1. Introduction
Oxidative stress has long been implicated as a central player in aging, cellular dysfunction and disease progression [1-4] and reactive oxygen species (ROS) have traditionally been viewed as toxic byproducts of metabolism that cause non-specific damage to cells. ROS includes oxygen ions [singlet oxygen, superoxide (O2·−)] or oxygen-containing radicals [e.g. hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)] and related species [
5,
6]. The propensity of unregulated ROS to modify proteins and DNA can disrupt multiple cellular organelles and processes and disrupt normal physiology [
5]. Multiple models of stress and disease across diverse species evidence deleterious ROS signaling [
7,
8]. Oxidative damage has also been linked to aging [
2], as chemical changes to macromolecules will accumulate unless repaired or replaced. Thus, managing the production and consequences of cellular or environmentally generated ROS is critical to maintaining homeostasis in a range of organisms across evolution including humans [
5,
9].
The oxidizing equivalents of ROS can modify many cellular targets, but in proteins sulfur containing residues are the most susceptible including methionine which can be oxidized to methionine sulfoxide. Methionine oxidation is known to have broad effects on protein structure and function as oxidation alters methionine’s hydrophobicity and steric bulk [
6], which can unfold proteins and expose hydrophobic cores. These kinds of structural changes, if allowed to accumulate can logically lead to changes in protein functions. Reversal of methionine oxidation can be accomplished by methionine sulfoxide reductases (MsR), which are seen in organisms from bacteria to human. Oxidation of methionine generates a chiral center, the S and R stereoisomers are reduced by the enzymes MsrA and MsrB respectively, both using thioredoxin linked redox cycles [
10,
11]. This provides a reversible redox based system to control MS
ox mediated changes in protein structure and activity in response to oxidative signaling. The CaMKII ( Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II) exemplifies this concept [
12]. Beyond the canonical phosphorylated-based activation mechanisms, CaMKII’s activity is also modulated through the oxidation of specific methionine residues (Met 281 and 282) [
13]. This links oxidation with a key control enzyme in cardiovascular and brain development and disease pathology. Actin as well has reversible modifications at Met 44 and Met 47 modulating cytoskeletal rearrangements in multiple vertebrate models relevant to cell growth and cancer under regulation of the MICAL family of enzymes [
14,
15]. Thus, MS
ox speciation is a novel regulatory control mechanism potentially operating to connect ROS to other signaling pathways.
Beyond these specific regulatory switches at a global level, methionine oxidation may act as a sensor of cellular stress [1,2,16-23] where protein incorporated MS
ox is accumulated, depleted, and regulated by the inducible system of Msr or related enzymes. The biological effects of Msr variation by knockout or knock-in have showed lifespan variation in flies related to antioxidant defense but results in mouse were equivocal, showing tissue specific mouse functions affected [
24]. Global proteomics studies to discover and validate both enzymatic and chemical sites of methionine oxidation speciation, that would help inform such studies, are scarce. Furthermore, quantification of methionine oxidation is considered challenging due to potential instabilities of the modifications during proteomics workups and in handling and storage of samples. The development of reliable models and workflows to discover, verify and validate MS
ox based regulatory phenomenon will assist connecting MS
ox to ROS mediated biology.
As examples, ROS and oxidation mediated effects are associated with both disease and aging across a range of models and species [1,2,24-29]. For example, Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and oxidation are strongly associated with evidence of lipid, DNA, and protein-based oxidation via glycation [
30]. Further, amyloid peptides can mediate free radical reactions via Met 35 oxidation with enhanced neuronal toxicity [
3,
31,
32]. Specific connections between AD and MS
ox are suggested by decreased MsrA activity in AD patient brain [
33] while methionine sulfoxide reductase B2 (MsrB2) was inhibited in an AD mouse model. Further, compensation for the loss of MsrB2 in AD cell culture and animal models reverses AD-like pathology [
34]. This argues that studies of MSox speciation are needed to better understand ROS mediated oxidation linked processes in AD.
Mouse models offer an excellent opportunity to study aging and AD-disease pathology linked aspects of MS
ox speciation. 5XFAD mice on a C57BL/6 background co-express five familial AD (FAD) mutations (amyloid precursor protein and presenilin 1 genes) that cause accumulation of amyloidogenic Aβ
42 which spreads to cover most of the brain in parallel with astrocytosis and microgliosis by 4 months of age [
35]. The mice later develop neuron loss around 9 months of age at the cortex and subiculum. Memory and cognitive impairments are observed in the mice as early as 4 months of age, which correlates with hippocampal synaptic dysfunction and age-dependent behavioral deficits. Metabolomics studies of this model revealed dysregulation in brain-based glucose and lipid metabolism prior to AD pathogenesis [
36]. Proteome studies in the brain revealed temporal and sex linked variation in proteins related to neuroinflammation [
37]. This model is ideal for our initial exploration of MS
ox speciation.
We examined proteome wide levels of MSox in the 5XFAD mouse hippocampus at 3, 6 ,and 9 months for AD and C57BL/6 (wild type) mice, with replicates including a balanced design of males and females as shown in
Figure 1. This provides examination of the MS
ox variation in the AD model from early Aβ
42 deposition to full blown neuroinflammation [
37] and an examination of MS
ox variation in C57BL/6 from and “end of youth” stage (month 3) through late middle age (month 9) [
38]. Thus, this study is designed to:
Examine the early aging, sex, and disease dependent changes in MSox levels,
Identify peptide and protein targets specifically sensitive and resistant to oxidation of methionine,
Validate key changes with peptide based absolute quantification, and
Explore the stability of key MSox sites to handling and storage.
The results form a basis for a rigorous and reproducible MSox-omics for biological discovery of novel links between oxidation and disease biology to drive development of new therapeutic targets in contexts including neurodegeneration, cancer and beyond.
2. Results
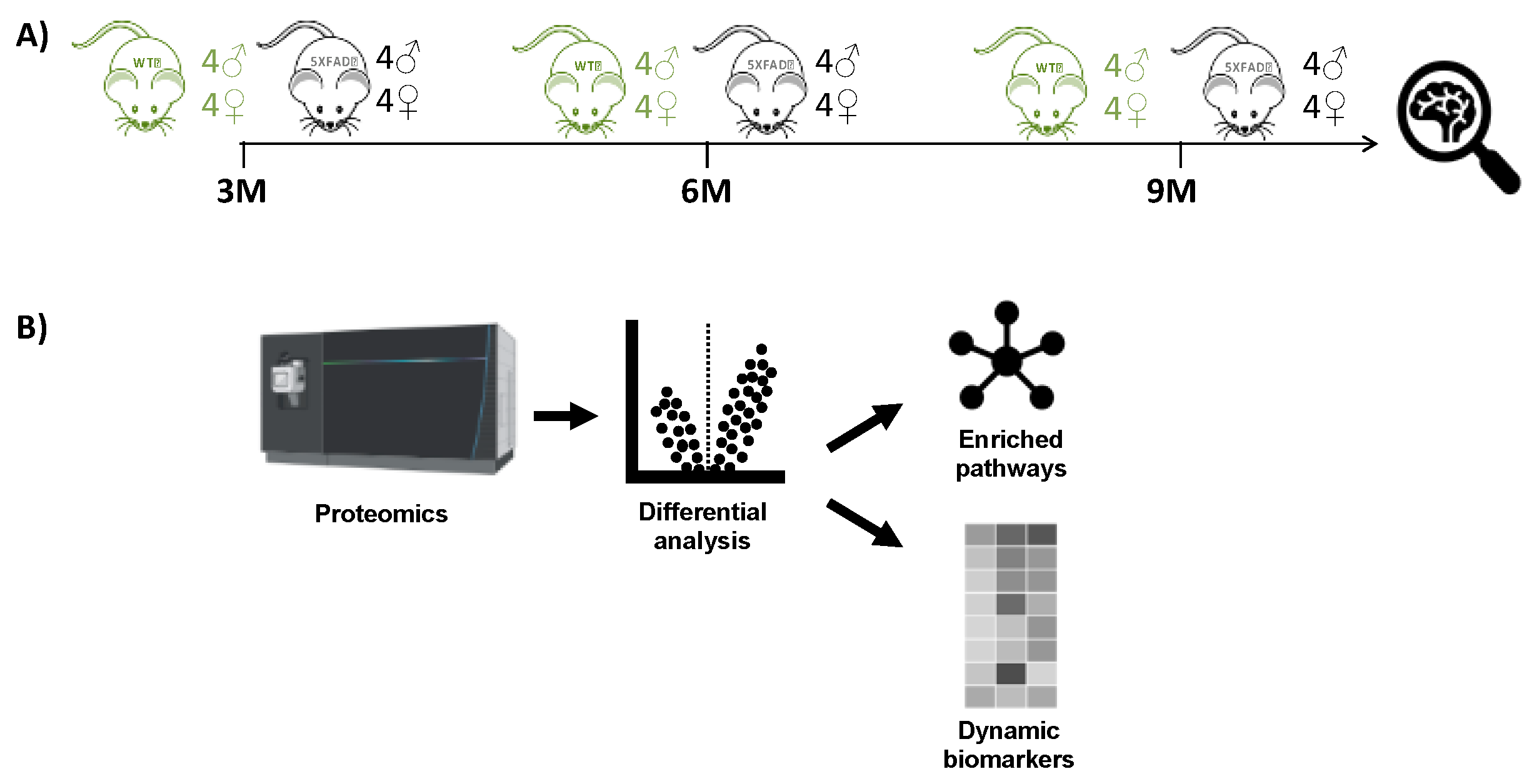
2.1. Experimental Design
Global MS
ox proteome profiling of mouse hippocampus was conducted across various time points representing AD hallmarks. The experimental design in
Figure 1 involved the collection of hippocampus tissue from 16 mice at each point and then processing sample immediately for comparisons at that month. At each time point, there were eight WT C57BL/6 mice and eight 5XFAD mice, comprising four male and four female biological replicates. Label-free LC-MS analysis was performed on each set of 16 samples without fractionation.
Statistical analysis in the parent study (
Figure 1a) focused on WT versus 5XFAD comparisons, followed by sex-linked analysis at each of the three individual time points. Although processing all samples from a time point shortly after sacrifice in batches offered certain advantages, such as efficiency and sample stability, it posed challenges in comparing individual groups
across time points due to difficulties in absolute standardization of these different batches over time. Thus, in comparisons across time points, we focused on peptide and protein identifications similarities and differences at each time point. With that caveat, we filtered peptides from the available data that featured methionine oxidation as a variable modification (
Table S1). We the used this data to characterize the MS
ox-ome, identify differentially expressed MS
ox-proteins, and identify pathways possibly enriched in these signatures compared to the background mouse brain protein expression patterns.
2.2. Age-Dependent Increase of Global MSox
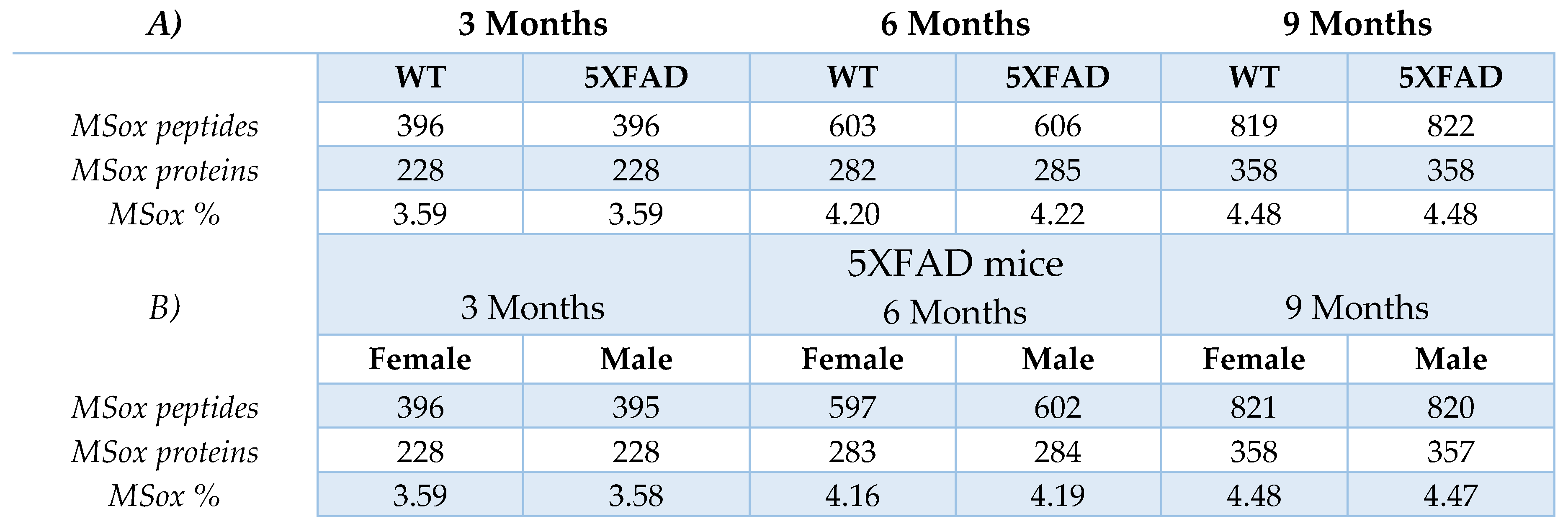
To characterize the MSox-ome in our cohort we used Peaks v10.0, this software takes raw LC-MS/MS files and provides peptide sequencing, protein identification, and quantification information. To extract specific MSox data from our raw files, we included methionine oxidation as a variable modification as a PEAKS search parameter. We found 396 total MSox peptides in the 3-month mice of both WT and 5XFAD, 603 and 606 MSox peptides in 6-month WT and 5XFAD mice, and 819 and 822 MSox peptides in 9-month WT and 5XFAD mice, reaching a total hippocampal MSox coverage of 1095 peptides (
Table 1,
Table S1). Differences in the amount of MSox proteins identified in 5XFAD compared to WT are negligible. Overall, the percentage of MSox peptides as a function of the whole proteome increased over time from 3.59% to 4.48% (
Table 1), showing that age and not genetic background dominates global MSox changes in these mice.
2.3. Pathway Analysis Reveal Distinct Age-Dependent Signatures
To further characterize if oxidation targets different protein based methionine residues over time, we analysed the overlap of each time-specific MSox-ome. The Venn diagram highlights the temporal dynamics of the MSox-ome in 5XFAD mice (
Figure 2). Roughly a third of all MSox proteins in this study are detected across all timepoints (
Figure 2). Early timepoints (3- and 6-Months) account for the ~80% of the MSox-ome (
Figure 2). Morever, 6%, 13%, and 20% of the MSox-ome are time-specific expression signatures for 3, 6, and 9 months respectively (
Figure 2). Altogether the data indicates that the MSox-ome can be divided into two groups: constant oxidation targets (~33%) and dynamic targets (~66%).
To further understand whether these MS
ox-dynamics are associated with distinct biological processes, we performed separate enrichment pathway analysis using Reactome and cellular component perspectives to classify the MSox proteins detected at 3-, 6-, or 9-month time points. Indeed, we found different pathways to be enriched at different times and found those signatures to be distinct from whole proteome signatures (
Table 2).
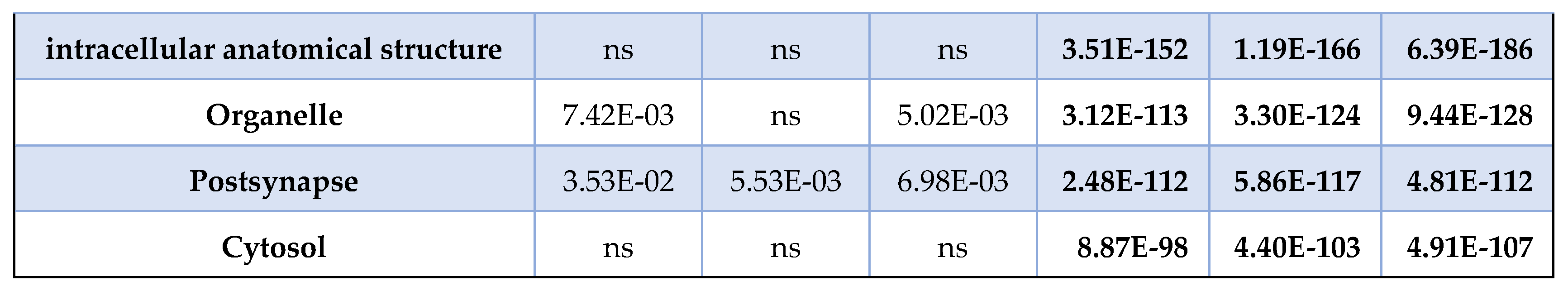
For example, at 3 months no significant MSox Reactome signatures were observed (at E10-3 or more). However, by six months the Reactome pathway analysis revealed several significant enriched signatures including glycolytic metabolism, glucose metabolism, and gluconeogenesis. Further L1CAM interactions, small molecule transport and chemical synapse transmission are seen to be significant at 6-months. At 9-months the MSox Reactome signatures also includes Innate Immune Systems and Signal Transduction as significant, while the glucose related metabolic themes are even more significant. For cellular component enrichments, L1 recycling and neurotransmitter release pathways are significant for MSox annotated proteins at 6 -months along with Glycolysis. Altogether, this data highlights that MSox speciation accumulated in different proteins across coherent pathways across time.
Comparing the MS
ox-ome with the whole brain proteome enriched pathways, we found that the MS
ox enriched pathways are not an artifact of the proteome coverage. Indeed, many pathways in bold show a significant enrichment exclusively in the MS
ox-ome (
Table 2). The proteome showed significance in all cellular components, this was expected as our MS approach is a reliable approach to generate global proteome coverage. However, the MS
ox-ome showed a distinct cellular coverage, notably the lack of coverage in: cytoplasm, cytosol, organelle (
Table 2). On the other hand, the MS
ox-ome retained coverage of: axon, myelin sheath, mitochondrion (data not shown). Altogether, the data highlights the interest of characterizing the MS
ox-ome as it provides biological insights beyond what the whole proteome provides.
2.3. High Abundance Proteins Are Susceptible to MSox Accumulation
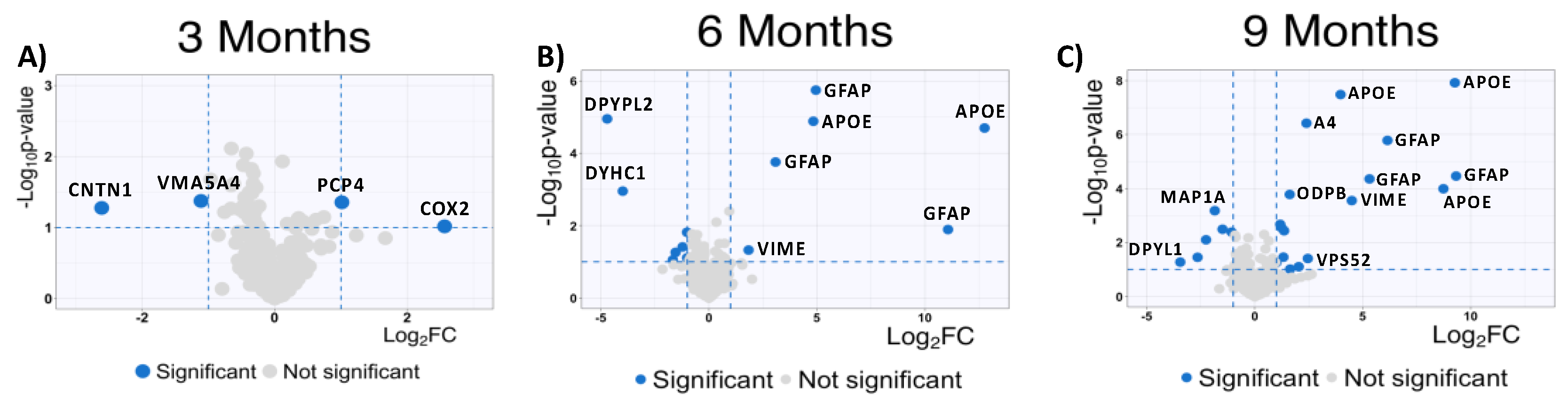
To complement our analysis of the MSox-ome, we computed the fold-changes of specific MSox peptides in WT mice compared to 5XFAD mice, these detailed quantitative comparisons at a specific time point are enabled by the experimental design of the parent study. We found some MSox peptides being differentially expressed in all timepoints (
Figure 3a). Interestingly, starting at 6 Months, the top up-regulated peptides annotate to proteins known to be involved in neuroinflammation: GFAP, APOE, and VIME (
Figure 3 b-c).
At 9 Months, MSox peptides from GFAP (AEM[M]ELNDR, EQLAQQQVHVE[M]DVAKPDLTAALR and TQYEAVATSN[M]QETEEWYR), APOE (LGAD[M]EDLR, NEVT[M]LGSTEEIR and GWFEPIVED[M]HR), and VIME (E[M]EENFALEAANYQDTIGR) are significantly up regulated in 5XFAD (
Figure 3). This is not surprising as these same peptides were found to be the most dysregulated in our whole proteome analysis [
37]. However, these results are associated with a pattern of MSox targeting highly expressed proteins (
Figure 3).
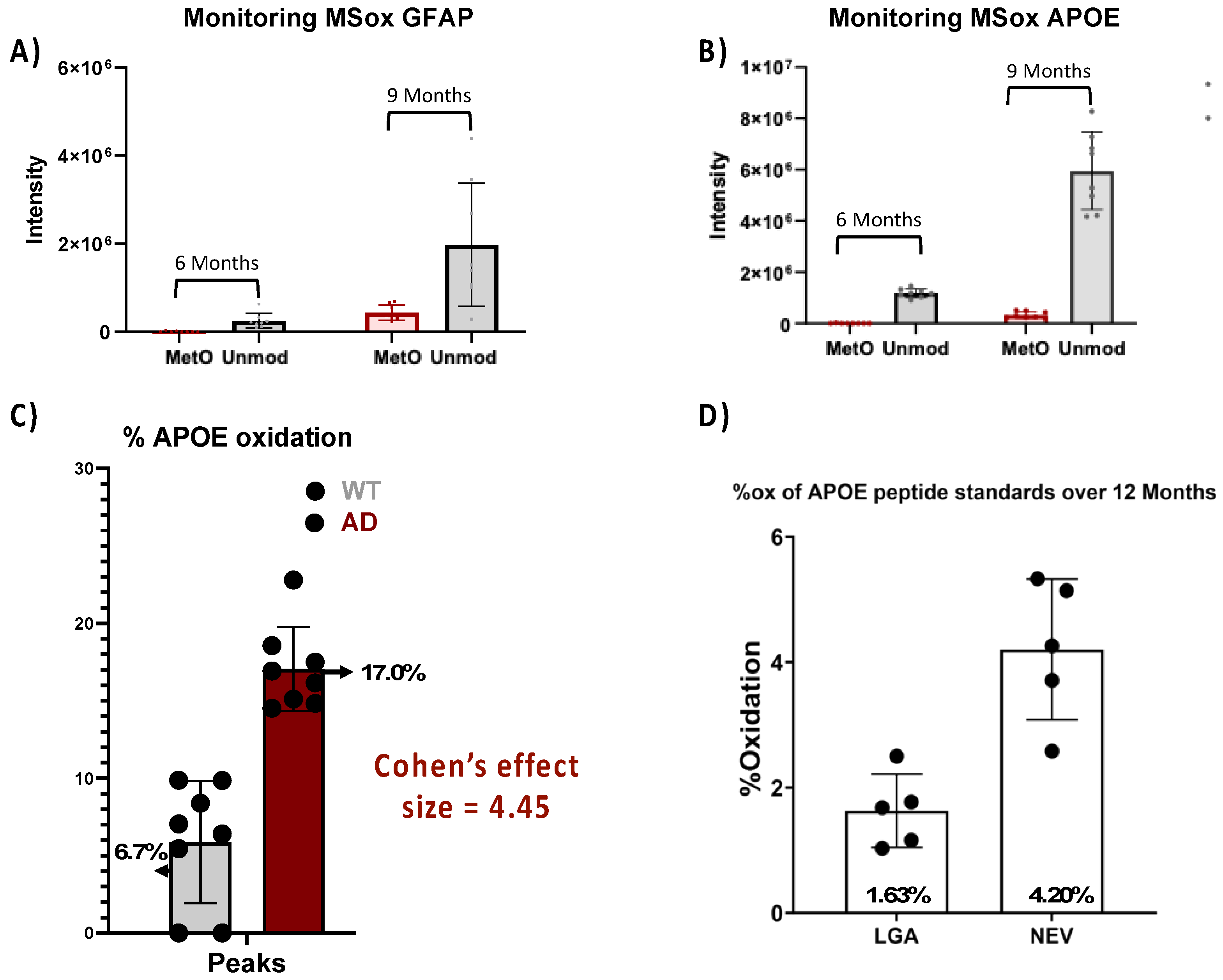
To further explore the translational potential of ox-APOE and ox-GFAP peptides as biomarkers, we need to clarify whether the differential expression of GFAP and APOE MSox peptides is an artifact of the differential total protein expression (
Figure 4). To do so, we looked at the Area Under the Curve (AUC) summing APOE peptides LGAD[M]EDLR, NEVT[M]LGSTEEIR and GWFEPIVED[M]HR GFAP peptides AEM[M]ELNDR, EQLAQQQVHVE[M]DVAKPDLTAALR and TQYEAVATSN[M]QETEEWYR, and their total unoxidized peptide AUC values. No MSox APOE nor MSox GFAP were detected at 3 Months (data not shown). At 6 months, levels close to the lower limit of detection were registered for both MSox APOE (NEVT[M]LGSTEEIR) and MSox GFAP (AEM[M]ELNDR and EQLAQQQVHVE[M]DVAKPDLTAALR) in one sample (
Figure 4a-b). At 9 months, there is an increase in the AUC of both unmodified GFAP & APOE by ~14% and~100%, and MSox GFAP & APOE by ~73% and 51%, respectively (
Figure 4a-b). To understand if these increase in MSox levels reflected changes in stoichiometry we chose to focus our analysis on the APOE protein at 9 Months (
Figure 4c-d). Therefore, we compared the average MSox-APOE% between WT(n=8) and 5XFAD (n=8) mice for the two APOE peptides above. For WT mice an average of 6.7% APOE oxidation was seen while for 5XFAD mice an average of 17.1% oxidation for the two peptides was seen. These results reflect a 4.45 Cohen’s effect size among the two groups (
Figure 4c). This data confirms a significant difference in MSox APOE stoichiometry between WT and 5XFAD, thus MSox speciation targets APOE in this model. To further explore the ability to monitor MSox APOE peptides as biomarkers, we tested whether targeted MS approaches would be adequate to monitor these peptides. The scientific community resistance towards MSox being a biologically relevant PTM hinges in part on the fact that MSox can also occur potentially occur or be removed spontaneously. However, the data here shows very reproducible MSox measurements, even on samples analyzed at separate times. Further, to assess whether Parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) would be adequate to monitor MSox APOE changes, we decided to track the spontaneous oxidation levels of unmodified APOE peptide standards (LGADMEDLR and NEVHTMLGQSTEEIR) over a 12-month period.
We developed a PRM quantitative assay specific for LGADMEDLR (
Table S2) and NEVHTMLGQSTEEIR(
Table S2) and their MSox forms LGAD[M]EDLR (
Table S2) and NEVHT[M]LGQSTEEIR (
Table S2), for which we achieved linearity (R
2 of >0.996) in all standard curves demonstrating the rigor and reproducibility of this assay. Once linearity was established, we measured the oxidation in LGADMEDLR and NEVHTMLGQSTEEIR standards over time, we found average oxidation levels of 1.63% and 4.20%, respectively with modest variability across the 5 samplings (
Figure 4d,
Table S2). Both levels of oxidation register lower than the MSox levels in both WT and 5XFAD mice (
Figure 4c), indicating that PRM is a reliable method to monitor MSox APOE peptides.
3. Discussion
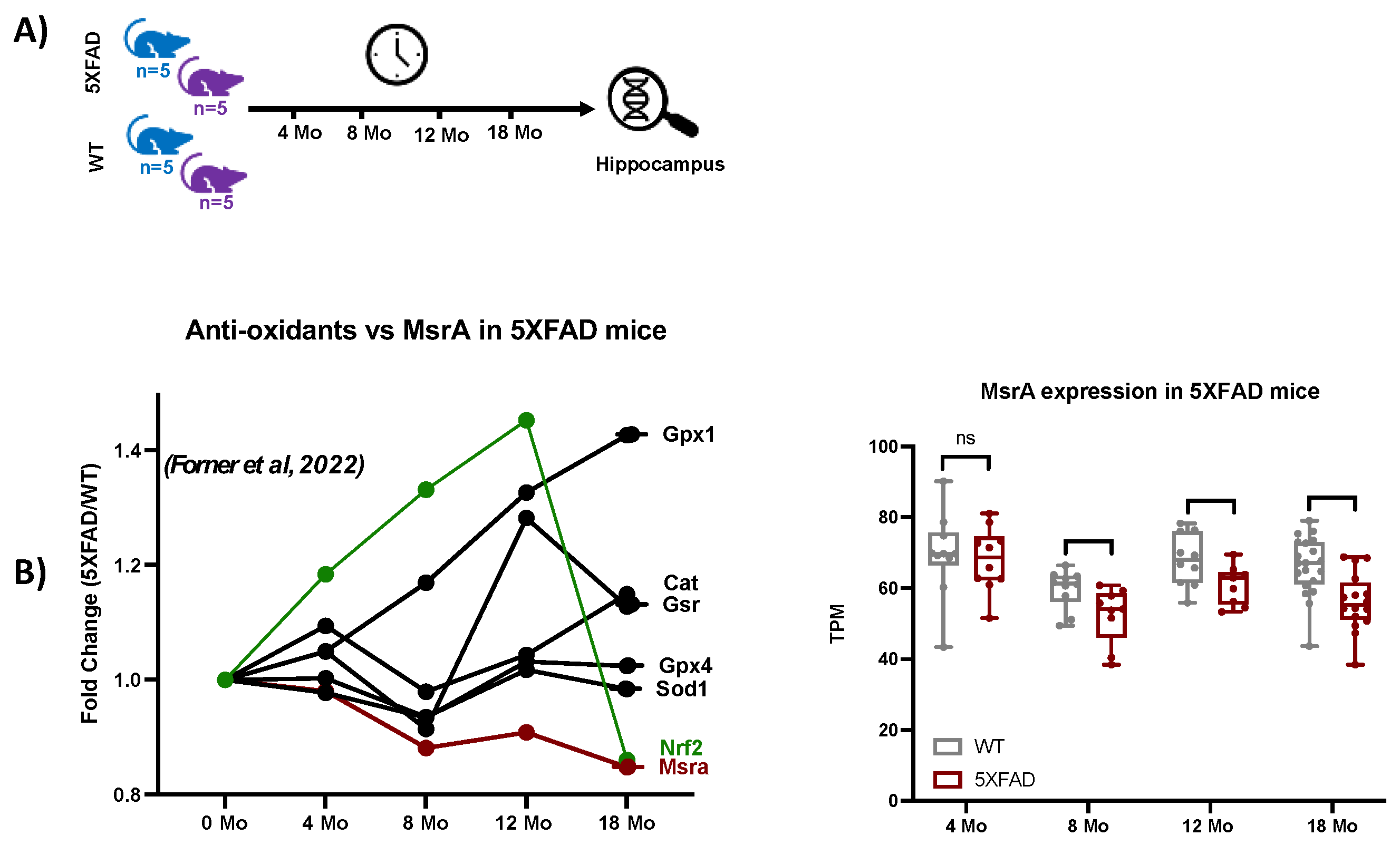
This study analyzed the global MSox proteome of mouse hippocampus across various time points representative of Alzheimer's disease (AD) hallmarks. To provide context for the functional genomics background of the 5XFAD model, we extracted selected gene expression data from a study like that of the proteomics study, with slightly different time points as seen in
Figure 5a, where the first time point of 4 -months is near the 3-months point in proteomics and data out to 18-months is seen. Examination of the data showed strong evidence of ROS related activation in the 5XFAD model vs. WT as Nrf2, a classic transcription factor mediating gene expression of oxidation defense is upregulated through 12 months (
Figure 5b). Attendant oxidation defense proteins like glutathione peroxidases, catalase, and superoxide dismutase also show increased gene expression confirming the signaling landscape (
Figure 5b). On the other hand, MsrA levels are trending lower with age and disease. These data drove our interest in specifically measuring MS
ox speciation across the same time frames.
We identified a total of 1095 M
Sox peptides in WT and 5XFAD mouse hippocampus, however not all M
Sox peptides were identified across all time points, indeed by comparing MS
ox-omes we found an accumulation of M
Sox peptides with progression of time: 396, 606, 822 at 3-, 6-,and 9-moths respectively (
Figure 2). We found that only roughly a third of all MSox annotated proteins are detected at all three time points (
Figure 2), which highlights the temporal variation of MS
ox targets in mouse brain. We cannot without further study directly understand whether temporal effects are driven by accumulating MS
ox vs potentially decreased repair or how local speciation influences observed MSox. However, pathway analysis at 3-, 6-, and 9-month intervals revealed transitions between glycolytic metabolism and small molecule transport and chemical synapse transmission between the 6- and 9-month time points. Comparison with the whole proteome confirmed that MSox-enriched pathways were not mere artifacts, highlighting their specific biological relevance. Furthermore, cellular component analysis revealed unique coverage patterns of the MS
ox-ome, underscoring its importance for providing insights beyond conventional proteomic analyses.
With a goal to identify M
Sox candidate biomarkers we compared M
Sox levels for selected peptides in WT and 5XFAD mice, which revealed significant upregulation of selected peptides for GFAP, APOE, and VIME in 5XFAD mice starting at 6 months. This aligns with previous findings identifying these proteins as highly dysregulated in protein expression in 5XFAD. More detailed analysis of M
Sox APOE showed a significant difference in M
Sox APOE stoichiometry observed in 9-month mice for 5XFAD vs. WT. Parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) proved reliable for monitoring M
Sox APOE peptides, as evidenced by low and relatively constant oxidation levels in peptide standards compared to mouse models (
Figure 4c-d,
Table S2). Our study underscores the potential clinical relevance of M
Sox peptides in AD pathology and highlights the potential of PRM in clinical biomarker discovery for AD. Future research may focus on exploring the functional consequences of M
Sox alterations and further validating PRM as a diagnostic tool for AD.
In a broader context, our findings contribute to a growing body of literature on the role of senescence and protein oxidation in AD and connect this literature to specific MSox speciation. We provide a benchmark for MSox-ome information in mice across time, which includes preferentially targeted MSox proteins and their associated biological pathways. Future research directions may involve investigating the functional implications of the identified MSox-proteins (e.g. MSox APOE), exploring potential therapeutic targets within enriched pathways, and further elucidating the interplay between senescence and protein oxidation in AD pathogenesis. Knockout studies of Msr mouse models may help identify specifically regulated MSox sites, while longitudinal studies in human cohorts may provide insights into the development of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for AD.
4. Materials and Methods
To characterize the temporal changes of MSox expression levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, we mined our previously published global proteome profiling data from 5XFAD [
37].
4.1. Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis
Raw LC-MS/MS data was processed using Peaks v10.0 Software (Bioinformatics Solutions) as described [40, 41]. Peptide identification was performed within Peaks using UNIPROT database (UNIPROT_MOUSE_091219, # entries= 17,026). PEAKS search parameters were set to determine the following: mass error tolerance for precursor ions of 10 ppm, mass tolerance for fragment ions of 0.6 Da, trypsin enzyme specificity and included carbamidomethylation as a fixed variation plus methionine oxidation as a variable modification, and one missed cleavage. Label-free peptide identification was performed using default target decoy approach, which included PEAKS peptide score (−10logP) ≥15 and FDR threshold of 1%. Individual peptide abundance was determined by area under the curve. All raw LC-MS/MS files and peptide abundance matrixes used in this article are publicly available at ProteomeXchange [
42] and Consortium via the PRIDE [
43] partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD030161 and can be found at
https://doi.org/10.6019/PXD30161.
4.2. PRM
4.2.1. Sample Preparation for PRM Assay
LGADMEDLR and NEVHTMLGQSTEEIR and their MSox forms LGAD[M]EDLR and NEVHT[M]LGQSTEEIR. were synthesized (Thermo Fisher Scientific, AQUA Basic-grade, >95% purity) and used as the standard for stability and lineraty studies. Synthesized peptides were diluted in water to yield a final concentration of 1 pmol/μl for each standard peptide. Each standard was aliquoted and frozen at -80oC. Aliquots were thawed for analysis at 0 ,1 ,2 ,6 and 11 months. Dilutions were performed for each standard in 0.1% formic acid to yield a concentration of 50 fmoles/μl. Standard peptides were also diluted in 0.1% formic acid to yield concentrations of 0.1, 0.5, 1, 10, 25 ,50, and 100 fmoles/ μl for the linearity study.
4.2.2. Development and Analytical Validation Targeted MS Assays/Measurements
Both the stability and linearity study were analyzed by LC/MS using a Thermo Vanquish Ultra performance liquid chromatography system and an Orbitrap Exploris 480 mass spectrometer (Thermo). The platform was operated in the positive nano-LC mode using Easy Spray source The peptides were first desalted on a reversed-phase C18 trapping column (PepMap Neo Trap column Thermo) by washing with 0.1% formic acid at 10 μl/min for 4 min. Subsequent chromatographic separation was performed using a reverse-phase C18 column (PepMap Neo 75μm x 15 cm), and peptides were separated using a linear gradient of acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid from 1% to 5% in 1 min followed by another linear gradient from 5% to 30% over a period of 29 min at a flow rate of 0.30 μl/min. PRM experiment was employed to detect the standard peptides. The PRM approach was accomplished by specifying the parent mass of each peptide to be quantified for MS/MS fragmentation and then monitoring its fragment ions. AUC values were extracted for each peptide species using manual integration for stability and linearity analysis. The acquired data is processed and analyzed using Xcalibur 4.1.31.9 Quan Browser software (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Each peptide was confirmed by comparing its retention time to the synthesized peptide. The % of oxidation for each peptide standard was calculated by following calculation: ((MSox of standard/ MSox of standard + standard)*100). Linear regression was performed for standard curves using Excel.
4.3. Enrichment Pathway Analysis
A PANTHER Overrepresentation Test with Reactome pathways annotation (Fischer’s exact test and FDR correction FDR
p < 0.05) was performed on highly upregulated peptides in AD mice (5XFAD/WT Log2FC ≥ 4 and
p ≤ 0.1, unpaired
t test) [
44].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Table S1: MSox-ome datasets; Table S2: PRM stability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.B.T.P.L., D.S., M.A., M.K., M.R.C.; methodology, F.B.T.P.L., D.S., M.K., M.R.C.; validation, F.B.T.P.L. and D.S.; formal analysis, F.B.T.P.L., D.S. and M.L.; investigation, F.B.T.P.L., D.S and R.W.; resources, X.Q. and M.R.C.; data curation, F.B.T.P.L.; writing—original draft preparation, F.B.T.P.L. and M.R.C.; writing—review and editing, F.B.T.P.L., D.S., X.Q., M.A., M.K. and M.R.C.; visualization, F.B.T.P.L., D.S., M.L. and S.Y.; supervision, M.R.C.; project administration, M.R.C.; funding acquisition, M.R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institutes of General Medical Sciences, United States under R01 GM117208 (M. R. C.) and R01 GM117208-03S1 (M. R. C.), by the Office of the Director, National Institutes of Health, United States under S10 OD026882-01 (M.R.C.), S10 OD028614-01 (M.R.C.),and National Institute on Drug Abuse, United States under P30DA054557 (M.R.C.) in addition to the National Library of Medicine, United States under R01 LM12980 (M. K.). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Case Western Reserve University and performed according to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Sufficient procedures were employed to reduce the pain and discomfort of the mice during the experiments. The mice were mated, bred, and genotyped in the animal facility of Case Western Reserve University. All mice were maintained under a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle (light on at 6 AM and off at 6 PM). All mice used in this study were maintained on a C57BL/6J background. 5XFAD transgenic mice [Tg(APPSwFlLon,PSEN1∗M146L∗L286V)6799Vas, JAX Stock No: 34840] breeders were purchased from Jackson Laboratory.
Data Availability Statement
The mass spectrometry proteomics data relative to the original label free mass spectra have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange [
42] Consortium via the PRIDE [
43] partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD030161 and can be found at
https://doi.org/10.6019/PXD30161.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Levine RL, Moskovitz J, Stadtman ER. Oxidation of methionine in proteins: roles in antioxidant defense and cellular regulation. IUBMB Life. 2000;50(4-5):301-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtman ER, Van Remmen H, Richardson A, Wehr NB, Levine RL. Methionine oxidation and aging. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1703(2):135-40. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoneich, C. Redox processes of methionine relevant to beta-amyloid oxidation and Alzheimer's disease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2002;397(2):370-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shringarpure R, Davies KJ. Protein turnover by the proteasome in aging and disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;32(11):1084-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auten RL, Davis JM. Oxygen toxicity and reactive oxygen species: the devil is in the details. Pediatr Res. 2009;66(2):121-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu G, Chance MR. Hydroxyl radical-mediated modification of proteins as probes for structural proteomics. Chem Rev. 2007;107(8):3514-43. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen X, Guo C, Kong J. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(5):376-85. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnham KJ, Masters CL, Bush AI. Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(3):205-14. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies H, Jones DP. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(7):363-83. Epub 20200330. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taungjaruwinai WM, Bhawan J, Keady M, Thiele JJ. Differential expression of the antioxidant repair enzyme methionine sulfoxide reductase (MSRA and MSRB) in human skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009;31(5):427-31. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriani FM, Kress MR, Fagundes de Gouvea P, Malavazi I, Savoldi M, Gallmetzer A, Strauss J, Goldman MH, Goldman GH. Functional characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans methionine sulfoxide reductases (msrA and msrB). Fungal Genet Biol. 2009;46(5):410-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocco-Machado N, Lai L, Kim G, He Y, Luczak ED, Anderson ME, Levine RL. Oxidative stress-induced autonomous activation of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II involves disulfide formation in the regulatory domain. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(11):102579. Epub 20221008. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luczak ED, Anderson ME. CaMKII oxidative activation and the pathogenesis of cardiac disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;73:112-6. Epub 20140213. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fremont S, Romet-Lemonne G, Houdusse A, Echard A. Emerging roles of MICAL family proteins - from actin oxidation to membrane trafficking during cytokinesis. J Cell Sci. 2017;130(9):1509-17. Epub 20170403. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon J, Terman JR. MICAL redox enzymes and actin remodeling: New links to classical tumorigenic and cancer pathways. Mol Cell Oncol. 2018;5(1):e1384881. Epub 20171106. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrieu C, Vergnes A, Loiseau L, Aussel L, Ezraty B. Characterisation of the periplasmic methionine sulfoxide reductase (MsrP) from Salmonella Typhimurium. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:506-12. Epub 20200801. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias DG, Cabeza MS, Echarren ML, Faral-Tello P, Iglesias AA, Robello C, Guerrero SA. On the functionality of a methionine sulfoxide reductase B from Trypanosoma cruzi. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;158:96-114. Epub 20200715. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha HN, Woo CH, Kim HY, Park SY. Methionine sulfoxide reductase B3 deficiency inhibits the development of diet-induced insulin resistance in mice. Redox Biol. 2021;38:101823. Epub 20201201. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das K, Garnica O, Flores J, Dhandayuthapani S. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA) modulates cells and protects against Mycoplasma genitalium induced cytotoxicity. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:323-35. Epub 20200325. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javitt G, Cao Z, Resnick E, Gabizon R, Bulleid NJ, Fass D. Structure and Electron-Transfer Pathway of the Human Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase MsrB3. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020;33(10):665-78. Epub 20200811. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang B, Adams Z, Moonah S, Shi H, Maupin-Furlow J, Moskovitz J. The Antioxidant Enzyme Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase A (MsrA) Interacts with Jab1/CSN5 and Regulates Its Function. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(5). Epub 20200524. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li H, Liang M, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Wu Q, Yang L. Rice Protein Exerts Endogenous Antioxidant Capacity via Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase and the Nrf2 Antioxidant System Independent of Age. J Med Food. 2020;23(6):565-74. Epub 20200218. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasreen M, Dhouib R, Hosmer J, Wijesinghe HGS, Fletcher A, Mahawar M, Essilfie AT, Blackall PJ, McEwan AG, Kappler U. Peptide Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase from Haemophilus influenzae Is Required for Protection against HOCl and Affects the Host Response to Infection. ACS Infect Dis. 2020;6(7):1928-39. Epub 20200622. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon AB, Kim G, Liu C, Wren JD, Georgescu C, Richardson A, Levine RL. Effects of transgenic methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA) expression on lifespan and age-dependent changes in metabolic function in mice. Redox Biol. 2016;10:251-6. Epub 20161025. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevion M, Berenshtein E, Stadtman ER. Human studies related to protein oxidation: protein carbonyl content as a marker of damage. Free Radic Res. 2000;33 Suppl:S99-108. [PubMed]
- Lee BC, Lee YK, Lee HJ, Stadtman ER, Lee KH, Chung N. Cloning and characterization of antioxidant enzyme methionine sulfoxide-S-reductase from Caenorhabditis elegans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005;434(2):275-81. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine RL, Wehr N, Williams JA, Stadtman ER, Shacter E. Determination of carbonyl groups in oxidized proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 2000;99:15-24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz J, Poston JM, Berlett BS, Nosworthy NJ, Szczepanowski R, Stadtman ER. Identification and characterization of a putative active site for peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase (MsrA) and its substrate stereospecificity. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(19):14167-72. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtman ER, Levine RL. Protein oxidation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;899:191-208. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gella A, Durany N. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. Cell Adh Migr. 2009;3(1):88-93. Epub 20090113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadarajan S, Yatin S, Kanski J, Jahanshahi F, Butterfield DA. Methionine residue 35 is important in amyloid beta-peptide-associated free radical oxidative stress. Brain Res Bull. 1999;50(2):133-41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoneich, C. Methionine oxidation by reactive oxygen species: reaction mechanisms and relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1703(2):111-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbita SP, Aksenov MY, Lovell MA, Markesbery WR. Decrease in peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase in Alzheimer's disease brain. J Neurochem. 1999;73(4):1660-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang XJ, Song L, Deng XJ, Tang Y, Min Z, Luo B, Wen QX, Li KY, Chen J, Ma YL, Zhu BL, Yan Z, Chen GJ. Mitochondrial methionine sulfoxide reductase B2 links oxidative stress to Alzheimer's disease-like pathology. Exp Neurol. 2019;318:145-56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oblak AL, Lin PB, Kotredes KP, Pandey RS, Garceau D, Williams HM, Uyar A, O'Rourke R, O'Rourke S, Ingraham C, Bednarczyk D, Belanger M, Cope ZA, Little GJ, Williams SG, Ash C, Bleckert A, Ragan T, Logsdon BA, Mangravite LM, Sukoff Rizzo SJ, Territo PR, Carter GW, Howell GR, Sasner M, Lamb BT. Comprehensive Evaluation of the 5XFAD Mouse Model for Preclinical Testing Applications: A MODEL-AD Study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:713726. Epub 20210723. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurel B, Cansev M, Koc C, Ocalan B, Cakir A, Aydin S, Kahveci N, Ulus IH, Sahin B, Basar MK, Baykal AT. Proteomics Analysis of CA1 Region of the Hippocampus in Pre-, Progression and Pathological Stages in a Mouse Model of the Alzheimer's Disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2019;16(7):613-21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco Tavares Pereira Lopes F, Schlatzer D, Wang R, Li X, Feng E, Koyuturk M, Qi X, Chance MR. Temporal and sex-linked protein expression dynamics in a familial model of Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2022:100280. Epub 20220806. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson SJ, Andrews N, Ball D, Bellantuono I, Gray J, Hachoumi L, Holmes A, Latcham J, Petrie A, Potter P, Rice A, Ritchie A, Stewart M, Strepka C, Yeoman M, Chapman K. Does age matter? The impact of rodent age on study outcomes. Lab Anim. 2017;51(2):160-9. Epub 20160710. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, S. , Kawauchi, S., Balderrama-Gutierrez, G. et al. Systematic phenotyping and characterization of the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Data 8, 270 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Tran NH, Qiao R, Xin L, Chen X, Liu C, Zhang X, Shan B, Ghodsi A, Li M. Deep learning enables de novo peptide sequencing from data-independent-acquisition mass spectrometry. Nat Methods. 2019 Jan;16(1):63-66. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran NH, Zhang X, Xin L, Shan B, Li M. De novo peptide sequencing by deep learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 1;114(31):8247-8252. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch EW, Bandeira N, Sharma V, Perez-Riverol Y, Carver JJ, Kundu DJ, García-Seisdedos D, Jarnuczak AF, Hewapathirana S, Pullman BS, Wertz J, Sun Z, Kawano S, Okuda S, Watanabe Y, Hermjakob H, MacLean B, MacCoss MJ, Zhu Y, Ishihama Y, Vizcaíno JA. The ProteomeXchange consortium in 2020: enabling 'big data' approaches in proteomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 8;48(D1):D1145-D1152. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol Y, Csordas A, Bai J, Bernal-Llinares M, Hewapathirana S, Kundu DJ, Inuganti A, Griss J, Mayer G, Eisenacher M, Pérez E, Uszkoreit J, Pfeuffer J, Sachsenberg T, Yilmaz S, Tiwary S, Cox J, Audain E, Walzer M, Jarnuczak AF, Ternent T, Brazma A, Vizcaíno JA. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 8;47(D1):D442-D450. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas PD, Campbell MJ, Kejariwal A, Mi H, Karlak B, Daverman R, Diemer K, Muruganujan A, Narechania A. PANTHER: a library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res. 2003 Sep;13(9):2129-41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).