Submitted:
26 April 2024
Posted:
26 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
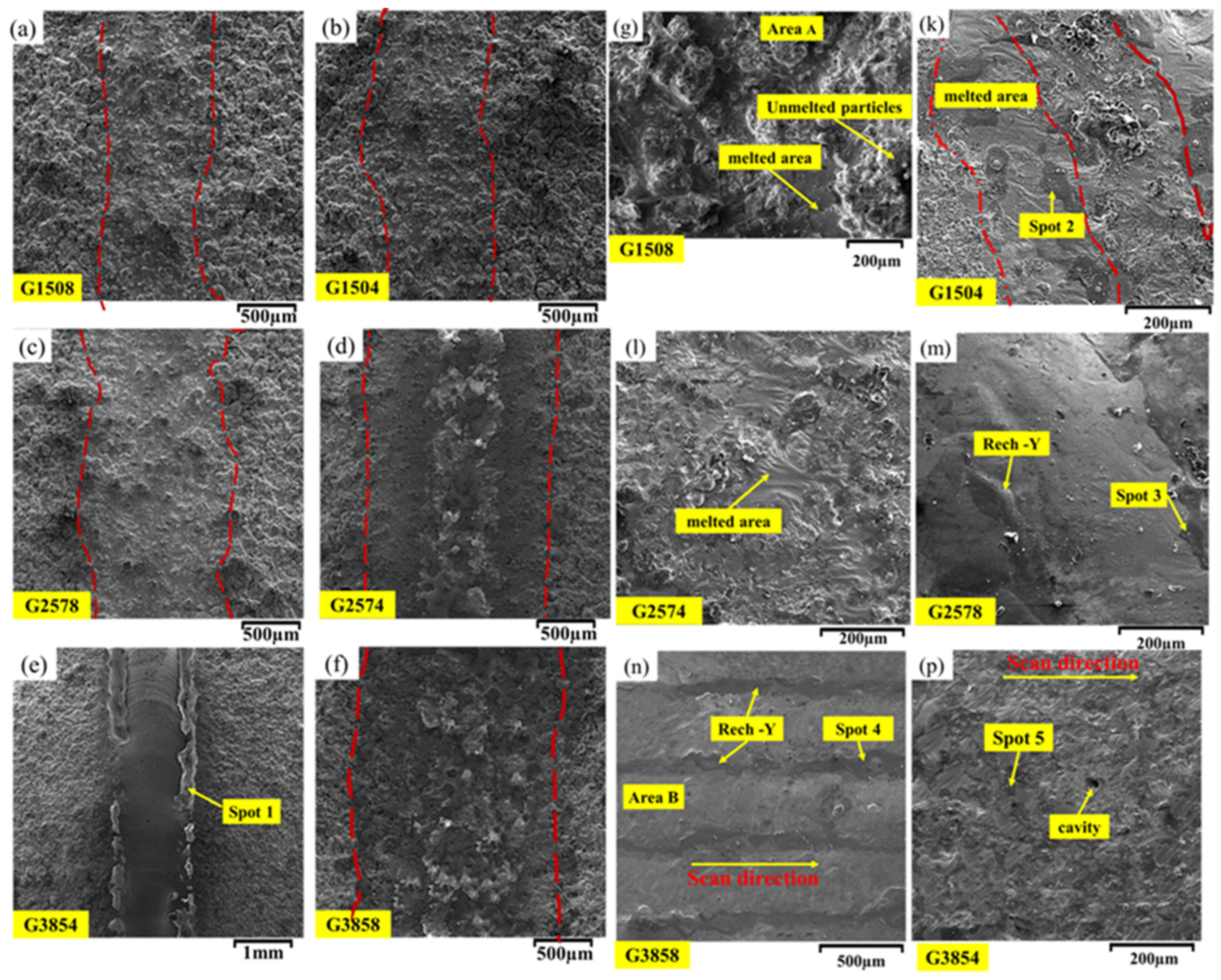
3.1. NiCrAlY-APS Coating
3.2. Remelting
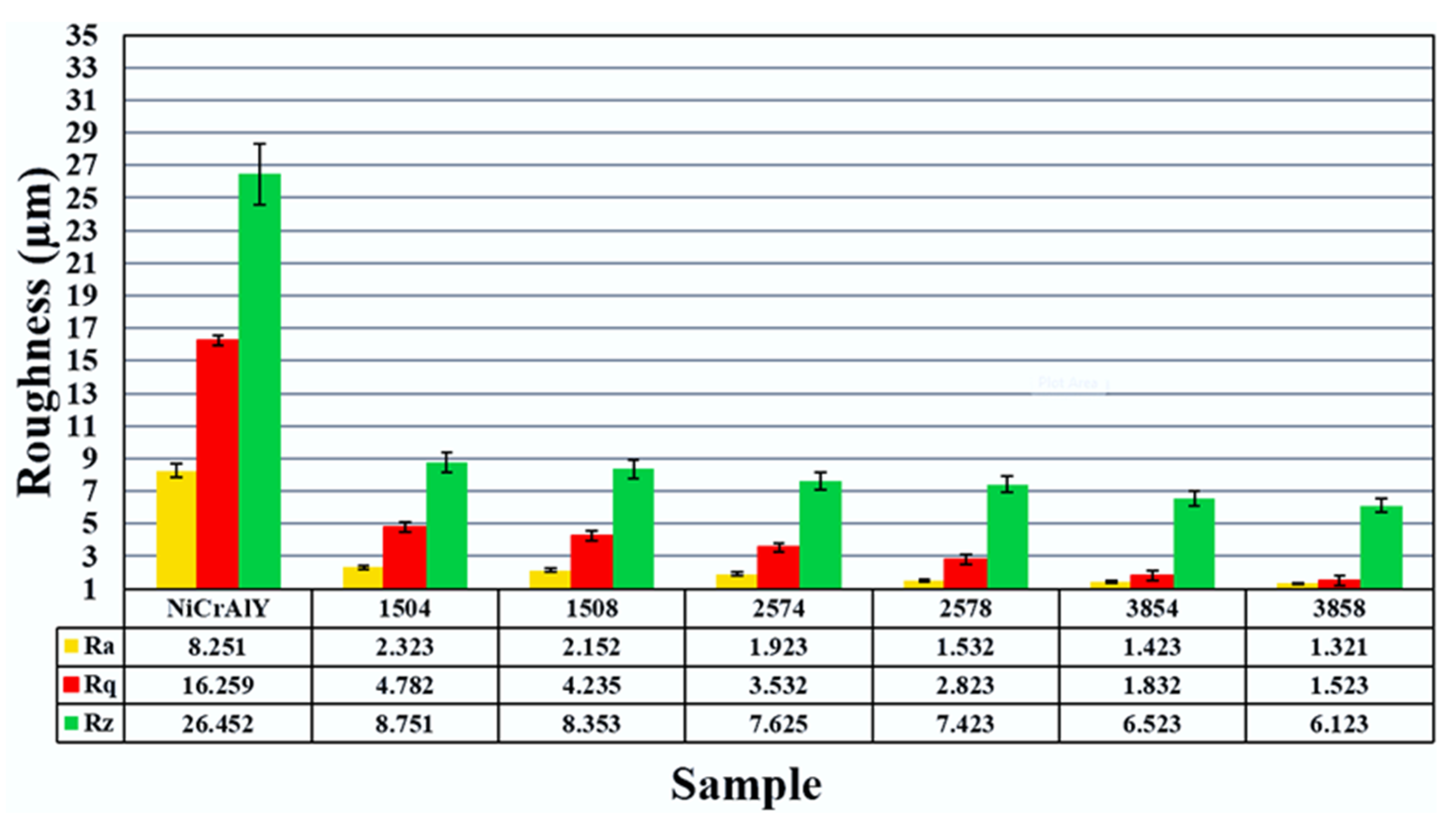
3.3. Surface Roughness
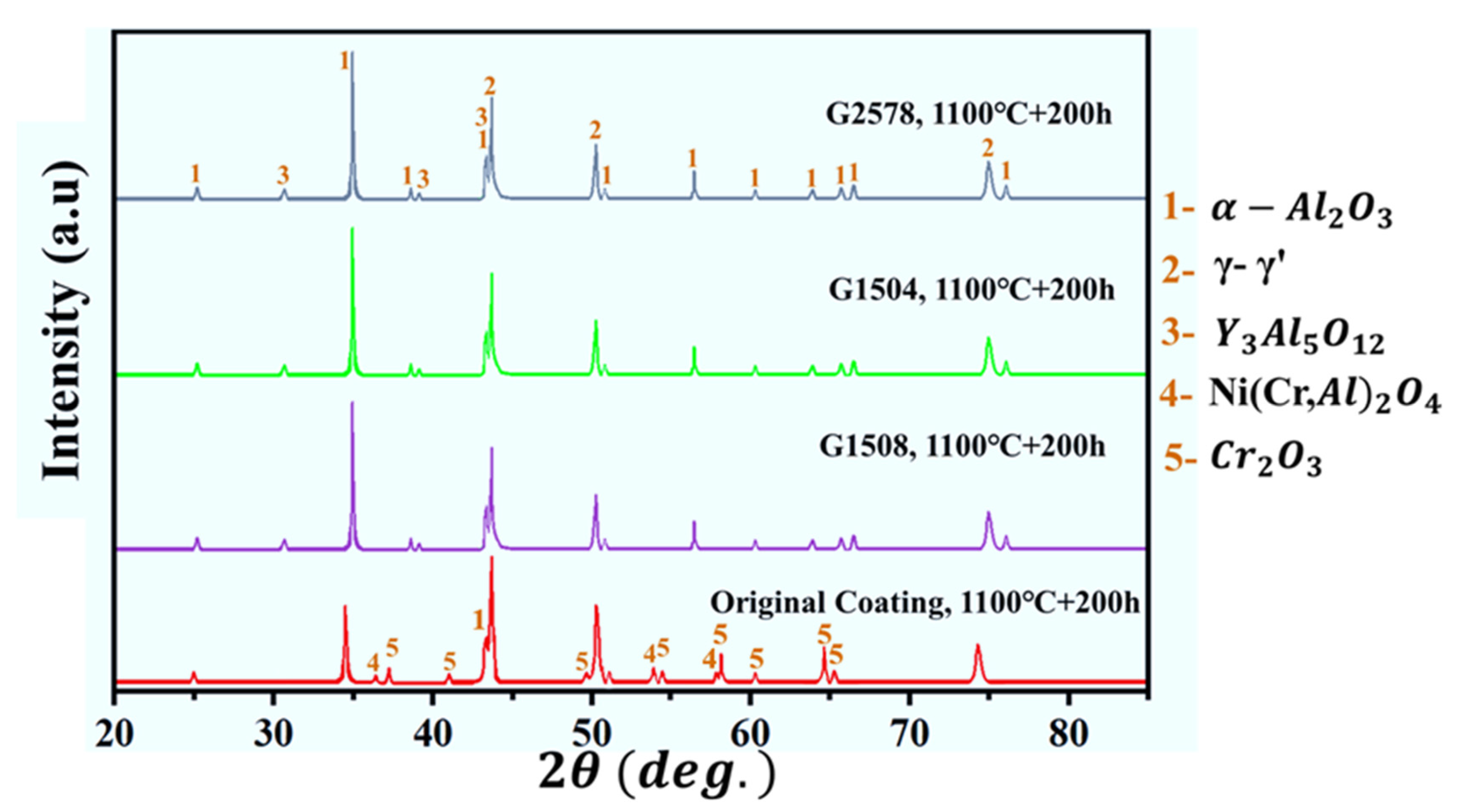
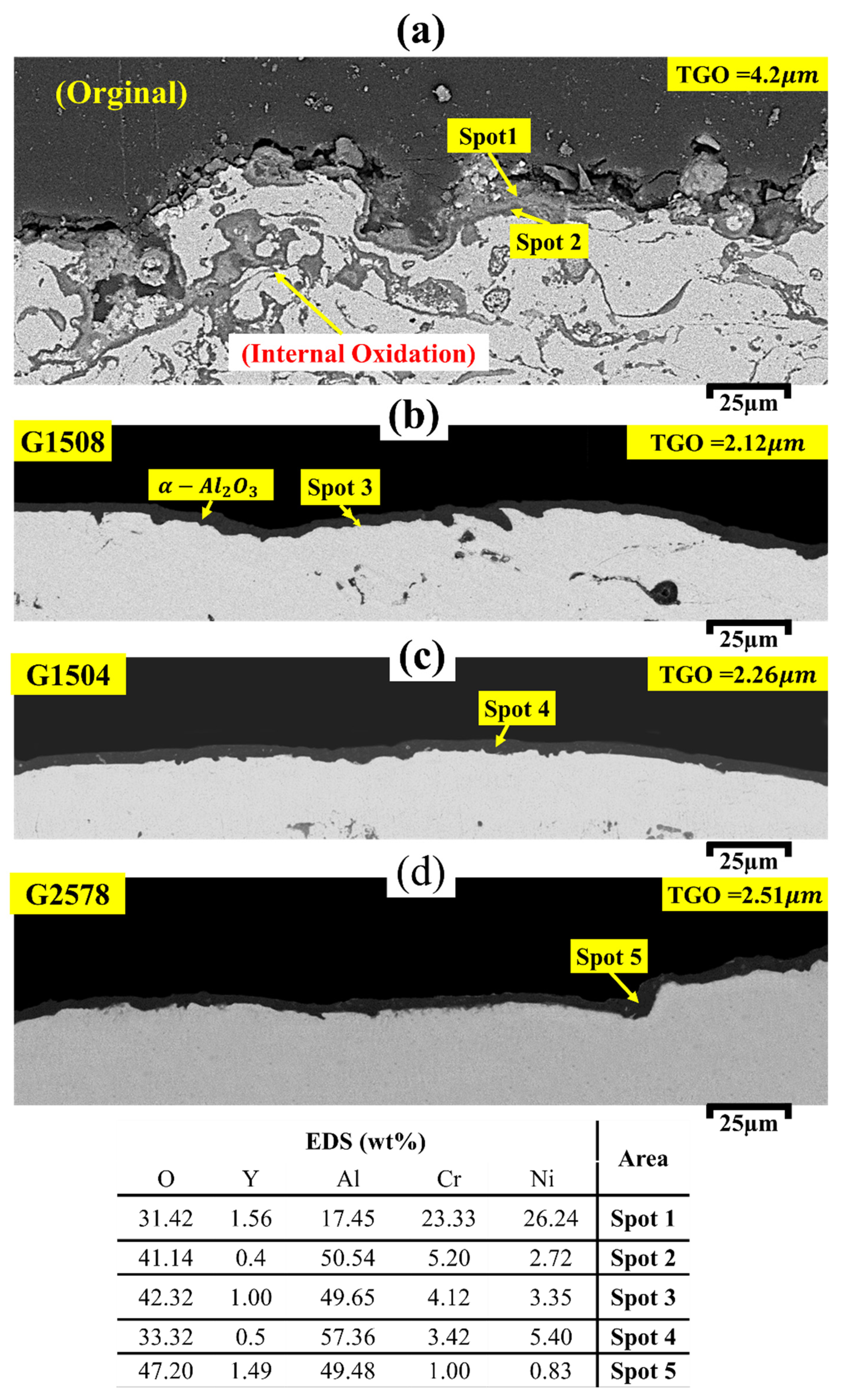
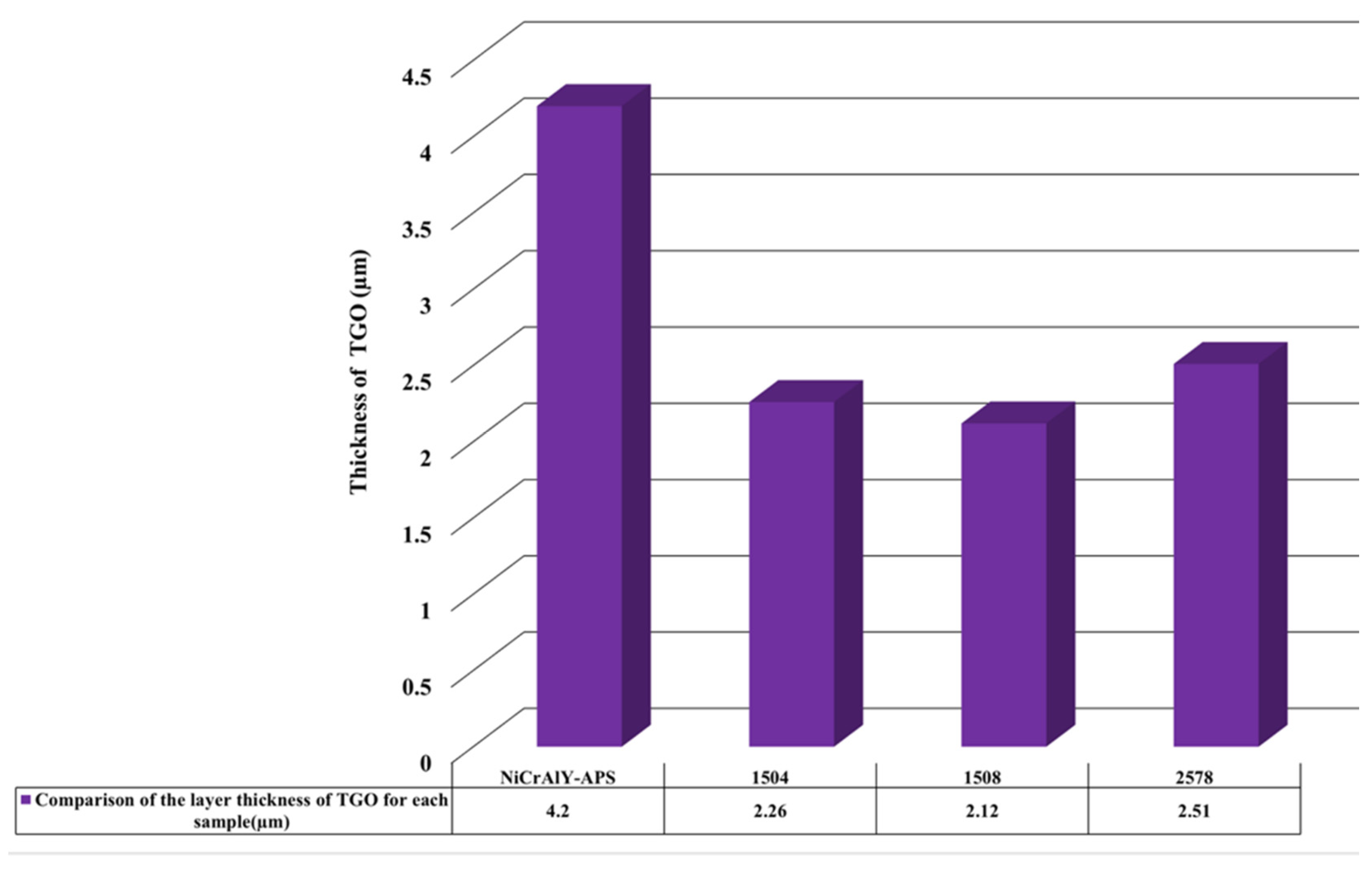
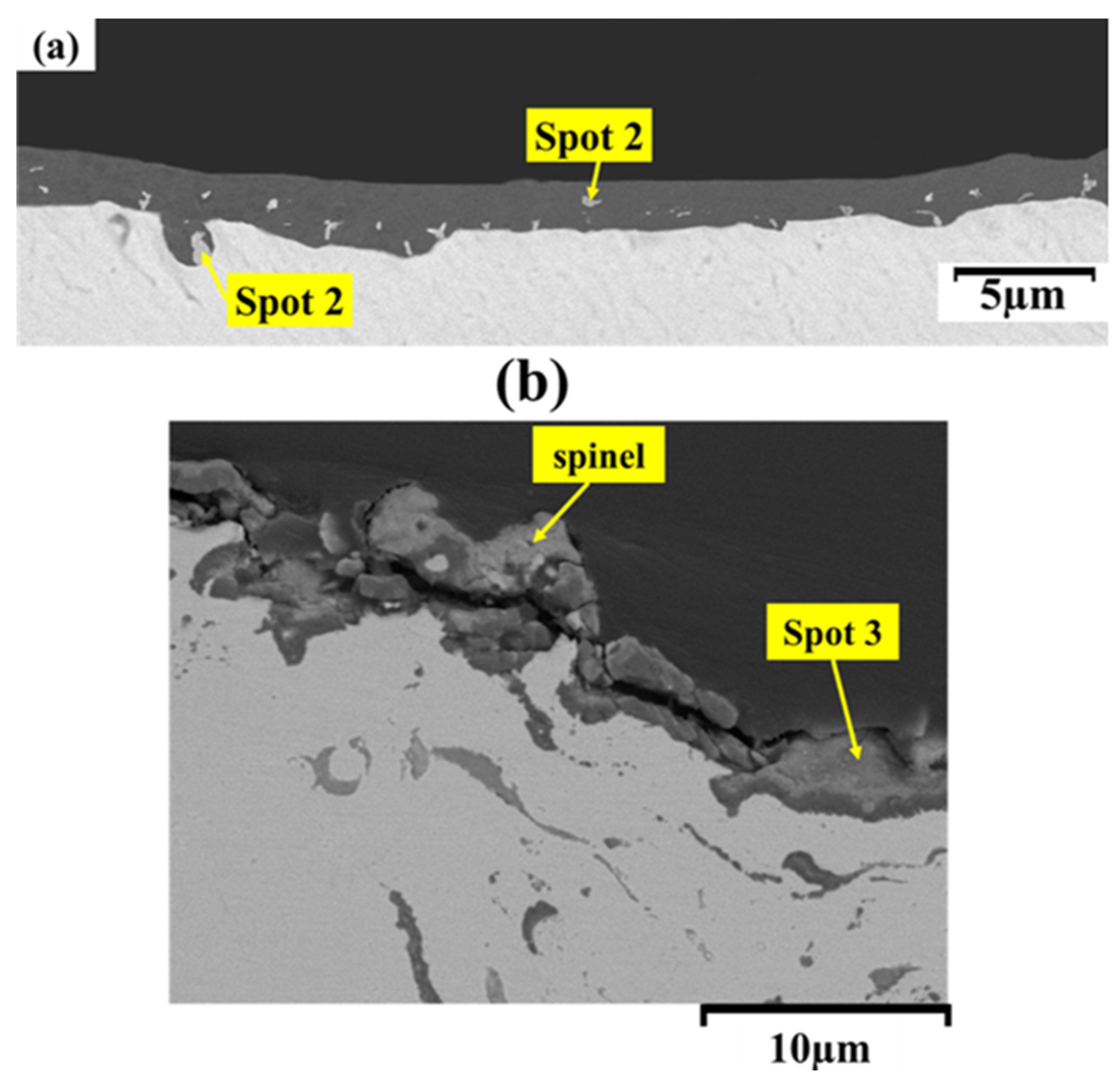
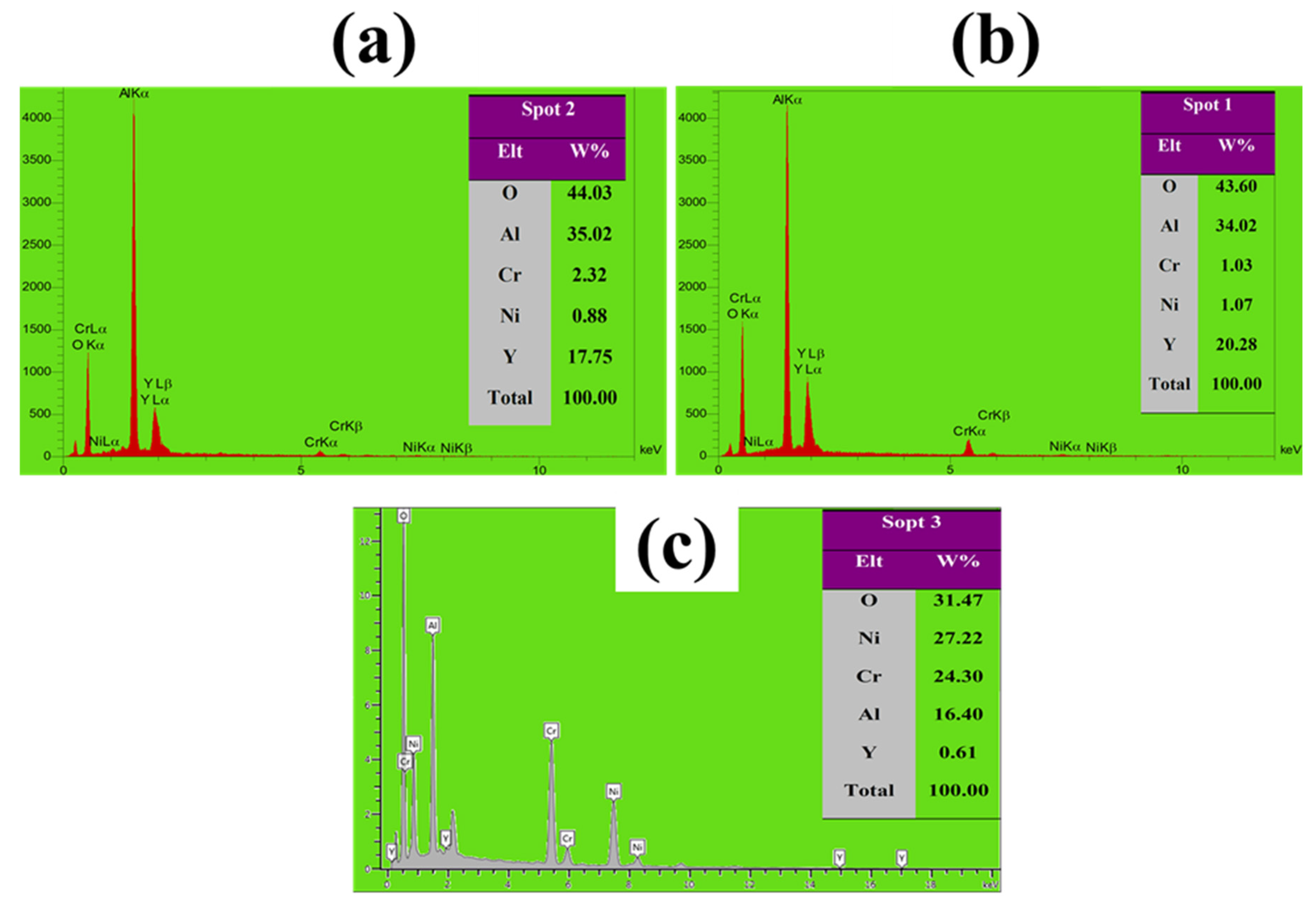
3.4. High-Temperature Oxidation Behavior
5. Conclusion
References
- Padture, N.P. Advanced structural ceramics in aerospace propulsion. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, D.R.; Oechsner, M.; Padture, N.P. Thermal-barrier coatings for more efficient gas-turbine engines. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, W.; Grabke, H.; Toma, D.; Krüger, J. The oxidation behaviour of sprayed MCrAlY coatings. Surf. Coatings Technol. 1996, 86-87, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.G.; Mumm, D.R.; Hutchinson, J.W.; Meier, G.H.; Pettit, F.S. Mechanisms controlling the durability of thermal barrier coatings. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 505–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadami, F.; Aghdam, A.S.R.; Ghadami, S. Microstructural characteristics and oxidation behavior of the modified MCrAlX coatings: A critical review. Vacuum 2020, 185, 109980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijdam, T.J.; Kwakernaak, C.; Sloof, W.G. The effects of alloy microstructure refinement on the short-term thermal oxidation of NiCoCrAlY alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Shemet, V.; Vassen, R.; Subanovic, M.; Toscano, J.; Naumenko, D.; Singheiser, L.; Quadakkers, W. Effect of surface condition on the oxidation behaviour of MCrAlY coatings. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2006, 201, 3824–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, A.; Bahmani, E.; Aghdam, A.S.; Saeedi, B. A comparative study on the microstructure evolution of conventional and nanostructured MCrAlY powders at high-temperature. Surface and Coatings Technology 2020, 389, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, P. Effect of microstructure on early oxidation of MCrAlY coatings. Acta Materialia 2018, 159, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golightly, F.A.; Stott, F.H.; Wood, G.C. The influence of yttrium additions on the oxide-scale adhesion to an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy. Oxid. Met. 1976, 10, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Cai, J.; Xin, Z.; Ye, Y.; Dai, F.; Hua, Y. Femtosecond laser polishing with high pulse frequency for improving performance of specialised aerospace material systems: MCrAlY coatings in thermal barrier coating system. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2022, 182, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, X.; Guan, H.; Hu, Z. Improvement of the oxidation resistance of NiCrAlY coatings by the addition of rhenium. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2006, 201, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragos, U.; Gabriela, M.; Waltraut, B.; Ioan, C. Improvement of the oxidation behaviour of electron beam remelted MCrAlY coatings. Solid State Sci. 2005, 7, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Razavi, R.S.; Barekat, M. An empirical-statistical model for coaxial laser cladding of NiCrAlY powder on Inconel 738 superalloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 86, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yao, Y.; Gao, C.; Lyu, P.; Meng, X.; Guan, Q.; Li, Y.; Han, Z. Comparison of microstructure and oxidation behavior of NiCoCrAlYSi laser cladding coating before and after high-current pulsed electron beam modification. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 881, 160651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Dong, T.-S.; Li, G.-L.; Wang, R.; Zhao, X.-W.; Liu, Q. High temperature oxidation resistance and TGO growth mechanism of laser remelted thermal barrier coatings. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 828, 154266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharkhiz, R.; Valefi, Z.; Mirjani, M.; Abdollahi, A.; Taghi-Ramezani, S. Effect of hydrogen and argon shrouding gas flow rate on high-temperature oxidation behavior of NiCrAlY coating by solid shielding shrouded plasma spray (SSPS). Surf. Coatings Technol. 2020, 394, 125818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolpygo, V.K.; Clarke, D.R. Surface rumpling of a (Ni, Pt)Al bond coat induced by cyclic oxidation. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3283–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Li, C.; Yao, Y.; Lyu, P.; Guan, Q.; Li, Y.; Lu, J. Microstructural modifications and high-temperature oxidation resistance of arc ion plated NiCoCrAlYSiHf coating via high-current pulsed electron beam. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcı, A.; Karabaş, M.; Eker, A.A.; Akman, E.; Aslan, C. Hot corrosion and CMAS degradation of laser-glazed YSZ coating with optimum parameter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L: J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2023, 237, 2322–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Peng, S.; Liu, W.; Guo, J. Effects of Process Parameters on Microstructure and High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Laser-Clad IN718 Coating on Cr5Mo Steel. Coatings 2023, 13, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Qiao, Y. The Oxidation Properties of a NiCrAlY Coating Fabricated by Arc Ion Plating. Coatings 2022, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Feng, X.L.; Yang, C.; Guo, C.A.; Zhang, J. High-temperature oxidation resistance of NiCrAlY columnar microcrystalline coating deposited by EDS. Chalcogenide Lett. 2022, 19, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchtík, M.; Březina, M.; Mrňa, L.; Palán, M.; Filipenský, J.; Doležal, P.; Nečas, D.; Frýza, J.; Kajánek, D.; Wasserbauer, J.; et al. Effect of Laser Remelting of Fe-Based Thermally Sprayed Coating on AZ91 Magnesium Alloy on Its Structural and Tribological Properties. Coatings 2023, 13, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Di, R.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Raoelison, R.N.; Rachik, M. Effect of laser scanning velocity on the microstructural changes and mechanical properties of the H13 steel part treated by laser surface remelting. InIOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2023, 1274, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.d.M.; Curi, E.I.M.; Inacio, L.F.F.; Rocha, A.d.S.; Pereira, M.; Silva, R.G.N.; Pereira, A.d.S.P. Laser remelting of WC-CoCr surface coated by HVOF: Effect on the tribological properties and energy efficiency. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2021, 427, 127841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doleker, K.M.; Erdogan, A.; Zeytin, S. Laser re-melting influence on isothermal oxidation behavior of electric current assisted sintered CoCrFeNi, CoCrFeNiAl0.5 and CoCrFeNiTi0.5Al0.5 high entropy alloys. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2020, 407, 126775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Y.; Koval, N.N. Enhancing the Oxidation Resistance of NiCrAlY Bond Coat by High-Current Pulsed Electron Beam Irradiation. Coatings 2021, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S. Effects of Laser Remelting on Microstructural Characteristics and Hot Corrosion Behavior of MСrAlY Coating Prepared by Plasma Spraying. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 971, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, C.G.; Guo, Z.X.; Xiao, J.G. Effect of laser remelting treatment on Al85Ni8Y4Ce3 amorphous coating. Surf. Eng. 2020, 37, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, M.G.; Razavi, R.S.; Valefi, Z.; Naderi-Samani, H.; Taghi-Ramezani, S. Evaluating laser surface melting of NiCrAlY-APS coating and its effect on high-temperature oxidation behavior of NiCrAlY/YSZ thermal barrier coating before and after surface melting. Heliyon 2023, 9, e23094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, A.; Shemet, V.; Vassen, R.; Subanovic, M.; Toscano, J.; Naumenko, D.; Singheiser, L.; Quadakkers, W. Effect of surface condition on the oxidation behaviour of MCrAlY coatings. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2006, 201, 3824–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Pu, W.; Li, S.; Bao, Z.; Cheng, R.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; et al. High-temperature performance of Pt-modified Ni-20Co-28Cr-10Al-0.5Y coating: Formation mechanism of Pt-rich overlayer and its effect on thermally grown oxide failure. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2023, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cai, J.; Lv, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, H.; Guan, Q. Surface microstructure and properties of Cu-C powder metallurgical alloy induced by high-current pulsed electron beam. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 697, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
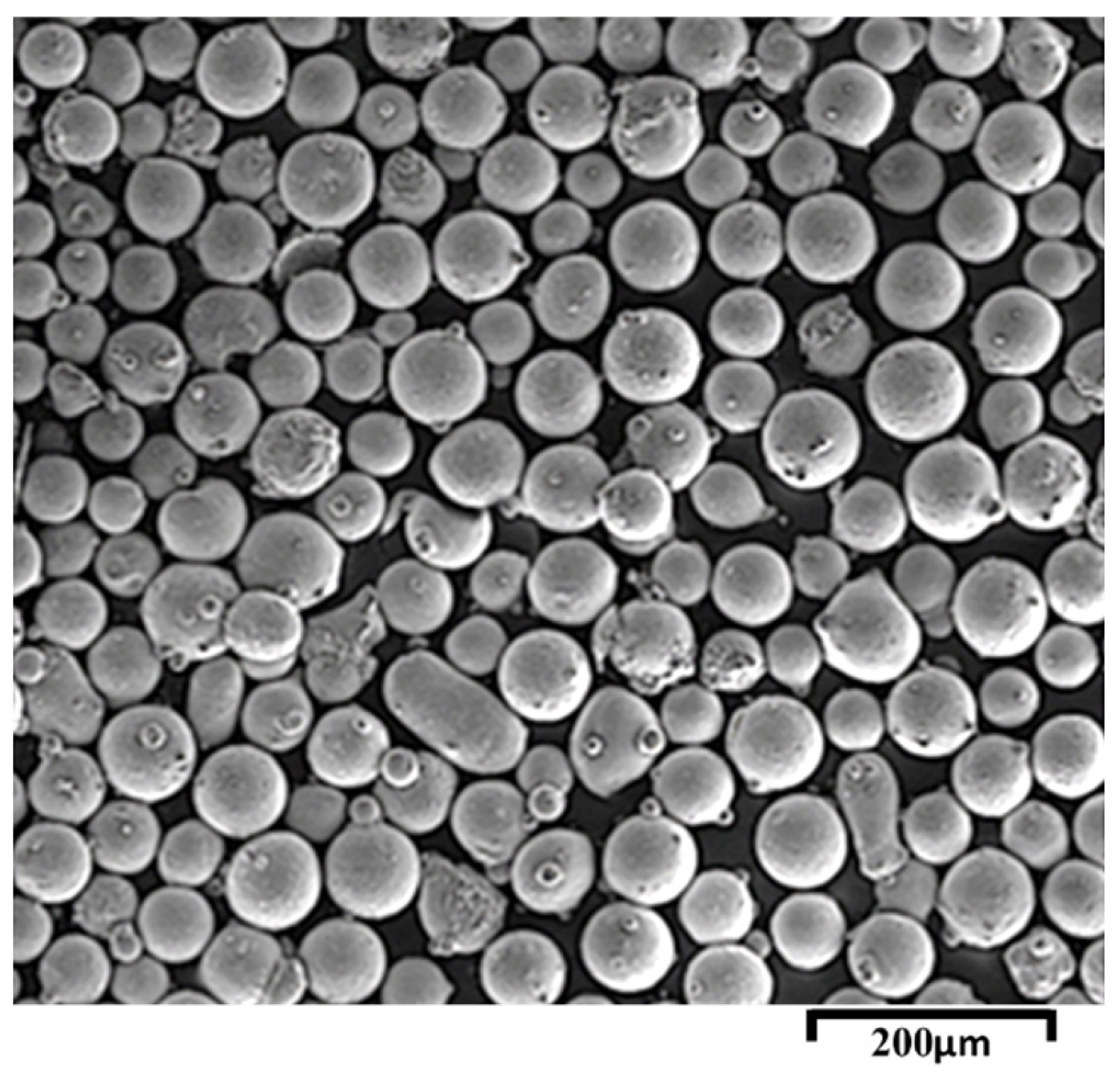
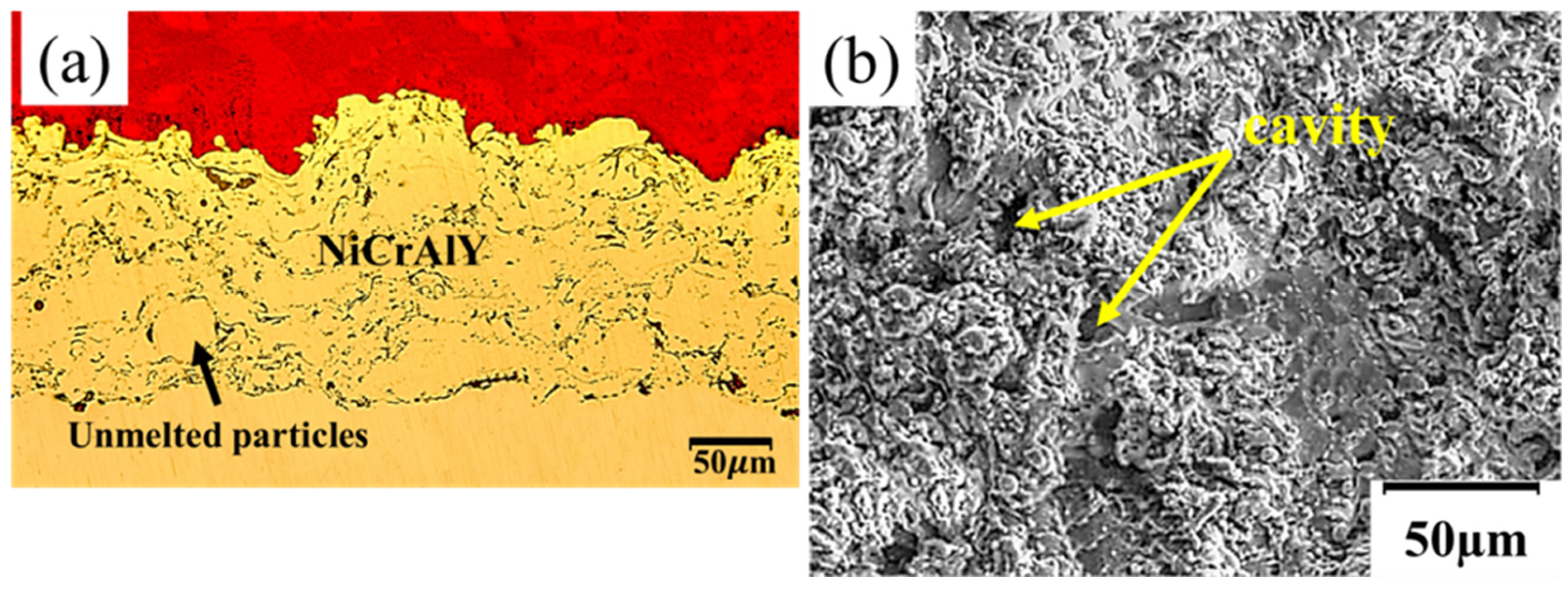

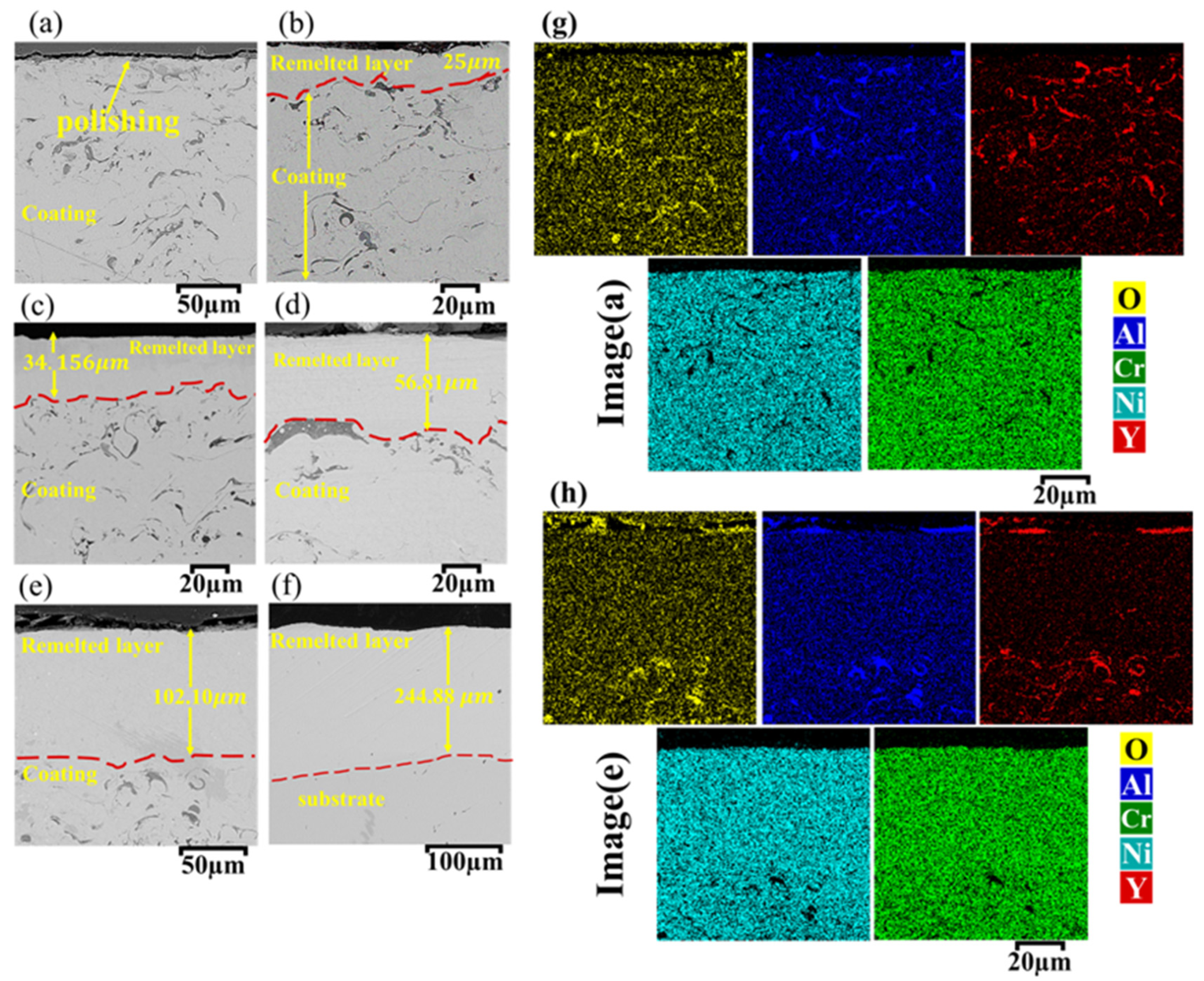
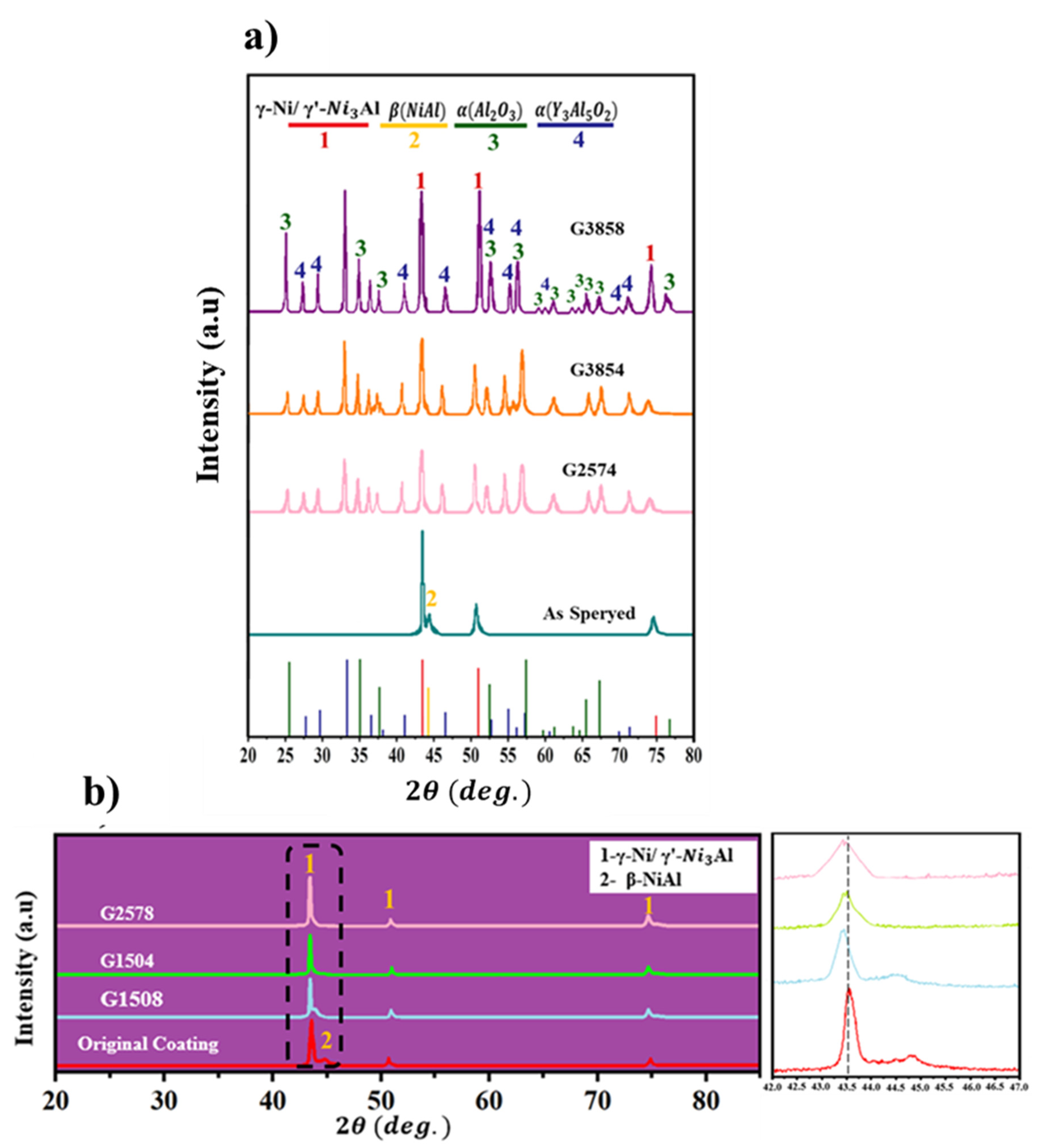
| Ni | Cr | Fe | Mo | Co | W | Si | C | Mn | Al | S | Ti | B | element |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48.80 | 21.47 | 1 | 7.50 | 8.98 | 1.23 | 0.67 | 0.49 | 0.095 | 0.42 | 0.059 | 0.13 | 0.005 | Wt% |
| NiCrAlY | Unit | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| 550 | A | current |
| 75 | l/min | Argon gas flow rate |
| 11 | SLPM | Hydrogen gas flow rate |
| 2.5 | l/min | Powder carrier gas flow rate (argon) |
| 15 | g/min | Powder feed rate |
| 120 | mm | Spray distance |
| Laser type | Continuous fiber |
|---|---|
| Wavelength (nm) | 1080 |
| Diameter of laser beam | 30 |
| Line distance | d1=d2=40 |
| Laser Power (w) | 150-257-385 |
| Scan speed (mm/s) | 4-8 |
| Laser Power (W) | Scan speed (mm/s) |
|---|---|
| 150 | 4 |
| 257 | 4 |
| 385 | 4 |
| 150 | 8 |
| 257 | 8 |
| 385 | 8 |
| EDS (wt%) | Area | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | Y | Al | Cr | Ni | |
| 5.7 | 0.48 | 14.32 | 20.9 | 58.6 | Area A |
| 4.3 | 0.84 | 10.3 | 24.26 | 60.3 | Area B |
| 52.64 | 9 | 37.33 | 0.38 | 0.65 | Spot 1 |
| 49.06 | 4.3 | 258.83 | 6.51 | 14.31 | Spot 2 |
| 25.80 | 12.56 | 22.90 | 11.13 | 27.61 | Spot 3 |
| 50.71 | 3.28 | 23.95 | 7.79 | 14.27 | Spot 4 |
| 40.60 | 22.90 | 34.16 | 1.27 | 1.07 | Spot 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





