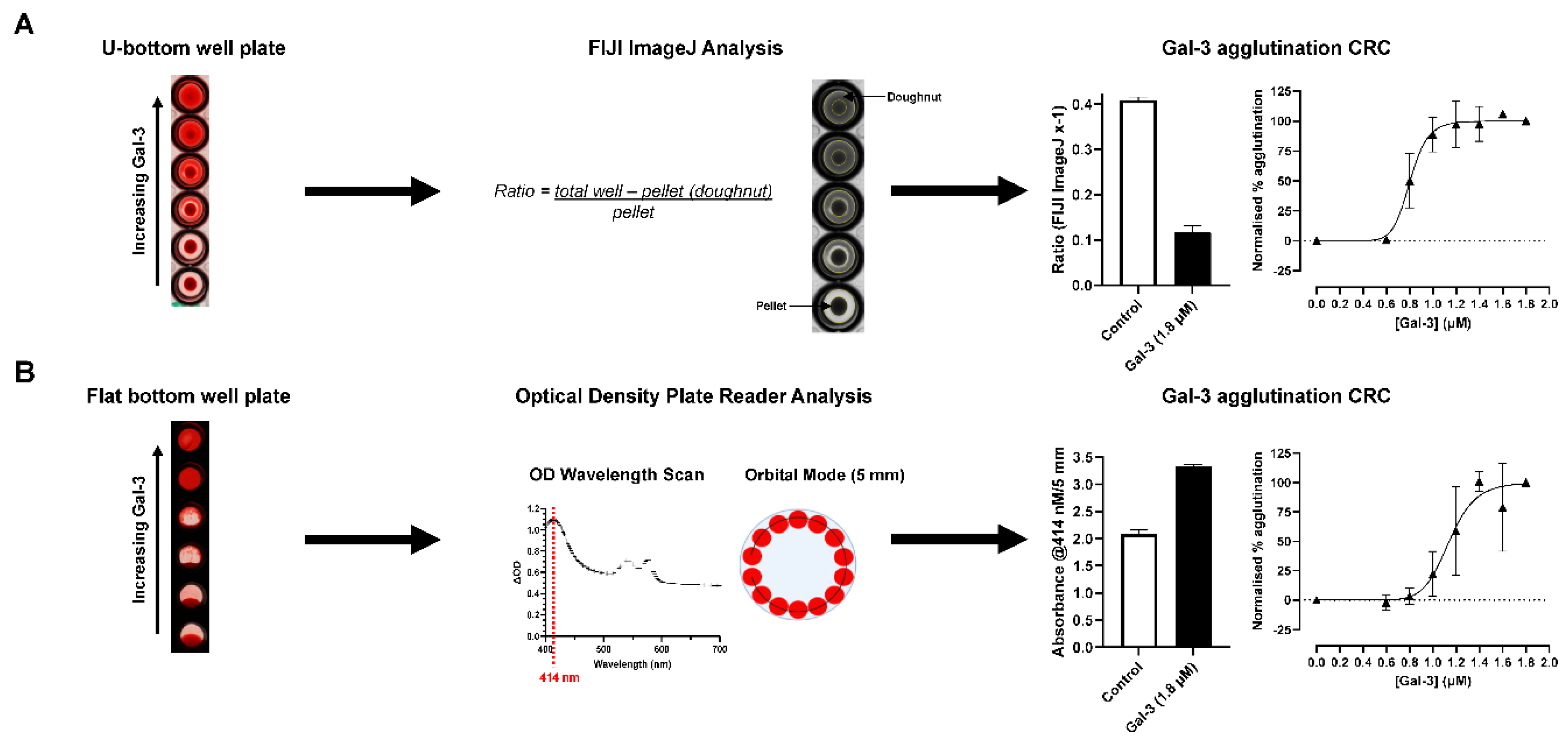
2.3.1. Optimisation of Hemagglutination Quantification
For measuring galectin-induced hemagglutination, 50 µl galectin (at varying concentrations) and 50 µl of 3.75% whole blood in Alsever’s solution were added to either a flat (flat clear bottom black polystyrene TC-treated 96-well microplate (Corning, AZ, USA)) or round (U) bottom (Nunc™ round bottom clear polystyrene 96-well microplate) plate, then solutions mixed gently using a pipette. Plates were incubated on a plate shaker for 30 min followed by 1 h on the bench, both at room temperature. Flat bottom plates were then tilted at a 45° angle and incubated for 18 h prior to reading absorbance at 414 nm (orbital scan with the reader measuring each well along a defined orbit (5 mm) calculating an average from the data collected) on a CLARIOstar® multi-mode plate reader (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany). U-bottom plates remained flat on the bench for 3 h prior to imaging on an ImageQuant™ 800 (Cytiva, IL, USA). Images from U-bottom plates were then analysed using FIJI ImageJ software to determine the relative intensity of the RBC pellet and non-RBC pellet (defined as doughnut area) well areas that were then ratioed (see
Figure 1).
EC50 values for galectin-3, galectin-1 and galectin-1 concatemer were determined across blood groups using optimised conditions.
2.3.2. Determining Galectin Inhibitor Hemagglutination IC50 Values
To determine the IC50 values for galectin inhibitors in the hemagglutination assay, inhibitors at a range of concentrations were tested at a fixed concentrations of galectin using the general protocol described above and quantification with the FIJI Image J analysis method. Blood group O was selected based on availability and most robust donor to donor galectin EC50 values to then investigate the profile of galectin-1 and galectin-3 small molecule inhibitors. For optimised signal window, the fixed galectin concentrations were selected based on the EC50 value determined for each galectin against blood group O. For galectin-3 a standardised concentrations of 1.6 µM for blood group O was selected whilst for galectin-1 concatemer 1.2 µM was selected.
2.4. Data Analysis
Statistical analyses were completed using Prism 10.2 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). A Student’s t-test was used to compare two datasets and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for comparison of more than two datasets with an appropriate post-test completed where significance was observed. Hemagglutination data were normalized to vehicle control and the maximum concentration of galectin (EC50 determination) or galectin inhibitor (IC50 determination), respectively. Concentration-response curve data were fitted to a non-linear regression curve (four parameter, variable slope) to obtain EC50 or IC50 values. Each condition tested within each individual experiment (donor) was the mean of three technical replicates.
3. Results
3.1. Optimisation of Hemagglutination Assay
In order to optimise the quantification of galectin-induced RBC agglutination, different plates and analysis methods were applied. As part of the initial assay development the concentration of blood resuspended in Alsever’s was optimised with 3.75% shown to be the most robust in respect to the control RBC pellet size not being too large that the whole well was occluded, an observable smooth gradient effect across the concentrations of galectin-3 and full induction of RBC agglutination at the highest concentration of galectin-3 (
Figure S1). In addition, with 3.75% Alsever’s the hemagglutination was shown to be more stable overtime to enable multiple experiments to be completed from a single donor (data shown). Using the optimised 3.75% blood in Alsever’s concentration, U-bottom and flat bottom plates were used to compare quantification techniques using either FIJI ImageJ or plate reader analysis, respectively (
Figure 1). Over 4 donors of blood group A, a signal to background of 3.5 was observed for U-bottom/FIJI ImageJ analysis compared with 1.6 for flat bottom/plate reader analysis. In addition, the variability between technical replicates and quality of
EC50 fit for galectin-3 within a single donor was better for FIJI ImageJ (r
2 = 0.94) compared with an optical density plate reader analysis (r
2 = 0.83) (
Figure 1).
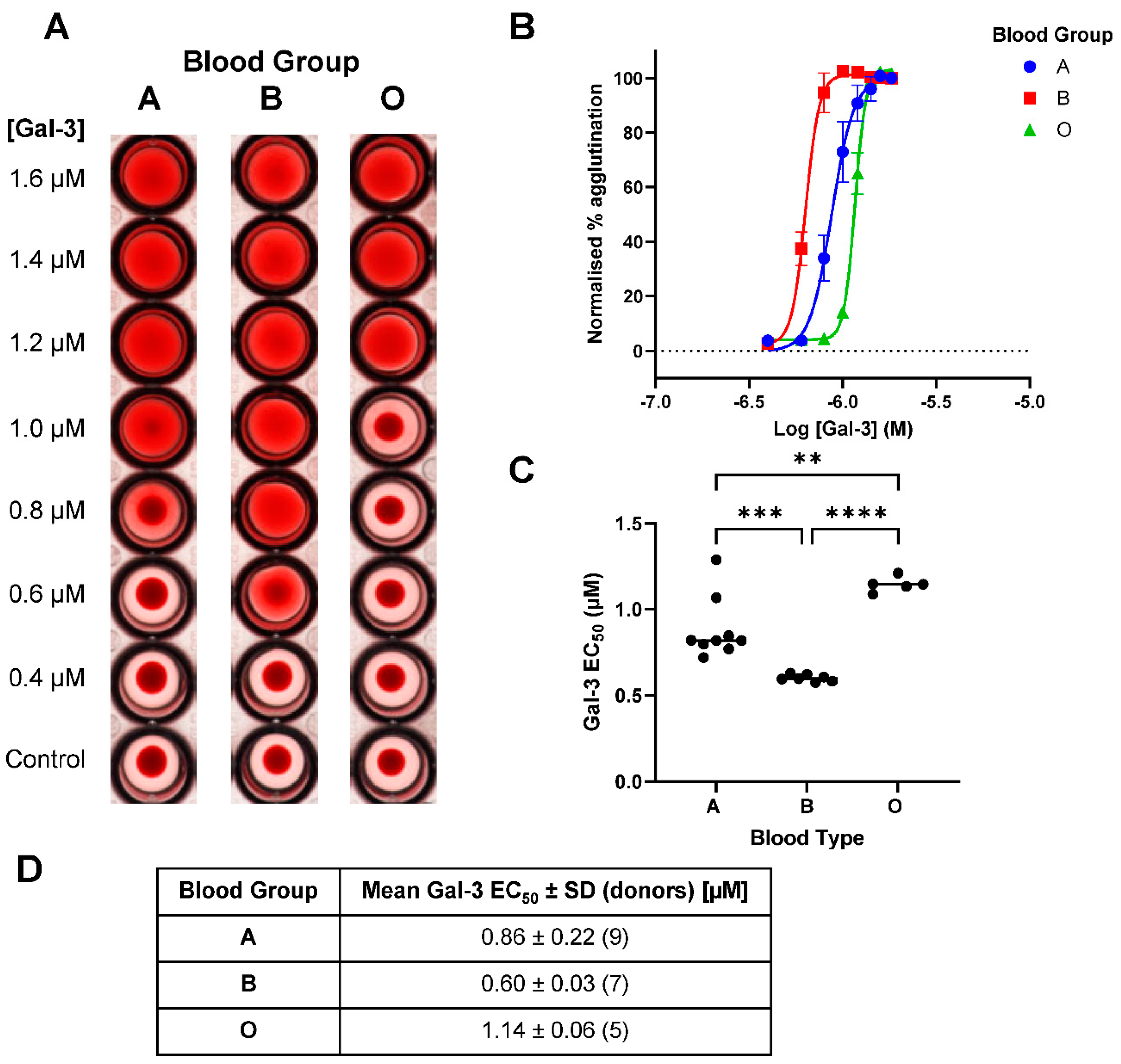
3.2. Comparison of Galectin-3-Induced Hemagglutination across Blood Groups A, B and O
When comparing concentration curves a clear difference between galectin-3-induced hemagglutination across blood groups A, B and O was visually observed (
Figure 3A). This was further confirmed across multiple donors when data was analysed in FIJI ImageJ (
Figure 3B). The resulting
EC50 values showed a significant difference between all blood groups tested (
Figure 3C and 3D) with the order of increasing efficacy from O though A and then B demonstrated.
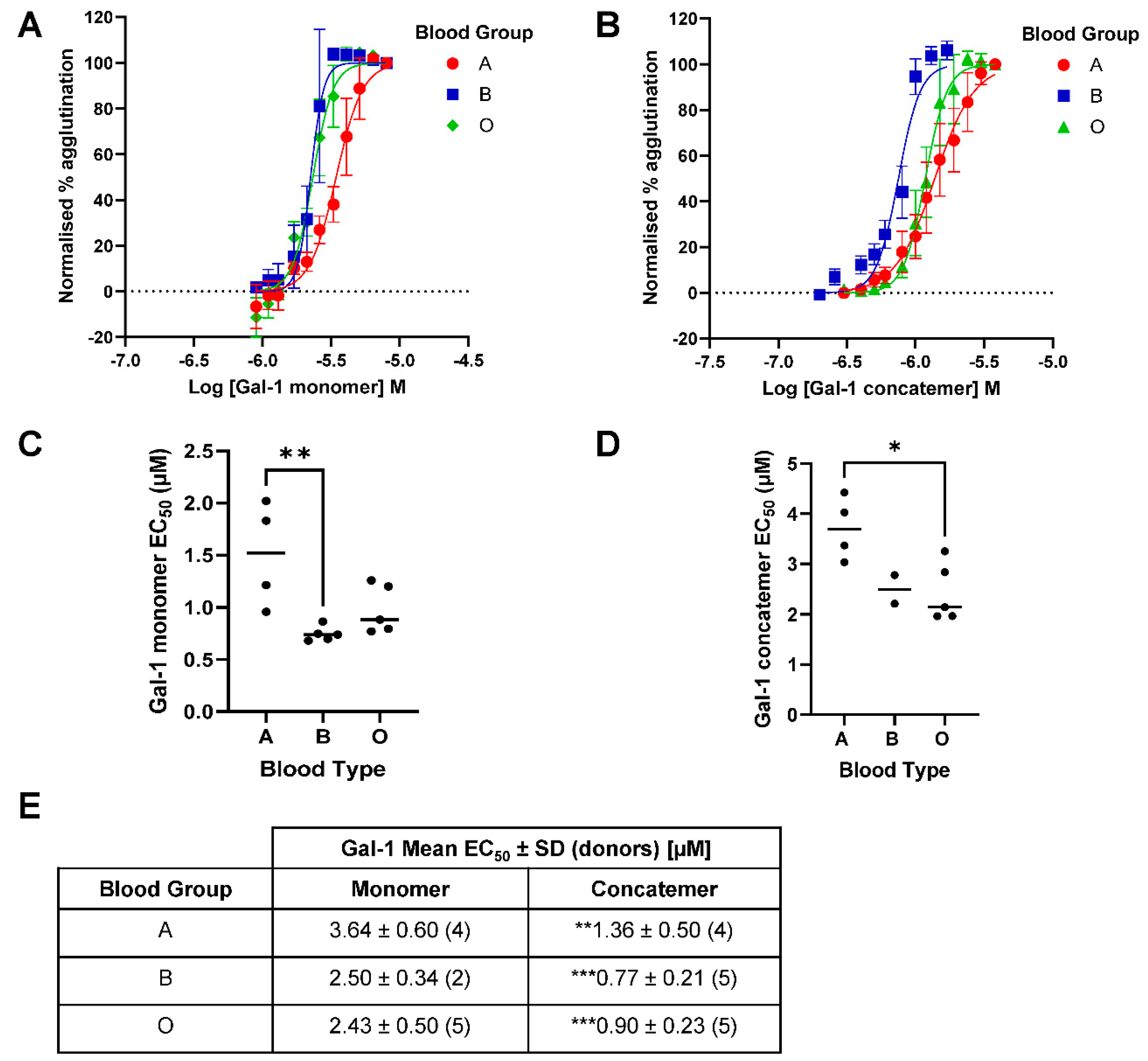
3.3. Comparison of Galectin-1-Induced Hemagglutination across Blood Groups A, B and O
The variability of galectin-1 induced hemagglutination across blood groups was greater with both the monomer and concatemer forms (
Figure 4) compared with that observed with galectin-3 (
Figure 3). This made comparison between the effects in different blood groups more difficult. However, for the galectin-1 monomer, a more potent
EC50 for RBC agglutination was observed in blood group B and O compared with A, though this was only significant between A and B. For the galectin-1 concatemer, a similar trend was observed with a more potent
EC50 for RBC agglutination observed in blood group B and O compared with A, though for the concatemer it was only significant between A and O. The concatemer of galectin-1 demonstrated a more potent hemagglutination effect than that observed for the monomer within in each of the blood groups tested. The concatemer of galectin-1 had comparable
EC50 values to galectin-3 for each blood group whilst the monomer was weaker.
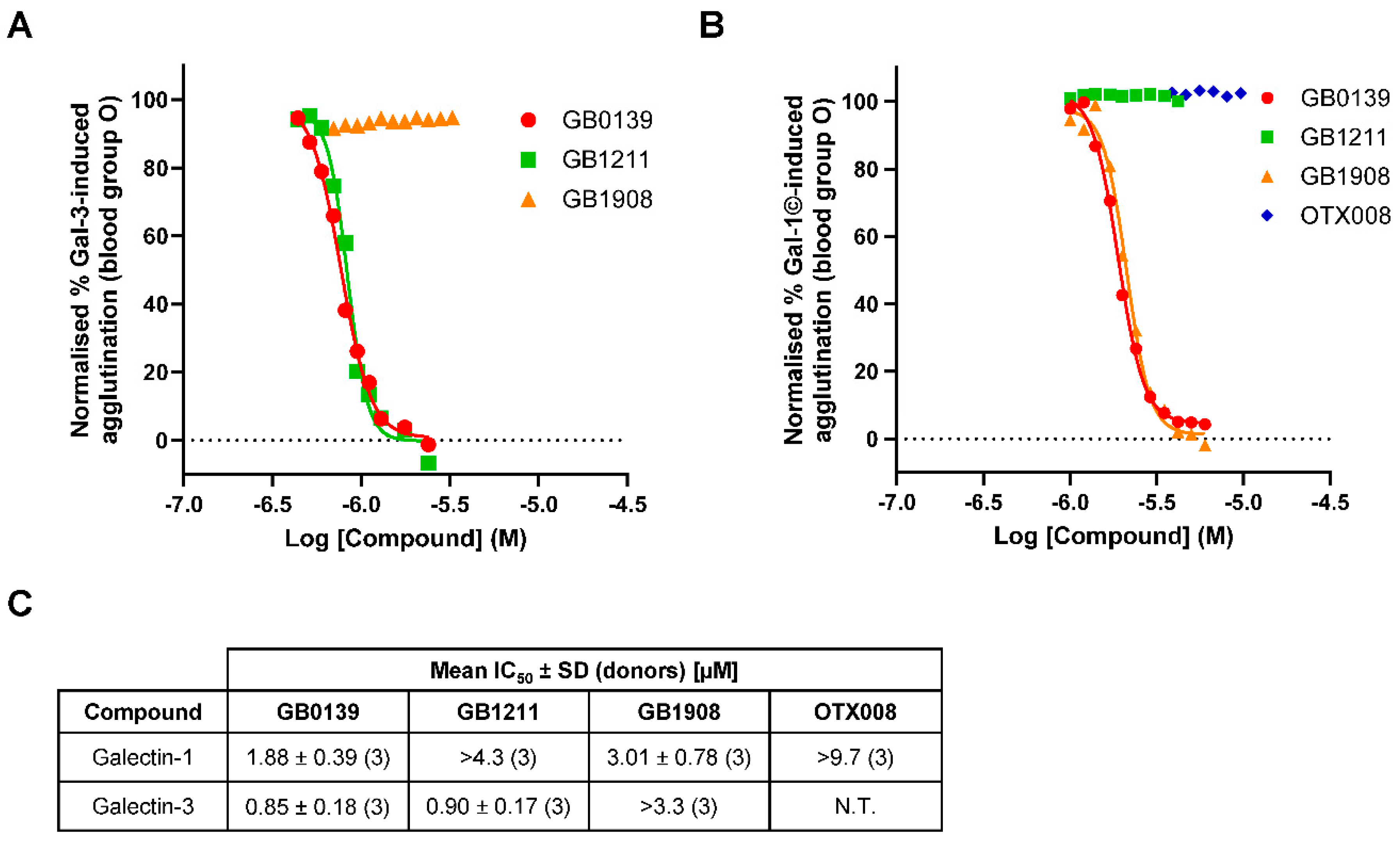
3.4. Inhibition of Galectin-Induced Hemagglutination with Small Molecule Glycomimetic and Allosteric Inhibitors
To investigate the selective inhibition of galectin-1 and galectin-3 inhibitor and determine IC
50 values, hemagglutination at fixed concentrations of galectins was investigated in blood group O (
Figure 5). The galectin-3 inhibitors GB0139 and GB1211 demonstrated a concentration-dependent inhibition of galectin-3-induced RBC agglutination with comparable
IC50 values (
Figure 5A and C). The selective galectin-1 inhibitor GB1908 showed no inhibition across the concentrations tested up to 3.3 µM. The dual galectin-1 and -3 inhibitor GB0139 and selective galectin-1 inhibitor GB1908 both demonstrated a concentration-dependent inhibition of galectin-1 concatemer-induced RBC agglutination with comparable
IC50 values (
Figure 5B and C). The selective galectin-3 inhibitor GB1211 showed no inhibition across the concentrations tested up to 4.3 µM. Interestingly, the allosteric galectin-1 inhibitor OTX008 also showed no inhibition across the concentrations tested up to 9.7 µM.
4. Discussion
Galectins are rapidly becoming of interest as drug targets due to their negative pleotropic role in many diseases and with a number of companies now having small and large molecule inhibitors in clinical development [
1,
2,
3,
6]. One of the routine academic assays that has been used for measuring effects of galectins on biological function, that has included differences between protein sequences and blood groups, has been hemagglutination of RBCs [
8,
9,
10]. Although useful for demonstrating effects of these variables the results have usually been binary in respect to response. Therefore, in this study our aim was to further develop these assays into a format that was able to be more quantitative and enable generation of robust concentration response effects not only for galectins but also for inhibitors thereof.
The readout for RBC agglutination has relied on visual inspection of the reaction vessel that only enables a crude estimate of the concentration effect of stimulant or inhibitor. Therefore, quantification of hemagglutination was investigated using either an absorbance plate reader or plate imaging combined with a FIJI ImageJ analysis to improve the sensitivity of readout. Both these approaches came with their strengths and weaknesses. The plate reader output required a longer incubation period to enable a robust absorbance measurement but with the benefit of no manual data analysis. This compared with a shorter incubation period with the imaged plate format but a more manual and labour-intensive data analysis. In comparison, these pros and cons equated to a similar length of time for each assay format to be completed that meant the method with the optimal performance in respect to data quality would be selected to be taken forward for further experiments. This was demonstrated to be the method of imaging the plate and applying a ratio analysis with FIJI ImageJ that allowed a more robust differentiation between the non-agglutinated cell pellet and agglutinated RBCs in the well of a U-bottom plate. The requirement for a flat bottom well to enable an absorbance readout on a plate reader resulted in a more variable output as plates were required to be incubated at an angle to allow differentiation between agglutinated and non-agglutinated RBCs. The aid of a natural basin for cell pellets in the U-bottom well likely resulted in providing the more robust analysis output.
With the optimal quantification method identified, a comparison of galectin-1 and -3-induced hemagglutination was completed against blood groups A, B and O to allow comparison with historical analysis using the visual binary readouts in the literature. For galectin-3, hemagglutination across blood groups A, B and O significantly differed with increasing efficacy from O though A and then B. This confirmed historical observations when demonstrating a difference between A and B compared with O [
8], however the more sensitive analysis in our method allowed a significant difference to also be observed between blood group A and B for the first time. For galectin-1, the difference observed by Shu and co-workers [
10] between the monomer and concatemer of this galectin was repeated and now shown to be significant with a 2.7-3.3-fold increase in
EC50 values across the 3 blood groups tested. Although the galectin-1 effects were overall more variable, differences could be observed between blood groups that had not been observed below. In previous studies it has been suggested there were no difference in the ability of a monomer of galectin-1 to induce RBC agglutination across blood groups A, B and O [
8]. Interestingly we have shown that there is a difference between blood groups B and O compared with A, with a weaker effect in the latter. This observation suggests that there is a preference of galectin-1 for blood group cell surface glycans.
Full inhibition curves for small molecule glycomimetic inhibitors of both galectin-1 and -3 were generated for the first time using this assay method that enabled
IC50 values to be generated and compared. In an assay where a galectin is exogenously added the
IC50 values for an inhibitor will be directly related to the galectin concentration [
20]. Therefore, it would be expected that in the assays completed in the study that
IC50 values would be the same for all compounds even if their affinity for the galectin differed, as was observed. This assumes that the concentration of galectin added (µM) is much higher than the compound affinities as was the case here as all small molecule glycomimetics have been demonstrated to have nM affinities [
11,
14,
16]. The expected selectivity profile of the inhibitors tested was observed with the dual galectin-1 and -3 inhibitor GB0139 attenuating the effects of both galectins tested and the selective galectin-3 inhibitor GB1211 and selective galectin-1 inhibitor GB1908 only inhibiting their respective lectin binding partner. Interestingly, the proposed allosteric inhibitor of galectin-1, OTX008, showed no inhibition in the galectin-1 hemagglutination assay. This would either suggest the concentrations tested were not high enough, as it has been shown to be weak allosteric binder [
17] or this binding modality did not influence the galectin-1 CRD engagement and induction of RBC agglutination in this assay.
To increase throughput, speed and thus enable a more screening application for the method we describe here, the assay could be further improved by applying an automated analysis in FIJI ImageJ and potentially investigating miniaturisation into a 384 well plate format. In summary, we have demonstrated in this study that the basic, binary galectin-induced hemagglutination assays can be optimised to be more robust and quantitative, enabling more detailed pharmacological characterisation of galectin, and galectin inhibitor effects, in a functional cell system.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Funding
All studies were funded by Galecto Biotech AB.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors have been, or are currently, employees of Galecto Biotech AB.
References
- R.-Y. Yang, G.A. Rabinovich, F.-T. Liu, Galectins: structure, function and therapeutic potential, Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 10 (2008) e17. [CrossRef]
- R.J. Slack, R. Mills, A.C. Mackinnon, The therapeutic potential of galectin-3 inhibition in fibrotic disease, Int J Biochem Cell Biology (2020) 105881. [CrossRef]
- P.P. Ruvolo, Galectin 3 as a guardian of the tumor microenvironment, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 1863 (2016) 427–437. [CrossRef]
- I.R. Nabi, J. Shankar, J.W. Dennis, The galectin lattice at a glance, J Cell Sci 128 (2015) 2213–2219. [CrossRef]
- M.F. Troncoso, M.T. Elola, A.G. Blidner, L. Sarrias, M.V. Espelt, G.A. Rabinovich, The universe of galectin-binding partners and their functions in health and disease, J. Biol. Chem. 299 (2023) 105400. [CrossRef]
- K.V. Mariño, A.J. Cagnoni, D.O. Croci, G.A. Rabinovich, Targeting galectin-driven regulatory circuits in cancer and fibrosis, Nat Rev Drug Discov (2023) 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Y. Huang, H.-C. Wang, J. Zhao, M.-H. Wu, T.-C. Shih, Immunosuppressive Roles of Galectin-1 in the Tumor Microenvironment, Biomol 11 (2021) 1398. [CrossRef]
- S.R. Stowell, C.M. Arthur, P. Mehta, K.A. Slanina, O. Blixt, H. Leffler, D.F. Smith, R.D. Cummings, Galectin-1, -2, and -3 Exhibit Differential Recognition of Sialylated Glycans and Blood Group Antigens*, J. Biol. Chem. 283 (2008) 10109–10123. [CrossRef]
- J. Stegmayr, A. Lepur, B. Kahl-Knutson, M. Aguilar-Moncayo, A.A. Klyosov, R.A. Field, S. Oredsson, U.J. Nilsson, H. Leffler, Low or No Inhibitory Potency of the Canonical Galectin Carbohydrate-binding Site by Pectins and Galactomannans., The Journal of Biological Chemistry 291 (2016) 13318–34. [CrossRef]
- Z. Shu, J. Li, N. Mu, Y. Gao, T. Huang, Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, M. Li, Q. Hao, W. Li, L. He, C. Zhang, W. Zhang, X. Xue, Y. Zhang, Expression, purification and characterization of galectin-1 in Escherichia coli, Protein Expres Purif 99 (2014) 58–63. [CrossRef]
- T. Delaine, P. Collins, A. MacKinnon, G. Sharma, J. Stegmayr, V.K. Rajput, S. Mandal, I. Cumpstey, A. Larumbe, B.A. Salameh, B. Kahl-Knutsson, H. van Hattum, M. van Scherpenzeel, R.J. Pieters, T. Sethi, H. Schambye, S. Oredsson, H. Leffler, H. Blanchard, U.J. Nilsson, Galectin-3-Binding Glycomimetics that Strongly Reduce Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis and Modulate Intracellular Glycan Recognition., Chembiochem : A European Journal of Chemical Biology 17 (2016) 1759–70. [CrossRef]
- A.C. MacKinnon, M.A. Gibbons, S.L. Farnworth, H. Leffler, U.J. Nilsson, T. Delaine, A.J. Simpson, S.J. Forbes, N. Hirani, J. Gauldie, T. Sethi, Regulation of transforming growth factor-β1-driven lung fibrosis by galectin-3., American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 185 (2012) 537–46. [CrossRef]
- N. Hirani, A.C. MacKinnon, L. Nicol, P. Ford, H. Schambye, A. Pedersen, U.J. Nilsson, H. Leffler, T. Sethi, S. Tantawi, L. Gravelle, R.J. Slack, R. Mills, U. Karmakar, D. Humphries, F. Zetterberg, L. Keeling, L. Paul, P.L. Molyneaux, F. Li, W. Funston, I.A. Forrest, A.J. Simpson, M.A. Gibbons, T.M. Maher, Target inhibition of galectin-3 by inhaled TD139 in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Eur Respir J 57 (2021) 2002559. [CrossRef]
- F.R. Zetterberg, A. MacKinnon, T. Brimert, L. Gravelle, R.E. Johnsson, B. Kahl-Knutson, H. Leffler, U.J. Nilsson, A. Pedersen, K. Peterson, J.A. Roper, H. Schambye, R.J. Slack, S. Tantawi, Discovery and Optimization of the First Highly Effective and Orally Available Galectin-3 Inhibitors for Treatment of Fibrotic Disease, J Med Chem (2022). [CrossRef]
- V. Aslanis, R.J. Slack, A.C. MacKinnon, C. McClinton, S. Tantawi, L. Gravelle, U.J. Nilsson, H. Leffler, A. Brooks, S.K. Khindri, R.P. Marshall, A. Pedersen, H. Schambye, F. Zetterberg, Safety and pharmacokinetics of GB1211, an oral galectin-3 inhibitor: a single- and multiple-dose first-in-human study in healthy participants, Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. (2023) 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Zetterberg, Discovery of the selective and orally available galectin-1 inhibitor GB1908 as a potential treatment for lung cancer, J Med Chem (under Review) (2024).
- R.P. Dings, M.C. Miller, I. Nesmelova, L. Astorgues-Xerri, N. Kumar, M. Serova, X. Chen, E. Raymond, T.R. Hoye, K.H. Mayo, Antitumor Agent Calixarene 0118 Targets Human Galectin-1 as an Allosteric Inhibitor of Carbohydrate Binding, 55 (n.d.). [CrossRef]
- E. Salomonsson, A. Larumbe, J. Tejler, E. Tullberg, H. Rydberg, A. Sundin, A. Khabut, T. Frejd, Y.D. Lobsanov, J.M. Rini, U.J. Nilsson, H. Leffler, Monovalent Interactions of Galectin-1, Biochemistry-Us 49 (2010) 9518–9532. [CrossRef]
- E. Salomonsson, M.C. Carlsson, V. Osla, R. Hendus-Altenburger, B. Kahl-Knutson, C.T. Öberg, A. Sundin, R. Nilsson, E. Nordberg-Karlsson, U.J. Nilsson, A. Karlsson, J.M. Rini, H. Leffler, Mutational Tuning of Galectin-3 Specificity and Biological Function*, The Journal of Biological Chemistry 285 (2010) 35079–35091. [CrossRef]
- P. Sörme, B. Kahl-Knutsson, M. Huflejt, U.J. Nilsson, H. Leffler, Fluorescence polarization as an analytical tool to evaluate galectin–ligand interactions, Anal Biochem 334 (2004) 36–47. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).