Submitted:
29 April 2024
Posted:
30 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
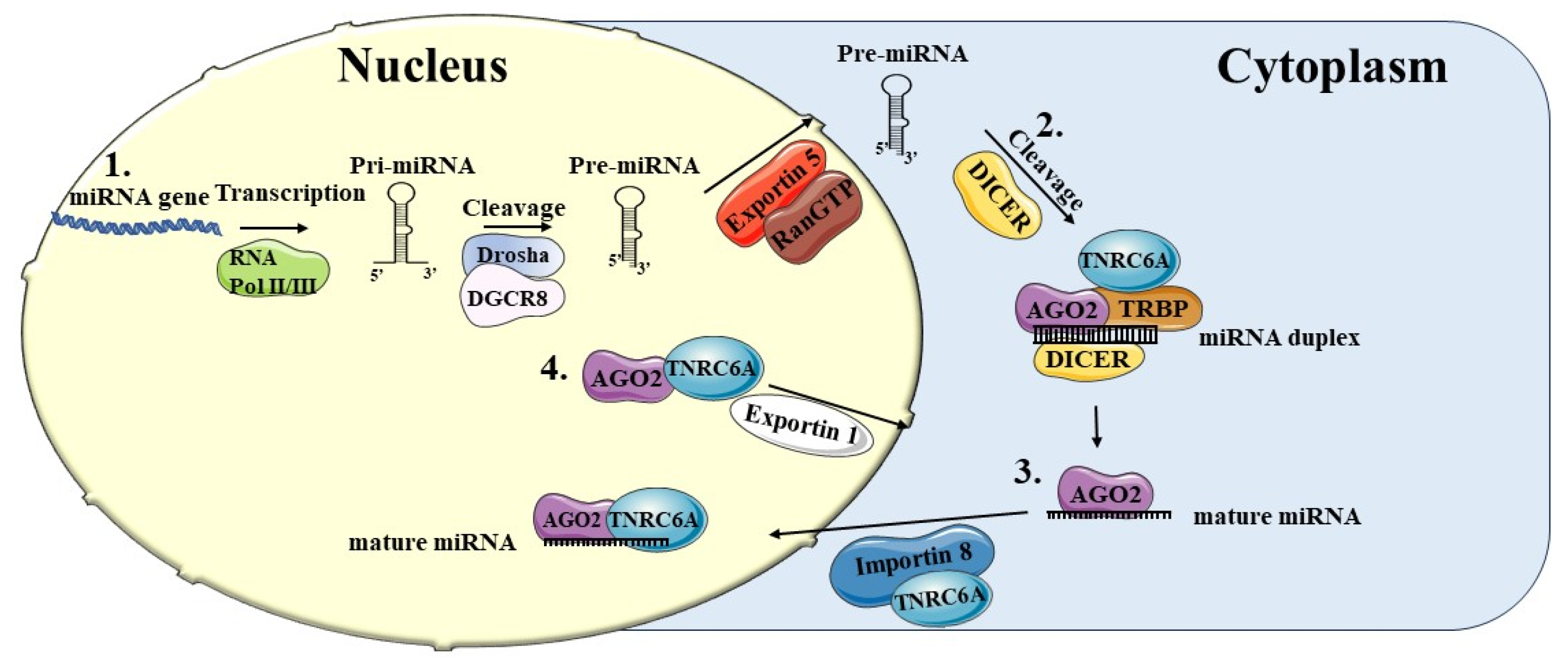
2. Biogenesis of MicroRNAs
3. Evidence of miRNAs in the Nucleus
4. Functions of miRNAs in the Nucleus
5.1. Transcriptional Activation
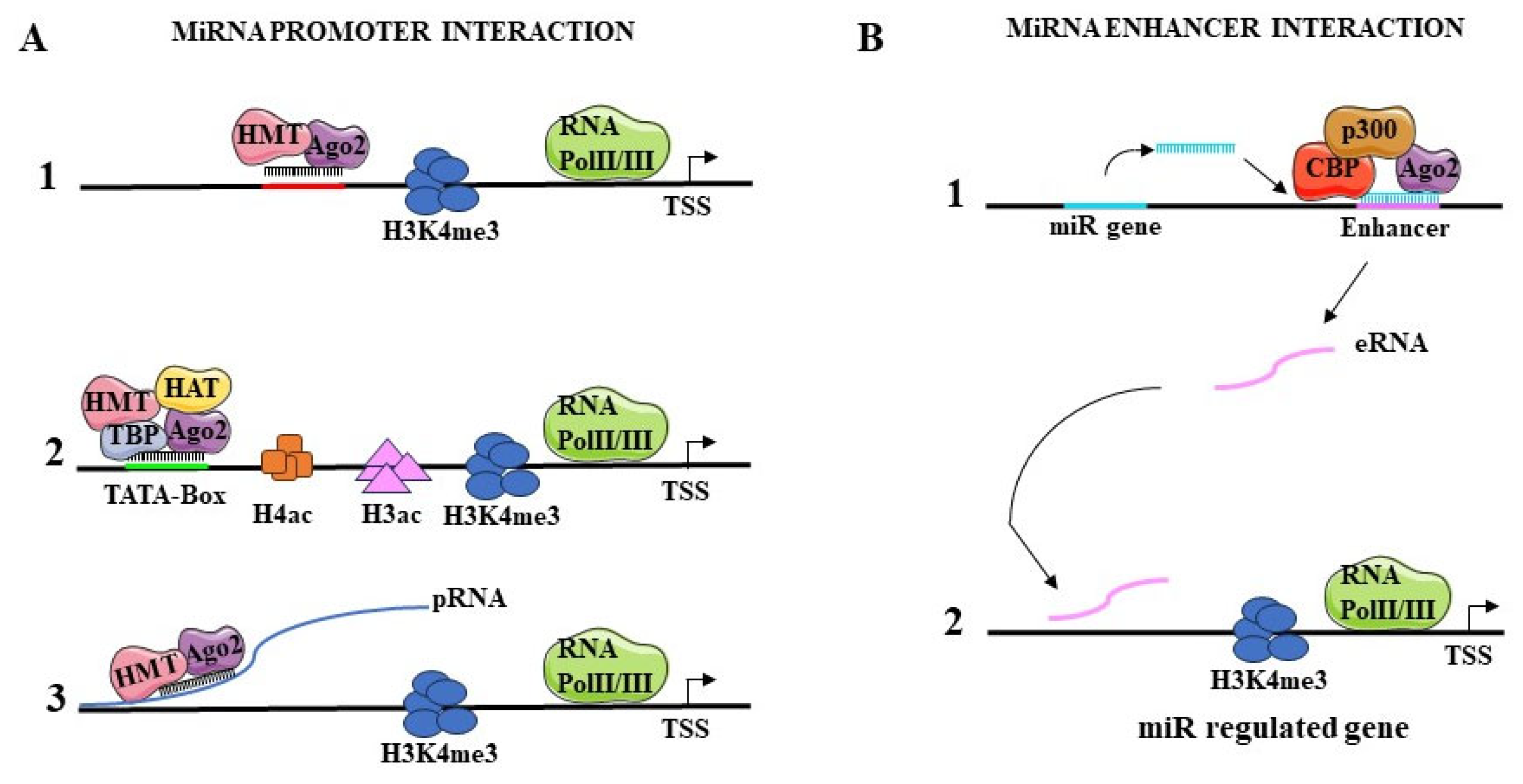
5.1.1. Interaction with Promoters
5.1.2. Interaction with Enhancers
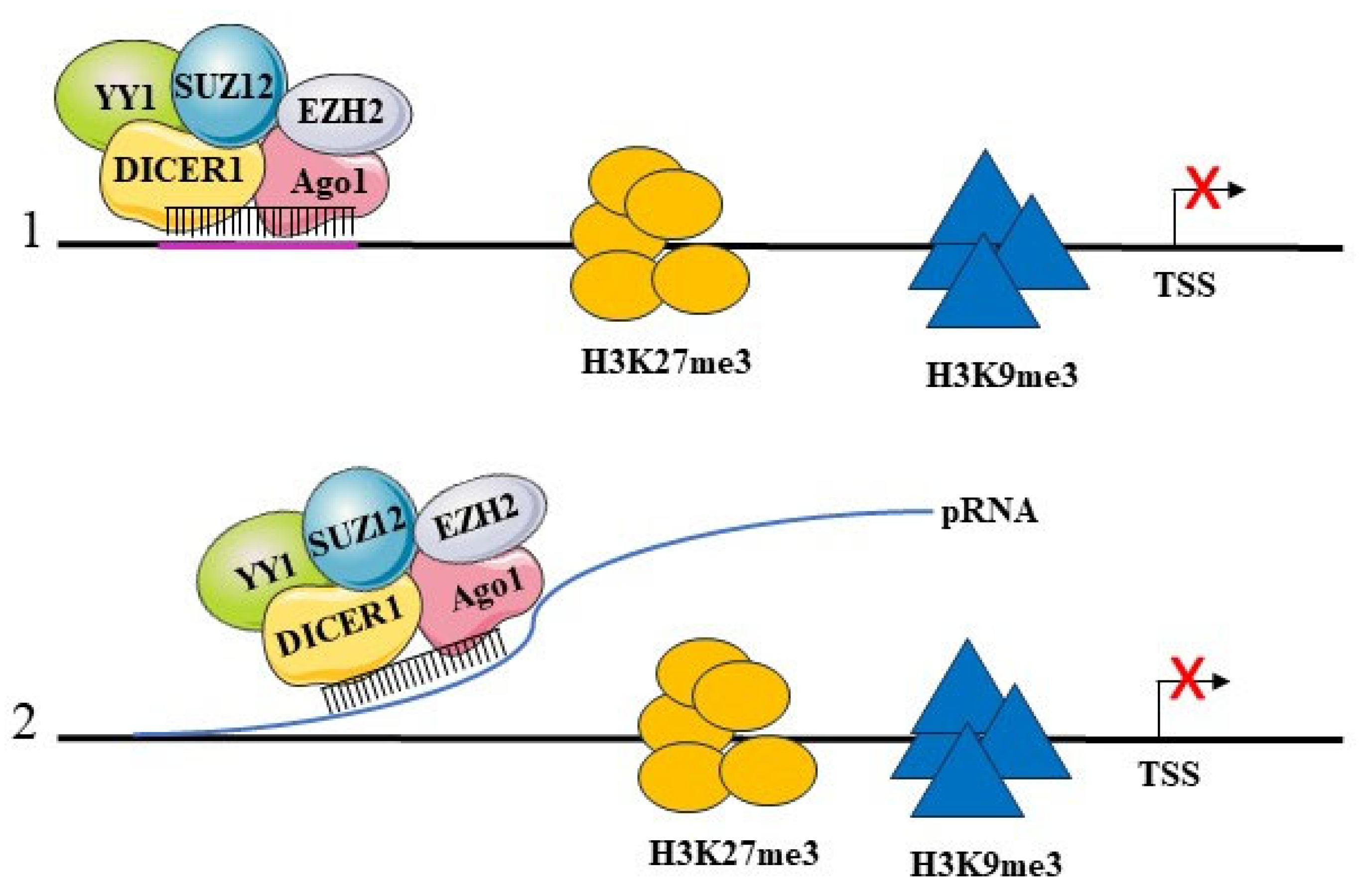
5.2. Transcriptional Repression
6. Nuclear miRNAs in Hematopoiesis
7. Non Transcriptional Activities of Nuclear miRNAs
8. Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, C.D. , Fried, H.M; Perkins, D.O. Nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of neural stem cell microRNAs. RNA 2011, 17, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavast, C. , Erkeland, S. The non-canonical aspects of MicroRNAs: many roads to gene regulation. Cells, 2019; 8, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. , Ahn, C., Han, J., Choi, H., Kim, J., Yim, J., Lee, J., Provost, P., Rådmark, O., Kim, S. and Kim, V.N. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature, 2003; 425, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partin, A. C. Zhang, K. Jeong, B. C. Herrell, E. Li, S. Chiu, W. et al Cryo-EM structures of human Drosha and DGCR8 in complex with primary MicroRNA. Mol Cell 2020, 78, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, G.M. , Shivashankar V., Ma E.J., Baryza J.L., Nutiu R. Functional Atlas of Primary miRNA Maturation by the Microprocessor. Mol Cell 2020, 80, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, A.D.; Jaskiewicz, L.; Zhang, H.; Laine, S.; Sack, R.; Gatignol, A.; Filipowicz, W. TRBP, a regulator of cellular PKR and HIV-1 virus expression, interacts with Dicer and functions in RNA silencing. EMBO Rep 2005, 6, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T; He, Y. ; Wang, T.; Yu, J.; Ma, X.; Zhou, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Li, L.; Peng, H.; Li, S. et al.; Discovery of a Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor Disrupting TRBP-Dicer Interaction against Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the Modulation of microRNA Biogenesis. J Med Chem 2022, 65, 11010–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Qin, Y.; Macara, I.G. and Cullen, B.R. Exportin-5 mediates the nuclear export of pre-microRNAs and short hairpin RNAs. Gene Dev 2003, 17, 3011–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chendrimada, T.P.; Gregory, R.I.; Kumaraswamy, E.; Norman, J.; Cooch, N.; Nishikura, K.; Shiekhattar, R. TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature 2005, 436, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, E.; Güttinger, S.; Calado, A.; Dahlberg, J.E.; Kutay, U. Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science 2004, 303, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, J.; Meister, G. The Argonaute protein family. Genome Biol 2008, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, A. L.; Enguita, F. J. A structural view of miRNA biogenesis and function. Non coding RNA 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H; Lei, C. ; He, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, D. and Tao, Y.. Nuclear functions of mammalian microRNAs in gene regulation, immunity and cancer. Mol Cancer 2018, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, K.T. , Li, L., Chu, Y., Janowski, B.A. and Corey, D.R. RNAi factors are present and active in human cell nuclei. Cell Rep 2014, 6, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, R.; Hicks, J.A.; Li, L.; Gagnon, K.T.; Sridhara, V.; Lemoff, A.; Mirzaei, H.; and Corey, D.R. Stable association of RNAi machinery is conserved between the cytoplasm and nucleus of human cells. RNA 2016, 22, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rocca. G.; Cavalieri. V. Roles of the Core Components of the Mammalian miRISC in Chromatin Biology. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinmann, L. , Höck, J., Ivacevic, T., Ohrt, T., Mutze, J., Schwille, P., Kremmer, E., Benes, V., Urlaub, H.; and Meister, G. Importin 8 is a gene silencing factor that targets argonaute proteins to distinct mRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 21. Shuaib M, Parsi KM, Thimma M, Adroub SA, Kawaji H, Seridi L, Ghosheh Y, Fort A, Fallatah B, Ravasi T, et al. Nuclear AGO1 Regulates Gene Expression by Affecting Chromatin Architecture in Human Cells. Cell Systems. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.Y. and Zen, K. Importin 8 regulates the transport of mature microRNAs into the cell nucleus. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 10270–10275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.S.; Uddin, M.H. and Mohammad, R.M. The nuclear export protein XPO1-from biology to targeted therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2021, 18, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, N.G.; Li, Y. XPO1-dependent nuclear export as a target for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol 2020, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Nishi, A.; Nagasawa, T. and Ui-Tei, K. Human TNRC6A is an argonaute-navigator protein for microRNA-mediated gene silencing in the nucleus. RNA, 2013; 17, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perconti, G.; Rubino, P.; Contino, F.; Bivona, S.; Bertolazzi, G.; Tumminello, M.; Feo, S.; Giallongo, A.; Coronnello, C. RIP-Chip analysis supports different roles for AGO2 and GW182 proteins in recruiting and processing microRNA targets. BMC Bioinformatics 2019, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Takahashi, T.; Suzawa, M.; Miyakawa, T.; Nagasawa, T.; Ming, Y.; Tanokura, M. and Ui-Tei, K. Control of the localization and function of a miRNA silencing component TNRC6A by argonaute protein. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, 9856–9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, J.A.; Li, L.; Matsui, M.; Chu, Y.; Volkov, O.; Johnson, K.C. and Corey, D.R. Human GW182 paralogs are the central organizers for RNA-Mediated control of transcription. Cell Rep 2017, 20, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanotto, D.; Lingeman, R.; Riggs, A.D. and Rossi, J.J. CRM1 medi- ates nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of mature microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009, 106, 21655–21659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, G.; Landthaler, M.; Patkaniowska, A.; Dorsett, Y.; Teng, G.; Tuschl, T. Human Argonaute2 mediates RNA cleavage targeted by miRNAs and siRNAs. Mol Cell 2004, 15, 185–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshinari Ishikawa, Ko Sugawara, Junwei Zhang, Takashi Funatsu, Kohki Okabe Direct observation of cytoskeleton-dependent trafficking of miRNA visualized by the introduction of pre-miRNA iScience 2024, 27, 108811. [CrossRef]
- Földes-Papp. Z.; König, K.; Studier, H.; Bückle, R.; Breunig, H.G.; Uchugonova, A. et al. Trafficking of mature miRNA-122 into the nucleus of live liver cells. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2009, 10, 569–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.Y.; Ma, L.M.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhou, H.; Shao, P. Deep sequencing of human nuclear and cytoplasmic small RNAs reveals an unexpectedly complex subcellular distribution of miRNAs and tRNA 3’ trailers. PloS One 2010, 5, e10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politz, J.C.R.; Hogan, E.M.; Pederson, T. MicroRNAs with a nucleolar location. RNA 2009, 15, 1705–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.J.; Ritchie, W.; Gao, D.; Lau, K.A.; Gonzalez, M.; Choudhary, A.; Taft, R.J.; Rasko, J.E.; Holst, J. Identification of nuclear-enriched miRNAs during mouse granulopoiesis. J Hematol Oncol 2014, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardo, G. Ciolfi, A. Vian, L. Starnes, L.M. Billi, M. Racanicchi, S. Maresca, C. Fazi, F. Travaglini, L. Noguera, N. Mancini, M. Nanni, M. Cimino, G. Lo-Coco F, Grignani F, Nervi C. Polycombs and microRNA-223 regulate human granulopoiesis by transcriptional control of target gene expression. Blood, 2012; 119, 4034–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.W.; Wentzel, E.A.; Mendell, J.T. Nucleotide motifs providing localization elements and methods of use. Geneva: World Intellectual Property Organization 2007, Patent No. WO 2007/149521 A2.
- Hwang, H.W.; Wentzel, E.A.; Mendell, J.T. A hexanucleotide element directs microRNA nuclear import. Science 2007, 315, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cheng, M.; Gu, B.; Wang, J.; Yan, S.; Xu, D. ; CircRNA_09505 aggravates inflammation and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis mice via miR-6089/ AKT1/NF-κB axis. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gao, G.; Yan, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, J. MiR-548a-3p regulates inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Biochem 2019, 120, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhan, X.; Silver, H. and Li, J. MicroRNA 195-5p targets foxo3 promoter region to regulate its expression in granulosa cells. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, S.; Dar, A.A.; Saini, S.; Yamamura, S.; Hirata, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Deng, G. MicroRNA-205-directed transcriptional activation of tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 5637–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Manojkumar, A.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C.; Yallapu, M.M. MicroRNA-205 in prostate cancer: Overview to clinical translation. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2022, 1877, 188809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, M.; Place, R.F.; Portnoy, V.; Wang, J.; Qi, Z.; Jia, Z.; et al. Upregulation of cyclin B1 by miRNA and its implications in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, 1695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, F.; Wu, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Luo, H.; Tao, L.; et al. Cellular microRNAs up-regulate transcription via interaction with promoter TATA-box motifs. RNA, 2014; 20, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, C.; He, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, D. , Tao Y. Nuclear functions of mammalian MicroRNAs in gene regulation, immunity and cancer. Mol Cancer 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano-Garibay, J.D.; Aquino-Jarquin, G. Transcriptional regulation mechanism mediated by miRNA-DNA*DNA triplex structure stabilized by Argonaute. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1839, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gagnon, K.T.; Shaikh, S.; Kuchimanchi, S.; Manoharan, M.; Corey, D.R.; Janowski, B.A. Promoter RNA links transcriptional regulation of inflammatory pathway genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41, 10086–10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellini L, Frezza V and Paronetto MP: Dissecting the transcrip- tional regulatory networks of promoter-associated noncoding RNAs in development and cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2020; 39, 51. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Zhan J, Zhao Y, Fan J, Yuan S, Yin Z, Dai B, Chen C, Wang DW. Identification of ncRNA-Mediated Functions of Nucleus-Localized miR-320 in Cardiomyocytes. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odame, E.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, S.; Dai, D.; Kyei, B.; Zhan, S.; Cao, J.; et al. Enhancer RNAs: transcriptional regulators and workmates of NamiRNAs in myogenesis. Cell Mol Biol Lett 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Liu, Y.; Liao, X.; Zhan, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W. Enhancer RNAs (eRNAs): new insights into gene transcription and disease treatment. J Cancer 2018, 9, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. MicroRNAs activate gene transcription epigenetically as an enhancer trigger. RNA Biol 2017, 14, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, F.; Zou, Q.; et al. Reactivation of tumour suppressor in breast cancer by enhancer switching through NamiRNA network. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, 8556–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardo, G.; Cimino, G.; Nervi, C. Epigenetic plasticity of chromatin in embryonic and hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells: therapeutic potential of cell reprogramming. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuettengruber, B.; Chourrout, D.; Vervoort, M.; Leblanc, B.; Cavalli, G. Genome regulation by polycomb and trithorax proteins. Cell 2007, 128, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardo, G.; Ciolfi, A.; Vian, L.; Starnes, L.M.; Billi, M.; Racanicchi, S.; Maresca, C, et al. Polycombs and microRNA-223 regulate human granulopoiesis by transcriptional control of target gene expression. Blood 2012, 119, 4034–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamed, M.; Herbig, U.; Ye, T.; Dejean, A.; Bischof, O. Senescence is an endogenous trigger for microRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Nat Cell Biol 2012, 14, 266–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, Y.; Ye, L.; Jiao, W.; Song, H.; Mei, H.; Li, D.; Yang, F. , Li, H., Huang, K., Tong, Q. miRNA-584-3p inhibits gastric cancer progression by repressing Yin Yang 1- facilitated MMP-14 expression. Scientific reports 2017, 7, 8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiyalagan, P.; Okabe, J.; Chang, L.; Su, Y.; Du, X.J.; El-Osta, A. The primary microRNA-208b interacts with Polycomb-group protein, Ezh2, to regulate gene expression in the heart. Nucleic Acids Res 2014, 42, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Saetrom, P.; Snøve, O. Jr.; Rossi, J.J. MicroRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16230–16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santovito, D.; Egea, V.; Bidzhekov, K.; Natarelli, L.; Mourão, A.; Blanchet, X.; et al. Noncanonical inhibition of caspase-3 by a nuclear microRNA confers endothelial protection by autophagy in atherosclerosis. Sci Transl Med 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Yao, H.; Li, C.; Pu, M.; Yao, X.; Yang, H.; Qi, X.; et al. A dual inhibition: microRNA-552 suppresses both transcription and translation of cytochrome P450 2E1. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mech 2016, 1859, 650–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, S.T.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Corey, D.R. Predicting potential miRNA target sites within gene promoters. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2009, 19, 3791–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, S.T.; Corey, D.R. Transcriptional gene silencing in mammalian cells by miRNA mimics that target gene promoters. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, 5682–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Z.; Li, L.; Lodish, H.F.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 2004, 303, 83–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikhat, S.; Yadavalli, A.D.; Prusty, A.; Narayan, P.K.; Palakodeti, D.; Murre, C.; Pongubala, J.M.R. A regulatory network of microRNAs confers lineage commitment during early developmental trajectories of B and T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118, e2104297118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.; Lovat, F.; Shih, A.J.; Ma, Y.; Pekarsky, Y.; DiCaro, F.; Crichton, L.; Sharma, E.; Yan, X.J.; Sun, D.; Song, T.; Zou, Y.R.; Will, B.; Croce, C.M.; Chiorazzi, N. Complete miRNA-15/16 loss in mice promotes hematopoietic progenitor expansion and a myeloid-biased hyperproliferative state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2308658120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, S.M.; Ahmadi Afshar, N.; Almasi, P. Insight into microRNAs' involvement in hematopoiesis: current standing point of findings. Stem Cell Res Ther 2023, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, R.; Li, Z.; Ming, Y.; Liu, L.; Peng, D.; Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Insights into Regulatory Factors in Megakaryocyte Development and Function: Basic Mechanisms and Potential Targets. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2022, 27, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, X. Nuclear microRNAs and their unconventional role in regulating non-coding RNAs. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 325–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Ghadami, E.; Dadkhah, T.; Akhavan-Niaki, H.J. PI3k/AKT signaling pathway: Erythropoiesis and beyond. Cell Physiol 2019, 234, 2373–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaway, M.; Chwat-Edelstein, T.; Vuong, B.Q. Regulatory Non-Coding RNAs Modulate Transcriptional Activation During B Cell Development. Front Genet 2021, 12, 678084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Rayabaram, J.; Ijee, S.; Bagchi, A.; Chaudhury, A.D.; Roy, D.; Chambayil, K.; Singh, J.; Nakamura, Y.; Velayudhan, S.R. Comprehensive Analysis of microRNAs in Human Adult Erythropoiesis. Cells 2021, 10, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, W.J.; Derudder, E. The miR-142 miRNAs: Shaping the naive immune system. Immunol Lett 2023, 261, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazi, F.; Rosa, A.; Fatica, A.; Gelmetti, V.; De Marchis, M.L.; Nervi, C.; Bozzoni, I. A minicircuitry comprised of microRNA-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and CEBPalpha regulates human granulopoiesis. Cell 2005, 123, 819–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vian, L.; Di Carlo, M.; Pelosi, E.; Fazi, F.; Santoro, S.; Cerio, A.M.; Boe, A.; Rotilio, V.; Billi, M.; Racanicchi, S.; Testa, U.; Grignani, F.; Nervi, C. Transcriptional fine-tuning of microRNA-223 levels directs lineage choice of human hemaopoietic progenitors. Cell Death Differ 2014, 21, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazi, F.; Racanicchi, S.; Zardo, G.; Starnes, L.M.; Mancini, M.; Travaglini, L.; Diverio, D.; Ammatuna, E.; Cimino, G.; Lo-Coco, F.; Grignani, F.; Nervi, C. Epigenetic silencing of the myelopoiesis regulator microRNA-223 by the AML1/ETO oncoprotein. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 457–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Connell, R. M.; Zhao, J. L.; Rao, D. S. MicroRNA function in myeloid biology. Blood 2011, 118, 2960–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, B.; Garzon, R. Clinical Applications of MicroRNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Mini-Review. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 679022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, L.; Zhu, D.; Hou, D.; Cao, T.; Gu, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K. Mouse miRNA-709 directly regulates miRNA-15a/16-1 biogenesis at the posttranscriptional level in the nucleus: evidence for a microRNA hierarchy system. Cell Res 2011, 22, 504–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (34) Wong, J.J.; Ritchie, W.; Gao, D.; Lau, K.A.; Gonzalez, M.; Choudhary, A.; Taft, R.J.; Rasko, J.E.; Holst, J. Identification of nuclear-enriched miRNAs during mouse granulopoiesis. J Hematol Oncol 2014, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørom, U.A.; Nielsen, F.C.; Lund, A.H. MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Mol Cell 2008, 30, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.H.; Shin, S.; Jung, S.R.; Kim, E.; Song, J.J.; Hohng, S. Human argonaute 2 has diverse reaction pathways on target RNAs. Mol Cell 2015, 59, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasanaro, P.; Greco, S.; Lorenzi, M.; Pescatori, M.; Brioschi, M.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Banfi, C.; et al. An integrated approach for experimental target identification of hypoxia-induced miR-210. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 35134–35143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turunen, T.A.; Roberts, T.C.; Laitinen, P.; Vaananen, M.A.; Korhonen, P.; Malm, T.; Yla-Herttuala, S.; Turunen, M.P. Changes in nuclear and cytoplasmic microRNA distribution in response to hypoxic stress Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10332; [CrossRef]
- Foekens, J. A.; Sieuwerts, A. M.; Smid, M.; Look, M. P.; de Weerd, V.; Boersma, A. W.; Klijn, J. G.; Wiemer, E. A.; Martens, J. W. Four miRNAs associated with aggressiveness og linfonode-negative, estrogen receptor positive human breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2008, 105, 13021–13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, C.; Buffa, F. M.; Colella, S.; Moore, J.; Sotiriou, C.; Sheldon, H.; Harris, A.L.; Gleadle, J.M. Ragoussis. Hsa-miR-210 is induced by hypoxia and is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. J Clin Cancer Res 2008, 14, 1340–13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, X.; Wei, Y.; Liang, H.; Yuan, M.; Jin, F.; Chen, X.; et al. Nuclear miR-122 directly regulates the biogenesis of cell survival oncomiR miR21 at the post-transcriptional level. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, 2012–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Liu, H.; Laiho, M. Small RNA expression and deep sequencing analyses of the nucleolus reveal the presence of nucleolus-associated microRNAs. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 441–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, B.L.; Woolnough, J.L.; Lefevre, G.M.; Saint Just Ribeiro, M.; Felsenfeld, G.; Giles, KE. Human argonaute 2 is tethered to ribosomal RNA through MicroRNA interactions. J Biol Chem 2016, 291, 17919–17928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böğürcü-Seidel, N.; Ritschel, N.; Acker, T.; Németh, A. Beyond ribosome biogenesis: noncoding nucleolar RNAs in physiology and tumor biology. Nucleus 2023, 14, 2274655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Gutierrez, P.; Ritland Politz, J.C.; Pederson, T. A. mRNA and cognate microRNAs localize in the nucleolus. Nucleus 2014, 5, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 94. Pu M, Chen J, Tao Z, Miao L, Qi X, Wang Y, Ren J. Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: coordination between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019; 76, 441–451. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




