Submitted:
30 April 2024
Posted:
01 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The Environmental Impacts of Animal-Based Production
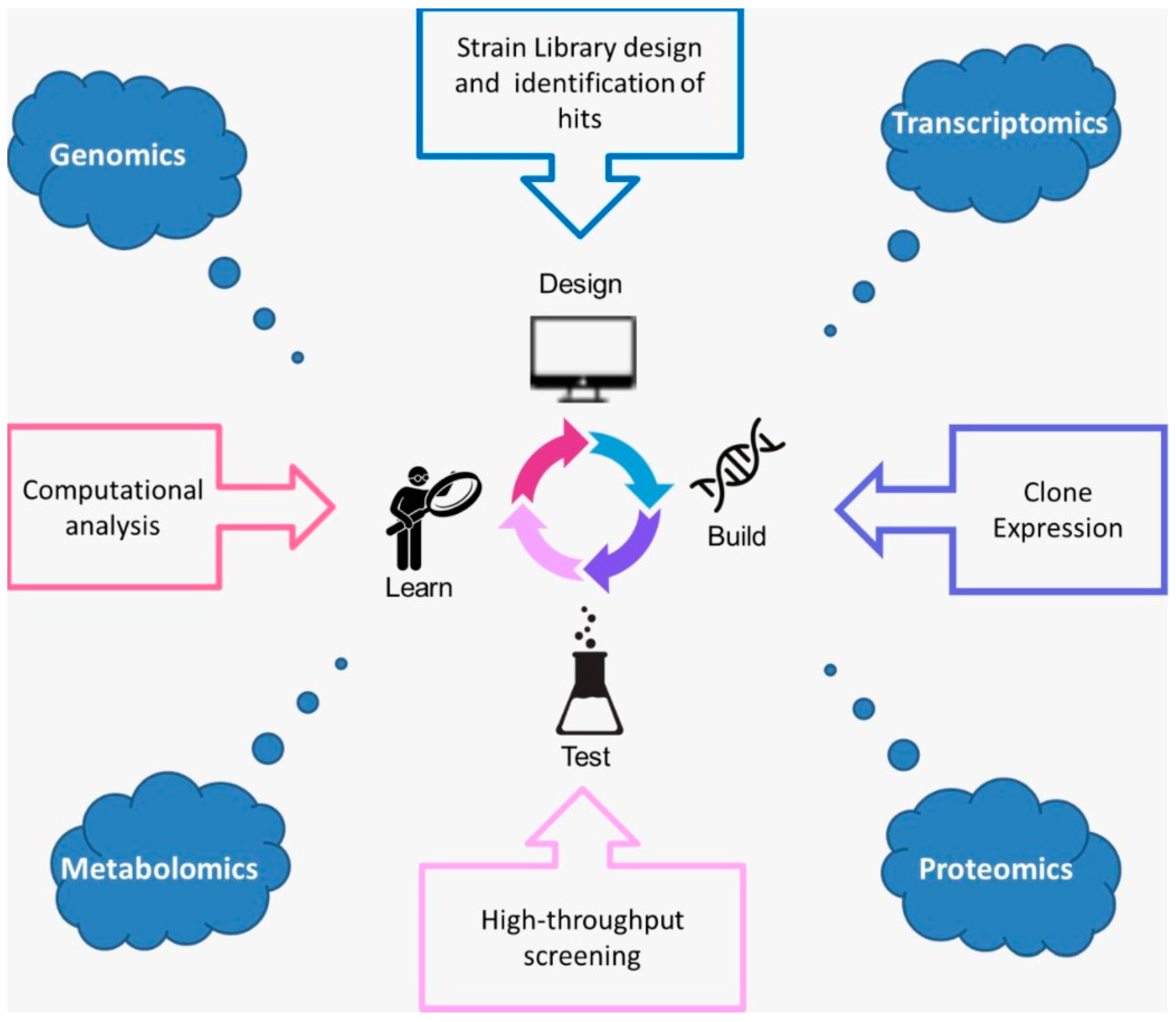
3. Precision Fermentation as part of the Solution
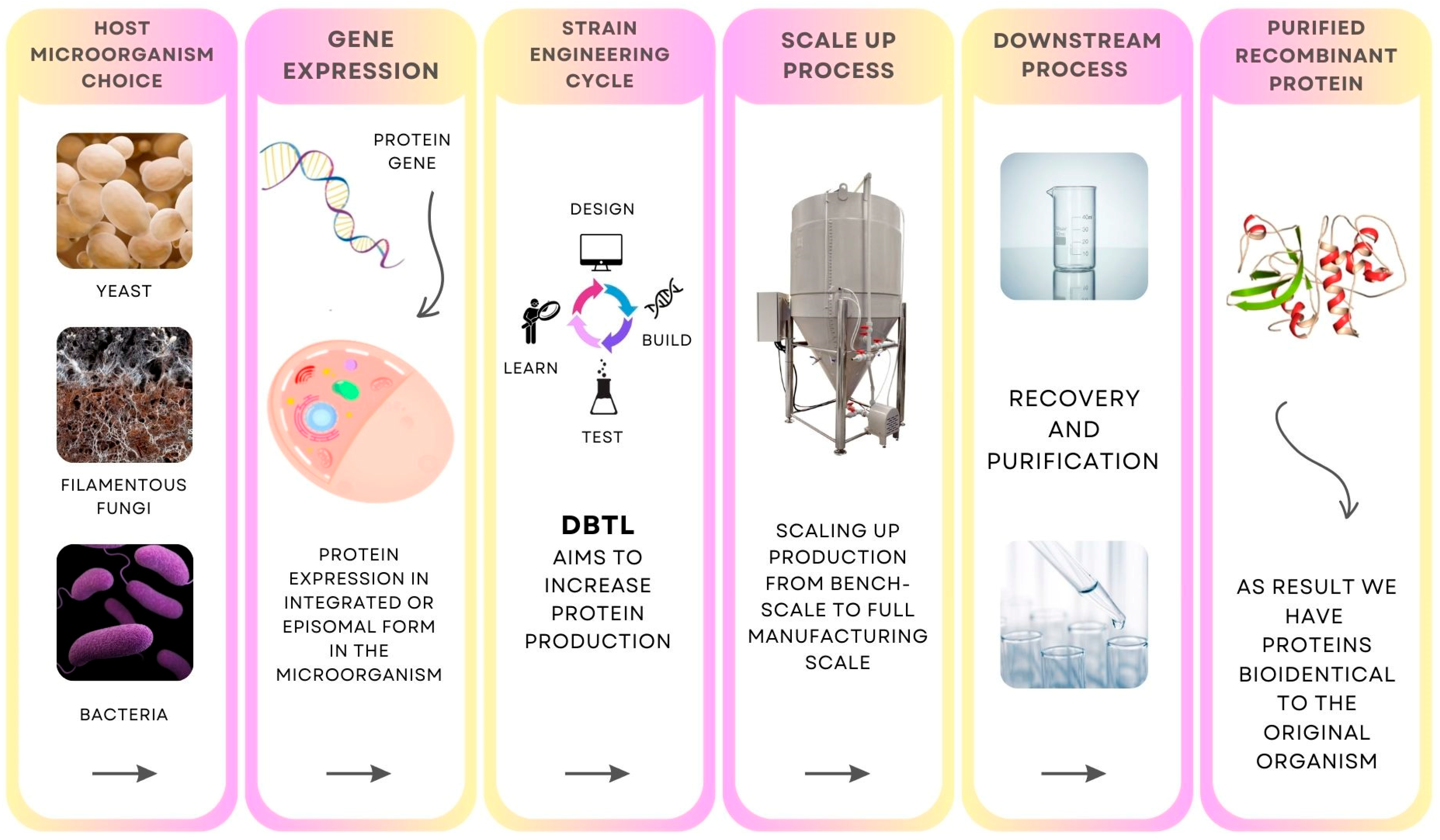
4. The Precision Fermentation Process
5. Animal Proteins Produced by Precision Fermentation
5.1. Milk Proteins
5.2. Egg-White Proteins
5.3. Structural Proteins
5.4. Flavoring Proteins
5.4. Other Proteins
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Sullivan, J.N. Demographic delusions: World population growth is exceeding most projections and jeopardising scenarios for sustainable futures. World 2023, 4, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Solazzo, E.; Guizzardi, D.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Tubiello, F. N.; Leip, A. Food systems are responsible for a third of global anthropogenic GHG emissions. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammarata, M.; Timpanaro, G.; Incardona, S.; La Via, G.; Scuderi, A. The quantification of carbon footprints in the agri-food sector and future trends for carbon sequestration: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, P.; Tavan, M. A review of the alternative protein industry. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. The future of food. Foods 2024, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Oytam, Y.; Hughes, J.; McDonnell, C.K.; Buckow, R. Sensory Perceptions and New Consumer Attitudes to Meat. In New Aspects of Meat Quality, 2nd ed.; Purslow, P.P., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2022; pp. 853–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, C.S. Cellular Agriculture: The Coming Revolution in Food Production. Bull. At. Sci. 2018, 74, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, N.; Di Silvio, L.; Dunsford, I.; Ellis, M.; Glencross, A.; Sexton, A. Bringing Cultured Meat to Market: Technical, Socio-Political, and Regulatory Challenges in Cellular Agriculture. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, T. Beyond agriculture─How microorganisms can revolutionize global food production. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Bekhit, A.E.D.; Jambrak, A.R.; Regenstein, J.M.; Chemat, F.; Morton, J.D.; Gudjónsdóttir, M.; Carpena, M.; et al. The Fourth Industrial Revolution in the Food Industry—Part II: Emerging Food Trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 407–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, L.; Crosser, N.; State of the Industry Report. Fermentation: An Introduction to a Pillar of the Alternative Protein Industry. Available online: https://gfi.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/INN-Fermentation-SOTIR-2020-0911.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Teng, T.S.; Chin, Y.L.; Chai, K.F.; Chen, W.N. Fermentation for Future Food Systems. EMBO Rep 2021, 22, e52680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A. An Introduction to Cellular Agriculture. Available online: https://www.cell.ag/ebook (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Clark, M.A.; Domingo, N.G.G.; Colgan, K.; Thakrar, S.K.; Tilman, D.; Lynch, J.; Azevedo, I.L.; Hill, J.D. Global Food System Emissions Could Preclude Achieving the 1.5° and 2°C Climate Change Targets. Science 2020, 370, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwatt, H.; Ripple, W.J.; Chaudhary, A.; Betts, M.G.; Hayek, M.N. Scientists Call for Renewed Paris Pledges to Transform Agriculture. Lancet Planet Health 2020, 4, e9–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cop28 UAE Declaration On Sustainable Agriculture, Resilient Food Systems, And Climate Action. Available online: www.cop28.com/en/food-and-agriculture (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing Food’s Environmental Impacts through Producers and Consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sharma, P.; Shu, S.; Lin, T.-S.; Ciais, P.; Tubiello, F.N.; Smith, P.; Campbell, N.; Jain, A.K. Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Animal-Based Foods Are Twice Those of Plant-Based Foods. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiello, F.N.; Karl, K.; Flammini, A.; Gütschow, J.; Obli-Laryea, G.; Conchedda, G.; Pan, X.; Qi, S.Y.; et al. Pre- and Post-Production Processes Increasingly Dominate Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Agri-Food Systems. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.M.; Beare, D.J.; Bennett, E.M.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Ingram, J.S.I.; Jaramillo, F.; Ortiz, R.; Ramankutty, N.; Sayer, J.A.; Shindell, D. Agriculture Production as a Major Driver of the Earth System Exceeding Planetary Boundaries. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22, art8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Junior, C.H.L.; Pessôa, A.C.M.; Carvalho, N.S.; Reis, J.B.C.; Anderson, L.O.; Aragão, L.E.O.C. The Brazilian Amazon Deforestation Rate in 2020 Is the Greatest of the Decade. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 5, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Ciais, P.; Brandt, M.; Fan, L.; Li, X.; Crowell, S.; Wu, X.; Doughty, R.; et al. Carbon Loss from Forest Degradation Exceeds That from Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machovina, B.; Feeley, K.J.; Ripple, W.J. Biodiversity Conservation: The Key Is Reducing Meat Consumption. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, S.M.; Settele, J.; Brondízio, E.; Ngo, H.; Guèze, M.; Agard, J.; Arneth, A.; Balvanera, P.; Brauman, K. A.; Butchart, S. H. et al. IPBES: Summary for policymakers of the global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services. IPBES, Bonn, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–56. [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. A Global Assessment of the Water Footprint of Farm Animal Products. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Bartak, D.; Caldwell, P.; Davis, K.F.; Debaere, P.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Li, T.; Marston, L.; McManamay, R.; et al. Water Scarcity and Fish Imperilment Driven by Beef Production. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Hall, J.W. Where Is the Planetary Boundary for Freshwater Being Exceeded Because of Livestock Farming? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Hejazi, M.; Tang, Q.; Vernon, C.R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Calvin, K. Global Agricultural Green and Blue Water Consumption under Future Climate and Land Use Changes. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Tilman, D. Comparative Analysis of Environmental Impacts of Agricultural Production Systems, Agricultural Input Efficiency, and Food Choice. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon Matthews, H.; Tokarska, K.B.; Rogelj, J.; Smith, C.J.; MacDougall, A.H.; Haustein, K.; Mengis, N.; Sippel, S.; Forster, P.M.; Knutti, R. An integrated approach to quantifying uncertainties in the remaining carbon budget. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugonnet, R.; McNabb, R.; Berthier, E.; Menounos, B.; Nuth, C.; Girod, L.; Farinotti, D.; Huss, M.; Dussaillant, I.; Brun, F.; et al. Accelerated Global Glacier Mass Loss in the Early Twenty-First Century. Nature 2021, 592, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovich, C.C.; Sun, T.; Gordon, D.R.; Ocko, I.B. Future Warming from Global Food Consumption. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järviö, N.; Parviainen, T.; Maljanen, N.-L.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kujanpää, L.; Ercili-Cura, D.; Landowski, C.P.; Ryynänen, T.; Nordlund, E.; Tuomisto, H.L. Ovalbumin Production Using Trichoderma reesei Culture and Low-Carbon Energy Could Mitigate the Environmental Impacts of Chicken-Egg-Derived Ovalbumin. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comparative Cycle Assessment of Perfect Day Protein. Perfect Day Inc. Available in: www.perfectday. (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Finnigan, T.; Needham, L.; Abbott, C. Mycoprotein: A Healthy New Protein with a Low Environmental Impact. In Sustainable Protein Sources, 2nd ed.; Nadathur, S., Wanasundara, J.P.D., Scanlin L. Eds.; Academic Press, London, United Kingdom, 2024; pp. 539-566. [CrossRef]
- IPCC Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Available online: www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Denkenberger, D.C.; Pearce, J.M. Feeding Everyone: Solving the Food Crisis in Event of Global Catastrophes That Kill Crops or Obscure the Sun. Futures 2015, 72, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, D.; Martin, W.; Swinnen, J.; Vos, R. COVID-19 Risks to Global Food Security. Science 2020, 369, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira Gomes, A.; Souza Carmo, T.; Silva Carvalho, L.; Mendonça Bahia, F.; Parachin, N. Comparison of Yeasts as Hosts for Recombinant Protein Production. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, H.; Peterson, R.; Curach, N. Overview of Gene Expression Using Filamentous Fungi. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2018, 92, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezonov, G.; Joseleau-Petit, D.; d'Ari, R. Escherichia coli physiology in Luria-Bertani broth. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8746–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-J.; Lin, H.; Yang, X. Industrial Production of Recombinant Therapeutics in Escherichia coli and Its Recent Advancements. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 39, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahdev, S.; Khattar, S.K.; Saini, K.S. Production of Active Eukaryotic Proteins through Bacterial Expression Systems: A Review of the Existing Biotechnology Strategies. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 307, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta, B.; Boyd, D.; Berkmen, M. Disulfide Bond Formation in the Periplasm of Escherichia Coli. EcoSal Plus 2019, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosnjak, I.; Bojovic, V.; Segvic-Bubic, T.; Bielen, A. Occurrence of Protein Disulfide Bonds in Different Domains of Life: A Comparison of Proteins from the Protein Data Bank. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2014, 27, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenthal, C.; Elsinghorst, E.A. Identification of a Glycoprotein Produced by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4084–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.C.; Haitjema, C.H.; Guarino, C.; Çelik, E.; Endicott, C.E.; Reading, C.A.; Merritt, J.H.; Ptak, A.C.; Zhang, S.; DeLisa, M.P. Production of Secretory and Extracellular N-Linked Glycoproteins in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamionka, M. Engineering of Therapeutic Proteins Production in Escherichia coli. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukens, B.; Jacobs, P.P.; Geysens, K.; Martins, J.; De Wachter, C.; Ameloot, P.; Morelle, W.; Haustraete, J.; Renauld, J.; et al. Off-target Glycans Encountered along the Synthetic Biology Route toward Humanized N -glycans in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei, M.; Rezaee, S.A.; Farsiani, H. Pichia pastoris : A Highly Successful Expression System for Optimal Synthesis of Heterologous Proteins. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5867–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, J.; Liu, D.; Ren, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X. Advances in Metabolic Engineering of Pichia pastoris Strains as Powerful Cell Factories. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damasceno, L.M.; Huang, C.-J.; Batt, C.A. Protein Secretion in Pichia pastoris and Advances in Protein Production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, C.V.G.C.; Serra, L.A.; Pacheco, T.F.; Ferreira, L.M.M.; Brandão, L.T.D.; Freitas, M.N. de M.; Trichez, D.; de Almeida, J.R.M. de Advances in Komagataella phaffii Engineering for the Production of Renewable Chemicals and Proteins. Fermentation 2022, 8, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.D.; Emmerstorfer-Augustin, A.; Biundo, A.; Pisano, I.; Coccetti, P.; Mapelli, V.; Camattari, A. Industrial Production of Proteins with Pichia pastoris-Komagataella phaffii. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, K.; Van Herpe, D.; Vanluchene, R.; Roels, C.; Van Moer, B.; Wyseure, E.; Vandewalle, K.; Eeckhaut, H.; Yilmaz, S.; Vanmarcke, S.; et al. OPENPichia: licence-free Komagataella phaffii chassis strains and toolkit for protein expression. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, K.F.; Ng, K.R.; Samarasiri, M.; Chen, W.N. Precision Fermentation to Advance Fungal Food Fermentations. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 47, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, A.; Arun, K.; Sindhu, R.; Alphonsa Jose, A.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Binod, P.; Sirohi, R.; Reshmy, R.; Kumar Awasthi, M. Engineering Interventions in Industrial Filamentous Fungal Cell Factories for Biomass Valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. Effect and Mechanism of Signal Peptide and Maltose on Recombinant Type III Collagen Production in Pichia pastoris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 4369–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, O.P. Production of Recombinant Proteins by Filamentous Fungi. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1119–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Keasling, J.D. Engineering Cellular Metabolism. Cell 2016, 164, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillson, N.; Caddick, M.; Cai, Y.; Carrasco, J.A.; Chang, M.W.; Curach, N.C.; Bell, D.J.; Le Feuvre, R.; Friedman, D.C.; Fu, X.; et al. Building a Global Alliance of Biofoundries. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, E.A.; Shaw, R.E.; Reynolds, C.R. Prediction of Strain Engineerings That Amplify Recombinant Protein Secretion through the Machine Learning Approach MaLPHAS. Eng. Biol. 2022, 6, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun. M.; Gao, A.X.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Bai, Z. High-throughput process development from gene cloning to protein production. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freemont, P.S. Synthetic Biology Industry: Data-Driven Design Is Creating New Opportunities in Biotechnology. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2019, 3, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xin, F.; Alper, H.S. Bio-Synthesis of Food Additives and Colorants-a Growing Trend in Future Food. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 47, 107694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.A.; Han, T.; Kim, G.B.; Park, J.E.; Lee, S.Y. Tools and Strategies of Systems Metabolic Engineering for the Development of Microbial Cell Factories for Chemical Production. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4615–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, E.; Andrion, J.; Apel, A.; Biggs, M.; Chaves, J.; Cheung, K.; Ciesla, A.; Clark-ElSayed, A.; Clay, M.; Contridas, R.; Fox, R.; et al. Optimizing the strain engineering process for industrial-scale production of bio-based molecules. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 50, kuad025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crater, J.S.; Lievense, J.C. Scale-up of industrial microbial processes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, NK.; Shrivastava, A. Recent Developments in Bioprocessing of Recombinant Proteins: Expression Hosts and Process Development. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrella, S.; Gridneva, Z.; Lai, C.T.; Stinson, L.; George, A.; Bilston-John, S.; Geddes, D. Human Milk Composition Promotes Optimal Infant Growth, Development and Health. Semin. Perinatol. 2021, 45, 151380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNICEF. Breastfeeding. Last update: December 2023. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/nutrition/breastf (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Kunz, C.; Lönnerdal, B. Re-evaluation of the Whey Protein/Casein Ratio of Human Milk. Acta Paediatr. 1992, 81, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive Proteins in Breast Milk. J. Paediatr. Child Health. 2013, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B. Infant Formula and Infant Nutrition: Bioactive Proteins of Human Milk and Implications for Composition of Infant Formulas. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 712S–717S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Séverin, S.; Wenshui, X. Milk Biologically Active Components as Nutraceuticals: Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layman, D.K.; Lönnerdal, B.; Fernstrom, J.D. Applications for α-Lactalbumin in Human Nutrition. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbrow, B.; Burd, N.A.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Moore, D.R.; Elliott-Sale, K.J. Nutrition for Special Populations: Young, Female, and Masters Athletes. Int. J. Sport. Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulding, D.A.; Fox, P.F.; O’Mahony, J.A. Milk Proteins: An Overview. In Milk Proteins; 3nd ed.; Boland, M., Singh, H. (eds); Academic Press, Newbridge, Ireland, 2020; pp. 21–92. [CrossRef]
- Donovan, S. M. Human milk proteins: composition and physiological significance. In Human milk: composition, clinical benefits and future opportunities, Donovan, S.M., German, J.B, Lönnerdal, B., Lucas, A. Eds.; Karger Publishers,, Basel, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 9, pp. 93–101. [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; Ryan, A.C.; Kelly, A.L. (2021). The composition and physico-chemical properties of human milk: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.P.; Bhandari, B.; Cichero, J.; Prakash, S. A Comprehensive Review on in Vitro Digestion of Infant Formula. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permyakov, E.A. α-Lactalbumin, Amazing Calcium-Binding Protein. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Xu, R.; Wang, Q. β-Lactoglobulin-Based Encapsulating Systems as Emerging Bioavailability Enhancers for Nutraceuticals: A Review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35138–35154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterton, D.E.W.; Nguyen, D.N.; Bering, S.B.; Sangild, P.T. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Bioactive Milk Proteins in the Intestine of Newborns. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1730–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, P.; Kaczyńska, K.; Kleczkowska, P.; Bukowska-Ośko, I.; Kramkowski, K.; Sulejczak, D. The Lactoferrin Phenomenon—A Miracle Molecule. Molecules 2022, 27, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Han, K.; Liu, H.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Fan, S.; Peng, W.; et al. The Effect of Lactoferrin in Aging: Role and Potential. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Mejía, F.; Vega-Bautista, A.; Molotla-Torres, D.E.; Aguirre-Garrido, J.F.; Drago-Serrano, M.E. Bovine Lactoferrin as a Modulator of Neuroendocrine Components of Stress. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Lv, X.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Cell Factory-Based Milk Protein Biomanufacturing: Advances and Perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, J.H.; Cheung, L.K.Y.; Newman, L.; Dee, D.R.; Yada, R.Y. Precision Cellular Agriculture: The Future Role of Recombinantly Expressed Protein as Food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 882–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yart, L.; Wijaya, A.W.; Lima, M.J.; Haller, C.; van der Beek, E.M.; Carvalho, R.S.; Kraus, M.R.-C.; Mashinchian, O. Cellular Agriculture for Milk Bioactive Production. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.B.; Meyer, A.S.; Arnau, J. The Next Food Revolution Is Here: Recombinant Microbial Production of Milk and Egg Proteins by Precision Fermentation. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 15, in. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.; Carver, J.A.; Ecroyd, H.; Thorn, D.C. Invited Review: Caseins and the Casein Micelle: Their Biological Functions, Structures, and Behavior in Foods. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 6127–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshwal, G.K.; Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Fenelon, M.; Huppertz, T. A Review on the Effect of Calcium Sequestering Salts on Casein Micelles: From Model Milk Protein Systems to Processed Cheese. Molecules 2023, 28, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runthala, A.; Mbye, M.; Ayyash, M.; Xu, Y.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Caseins: Versatility of Their Micellar Organization in Relation to the Functional and Nutritional Properties of Milk. Molecules 2023, 28, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettinga, K.; Bijl, E. Can Recombinant Milk Proteins Replace Those Produced by Animals? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 75, 102690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-K.; Jiménez-Flores, R. Expression and Purification of Glycosylated Bovine β-Casein (L70S/P71S) in Pichia pastoris. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Oh, Y.-K.; Kang, W.; Lee, E.Y.; Park, S. Production of Human Caseinomacropeptide in Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 32, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Lv, X.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Efficient Bioproduction of Human Milk α-Lactalbumin in Komagataella phaffii. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2022, 70, 2664–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.R.; Goto, Y.; Hirota, N.; Kuwata, K.; Denton, H.; Wu, S.Y.; Sawyer, L.; Batt, C.A. High-Level Expression of Bovine β-Lactoglobulin in Pichia pastoris and Characterization of its Physical Properties. Protein Eng. 1997, 10, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, G.; Ragona, L.; Brocca, S.; Pedrazzoli, E.; Molinari, H.; Morandini, P.; Catalano, M.; Lotti, M. Heterologous Expression of Bovine and Porcine β-Lactoglobulins in Pichia pastoris: Towards a Comparative Functional Characterisation. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 109, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, N.; Ercili-Cura, D.; Andberg, M.; Silventoinen, P.; Lille, M.; Hosia, W.; Nordlund, E.; Landowski, C.P. Production of Bovine β-Lactoglobulin and Hen Egg Ovalbumin by Trichoderma reesei Using Precision Fermentation Technology and Testing of their Techno-Functional Properties. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.P.; Piddington, C.S.; Cunningham, G.A.; Zhou, X.; Wyatt, R.D.; Conneely, O.M. A System for Production of Commercial Quantities of Human Lactoferrin: A Broad Spectrum Natural Antibiotic. Biotechnology 1995, 13, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-L.; Lai, Y.-W.; Yen, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Lu, C.-Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Tsai, T.-C.; Lin, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-W.; Chen, C.-M. Production of Recombinant Porcine Lactoferrin Exhibiting Antibacterial Activity in Methylotrophic Yeast, Pichia pastoris. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 8, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Chen, L.; Jia, S.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y. High-Level Expression and Production of Human Lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.K.; Actor, J.K.; Rios, S.; D’Anjou, M.; Stadheim, T.A.; Warburton, S.; Giaccone, E.; Cukan, M.; Li, H.; Kull, A.; et al. Recombinant human lactoferrin expressed in glycoengineered Pichia pastoris: effect of terminal N-acetylneuraminic acid on in vitro secondary humoral immune response. Glycoconj. J. 2008, 25, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Figueroa, B.; Valdiviezo-Godina, N.; Siqueiros-Cendón, T.; Sinagawa-García, S.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. High-Level Expression of Recombinant Bovine Lactoferrin in Pichia pastoris with Antimicrobial Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaohui, Y.; Chen, G.; Yu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, J. Cloning of a Novel Ovalbumin Gene from Quail Oviduct and Its Heterologous Expression in Pichia pastoris. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2009, 49, S73–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, K.; Okamoto, I.; Fujita, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Hirose, M. Structural and Functional Characterization of Ovotransferrin Produced by Pichia pastoris. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Ueno, Y.; Kitabatake, N. High Yield Secretion of the Sweet-Tasting Protein Lysozyme from the Yeast Pichia pastoris. Protein. Expr. Purif. 2005, 39, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zocchi, A.; Marya Jobé, A.; Neuhaus, J.-M.; Ward, T.R. Expression and Purification of a Recombinant Avidin with a Lowered Isoelectric Point in Pichia pastoris. Protein. Expr. Purif. 2003, 32, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Luo, Y.; Fan, D.; Yang, B.; Gao, P.; Ma, X.; Zhu, C. Medium Optimization Based on the Metabolic-flux Spectrum of Recombinant Escherichia coli for High Expression of Human-like Collagen II. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2010, 57, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellermann, P.; Schneider-Barthold, C.; Bolten, S.N.; Overfelt, E.; Scheper, T.; Pepelanova, I. Production of a Recombinant Non-Hydroxylated Gelatin Mimetic in Pichia pastoris for Biomedical Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2019, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Liang, X.; Yu, S.; Zhou, J. Expression, Characterization, and Application Potentiality Evaluation of Recombinant Human-like Collagen in Pichia pastoris. Bioresour. Bioproc. 2022, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie W, Wu Q, Kuang Z, Cong J, Zhang Q, Huang Y, Su Z, Xiang Q. Temperature-Controlled Expression of a Recombinant Human-like Collagen I Peptide in Escherichia coli. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fan, D.; Ma, X.; Deng, J.; He, J. ; High-level secretory expression and purification of unhydroxylated human collagen α1(III) chain in Pichia pastoris GS115. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2015, 62, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.X.; Gong, J.S.; Shi, J.H.; Liu, C.F.; Li, H.; Su, C.; Jiang, M.; Xu, Z.H.; Shi, J.S. High-efficiency secretory expression and characterization of the recombinant type III human-like collagen in Pichia pastoris. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipperus, R.; Eggink, G.; De Wolf, F.A. Secretion of elastin-like polypeptides with different transition temperatures by Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.J.; Gutierrez, P.; Guerrero, E.; Brewer, C.J.; Henderson, D.P. Development of a method to produce hemoglobin in a bioreactor culture of Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) transformed with a plasmid containing Plesiomonas shigelloides heme transport genes and modified human hemoglobin genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6703–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Lu, W.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Du, G. Biosynthesis of High-Active Hemoproteins by the Efficient Heme-Supply Pichia pastoris Chassis. Adv. Sci, 2023, 10, e2302826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Li, J. Efficient Secretory Expression and Purification of Food-Grade Porcine Myoglobin in Komagataella phaffii. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 10235–10245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Xue, C.; Liu, W.; Zuo, S.; Wei, P.; Huang, L.; Lian, J.; Xu, Z. High-level secretory production of leghemoglobin in Pichia pastoris through enhanced globin expression and heme biosynthesis. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Wu, X.; Wu, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y.; Lu, H. High-level expression of leghemoglobin in Kluyveromyces marxianus by remodeling the heme metabolism pathway. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 11, 1329016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khersonsky, O.; Goldsmith, M.; Zaretsky, I.; Hamer-Rogotner, S.; Dym, O.; Unger, T.; Yona, M.; Fridmann-Sirkis, Y.; Fleishman, S.J. Stable mammalian serum albumins designed for bacterial expression. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 168191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Choi, E.S.; Hong, W.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Ko, S.M.; Sohn, J.H.; Rhee, S.K. Proteolytic stability of recombinant human serum albumin secreted in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 575–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, L.; Hughes, M.; Waters, J.; Cameron, J.; Dodsworth, N.; Tooth, D.; Greenfield, A.; Sleep. D. The production, characterisation and enhanced pharmacokinetics of scFv-albumin fusions expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Protein. Expr. Purif. 2010, 73, 113–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliola, M.; Mazzoni, C.; Solimando, N.; Crisà, A.; Falcone, C.; Jung, G.; Fleer, R. Use of the KlADH4 promoter for ethanol-dependent production of recombinant human serum albumin in Kluyveromyces lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Gong, G.; Pan, J.; Han, S.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Xie, L. High level expression and purification of recombinant human serum albumin in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2018, 147, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallem, M.; Warburton, S.; Li, F.; Shandil, I.; Nylen, A.; Kim, S.; Jiang, Y.; Meehl, M.; d'Anjou, M.; Stadheim, T.A.; Choi, B.K. Maximizing recombinant human serum albumin production in a Mut(s) Pichia pastoris strain. Biotechnol. Prog. 2014, 30, 1488–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, T.; Ohyama, M.; Kobayashi, K. Optimization of human serum albumin production in methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris by repeated fed-batch fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 876–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, R.; Gong, G.; Xu, L.; Hu, Y.; Xie, L. Medium optimization for high yield production of human serum albumin in Pichia pastoris and its efficient purification. Protein. Expr. Purif. 2021, 181, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Culture’s Animal-Free Dairy Protein Reaches Milestone Scale, Poised to Disrupt $154 Billion Global Cheese Industry Available online:. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/new-cultures-animal-free-dairy-protein-reaches-milestone- scale-poised-to-disrupt-154-billion-global-cheese-industry-301900344.html (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Lien, E.L. Infant Formulas with Increased Concentrations of α-Lactalbumin. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1555S–1558S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, N.; Teng, D.; Wang, X.; Mao, R.; Wang, J. A Review of the Design and Modification of Lactoferricins and Their Derivatives. BioMetals 2018, 31, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, J.; Beeraka, N.M.; Li, J.; Sinelnikov, M.Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Zakharova, D.K.; Nikolenko, V.N.; Reshetov, I.V.; Lu, P. Novel Perspectives on Nanotechnological and Biomedical Implications of Monotherapy or Combination Regimen of Lactoferrin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, W.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Yang, N.; Hao, Y.; Wang, J. Interaction between Dietary Lactoferrin and Gut Microbiota in Host Health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 7596–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; An, Q.; Huang, K.; Dai, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Unlocking the power of Lactoferrin: Exploring its role in early life and its preventive potential for adult chronic diseases. Food Res Int. 2024, 182, 114143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancocks, N. Lactoferrin Market Set to Surpass €265 Million by 2027. Available online: https://www.nutraingredients.com/Article/2021/04/09/Lactoferrin-market-set-to-surpass-265-million-by-2027 (accessed on 9 April 2024).
- Mao, R.; Ma, X.; Hao, Y.; Pen, G.; Zheng, X.; Yang, N.; Teng, D.; Wang, J. Perspective: A Proposal on Solutions of Modern Supply Chain Construction for Lactoferrin. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 7329–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs-Nolan, J.; Phillips, M.; Mine, Y. Advances in the Value of Eggs and Egg Components for Human Health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8421–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Ahn, D.U. Egg White Proteins and Their Potential Use in Food Processing or as Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Agents—A Review. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 3292–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, R.; Sugano, M. Health Functions of Egg Protein. Foods 2022, 11, 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.Q. An insight on egg white: From most common functional food to biomaterial application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Tang, Q.; Ma, M.; Jin, Y.; Sheng, L. Functional Properties and Extraction Techniques of Chicken Egg White Proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lyu, S.; Xu, M.; Li, S.; Du, Z.; Liu, X.; Shang, X.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T. Potential Benefits of Egg White Proteins and Their Derived Peptides in the Regulation of the Intestinal Barrier and Gut Microbiota: A Comprehensive Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 13168–13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wu, N.; Chen, S.; Xu, L.; Tu, Y. Characteristics of hen egg white lysozyme, strategies to break through antibacterial limitation, and its application in food preservation: A review. Food Res. Int. 2024, 181, 114114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legros, J.; Jan, S.; Bonnassie, S.; Gautier, M.; Croguennec, T.; Pezennec, S.; Cochet, M.F.; Nau, F.; Andrews, S.C.; Baron, F. The Role of Ovotransferrin in Egg-White Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspanti. M.; Reguzzoni, M.; Protasoni, M.; Basso, P. Not only tendons: The other architecture of collagen fibrils. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Antonio, J.D.; Jacenko, O.; Fertala, A.; Orgel, J.P.R.O. Collagen Structure-Function Mapping Informs Applications for Regenerative Medicine. Bioengineering 2020, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M. Processing of collagen based biomaterials and the resulting materials properties. Biomed. Eng. Online. 2019, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Liu, F.; Dai, H.; Fu, Y.; Huang, T.; Farooq, S.; Zhang, H. Collagen and gelatin: Structure, properties, and applications in food industry. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 128037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.X.; Gong, J.S.; Li, H.; Shi, W.T.; Jiang, M.; Xu, Z.H.; Shi, J.S. Heterologous Expression, Fermentation Strategies and Molecular Modification of Collagen for Versatile Applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5268–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 152. Xu S, Zhao Y, Song W, Zhang C, Wang Q, Li R, Shen Y, Gong S, Li M, Sun L. Improving the Sustainability of Processing By-Products: Extraction and Recent Biological Activities of Collagen Peptides. Foods. [CrossRef]
- Aly, N.; Benoit, E.; Chaubard, J.L.; Chintalapudi, K.; Choung, S.; de Leeuw, M.; Diaz, M.; Dueppen, D.; Ferraro, B.; Fischetti, V.; et al. Cosmetic Potential of a Recombinant 50 kDa Protein. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadach, B.; Mielcarek, Z.; Osmałek, T. Use of Collagen in Cosmetic Products. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 2043–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertala, A. Three Decades of Research on Recombinant Collagens: Reinventing the Wheel or Developing New Biomedical Products? Bioengineering 2020, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, V.; Salgueiro, S.P. From Small to Large-Scale: A Review of Recombinant Spider Silk and Collagen Bioproduction. Discov. Mater. 2022, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lew, J.; Premkumar, J.; Poh, C.L.; Win Naing, M. Production of Recombinant Collagen: State of the Art and Challenges. Eng. Biol, 2017, 1, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, L.N.; Zhu, C.H.; Fan, D.D.; Ma, X.X.; Mi, Y.; Xing, J.Y. Co-expression of recombinant human prolyl with human collagen α1 (III) chains in two yeast systems. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, X.; Hang, B.; Li, J.; Huang, L.; Huang, F.; Xu, Z. Efficient Production of Hydroxylated Human-Like Collagen Via the Co-Expression of Three Key Genes in Escherichia coli Origami (DE3). Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 1458–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Ma, X.; Gao, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhu, C.; Mi, Y.; Xue, W. Hydroxylation of Human Type III Collagen α Chain by Recombinant Coexpression with a Viral Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase in Escherichia coli. Protein J. 2017, 36, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, S.; Zheng, S.; Wu, H.; Xia, P.; Chen, X.; Yang, R.; Hao, L.; Zhang, Y. Co-expression of recombinant human collagen α1(III) chain with viral prolyl 4-hydroxylase in Pichia pastoris GS115. Protein. Expr. Purif. 2023, 201, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindin, H.; Mithieux, S.M.; Weiss, A.S. Elastin Architecture. Matrix Biol. 2019, 84, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toonkool, P.; Weiss, A.S. Expression of recombinant human tropoelastin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing a synthetic gene with a high codon adaptation index coupled to the SUC2 invertase signal sequence. Acta Biotechnol. 2001, 21, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallach, R.E.; Conticello, V.P.; Chaikof, E.L. Expression of a recombinant elastin-like protein in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol, Prog. 2009, 25, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werten, M.W.T.; Eggink, G.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; de Wolf, F.A. Production of protein-based polymers in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 642–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandiera, A.; Colomina - Alfaro, L.; Sist, P.; Gomez d’Ayala, G.; Zuppardi, F.; Cerruti, P.; Catanzano, O.; Passamonti, S.; Urbani, R. Physicochemical characterization of a biomimetic, elastin-inspired polypeptide with enhanced thermoresponsive properties and improved cell adhesion. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 5277–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, F.; Yu, W.; Wang, T.; Xiong, J.; Zhou, L.; Hu, F.; Ye, X.; Liang, X. Construction of a collagen-like protein based on elastin-like polypeptide fusion and evaluation of its performance in promoting wound healing. Molecules 2023, 28, 6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
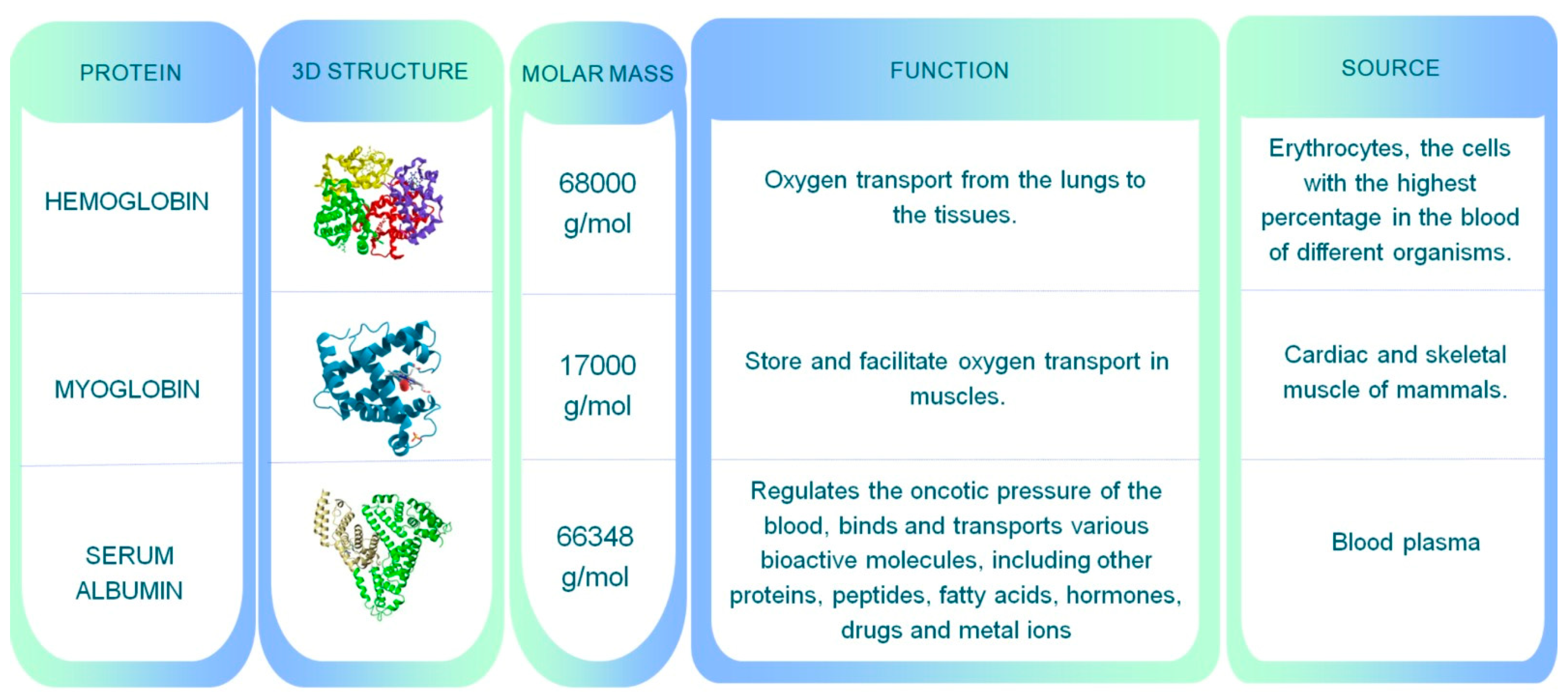
- Giardina, B. Hemoglobin: Multiple molecular interactions and multiple functions. An example of energy optimization and global molecular organization. Mol. Aspects Med. 2022, 84, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordway, G.A.; Garry, D.J. Myoglobin: an essential hemoprotein in striated muscle. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 3441–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garry, D.J.; Mammen, P.P. Molecular insights into the functional role of myoglobin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 618, 181–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholi, I.E.; Elsherbiny, M.E.; Emara, M. Myoglobin: From physiological roles to potential implications in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnado, C.L.; Mollan, T.L.; Birukou, I.; Smith, B.J.Z.; Henderson, D.P.; Olson, J.S. Development of Recombinant Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carriers. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 2314–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, A.T.; Jacobsen, I.H.; Worberg, A.; Martínez, J.L. How synthetic biology and metabolic engineering can boost the generation of artificial blood using microbial production hosts. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Palmer. A.F.; ZIF-8 Metal–organic framework nanoparticles loaded with hemoglobin as a potential red blood cell substitute. ACS Appl. Nano Mat. 2022, 5, 5670–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaere, J.; De Winne, A.; Dewulf, L.; Fraeye, I.; Šoljić, I.; Lauwers, E.; de Jong, A.; Sanctorum, H. Improving the aromatic profile of plant-based meat alternatives: effect of myoglobin addition on volatiles. Foods 2022, 11, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.Z.; Shitut, M.; Agrawal, P.; Mendes, O.; Klapholz, S. Safety Evaluation of Soy Leghemoglobin Protein Preparation Derived From Pichia pastoris, Intended for Use as a Flavor Catalyst in Plant-Based Meat. Int. J. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsa, R.; Yuen, J.; Stout, A.; Rubio, N.; Fogelstrand, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Extracellular heme proteins influence bovine myosatellite cell proliferation and the color of cell-based meat. Foods 2019, 8, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Chatli, M.K.; Mehta, N.; Singh, P.; Malav, O.P.; Verma, A.K. Meat Analogues: Health Promising Sustainable Meat Substitutes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegrist, M.; Sütterlin, B. Importance of Perceived Naturalness for Acceptance of Food Additives and Cultured Meat. Appetite 2017, 113, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tu, T.; Qin, X.; Su, X.; Luo, H.; Yao, B.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J. Engineering Escherichia coli for Efficient Assembly of Heme Proteins. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2023, 22, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, X. Systematic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient synthesis of hemoglobins and myoglobins. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 370–128556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Recent advances in the microbial synthesis of hemoglobin. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishchuk, O.P.; Frost, A.T.; Muñiz-Paredes, F.; Matsumoto, S.; Laforge, N.; Eriksson, N.L.; Martínez, J.L.; Petranovic, D. Improved production of human hemoglobin in yeast by engineering hemoglobin degradation. Metab. Eng. 2021, 66, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan, R.; Szabo, A.; Boxer, S.G. Cloning, expression in Escherichia coli, and reconstitution of human myoglobin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 5681–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, G.; Ahn, S.N. Structure, enzymatic activities, glycation and therapeutic potential of human serum albumin: A natural cargo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, G.; di Masi, A.; Ascenzi, P. Serum Albumin: A Multifaced Enzyme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Shi, B.; Yang, D. Human serum albumin from recombinant DNA technology: challenges and strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013, 1830, 5515–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodsworth, N.; Harris, R.; Denton, K.; Woodrow, J.; Wood, P.C.; Quirk, A. Comparative studies of recombinant human albumin and human serum albumin derived by blood fractionation. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 1996, 24, 171–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosse, D.; Praus, M.; Kiessling, P.; Nyman, L.; Andresen, C.; Waters, J.; Schindel, F. Phase I comparability of recombinant human albumin and human serum albumin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiang, W.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Yang, T.; Mai, J.; Chi, X.; Gao, X.; Ding, Y.; Niu, J. A randomized dose-escalation study on the safety, tolerability, immunogenicity, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a novel recombinant human albumin in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 165, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, N.; Jaswal, A.S.; Gautam, A.; Sahai, V.; Mishra, S. High level production of stable human serum albumin in Pichia pastoris and characterization of the recombinant product. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recombumin® Recombinant Human Albumin. Available online: https://www.sartorius.com/en/products/ cell-culture-media/cell-culture-reagents-supplements/recombinant-human-albumin?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=ww_en_search_CGT-Seeding_Albumedix-HumanAlbumin&gad_source=1&gclid=CjwKCAjwxLKxBhA7EiwAXO0R0K9DRbQLbTIpi18Z0h6GBHdrB3ilQ88_oZGGSQgLU65WZExlfKuj3RoCnWUQAvD_BwE (accessed on 27 April 2024).
| Content (g/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk proteins | Human | Bovine | |
| Caseins | αs1-CN | 0.09 – 0.87 | 8.0 – 10.7 |
| αs2-CN | – | 2.8 – 3.4 | |
| β-CN | 0.28 – 2.47 | 8.6 – 9.3 | |
| κ-CN | 0.36 – 1.12 | 2.3 – 3.3 | |
| Whey proteins | α-lactalbumin | 0.86 – 3.67 | 1.2 – 1.3 |
| β-lactoglobulin | – | 3.2 | |
| lactoferrin | 0.93 – 3.0 | 0.1 – 0.5 | |
| lysozyme | 0.07 – 0.51 | Trace | |
| IgA | 0.49 – 1.85 | 0.1 – 0.2 | |
| Proteins | Source | Host | Production (g/L) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casein | β-CN | Bovine | K. phaffii | 0.245 | [96] |
| MP-κ-CN | Human | S. cerevisiae | 2.5 | [97] | |
| Whey proteins | α-lactalbumin | Human | K. phaffii | 0.056 | [98] |
| β-lactoglobulin | Bovine | K. phaffii | 1.0 | [99] | |
| Porcine | K. phaffii | 0.200 | [100] | ||
| Bovine | T. reesei | 1.0 | [101] | ||
| lactoferrin | Human | Aspergillus awamori | 2.0 | [102] | |
| Porcine | K. phaffii | 0.760 | [103] | ||
| Human | K. phaffii | 1.2 | [104] | ||
| Human | glycoengineered K. phaffii | 0.100 | [105] | ||
| Bovine | K. phaffii | 3.5 | [106] | ||
| Eggwhite | ovalbumin | Quail | K. phaffii | 5.45 | [107] |
| ovotransferrin | Chicken | K. phaffii | 0.100 | [108] | |
| lysozyme | Chicken | K. phaffii | 0.400 | [109] | |
| avidin | Chicken | K. phaffii | 0.330 | [110] | |
| Structural proteins | unhydroxylated collagen II | Human* | E. coli | 10.8 | [111] |
| “gelatin-mimetic” hyd-collagen I | Human* | K. phaffii | 3.4 | [112] | |
| collagen(I and III)-like** | Human* | K. phaffii | 2.33 | [113] | |
| collagen I** | Human* | E.coli | 1.88 | [114] | |
| unhydroxylated collagen III | Human* | K. phaffii | 4.68 | [115} | |
| collagen III** | Human* | K. phaffii | 1.05 | [116] | |
| elastin-like | synthetic | K. phaffii | 0.150-0.700 | [117] | |
| Flavoring proteins | hemoglobin*** | Human | E. coli | 11.92 | [118] |
| myoglobin | Porcine | K. phaffii | 0.247 | [119] | |
| myoglobin | Porcine | K. phaffii | 0.285 | [120] | |
| leghemoglobin | Soy | K. phaffii | 3.5 | [121] | |
| leghemoglobin | Soy | K. marxianus | 7.27 | [122] | |
| Other proteins | serum albumin*** | Human | E. coli | 0.100 | [123] |
| serum albumin | Human | S. cerevisiae | 0.200 | [124] | |
| serum albumin**** | Human | S. cerevisiae | 5.5 | [125] | |
| serum albumin | Human | Kluyveromyces lactis | 1.05 | [126] | |
| serum albumin | Human | K. phaffii | 8.86 | [127] | |
| serum albumin | Human | K. phaffii | 10.0 | [128] | |
| serum albumin | Human | K. phaffii | 11.0 | [129] | |
| serum albumin | Human | K. phaffii | 17.47 | [130] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





