1. Introduction
The Ionian Sea is a central sub-basin of the Mediterranean Sea, communicating with the Western Mediterranean (WMed) through the Channel of Sicily, with the Adriatic to the north, and with the Aegean and Levantine basins to the east. Due to its interconnectivity, it serves as a crossroads for various water masses and numerous studies emphasized the importance of the Ionian hydrography and dynamics, which play a key role in the seawater budgets [
1,
2], biogeochemistry [
3] and biodiversity [
4,
5,
6] of the adjacent basins.
The vertical structure of the Ionian is, at first approximation, characterized by three layers. The first layer, which extends from the surface to a depth of approximately 150 meters, consists of waters originating from the Atlantic Ocean, known as Modified Atlantic Water (MAW). The second layer, spanning from 150 m to 500 m of depth, is an interface layer composed of waters from the Levantine region, commonly referred to as Levantine Intermediate Water (LIW). Finally, the third layer, from 500 m to the bottom, is made up of deep waters originating from the Adriatic and/or Aegean Seas (see e.g. [
7,
8]) that we shall collectively name to as Ionian deep waters (IdW).
The general circulation of the Ionian Sea is typically dominated by a large-scale eddy system occupying the central and northern parts of the basin; this system, which is characterized by intense inter-annual variability, is known as the Northern Ionian Gyre (NIG). For over five decades, thermohaline oscillations of the Adriatic-Ionian system were studied extensively [
9,
10]. However, despite the efforts, the reconstruction of the dynamics underlying this variability remained a puzzle until 2010, when Gačić et al. [
1] linked changes in the hydrographic properties of Adriatic water masses to the inter-annual variability of the Ionian dynamics. These authors observed that the Ionian eddy system is characterized by two basic circulation regimes: cyclonic and anticyclonic. Depending on the prevalence of one or the other, the relative volumes of waters of Levantine and Atlantic origin entering the Adriatic change and trigger the decadal variability of the thermohaline properties of the Adriatic. This mechanism, denoted as the Adriatic-Ionian Bimodal Oscillating System (BiOS), correlates the Adriatic oceanographic variability to changes in the Ionian dynamics [
11].
In the past decade, extensive research has been conducted to explain the physics behind the reversals of the Ionian near-surface circulation, resulting in the development of several theories. A first group of theories suggests that the Ionian current reversal is due to changes in the atmospheric forcing [
12,
13,
14], while a second group relates it to baroclinic (internal) vorticity production induced by changes in the horizontal pressure gradient due to injections of Adriatic Deep Water (AdDW) [
15]. Indeed, Rubino et al. [
16] and Gačić et al. [
17], using tank experiments and numerical modeling, demonstrated that the injection of dense water on a sloping bottom generates near-surface oceanic vorticity and can be responsible for the switch of polarity of the Ionian near-surface circulation.
Despite the significant efforts, none of the theories proposed to explain the inversion of the Ionian dynamics have been able to reproduce quantitatively the characteristic temporal and spatial scales of the near-surface current variability, until recently, when Eusebi Borzelli and Carniel [
18] proposed an analytical model, called the Kelvin-like wave model, which provided estimates of these scales that align with observations. According to Eusebi Borzelli and Carniel [
18], the sub-surface memory of the ocean (i.e. the energy stored in the water column), depends on the shape of the isopycnal surfaces, which are deformed by the action of a rotating wind. When the internal fluid pressure exceeds the stress exerted by the wind, the equilibrium between the ocean and external forcing is broken, causing the potential energy stored in the water column to be released and determining the oscillations of the near surface dynamics.
However, it should be noted that in the vision proposed by Eusebi Borzelli and Carniel [
18], there are still theoretical flaws. Indeed, the Kelvin-like wave model assumes that the internal structure of the Ionian can be described by a double-layered system but, according to the literature on the Ionian hydrography, this is not the case. This descriptive flaw is also present in other traditional theories of the BiOS [
1,
15,
16,
17]. These theories indeed suggest that changes in the sea surface structure of the Ionian are driven solely by deformations of the interface between deep and intermediate waters. They also assume that the interface between surface and intermediate waters plays no role in the transition between the two states of Ionian dynamics.
Based on Wunsch's theory regarding the intensification of baroclinic components at the surface [
19], which implies that altimeter data primarily reflect the motion of the first baroclinic mode, Ioannone et al. [
20], in a pioneering yet overlooked study on the decadal variability of the surface structure of the Ionian, assuming the main pycnocline depth between 500 and 700 m, demonstrated that the two phases of the BiOS (cyclonic/anticyclonic) were characterized by different horizontal scales, which were linked to changes in the first Rossby baroclinic radius. The assumption on the depth of the main pycnocline was supported by the findings of Klein et al. [
21], who observed that the main pycnocline in the Ionian Sea was located between 400 and 800 m, but the results of Ioannone et al. [
20] raise questions about the role of the interface between MAW and LIW during the transition of the near-surface dynamics in the Ionian Sea.
The above quoted findings, along with the fact that changes in the hydrographic properties of the Adriatic and the Eastern Mediterranean (EMed) are in phase with the Ionian dynamics [
1,
2,
11,
22,
23,
24], indirectly confirm that the variability of the Ionian surface structure is primarily driven by the deformations of the interface between deep and intermediate waters, but open an interesting theoretical issue concerning the dynamical mechanism that constrains the intermediate and surface layer to move rigidly in phase one with the other.
Here we address this issue and by decomposing the horizontal dynamics of the Ionian into baroclinic modes, we investigate how the first and the second baroclinic components compete with each other to determine the observed horizontal circulation patterns. We show that the Ionian does behave dynamically as a two-layered system with only one baroclinic mode determining the horizontal patterns of circulation.
3. Results and Discussion
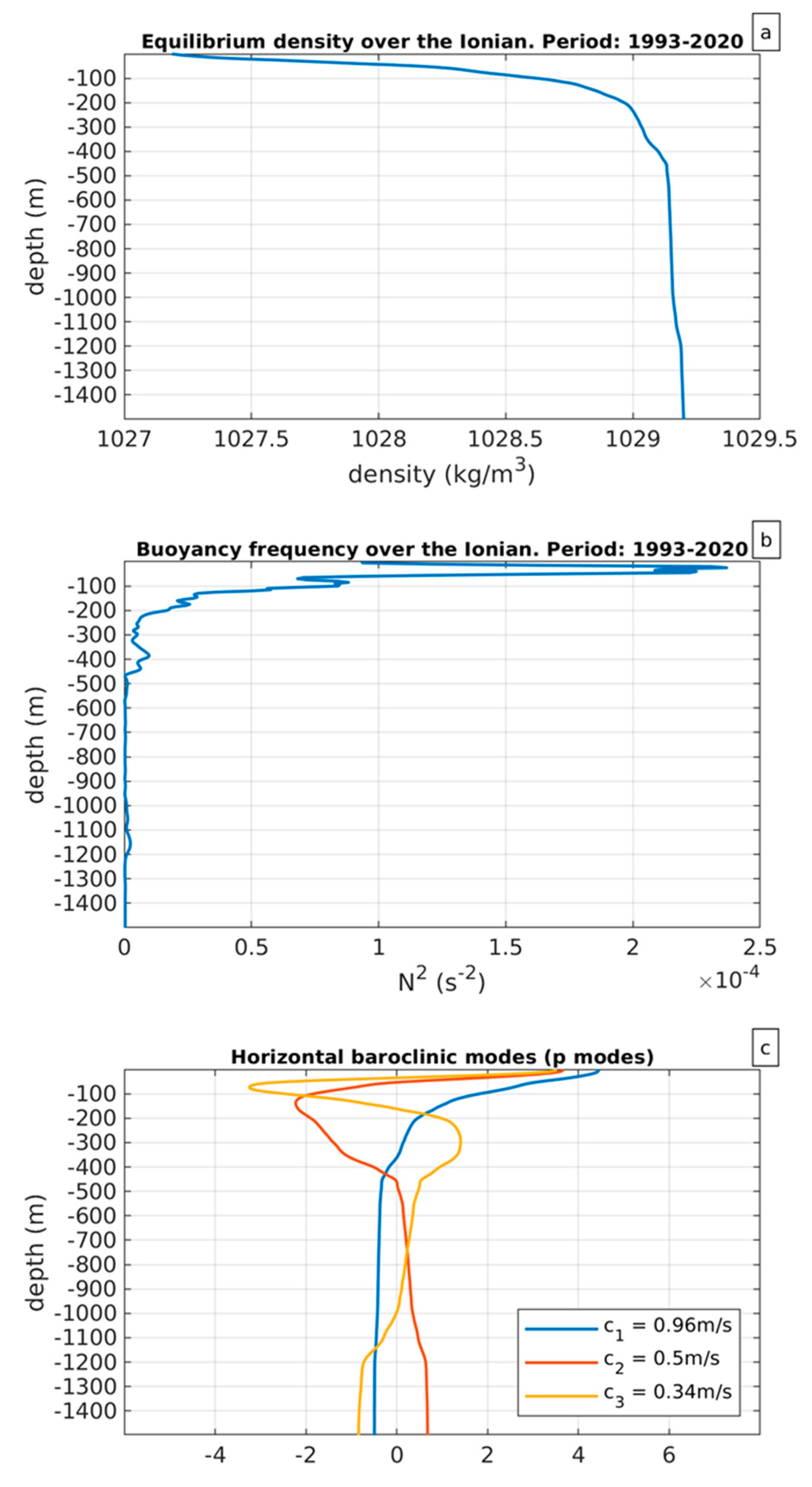
Figure 1a and 1b show the average equilibrium density and the average buoyancy frequency, respectively.
Figure 1a does not allow for an easy identification of transition regions between different water masses, but the picture becomes clearer when looking at the buoyancy frequency.
Figure 1b reveals that the water column is characterized by four high buoyancy regions: one sharp region located between 20 m and 30 m, which is obviously associated with the mixed layer. Over the Ionian, this layer is typically located between 10 m and 60 m [
33]. Another sharp region is located between 80 m and 90 m, indicating the border between MAW and LIW. Additionally, there are two fairly thick transition regions located between 380 m and 480 m and between 1100 m and 1200 m. The first of these regions indicates a gradual transition between LIW and IdW, while the second is likely associated with waters of Adriatic origin with relatively uniform salinity (i.e. 38.745) and temperature decreasing from 13.575
oC to 13.55
oC [
8]. Note, from
Figure 1c the surface intensification of baroclinic modes and, more consistently, the intensification of the first baroclinic mode. Note also that the internal wave velocity associated with the first baroclinic mode is
c1 = 0.96 m/s.
To evaluate how the complex vertical structure of the Ionian, even when averaged over a long period, determines horizontal circulation patterns, we expanded the horizontal currents over the basis formed by the first three baroclinic modes.
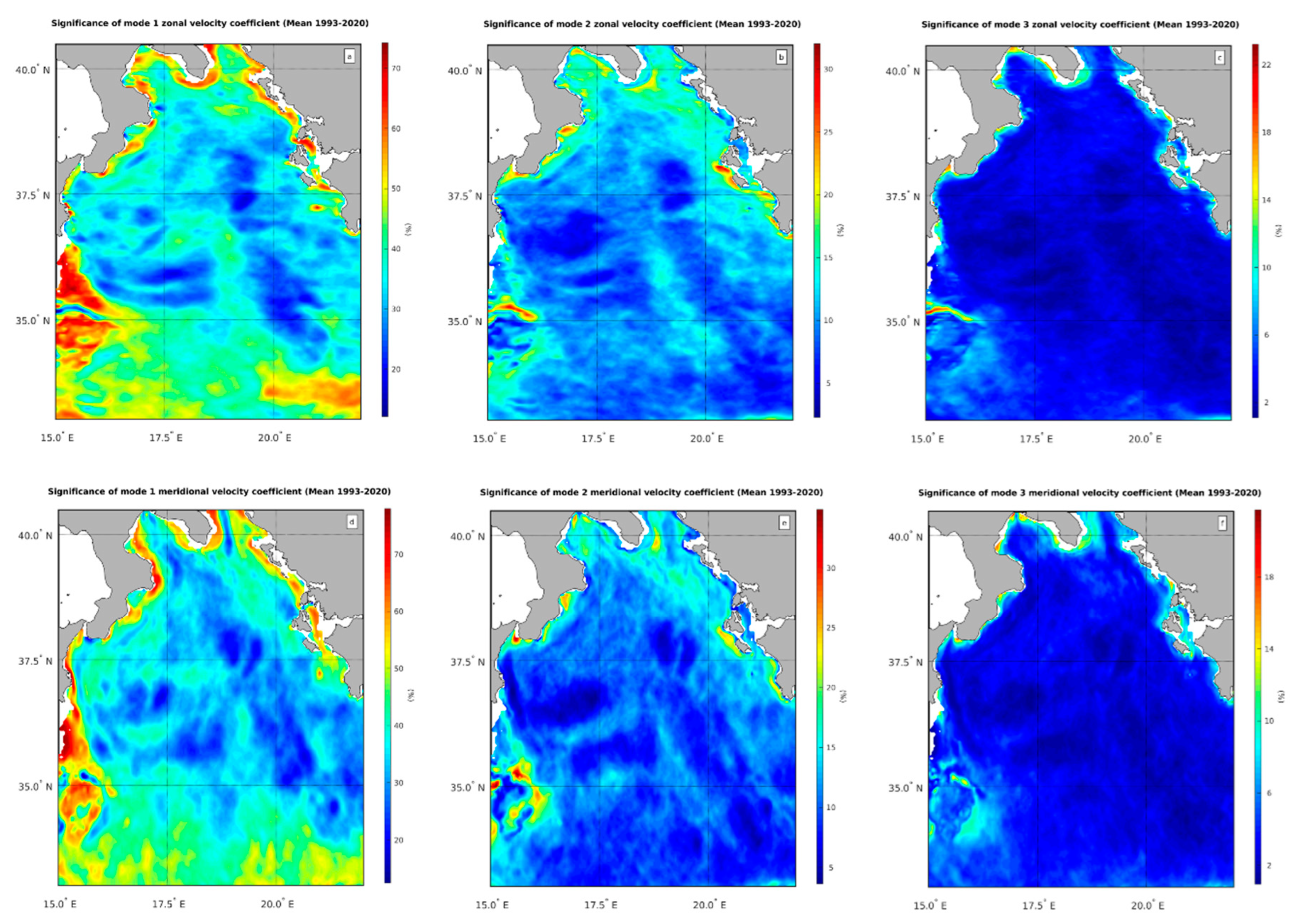
Figure 2 illustrates the significance of these modes (i.e. the ratio between the energy contained in each mode and the total energy of the signal, see eq. 5 of section 2) for the zonal and meridional components of the current field. The first baroclinic mode is particularly significant, with values higher than 60% along the coasts, in the western part of the basin, at the border with the Channel of Sicily, and south of 35
oN in both the zonal (
Figure 2a) and meridional (
Figure 2d) directions of the velocity field. On average, this mode accounts for 45%-50% of the total energy in the horizontal current. This estimate is consistent with previous findings for the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean [
19], although it is slightly lower. The second baroclinic mode is consistently less significant than the first (note that the color bars for the different baroclinic modes indicate different scales of variability), with significance values ranging from 5% to 15% for both the zonal (
Figure 2b) and meridional (
Figure 2e) components, except for some isolated regions along the southern Italian and Hellenic coasts. On average, for both components, the second baroclinic mode explains approximately 10% of the overall current field energy. The third baroclinic mode, overall, explains negligible fractions of the current energy with the significance of modes in both the zonal (
Figure 2c) and meridional (
Figure 2f) nearly uniformly distributed around 5%.
These results suggest that the horizontal circulation of the Ionian Sea is dominated by the superposition of the barotropic and the first baroclinic mode, with the second baroclinic mode contributing only 10% to the overall energy of the circulation field. The significance of the barotropic mode can be estimated by subtracting the energy contained in the first three baroclinic modes from the total energy of the velocity field. This yields a barotropic mode significance of approximately 35%, which is consistent with estimates of other authors in the Atlantic Ocean [
19].
The results presented above suggest that, despite the complex vertical structure of the Ionian, only one of the four layers identified in
Figure 1 is dynamically active. This finding is in line with the assumption made by several authors (e.g. [
1,
2,
15,
16,
17,
18]), according to which the Ionian can be described as a two-layer system. However, it raises the question on where over the water column the interface between these two layers is located. To address this issue, it would be possible to represent the water column as a double-layered system using the technique proposed by Eusebi Borzelli and Sullivan [
34] and used by Eusebi Borzelli and Carniel [
35] to expand a continuously stratified fluid system into a finite number of step functions. However, we believe that this complex approach is beyond the scopes of the present study. Instead, we note that a reasonable value for the reduced gravity in the Ionian is
g' ≈ 1.9∙10
-3 m/s
2. This corresponds to a surface layer with a density of 1028.9 kg/m
3 and a bottom layer with a density of 1029.1 kg/m
3 (see also [
15,
17]). In a two-layer approximation we have that
c1 =
[g' ∙H1∙H2/(H1+H2)]1/2 ≈ (g' ∙H1)1/2, where
H1 and
H2 are the depths of the surface and bottom layer, respectively, and the last step holds when
H2 ≫H1. Taking
c1=0.96 m/s, we get
H1 ≈ 480 m, which indicates that the dynamically active layer is far below the MAW-LIW interface and, consistently with the observations of Ioannone et al. [
20] and Klein et al. [
21], can be reasonably identified as the interface between LIW and IdW.
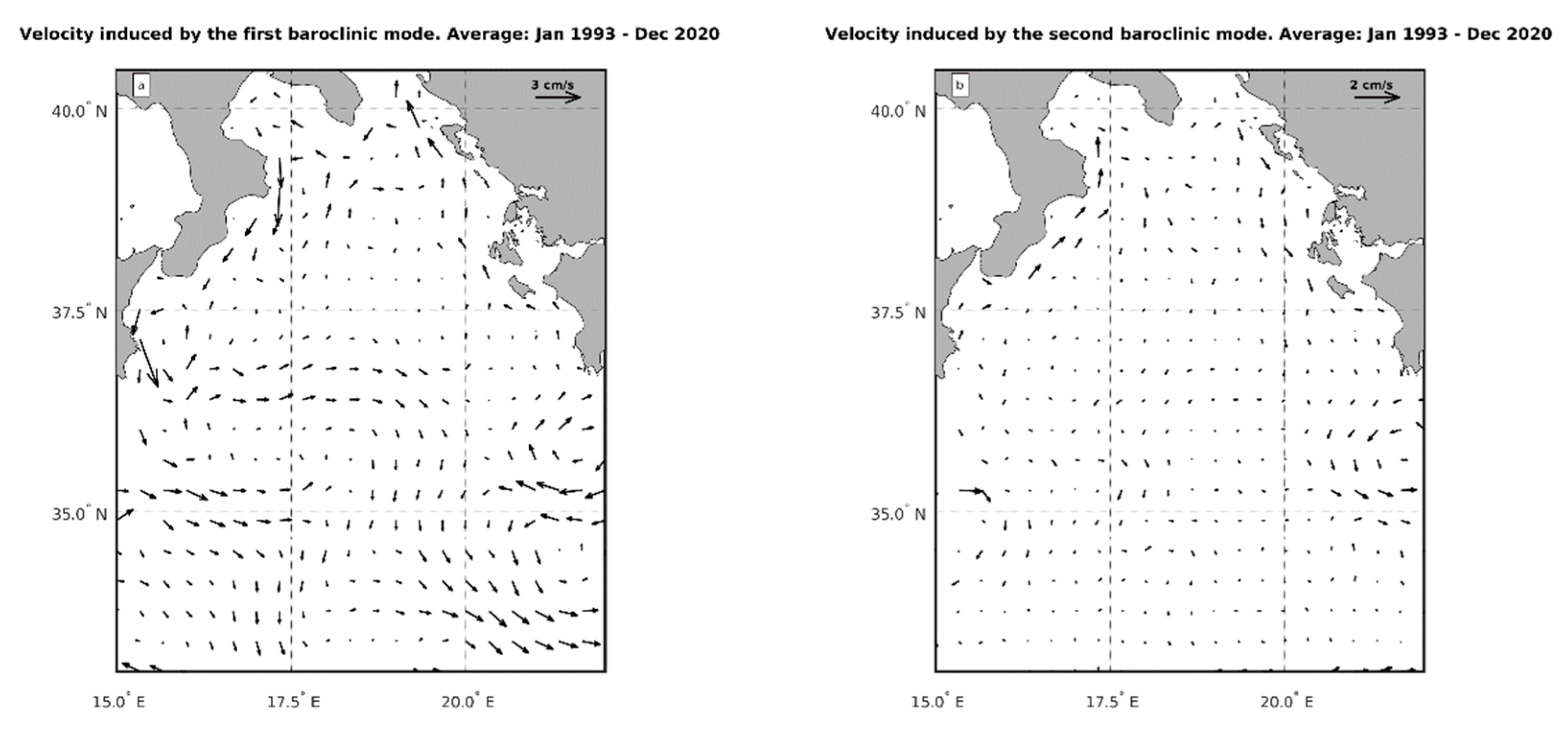
Figure 3a shows the contribution of the first baroclinic mode to the horizontal dynamics, averaged over the entire observation period (i.e. 1993-2020). The corresponding circulation pattern closely resembles the surface circulation pattern described by Kalimeris and Kassis [
36] for the period 1997-2015. This pattern can be described as a large zonal current entering the basin, subdivided in two branches, one in the north, which bifurcates at approximately (17.5
oE, 37
oN), partially recirculates northward, forming the southern and eastern branch of the NIG (see also [
37]), and partially flows southward, forming what is sometimes referred to as the Mid-Ionian-Jet [
37] or Mid-Ionian-Stream. The southern branch of the current entering the Ionian deviates southward at (17.5
oE, 35
oN), bordering the northeastern side of the Sidra Gyre. It is worth noting that on the eastern side of the observation region, there is an eddy system off the Hellenic coast known as the Pelops Gyre, as well as a recirculation region that marks the eastern border of the Mid-Mediterranean Jet.
Figure 3b shows that, consistently with the discussion on the significance of internal modes (
Figure 2), the contribution of the second baroclinic mode to the horizontal dynamics is weak almost everywhere. It does not contribute to the most important Ionian circulation patterns, except for the Pelops Gyre and the along-shore current off the southern Italian coast, where it acts in opposite direction with respect to the first baroclinic mode.
To get insight about the temporal variability of the first baroclinic mode contribution to the horizontal current, we conducted a V-EOF analysis as described in section 2. Since the second baroclinic mode does not contribute significantly to the horizontal circulation, the V-EOF analysis was only performed on the first baroclinic mode.
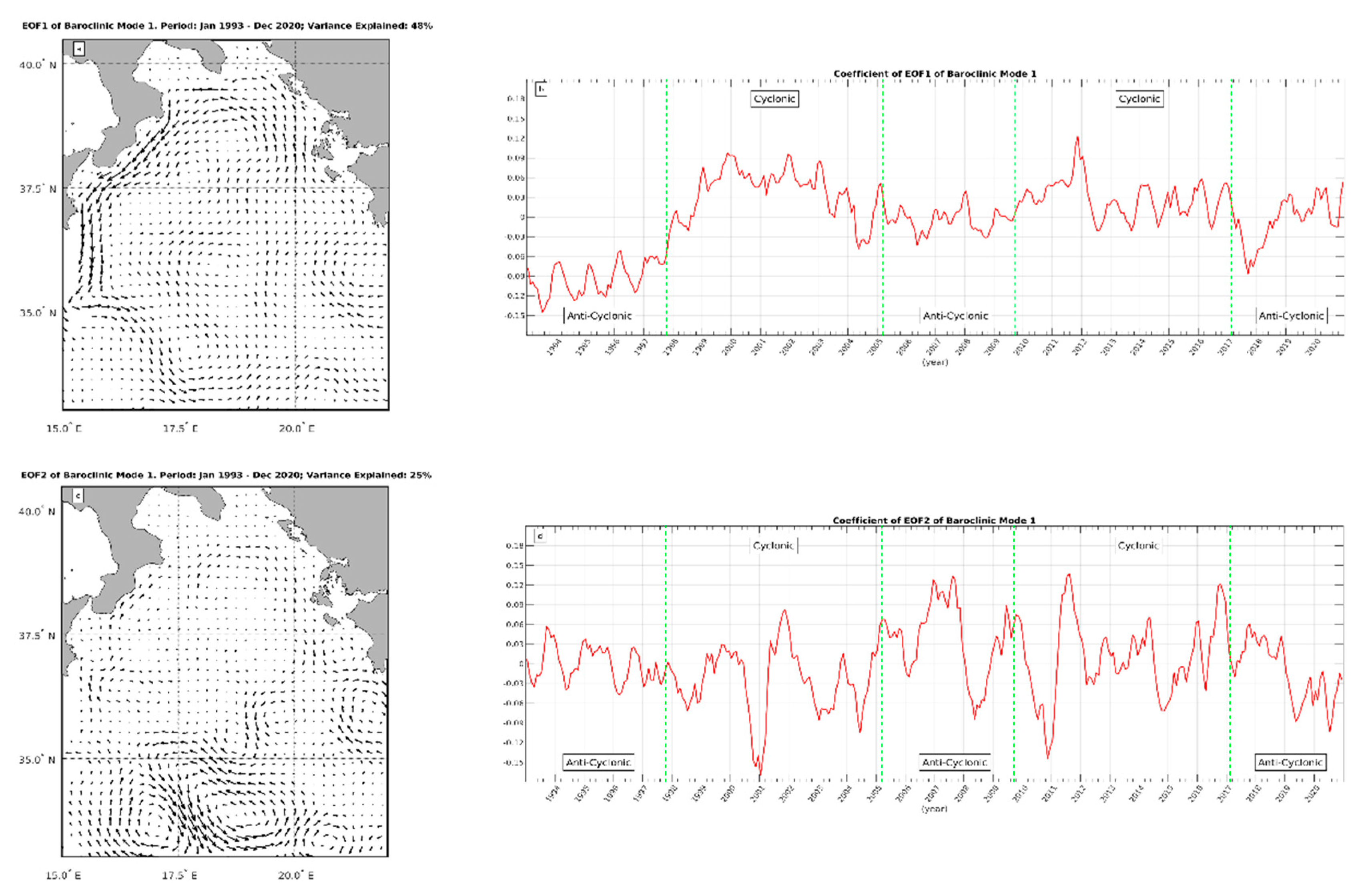
Figure 4a and c display the first and second V-EOF, which together account for 73% of the total data set variance.
Figure 4b and d show the corresponding temporal amplitudes. Note that, the interpretation of the results provided by the V-EOF analysis requires, as in the EOF analysis of scalar fields, multiplication of the V-EOFs by their temporal amplitudes. For the convenience of the reader, in
Figure 4b and d, transition periods of the NIG, as deduced from the published literature [
18], are drawn as green, vertical lines. In the first anticyclonic period of the NIG (1993-1998), the V-EOF1 temporal amplitude is predominantly negative (
Figure 4b), resulting in two large anticyclonic patterns that cover the entire western part of the basin. The first, nearly circular in shape, is centered at (17.7
oE, 34.2
oN). The second, which covers the NIG region, appears as an ellipsoid chipped towards the Italian coast, with a semi-major axis directed towards the northeast. In the second period (NIG cyclonic, i.e. 1998-2005), the V-EOF1 temporal amplitude becomes predominantly positive, and the circulation pattern that characterizes the northern Ionian in the preceding period, switches from anticyclonic to cyclonic, indicating the inversion of the NIG circulation described by Eusebi Borzelli and Carniel [
18] and Gačić et al. [
38]. In the third (2005-2010) and the fourth period (2010-2017), when the NIG circulation was anticyclonic and cyclonic, the V-EOF1 temporal amplitude oscillates around zero, but on average it is slightly below zero in 2005-2010 and on average it is slightly above zero in 2010-2017, indicating a predominantly anticyclonic circulation in 2005-2010 and a predominantly cyclonic circulation in 2010-2017. Finally, from 2017 to 2022, the V-EOF1 temporal amplitude becomes, on average, significantly negative, indicating that the predominant circulation pattern that characterizes the Ionian in this period is anticyclonic.
V-EOF2 (
Figure 4c) is characterized by several eddy regions, and its temporal amplitude oscillates around zero with an increased amplitude after 2000 (
Figure 4d). This indicates that the spatial structures displayed by
Figure 4c, alternatively cyclonic and anticyclonic, become more important in determining the surface circulation after 2010. However, these spatial structures explain only approximately half of the variance explained by the spatial structures evidenced by V-EOF1 and, therefore, should be interpreted as modulations to the variability of the background current described by V-EOF1.
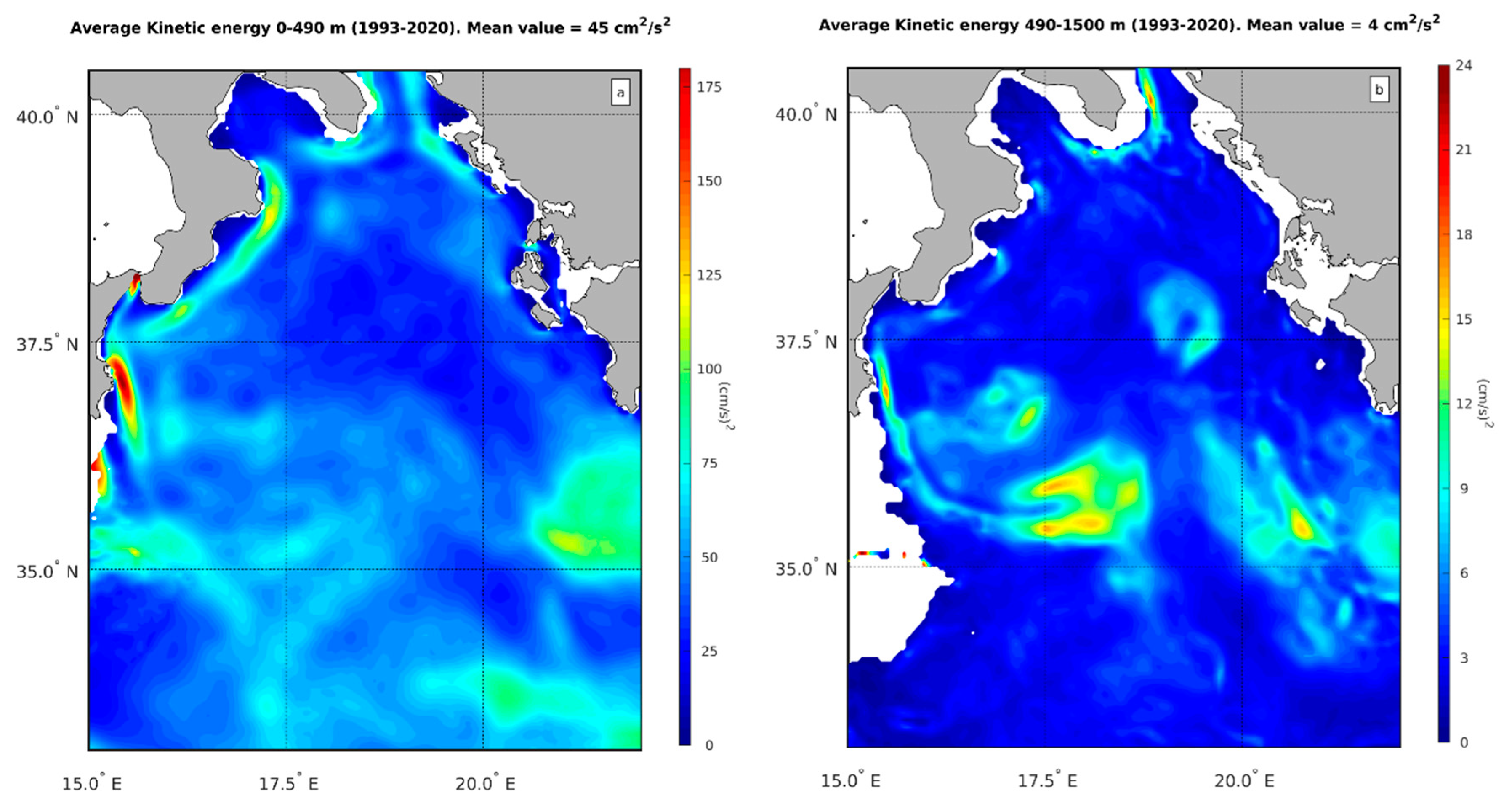
In the previous paragraphs, we explored the dynamics of the Ionian Sea and demonstrated that the variability of the first baroclinic mode can explain most of its dynamics. We also observed that, while the water column is divided into four layers, only one interface is dynamically active. This interface, located at a depth between 480 m and 500 m, separates LIW and IdW. To further understand the dynamics, we estimated the average kinetic energy in the layer above 490 m, which is collectively constituted by MAW and LIW, and the average kinetic energy in the layer below 490 m, which is constituted by IdW and includes waters from the Adriatic and Aegean. The results of this analysis are presented in
Figure 5a and b (note the difference in the colorbars, which highlights the different variability of the signals). We find that nearly 90% of the overall kinetic energy in the water column is contained in the layer above 490 m, since the spatial average of the kinetic energy in the lower layer is 4 cm2/s2, while in the upper layer it is 45 cm2/s2 (
Figure 5a), which implies an average velocity field intensity of |v|≈6.7 cm/s. This result is consistent with the findings shown in
Figure 2, indicating that the first baroclinic mode contributes to about 50% of the near surface circulation variability (see also
Figure 3a, which shows an average spatial value of the velocity field induced by the first baroclinic mode of the order of 3-4 cm/s). It is worth noting that the majority of the kinetic energy above 490 m is concentrated in the upper portion of the water column, approximately above 300 m of depth. This is due to the surface intensification of the first baroclinic mode, as described by Wunsch [
19]. In the Ionian region, this intensification begins to occur in the water column above 300 m, as it is evident from
Figure 1c (blue line). Finally, note that while the deep dynamics of the Ionian is nearly spatially homogeneous (
Figure 5b), except for some isolated regions where the kinetic energy, however, remains below 15 cm2/s2. (i.e. |v| ≈ 3.9 cm/s), the Mid-Ionian Jet, the Sidra Gyre, the Pelops Gyre along with the NIG, leave their signature on the dynamics of the upper layer (
Figure 5a).
4. Conclusions
In this research, we showed that the horizontal dynamics of the Ionian Sea can be effectively described by the barotropic and first baroclinic modes. Together, these modes account for over 90% of the variability. However, our focus was on the baroclinic components, as the barotropic contribution and its interactions with the baroclinic mode will be the subject of future research. We discovered that, despite the Ionian Sea being characterized by four hydrological layers, the primary patterns of horizontal circulation can be explained by the first baroclinic mode. This implies that, out of the three interfaces separating these layers, only one is active in determining the Ionian circulation. We have estimated the depth of this layer to be about 490 m, which is commonly believed to separate Levantine Intermediate Waters from Ionian deep Waters, term coined to collectively designate dense waters of Aegean and/or Adriatic origin. Therefore, we wish to emphasize the fact that, unlike the rest of the Mediterranean, the surface layer (consisting of waters of Atlantic origin) and the intermediate layer (formed by waters from the Levantine part of the Mediterranean) move strictly in phase with each other in the Ionian Sea. These results are significant because they not only justify the commonly used two-layer approximation for describing Ionian dynamics [
1,
15,
16,
17,
18,
39], but also provide insight into the relationships between changes in the Ionian dynamics and hydrographic and bio-geo-chemical properties of the Adriatic and Eastern Mediterranean [
1,
2,
3,
11,
22,
23,
24]. Specifically focusing on the biology, previous studies have shown that changes in the Ionian circulation can affect connectivity patterns between different Mediterranean ecosystems, thereby modulating Lessepsian migrations in the Adriatic [
6]. However, Lessepsian species are typically found in the upper layer of the water column and are rarely present below 300 m. Our research, indeed, revealed that the majority of the kinetic energy in the Ionian Sea is concentrated in the upper 300 m of the water column, due to the surface intensification of the first baroclinic mode.
One important aspect of the Ionian Sea is the reversal of the Northern Ionian Gyre circulation. In the past decade, significant efforts have been made to understand the underlying dynamics of this reversal [
1,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. Our findings suggest that the reversal of the Northern Ionian Gyre can be linked to the circulation field associated with the first baroclinic mode. However, we have noticed some minor discrepancies compared to the observations. These discrepancies may be due to the fact that the Vector-Empirical Orthogonal Function Analysis was conducted over a larger area than the region occupied by the Northern Ionian Gyre, thus taking into account current variability beyond the gyre itself.
The Ionian Sea serves as a crossroads for various water masses in the Mediterranean. Therefore, comprehending the horizontal dynamics of the basin is crucial to enhance our understanding of the processes that define the Mediterranean's overall dynamics and its variability. Our findings provide valuable insight into the physical processes at play in this basin and the methodology used can be extended to other sub-basins of the Mediterranean.